High-Throughput Phenotyping: Application in Maize Breeding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
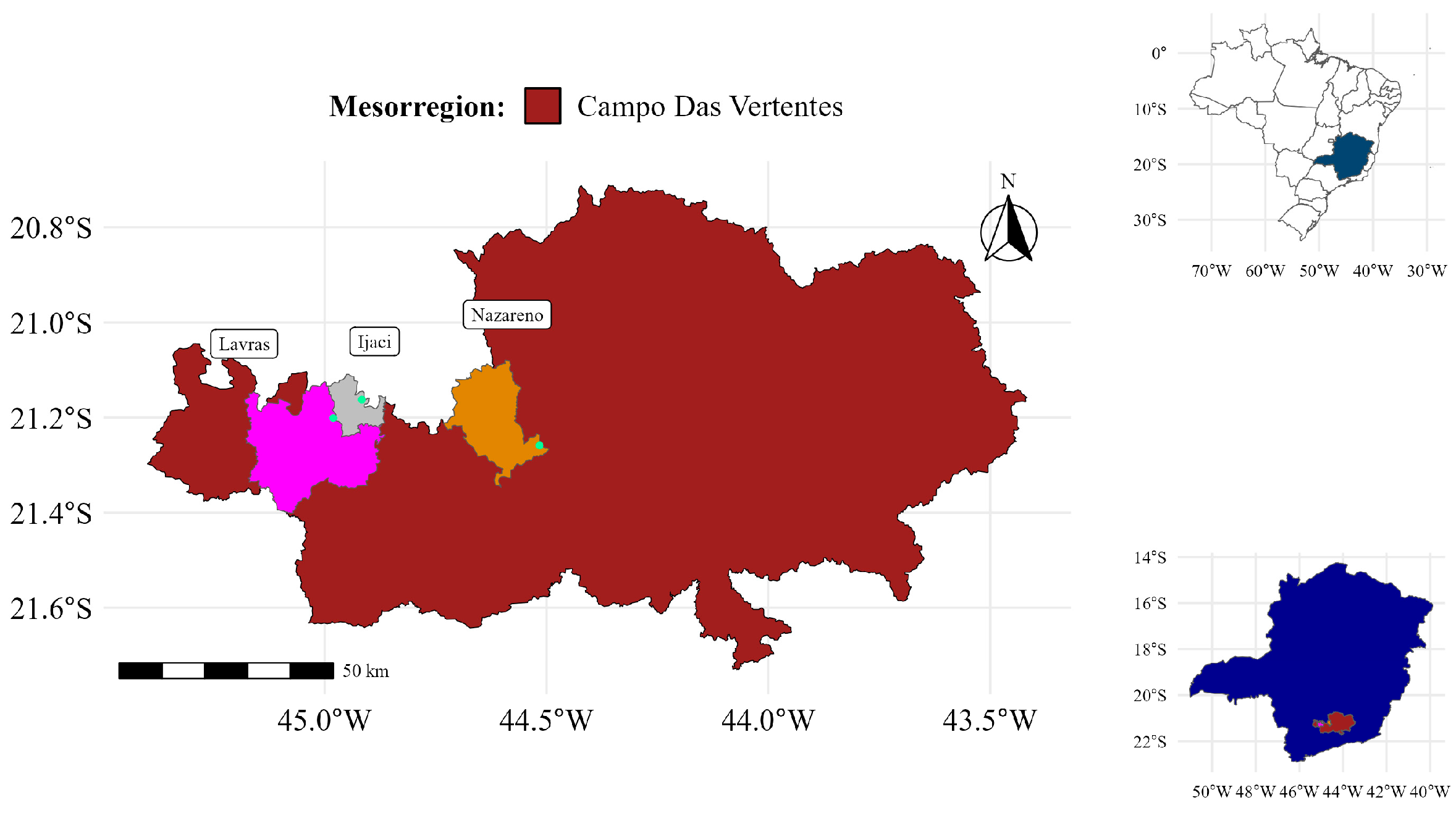
2.1. Study Area
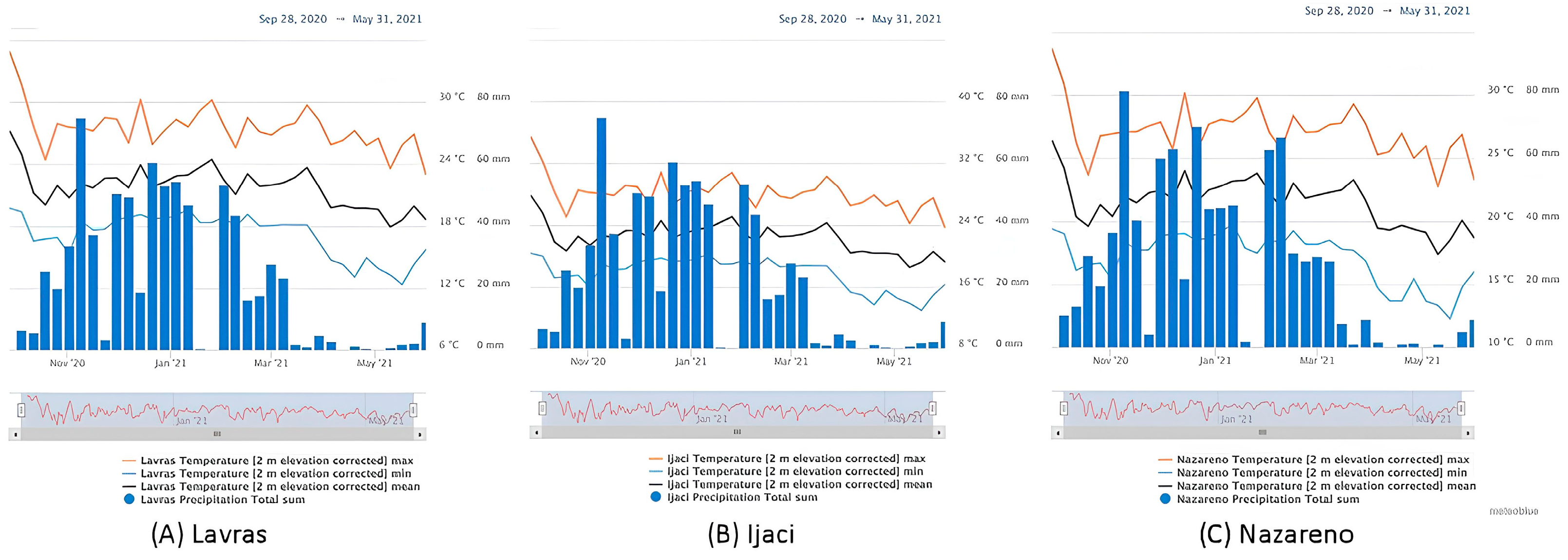
2.2. Environmental Conditions
2.3. Experimental Management
2.4. Experimental Scheme
2.5. Data Acquisition in the Field
2.6. Image Acquisition and Processing
| Index | Equations | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NGRDI | (G − R)/(G + R) | (1) | [37] |
| VARI | (G − R)/(G + R − B) | (2) | [38] |
| GLI | (2 ∗ G − R − B)/(2 ∗ G + R + B) | (3) | [39] |
| ExG COLOR INDEX | 2 ∗ g − r − b | (4) | [40] |
2.7. Pre-Processing of Data and Statistical Analysis
- yij: observed value for the plot that received hybrid i in block j.
- µ: constant associated with every observation.
- hi: effect of hybrid i.
- bj: effect of block j.
- eij: error associated with hybrid i in block j.
- yijk: observed value for the plot that received hybrid i in block j at location l.
- µ: constant associated with every observation.
- hi: effect of hybrid i.
- bj: effect of block j in location k.
- lk: effect of location k.
- h ∗ lik: effect of hybrid-by-location interaction.
- eijk: error associated with hybrid i in block j at location k.
- residual variation.
- hybrid means.
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dos Santos, C.V.; de Moraes, F.A.; Torres, L.G.; da Silva, R.A.; da Silva, K.J.; Moreira, S.G.; de Menezes, C.B.; Borém, A. Fenotipagem de raízes de milho visando tolerância à seca: Uma revisão. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e24119817265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.F.; Oliveira, H.R.; Volenec, J.J.; Rainey, K.M.; Brito, L.F. Integrating high-throughput phenotyping and statistical genomic methods to genetically improve longitudinal traits in crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wu, F.; Ao, Z.; Jin, S.; Qin, F.; Liu, B.; Pang, S.; Liu, L.; Guo, Q. Evaluating Maize Phenotype Dynamics under Drought Stress Using Terrestrial Lidar. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wen, W.; Guo, X.; Yu, Z.; Gu, S.; Yan, H.; Zhao, C. High-Throughput Phenotyping Analysis of Maize at the Seedling Stage Using End-to-End Segmentation Network. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0241528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazakos, C.; Hanemian, M.; Trontin, C.; Jiménez-Gómez, J.M.; Loudet, O. New Strategies and Tools in Quantitative Genetics: How to Go from the Phenotype to the Genotype. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, W.; Zhao, C. High-Throughput Phenotyping: Breaking through the Bottleneck in Future Crop Breeding. Crop J. 2021, 9, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, H.B.; Xu, X.Q.; He, J.Y.; Ge, X.K.; Yao, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.X.; Tian, Y.C. Predicting Grain Yield in Rice Using Multi-Temporal Vegetation Indices from UAV-Based Multispectral and Digital Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, S.F.; Rizza, F.; Badeck, F.W.; Berton, A.; Delbono, S.; Gioli, B.; Toscano, P.; Zaldei, A.; Matese, A. UAV-Based High-Throughput Phenotyping to Discriminate Barley Vigour with Visible and near-Infrared Vegetation Indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5330–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewes, A.; Schellberg, J. Towards Remote Estimation of Radiation Use Efficiency in Maize Using UAV-Based Low-Cost Camera Imagery. Agronomy 2018, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Bian, C.; Jin, L.; Liu, J. The Estimation of Crop Emergence in Potatoes by UAV RGB Imagery. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Zhou, J.; Han, Z.; Li, D.; Cao, Q.; Yao, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Cheng, T. Improved Estimation of Aboveground Biomass in Wheat from RGB Imagery and Point Cloud Data Acquired with a Low-Cost Unmanned Aerial Vehicle System. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimaitijiang, M.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Hartling, S.; Esposito, F.; Fritschi, F.B. Soybean Yield Prediction from UAV Using Multimodal Data Fusion and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannoura, R.; Brinkmann, K.; Uteau, D.; Bruns, C.; Joergensen, R.G. Monitoring of Crop Biomass Using True Colour Aerial Photographs Taken from a Remote Controlled Hexacopter. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 129, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, H.; Flores-Magdaleno, H.; Ascencio-Hernández, R.; Khalil-Gardezi, A.; Tijerina-Chávez, L.; Mancilla-Villa, O.R.; Vázquez-Peña, M.A. Corn Grain Yield Estimation from Vegetation Indices, Canopy Cover, Plant Density, and a Neural Network Using Multispectral and RGB Images Acquired with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Agriculture 2020, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araus, J.L.; Kefauver, S.C.; Zaman-Allah, M.; Olsen, M.S.; Cairns, J.E. Translating High-Throughput Phenotyping into Genetic Gain. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Duan, L. High-Throughput Phenotyping (HTP) and Genetic Analysis Technologies Reveal the Genetic Architecture of Grain Crops. In High-Throughput Crop Phenotyping; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duddu, H.S.N.; Johnson, E.N.; Willenborg, C.J.; Shirtliffe, S.J. High-Throughput UAV Image-Based Method Is More Precise than Manual Rating of Herbicide Tolerance. Plant Phenom. 2019, 2019, 6036453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, K.; Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Yang, W. A High-Throughput Maize Kernel Traits Scorer Based on Line-Scan Imaging. Measurement 2016, 90, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.D.; Haase, N.J.; Lee, J.; Kaeppler, S.M.; de Leon, N.; Spalding, E.P. A Robust, High-throughput Method for Computing Maize Ear, Cob, and Kernel Attributes Automatically from Images. Plant J. 2017, 89, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makanza, R.; Zaman-Allah, M.; Cairns, J.E.; Eyre, J.; Burgueño, J.; Pacheco, Á.; Diepenbrock, C.; Magorokosho, C.; Tarekegne, A.; Olsen, M.; et al. High-Throughput Method for Ear Phenotyping and Kernel Weight Estimation in Maize Using Ear Digital Imaging. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipindu, L.; Mupangwa, W.; Mtsilizah, J.; Nyagumbo, I.; Zaman-Allah, M. Maize Kernel Abortion Recognition and Classification Using Binary Classification Machine Learning Algorithms and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. AI 2020, 1, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, F.I.; Caraza-Harter, M.V.; Endelman, J.B. FIELDimageR: An R Package to Analyze Orthomosaic Images from Agricultural Field Trials. Plant Phenome J. 2020, 3, e20005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cai, Z.; Han, J.; Qin, H. Automatic Kernel Counting on Maize Ear Using RGB Images. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienbaum, L.; Correa Abondano, M.; Blas, R.; Schmid, K. DeepCob: Precise and High-Throughput Analysis of Maize Cob Geometry Using Deep Learning with an Application in Genebank Phenomics. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warman, C.; Sullivan, C.M.; Preece, J.; Buchanan, M.E.; Vejlupkova, Z.; Jaiswal, P.; Fowler, J.E. A Cost-effective Maize Ear Phenotyping Platform Enables Rapid Categorization and Quantification of Kernels. Plant J. 2021, 106, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darrah, L.L.; McMullen, M.D.; Zuber, M.S. Breeding, genetics and seed corn production. In Em Corn; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 19–41. ISBN 9780128119716. [Google Scholar]
- Rebetzke, G.J.; Jimenez-Berni, J.; Fischer, R.A.; Deery, D.M.; Smith, D.J. Review: High-Throughput Phenotyping to Enhance the Use of Crop Genetic Resources. Plant Sci. 2019, 282, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Song, H. Corn Ear Test Using SIFT-Based Panoramic Photography and Machine Vision Technology. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dados Históricos Simulados de Clima e Tempo Para Lavras. Available online: https://www.meteoblue.com/pt/tempo/historyclimate/climatemodelled/lavras_brasil_3458696 (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Salomão, P.E.A.; Kriebel, W.; dos Santos, A.A.; Martins, A.C.E. A importância do sistema de plantio direto na palha para reestruturação do solo e restauração da matéria orgânica. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e154911870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, J.O.; Monteiro, P.A.; Miranda Filho, H.S.; Raij, B. Recomendações de Adubação e Calagem para o Estado de São Paulo; IAC: Campinas, Brazil, 1997; Volume 100, pp. 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Resende, E.L.; Pinho, R.G.V.; Silva, E.V.V.; Massitela, J.J.; de Souza, V.F.; Souza, J.L.D. Mean components for choosing maize populations to extract inbred lines. Ciênc. Agrotecnologia 2020, 44, e017820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.python.org/success-stories/category/scientific/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Professional Photogrammetry and Drone Mapping Software. Available online: https://www.pix4d.com/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Agisoft Metashape: Agisoft Metashape. Available online: https://www.agisoft.com/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Stark, R.; Rundquist, D. Novel Algorithms for Remote Estimation of Vegetation Fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhaichi, M.; Borman, M.M.; Johnson, D.E. Spatially Located Platform and Aerial Photography for Documentation of Grazing Impacts on Wheat. Geocarto Int. 2001, 16, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.E.; Neto, J.C. Verification of Color Vegetation Indices for Automated Crop Imaging Applications. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 63, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Gitelson, A.A.; Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Wardlow, B.D.; Suyker, A.E.; Verma, S.B.; Shibayama, M. An Alternative Method Using Digital Cameras for Continuous Monitoring of Crop Status. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 154–155, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitijiang, M.; Ghulam, A.; Paheding, S.; Hartling, S. Unmanned aerial system (UAS)—Based phe-notyping of soybean using multi-sensor data fusion and extreme learning machine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Resende, M.D.V.; Duarte, J.B. Precisão e controle de qualidade em experimentos de avaliação de cultivares. Pesqui. Agropecuária Trop. 2007, 37, 182–194. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, C.D. GENES—A software package for analysis in experimental statistics and quantitative genetics. Acta Sci. Agron. 2013, 35, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.J. Robust Regression: Asymptotics, Conjectures and Monte Carlo. Ann. Stat. 1973, 1, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, E.M.; Huber, P.J. Robust Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rodene, E.; Xu, G.; Palali Delen, S.; Zhao, X.; Smith, C.; Ge, Y.; Schnable, J.; Yang, J. A UAV-based High-throughput Phenotyping Approach to Assess Time-series Nitrogen Responses and Identify Trait-associated Genetic Components in Maize. Plant Phenome J. 2022, 5, e20030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M. Integração de ganho genético e análise de lacunas para prever melhorias na produtividade das culturas. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 582–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.J.; Knott, M. A cluster analysis method for grouping means in the analysis of variance. Biometrics 1974, 30, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivasa, W.; Onísimo; Burgueno, J. Fenotipagem de alto rendimento baseada em UAV para aumentar a precisão da previsão e seleção em variedades de milho sob inoculação artificial de MSV. Comput. E Eletrônica Na Agric. 2021, 184, 106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galon, L. Períodos de interferência de plantas daninhas infestando a cultura do milho. Rev. De Ciências Agrárias 2018, 17, 197–205. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, N.; Li, L.; Schmitz, N.; Tian, L.F.; Greenberg, J.A.; Diers, B.W. Development of Methods to Improve Soybean Yield Estimation and Predict Plant Maturity with an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Based Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Rahimi-Eichi, V.; Haefele, S.; Garnett, T.; Miklavcic, S.J. Estimation of vegetation indices for high-throughput phenotyping of wheat using aerial imaging. Métodos Veg. 2018, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefauver, S.C.; El-Haddad, G.; Vergara-Diaz, O.; Araus, J.L. RGB picture vegetation indexes for High-Throughput Phenotyping Platforms (HTPPs). In Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XVII; SPIE: St Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; pp. 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lussem, U. Avaliação de índices de vegetação baseados em RGB a partir de imagens de UAV para estimar a produção de forragem em pastagens. Os Arquivos Internacionais de Fotogrametria. Sensoriamento Remoto E Ciências Da Informação Espac. 2018, 42, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, F. Estimativa da Produtividade e Biomassa Aérea do Milho (Zea mays) através de Índices de Vegetação na Ilha da Madeira. Agricultura 2023, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar]
- Vian, A.L.; Bredemeier, C.; Silva, P.R.F.D.A.; Santi, A.L.; Silva, C.P.G.D.A.; Santos, F.L.D.O.S. Limites críticos de ndvi para estimativa do potencial produtivo do milho. Rev. Bras. Milho Sorgo 2018, 17, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, G. Genetic and Molecular Control of Grain Yield in Maize. Mol. Breed. 2021, 41, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.D.; Pereira, M.D.; Silva, J.A. Processamento digital de imagens na determinação do vigor de sementes de milho. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Agrar./Braz. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhu, K.; Guan, H.; Feng, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, G. High-throughput phenotyping analysis of potted soybean plants using colorized depth images based on a proximal platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komyshev, E.; Genaev, M.; Afonnikov, D. Evaluation of the SeedCounter, A mobile application for grain phenotyping. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, F. Leaf blade area of different plants estimated by linear and dry matter measures, calibrated with the ImageJ software. Interciencia 2015, 40, 570–575. [Google Scholar]


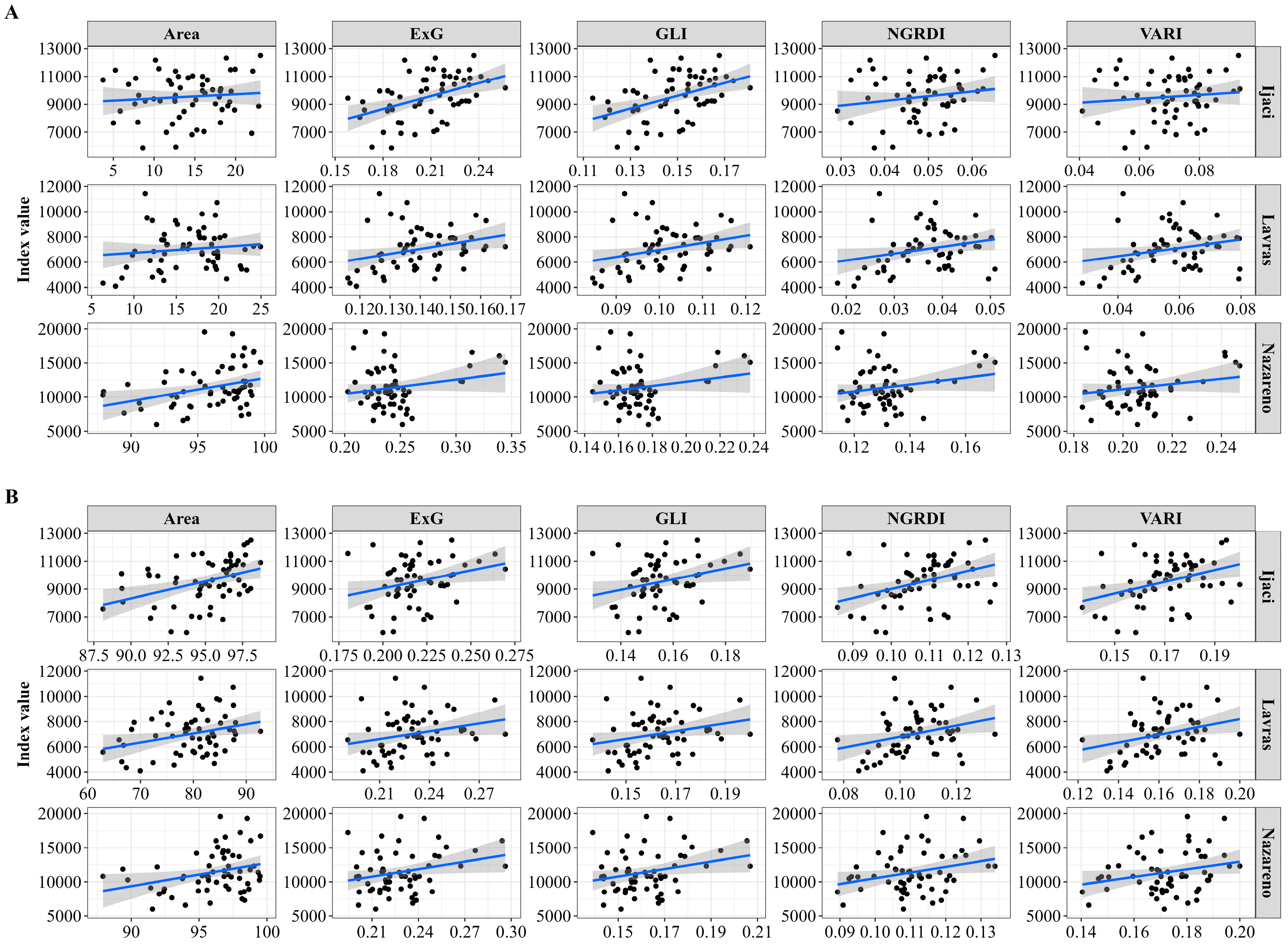
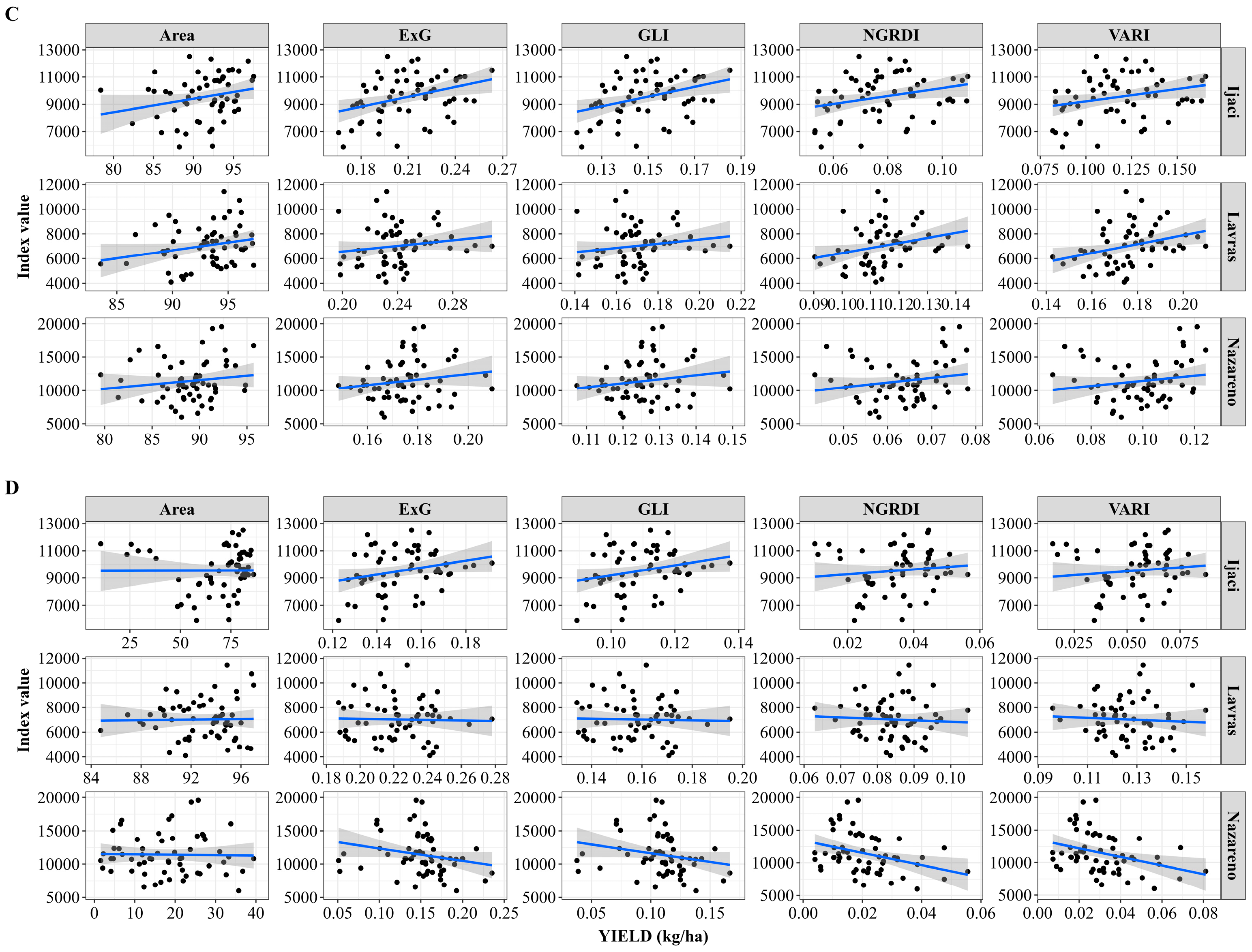
| Flight 1 | Flight 2 | Flight 3 | Flight 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ijaci | V5 | VT | R3 | R5 |
| Lavras | V5 | V10 | VT | R3 |
| Nazareno | V8 | VT | R4 | R6 |
| Hybrids AB | AB Mean | Hybrids CD | CD Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| RB 9077 | 12,156 a | RB 9077 | 12,930 a |
| DKB 230 | 10,623 a | DKB 230 | 11,151 a |
| Hybrid AB 2 | 9707 b | Hybrid CD 2 | 7445 b |
| Hybrid AB 1 | 9559 b | Hybrid CD 1 | 10,235 a |
| Hybrid AB 4 | 9468 b | Hybrid CD 4 | 8242 b |
| Hybrid AB 5 | 9466 b | Hybrid CD 5 | 8711 b |
| Hybrid AB 6 | 9363 b | Hybrid CD 6 | 6236 b |
| Hybrid AB 3 | 8868 b | Hybrid CD 3 | 8732 b |
| Hybrid AB | 8306 b | Hybrid AB | 10,108 a |
| Hybrid CD | 6739 b | Hybrid CD | 7525 b |
| Flight 1 | Flight 2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGRDI | VARI | GLI | ExG | Area | NGRDI | VARI | GLI | ExG | Area | |
| Lavras | 0.07 * | 0.05 | 0.09 * | 0.09 * | 0.02 | 0.09 * | 0.09 * | 0.07 * | 0.07 * | 0.09 ** |
| Ijaci | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.19 ** | 0.19 ** | 0.01 | 0.14 * | 0.14 ** | 0.08 * | 0.06 * | 0.15 ** |
| Nazareno | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.04 * | 0.11 ** | 0.07 * | 0.06 * | 0.07 * | 0.07 * | 0.09 ** |
| Flight 3 | Flight 4 | |||||||||
| NGRDI | VARI | GLI | ExG | Area | NGRDI | VARI | GLI | ExG | Area | |
| Lavras | 0.08 ** | 0.10 ** | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.0003 |
| Ijaci | 0.08 * | 0.07 * | 0.12 ** | 0.13 ** | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.06 * | 0.06 * | 0.00 |
| Nazareno | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.12 ** | 0.12 ** | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.001 |
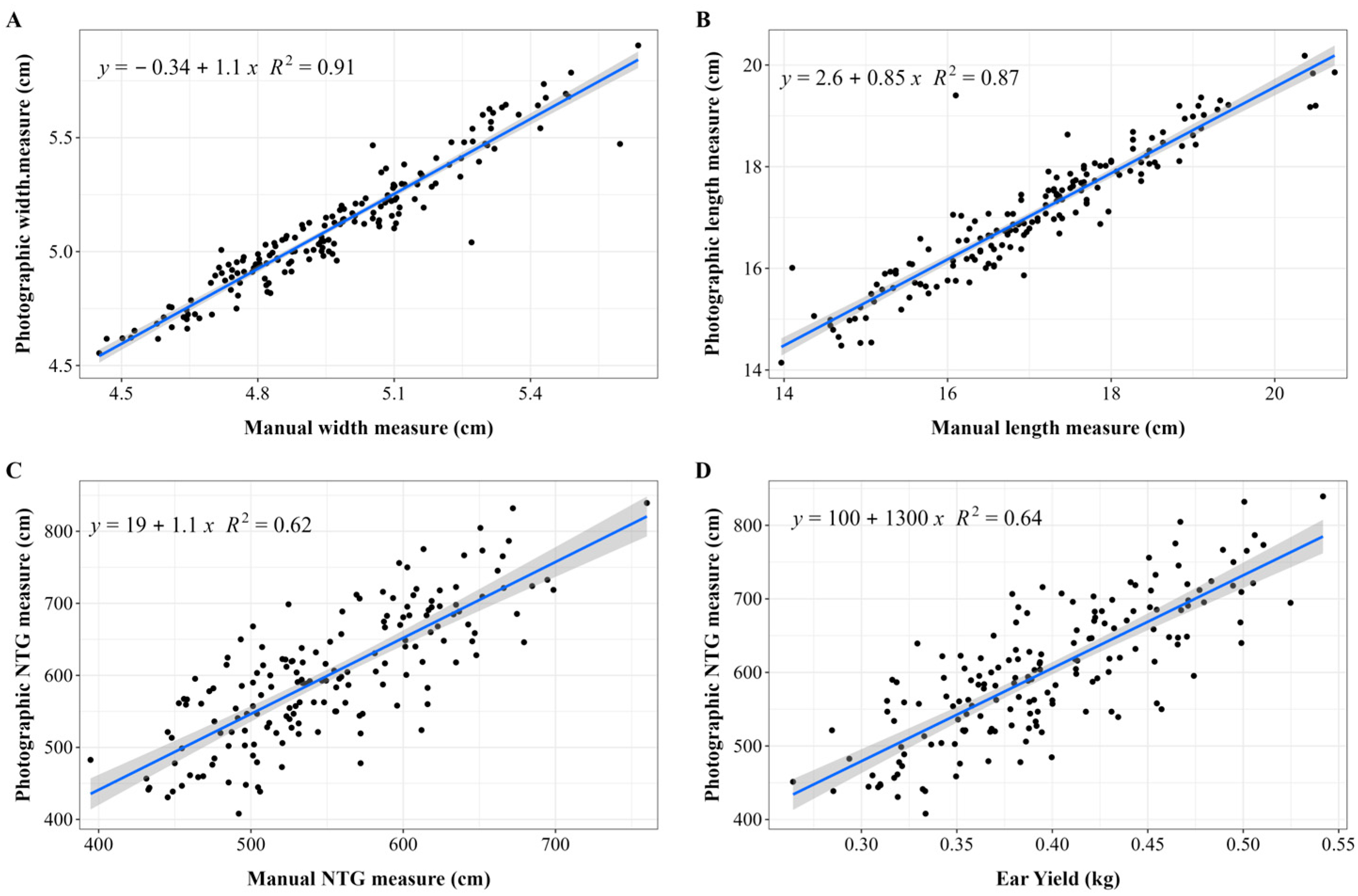
| Manual Accuracy | Photographic Accuracy | Correlation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width | Length | TNG | Width | Length | TNG | Width | Length | TNG | |
| Ijaci AB | 68.95 | 67.94 | 84.56 | 77.12 | 72.85 | 84.58 | 0.90 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.65 ** |
| Ijaci CD | 85.55 | 74.48 | 76.00 | 82.58 | 73.27 | 87.86 | 0.96 ** | 0.98 ** | 0.70 ** |
| Lavras AB | 65.99 | 72.54 | 65.26 | 81.96 | 75.20 | 83.31 | 0.95 ** | 0.95 ** | 0.79 ** |
| Lavras CD | 92.39 | 17.78 | 78.82 | 93.66 | 69.47 | 83.77 | 0.98 ** | 0.83 ** | 0.80 ** |
| Nazareno AB | 57.02 | 80.58 | 83.73 | 71.58 | 79.97 | 93.52 | 0.97 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.75 ** |
| Nazareno CD | 79.78 | 82.20 | 51.23 | 78.62 | 80.78 | 64.96 | 0.98 ** | 0.97 ** | 0.71 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Resende, E.L.; Bruzi, A.T.; Cardoso, E.d.S.; Carneiro, V.Q.; Pereira de Souza, V.A.; Frois Correa Barros, P.H.; Pereira, R.R. High-Throughput Phenotyping: Application in Maize Breeding. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 1078-1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020062
Resende EL, Bruzi AT, Cardoso EdS, Carneiro VQ, Pereira de Souza VA, Frois Correa Barros PH, Pereira RR. High-Throughput Phenotyping: Application in Maize Breeding. AgriEngineering. 2024; 6(2):1078-1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleResende, Ewerton Lélys, Adriano Teodoro Bruzi, Everton da Silva Cardoso, Vinícius Quintão Carneiro, Vitório Antônio Pereira de Souza, Paulo Henrique Frois Correa Barros, and Raphael Rodrigues Pereira. 2024. "High-Throughput Phenotyping: Application in Maize Breeding" AgriEngineering 6, no. 2: 1078-1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020062
APA StyleResende, E. L., Bruzi, A. T., Cardoso, E. d. S., Carneiro, V. Q., Pereira de Souza, V. A., Frois Correa Barros, P. H., & Pereira, R. R. (2024). High-Throughput Phenotyping: Application in Maize Breeding. AgriEngineering, 6(2), 1078-1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering6020062









