Abstract
Background/Objectives: The gut–liver axis is bidirectional and influences the body’s homeostasis. Pathologies such as metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver (MASL) can have detrimental effects on the human microbiome, with multiple systemic effects. Furthermore, the geographical particularities of the intestinal microbiome may influence liver disease. The study’s outcome was to identify dysbiosis in a group of patients with MASL from the western region of Romania. Methods: The NGS shotgun genomic sequencing (WGS metagenomics) method was used to identify bacteria in fecal samples. The data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics software [version 29.0.2.0 (20)]. Results: Out of the 122 MASL patients included in the study, 43 (35.24%) exhibited low alpha diversity. In the subgroup with a normal biodiversity index, approximately half were identified with a Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio below the lower reference value, while the remaining patients presented dysbiosis based on decreased concentrations of Proteobacteria and Prevotella, considered among the most relevant species supporting dysbiosis. A higher prevalence of Prevotella species (15.99 ± 13.65%) was identified in the study cohort. Conclusions: The present study demonstrates that patients with MASL from the western region of Romania exhibit criteria for intestinal dysbiosis, namely reduced bacterial diversity, along with significant alterations in populations of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Prevotella. Together, these findings suggest a possible influence of geo-cultural factors on the intestinal microbiome, highlighting the need for regionally adapted therapeutic interventions to support liver health.
1. Introduction
Liver health directly reflects a person’s general health since it is involved in fundamental functions such as detoxification and metabolism, storage of nutrients, and regulation of the immune system. This balance is increasingly threatened by the growing prevalence of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver (MASL), which has emerged as one of the most common chronic states of the liver worldwide. MASL, a condition now affecting approximately 30% of the world’s population, is usually associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and a host of other metabolic disorders [1]. With increasing knowledge of liver disease comes a growing appreciation for its intricate links with other bodily systems—most notably, the gut. A better understanding of gut microbiota through the latest research has revealed its profound interplay with liver health, offering new insights into the pathogenesis and potential therapeutic strategies for fatty liver diseases.
1.1. The Gut–Liver Axis and the Role of Gut Microbiota in Liver Diseases
The gut–liver axis describes the two-way link between gut bacteria and the liver. The portal vein connects the two by carrying microbe byproducts and other gut substances straight to the liver [2]. Gut microbes, a diverse community of trillions of microorganisms, play a key part in controlling metabolism, immune defences, and inflammation, which affect liver health. A balanced gut microbiome helps the liver work properly and keeps metabolism steady. However, dysbiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiome, can disrupt these processes. This leads to increased gut permeability, inflammation, and liver disease. To grasp how liver diseases like MASL start, we need to know how microbe changes impact the liver. These conditions share common paths involving both metabolism and microbes [3].
MASL and alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) are the two primary forms of steatotic liver disease (SLD). Both involve an accumulation of excess fat in the liver. Chronic alcohol consumption causes ALD. Metabolic-associated steatohepatitis and liver disease (MASLD) happens without much alcohol use and stems from metabolic issues such as obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. MASLD covers a spectrum of liver conditions. These range from simple steatosis (MASL) to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), which involves inflammation and cell damage of the liver, which could potentially progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer [4]. The underlying pathophysiology of these conditions involves fat buildup, oxidative stress, inflammation, and insulin resistance. MASLD is becoming more common as obesity and sedentary lifestyles are rising, making it a leading cause of liver disease-related morbidity and mortality. As liver disease progresses, the role of gut microbial imbalances becomes increasingly apparent, with research suggesting that alterations in specific microbial populations may drive disease severity and progression [5].
Emerging studies recognize the gut microbiota as a main player in the development and progression of fatty liver disease. The studies revealed that patients with MASL usually have specific gut microbial profiles characterized by reduced beneficial bacteria and an overgrowth of harmful species. These alterations induce liver pathology through several mechanisms [6]. For example, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and bile acids represent important microbial metabolites known to modulate lipid metabolism and inflammation and thus directly impact the liver. In addition, lipopolysaccharides (LPSs)—structural components of the cell walls of Gram-negative bacteria—after crossing the impaired intestinal barrier (“leaky gut”), enter the general bloodstream and promote systemic inflammation, which plays a key role in the initiation of liver steatosis [7].
Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes represent the predominant phyla, accounting for over 90% of the normal, resident gut microbiota. Firmicutes, primarily composed of the classes Clostridia (with key members such as Clostridium spp., Ruminococcus spp., Eubacterium spp., Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Roseburia spp.) and Bacilli (including Lactobacillus spp., Enterococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Bacillus spp.), perform essential functions such as the production of SCFAs (with anti-inflammatory effects, insulin resistance reduction, and maintenance of intestinal barrier integrity), metabolism of complex dietary fibres (preventing the hepatic accumulation of toxic metabolites), and involvement in lipid metabolism (preventing hepatic fat accumulation). Dysregulation of this phylum can lead to systemic inflammation and fat accumulation in the liver, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of MASL.
On the other hand, Bacteroidetes, which include the essential classes Bacteroidia (Bacteroides spp., Prevotella spp., Parabacteroides spp.) and Flavobacteria (Flavobacterium spp., Chryseobacterium spp.), play a significant role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, fibre fermentation, and SCFA production. A decrease in the proportion of Bacteroidetes leads to increased intestinal permeability, systemic inflammation, and fat accumulation in the liver, thus promoting the progression of liver diseases.
A better understanding of microbiota in liver disease can uncover new therapeutic targets, from prebiotics to probiotics and microbiome-modulating drugs that might help prevent or cure fatty liver diseases.
1.2. External Influences on Microbiota and Regional Implications
The gut microbiome is influenced by many factors, among which diet, obesity, physical activity, diabetes, immunosuppression, stress, and medication play an important role. Diet can have positive and negative effects on bacterial balance; consuming yoghurt and fiber positively influences the gut microbiome, while consuming carbohydrates decreases the concentrations of beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. This can also stimulate the proliferation of opportunistic and potentially harmful bacteria, such as Clostridium and Enterococcus; promote inflammation by stimulating the release of LPSs from Gram-negative bacteria; increase intestinal permeability; and ultimately lead to obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Obesity is responsible for increasing the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, reducing bacterial diversity, promoting pro-inflammatory bacteria, increasing intestinal permeability, altering SCFA production, and reducing beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, which have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory roles. Thus, diet can induce dysbiosis, which leads to obesity, and obesity, in turn, induces dysbiosis, creating a negative feedback loop that exacerbates obesity and its associated diseases.
The western region of Romania is known for various cultural and dietary influences (Hungarian, German, and Serbian). The diet is often focused on a high intake of carbohydrates, animal fats, and pickles. These culinary habits may influence the microbiome of the population in the area.
Although advances in our understanding of the gut–liver axis have been enormous, there are some important gaps. Unless information on the changes in the microbiome and how these relate to changes in disease severity is provided, dysbiosis is largely accepted as a central player in fatty liver disease. In addition, whether microbial metabolites interact with the liver cells themselves opens up new areas of exploration. This article aims to address the existing gaps in the current medical literature by synthesizing recent cutting-edge research on the influence of microbiota on liver health, with a special focus on MASL. Additionally, considering the variations in the microbiota based on the geographic location of the studied population, this study analyzes, for the first time, the relationship between the microbiota and hepatic steatosis in adult patients from the western region of Romania. The paper’s main objective is to identify relevant connections between the microbiota and MASL in this specific context, thereby contributing to a better understanding of underlying mechanisms and potential region-specific personalized therapeutic interventions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
A prospective study was conducted between January and June 2024 on 130 patients who presented to the Venus Vascular Center in Oradea, Romania, with a diagnosis of MASL. All patients signed informed consent forms. The Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Oradea (Approval No. CEFMF/5 din 28 February 2024) approved the study and adhered to the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to the initial cohort of patients.
The diagnosis of MASL was established based on imaging results (abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging), excluding other hepatic causes and in the presence of clinical risk factors (obesity, diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia). The degree of fibrosis was assessed using transient elastography (FibroScan), with all patients evaluated in an outpatient clinic or a private healthcare setting.
- Inclusion Criteria:
- age over 18 years;
- at least 4 weeks after a colonoscopy or enema;
- confirmed diagnosis of MASL;
- absence of fibrosis (F0–F1 on FibroScan);
- signed informed consent to participate in the study;
- born and having lived only in the western region of Romania.
- Exclusion Criteria:
- age under 18;
- treatment with antibiotics, antifungals, probiotics, proton pump inhibitors, bismuth, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, rectal suppositories, enemas, activated charcoal, digestive enzymes, laxatives, mineral oil, castor oil, and/or bentonite clay and quercetin within 90 days;
- medical history of severe liver disease, gastrointestinal disorders, gastrointestinal surgery within the last 6 months;
- active gastrointestinal/rectal bleeding or menstruation;
- long-term treatment with immune suppression therapy;
- chronic alcohol/illicit substance use;
- pregnancy or breastfeeding;
- restrictive diet;
- food allergies or intolerances.
Figure 1 illustrates the flowchart of the study.
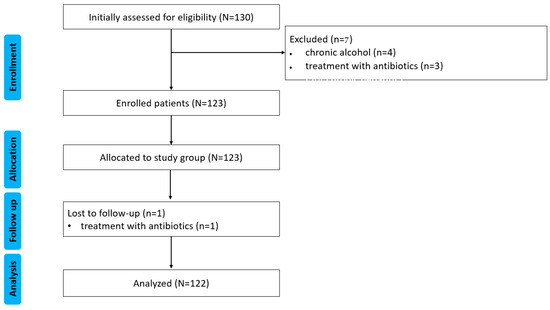
Figure 1.
CONSORT flow diagram of the study. N, n—number.
2.2. Data Collection
Demographic data (age, sex, place of origin, living) and clinical data (diet, medication use, medical history, toxic substance use, exposure to risk factors) were collected from each patient upon enrollment in the study. For each subject, venous blood samples were collected on the morning of enrollment, after a minimum of 6 h of fasting, in standardized vacutainers. The samples were immediately sent to the central laboratory. The values of aspartate aminotransferase (AST, reference range < 35 U/L) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT, reference range < 45 U/L) were determined. Hepatic markers for the exclusion of hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D, and E were provided by each patient upon presentation at the centre, and these tests were conducted within the last two weeks. An abdominal ultrasound was performed for each subject to verify the diagnosis of MASL (suggestive appearance of fatty liver) on the day of study enrollment after a minimum of 6 h of fasting.
Each participant collected a stool sample to determine intestinal microbiota. The collection was performed using standardized methods with a special collection kit, and the sample was immediately sent to a private laboratory for processing. The transport was carried out in a refrigerated bag with a thermometer at 2–8 °C. Samples were collected and analyzed in a private regional laboratory using whole-genome shotgun (WGS) metagenomic sequencing, which was performed using the next-generation sequencing (NGS) method to analyze the composition of fecal microbiota in order to identify and quantify bacterial species present in the samples [8]. This method involves sequencing the entire genomic content of the targeted microbiota. The sequencing data were analyzed using bioinformatics methods. The reference intervals used in the present study to compare intestinal microbiota parameters are those provided by the laboratory that performed the sample analysis.
2.3. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
A total of 130 patients with MASL were initially included in the study; after applying the exclusion criteria, 122 remained. The clinical characteristics of the study cohort are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Descriptive data of the study cohort.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The collected data were processed using IBM SPSS Statistics software [version 29.0.2.0 (20)]. A descriptive analysis of the entered data was performed, with charts generated and edited using Adobe Photoshop (version 24.5) and Microsoft Excel (version 2021). The normal distribution of the data was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. The results indicated a significant deviation from normality for all analyzed datasets (p < 0.05). Consequently, the median and interquartile ranges (IQRs) were used to represent the central tendency, as these measures are appropriate for non-normally distributed data. These were visualized in boxplots, which display the median (50th percentile), interquartile range (IQR, 25th–75th percentiles), and whiskers representing data within 1.5 × IQR. Extreme values (outliers), if present, were plotted separately. Considering the absence of a control group of healthy subjects, the analyzed parameter values were compared with the standardized reference intervals provided by the laboratory to assess potential deviations associated with hepatic steatosis. The binomial test was used to evaluate the differences between the observed proportions in the study cohort and the expected proportions in a healthy population. The expected proportion for the healthy population during the binomial test was 0.001; the purpose of this was to respect the rarity of deviations outside the reference range. A significance threshold of p < 0.05 was applied.
3. Results
Patients with MASL showed significant changes in biodiversity index and bacterial strains, highlighting the presence of intestinal dysbiosis.
3.1. Biodiversity Index and Fecal pH
A total of 1 out of 2.83 patients showed a low alpha diversity of ecological communities, as shown in Figure 2a. The binomial test indicated a highly statistically significant decrease between the analyzed cohort (35.24% of patients had a low Shannon’s index) and the proportion expected in a healthy population (p < 0.001). A total of 82 (67.21%) cases had a fecal pH within the reference range of 5.5–6.5. In contrast, the remainder had values above the maximum reference value, 37 (30.32%), and below the minimum reference value, 3 (2.4%), as shown in Figure 2b. The binomial test presented a highly statistically significant increase compared to the healthy population (p < 0.001).
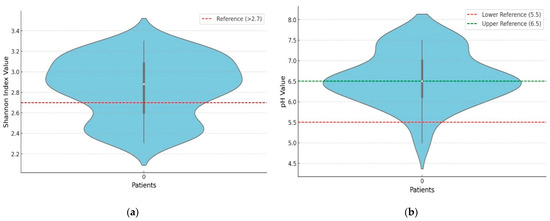
Figure 2.
(a). Distribution of the biodiversity index. (b). Distribution of fecal pH.
3.2. Alterations in Gut Microbiota Composition
The proportion of Firmicutes was 52.12% (48.69–54.02%), while that of Bacteroidetes was 33.92% (31.79–40.52%), both reported as the median and IQR, as shown in Figure 3a,b. Some 51 (41.80%) cases presented the Firmicutes species outside the reference range, representing 1 out of 2.39 cases, with p < 0.001, suggesting a significantly higher prevalence of abnormal Firmicutes values among the analyzed patients. Bacteroidetes species were found outside the reference interval in 72 (59.01%) cases, meaning 1 out of 1.69 cases. Compared to a healthy population, the binomial test suggests a significantly higher prevalence of abnormal Bacteroides values among the analyzed patients (p < 0.001). Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio values for the median and IQR were 1.24% (0.89–1.54%), reference range (0.9–1.5), Figure 3c. One case out of 2.39 had an index outside the normal values. The analysis of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio values showed that 51 patients (41.8%) presented values outside the reference range, with 32 (26.23%) below and 19 (15.57%) above the range. The binomial test identified a significantly higher prevalence of abnormal Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratios in the study cohort compared to a healthy population (p < 0.001).
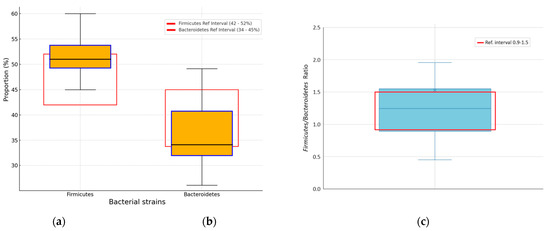
Figure 3.
Percentage distribution of Firmicutes (a) and Bacteroides (b) strains. (c) Distribution of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio. Black horizontal line in box median value; box edges—interquartile range; whiskers—range of data within 1.5 times the interquartile range.
The proportion of Proteobacteria strains was 6.98% (3.72–8.85%), as the median and IQR, in the general microbiome population, as shown in Figure 4a. Increases in Proteobacteria strains above 8.8% were recorded in 33 (27.05%) of the patients in the monitored cohort (1 in 3.69 cases). The binomial test result of p < 0.001 indicated a significantly higher prevalence of this bacterium in the patient cohort. Recorded values for Actinobacteria were 0.33% (0.15–0.64%), as shown in Figure 4b. Some 21 (17.2%) patients showed elevated values above the upper limit of the reference interval. The binomial test indicated a significantly higher prevalence of Actinobacteria values among the analyzed patients (p < 0.001). Prevotella species were increased, with a median and IQR at 14.24% (2.19–22.31%), as shown in Figure 4c. The analysis of Prevotella spp. values showed that 63 patients (51.6%) had levels exceeding the upper limit of the reference range (5.1%). The binomial test revealed a significantly higher prevalence of these elevated values in the study cohort compared to a healthy population (p < 0.001).
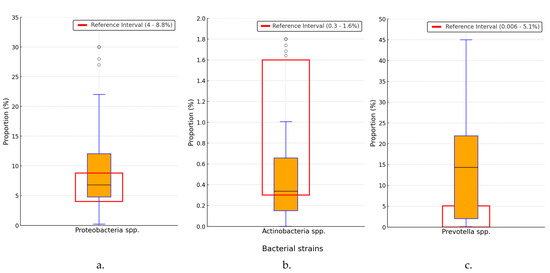
Figure 4.
Distribution of Proteobacteria (a), Actinobacteria (b) and Prevotella (c) strains. spp.—species; black horizontal line in box—median value; box edges—interquartile range; whiskers—range of data within 1.5 times the interquartile range; °—outliers.
The Escherichia species’ median and IQR were 0.38% (0.17–1.2%), with 66 (54.09%) cases above the upper normal value (with a binomial test p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 5a. Ruminococcus species had values of 3.06% (2.42–3.92%), with decreased values in 24 (19.67%) cases, with a binomial test of p < 0.001, as shown in Figure 5b. Roseburia species had a value of 0.84% (0.46–1.08%) in the general microbiome population of the study cohort, with a decrease below the lower limit in 12 (9.84%) cases, p < 0.001, as shown in Figure 5c. In the case of Escherichia species, a statistically significant increase in prevalence was observed in the study cohort, while a statistically significant decrease in prevalence was noted for Ruminococcus and Roseburia species, compared with the healthy population.
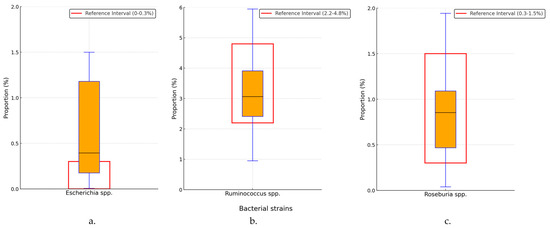
Figure 5.
Percentage distribution of Escherichia (a), Ruminococcus (b) and Roseburia (c) species. spp.—species; black horizontal line in box—median value; box edges—interquartile range; whiskers—range of data within 1.5 times the interquartile range.
Lactobacillus species were identified with a median of 0.011% and an IQR of (0.007–0.015%) of the general microbiome population, with 14 (11.48%) patients recording values below the lower limit of the reference range; the binomial test result was p < 0.001, as shown in Figure 6a. Bifidobacterium species were identified at a proportion of 0.097% (0.049–0.429%), but one out of 2.65 (46, 37.70%) presented values below the lower limit of the reference range, as shown in Figure 6b. The binomial test analysis determined a statistically significant difference compared to a healthy population (p < 0.001).
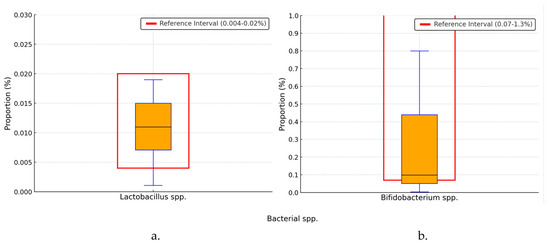
Figure 6.
Percentage distribution of Lactobacillus (a) and Bifidobacterium (b) species. spp.—species; black horizontal line in box—median value; box edges—interquartile range; whiskers—range of data within 1.5 times the interquartile range.
3.3. General Dysbiosis Observations
All patients with MASL exhibited dysbiosis, supported by changes in the alpha diversity of ecological communities and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, as well as an increase in the proportion of Proteobacteria to over 8.8% of the total species identified in the gut microbiome and Prevotella to over 5.1% of the same microbiome, as shown in Figure 7.
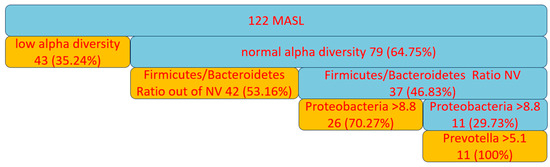
Figure 7.
Dysbiosis in patients with MASL. NV—normal value.
4. Discussion
The fecal microbiota largely reflects the composition of the intestinal microbiome, primarily the colonic microbiota, but may not include bacteria from other parts of the intestine. Nevertheless, it represents an effective and non-invasive method for diagnosing general intestinal dysbiosis. In the present study, the composition of the fecal microbiota was used to gain insights into dysbiosis in patients with MASL.
The gut–liver axis is integral to understanding MASL, as gut dysbiosis—an imbalance in the gut microbiome—can lead to increased gut permeability, systemic inflammation, and subsequent liver damage.
4.1. Biodiversity Index and Fecal pH
Microbial diversity is often considered a distinctive sign of a healthy intestinal microbiome, being one of the relevant signs of dysbiosis in conditions of a decrease in the biodiversity index. A greater diversity is generally associated with disease resistance and more robust metabolic functions. The biodiversity index results from the current study show that 1 in 2.83 patients displayed low alpha diversity of ecological communities. This finding is consistent with several studies linking MASL to reduced microbial diversity [9,10,11,12]. For example, Leung et al. (2016) reported a notable decrease in microbial diversity in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [11]. Loomba et al. (2017) suggested that lower diversity may correlate with more significant metabolic dysfunction [12]. The decrease in the biodiversity index implies the presence of systemic inflammation, increased intestinal permeability, and microbial translocation [10,13,14,15]. These correlated mechanisms are responsible for the onset of leaky gut syndrome, which negatively affects liver pathologies, aggravating hepatic diseases through endotoxemia-related mechanisms [16,17,18].
Fecal pH is a critical factor that influences the composition of the gut microbiota and its metabolic activities, where a balanced pH is essential for maintaining microbial homeostasis. While approximately half of the pH values recorded in the study cohort were within the normal reference range, 30.32% of patients exhibited elevated pH levels. This may indicate a decrease in the proportion of species producing SCFA (butyrate, acetate, propionate) and an increase in proteolytic strains, which may subsequently lead to dysbiosis, inflammation, and leaky gut syndrome, exacerbating liver pathology [19,20,21]. The elevated pH observed in the current study suggests that MASL may involve microbial compositional shifts and functional changes in the intestinal ecosystem. These results differ from findings in similar studies, which often report decreased pH and increased butyrate levels in patients with liver diseases, such as in Bajaj et al. (2012) [22]. This divergence could be due to differences in patient populations or disease severity, indicating that the relationship between pH, SCFA production, and liver health in MASL is more complex than previously understood. Patients with fecal pH below 5.5, identified in a small number in the study cohort (3, 2.4%), experience acidification of the intestinal environment, which creates a favorable setting for the development of SCFA-producing species and organic acids (lactate and succinate) that generally have beneficial effects on inflammation and leaky gut syndrome. However, the presence of an extremely low pH may contribute to the onset of dysbiosis.
4.2. Alterations in Gut Microbiota Composition
The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio is the second relevant indicator used as a marker for the health of the gut microbial flora. The analysis of the specific bacterial phyla in this study showed that the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio was outside the reference range in one out of 2.39 patients. The imbalance appears to be due to an increase in the percentage of Firmicutes. The results are supported by studies that have associated a higher Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio with obesity or metabolic issues. In particular, the study by Ridaura et al. (2013) showed that obese individuals tend to have more Firmicutes than Bacteroidetes, supporting a potential role in the metabolic dysfunction observed in MASL [23]. This subtle change in our findings underscores the importance of monitoring microbial ratios as potential biomarkers for metabolic health in MASL.
Elevated Firmicutes are important because many phylotypes of this phylum, such as Lactobacillus spp., Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Ruminococcus spp., and Eubacterium spp., are considered beneficial bacteria for maintaining gut health. They help ferment fibers, produce SCFAs, have anti-inflammatory effects, and maintain intestinal barrier integrity. Furthermore, certain species within the same phylum, such as Clostridium and Lactobacillus, produce bile salt hydrolase enzymes, which deconjugate bile acids, leading to the production of secondary bile acids (deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid). These secondary bile acids have mixed effects; they may be beneficial (e.g., deoxycholic acid, through its action on Farnesoid X Receptors, can regulate lipid, glucose, bile acid metabolism, and inflammation) and harmful (lithocholic acid is hepatotoxic at high concentrations, causing direct cellular toxicity, inducing oxidative stress, inflammation, disrupting the intestinal barrier, altering enterohepatic circulation, and resulting in bile acid accumulation in the liver, and subsequent cholestasis, which is responsible for secondary liver damage) [24,25,26,27]. However, the same phylum, Firmicutes, also includes opportunistic bacteria, such as Clostridium difficile and Enterococcus faecalis, which can cause severe pathologies.
Prevotella species are sensitive to dietary intake, particularly to diets rich in fibers derived from complex carbohydrates, which are common in plant-based diets. The relationship between Prevotella and metabolic health is complex and under ongoing evaluation. Prevotella has been associated with pro-inflammatory effects, being present in the gut flora of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, periodontitis, and metabolic diseases, yet it also plays a role in stimulating glucose metabolism and producing SCFA (propionate and acetate) [28,29]. Propionate is considered beneficial as it decreases lipogenesis and improves insulin sensitivity, playing a role in glucose metabolism regulation. However, when synthesized in excess, propionate can have a paradoxical effect. Dysbiosis with a predominance of Prevotella may lead to an overproduction of propionate, which can negatively impact hepatic steatosis. Excess acetate exacerbates hepatic steatosis by promoting fat accumulation in the liver, especially in the context of caloric excess and high carbohydrate intake. Additionally, due to its pro-inflammatory effects, acetate may contribute to the progression of the disease towards steatohepatitis. In the western region of Romania, the tradition of frequent pickle consumption may support the growth of Prevotella in the gut flora, but excessive consumption of fats and meat may have a negative impact on hepatic steatosis. Understanding the balance between the beneficial and potentially harmful effects of Prevotella is crucial in deciphering its role in MASL [30].
Proteobacteria are often considered a microbial marker of dysbiosis, particularly in chronic diseases where their overrepresentation can indicate microbial imbalance and inflammation. The increased levels of Proteobacteria and relatively low levels of beneficial bacteria, including Bifidobacterium species and Lactobacillus, demonstrated dysbiosis characteristics in MASL patients. This is in line with the results of Miele et al. (2009), which found higher proportions of Proteobacteria, mostly Escherichia, in NAFL patients, possibly due to increased intestinal permeability and systemic inflammation [31]. Another equally concerning finding is the reduced levels of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, which are two key beneficial bacteria. The same trend has been confirmed by other studies, such as that of Del Chierico et al., 2017, focusing on NAFL evidence of a diminishment in these health-supporting gut bacteria attributed to the degradation of the epithelial barrier and inflammation, which drives disease advancement [32].
Elevated levels of Proteobacteria, such as Escherichia coli, are particularly problematic as they are known to produce LPS, a potent endotoxin that can exacerbate systemic inflammation and promote liver injury. A decrease in beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus could further impair the gut barrier, allowing for more translocation of harmful bacteria and endotoxins into the liver, thereby fueling the cycle of inflammation and fibrosis typical in MASL [33].
The phylum Actinobacteria represents an important group in the intestinal ecosystem. Its beneficial effects include the production of SCFA (butyrate), which has anti-inflammatory effects, modulates the host immune system, and regulates lipid metabolism [34,35]. Their decrease, especially Bifidobacterium, is associated with dysbiosis, metabolic diseases, and inflammatory bowel diseases [35,36].
Ruminococcus and Roseburia are bacterial species involved in the synthesis of SCFAs such as butyrate, a metabolite known to have anti-inflammatory effects and to maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier. A reduction in their concentrations in the gut microbiome is associated with inflammation and metabolic diseases. In the present study, these bacteria were identified at optimal concentrations, with a small number of subjects showing a decrease in their levels. The medical literature is inconsistent regarding the correlation between the concentration of these species and the presence of MASL [37,38,39].
The intestinal dysbiosis present in all patients in the study cohort—characterized by reduced intestinal biodiversity, an altered Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, increased Proteobacteria concentrations, and Prevotella species—contributes to the progression of MASL through a series of mechanisms. Reduced biodiversity and an imbalance between Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes support proinflammatory processes and hepatic fat accumulation. The decrease in Proteobacteria is associated with reduced SCFA synthesis, which is crucial for regulating inflammation and maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. Additionally, proinflammatory mechanisms are stimulated by the excess presence of Prevotella. Thus, dysbiosis induces a vicious cycle of inflammation and increased intestinal permeability, leading to the progression of MASL.
4.3. General Dysbiosis Observations
The present study identified intestinal dysbiosis in all patients with MASL from the western region of Romania, an alarming finding considering the central role of the gut microbiome in maintaining overall health. The results summarized in Figure 7 support the presence of microbial imbalance based on several well-recognized criteria [40]. Low alpha diversity, observed in 43 out of 122 patients, represents a marker of dysbiosis frequently associated with systemic inflammation and impaired intestinal barrier function [40]. Among patients with normal alpha diversity, an imbalance in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio (present in 42 out of 122 cases outside the normal range) reflects disruptions in intestinal energy metabolism and a predisposition to lipid accumulation and inflammation [40,41].
A significant increase in Proteobacteria levels, identified in 26 out of 122 patients who did not present the previously mentioned imbalances, further supports the presence of dysbiosis due to the association of this bacterial group with increased intestinal permeability and chronic inflammation [40,42]. The remaining patients, who did not exhibit the above dysbiosis criteria, showed elevated levels of Prevotella (11 out of 122 patients), suggesting a pro-inflammatory microbial profile [28]. Thus, all patients in the study exhibited at least one dysbiosis criterion.
The traditional diet in the western region of Romania, characterized by high consumption of carbohydrates, animal fats, and fermented foods, may contribute to microbial imbalances by promoting the excessive growth of pro-inflammatory bacterial species. These bacteria can increase intestinal permeability and cause systemic inflammation, both associated with the progression of MASL. Therefore, dietary and therapeutic interventions targeting at-risk populations are essential to help restore microbiota balance. Tailoring these interventions to regional dietary patterns could be beneficial in managing MASL and preventing other conditions associated with dysbiosis, thereby supporting the health and well-being of these communities.
4.4. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
This study provides insights into the relationship between intestinal dysbiosis and MASL in a population from western Romania, offering a regional perspective on how geo-cultural factors may influence the gut microbiota in individuals with liver disease. Using the WGS technique allowed for a comprehensive assessment of microbiota composition.
The study’s limitations include the lack of a healthy control group from the same region as the study cohort. Additional limitations are that factors such as obesity, which is common among patients with MASL, and other factors (physical activity, stress exposure, and diet) that may influence the gut microbiota could not be excluded from the study. Further studies with diverse regional groups are needed to validate these findings.
5. Conclusions
The present study highlights the significant connection between intestinal dysbiosis and MASL. The observed changes in microbial populations, including the increased prevalence of species from the genus Prevotella, support the notion that geo-cultural factors can influence the composition of the gut microbiome and, consequently, liver health. Consequently, personalized therapeutic interventions adapted to the regional specificity of the gut microbiome are necessary. Certain geographical areas’ diet, habits, and lifestyle characteristics can influence the microbiome, and understanding these variations is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
This study emphasizes the role of the local microbiome in liver health, offering a new perspective on the importance of tailoring therapeutic approaches. It paves the way for future research aimed at optimizing medical interventions. These findings, with their potential to significantly improve liver disease management and patient quality of life, offer a hopeful outlook for the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.I.M. and N.N.; methodology, P.M. and A.I.M.; software, H.T.J. and N.N.; validation, N.N., A.I.M. and F.M.; formal analysis, A.I.M. and F.M.; investigation, A.F. and N.N.; resources, A.I.M., P.M., A.F., and H.T.J.; data curation, H.T.J. and A.F.; writing—original draft preparation, A.I.M. and P.M.; writing—review and editing, N.N. and H.T.J.; visualization, H.T.J. and F.M.; supervision, N.N. and F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by the University of Oradea, Romania.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Oradea (Approval No. CEFMF/5 din 28 February 2024), approved the study and adhered to the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the data are part of an ongoing study. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to Adina Ioana Mihele.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the University of Oradea for the logistic facilities they have used.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The gut–liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, E.; Yilmaz, Y. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): A multi-systemic disease beyond the liver. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 10, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut 2012, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, B.; Brenner, D.A. Interactions between the intestinal microbiome and liver diseases. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushothaman, S.; Meola, M.; Egli, A. Combination of Whole Genome Sequencing and Metagenomics for Microbiological Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, M.; Rehman, A.; Dittrich, M.; Groen, A.K.; Hermanns, H.M.; Seyfried, F.; Beyersdorf, N.; Dandekar, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Geier, A. Fecal SCFAs and SCFA-producing bacteria in gut microbiome of human NAFLD as a putative link to systemic T-cell activation and advanced disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, E.T.; Palacios, T.; Thomsen, M.; Vitetta, L. Intestinal Microbiome Shifts, Dysbiosis, Inflammation, and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Rivera, L.; Furness, J.B.; Angus, P.W. The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Seguritan, V.; Li, W.; Long, T.; Klitgord, N.; Bhatt, A.; Dulai, P.S.; Caussy, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Highlander, S.K.; et al. Gut microbiome-based metagenomic signature for non-invasive detection of advanced fibrosis in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, R.; Francés, R.; Gutiérrez, A.; Juanola, O. Bacterial Translocation as Inflammatory Driver in Crohn’s Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 703310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakaroun, R.M.; Massier, L.; Kovacs, P. Gut Microbiome, Intestinal Permeability, and Tissue Bacteria in Metabolic Disease: Perpetrators or Bystanders? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilan, Y. Leaky gut and the liver: A role for bacterial translocation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Iwaki, M.; Nakajima, A.; Nogami, A.; Yoneda, M. Current Research on the Pathogenesis of NAFLD/NASH and the Gut–Liver Axis: Gut Microbiota, Dysbiosis, and Leaky-Gut Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Gut-liver axis in liver cirrhosis: How to manage leaky gut and endotoxemia. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaBouyer, M.; Holtrop, G.; Horgan, G.; Gratz, S.W.; Belenguer, A.; Smith, N.; Walker, A.W.; Duncan, S.H.; Johnstone, A.M.; Louis, P.; et al. Higher total faecal short-chain fatty acid concentrations correlate with increasing proportions of butyrate and decreasing proportions of branched-chain fatty acids across multiple human studies. Gut Microbiome 2022, 3, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecklu-Mensah, G.; Choo-Kang, C.; Maseng, M.G.; Donato, S.; Bovet, P.; Viswanathan, B.; Bedu-Addo, K.; Plange-Rhule, J.; Oti Boateng, P.; Forrester, T.E.; et al. Gut microbiota and fecal short chain fatty acids differ with adiposity and country of origin: The METS-microbiome study. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, S.H.; Belenguer, A.; Holtrop, G.; Johnstone, A.M.; Flint, H.J.; Lobley, G.E. Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Ridlon, J.M.; Heuman, D.M.; Daita, K.; White, M.B.; Monteith, P.; Noble, N.A.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Colonic mucosal microbiome differs from stool microbiome in cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy and is linked to cognition and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ciaula, A.; Bonfrate, L.; Khalil, M.; Portincasa, P. The interaction of bile acids and gut inflammation influences the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 18, 2181–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Bajaj, J.S. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Cowley, E.S.; Wolf, P.G.; Doden, H.L.; Murai, T.; Caicedo, K.Y.O.; Ly, L.K.; Sun, F.; Takei, H.; Nittono, H.; et al. Formation of secondary allo-bile acids by novel enzymes from gut Firmicutes. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2132903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna-Prieto, F.J.; Xu, H.; Ortiz-Alvarez, L.; Di, X.; Kohler, I.; Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Rubio-Lopez, J.; Plaza-Díaz, J.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Link, A.; et al. The relative abundance of fecal bacterial species belonging to the Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes phyla is related to plasma levels of bile acids in young adults. Metabolomics 2023, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljazovic, A.; Amend, L.; Galvez, E.J.C.; de Oliveira, R.; Strowig, T. Modulation of inflammatory responses by gastrointestinal Prevotella spp.—From associations to functional studies. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 311, 151472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamberg, S.; Adamberg, K. Prevotella enterotype associates with diets supporting acidic faecal pH and production of propionic acid by microbiota. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancur-Murillo, C.L.; Aguilar-Marín, S.B.; Jovel, J. Prevotella: A key player in ruminal metabolism. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, L.; Valenza, V.; La Torre, G.; Montalto, M.; Cammarota, G.; Ricci, R.; Mascianà, R.; Forgione, A.; Gabrieli, M.L.; Perotti, G.; et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandonà, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2016, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, L.; Wirth, U.; Koch, D.; Schirren, M.; Drefs, M.; Koliogiannis, D.; Nieß, H.; Andrassy, J.; Guba, M.; Bazhin, A.V.; et al. The role of gut-derived lipopolysaccharides and the intestinal barrier in fatty liver diseases. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Lee, T.H.; Cheng, M.J. Secondary Metabolites with Anti-Inflammatory Activities from an Actinobacteria Herbidospora daliensis. Molecules 2022, 27, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Rizzatti, G.; Gibiino, G.; Cennamo, V.; Gasbarrini, A. Actinobacteria: A relevant minority for the maintenance of gut homeostasis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.T.; Amos, G.C.A.; Murphy, A.R.J.; Murch, S.; Wellington, E.M.H.; Arasaradnam, R.P. Microbial imbalance in inflammatory bowel disease patients at different taxonomic levels. Gut Pathog. 2020, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, H.E.; Teterina, A.; Comelli, E.M.; Taibi, A.; Arendt, B.M.; Fischer, S.E.; Lou, W.; Allard, J.P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with dysbiosis independent of body mass index and insulin resistance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.; Luo, F.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W.; Hu, M. Gut microbiota and metabolic biomarkers in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagiakrishnan, K.; Morgadinho, J.; Halverson, T. Approach to the diagnosis and management of dysbiosis. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1330903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The critical role of gut microbiota in obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1025706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzatti, G.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Gibiino, G.; Binda, C.; Gasbarrini, A. Proteobacteria: A Common Factor in Human Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9351507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).