Abstract
The pathophysiology of nausea and vomiting in gastroparesis is complicated and multifaceted involving the collaboration of both the peripheral and central nervous systems. Most treatment strategies and studies performed in gastroparesis have focused largely on the peripheral effects of this disease, while our understanding of the central nervous system mechanisms of nausea in this entity is still evolving. The ability to view the brain with different neuroimaging techniques has enabled significant advances in our understanding of the central emetic reflex response. However, not enough studies have been performed to further explore the brain–gut mechanisms involved in nausea and vomiting in patients with gastroparesis. The purpose of this review article is to assess the current status of brain imaging and summarize the theories about our present understanding on the central mechanisms involved in nausea and vomiting (N/V) in patients with gastroparesis. Gaining a better understanding of the complex brain circuits involved in the pathogenesis of gastroparesis will allow for the development of better antiemetic prophylactic and treatment strategies.
1. Introduction
Gastroparesis is a chronic heterogeneous motor disorder with variable clinical manifestations including episodic nausea, vomiting, retching, post-prandial fullness, early satiety, and/or upper abdominal pain in the absence of mechanical obstruction [1]. The sensation of nausea is an unpleasant subjective sensation that is difficult to define, and can occur alone or in conjunction with vomiting [2]. The pathophysiology of nausea and vomiting (N/V) is complex and involves the transmission of sympathetic and parasympathetic visceral afferent pathways to the nucleus tractus solitarius in the medulla which activates the emetic circuitry [3]. Over the last few decades, various functional brain imaging techniques have been performed in patients with N/V to better characterize functional and structural changes that occur in the brain during symptomatic episodes. In the field of gastroenterology, for example, several entities dominated by symptoms of N/V have been studied with various neuroimaging modalities which have greatly enhanced our understanding of the brain–gut interactions in diseases like cyclic vomiting syndrome [4,5,6], motion sickness [7,8], and irritable bowel syndrome [9,10,11,12]. Imaging techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) studies have helped to better define central nervous system mechanisms and abnormalities in these patients [13]. However, the amount of literature that exists on the central arousal systems involved in gastroparesis patients during episodes of N/V is very sparse. In the spirit of contributing to the Special Issue “Gastroparesis” in Gastrointestinal Disorders, this article will review the current status of brain imaging and the theories regarding our present understanding of the central mechanisms involved in N/V in patients with gastroparesis.
2. Background
Gastroparesis is a chronic debilitating disorder characterized by slowed gastric emptying with accompanying symptoms thereof in the absence of mechanical obstruction [14]. Symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, early satiety, bloating and/or postprandial fullness. Treatment options for gastroparesis are limited. Thus, gastroparesis remains a difficult disorder to treat, with only a few approved pharmacologic agents available to provide symptom control by targeting underlying peripheral or central mechanisms [15]. Additionally, gastroparesis poses a significant burden on the health-care system and greatly impacts the quality of life and well-being of patients afflicted with this disorder [16]. Although the incidence is not well-established [17], there is significant morbidity associated with gastroparesis with a notable increase in prevalence, incidence, and hospitalization rates over the last few decades. For example, from 1995 to 2004, gastroparesis-related hospitalizations in the United States increased by nearly 158% [18]. While the pathogenesis of gastroparesis is multifactorial, complex, and still evolving, we know that the stomach transmits information to the central nervous system via the vagus nerve [19]. Activation of the emetic circuitry begins with signals from the pharynx, stomach, and small intestine that are then transmitted to the nucleus tractus solitarius in the medulla via sympathetic and parasympathetic visceral afferent pathways [20]. In gastroparesis, gastric distension is the “signal” that stimulates visceral afferent input to the central nervous system (CNS) that subsequently stimulates nausea and the act of emesis acting through the chemoreceptor trigger zone and the “vomiting center” [20] (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Within the emetic circuitry, there are many integrated neurotransmitters providing numerous potential therapeutic targets for pharmacologic therapy [3]. Therefore, a better understanding of how the brain processes afferent information coming from the stomach is very much needed. To be able to better elucidate and map out CNS mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of gastroparesis symptomatology means that more effective treatment strategies can potentially be developed to manage symptoms such as visceral pain, nausea, and vomiting [21]. Brain imaging provides quantitative objective measurable viscerosensory data encoded by afferents in the gut that reach the brain; this allows for a better understanding of the phenotypic, emotional, and behavioral components involved in gastroparesis [22].
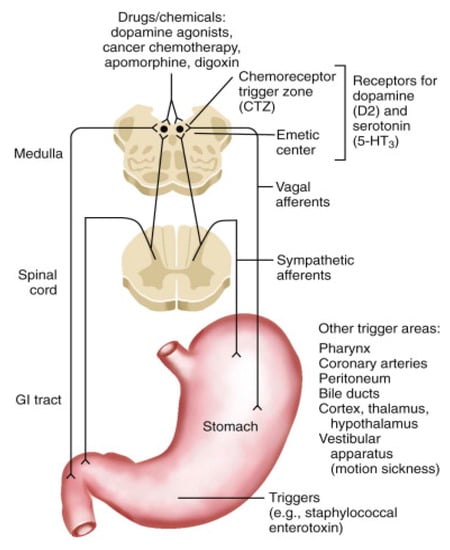
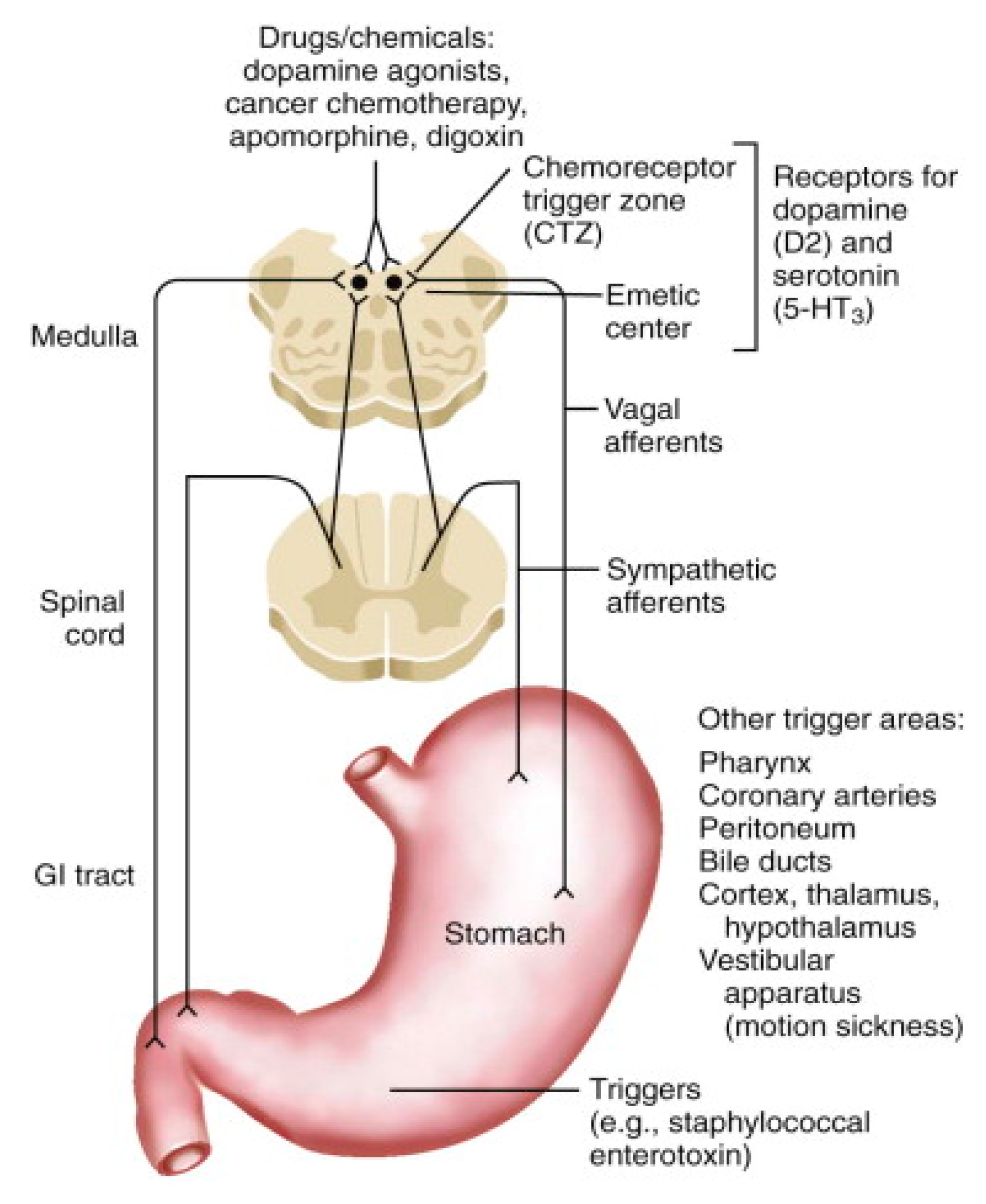
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of proposed neural pathways that mediate vomiting. 5-HT: 5-hydroxytryptamine; GI: gastrointestinal. Reprinted from [23]. Copyright 2016, with permission from Elsevier.
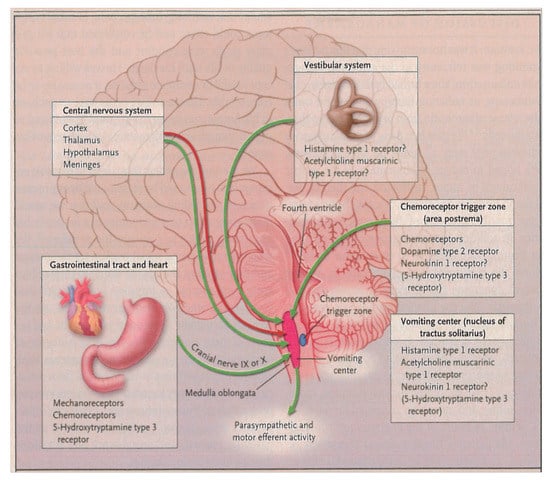
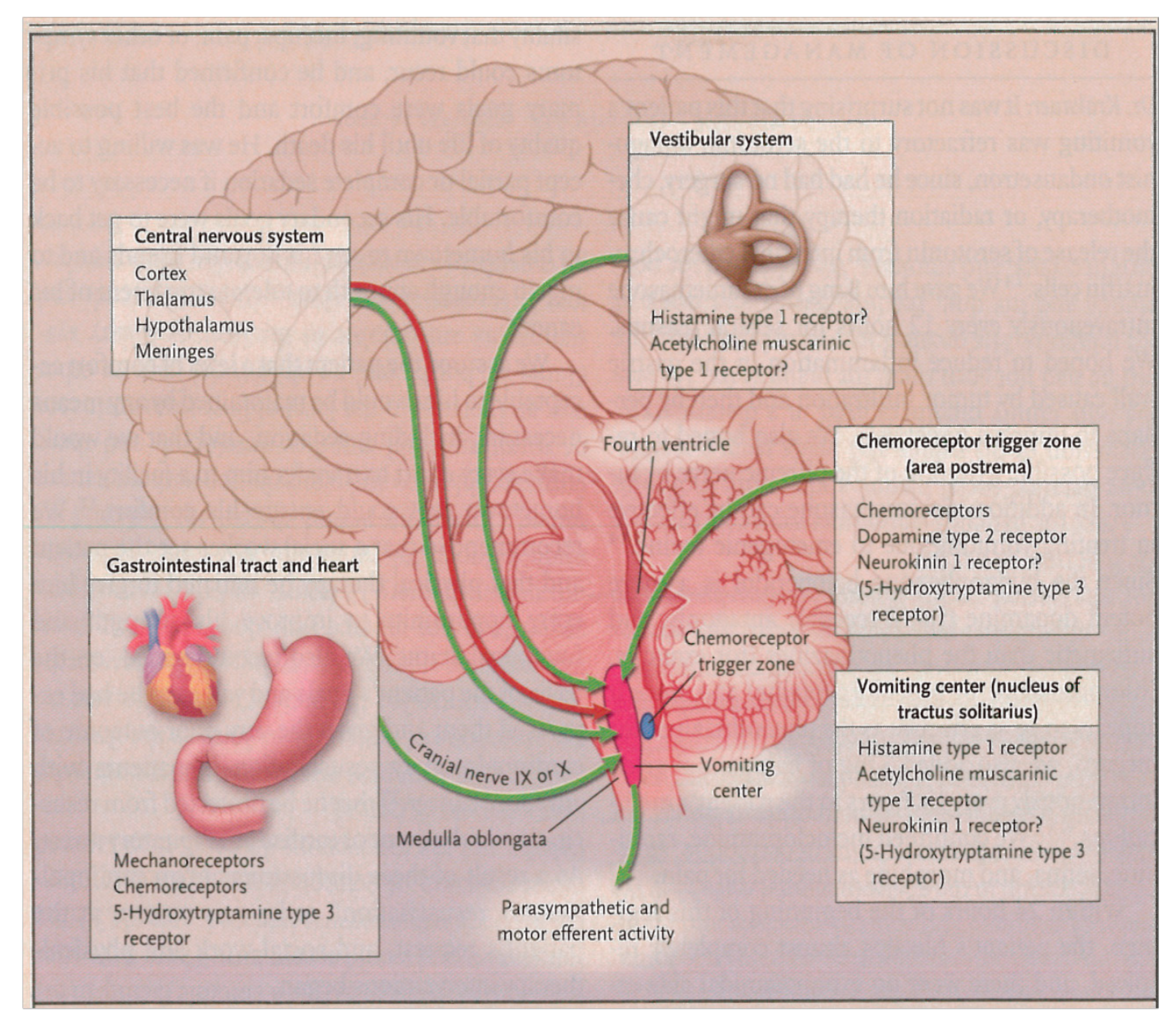
Figure 2.
The Pathophysiology of Nausea and Vomiting. Permission obtained from [24]. Copyright © 2005. Massachusetts Medical Society. Reprinted with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society.
Functional MRI (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) are two basic classes of brain imaging techniques that allow for measurement of brain activity [22]. They can map local metabolic or physiological consequences of altered brain activity. There are several factors which make fMRI an ideal brain imaging modality. First, fMRI has good sensitivity, is non-invasive, and clinically convenient (does not require injection of contrast) [25]. Second, it provides relatively high-quality spatial and temporal resolution with the ability to notice morphological changes in the brain without having to apply radioactive tracers (such as in a PET scan or technetium scan) [25]. Since fMRI does not require use of radioactive tracers, it is an ideal imaging technique for longitudinal studies as it provides repeatability and ease of use. Thirdly, fMRI imaging has the ability to reveal micro and macroscopic structural aberrations in gray and white matter and can also detect altered brain connectivity revealing disturbed areas of communication. Fourth, fMRI does not only allow the ability to assess alterations in morphology in certain brain regions [25]. Limitations of fMRI are that it is expensive and does not directly measure neural activity; instead, fMRI measures the indirect consequences of neural activity based on surrounding blood flow changes [26], and this can impose constraints on spatial and temporal resolution [27].
PET brain imaging is a noninvasive imaging modality that uses radioactive tracers to assess various areas of brain activity by measuring regional cerebral blood perfusion. It can also assess neurotransmitter concentrations in the brain [28]. Compared to fMRI, PET spatial and temporal resolutions are generally poorer [22]. In addition, PET brain imaging does not look at micro and macroscopic structural aberrations in gray and white matter, such as with fMRI, nor can it be used to identify rapid changes in brain activation [25]. Since radioactive tracers decay rapidly, the labeling of compounds results in time constraints when it comes to PET radiolabeling and can involve significant amounts of radioactivity [29]. However, one reason PET may be preferred over fMRI in some studies is because of the relatively long acquisition times, which increases test sensitivity and is thus less subject to variation over time. In addition, MRI may not be possible in certain patients where “hardware” has been previously implanted. Although the central nervous system (CNS) mechanisms of N/V are still evolving, the ability to view the brain with different neuroimaging techniques has enabled significant advances in our understanding of the central emetic reflex response.
3. Physiology of Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting involves multiple complex systems including neuroendocrine, autonomic nervous system, central nervous system, and psychological. During an episode of nausea and vomiting, the autonomic nervous system coordinates an emetic response with the CNS through central pathways of N/V in the chemoreceptor trigger zone and “vomiting center” in the medulla at the base of the fourth ventricle. Brainstem nuclei (nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS)) and higher brain centers receive input from abdominal vagal afferent sensory nerves [3]. Additionally, NTS neurons then project to a central pattern generator (CPG), or neuronal network, which projects neurons to the hypothalamus and ventral medulla. These different neurons in the medulla and the CPG then coordinate the organized motor actions that elicit vomiting (increased abdominal cavity pressure, diaphragm contraction, expulsion of gastric content). Some studies have used fMRI to show that extensive brain networks are involved in nausea evoked by visual stimulation. For example, Napadow et al. showed that different brain regions can be activated by visually-evoked nausea with worsening nausea associated with an increasing phasic brain response involving an extensive network of different brain regions [30]. In their study, prior to nausea, regions of the brain that were activated were the amygdala, ventral putamen, and locus coeruleus—areas know to process stress, fear, and emotion. Then, during transitioning to higher-intensity nausea, it was noted that recruitment of more brain regions occurred including the insular, anterior cingulate, prefrontal, and orbitofrontal cortices, as well as activation of subcortical regions (ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, putamen). During periods of intense nausea, a linkage between the anterior insula and midcingulate areas was sustained. Altogether a large network of brain neurons in supratentorial regions including limbic, cognitive, somatosensory, and interoceptive areas were noted as important neural circuits in the production of the emetic response.
Other studies have also suggested that the cerebral cortex is involved in the nausea pathway. By using fMRI imaging techniques, Kim et al. also substantiated that regions of higher cortical function and emotion are positively correlated with an increase in heart rate during nausea [7]. These cortical regions included the anterior insula, medial prefrontal cortex, inferior frontal gyrus, and orbitofrontal regions—areas involved in basic visuo-spatial processing and interoception (precuneus) and motor function (precentral gyrus is part of the primary motor cortex). These observations collectively point towards various cognitive and emotional centers being involved in the N/V response in the brain, and not just one solitary “vomiting center.” Additionally, brain regions such as the insula are involved in both the parasympathetic and sympathetic response to N/V during both phasic and sustained autonomic responses to nausea [31]. Thus, even though N/V can be triggered by one stimulus, the emetic response can be mediated through various different neural circuits relying on and initiated by different receptors, similar to the pain response. For example, painful stimuli can be mediated by spinal cord circuits as well as different perceptual components that can be mediated through the limbic system in the brain [32].
4. Discussion and Review of the Literature
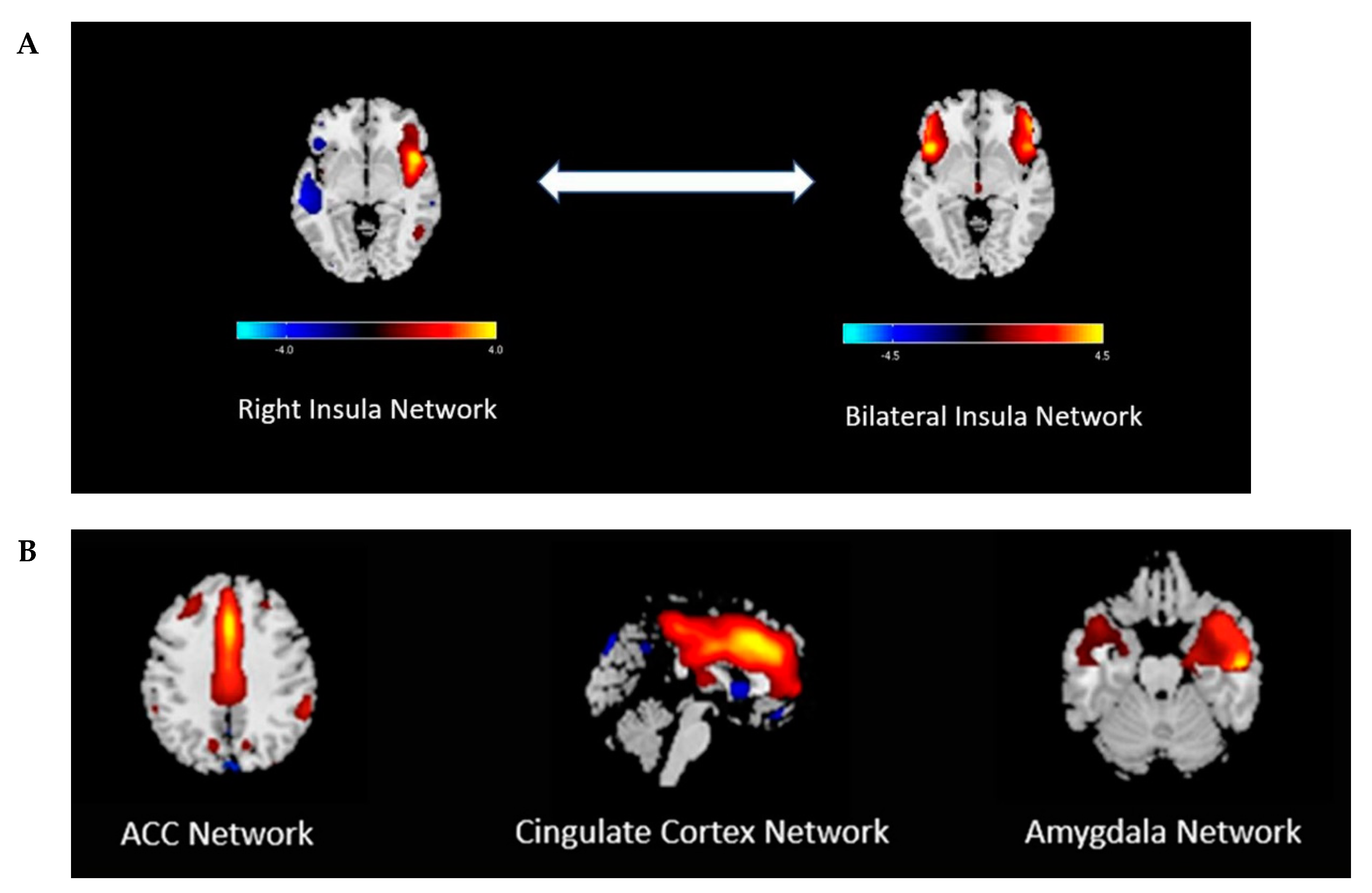
A review of the literature only yielded a few studies on brain imaging modalities that investigated CNS mechanisms during nausea and vomiting in adult patients with gastroparesis. In a recent case-control study, our research group used functional MRI to further explore the central nervous system mechanisms of nausea in 10 gastroparetic patients (7 idiopathic, 3 diabetic) [19]. In this study, 30 minutes of nausea was induced in participants by using visual stimulation of a flashing/rotating checkerboard image on a computer screen in a room immediately adjacent to an fMRI scanner. At baseline, fMRI data showed there were no significant differences in functional network connectivity (FNC) in the bilateral insular network between gastroparetic patients and healthy controls. However, with nausea induction, a significant decrease in bilateral insular connectivity was appreciated compared to the right insula and temporal lobe in gastroparetic patients versus healthy controls (Figure 3A). Further analysis of the fMRI data showed there was no significant difference in FNC among or between other brain components in post-stimulated gastroparesis patients versus healthy controls (amygdala, anterior cingulate cortex, or cingulate networks) (Figure 3B). To our knowledge, this is the first report that explores potential central nervous system mechanisms for nausea in patients with gastroparesis. One of the important take-home messages in this study is that the insular cortex plays a significant role in the processing of nausea. Might these fMRI changes, or phenomenon observed, be due to a preprogrammed brain circuitry that exists in gastroparetic patients by an environment of chronic nausea? Or do gastroparetic patients have a lower threshold for “nausea-inducing” settings in the CNS? These are important questions for which further studies are needed to explore.
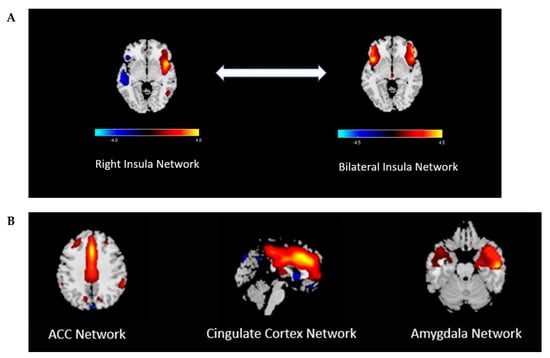
Figure 3.
(A) Central nervous system mechanisms of nausea in patients with gastroparesis depicted by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) brain images (bidirectional arrow). The first image is described as the “Right Insula Network” and it depicts maximal values in the right insula that extend into the left temporal lobe. The second image contains both the right and left insula and is described as “Bilateral Insula Network” and it represents comparison after exposure to a nausea-inducing visual stimulus in 10 gastroparetics and 8 healthy controls. The functional network connectivity was significantly reduced (p < 0.001) in gastroparetic patients versus healthy controls after visual stimulation between the right insula network and bilateral insula network. The highlighted areas illustrate the locations of reduced connectivity in gastroparesis. (B) These fMRI images depicting the anterior cingulate cortex, cingulate cortex, and amygdala networks were compared for functional network connectivity differences in the 10 gastroparetic patients versus 8 healthy controls at baseline and after visual stimulation. These three networks did not show significant functional network connectivity differences after induction of nausea between the gastroparetic patients and healthy controls. Reprinted by permission from Nature/Springer. Copyright 2020. [19].
In another study by Frokaer et al. including patients with diabetes and gastrointestinal symptoms, microstructural changes were detected using diffusion weighted MRI in areas of the brain involved with visceral sensory processing [33]. The brain changes in some areas correlated with clinical parameters including bloating (anterior insula), mental well-being (anterior insula, prefrontal cortex, and mid-cingulated and corona radiate), autonomic function based on electrocardiography (Holter monitoring) results (posterior insula and anterior cingulate), and symptoms of gastroparesis based on reported symptoms using the Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI) [33], a reliable and valid tool for measuring symptom severity in patients with gastroparesis [34]. The study suggested that microstructural brain changes can be involved in the pathogenesis as well as the persistence of gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetic patients.
Complementary alternative therapies have been used to treat symptoms of uncontrolled nausea, and the central effects in response to these treatments in patients with diabetic gastroparesis have been investigated by our group. Specifically, central and peripheral responses to transcutaneous needleless electrical acupuncture (TEA) were monitored by simultaneously measuring electroencephalography (EEG) and cutaneous electrogastrography (EGG) responses in 11 diabetic gastroparesis patients [35]. With nausea provocation by visual stimuli, EEG waves revealed activation of the right inferior frontal lobe, an area of the brain associated with the perception of unpleasant stimuli. With TEA therapy however, there was improvement in nausea. There was also a reduction in gastric slow wave abnormalities by EGG, which reflected the gastric electrical signal regarded as the gastric response to the sensation of nausea - or processing of nausea - through CNS receptors. In addition, the EEG brain waves shifted from the right to the left inferior frontal lobe, an area of the brain related to the expectancy of pleasant stimuli [36]. These findings support that the therapeutic effects of TEA on gastroparetic patients may be centrally-mediated.
The gastric electrical stimulator (GES) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March of 2000 through a Humanitarian Device Exemption as a treatment option for chronic, severe, medically-refractory diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis. Studies have shown that GES can result in significant and sustained improvement of nausea and vomiting, with symptom-control persisting up to 10 years in patients with refractory symptoms of gastroparesis [37,38]. Additionally, GES has been shown to improve quality of life, nutritional status, glycemic control, serum albumin, and reduces the need for hospitalizations as well as anti-emetic medications in patients with refractory gastroparesis [39,40,41,42,43]. One proposed mechanism of action is that GES works by enhancing vagal autonomic function with activation of central control mechanisms. In rats, GES was shown to have excitatory effects on neurons of the nucleus tractus solitarii of the medulla, that receives input from the stomach, which confirms involvement of vagal afferent pathways [44]. The nucleus tractus solitarii is an important center that relays vagal sensory afferents with cell bodies and neural endings in the stomach [44]. In another animal study receiving GES with parameters similar to those in gastroparesis, GES activated gastric-related neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, a region considered to be one of the most important autonomic control centers in the brain involved in the regulation of gastrointestinal motor functions [45,46].
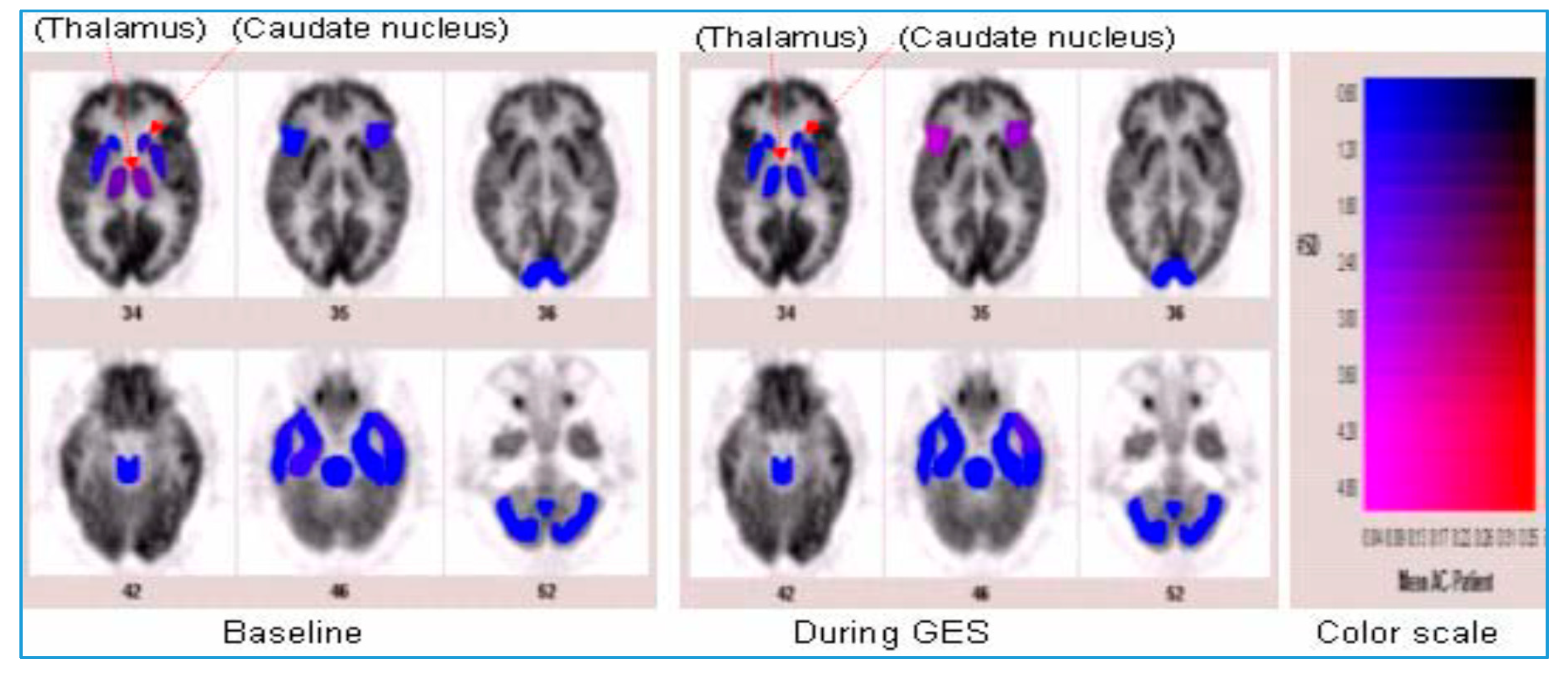
In humans with refractory gastroparesis, GES increased thalamic activity as detected by PET central nervous imaging [47] (Figure 4). Enhanced vagal activity was also appreciated through significantly decreased sympathovagal balance through power spectral analysis of heart rate variability. These findings suggest that GES may provide symptomatic improvement by enhancing relaxation of the gastric fundus, which occurs by improvement of vagal autonomic function as well as by the activation of central control mechanisms of nausea and vomiting through thalamic pathways [47]. These findings were replicated in another study from the same research group using chronic GES therapy [48]. After 12 weeks of GES therapy, 10 patients with refractory gastroparesis were observed to have enhanced vagal function and an increase in both thalamic and caudate activity on their brain PET scans suggesting an influence on central nervous system control mechanisms and activation of vagal afferent neural pathways. Consistent with these results, another study aiming to investigate if changes in cerebral activity occur on PET scans in 11 patients with refractory gastroparesis (8 diabetic, 3 idiopathic) with chronic GES therapy also noted increased thalamic and caudate activity [49]. This suggests that the central mechanisms for nausea and vomiting are mediated and activated via thalamic pathways in the central nervous system in severe gastroparetic patients after GES therapy and that indeed, the major symptomatic benefit of GES therapy for severe gastroparesis is by being an anti-emetic, albeit a very powerful anti-emetic. This explains the symptom relief provided by GES, an anti-emetic prescription for gastroparetics when there is no improvement with other standard medical therapies.
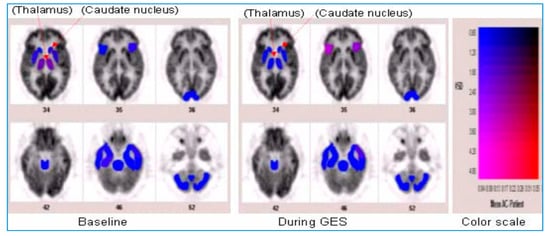
Figure 4.
Results of positron emission tomography (PET) images of a brain before (left panel) and during (right panel) gastric electrical stimulation (GES) at a 3-month follow-up visit. These images represent differences in centrally acting anti-emetic areas identified by PET scan in the thalamus and caudate lobe associated with GES therapy. Reprinted by permission from [46].
Although many studies have demonstrated that GES has significantly improved symptoms associated with gastroparesis [43,50], it has not been shown to significantly change gastric emptying rates. A recent large, multicenter, randomized, double-blind cross-over study by Ducrotte et al. of 172 patients (72 diabetic) with chronic (> 12 months) drug-refractory vomiting reported a significant reduction in vomiting frequency after GES therapy for four months in both nondiabetic and diabetic patients [51]. A gastric emptying test was performed at baseline in all patients and 79% had delayed gastric emptying. However, having delayed emptying did not predict the patients’ response to GES therapy. Consistent with previous studies [42,52,53,54,55], gastric emptying rates did not improve during GES treatment despite the therapeutic effectiveness of GES. The authors concluded that this large important trial showed effectiveness in reduction of refractory nausea and vomiting by GES therapy. This is consistent with the literature, that GES is viewed as working as an anti-emetic. Several factors predict the clinical outcomes of GES. Predictive factors that determine a favorable response to GES include the following: diabetic gastroparesis, quality of life impairment, nausea, and vomiting [56,57]. Predictive factors that determine a negative response to GES include the following: idiopathic gastroparesis, narcotic use, main symptom of abdominal pain, or having a previous history of gastric surgery [56,57].
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a chronic sensorimotor disorder of the upper gastrointestinal tract that shares several similarities and overlapping features with gastroparesis. For example, delayed gastric emptying has been observed in up to 40% of patients with FD [21]. Based on the Rome IV criteria, FD can be defined by symptoms of dyspepsia that have been present for at least six months in the presence of one or more of the following main symptoms after an underlying organic disorder has been excluded: early satiety, postprandially-driven fullness, and epigastric pain—which are sometimes referred to as “postprandial distress syndrome” [58]. Similar to gastroparesis, putative pathophysiological mechanisms in FD also involve both the CNS as well as peripheral disease processes. One important similarity between both disorders is that gastric distension is an important trigger in both; however, abnormal central regulation and heightened mechanical and chemical hypersensitivity appear to be clinical hallmarks in FD [59], whereas abnormal gastric emptying is a key diagnostic characteristic in gastroparesis [14]. Visceral hypersensitivity can be defined as enhanced perception of physiological signals from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract [21]. Studies using a gastric barostat have demonstrated that patients can be hypersensitive to balloon distension in the setting of normal stomach compliance [60,61]. The degree to which this sensitization occurs along central pathways that convey information from the stomach to the CNS is not well understood, and consequently, treatment options for FD are limited [60]. Hence, a better understanding of the CNS mechanisms underlying visceral hypersensitivity in FD could help provide insights for future therapeutic options.
Several functional brain imaging studies have demonstrated abnormal sensory processing in FD patients compared to healthy controls [62]. In a study by Lueven et al. involving 25 patients with FD and 11 controls, brain PET imaging performed during a resting state versus gastric distension demonstrated that patients with FD had a lower threshold for discomfort along with higher sensation scores [63]. This was characterized by activation of homeostatic-interoceptive brain regions (i.e., insula, somatosensory cortex) in patients with FD compared to controls at lower intragastric pressures. Another neuroimaging study by the same group with PET imaging performed during proximal stomach distension in hypersensitive FD patients resulted in activation of the following brain components at significantly lower gastric distension pressures when compared to healthy volunteers: lateral pain system and bilateral frontal inferior gyri—putatively involved in the regulation of hunger and satiety [64]. This data supports findings that FD patients sense gastric distension as painful or unpleasant at significantly lower gastric pressures compared to healthy subjects [65]. These neuroimaging studies support the existence of altered brain–gut interactions in FD and also provide evidence for some of the abnormal central mechanisms responsible for the heightened hypersensitivity noted in patients with FD. Buspirone is a selective serotonin (5-hydroxytratamine, 5-HT) partial agonist shown to relax the proximal stomach in healthy individuals [66]. A proposed mechanism of action through which gastric relaxation is mediated by buspirone is by the activation of central pathways as some studies have shown enhanced sensitivity of 5-HT1a receptors in the CNS in patients with FD [67]. Thus, it is important to understand the differences in altered CNS responses to gastric stimuli between FD and gastroparesis in order to develop more effective treatment strategies for both of these disorders in the future.
Several CNS-targeted medications have been shown to improve symptoms of nausea and vomiting by targeting neurochemical and visceral hypersensitivity pathways. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), for example, have been shown to improve nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain in patients with diabetic gastroparesis [68] and other functional gastrointestinal disorders [69,70,71,72]. The Gastroparesis Clinical Research Consortium (GpCRC) Nortriptyline study for patients with Idiopathic Gastroparesis (NORIG Trial) showed there was improvement in nausea and abdominal pain after three weeks of treatment at initial low doses (10 mg), but this effect was not sustained over time when dosing was increased at 15 weeks of treatment [73]. One possible mechanism by which TCAs may play a role in the amelioration of gastrointestinal symptoms is believed to be centrally-mediated [71]. For example, low doses of amitriptyline have been proposed to reduce both visceral hypersensitivity and sensory processes at both central and peripheral locations [74,75].
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) have been shown to be no better than placebo in treating gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with FD in a systematic review and meta-analysis of 13 randomized controlled trials (1241 patients) [76]. In the multicenter Functional Dyspepsia Treatment Trial, 292 patients with FD were randomly assigned to groups to receive either placebo, 50 mg of amitriptyline (TCA), or 10 mg of escitalopram (SSRI) for 10 weeks [77]. The primary end point was defined as adequate relief of functional dyspepsia symptoms for ≥5 weeks of the last 10 weeks. After 10 weeks, the rate of response was 53% with amitriptyline, 38% with escitalopram, and 40% with placebo. Thus, this study demonstrated that TCAs appear to provide a greater benefit in reducing gastrointestinal symptoms over SSRIs in some patients with FD. In line with the previously referenced systematic review and meta-analysis [76], SSRIs did not perform better than placebo. Mirtazapine, an antidepressant with serotonergic activity and central adrenergic properties, was shown to significantly improve nausea, vomiting, retching, and perceived loss of appetite in an open-label study of 30 patients with gastroparesis [78]. As previously mentioned, buspirone, an anxiolytic that acts as a 5-HT1a agonist, can improve receptive relaxation of the gastric fundus in healthy individuals with minimal side effects and no risk for physical dependency [66]. Buspirone has also been shown to improve meal-related symptom severities of postprandial fullness, nausea, and upper abdominal bloating in patients with functional dyspepsia [79].
Overall, the underlying mechanisms of nausea are very complex and involve central pathways (among other systems including autonomic, endocrine, psychological, gastric dysrhythmias) that are closely related to chronic neuropathic pain. As such, it is recommended that neuromodulators such as low-dose TCAs be trialed for the therapeutic relief of chronic nausea [80]. Dose titration should be utilized by beginning at 10 mg po every evening (qhs) and increasing by 10 mg every 1–2 weeks, up to a dose ranging from 50–100 mg po qhs, as can be tolerated by the patient; certainly, a number of gastroparesis patients have a clear “stress” and anxiety component. Nocturnal TCAs address the “brain–gut” relationship as well as improve sleep which leads to better patient tolerability and resilience. An important observation from the Functional Dyspepsia Treatment Trial [77] was that amitriptyline did not worsen gastric emptying in gastroparesis patients, and hence, this is not a liability. Prokinetics can also be simultaneously administered with TCAs in a documented gastroparesis setting.
5. Conclusion and Future Directions
The phenomena of N/V are complicated and mediated by both the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. While tremendous efforts have been made over the years to better understand the peripheral mechanisms responsible for the pathophysiology associated with gastroparesis, not enough research has been done to map out the CNS mechanisms and processes involved in N/V in patients with gastroparesis. As such, treatment strategies developed over the years for gastroparesis have yielded disappointing results, with most currently-available therapeutic options being largely ineffective. It is therefore important to elucidate and map out central nervous mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of the symptomatology involved in gastroparesis including visceral pain, nausea, and vomiting [21]. The ability to image the human brain with different neuroimaging modalities has greatly enhanced our understanding and appreciation of the brain–gut interactions involved in the complex behaviors of nausea and vomiting. Nevertheless, more neuroimaging studies are needed to further explore the gut-brain mechanisms involved in nausea and vomiting in patients with gastroparesis. It is important to open our minds and explore new hypothesis-driven analyses and further explore contributions of afferent input, as well as cortico-limbic pontine interactions in both healthy and gastroparetic patients [23]. A better understanding and delineation of the central mechanisms and neuroanatomical pathways involved in nausea and vomiting that delineate gastroparesis will be an important topic of future research and potential therapeutics.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Parkman, H.P.; Hasler, W.L.; Fisher, R.S. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: Diagnosis and treatment of gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1589–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, E.M.M.; Hasler, W.L.; Parkman, H.P. AGA Technical Review on Nausea and Vomiting. Gastroenterology 2001, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornby, P.J. Central neurocircuitry associated with emesis. Am. J. Med. 2001, 111 (Suppl. 8A), 106s–112s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsen, D.M.; Garcia, R.G.; Lee, J.; Lin, R.L.; Kim, J.; Thurler, A.H.; Castel, S.; Dimisko, L.; Rosen, B.R.; Hadjikhani, N.; et al. Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome is characterized by altered functional brain connectivity of the insular cortex: A cross-comparison with migraine and healthy adults. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namin, F.; Patel, J.; Lin, Z.; Foran, P.; Dusing, R.; Mccallum, R. Recognizing abnormal patterns on PET brain images in adults patients with the cyclic vomiting syndrome: 52. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 681. [Google Scholar]
- Oki, J.; Miyamoto, A.; Takahashi, S.; Itoh, J.; Sakata, Y.; Okuno, A. Cyclic vomiting and elevation of creatine kinase associated with bitemporal hypoperfusion and EEG abnormalities: A migraine equivalent? Brain Dev. 1998, 20, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Napadow, V.; Kuo, B.; Barbieri, R. A combined HRV-fMRI approach to assess cortical control of cardiovagal modulation by motion sickness. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; Volume 2011, pp. 2825–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toschi, N.; Kim, J.; Sclocco, R.; Duggento, A.; Barbieri, R.; Kuo, B.; Napadow, V. Motion sickness increases functional connectivity between visual motion and nausea-associated brain regions. Auton. Neurosci. 2017, 202, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Berman, S.; Suyenobu, B.; Labus, J.; Mandelkern, M.A.; Naliboff, B.D.; Chang, L. Differences in brain responses to visceral pain between patients with irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis. Pain 2005, 115, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.B.; Berkley, K.J.; Geary, N.; Hampson, E.; Herman, J.P.; Young, E. Sex Differences in the Brain: From Genes to Behavior; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Naliboff, B.D.; Berman, S.; Chang, L.; Derbyshire, S.W.G.; Suyenobu, B.; Vogt, B.A.; Mandelkern, M.; Mayer, E.A. Sex-related Differences in IBS Patients: Central Processing of Visceral Stimuli. Gastroenterology 2003, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, S.; Munakata, J.; Naliboff, B.D.; Chang, L.; Mandelkern, M.; Silverman, D.; Kovalik, E.; Mayer, E.A. Gender Differences in Regional Brain Response to Visceral Pressure in IBS Patients. Eur. J. Pain (Lond. Engl.) 2000, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, T.L.; Adams, K.A.; Boles, R.G.; Bousvaros, A.; Chong, S.K.; Fleisher, D.R.; Hasler, W.L.; Hyman, P.E.; Issenman, R.M.; Li, B.U.; et al. Cyclic vomiting syndrome in adults. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkman, H.P.; Hasler, W.L.; Fisher, R.S. American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the diagnosis and treatment of gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1592–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, P.; Gianrico, F. Diabetic Gastroparesis: What We Have Learned and Had to Unlearn in the Past 5 Years. Gut 2010, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshiree, B.; Potter, M.; Talley, N.J. Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Gastroparesis. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P. Gastroparesis. In Functional and GI Motility Disorders; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 33, pp. 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.R.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Gastroparesis-related hospitalizations in the United States: Trends, characteristics, and outcomes, 1995–2004. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, P.; Sandoval, H.; Calhoun, V.D.; Ramos-Duran, L.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Alvarado, B.; Bashashati, M.; Sarosiek, I.; McCallum, R.W. Central Nervous System Mechanisms of Nausea in Gastroparesis: An fMRI-Based Case-Control Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, J.; Wo, J.M. Current Treatment of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Gastroparesis: Antiemetics, Prokinetics, Tricyclics. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 19, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Camilleri, M.; Farrugia, G.; McCallum, R.W.; Bharucha, A.E.; Mayer, E.A.; Tack, J.F.; Spiller, R.; Horowitz, M.; Vinik, A.I.; et al. Gastroparesis and Functional Dyspepsia: Excerpts from the AGA/ANMS Meeting. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Aziz, Q.; Coen, S.; Kern, M.; Labus, J.S.; Lane, R.; Kuo, B.; Naliboff, B.; Tracey, I. Brain Imaging Approaches to the Study of Functional GI Disorders: A Rome Working Team Report. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagelada, J.-R.; Malagelada, C. Nausea and Vomiting. In Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease, 10th ed.; Feldman, M., Friedman, L.S., Brandt, L.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Chapter 15; pp. 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer, E.L.; Zhu, A.X.; Bounds, B.C.; Sahani, D.; McDonald, K.R.; Brachtel, E.F. Case 6-2005: A 58-Year-Old Man with Esophageal Cancer and Nausea, Vomiting, and Intractable Hiccups. New Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthurs, O.J.; Boniface, S. How Well Do We Understand the Neural Origins of the fMRI BOLD Signal? Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, N.K. What We Can Do and What We Cannot Do With fMRI. Nature 2008, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macapinlac, H.A. Positron Emission Tomography of the Brain. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2006, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Aboagye, E. Development of Radiotracers for Oncology—The Interface with Pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napadow, V.; Sheehan, J.D.; Kim, J.; Lacount, L.T.; Park, K.; Kaptchuk, T.J.; Rosen, B.R.; Kuo, B. The brain circuitry underlying the temporal evolution of nausea in humans. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, B.; Singh, P. Nausea and Vomiting Related to the Central Nervous System Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Balaban, D.H.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Tribble, C.G.; McCallum, R.W. Median arcuate ligament syndrome: A possible cause of idiopathic gastroparesis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Frøkjaer, J.B.; Andersen, L.W.; Brock, C.; Simrén, M.; Ljungberg, M.; Søfteland, E.; Dimcevski, G.; Yavarian, Y.; Gregersen, H.; Drewes, A.M. Altered Brain Microstructure Assessed by Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Patients With Diabetes and Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Diabetes Care 2013, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revicki, D.A.; Rentz, A.M.; Dubois, D.; Kahrilas, P.; Stanghellini, V.; Talley, N.J.; Tack, J. Development and validation of a patient-assessed gastroparesis symptom severity measure: The Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosiek, I.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Sandoval, H.; Sands, S.; Chen, J.; McCallum, R.W. Central and Peripheral Effects of Transcutaneous Acupuncture Treatment for Nausea in Patients with Diabetic Gastroparesis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Okada, G.; Yamashita, H.; Hori, T.; Yamawaki, S. Brain Activity During Expectancy of Emotional Stimuli: An fMRI Study. Neuroreport 2003, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; Lin, Z.; Forster, J.; Roeser, K.; Hou, Q.; Sarosiek, I. Gastric electrical stimulation improves outcomes of patients with gastroparesis for up to 10 years. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, T.; Lou, J.; Tabbaa, M.; Batista, O.; Malinowski, S.; Al-Juburi, A. Gastric electrical stimulation for gastroparesis improves nutritional parameters at short, intermediate, and long-term follow-up. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2003, 27, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; McElhinney, C.; Sarosiek, I.; Forster, J.; McCallum, R. Chronic gastric electrical stimulation for gastroparesis reduces the use of prokinetic and/or antiemetic medications and the need for hospitalizations. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Sarosiek, I.; Forster, J.; McCallum, R.W. Symptom responses, long-term outcomes and adverse events beyond 3 years of high-frequency gastric electrical stimulation for gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Forster, J.; Sarosiek, I.; McCallum, R.W. Treatment of gastroparesis with electrical stimulation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, T.; McCallum, R.; Hocking, M.; Koch, K.; Abrahamsson, H.; Leblanc, I.; Lindberg, G.; Konturek, J.; Nowak, T.; Quigley, E.M.; et al. Gastric electrical stimulation for medically refractory gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, J.; Sarosiek, I.; Delcore, R.; Lin, Z.; Raju, G.S.; McCallum, R.W. Gastric pacing is a new surgical treatment for gastroparesis. Am. J. Surg. 2001, 182, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.D.Z.; Foreman, R.D. Gastric Electrical Stimulation Modulates Neuronal Activity in Nucleus Tractus Solitarii in Rats. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2005, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.D.Z. Central Mechanisms of Gastric Electrical Stimulation Involving Neurons in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus in Rats. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Li, J.; Tang, K. The Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus: Development, Function, and Human Diseases. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 3458–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; Dusing, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Cocjin, J.; Forster, J.; Lin, Z. Mechanisms of high-frequency electrical stimulation of the stomach in gastroparetic patients. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2006, 1, 5400–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; Dusing, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Cocjin, J.; Forster, J.; Lin, Z. Mechanisms of symptomatic improvement after gastric electrical stimulation in gastroparetic patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, e150–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, Z.; Dusing, R.; McCallum, R.; McMillin, C.; Lin, Z.; Forster, J. Comparison of positron emission tomography (PET) imaged cerebral activity in gastroparetic patients before and during gastric electrical stimulation (GES). J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Abell, T.L.; Van Cutsem, E.; Abrahamsson, H.; Huizinga, J.D.; Konturek, J.W.; Galmiche, J.P.; VoelIer, G.; Filez, L.; Everts, B.; Waterfall, W.E.; et al. Gastric electrical stimulation in intractable symptomatic gastroparesis. Digestion 2002, 66, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrotte, P.; Coffin, B.; Bonaz, B.; Fontaine, S.; Bruley Des Varannes, S.; Zerbib, F.; Caiazzo, R.; Grimaud, J.C.; Mion, F.; Hadjadj, S.; et al. Gastric Electrical Stimulation Reduces Refractory Vomiting in a Randomized Crossover Trial. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; Snape, W.; Brody, F.; Wo, J.; Parkman, H.P.; Nowak, T. Gastric electrical stimulation with Enterra therapy improves symptoms from diabetic gastroparesis in a prospective study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Parkman, H.; Snape, W.; Brody, F.; Wo, J.; Nowak, T. Gastric electrical stimulation with Enterra therapy improves symptoms of idiopathic gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Hou, Q.; Sarosiek, I.; Forster, J.; McCallum, R. Association between changes in symptoms and gastric emptying in gastroparetic patients treated with gastric electrical stimulation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, F.; Vaziri, K.; Saddler, A.; Ali, A.; Drenon, E.; Hanna, B.; Akin, E.; Gonzalez, F.; Soffer, E. Gastric electrical stimulation for gastroparesis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 207, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranki, J.L.; Lytes, V.; Meilahn, J.E.; Harbison, S.; Friedenberg, F.K.; Fisher, R.S.; Parkman, H.P. Predictive factors for clinical improvement with Enterra gastric electric stimulation treatment for refractory gastroparesis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourcerol, G.; Chaput, U.; LeBlanc, I.; Gallas, S.; Michot, F.; Leroi, A.M.; Ducrotte, P. Gastric electrical stimulation in intractable nausea and vomiting: Assessment of predictive factors of favorable outcomes. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2009, 209, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.L.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Fischler, B.; Piessevaux, H.; Janssens, J. Symptoms associated with hypersensitivity to gastric distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Corsetti, M.; Janssens, J. Role of tension receptors in dyspeptic patients with hypersensitivity to gastric distention. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notivol, R.; Coffin, B.; Azpiroz, F.; Mearin, F.; Serra, J.; Malagelada, J.-R. Gastric tone determines the sensitivity of the stomach to distention. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oudenhove, L.; Vandenberghe, J.; Dupont, P.; Geeraerts, B.; Vos, R.; Dirix, S.; Bormans, G.; Vanderghinste, D.; Van Laere, K.; Demyttenaere, K. Abnormal regional brain activity during rest and (anticipated) gastric distension in functional dyspepsia and the role of anxiety: A H215O-PET study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, W.; Mier, D. Advantages in functional imaging of the brain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, J.; Dupont, P.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Bormans, G.; Demyttenaere, K.; Fischler, B.; Geeraerts, B.; Janssens, J.; Tack, J. Regional cerebral blood flow during gastric balloon distention in functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, J.; Bisschops, R.; Sarnelli, G. Pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oudenhove, L.; Kindt, S.; Vos, R.; Coulie, B.; Tack, J. Influence of buspirone on gastric sensorimotor function in man. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.; Mahmud, N.; Rathore, O.; Thakore, J.; Scott, L.; Carr, E.; Naesdal, J.; O’Morain, C.; Keeling, P. A double-blind placebo-controlled study of buspirone-stimulated prolactin release in non-ulcer dyspepsia—are central serotoninergic responses enhanced? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawhney, M.S.; Prakash, C.; Lustman, P.J.; Clouse, R.E. Tricyclic antidepressants for chronic vomiting in diabetic patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clouse, R.E. Antidepressants for functional gastrointestinal syndromes. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1994, 39, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loldrup, D.; Langemark, M.; Hansen, H.J.; Olesen, J.; Bech, P. Clomipramine and mianserin in chronic idiopathic pain syndrome. Psychopharmacology 1989, 99, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, H.; Fass, R.; Kodner, A.; Yan-Go, F.; Fullerton, S.; Mayer, E. Effect of amitryptiline on symptoms, sleep, and visceral perception in patients with functional dyspepsia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Lustman, P.J.; Freedland, K.E.; Clouse, R.E. Tricyclic antidepressants for functional nausea and vomiting (clinical outcome in 37 patients). Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkman, H.P.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abell, T.L.; McCallum, R.W.; Sarosiek, I.; Nguyen, L.; Snape, W.J.; Koch, K.L.; Hasler, W.L.; Farrugia, G.; et al. Effect of nortriptyline on symptoms of idiopathic gastroparesis: The NORIG randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Jiang, S.-M.; Jia, L.; You, L.-Q.; Huang, Y.-X.; Gong, Y.-M.; Wang, G.-Q. Effect of amitriptyline on gastrointestinal function and brain-gut peptides: A double-blind trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, K. A brief review of the pharmacology of amitriptyline and clinical outcomes in treating fibromyalgia. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Luthra, P.; Tack, J.; Boeckxstaens, G.E.; Moayyedi, P.; Talley, N.J. Efficacy of psychotropic drugs in functional dyspepsia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2017, 66, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J.; Locke, G.R.; Saito, Y.A.; Almazar, A.E.; Bouras, E.P.; Howden, C.W.; Lacy, B.E.; DiBaise, J.K.; Prather, C.M.; Abraham, B.P. Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: A multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamood, M.; Roberts, A.; Kataria, R.; Parkman, H.P.; Schey, R. Mirtazapine for symptom control in refractory gastroparesis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tack, J.; Janssen, P.; Masaoka, T.; Farré, R.; Van Oudenhove, L. Efficacy of Buspirone, a Fundus-Relaxing Drug, in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Yoon, S.S.; Kuo, B. Nausea: A review of pathophysiology and therapeutics. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Naliboff, B.D.; Craig, A.D.B. Neuroimaging of the Brain-Gut Axis: From Basic Understanding to Treatment of Functional GI Disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).