Abstract
There is still much controversy concerning the impact of gender on mortality during ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The COVID-19 pandemic deeply affected the clinical history of these patients, both in terms of presentation time and management. Our study focuses on STEMI patients hospitalized during the darkest period of the pandemic. From a total of 283 patients, women represented 26.8% of the population, with a mean age of 72 ± 11.2 years vs. 64.7 ± 12.6 years in men. Anterior STEMI was the most represented with a mildly reduced ejection fraction (EF 48.3 ± 11.8%) similar between genders. Coronary angiography showed more extensive disease in man, while women presented with a higher Killip class at admission and a more pronounced anemic status. In-hospital and 1-year mortality of the whole cohort were 11.4% and 7.5%, respectively, with no significant differences between genders (14.5% women vs. 10.6% men, p = ns; 9.2% women vs. 7% man, p = ns). EF resulted in being the only independent predictor of mortality in the short-term and at 1-year follow up in both genders. In the acute phase, the only other independent predictor of mortality was COVID-19 infection, secondary to the higher rate of respiratory complications, without any difference in terms of major adverse cardiac events. The impact of COVID-19 infection on mortality was completely lost at 1-year follow up.
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases remain a leading cause of death nowadays, although in Western countries there has been a decrease in mortality [] and the relative incidence of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is reducing and increasing, respectively []. STEMI is relatively more common in younger patients and men than in women []. Acute coronary syndromes (ACS) under the age of 60 are more habitual in men, but over the age of 75 years, women represent the great majority []. In up to 30% of women, there are atypical clinical presentations compared to men (in some cases without chest pain), which could be prone to be underrecognized and undertreated with consequent greater morbidity and mortality []. Even if STEMI guidelines highly emphasize similar management in both genders [], women are often undertreated, especially in specific cultural and economic contests [,]. Several studies in literature reported poorer outcomes in women, often secondary to older age, higher comorbidities, later presentation and less reperfusion therapy compared to men [,]. On the other side, women seem to be relatively protected from SARS-CoV2. In the available literature, women are less susceptible to the infection [] and less prone to disease progression and worse outcomes []. Sex-specific biological differences, such as discrepancies in immunity and inflammation, genetic profiles [,], levels of sex hormones [,,,,], different expression of ACE2 receptor, behavior and lifestyle [,,] may explain these findings. Even though, during the pandemic, there was an effective reorganization of the emergency systems [], the number of ACS patients admitted to the emergency room was reduced, probably due to fear of COVID-19 infection, with consequent late diagnosis and poor prognosis [,]. The aim of our study was to evaluate the impact of female gender on acute and mid-term mortality in STEMI patients hospitalized during the pandemic period.
2. Results
Our population was represented by 283 consecutive STEMI patients treated with urgent coronary angiography and subsequent pPCI. Baseline clinical and demographical characteristics are detailed in Table 1. A total of 25 patients (8.6%) resulted positive for COVID-19 at nasopharyngeal swab test. Women represented 26.8% of the population with a mean age of 72 ± 11.2 years vs. 64.7 ± 12.6 in men. Regarding cardiovascular risk factors, hypertension was reported in 55.2% of patients, diabetes mellitus in 20%, dyslipidemia in 28.6%, overweight in 20%, a family history of coronary artery disease (CAD) in 13.4%, without any significant difference in terms of gender except for active and previous smoking that was more prevalent among males (37.6% vs. 26.3% and 14.1% vs. 2.6%, p = 0.001). In the majority of cases STEMI diagnosis was assessed in a pre-hospital setting (61%), 7.2% of the patients experienced out of hospital cardiac arrest and anterior MI was the most represented (45.9%) in the entire population. A Killip class ≥ II was recorded in 12.1% of the whole population, with a significantly higher incidence among women (20.8% vs. 9.9%; p = 0.01). Regarding the echocardiographic evaluation, left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) showed no differences in terms of gender with a mean value of 48.3 ± 11%. Females were significantly more anemic (hemoglobin levels 12.9 ± 2 g/dL in women vs. 14 ± 1.8 g/dL in men, p < 0.001) with a lower renal function (eGFR 64.1 ± 24.7 mL/min × 1.73 m2 vs. 90.1 ± 37.9 mL/min × 1.73 m2, p < 0.0001). Focusing on procedural characteristics, the radial access was the most performed (73.8%). A different distribution of MI localization was evident with a higher incidence of lateral MI among women (15.8% vs. 9%, p = 0.03). The number of pathological vessels was higher among men (1.8 ± 0.8 vs. 1.6 ± 0.8, p = 0.04). No patients underwent surgical revascularization. The mean hospitalization period in the general population was 9.4 ± 7.3 days with no differences between genders (8.9 ± 7.2 female vs. 10.8 ± 7.2 male, p = ns). The total in-hospital mortality was 11.4%, with a difference between genders that did not reach statistical significance (14.5% women vs. 10.6% men, p = ns). Respiratory complications were 6.4% and in-hospital adverse events were 15.9% in the global population with no differences between the two groups (6.6% male vs. 6.3% female and 19.7% women vs. 14.5% men, respectively; p = ns). The two subgroups received the same kind of therapy at discharge except for direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) that were more prescribed among women (11.6% vs. 4.1%; p = 0.02).

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the population.
In the multivariate analysis of the whole population, reduced ejection fraction (HR [95% CI] = 0.9 [0.87–0.94], p < 0.0001) and COVID-19 diagnosis (HR [95% CI] = 3.2 [1.2–8.3], p < 0.019) were the only two independent predictors of in-hospital mortality. In Figure 1, in-hospital adverse events are graphically represented, highlighting the higher mortality of COVID-19 patients, who recorded a greater number of respiratory complications in the absence of a statistically significant increase in cardiac death.
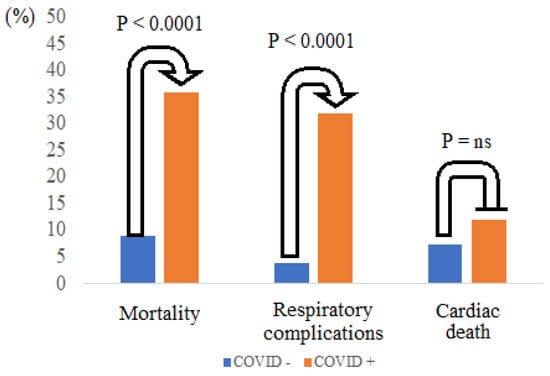
Figure 1.
In-hospital mortality according to cardiac death and COVID-19 infection.
Similar results were found if the analysis was performed according to female gender: ejection fraction (HR [95% CI] = 0.84 [0.74–0.95], p < 0.005) and COVID-19 diagnosis (HR [95% CI] = 10.45 [1.74–62.73], p < 0.01).
One year mortality was 7.5% in the whole population without significant gender-related differences in this setting (7.0% man vs. 9.2% women, p = ns). In the multivariate analysis, ejection fraction (HR [95% CI] = 0.94 [0.89–0.98], p < 0.007) and age (HR [95% CI] = 1.06 [1.02–1.11], p < 0.006) were the only two independent predictors of mortality, while the impact of COVID-19 infection was no longer significant. Similar results were reached performing the analysis only among women: age (HR [95% CI] = 1.2 [1.00–1.34], p < 0.045), ejection fraction (HR [95% CI] = 0.8 [0.76–0.94], p < 0.001). Finally, the Kaplan–Meier curve (Figure 2) representing long-term survival according to gender does not show significant differences for either in-hospital or 1-year mortality between the two groups examined.
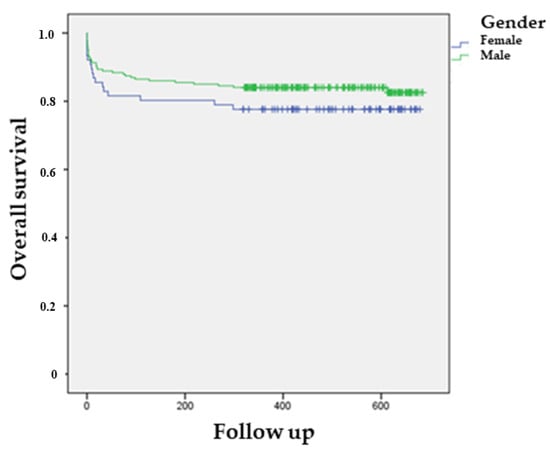
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curve representing in-hospital and 1-year mortality according to gender.
3. Discussion
Despite the great improvements both in technology and pharmacological therapy, STEMI remains a very high-risk clinical condition with a significant mortality rate []. The COVID-19 pandemic influenced both illness development and, above all, the management of patients hospitalized for STEMI starting from spring 2020. Several studies reported a drastic reduction of ACS during the pandemic, with, on the other hand, an increase in mortality, particularly among STEMI patients [,]. This could be explained by the lower access rate to the Emergency Department due to fear of COVID-19 infection, with consequent late diagnosis and poor prognosis. Moreover, due to the concomitant respiratory impairment and the multiorgan involvement typical of this pathology, patients presenting with STEMI and concomitant COVID-19 infection seem to have a poorer outcome [,]. As reported in literature [], our population showed a high in-hospital mortality, mainly driven by the dramatic mortality rate especially during the first phase of the pandemic period []. As reported in Figure 1, the high mortality rate was mainly driven by a six-times greater incidence of respiratory complications among COVID-19 patients. The female gender appeared to be less prone to COVID-19 infection, probably due to the differences in inflammatory and immune response to the genetic profile and to the different hormone levels, with consequent lower risk of developing severe symptoms and lower mortality [,]. On the other hand, several studies in the literature reported a higher mortality rate for female STEMI patients with a less invasive approach, above all in specific socio-economic and cultural areas [,]. A German national study showed a 7% increase in in-hospital mortality in STEMI female patients independently from the presence of the main cardiovascular risk factors at baseline []. Similar results were reported in a subanalysis of the large SWEDEHEART registry with a higher short-term mortality among female STEMI patients strongly related to age []. Nowadays, older STEMI patients are treated invasively, more and more. A study published in 2018 involved 337 elderly STEMI patients hospitalized and all treated with pPCI []. The patients were divided according to gender: female (n = 117, mean age 73.4 ± 9.6 years) and male (n = 220, mean age 71.7 ± 8.6 years). The incidence of in-hospital MACE was similar, confirming the safety and efficacy of pPCI in elderly patients, independent of gender. Our study focused on STEMI patients hospitalized in our hub center, treated with urgent coronary angiography and pPCI, if needed, in the darkest period of the COVID-19 pandemic. In line with the previous literature, our population was composed of 26.8% females with a mean age higher than the men (72.1± 11.2 vs. 64.7 ± 12.6 years, p < 0.001). The main cardiovascular risk factors were similar between the two groups except for smoker status, more common in men. Anterior STEMI was the most represented with a mildly reduced ejection fraction (EF 48.3 ± 11.8%) reported without significant differences between genders. Coronary angiography showed a more extensive CAD in men, while women presented with a higher Killip class at admission and a more pronounced anemic status, both well-recognized negative prognostic factors during STEMI []. Even though older age and comorbidities were reported as the most common causes of poor prognosis among women with STEMI, our study did not show any significant differences in mortality both at short- and mid-term follow up. Reduced ejection fraction was the only independent predictor for in-hospital and 1-year mortality, due to its strict correlation with acute myocardial damage and residual cardiac function [,]. In the acute phase, the only other independent predictor of mortality was COVID-19 infection, secondary to the higher rate of respiratory complications, without any difference in terms of cardiac death. Similar results were found when the data were analyzed according to gender. Conversely, the impact of COVID-19 infection was completely lost by the 1-year follow up, where the only other independent predictor of mortality for both genders, in addition to EF, was older age. Our study showed an absence of gender impact on STEMI patient outcomes, even during a historical period which should have negatively influenced the management of these high-risk patients. In line with our results, other studies showed similar short- and long-term mortality between genders among STEMI patients, identifying age as the only possible confounding factor. The large ISACS-TC registry involving a total of 8834 STEMI patients showed that younger age was associated with a higher mortality rate in women, even after adjustment for confounding factors such as medical treatment, pPCI and other comorbidities. This difference decreased after the age of 60 and disappeared in older age groups []. On the other hand, one ad hoc study, which enrolled a total of 212 young STEMI patients (aged between 18 and 40) treated with pPCI between 2015 and 2019, showed a similar mortality rate both at short-term and at 1-year follow up []. All these findings underline that several controversies regarding the impact of gender in the STEMI setting are still present, probably due to several biases in the available studies. In fact, the female gender is generally underrepresented in studies regarding cardiovascular diseases (often less than 1/3 of the whole population). This is more evident in observational studies due to the lower incidence of cardiovascular diseases in women, especially in the younger age group. Women included were consequently more often fragile and with higher comorbidities. This is also the major limitation of our observational study in which females were underrepresented and older than the men, as reported in literature, but with a similar outcome, probably due to the homogeneous treatment both from the interventional and the pharmacological points of view. European and American cardiology societies suggest improving this issue with equal gender representation, especially in the case of randomized controlled trials, in order to generate solid data with definite gender-specific results.
4. Materials and Methods
We retrospectively analyzed consecutive STEMI patients hospitalized from 15 March 2020 to 15 March 2021 in our Hub centre in Milan, Lombardy. All clinical, demographic, and procedural characteristics were collected in a dedicated database. Hypertension was defined as a systolic blood pressure of ≥140 mmHg and/or a diastolic blood pressure of ≥90 mmHg or the presence of specific therapy at admission. Diabetes mellitus was defined as a fasting blood glucose of >126 mg/dL, a random blood sugar of >200 mg and associated symptoms, a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) > 6.5% or specific therapy upon admission. Anemia was defined as hemoglobin levels below 13.0 g/dL in men and 12.0 g/dL in women. Renal function was evaluated using the Cockcroft–Gault formula deriving the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Blood tests and nasopharyngeal swab tests for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 were collected at admission and during hospitalization. Left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) was calculated using standard transthoracic echocardiography with Simpson’s biplane method. Total ischemic time (time from symptoms onset to the restoration of coronary flow) was calculated for each patient. Urgent coronary angiography and primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI) were performed using radial or femoral approach, at the discretion of the operator. Critical stenosis was defined if >70% and relative to vessels with dimensions ≥ 1.5 mm in diameter. Multivessel disease was defined as the presence of critical stenosis in at least two vessels (≥2 mm). Successful procedure was defined by a TIMI degree of coronary flow > 2 being obtained in all the coronary branches []. Cardiac death was defined as cases of fatal arrhythmia, cardiogenic shock or mechanical complication. Respiratory pattern was registered at admission and monitored during the recovery. Respiratory complication was defined as a need for an increase in ventilatory support in respect to the admission. Ischemic stroke, non-fatal MI, major bleeding, defined from type 3 to 5 according to Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) criteria and urgent unplanned revascularization were identified as in-hospital adverse events. Patient follow-up was carried out through clinical visits, telephone calls and remote monitoring through the “Lombardia Regional Registry”. The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and all patients signed a disclosure for the use of personal data that were collected anonymously. Statistical analysis was performed with the SPSS 23 statistical package. Continuous data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD), and categorical data as percentage. Analysis of variance and chi-square test were performed for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed by logistic regressions, and a p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
5. Limitations
This study has some limitations, starting with its retrospective nature and the lower sample size of the female subgroup as often reported in most of the current literature. Another important limitation is the low number of COVID-19 patients that limited the statistical analysis in this high-risk subgroup. Finally, the retrospective nature of the study and the kind of follow-up performed restricted the clinical endpoint to mortality only.
6. Conclusions
Our study has shown that female gender in STEMI patients does not represent an independent predictor of mortality both in the short- and in the mid-term follow up. Concomitant COVID-19 infection significantly influenced in-hospital mortality due to the higher rate of respiratory complications in both genders. The impact of COVID-19 on mortality was completely lost at follow-up, where age and a reduced EF remained the only independent predictors, regardless of gender.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.B., G.T. and S.C.; methodology, L.B., C.A. and A.D.; validation, L.B. and S.C.; formal analysis, G.T. and L.B.; investigation, D.G. and D.C.M.; writing—original draft preparation, C.A., A.D. and L.B.; writing—review and editing, L.B., G.T. and S.C.; supervision, S.C., L.B. and G.T.; project administration, L.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and all patients signed a disclosure for the use of personal data collected anonymously.
Informed Consent Statement
A disclosure for the use of personal data was signed by all patients.
Data Availability Statement
Not available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest in writing this paper.
References
- Hartley, A.; Marshall, D.C.; Salciccioli, J.D.; Sikkel, M.B.; Maruthappu, M.; Shalhoub, J. Trends in mortality from ischemic heart disease and cerebrovascular disease in Europe: 1980 to 2009. Circulation 2016, 133, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McManus, D.D.; Gore, J.; Yarzebski, J.; Spencer, F.; Lessard, D.; Goldberg, R.J. Recent Trends in the Incidence, Treatment, and Outcomes of Patients with ST and Non-ST-Segment Acute Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Med. 2011, 124, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khera, S.; Kolte, D.; Gupta, T.; Subramanian, K.S.; Khanna, N.; Aronow, W.S.; Ahn, C.; Timmermans, R.J.; Cooper, H.A.; Fonarow, G.C.; et al. Temporal trends and sex differences in revascularization and outcomes of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in younger adults in the United States. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The EUGenMed; Cardiovascular Clinical Study Group; Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Oertelt-Prigione, S.; Prescott, E.; Franconi, F.; Gerdts, E.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Maas, A.H.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; et al. Gender in cardiovascular diseases: Impact on clinical manifestations, management, and outcomes. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brieger, D.; Eagle, K.A.; Goodman, S.G.; Steg, P.G.; Budaj, A.; White, K.; Montalescot, G. Acute coronary syndromes without chest pain, an underdiagnosed and undertreated high-risk group: Insights from the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events. Chest 2004, 126, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ibanez, B.; James, S.; Agewall, S.; Antunes, M.J.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Bueno, H.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Crea, F.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Halvorsen, S.; et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 119–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dey, S.; Flather, M.D.; Devlin, G.; Brieger, D.; Gurfinkel, E.P.; Steg, P.G.; Fitzgerald, G.; Jackson, E.; Eagle, K.A.; GRACE Investigators. Sex-related differences in the presentation, treatment and outcomes among patients with acute coronary syndromes: The Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events. Heart 2009, 95, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, S.P.; Roos-Hesselink, J.W.; van Leeuwen, M.A.; Lenzen, M.J.; van Geuns, R.-J.; Regar, E.; van Mieghem, N.M.; van Domburg, R.; Zijlstra, F.; Serruys, P.W.; et al. Excess mortality in women compared to men after PCI in STEMI: An analysis of 11,931 patients during 2000–2009. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 176, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.T.; Berger, A.K.; Duval, S.; Luepker, R.V. Gender disparity in cardiac procedures and medication use for acute myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 2008, 155, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hvelplund, A.; Galatius, S.; Madsen, M.; Rasmussen, J.N.; Rasmussen, S.; Madsen, J.K.; Sand, N.P.; Tilsted, H.-H.; Thayssen, P.; Sindby, E.; et al. Women with acute coronary syndrome are less invasively examined and subsequently less treated than men. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amgalan, A.; Malinowski, A.K.; Othman, M. COVID-19 and Sex-/Gender-Specific Differences: Understanding the Discrimination. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 47, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Ellingson, M.K.; Wong, P.; Israelow, B.; Lucas, C.; Klein, J.; Silva, J.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; Tokuyama, M.; et al. Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes. Nature 2020, 588, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresta, C.; Rocca, M.S.; di Nisio, A. Gender susceptibility to COVID-19: A review of the putative role of sex hormones and X chromosome. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiering, A.E.; de Vries, T.J. Why Females Do Better: The X Chromosomal TLR7 Gene-Dose Effect in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Moulin, T.C.; Schiöth, H.B. Sex differences in COVID-19: The role of androgens in disease severity and progression. Endocrine 2021, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Ur Rasool, R.; Russell, R.M.; Natesan, R.; Asangani, I.A. Targeting androgen regulation of TMPRSS2 and ACE2 as a therapeutic strategy to combat COVID-19. iScience 2021, 24, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratchian, M.; McManus, J.M.; Berk, M.P.; Nakamura, F.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Xu, W.; Erzurum, S.; Drazba, J.; Peterson, J.; Klein, E.A.; et al. Androgen regulation of pulmonary AR, TMPRSS2 and ACE2 with implications for sex-discordant COVID-19 outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, A.T.; Heaton, N.S. The Impact of Estrogens and Their Receptors on Immunity and Inflammation during Infection. Cancers 2022, 14, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidecicchi, T.; Fruzzetti, F.; Lete Lasa, L.I.; Calaf, J. COVID-19, gender and estroprogestins, what do we know? Reprod. Health Care 2021, 27, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Wu, X.X.; Jiang, X.G.; Xu, K.J.; Ying, L.J.; Ma, C.L. Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) outside of Wuhan, China: Retrospective case series. BMJ 2020, 368, m606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abate, B.B.; Kassie, A.M.; Kassaw, M.W.; Aragie, T.G.; Masresha, S.A. Sex difference in coronavirus disease (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, T.; Lucia, B.; Stefano, L.; Gentile, D.; Barbara, C.; Marco, C.; Mafrici, A.; Carugo, S. Impact of COVID-19 on STEMI: Second youth for fibrinolysis or time to centralized approach? IJC Heart Vasc. 2020, 30, 100600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, S.S.; Basso, C.; Calabro, C.; Curcio, M.P.; Filardi, A.; Mancone, P.P.; Mercuro, M.; Muscoli, G.; Nodari, S.; Pedrinelli, S.; et al. Reduction of hospitalizations for myocardial infarction in Italy in the COVID-19 era. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2083–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippo, O.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Angelini, F.; Bocchino, P.P.; Conrotto, F.; Saglietto, A.; Secco, G.G.; Campo, G.; Gallone, G.; Verardi, R.; et al. Reduced Rate of Hospital Admissions for ACS during COVID-19 Outbreak in Northern Italy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, N.; Wilson, L.; Bhatnagar, P.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Rayner, M.; Nichols, M. Cardiovascular disease in Europe: Epidemiological update 2016. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 3232–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, L.; Tumminello, G.; Lucreziotti, S.; Gentile, D.; Centola, M.; Conconi, B.; Carlà, M.; Mafrici, A.; Carugo, S. Mortality in STEMI Patients During the COVID Era: Has the Pandemic Changed Our Clinical Practice? Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2021, 22, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Sole, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Loffredo, L.; Carnevale, R.; Menichelli, D.; Vicario, T.; Pignatelli, P.; Pastori, D. Features of severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, G.; di Trolio, R. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Italy: Analysis of Risk Factors and Proposed Remedial Measures. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tumminello, G.; Barbieri, L.; Toriello, F.; Lucreziotti, S.; Carlà, M.; Conconi, B.; Mafrici, A.; Carugo, S. Influence of different COVID-19 pandemic phases on STEMI: Experience from an Italian Hub centre. Cardiovasc. Revasc. Med. 2022, 37, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integrating WHO Sex-Disaggregated Data to the Tracker. 2021. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Spadea, T.; Di Girolamo, C.; Landriscina, T.; Leoni, O.; Forni, S.; Colais, P.; Fanizza, C.; Allotta, C.; Onorati, R.; Gnavi, R.; et al. Indirect impact of COVID-19 on hospital care pathways in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehnemund, L.; Koeppe, J.; Feld, J.; Wiederhold, A.; Illner, J.; Makowski, L.; Reinecke, H.; Freisinger, E. Gender differences in acute myocardial infarction—A nationwide German real-life analysis from 2014 to 2017. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figtree, G.A.; Vernon, S.T.; Hadziosmanovic, N.; Sundström, J.; Alfredsson, J.; Arnott, C.; Delatour, V.; Leósdóttir, M.; Hagström, E. Mortality in STEMI patients without standard modifiable risk factors: A sex-disaggregated analysis of SWEDEHEART registry data. Lancet 2021, 397, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Zhu, B.; Su, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, B. Gender differences among elderly patients with primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrante, G.; Barbieri, L.; Sponzilli, C.; Lucreziotti, S.; Salerno Uriarte, D.; Centola, M.; Verdoia, M.; Carugo, S. Predictors of Mortality and Long-Term Outcome in Patients with Anterior STEMI: Results from a Single Center Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.W.; Clare, R.M.; Schulte, P.J.; Pieper, K.S.; Shaw, L.K.; Califf, R.M.; Ohman, E.M.; Van de Werf, F.; Hirji, S.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Extent, location, and clinical significance of non-infarct-related coronary artery disease among patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. JAMA 2014, 312, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenko, E.; Yoon, J.; Kedev, S.; Stankovic, G.; Vasiljevic, Z.; Krljanac, G.; Kalpak, O.; Bugiardini, R.; Ricci, B.; Miličić, D.; et al. Sex differences in outcomes after STEMI effect modification by treatment strategy and age. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, B.; Kivanc, E.; Dizman, R.; Mert, G.O.; Murat, S. Gender differences in clinical characteristics and in-hospital and one-year outcomes of young patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction under the age of 40. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2021, 13, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewelde, S.Z.; Liu, S.S.; Winters, M.E. Cardiogenic Shock. Cardiol. Clin. 2018, 36, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).