Abstract
Despite many advances in the management of patients with colorectal cancer, this malignancy remains the second leading cause of cancer death worldwide. One of the keys to improve the prognosis of these patients is diagnosis in early stages, making them eligible for curative surgical treatment. Cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes can enhance the diagnostic management of these patients. The time elapsed from the appearance of skin lesions to the appearance of the first digestive symptoms can reach up to a decade. Thus, comprehensive paraclinical evaluation and the monitoring of patients with specific skin lesions play an important role in detecting an underlying cancer. Given these findings, it is imperative to increase the awareness of cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes among patients and medical professionals. Additionally, the investigation of the mechanisms that elucidate this pathogenic link has the potential to result in the identification of novel therapeutic targets.
1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks as the third most prevalent cancer worldwide and is a major cause of cancer-related mortality [1]. Global projections indicate that the number of new cases of CRC will reach 1.93 million in 2024, highlighting its significance as a public health issue [2]. The prevalence and incidence of CRC vary by region, with higher rates in developed countries influenced by factors such as diet, lifestyle, and an aging population [2]. Japan and Norway report some of the highest incidence rates, and the United States is also notable, with an estimated 152,810 new CRC cases expected in 2024 [2]. The mortality rate for CRC is also alarming, with approximately 904,019 deaths worldwide in 2022 [3]. Some of the nations with the highest mortality rates are Croatia and Hungary [3].
Cutaneous paraneoplastic manifestations bridge gastroenterology and dermatology, providing insights into the intricate relationship between cancer and the immune system. In CRC, these skin symptoms frequently appear before or alongside the diagnosis of the primary tumor and can also indicate disease recurrence or progression [3,4]. Studying these manifestations provides valuable insights for early detection and paves the way to understanding CRC’s underlying pathophysiology and systemic impact [3].
Paraneoplastic syndromes are systemic responses to tumors that are not directly related to the cancer’s local invasion or metastatic spread [5]. In CRC, a diverse array of paraneoplastic syndromes with cutaneous manifestations have been identified, demonstrating the intricate relationship between the tumor and the patient’s immune system [5]. These include conditions such as hypertrichosis, acanthosis nigricans, acrokeratosis, dermatomyositis, Cronkhite–Canada syndrome, Peutz–Jeghers syndrome, Muir–Torre syndrome, the Leser–Trélat sign, and paraneoplastic pemphigus (Table 1) [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. Each of these manifestations, discussed further in the following sections, highlights the need for a multidisciplinary approach in CRC diagnosis and management. Effective collaboration between dermatologists and oncologists is essential for identifying these syndromes, which can result in early cancer identification and enhanced patient outcomes. Examining these cutaneous signs in CRC enhances our understanding of the systemic effects of colorectal tumors and provides a broader perspective on the disease.

Table 1.
The literature reporting clinical cases that demonstrate a correlation between specific cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes and malignant or premalignant colorectal tumors [4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34].
2. Methods
In order to conduct this study, we thoroughly analyzed the specialist literature, searching for clinical cases that documented connections between specific paraneoplastic syndromes and CRC. Also, we presented the results of some research that investigated the mechanisms that could account for these pathogenic connections. The platforms utilized for the literature search were PubMed and Google. We note that we did not specify a precise timeframe for the analyzed case-report studies; nevertheless, for the original papers, we concentrated on those published during the recent decade. The keywords used were: cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes, CRC, hypertrichosis, acanthosis nigricans, acrokeratosis, dermatomyositis, Cronkhite–Canada syndrome, Peutz–Jeghers syndrome, Muir–Torre syndrome, Leser–Trélat sign, and paraneoplastic pemphigus.
3. Paraneoplastic Hypertrichosis Lanuginosa Acquisita
Paraneoplastic hypertrichosis lanuginosa acquisita (PHLA) is a skin condition associated with some cancers that is characterized by the sudden, aberrant, and excessive proliferation of lanugo hair [35]. The earliest documentation of this phenomenon was made by Turner in 1865 in a woman diagnosed with breast cancer [35]. These hairs are long, thin, and unpigmented, and they are almost parallel to the epidermal surface. They are typically found on body areas that are normally hairless [36]. Initially, they appear close to the eyebrows, on the forehead, ears, and nose, and they gradually spread downward across the entire body, reaching the axillae, trunk, and extremities [36]. The palmoplantar regions, suprapubic area, and genital regions are rarely affected. Unlike hirsutism, lanugo-type hypertrichosis does not follow a gender-specific distribution pattern [36,37]. Naturally, these hairs develop in the uterus and are typically lost during the final months of pregnancy or within the first few months following birth [36,37]. PHLA primarily affects women and is most frequently associated with CRC, followed by lung and breast cancers [36,38]. Conversely, among males, lung cancer is the primary malignancy associated with PHLA, with CRC closely following [36]. Additional studies have established a correlation between PHLA and lymphomas, extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma, and neoplasias of the kidney, pancreas, ovary, and uterus [35,36].
Hypertrichosis may either precede or follow the detection of an evident neoplasm by one to two years. As a result, the sudden appearance of lanugo hair necessitates a thorough assessment to determine whether there is an underlying malignancy [35,36]. This condition is typically associated with an advanced, metastatic stage of the cancer and frequently occurs between the ages of 40 and 70 years [35,36]. Thus, PHLA is indicative of an unfavorable prognosis [35,36].
Hypertrichosis lanuginosa acquisita (HLA) can also be associated with metabolic and endocrine disorders, such as porphyria and hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism [35,39]. Additionally, it may be induced by certain drugs, including ciclosporin, penicillamine, psoralens, glucocorticosteroids, diazoxide, interferon, minoxidil, phenytoin, or cetuximab [35,39].
The pathogenesis of PHLA is still not fully understood [35]. Nevertheless, it is hypothesized that hair follicles are stimulated by cytokines released by tumors [6]. The correlation of PHLA with other paraneoplastic conditions, such as acquired ichthyosis, acanthosis nigricans, palmoplantar keratoses, and glossitis with papillomatosis, further supports this theory [35]. The concurrent presence of PHLA and acanthosis nigricans implies potential insulin-like growth factor participation, but this theory has not been definitively determined [37]. In addition, other data suggest that fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and epidermal growth factors (EGFs), which are involved in controlling and differentiating hair growth, can play a role in HLA development [37].
In terms of treatment, PHLA often regresses with the removal of the underlying tumor; therefore, it is essential for the patient to undergo a thorough screening for malignancies [40]. Hence, it is imperative to carry out a screening for malignant disorders in a patient with HLA [40].
4. Acanthosis Nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans (AN) is a common dermatological condition that frequently indicates the presence of benign underlying disorders such as insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, other endocrine diseases, or obesity [41]. Furthermore, it can be associated with more severe diseases like cancer [41].
AN manifests in several forms, each linked to different underlying conditions [42]. Acral AN is frequently associated with benign conditions or yet-unidentified genetic factors. It is limited to the dorsal surfaces of the hands and feet, with elbows, knees, and knuckles being less affected [43]. Paraneoplastic AN is usually linked to gastrointestinal cancers, and the skin lesions are more severe in these cases [6]. The onset of this dermatological disorder is characterized by the symmetrical pigmentation of the skin in the axillary and inguinal folds, the submammary area, the periumbilical region, and the anogenital region [6]. Over time, skin lesions can take the form of pigmented, velvety, slightly hyperkeratotic plaques, surrounded by acrochordons [6,44]. Additionally, pigmented papillomatous lesions may be observed on the mucous membranes. Some studies have also reported the association of AN with leukonychia or non-cicatricial alopecia in the axillary and pubic regions [6].
This skin disease may be diagnosed concurrently or prior to a specific type of cancer, particularly gastric cancer [45]. Additionally, the presence of paraneoplastic AN is indicative of a poor prognosis, with an average survival time of two years from the diagnosis of cutaneous lesions [46].
The pathophysiological mechanisms that contribute to the development of paraneoplastic AN are still incompletely elucidated [46,47]. Studies in recent years suggest the involvement of cytokines secreted by cancer cells, such as transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha), fibroblast growth factor (FHF), insulin growth factor-like (IGF-1) or melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSHa) [46]. According to one hypothesis, TGF-alpha can interact with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) on the surface of epidemic cells due to its structure, which is similar to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) [47,48,49] (Figure 1). The improvement of malignant AN following tumor resection, along with a decrease in elevated circulating TGF-α, supports the involvement of EGFR signaling in paraneoplastic AN [50].
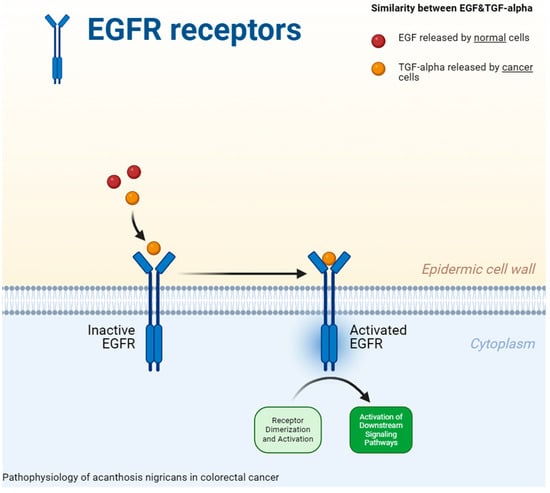
Figure 1.
The pathophysiology of acanthosis nigricans in colorectal cancer. The epidermal growth factor receptor [EGFR] on the surface of epidemic cells can interact with transforming growth factor alpha [TGF-alpha] as a result of its structure, which is analogous to that of the epidermal growth factor [EGF]) [47,48,49].
The therapeutic management of paraneoplastic AN is multidisciplinary and entails the surgical removal of the tumor as well as oral or topical medication treatments [51]. Numerous studies have widely documented the reduction in skin lesions that occurs as a result of the cancer surgery [52,53,54,55]. Following tumor excision, Koyama et al. identified a decrease in serum or urine levels of TGF-alpha, a biomarker that contributes to the pathogenesis of AN [56]. In some cases, chemotherapy can alleviate AN; in others, it may be toxic, necessitating adjustments or the discontinuation of the treatment. Topical treatment can also enhance the clinical aspect of AN and improve the quality of life of these patients [57]. Numerous studies and case reports have examined the efficacy of tretinoin in treating AN [58,59,60]. This topical retinoid has demonstrated significant advantages in improving the condition’s clinical appearance. It has resulted in a significant decrease in skin thickening and discoloration, improving the texture and overall appearance of the affected areas [58,59,60]. Their effectiveness can be attributed to the promotion of cell turnover and a reduction in hyperkeratosis [58,59,60]. Kritsanaviparkporn et al. conducted a comparison of the efficacy and safety profile of 0.025% and 0.05% tretinoin topical cream used for 8 weeks in the management of AN [60]. The results were similar in terms of efficacy, improvements, and local irritations [60]. An additional double-blind, randomized, controlled trial demonstrated substantial advantages for both 10% salicylic acid and 10% urea creams in the treatment of AN [61]. In the course of an eight-week application of these topical lotions, these authors observed a substantial improvement in hyperpigmented lesions on the neck [61]. Conversely, trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peels may provide a more efficient and time-saving alternative [62]. Salicylic acid, podophyllin, urea, and calcipotriol are topical treatments that require frequent application [62]. The most recent data indicates that laser therapy, including a fractional CO2 laser, a 1550 nm pulsed erbium fiber laser, and a long-pulsed alexandrite laser, provides superior results for the management of AN when compared to topical treatment [63].
Patients frequently experience pruritus due to afflicted areas, which can be quite distressing. In conclusion, these symptoms significantly impact the patients’ overall quality of life, underscoring the importance of addressing and treating the skin lesions [62,63].
5. Acrokeratosis
Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (AP) is a rare dermatological condition initially discovered by Bazex in 1965 [64]. Bazex et al. were the first to provide evidence linking psoriasis-like skin lesions with squamous cell carcinoma of the piriform fossa [64]. The authors described these peculiar lesions, characterized by erythema, edema, and scaling [64]. The lesions are observed on the palms and feet, as well as on other areas such as the cheeks, nose, and ears [64], and resemble psoriasis lesions, but they can also appear in atypical regions for psoriasis. This emphasized the syndrome’s paraneoplastic nature and established a significant link between cutaneous manifestations and an underlying malignancy [64]. Gradually, the lesions may manifest as painful plaques, often found on the palms and soles, and may be accompanied by nail anomalies [65]. Roy et al. discovered a variety of nonspecific nail changes such as thickening, onycholysis, and discoloration, that affected the majority of fingernails and toenails [66]. These changes frequently manifested prior to the diagnosis of malignancy, suggesting that nail abnormalities may function as early indicators of an underlying cancer [66]. Furthermore, the association between AP and severe interface dermatitis can lead to confusion with conditions such as lichen planus, systemic lupus erythematosus, or lichenoid drug eruption [65].
AP is primarily identified in men over the age of 40 who have been diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the upper respiratory tract or the upper digestive tract [67]. Furthermore, other research has documented the correlation between AP and adenocarcinomas of the colon, rectum, stomach, liver, or biliary system [68,69,70,71].
Regarding the pathogenesis of AP, it is still incompletely elucidated. The literature has so far outlined three hypotheses based on existing data:
- T-helper 2 (Th2) immune shift induced by squamous cell carcinoma: This aberrant immune response is characterized by increased serum levels of markers such as immunoglobulin E, eosinophils, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) [71]. Additionally, this pathogenic hypothesis argues that Th2 cells release elevated quantities of cytokines, including interleukins 4, 5, and 13, which stimulate the allergic hypersensitivity reaction [71].
- Growth factor relapsed by squamous cell carcinoma: This pathogenic hypothesis claims that during the proliferative phase of SCC, cancer cells secrete a spectrum of growth factors, such as TGF-alpha, EGF, and IGF-1 [72]. Subsequently, these growth factors induce the proliferation of epithelial and epidermal cells, which ultimately results in the development of skin lesions in the Bazex syndrome [72].
- Autoimmune reactions: According to this pathogenic hypothesis, the recross reaction between antibodies that are produced against tumor antigens and antigens that are present on keratinocytes or the basal membrane is supported (Figure 2) [73].
 Figure 2. The pathogenesis of acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (hypothesis 1—T-helper 2 [Th2] immune shift induced by squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), characterized by elevated serum levels of markers such as immunoglobulin E, eosinophils, and thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC). This aberrant immune response results in the release of increased quantities of cytokines, including interleukins 4, 5, and 13, which stimulate allergic hypersensitivity reactions and lead to an abnormal increase in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in keratinocytes, ultimately manifesting as skin lesions; hypothesis 2—growth factor relapsed by squamous cell carcinoma: during the proliferative phase of SCC, cancer cells secrete growth factors such as transforming growth factor-alpha [TGF-alpha], epidermal growth factor [EGF], and insulin-like growth factor 1 [IGF-1]. These growth factors drive the proliferation of epithelial and epidermal cells, culminating in the development of Bazex syndrome-related skin abnormalities; hypothesis 3—autoimmune reactions: cross-reactivity between antibodies targeting tumor antigens and those present on keratinocytes or the basal membrane contributes to the emergence of these lesions) [71,72,73].
Figure 2. The pathogenesis of acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (hypothesis 1—T-helper 2 [Th2] immune shift induced by squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), characterized by elevated serum levels of markers such as immunoglobulin E, eosinophils, and thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC). This aberrant immune response results in the release of increased quantities of cytokines, including interleukins 4, 5, and 13, which stimulate allergic hypersensitivity reactions and lead to an abnormal increase in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in keratinocytes, ultimately manifesting as skin lesions; hypothesis 2—growth factor relapsed by squamous cell carcinoma: during the proliferative phase of SCC, cancer cells secrete growth factors such as transforming growth factor-alpha [TGF-alpha], epidermal growth factor [EGF], and insulin-like growth factor 1 [IGF-1]. These growth factors drive the proliferation of epithelial and epidermal cells, culminating in the development of Bazex syndrome-related skin abnormalities; hypothesis 3—autoimmune reactions: cross-reactivity between antibodies targeting tumor antigens and those present on keratinocytes or the basal membrane contributes to the emergence of these lesions) [71,72,73].
Regarding the temporal relationship between skin manifestations and symptoms of the underlying malignant disease, the skin lesions typically occur at least six months prior to cancer symptoms [74]. Nevertheless, the cutaneous lesions were detected concurrently or after the cancer diagnosis in 30% of the cases reported in the literature [75]. Moreover, the lesions in Bazex syndrome develop in three successive stages, with a progressive severity that is directly proportional to the tumor stage [76].
AP treatment includes:
- ▪ Treatment of the underlying malignant condition (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.)—leads to improvement or resolution of AP;
- ▪ Traditional treatments for dermatological conditions such as psoriasis or eczema—with limited effectiveness;
- ▪ Oral psoralen—UVA phototherapy (PUVA)—with promising results;
- ▪ Topical and systemic steroids—with mixed results [77,78,79].
Although AP continues to pose diagnostic and therapeutic challenges, it provides a chance to diagnose cancer at an early stage.
6. Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a rare idiopathic inflammatory myopathy that is clinically defined by proximal muscle weakness and characteristic skin manifestations [80]. This includes periorbital heliotrope rash, Gottro papules (erythematous maculo-papular lesions located at the level of bony prominences), shawl sign (erythema with a “saddle” distribution on the neck, shoulders, and upper back), “mechanic’s hands hyperkeratosis”, photosensitive poikiloderma, scalp erythema, and cutaneous calcinosis [80]. The heliotrope rash is characterized by a confluent macular erythema that symmetrically affects the eyelids, the upper region of the cheeks, and the forehead. It is frequently accompanied by edema of the eyelids and periorbital tissues [80].
The diagnosis of dermatomyositis is established by corroborating the clinical examination with the results of paraclinical investigations, such as:
- ▪ An increase in the serum level of skeletal muscle enzymes;
- ▪ Increased serum levels of some autoantibodies [anti-Jo-1, anti-PL-7, anti-PL-12, anti-isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase (anti-OJ), anti-Mi2 or anti-signal recognition particle (anti-SRP)];
- ▪ Abnormal electromyography results;
- ▪ Inflammatory infiltrates identified during the anatomopathological examination of the muscle biopsy sample [6].
Dermatomyositis is widely considered to be an idiopathic disorder [81]. However, recent studies have indicated that around 15–30% of cases with dermatomyositis are linked to underlying malignancies such as ovarian, lung, pancreatic, stomach, and colorectal cancer, as well as non-Hodgkin lymphomas [81,82,83]. In addition, patients with paraneoplastic dermatomyositis have a worse prognosis than patients with idiopathic dermatomyositis [83]. This is mainly explained by the diagnosis of cancer in advanced stages, which do not allow for a curative surgical treatment [83].
The pathogenic mechanisms that explain the relationship between dermatomyositis and cancer, especially CRC, are still incompletely elucidated [83]. One hypothesis argues that the release of bioactive substances by tumor cells triggers a sequence of immune responses at the skin and muscle fiber levels [84]. Furthermore, the overexpression of certain autoantigens by both tumor cells and myofibroblasts was detected in these patients, suggesting a potential similarity in the antigens expressed by the two cell populations, potentially leading to a cross-reactive immune response [85]. In colon cancer patients, Kasuya et al. identified the superexpression of the TGF-beta signaling pathway [86]. This is linked to the decrease in T cell proliferation and attenuation of the host’s anti-tumor immune responses (Figure 3) [86].
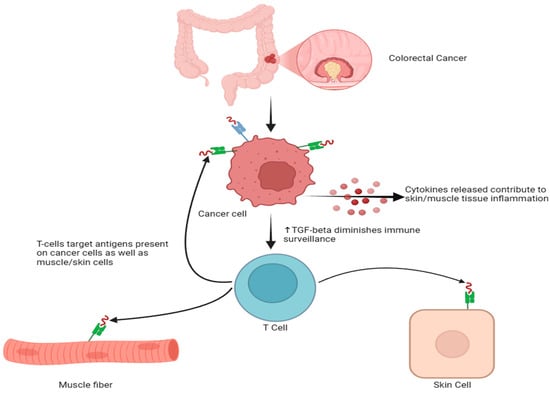
Figure 3.
Pathogenic mechanisms involved in the relationship between colorectal cancer and dermatomyositis (the superexpression of the TGF-beta signaling linked to the decrease in T cell proliferation and the attenuation of the host’s anti-tumor immune responses [86].
Given the often-observed correlation between dermatomyositis and cancer, several authors advise meticulous examination for malignant tumors during the initial three to five years following the diagnosis of the musculo-cutaneous disorder [6]. Nevertheless, the most effective screening algorithm for cancer in individuals with dermatomyositis is still unclear [6].
7. Cronkhite–Canada Syndrome
Cronkhite–Canada syndrome (CCS) is an uncommon and sporadic disease that is associated with significant morbidity [87]. It is characterized by an association between gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis and ectodermal alterations, commonly referred to as pigmentation–alopecia–onychatrophia disorder [87]. The disease was initially documented in 1955 and was subsequently named CCS by Jarnum and Jensen in 1966 [88]. The prevalence of CCS is increasing, with patients’ mean age of 61 years and an age of onset ranging from 26 to 85 years [88]. To date, more than 500 cases have been documented globally, the majority of whom were reported in Japan [89]. Genetic abnormalities, immune dysregulation, surgery, and psychological stress are all potential risk factors [88]. This condition continues to have a poor prognosis, with a 5-year mortality rate of 55% [88]. Complications, including malnutrition, hypoalbuminemia, recurrent infections, sepsis, cardiac failure, and gastrointestinal bleeding, are responsible for most deaths [87].
In patients with CCS, cutaneous lesions include hyperpigmentation, onychodystrophy, and alopecia [90,91]. Hyperpigmentation can be either diffuse or focal, with macules ranging from a few millimeters to 10 cm in diameter. It frequently affects the extremities, face, neck, scalp, and occasionally the lips [90,91]. Alopecia progresses quickly and can lead to full hair loss in certain cases. Fingernails and toenails may exhibit discoloration, atrophy, nail plate separation, and shedding [6].
Nevertheless, the most common symptoms of CCS are gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea and abdominal pain, which are frequently accompanied by other symptoms such as anorexia, acid reflux, parageusia, or fatigue [88]. Additionally, 88% of the patients afflicted exhibit hypoalbuminemia that is not linked to liver or renal dysfunction. This condition results in edema, particularly in the eyelids and extremities, which is slightly alleviated by rest [88].
CCS is distinguished from other polyposis syndromes by the presence of distinctive extraintestinal symptoms and the dissemination of polyps throughout the gastrointestinal tract, including the stomach, small intestines, and colon [20]. Over time, multiple studies have documented the progression of these polyps to gastrointestinal cancer [92,93,94]. For instance, Yashiro et al. conducted an analysis of the cases of CCS reported between 1967 and 2002 and determined that gastrointestinal malignancies were present in 50 of the 387 patients with CCS identified (31 patients with colon cancer and 19 patients with gastric cancer) [95]. Also, these authors identified men with CCS to be more susceptible to developing CRC [95]. Additional research has found that gastrointestinal cancer is associated in approximately 10–20% of patients with CCS [91]. In light of these data, the good practice guidelines recommend routine endoscopic examinations for patients with CCS to facilitate the early detection of certain malignant lesions [93].
The etiology of CCS remains incompletely elucidated [96,97]. However, the autoimmune etiopathogenesis of CCS is supported by the elevated serum titres of certain autoantibodies, such as anti-nuclear antibodies, and the favorable responses to corticosteroids or cyclosporine in these patients [96,97,98]. Furthermore, there are studies that have reported the correlation between CCS and other autoimmune diseases, including scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematous, rheumatoid arthritis, membranous nephropathy, and hypothyroidism [96,97,98]. Also, Riegert-Johnson et al. identified an immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) plasma cell infiltration of CCS polyps, indicating a potential association between this syndrome and IgG4-related autoimmune disease [99]. Another hypothesis supports the involvement of Helicobacter pylori infection in the pathogenesis of CCS, as well as a possible mitigation of polypoid lesions after the eradication of this infection [99].
Data on the pathogenic pathways involved in the progression of polypoid lesions to CRC are controversial. Thus, the hypothesis of polyp–adenoma–carcinoma progression has been supported by certain authors, while alternative oncogenic pathways are advocated by others [100,101,102]. Thus, Yashiro et al. identified the presence of serrated adenomas in 40% of CCS patients [95]. The same authors reported an overexpression of P53 protein and microsatellite instability in both malignant tumors and serrated adenomas in patients with CCS, suggesting the serrated adenoma–carcinoma pathway as a possible pathogenic mechanism for cancer development [95]. In contrast, Zugel et al. discovered a p53 gene mutation and ErbB2 proto-oncogene expression in a colorectal tumor of a CCS patient without APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) and ras-gene alteration, indicating an independent oncogenic pathway [102].
8. Peutz–Jeghers Syndrome
Peutz–Jeghers syndrome (PJS) is an autosomal dominant hereditary condition characterized by the presence of hamartomatous polyps at the gastrointestinal level in association with mucocutaneous pigmentation [103]. PJS was the initial hamartomatous polyposis syndrome to be described by Peutz in the Netherlands in 1921 and by Jeghers, McKusick, and Kats in the United States of America in 1949 [104]. Hamartomatous polyps are identifiable by their distinctive histological structure [105]. They are usually composed of branched bands of smooth muscle, covered by hyperplastic glandular mucosa, and can be identified at the level of the stomach, small intestine, or colon [105]. The most prevalent clinical manifestation is rectal bleeding with secondary anemia, followed by abdominal pain and diarrheal syndrome. Preventing complications, including obstruction, digestive hemorrhage, or malignant transformation, is the primary objective of the clinical management of these patients [105,106].
Approximately 95% of patients with PJS have pigmented mucocutaneous macules, which can be the first sign of the disease [107]. These hyperpigmented lesions measure 1–5 mm in diameter and are irregularly dispersed primarily on the buccal mucosa, lips, soft palate, and gums [107]. Additionally, these patients may develop enlarged macules on their palms and soles, although with a significantly lower frequency. The cutaneous lesions typically manifest in early childhood [107]. The average duration from the onset of mucocutaneous pigmentation to the onset of gastrointestinal symptoms is approximately 10 years [108]. These pigmented lesions are not associated with a risk of malignant transformation and do not necessitate specific therapies, except for those intended for aesthetic purposes [108].
Molecular sequencing investigations revealed that the STK11 tumor suppressor gene (also known as the LKB1 gene) located on chromosome 19p13.3 plays a significant role in the development of PJS [108,109,110,111]. This gene encodes an enzyme responsible for serine/threonine kinase activity, which plays a crucial role in regulating the cell cycle and cell proliferation [108,109,110,111]. Genetic mutations in the STK11 gene lead to a deficiency in the enzyme’s suppressing activity and are accountable for 50–90% of cases of PJS [109,110,111].
Patients with PJS are at an elevated risk of developing malignant tumors in the colon, stomach, small bowel, pancreas, mammary glands, testicles, or lungs [107]. The cumulative risk of developing CRC ranges from 12% to 39% [107]. The average age of diagnosis of CRC in patients with PJS is 46 years, although such malignant complications have also been reported in adolescents [112]. To screen for gastrointestinal benign or malignant tumors in PJS, the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPHAN) recommend endoscopy and colonoscopy in suspected children starting at the age of eight [113,114]. A repetition of investigations is required every 1–3 years in the presence of harmatomatous polyps [113,114]. Unless otherwise specified, screening should commence at the age of 18 years [113,114].
9. Muir–Torre Syndrome
MTS is an autosomal dominant hereditary disease characterized by the occurrence of certain malignancies (most commonly colon cancer) together with certain sebaceous neoplasms (adenomas, epitheliomas, carcinomas, keratoacanthomas) [115,116]. Muir et al. first reported it in 1967, followed by Torre in 1968 [117,118]. It is now acknowledged that this condition is a subgroup of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) syndrome [119].
The etiopathogenesis of HNPCC involves mutations at the level of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) mismatch repair genes (MLH-1, MSH-2, MSH-6, or PMS-2) [120]. To date, 56 mutations have been detected in individuals with HNPCC (mostly at the MLH-1 and MSH-2 levels, and less often at the MSH-6 and PMS-2 levels) [120]. sMTS phenotypes are more specifically associated with MSH-2 mutations [120]. As a result, the isolated identification of some sebaceous neoplasms necessitates additional immunohistochemical tests for the evaluation of MMR proteins in order to detect early MTS and improve the prognosis of these patients [120].
Sebaceous neoplasms may serve as the initial indication of MTS and may precede the diagnosis of malignant visceral tumors by several years [121]. Sebaceous adenoma is considered the most specific MTS lesion, and it can sometimes present cystic changes or architecture similar to keratoacanthoma [122]. Also, approximately 30% of patients with MTS associate sebaceous carcinomas [123]. Sebaceous adenomas are typically characterized by the presence of round, yellow, and painless papules or subcutaneous nodules. Some of these nodules may have a central umbilication, resembling molluscum contagiosum [124]. Sebaceous carcinomas primarily arise in the meibomian glands, although they can also manifest in anatomical sites such as the face, ears, and external genitalia [124]. These malignancies manifest on the eyelids as solid, yellow nodules with different levels of ulceration and may be confused with chalazia, chronic blepharoconjunctivitis, or carbuncle [124].
Most cutaneous neoplasms associated with MTS have low malignant potential and are unlikely to metastasize, with the exception of sebaceous carcinoma. Consequently, they can be effectively treated through complete surgical excision [125,126,127,128]. Nevertheless, sebaceous carcinomas associated with MTS, particularly those located in the periocular region, may be more aggressive, posing a risk of recurrence, angioinvasion, or distant metastasis [125,126,127,128]. In light of the relatively high incidence of metastasis (up to 25% in certain studies), it is recommended to perform Mohs micrographic surgery or wide surgical excision for these carcinomas [125,126,127,128].
CRC is the most frequent visceral malignancy in patients with MTS [129]. The predominant location of malignant tumors in the proximal colon is a distinctive characteristic of this syndrome [129]. From a histological point of view, colorectal tumors tend to be well differentiated and have a relatively good prognosis [129]. Additionally, CRC is diagnosed in these patients 10–20 years earlier than in the general population [129]. Therefore, it is recommended that patients with MTS initiate the screening strategy with a colonoscopic evaluation at the age of 18 years and repeat this investigation at intervals of 2–3 years [129].
10. Leser–Trelat Syndrome
The Leser–Trélat syndrome (LTS) is named in honor of Edmund Leser and Ulysse Trélat, who in the 1800s established a correlation between the occurrence of seborrheic keratoses and certain internal neoplasms [6].
The etiopathogenesis of LTS is not fully understood. Current data suggests that EGF, EGFR, human growth factor, and tumor-derived epidermal growth factor are involved in the development of the seborrheic keratoses [4,130].
An identifying characteristic of LTS is the sudden increase in both the number and dimensions of seborrheic keratosis lesions [4]. These are papular, verrucous lesions with well-defined borders that vary in color, ranging from brown to black or tan [46]. The thorax and back are the primary areas affected, with the extremities, face, abdomen, neck, and axilla also frequently affected. Inflammation and pruritus are frequently observed [46]. In older individuals, the significance of this indicator may be reduced because of the onset of seborrheic keratosis commonly seen with aging processes [46].
LTS is most frequently associated with gastrointestinal tract tumors (72%), as well as adenocarcinomas (76%) [131]. More than 60% of tumors associated with LTS are diagnosed in advanced stages [130]. Also, this syndrome has been rarely associated with cancer of the pancreas, liver, breast, bladder, kidney, ovary, prostate, lung, lymphomas, or melanomas [131]. Excision of the primary tumor can result in spontaneous regression or reduction in the extent of seborrheic keratosis [132].
11. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus
Paraneoplastic pemphigus (PNP) is a mucocutaneous acantholytic syndrome associated with various malignant diseases [33]. Among these, the most common are chronic lymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and Castleman’s disease [33]. Among non-hematological malignancies, PNP is most frequently associated with colonic adenocarcinoma [133].
Painful mucosal erosions, ulcers, and polymorphic lesions that develop into vesicles on the trunk and extremities are examples of skin lesions that characterize PNP [33]. These typically evolve in conjunction with the primary tumor. In about 17% of cases, the diagnosis of PNP is made prior to the identification of cancer [33].
PNP is associated with the DRB1*03 and HLA-Cw*14 alleles, which are more common in Caucasian and Chinese populations, according to recent studies [134]. Although the pathogenesis of PNP remains incompletely understood, current evidence suggests the involvement of both autoantibodies and cell-mediated immunity [134]. The most prevalent autoantibodies found in patients with PNP target the plakins family, including 210 kDa envoplakin, 190 kDa periplakin, 210 and 250 kDa desmoplakins I and II, 500 kDa plectin, and 230 kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen [134]. No specific data are currently available regarding the pathogenesis of PNP associated with CRC.
The mortality rate of PNP is approximately 90%, primarily attributed to septic complications, bronchiolitis obliterans, or gastrointestinal bleeding [134]. Skin lesions may continue to progress following the excision of tumor formations; however, the management of the malignant condition significantly influences the prognosis of these patients [134].
12. Conclusions
Currently, cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes are underdiagnosed, and the pathogenic mechanisms leading to their development remain incompletely elucidated. Intestinal dysbiosis, which is definitively correlated with colorectal oncogenesis, may be implicated in the onset of these paraneoplastic syndromes. Intestinal microorganisms and their metabolites, which cross the intestinal barrier, enter systemic circulation and trigger immune responses, leading to chronic inflammation. We consider this to be an important topic for future research studies.
The early identification of cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes could facilitate the early diagnosis of CRC and, in turn, enhance the prognosis of affected patients. Therefore, we consider that it is essential to perform an endoscopic examination of the digestive tract in all patients presenting with newly identified skin lesions, particularly in those with a family history of malignant tumors or other risk factors for CRC. Therefore, we propose that these patients necessitate specific screening strategies for CRC. This involves colonoscopic evaluation regardless of the age at which the skin lesions are identified, and the colonoscopy should be repeated at shorter intervals than the screening recommendations for the general population.
The novelty of our investigation is the particular emphasis on the pathogenic relationship between cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes and CRC. Given the high incidence of these malignancies, it is essential to evaluate clinical and paraclinical tools that may aid in early diagnosis and enhance the prognosis for patients with CRC.
Accordingly, additional research is required to assess the cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes that are linked to CRC. In addition to enhancing the diagnostic management, they can also aid in the comprehension of oncogenetic mechanisms and the identification of new therapeutic targets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.A.I. and G.G.; methodology, V.A.I. and T.F.G.; software, N.I.A. and L.-C.T.; validation, C.C.D.; formal analysis, V.A.I. and G.G.; investigation, V.B., M.-S.C., I.-A.C., B.B., M.B. and A.N.; resources, T.F.G., L.-C.T., N.B. and N.I.A.; data curation, L.-C.T., N.B., V.B., M.-S.C., I.-A.C., B.B., M.B. and A.N.; writing—original draft preparation, V.A.I. and G.G.; writing—review and editing, G.G. and C.C.D.; visualization, C.C.D., D.O.C. and R.S.C.; supervision, C.C.D.; project administration, C.C.D.; funding acquisition, V.A.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ionescu, V.A.; Gheorghe, G.; Bacalbasa, N.; Chiotoroiu, A.L.; Diaconu, C. Colorectal Cancer: From Risk Factors to oncogenesis. Medicina 2023, 59, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2023-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Montes, O.F.B.; Gil, T.E.; Solano, C.C.; Padilla, D. Leser-Trélat Syndrome, an Underdiagnosed Cutaneous Paraneoplastic Syndrome That Could Aid in Early Detection of Colon Cancer: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e44907. [Google Scholar]
- Schadt, C.R. The cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal malignancy. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourmishev, L.A.; Draganov, P.V. Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4372–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoki, Y.; Satoh, S.; Morioka, G.; Asano, M.; Nomura, K. Rectal cancer associated with acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa as a possible cutaneous marker of internal malignancy. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 33, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancic-Gajic, M.; Vujovic, S.; Dujmovic, I.; Basta, I.; Ivovic, M.; Marina, L.V.; Djordjevic, P.B.; Micic, D. Acquired Hypertrichosis Lanuginosa: Typical Presentation and Unusual Association. Arch. Iran. Med. 2015, 18, 450–452. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.Y.; Wen, G.D.; Che, D.D.; Shen, D.H.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhou, C. Gardner fibroma with localized hypertrichosis without adenomatous polyposis coli gene mutation. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 2129–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunduz, K.; Coban, M.; Ozturk, F.; Ermertcan, A.T. Malignant acanthosis nigricans associated with ileocecal adenocarcinoma. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yazdabadi, A.; Sinclair, R. Acanthosis Nigricans Associated with Morbid Obesity and Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2012, 2012, 545247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.T.; Massa, M.C.; Welykyj, S.E. Acanthosis nigricans and rectal carcinoid. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1991, 25, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.O.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.R.; Roh, J.Y. Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica with Adenocarcinoma of the Colon Treated with Topical Tretinoin. Ann. Dermatol. 2008, 20, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.S.; Lien, G.S.; Lai, H.H.; Cheng, Y.S.; Hu, C.H.; Hsieh, M.C.; Fang, C.L.; Pan, S. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome) with adenocarcinoma of the colon: Report of a case and review of the literature. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouahbi, H.; Benhami, M.; Nouikh, L.; Acharfi, N.; Kelati, A.; Oualla, K.; Benbrahim, Z.; Elmrabet, F.Z.; Arifi, S.; Menissi, F.; et al. Dermatomyositis and rectal cancer: Case study and literature review. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 18, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, K.; Shimomura, M.; Toyota, K.; Kagimoto, A.; Tsukiyama, N.; Shishida, M.; Oishi, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Shibata, S.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Successful resection of liver metastasis detected by exacerbation of skin symptom in a patient with dermatomyositis accompanied by rectal cancer: A case report and literature review. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; So, M.W.; Kim, S.G. Paraneoplastic dermatomyositis presenting myopathy combined with synchronous cervical and sigmoid colon cancer. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Shimura, T.; Fujikawa, H.; Okugawa, Y.; Hiro, J.; Toiyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Mohri, Y.; Kusunoki, M. Exacerbation of Dermatomyositis with Recurrence of Rectal Cancer: A Case Report. Case Rep. Oncol. 2015, 8, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, X.; Zong, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y. A Case of Recurrent Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome Containing Colon Cancer. Int. Surg. 2015, 100, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshadri, D.; Karagiorgos, N.; Hyser, M.J. A Case of Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome and a Review of Gastrointestinal Polyposis Syndromes. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 8, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi, S.; Noorali, S.; Alizadeh, A.H.M. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome Associated with Metastatic Colon Cancer. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2018, 12, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, N.; Fukuzaki, T.; Nakamura, T.; Hayashida, H.; Okazaki, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Hirai, T. Cronkhite-canada syndrome associated with colon cancer: Report of a case. Surg. Today 1993, 23, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.Y.; Sheng, J.Q. A case of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome associated with high-grade intramucosal neoplasia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7503–7505. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, W.H.; Kwon, C.I.; Ko, K.H.; Hahm, K.B.; Pa, P.W.; Hong, S.P. Gastrointestinal Cancers in a Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome Family: A Case Report. Clin. Endosc. 2013, 46, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.E.; Niu, B.Z.; Ji, W.Y.; Wu, B. Laparoscopic restorative proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for Peutz-Jeghers syndrome with synchronous rectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 5293–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, Y.; Ohtsuka, K.; Ishi, S.; Aso, N.; Ohki, A.; Hashimoto, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Ohnishi, H.; Abe, N. STK11 p.F354L Germline Mutation in a Case of Multiple Gastrointestinal Tumors. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2020, 14, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, D.; Hackett, C.B.; Healy, V.; Ramsay, B. Diagnostic error: What Muir-Torre syndrome has taught us. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2014206959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulpule, S.; Ibrahim, H.; Osman, M.; Zafar, S.; Kanta, R.; Shypula, G.; Islam, M.A.; Sen, S.; Yousif, A. Muir-Torre Syndrome Presenting as Sebaceous Adenocarcinoma and Invasive MSH6-Positive Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Case Rep. Oncol. 2016, 9, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivkin, A.C.; Bystrom, P.; Lin, A.Y.; Chaudhry, V. Recurrent colon cancer in a patient with Muir-Torre syndrome: A case report. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 2024, rjae015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Cai, Y.; Yin, W.; Huang, J. A locally advanced colon cancer patient with Muir-Torre syndrome obtains durable response to neoadjuvant and adjuvant immunotherapy. Tumori 2023, 109, NP27–NP31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, C.S.; Park, T.H.; Yoo, J.H.; Kim, K.J. A Case of Leser-Trelat Sign Associated with Adenocarcinoma of the Rectum. Ann. Dermatol. 2005, 17, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourmishev, L. Multiple seborrheic keratoses associated with rectal adenocarcinoma. CEEDVA 2004, 6, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Gao, Z.Y.; Lei, F.m.; Zhang, J.X.; Gu, J. A Case Report on Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Associated Colonic Carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1501–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Inayat, F.; Goraya, M.H.N.; Nawaz, G.; Mehran, A.; Aziz, A.; Saad, S. Colorectal carcinoma and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: Is there a possible paraneoplastic association? Clin. Endosc. 2023, 56, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendelin, D.S.; Pope, D.N.; Mallory, S.B. Hypertrichosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, V.F.; Barbosa, M.C.; Martelli, D.R.B.; Bonan, P.R.; Aguiar, M.J.B.; Martelli Junior, H. A review of genetic syndromes associated with hypertrichosis. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras 2021, 67, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slee, P.H.; van der Waal, R.I.; van Leeuwen, J.H.S.; Tupker, R.A.; Timmer, R.; Seldenrijk, C.A.; van Steensel, M.A.M. Paraneoplastic hypertrichosis lanuginosa acquisita: Uncommon or overlooked? Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, P.; Floridis, J. Hypertrichosis lanuginosa acquisita: A rare dermatological disorder. Clin. Pict. 2016, 387, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, M.R.; Chung, H.J.; Cho, Y.H.; Chung, K.Y. Hypertrichosis lanuginosa acquisita associated with autoimmune hepatitis. J. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorette, G.; Maruani, A. Images in clinical medicine. Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, S.P.; Freemark, M.; Prose, N.S. Acanthosis nigricans: A practical approach to evaluation and management—eScholarship. Dermatol. Online J. 2008, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Das, A.; Lahiri, K.; Chatterjee, M.; Padhi, T.; Rathi, S.; Dhar, S.; Sarma, N. Facial acanthosis nigricans: A morphological marker of metabolic syndrome. Indian J. Dermatol. 2017, 62, 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, V.; Das, A.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, R.; Hassan, S. Acral acanthosis nigricans (acral acanthotic anomaly). Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, S140–S141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kebria, M.M.; Belinson, J.; Kim, R.; Mekhail, T.M. Malignant acanthosis nigricans, tripe palms and the sign of Leser-Trelat, a hint to the diagnosis of early stage ovarian cancer: A case report and review of the literature. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 101, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, J.; Ihlesias, P.; Suarez, C.; Corredoira, Y.; Schnettler, K. Malignant acanthosis nigricans as a paraneoplastic manifestation of metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Womens Dermatol. 2019, 5, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, J.A.; Mesquita, K.C.; Igreja, A.C.S.M.; Lucas, I.C.R.N.; Freitas, A.F.; de Oliveira, S.M.; Costa, I.M.C.; Campbell, I.T. Paraneoplastic cutaneous manifestations: Concepts and updates. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentenero, M.; Carrozzo, M.; Pagano, M.; Gandolfo, S. Oral acanthosis nigricans, tripe palms and sign of leser-trélat in a patient with gastric adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Dermatol. 2004, 43, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipkin, C.A.; Lio, P.A. Cutaneous manifestations of internal malignancies: An overview. Dermatol. Clin. 2008, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinca, A.; Cardoso, J.C.; Brites, M.M.; Tellechea, Ó.; Figueiredo, A. Florid cutaneous papillomatosis and acanthosis nigricans maligna revealing gastric adenocarcinoma. Bras. Dermatol. 2011, 86, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubovic, B.D.; Sawires, H.F.; Adam, D.N. Occult cause of paraneoplastic acanthosis nigricans in a patient with known breast dcis: Case and review. Curr. Oncol. 2012, 19, e299–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, N.; Das, T.; Kundu, A.K.; Maity, A. Atypical presentation of acanthosis nigricans. Indian. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 1058–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagwani, A.V.; Reynu, R.; Affirul, C.A.; Mustafa, M.T.; Kosai, N.R. Resolution of acanthosis nigricans following curative gastric carcinoma resection. Clin. Ter. 2016, 167, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mosannen, M.P.; Salek, R.; Taghizadeh, A.; Yazdanpanah, M.J.; Mosannen, M.H.; Esmaeili, E. Diagnosis of an occult gastric adenocarcinoma by oral manifestations (acanthosis nigricans): A case report. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 12, S383–S387. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yu, P.J.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhu, S.M.; Zhang, C.W. Malignant acanthosis nigricans with Leser-Trélat sign and tripe palms: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 5632–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Araz, M.; Korkmaz, M.; Demirkiran, A. Early-stage gastric cancer presenting with tripe palm and acanthosis nigricans. Oncol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 17, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Ikeda, K.; Sato, M.; Shibahara, K.; Yuhara, K.; Fukutomi, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Kanazawa, N.; Yuzawa, K.; Fukao, K.; et al. Transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF alpha)-producing gastric carcinoma with acanthosis nigricans: An endocrine effect of TGF alpha in the pathogenesis of cutaneous paraneoplastic syndrome and epithelial hyperplasia of the esophagus. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-E-Silva, M.; Carvalho, J.C.; Carneiro, S.C. Cutaneous paraneoplasia. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 29, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, K.; Malakar, S. Topical tretinoin in acan-thosis nigricans. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 1996, 62, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swineford, S.L.; Drucker, C.R. Palliative treatment of paraneoplastic acanthosis nigricans and oral florid papillomatosis with retinoids. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2010, 9, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Kritsanaviparkporn, C.; Treesirichod, A. Comparing the efficacy and safety profiles of 0.025% and 0.05% tretinoin creams in treating acanthosis nigricans: A randomized double-blinded study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treesirichod, A.; Thaneerat, N.; Kangvanskol, W. A comparison of the efficacy and safety profiles of 10% salicylic acid and 10% urea creams in treating acanthosis nigricans in adolescents: A randomized double-blinded study. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phiske, M.M. An approach to acanthosis nigricans. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghane, Y.; Heidari, N.; Hosseini, S.; Heidari, A.; Pishraft-Sabet, H.; Eghbali, S.; Goodarzi, A. Efficacy and safety of lasers versus topical medications for acanthosis nigricans and pseudo-acanthosis nigricans treatment: A systematic review. Lasers Med. Sci. 2024, 39, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazex, A.; Salvador, R.; Dupre, A.; Christol, B. Syndrome paraneoplasieque a type d’hyperkeratose des extremites. Guerison apres le traitement de l’epithelioma larynge. Bull. Soc. Fr. Dermatol. Syphiligr. 1965, 72, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Räßler, F.; Goetze, S.; Elsner, P. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome)—A systematic review on risk factors, diagnosis, prognosis and management. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1119–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Lipner, S.R. A Review of Nail Changes in Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica (Bazex Syndrome). Ski. Appendage Disord. 2021, 7, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.H.; Ferrazzano, C.; Karthikeyan, A.; Hejazi, H.; Bhattacharya, A.; Awuah, W.A.; Isik, A. Bazex Syndrome (Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica): A Narrative Review of Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, and Therapeutic Approaches. Cureus 2023, 15, e45368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubenovic, M.S.; Ljubenovic, D.B.; Binic, I.I.; Jankovic, A.S.; Jovanovic, D.L. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex Syndrome). Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2009, 75, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzgruber, J.; Oberneder-Popper, J.; Guenova, E.; Hötzenecker, W. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome): A case report. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2022, 14, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofler, L.; Kofler, H. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica Bazex 6 years prior to diagnosis of gastric cancer (Article in Dutch). Hautarzt 2015, 66, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, M.; Hanafusa, T.; Chikazawa, S.; Ueno, M.; Namiki, T.; Igawa, K.; Miura, K.; Yokozeki, H. Bazex syndrome in lung squamous cell carcinoma: High expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in lesional keratinocytes with Th2 immune shift. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2016, 8, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognia, J.L.; Brewer, Y.P.; Cooper, D.L. Bazex syndrome (Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica). An analytic review. Medicine 1991, 70, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, J.; Healy, E.; Jain, A.; Hawkins, D.; Ho, Q.A.; Agrawal, A.; Ozer, E.; Rupert, R.; Diavolitsis, V.M.; Bhatt, A.D. A series of typical and atypical cases of Bazex syndrome: Identifying the red herring to avoid delaying cancer treatment. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2259–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Sharma, N.L.; Ranjan, N.; Tegta, G.R.; Sarin, S. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome): Case report and review of literature. Dermatol. Online J. 2006, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, R.; Powell, M. A case report of resolution of acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome) post resection of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2050313X19881595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarzour, J.G.; Singh, S.; Andea, A.; Cafardi, J.A. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome): Report of a case associated with small cell lung carcinoma and review of the literature. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2011, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu Velez, A.M.; Howard, M.S. Diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous paraneoplastic disorders. Dermatol. Ther. 2010, 23, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, D.; Fergin, P.; Kelly, J. Bullous lesions in Bazex syndrome and successful treatment with oral psoralen phototherapy. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2001, 42, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.A., Jr.; Gresta, L.T.; Cruz, R.C.; Carvalho, G.G.; Moreira, M.H. Bazex syndrome. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 209–211. [Google Scholar]
- Dourmishev, L.A.; Dourmishev, A.L.; Schwartz, R.A. Dermatomyositis: Cutaneous manifestations of its variants. Int. J. Dermatol. 2002, 41, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, N.P.; Zakaria, S.; Degnim, A.C.; Boughey, J.C. Dermatomyositis presenting as a paraneoplastic syndrome due to underlying breast cancer. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 2011, bcr1020103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, E.; Smrke, A.; Halai, K.; Patel, G.; Thway, K.; Jones, R.L.; Benson, C. Paraneoplastic dermatomyositis associated with metastatic leiomyosarcoma of unknown primary. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2020, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkegkes, I.D.; Minis, E.E.; Iavazzo, C. Dermatomyositis and colorectal cancer: A systematic review. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 187, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, G.; Chen, G.; Wu, B.; Lu, L.; Bao, L. Meta-analysis of the association of dermatomyositis and polymyositis with cancer. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, S.; Valente, M.; Adami, N.; Biral, D.; Ghirardello, A.; Rampudda, M.E.; Vecchiato, M.; Sarzo, G.; Corbianco, S.; Kern, H.; et al. Polymyositis, dermatomyositis and malignancy: A further intriguing link. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuya, A.; Hoshino, T.; Aoshima, M.; Tatsuno, K.; Fujiyama, T.; Tokura, Y. TGFbeta/SMAD4 signalling is inhibited in tumour cells and infiltrating lymphocytes of a patient with colon cancer-associated dermatomyositis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2265–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, P.; Gurung, R.B.; Shrestha, A.; Paudel, I.; Shrestha, P. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome: A Case Report. JNMA J. Nepal. Med. Assoc. 2022, 60, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Peng, T. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: Report of a rare case and review of the literature. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520922427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavik, T.; Montgomery, E.A. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome six decades on the many faces of an enigmatic disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R. Comprehensive treatment of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2023, 102, e32714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Sang, L.X.; Chang, B. Crinkhite-Canada syndrome: From clinical features to treatment. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2020, 8, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, V.A.; Gheorghe, G.; Varlas, V.; Stanescu, A.M.A.; Diaconu, C. Hepatobiliary impairments in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: The current approach. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 14, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, P. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome Associated With Superficial Esophageal Carcinoma: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 855336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Ma, N.; Che, J.; Li, H.; Cao, B. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome associated with colon cancer metastatic to liver: A case report. Medicine 2017, 96, e7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashiro, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Kubo, N.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Wakasa, K.; Hirakawa, K. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome containing colon cancer and serrated adenoma lesions. Digestion 2004, 69, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopacova, M.; Urban, O.; Cyrany, J.; Laco, J.; Bures, J.; Rejchrt, S.; Bartova, J.; Tacheci, I. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrime: Review of the Literature. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2013, 1, 856873. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, K.; Sato, K.; Okada, S.; Suto, D.; Otake, T.; Kohgo, Y. Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome Successfully Treated by Corticosteroids before Presenting Typical Ectodermal Symptom. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, G.; Ceobanu, G.; Ilie, M.; Stanescu, A.M.A.; Bratu, O.; Diaconu, C. Gastrointestinal and neurological manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosu. Arch. Balk. Med. Union 2019, 54, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegert-Johnson, D.L.; Osborn, N.; Smyrk, T.; Boardman, L.A. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome hamartomatous polyps are infiltrated with IgG4 plasma cells. Digestion 2007, 75, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Huang, Y.; Suo, Z.; Ma, X. Cronkhite-Canada syndrome: A case report and review of the literature. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 81, 104090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, J.; Kijima, H.; Hasumi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Shirai, T.; Mine, T. Adenocarcinoma and multiple adenomas of the large intestine, associated with cronkite-Canada syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2003, 35, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zügel, N.P.; Hehl, J.A.; Jechart, G.; Tannapfel, A.; Wienbeck, M.; Witte, J. Tumor association in cases of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome. Z. Fur Gastroenterol. 2001, 39, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Jin, X.W.; Li, B.R.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Mao, G.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Ning, S.B. Cancer risk in patients with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: A retrospective cohort study of 336 cases. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317705131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menko, F.H. LKB1/STK11, peutz-Jeghers syndrome and cancer, Introduction. Fam. Cancer 2011, 10, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boland, C.R.; Idos, G.E.; Durno, C.; Giardiello, F.M.; Anderson, J.C.; Burke, C.A.; Dominitz, J.A.; Gross, S.; Gupta, S.; Jacobson, B.C.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Cancer Risk in the Gastrointestinal Hamartomatous Polyposis Syndromes: Recommendations From the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, P2063–P2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, V.A.; Gheorghe, G.; Constantinescu, G.; Sandru, V.; Ilie, M.; Oprita, R.; Plotogea, O.; Gherghiceanu, F.; Diaconu, C. Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation in biliopancreatic tumours. Arch. Balk. Med. Union 2021, 56, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E.; Goto, T.; Honda, H. Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Jiang, L.X.; Chen, Y.R.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, P.F.; Dong, Z.W.; Yang, H.R.; Gu, G.L. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: Experience with 566 Chinese cases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, C.I.; Keitheri-Cheteri, M.B.; Sabripour, M.; Wei, C.; McGarrity, T.J.; Seldin, M.F.; Nations, L.; Lynch, P.M.; Fidder, H.H.; Friedman, E.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 41, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehenni, H.; Resta, N.; Guanti, G.; Mota-Vieira, L.; Lerner, A.; Peyman, M.; Chong, K.A.; Aissa, L.; Ince, A.; Cosme, A.; et al. Molecular and clinical characteristics in 46 families affected with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aretz, S.; Stienen, D.; Uhlhaas, S.; Loff, S.; Back, W.; Pagenstecher, C.; McLeod, D.R.; Graham, G.E.; Mangold, E.; Santer, R.; et al. High proportion of large genomic STK11 deletions in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Human Mutat. 2005, 26, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardiello, F.M.; Brensinger, J.D.; Tersmette, A.C.; Goodman, S.N.; Petersen, G.M.; Booker, S.V.; Cruz-Correa, M.; Offerhaus, J.A. Very high risk of cancer in familial Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latchford, A.; Cohen, S.; Auth, M.; Scaillon, M.; Viala, J.; Daniels, R.; Talbotec, C.; Attard, T.; Durno, C.; Hyer, W. Management of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome in children and adolescents: A Position paper from the ESPGHAN polyposis working group. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leerdam, M.E.; Roos, V.H.; van Hooft, J.E.; Dekker, E.; Jover, R.; Kaminski, M.F.; Latchford, A.; Neumann, H.; Pellisé, M.; Saurin, J.C.; et al. Endoscopic management of polyposis syndromes: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) guideline. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaijee, F.; Brown, A.S. Muir-Torre Syndrome. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponti, G.; Losi, L.; Di Gregorio, C.; Roncucci, L.; Pedroni, M.; Scarselli, A.; Benatti, P.; Seidenari, S.; Pellacani, G.; Lembo, L.; et al. Identification of Muir-Torre syndrome among patients with sebaceous tumors and keratoacanthomas: Role of clinical features, microsatellite instability, and immunohistochemistry. Cancer 2005, 103, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, E.G.; Bell, A.J.; Barlow, K.A. Multiple primary carcinomata of the colon, duodenum, and larynx associated with kerato-acanthomata of the face. Br. J. Surg. 1967, 54, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, D. Multiple sebaceous tumors. Arch. Dermatol. 1968, 98, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Peltomäki, P. Lynch syndrome and related familial colorectal cancers. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2008, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, G.; Manfredini, M.; Tomasi, A.; Pellacani, G. Muir-Torre Syndrome and founder mismatch repair gene mutations: A long gone historical genetic challenge. Gene 2016, 589, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, N.; Shaker, N.; Abid, A.; Shah, S.; Shakra, R.A.; Sangieza, O.P. Muir–Torre syndrome and recent updates on screening guidelines: The link between colorectal tumors and sebaceous adenomas in unusual locations. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 128, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simic, D.; Dummer, R.; Freiberger, S.N.; Ramelyte, E.; Barysch, M.J. Clinical and molecular features of skin malignancies in Muir-Torre syndrome. Genes 2021, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, A.J.; Lyle, S.; Calonje, E. Sebaceous neoplasia and Torre-Muir syndrome. Curr. Diagn. Pathol. 2007, 13, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.M.; Schwartz, R.A. Muir-Torre syndrome (MTS): An update and approach to diagnosis and management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, H.H.; Mahendraker, N.; Sarwate, S.; Tangella, K. Muir-Torre syndrome: A rare but important disorder. Cutis 2008, 82, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navi, D.; Wadhera, A.; Fung, M.A.; Fazel, N. Muir-Torre syndrome. Dermatol. Online J. 2006, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaad, K.O.; Obaidat, N.A.; Ghazarian, D. Skin adnexal neoplasms—Part 1: An approach to tumours of the pilosebaceous unit. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrago, W.; Joseph, A.K. Sebaceous carcinoma: The great masquerader: Emgerging concepts in diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol. Ther. 2008, 21, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubay, D.; Ohanisian, L.; Bank, M.P.; Kaur, N.; Genuit, T.; Ross, A. Muir-Torre Syndrome, a Rare Phenotype of Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer With Cutaneous Manifestations. ACG Case Rep. J. 2019, 6, e00188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero-Soto, P.; Sanchez-Vivaldi, J.; Rovira, O.; Arocho, J.; Pereira-Torrellas, G.; Martinez-Trabal, J.; Bolaños-Avila, G. Case report of Leser-Trelat sign as sequela of an atypical inflammatory process. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2022, 92, 106833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveri, O.C.; James, F.; Dickens, B. Variability of Leser-Trélat Sign Secondary to Melanoma In Situ. Cureus 2024, 16, e53639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siedek, V.; Schuh, T.; Wollenberg, A. Leser-Trelat sign in metastasized malignant melanoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2009, 266, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.R.; Boland, C.R.; Patel, M.; Thrash, B.; Menter, A. Cutaneous manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: Part I. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, e1–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, G.; Didona, D.; Magliulo, G.; Iannella, G.; Didona, B.; Mercuri, S.R.; Moliterni, E.; Donati, M.; Ciofalo, A.; Granata, G.; et al. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus: Insight into the Autoimmune Pathogenesis, Clinical Features and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).