Abstract
Two paintings by the Neapolitan Renaissance painter Colantonio were studied with two non-invasive techniques to enrich the technical–scientific documentation. Infrared reflectography (IR) and x-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyses were performed on Saint Jerome in the studio and Saint Francis delivering the Rule, paintings preserved in the Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte. The IR scanning was performed to look beyond the visible layers of the paint for the preparatory drawings and pentimenti, or changes made during the painting process. The XRF technique was applied in many points to determine the elemental composition and enable the identification of pigments and materials used in paint and in the preparatory layers. Elemental XRF mapping was also carried out on a region of particular interest. Results provide an initial overview and hypothesis of color palette and techniques used by the artist.
1. Introduction
During the twentieth century, critical studies [1,2,3,4,5,6] claimed that the paintings Saint Jerome in the studio and Saint Francis delivering the Rule, today in the Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte (Naples, Italy), were made by Colantonio, a Neapolitan Renaissance painter. According to the literary study of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, it is likely that the painter was trained between the end of the fourth and the beginning of the fifth decade of the fifteenth century, when Renato d’Angiò reigned in Naples. There is general consensus among critics in considering that Saint Jerome in the studio is the first part of the ‘Cona degli Ordini’, which was created probably following a Flemish model of Saint Jerome in the studio of the Lomellini lost triptych by Van Eyck. This is based on the testimony of the humanist Bartolomeo Facio in the Neapolitan collection of the sovereign Alfonso of Aragona in 1456. Furthermore, in Saint Jerome in the studio attributed to Colantonio, critics have identified elements of the Flandro-Provençal style of the painter Barthelemy d’Eyck, who was probably in Naples at the court of King Renato d’Angiò. The influence of the Provençal master is evident in the plastic construction of the figures and in the shelves full of books that punctually refer to those painted in the triptych of the Annunciation of Aix. Compared to Saint Jerome in the studio, Saint Francis delivering the Rule shows more of the influence of Hispano-Flemish culture, particularly the Valencian culture of Jacomart, official painter of Alfonso of Aragona since 1442. The painting has long been attributed to him.
In the present study, the two paintings were analyzed using the IR and XRF techniques with the aim of studying Colantonio’s painting technique.
Looking beyond the visible layers of a painting adds to the technical and scientific documentation of a work and sheds light on the artist who produced it. Nowadays, there are many scientific techniques [7,8,9] that provide insight into the nature of pigments and constituent materials or the identification of the preparatory drawing, pentimenti, or changes [10]. An in-depth study not only reveals the history of the object investigated, but possible criteria on conservation and restoration choices can emerge as well [11]. When sampling is impracticable, it is necessary to apply non-invasive techniques such as infrared reflectography (IR) and x-ray fluorescence (XRF) [12].
IR technique is a successful non-invasive method based on infrared light penetrating deeper than visible light [13]. It provides images useful for analyzing the underdrawings of paintings, if made with carbon-based materials, and the pentimenti or changes made during the painting process [14], including painting’s restoration. They become visible through the contrast that is produced between the materials used (pigments and/or inks) and the preparation of the support (the wooden boards in the case of Colantonio’s paintings). Infrared reflectography detects the electromagnetic radiation reflected from an object with a wavelength greater than 750 nm. Unlike visible light (wavelength is between 400 nm and 750 nm), it is able to detect preparative layers of a painting because the materials from which the pigments are made have optical properties; therefore, they are more transparent to IR [15]. The more reflective the preparatory layer of the painting (the so-called ‘primer’), the greater the reflection of the infrared component of the radiation incident on the painting towards the camera lens [16,17].
XRF technique is a widely used method for noninvasive and nondestructive preliminary screening [18,19]. It allows the investigation in point mode or by scanning the paint surface (MA-XRF), to identify chemical elements (not compounds) by acquiring X-ray fluorescence spectra [20,21]. Many measurements can be easily made because the measurement times are relatively short (a few tens of seconds); many instruments are portable, which means they avoid moving the artwork away from where it is exhibited. The technique is limited by skill in identifying light elements that are characteristic of organic materials such as lakes; therefore, the integration with other non-invasive techniques can be useful [22]. Quantitative analysis is also difficult because the measured intensities of the fluorescence lines related to an element depend on several factors such as the accompanying elements (matrix), the shape and thickness of the analyzed sample, and measurement conditions [23] but semi-quantitative results can give important information. XRF data can be subjected to various statistical processing methods such as principal component analysis (PCA) and the k-means method, which allow the identification of groupings using elemental concentrations, intensity of the fluorescence lines and full spectra [24,25].
Common and divergent elements in underdrawings of the two panels emerge from the IR analysis, and hypotheses on color palette and materials can be made through XRF analysis. It is noteworthy that the following contribution uses only some investigation techniques and fails to provide detailed information on the construction technique and the material conditions of the two paintings. Therefore, this is the first study to use IR and XRF to investigate the two paintings. Further insights will come from other ongoing and planned analyses.
2. Materials and Methods
In Summonte’s letter to Michiel (1524), Colantonio is presented as the greatest Neapolitan painter of the 15th century. The humanist reports that in the Aragonese age, the painting in vogue was the Flemish one and since Giotto’s arrival in Naples, Colantonio was the only important Neapolitan artist in the 15th century whose style followed ‘the work of Flanders’ [1].
2.1. Materials
Niccolò Antonio, known as Colantonio, was the main Neapolitan painter of the 15th century and protagonist of the southern Renaissance, capable of making a synthesis between the Flemish model and its Mediterranean variants [26]. This is shown by panel paintings Saint Jerome in the studio (tempera on wood, 125 × 151 cm2) and Saint Francis delivering the Rule (tempera on wood, 176 × 150 cm2), dated from the middle of the century during the reign of Alfonso (1442–1458), when Naples was one of the most important political and cultural centers in Mediterranean Europe, at the center of a system of relations with the other states of the confederation of the Crown of Aragona [5,27].
The two paintings, actually in the Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte, were part of a single and complex altarpiece together with the paintings Blessed Franciscans, originally on the altar of Saint Jerome in Saint Lawrence’s church in Naples as the central part of the ‘Cona degli Ordini’(Figure 1), reaching a height of about 3 m.

Figure 1.
Reconstruction of the ‘Cona degli Ordini’ (central part).
Saint Jerome in the studio, painted on a rectangular panel, represents Saint Jerome’s intent on removing a thorn from a lion’s paw, inside a library with volumes, papers, and writing instruments accurately depicted and well-defined by the light; in the foreground scene, there is a cardinal’s hat, the galero, on a small table to the left; on the right, there is a mouse in the shadows gnawing at the papers on the ground.
Traditional iconography holds Jerome in a cardinal’s robe and with the Vulgate book in his hand, or in the desert with a worn robe and with the galero, resting on the ground as a sign of renunciation of power. In this painting, however, the saint anachronistically wears the habit of the Franciscans (it is no coincidence that the painting was destined for one of the main churches of Franciscan friars in southern Italy).
In Saint Francis delivering the Rule, made on an arched panel with an engraved gold background, the saint is full-length on a foreshortened floor, with nuns and friars kneeling at his sides.
2.2. Methods
The spectroscopic portable equipment employed for the technical analysis of the two paintings is part of the ReD laboratory, devoted to Research and Didactics and established at the Department of Humanities and Cultural Heritage of the Università degli Studi della Campania ‘Luigi Vanvitelli’.
The analyses were conducted in the Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte where the paintings are exhibited.
Looking at the paintings, some very peculiar visible details emerge. Therefore, the available techniques, i.e., IR and XRF, were applied. With a close observation, in the painting Saint Jerome in the studio, there are traces of a curtain that was later hidden, or rather eliminated, as IR analysis confirmed, in the observation of the drawing below. Similarly, in the painting Saint Francis delivering the Rule, parts with restorations, pentimenti, and retouches were identified with the naked eye, confirmed by IR and XRF analysis. This is the case, for example, of the habit of Saint Francis with retouches (restorations) and pentimenti by the artist in the rendering of the side belt that descends along the habit. Further investigations and studies will be necessary for an in-depth analysis of Colantonio’s execution technique and the central decades of the 15th century (period of transition from tempera to oil painting). They will provide results of transparency and lightness resulting from the use of oil as a medium for the application of veiled color.
2.2.1. Infrared Reflectography (IR)
Infrared radiation occupies a large part of the electromagnetic spectrum with an approximate wavelength range between 750–400,000 nm. It is distinguished in NIR (near infrared) from about 750 to 3000 nm, in MIR (medium infrared) approximately from 3000 to 30,000 nm, and in FIR (far infrared) from 30,000 nm to microwaves. Some pictorial layers, normally opaque when observed with visible radiation (i.e., between 400 and 750 nm), can become transparent with the infrared and allow the underlying layers to be read. Infrared radiation at 1800 nm is ideal for infrared scanning studies of pictorial artwork. In fact, most pictorial drafts acquire transparency around this wavelength [17].
The IR investigation of Colantonio’s paintings was performed using Apollo, an infrared camera by Opus Instruments [28]. It uses state-of-the-art technology equipped with a sensor capable of capturing thousands of details that are stitched together through powerful imaging software (operation wavelength 900–1700 nm; >65,000 grey levels; sensor 128 × 128 px InGaAs area sensor; higher resolution up to 26 MP images). The results are high-quality and high-resolution infrared reflectograms.
Inside the museum, the operating procedure used a uniform lighting. The IR camera was placed in front of the painting analyzed and two 1000 W LED lamps were placed on the sides, about 30 degrees from the painting (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
(a) Apollo camera position while acquiring IR images; (b) Apollo IR camera.
Areas of the paintings were scanned by detecting IR response within 900–1700 nm wavelength range. The resulting images are portions of the picture of about 60 × 60 cm2. An appropriate graphic software (Ptgui, Huguin, and Adobe Photoshop) was used to improve the gray levels, the contrasts and, above all, to obtain the stitching of the entire painting in a single IR image, in digital format and high resolution.
2.2.2. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) and Scanning Macro-X-ray Fluorescence (MA-XRF)
Measurements were performed using Elio, a compact portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer produced by XGLab (Bruker). It weighs about 2 kg and is mounted on a tripod with the ability of movement on a motorized XY stage. The system consists of a 50 kV maximum Rh X-ray tube with a 0.2 mA maximum working current and a 1 mm collimator. A silicon drift detector (25 mm2 active area and energy resolution <140 eV at 5.9 keV) operates with a measuring spot of 1.2 mm wide. The working distance between the painting surface and the detector is 14 mm.
The compositional analysis was carried out on the surface layer in point mode by setting the tube with a voltage of 50 kV and a current of 80 μA. An acquisition time of 60 s was chosen for each point (in total, twenty-three points on the painting Saint Jerome in the studio and fifty points on Saint Francis delivering the Rule, Figure 3). Elio’s software allowed us to see each chosen point through an integrated microscopic camera. As a result of the measurement, the software’s qualitative analysis package was used to identify the chemical elements in the spectrum and calculate the deconvolution of the characteristic fluorescence peaks to obtain net area counts.
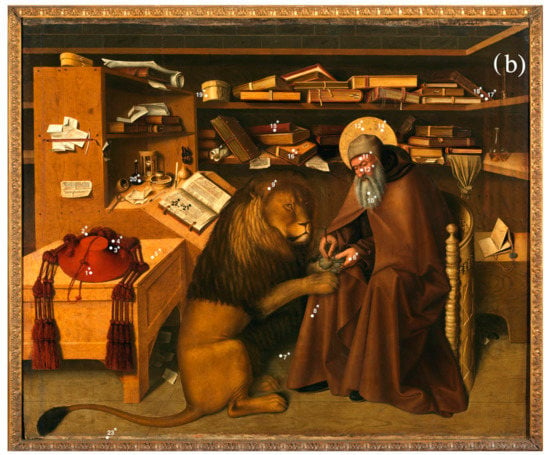


Figure 3.
Localization of measurement points on (a) Saint Francis delivering the Rule and on (b) Saint Jerome in the studio. In (a) the measurement points are numbered from 1 to 50 while in (b) they are numbered from 1* to 23*.
Principal component analysis (PCA) and the k-means method are two multivariate statistical analysis tools that were used to compare XRF data and obtain additional information. PCA uses a set of observations (in our case measurement points) that are characterized by many variables (in our case net area counts of chemical elements or unprocessed full spectrum in the energy range from 0 to 47 keV with 4096 acquisition channels) and processes a transformation of the original variables into a new set of uncorrelated variables, called principal components (PCs). The aim is to visualize possible clusters among the observations in the score plot so that their characteristics of similarity or difference emerge [24]. The loading plot is a useful graph to understand the contribution of each original variable in defining the PCs, while the biplot is the view of score plot and loading plot together. The k-means procedure groups the observations placed in the PCA score plot into k clusters. After the number k is chosen, the method calculates centroids, that is, points to which sum of the distances between objects in the same cluster is minimized [29,30].
MA-XRF was performed on an area of Saint Jerome in the studio. The instrument voltage and current measurement conditions were the same as for the point acquisition: a map of 50 rows × 50 columns with a step size of 1 × 1 mm2 was scanned for a total measurement time of 3250 s. The sum spectrum of the 2500-pixel matrix was stored in HDF5 format and processed with the PyMca software [31]. This program generated a map for each characteristic line that was considered for the fit of the spectrum. The maps were represented with linear intensity and grayscale color to better show the elemental distribution.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. IR Analysis
Saint Jerome in the studio is characterized by opaque tones, which is why the preparatory drawing is hardly detected by IR reflectography. Different shapes that are transparent in IR refer to the elements that Colantonio painted over the dark colors, sometimes reducing the overall dimensions, as in the case of the volumes on the shelves corrected several times (Figure 4).
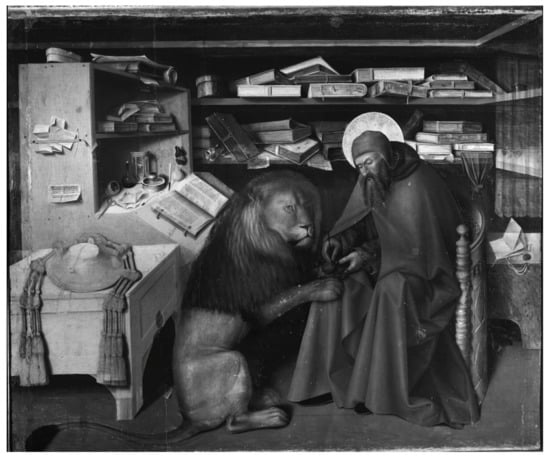

Figure 4.
IR image of Saint Jerome in the studio scanned by Apollo and stitched.
The main change affects the spatiality of the scene. In the right margin of the IR image, a curtain placed on the back wall is evident. The desk, on which the galero is placed, is effectively created in perspective, but a probable difficulty in rendering the foreshortening has led to the elimination of the circular opening on the front, visible in the IR image compared to the visible image (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
(a) IR and (b) visible images of the desk in Saint Jerome in the studio.
In the painting, attempts at perspective setting are not supported by the construction of an underlying geometric plant of the Albertian type with a single vanishing point (about the Italian Renaissance perspective [32,33]). Instead, an empirical perception of perspective seems to prevail, bringing the painting closer to a possible Flemish model (the panel of the lost Lomellini triptych?). However, bear in mind that the two major panels of the ‘Cona degli Ordini’ have different shapes. Although they have the same width, Saint Jerome in the studio has a rectangular shape, while Saint Francis delivering the Rule has a vertical development with cambering. This may have also contributed to the different perspective solution used in the two panels. This could help to place the painting in the first phase of the painter’s production, that is, before the polyptych of Episodes from the life of Saint Vincent Ferrer, placed in the phase Colantonio’s artistic maturity, where the painter successfully dominates the perspective solutions of spaces.
In Saint Francis delivering the Rule, the executive technique is refined and there are many drawing traces, including the pentimenti (Figure 6). Compared to Saint Jerome in the studio, in the painting, the vanishing point of the perspective lines is unique; nonetheless, the perfect symmetry of the composition makes it evident that the difficulty in the perspective construction is far less than that found in Saint Jerome in the studio. The dating of the two paintings, generally considered to be coeval, has sometimes been questioned [34,35]; investigations do not currently offer any useful indication to propose a different dating between the two paintings.
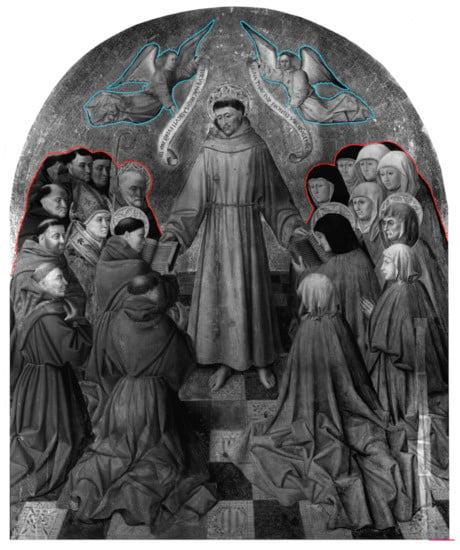

Figure 6.
IR image of Saint Francis delivering the Rule scanned by Apollo camera and stitched. The image shows the repetition of the guide modules.
For the definition of the figures, there are no traces of transfer from a drawing transfer and the symmetry of the various parts of the painting with repeated and mirrored modules clearly refer to the use of the patrons. The figures of the angels are marked by a thick black contour line that partly follows the underlying path made using a patron. Sometimes, the underdrawings of the profile are covered by paint showing slight modifications (Figure 7b, the angel’s left hand) or overlaps (Figure 7b, the angel’s hair) [36]. The figures of the angels are almost entirely underdrawn by brush. The hatching is used to build the shading, according to the Flemish custom; as some pentimenti present in the work, it is drawn by a charcoal (Figure 7a,b) [37]. It is possible that the painter used dry brushstrokes with charcoal for the general composition and refined the details with a brush and glazes for the shading.

Figure 7.
Visible image (a) and IR image (b) of the angel on the right in Saint Francis delivering the Rule. In (b) the lower profile band is covered by the pictorial layers in correspondence with the modification of the left hand and of the hair.
3.2. XRF and MA-XRF Analysis
XRF analysis revealed that all measurement points of the two paintings are characterized by calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), lead (Pb), iron (Fe), potassium (K) and copper (Cu) [36,37]. Calcium and strontium can be related to the presence of a preparatory layer composed by gypsum (CaSO4·2(H2O)) or chalk (CaCO3) with celestine (SrSO4) [36,37,38,39]; small amounts of iron are typical of this preparation for panel paintings [40]. The presence of sulfur (S) might suggest the gypsum; unfortunately, however, the K-fluorescence line of S overlaps with the M fluorescence line of Pb; therefore, sulfur is difficult to detect with XRF technique [41]. The distinction between chalk and gypsum is possible in damaged points of a painting when lead is absent [20] or using other techniques such as mid-FTIR or XRD [42], not used in this study. Potassium could be due to the presence of lakes [43] or colourless glass powder, in addition to paints [20,44], particularly for red colors (as the cardinal’s hat in Saint Jerome in the studio). Glass was used in red pigments in 15th-century paintings to achieve fast drying or special color effects; in our case, however, its use cannot be confirmed because of the absence of manganese [45]. Copper could be related to a copper-based pigment used for making dark shades [40]. One candidate is a copper resinate pigment used in the 15th and 16th centuries for its drying properties [46,47]. However, even though the XRF technique is unable to distinguish, other copper-based pigments, such as malachite, could be possible because they were used in the same historical period [46].
Cinnabar is used in many red points in the paintings: it is determined by the detection of high intensities of the Lα and Lβ peaks of mercury (Hg). Low contents of this element are present where pigments are obtained by mixing cinnabar with other pigments. In particular for skin tones, the use of minium [(2PbO·PbO2)] or lead white [(PbCO3)2·Pb(OH)2] and tin lead yellow [Pb2SnO4 or PbSnO3 or Pb(SnSi)O3] is possible [37]. Only Sn can be useful in the determination of the yellow pigment. Brown areas are characterized by high Fe intensities that represent the use of iron pigments; in some cases, they are also hypothesized by the traces of manganese [39].
The data obtained from the spectral analysis of the paintings are evident from the multivariate analyses (PCA and k-means) performed using the counts of the selected elements and the spectra as variables (for counts, see Supplementary Materials, Tables S1 and S2). These are explained in detail below.
For Saint Francis delivering the Rule, the main characteristic line of the elements Ca, K, Fe, Cu, Hg, Pb, Au, Sr and Sn was used in the PCA (see Supplementary Materials, Table S1). Both the Mα and Lα lines of lead were included to highlight the contribution of this element in the preparatory and pictorial layer, respectively. Through Pb-M radiation, which penetrates less deeply than Pb-L radiation, lead-based pigments can be detected in mixtures with other colorations more on the surface of the painting. In the PCA analysis. the set of observations consists of all fifty measurement points chosen according to the different chromatic samples on the painting. The first two principal components were chosen to highlight possible clustering of observations with a 53% cumulative variability. The biplot of PCA (Figure 8a) shows the distribution of the points (in red) according to the coordinates calculated by the method and the vectors identified by the variables (in blue).
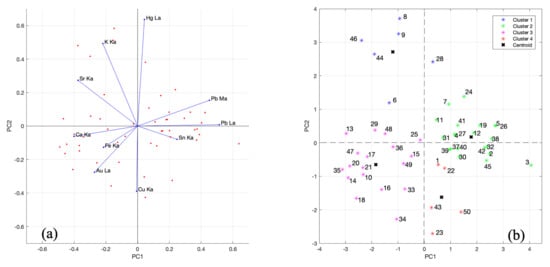
Figure 8.
(a) Biplot of PCA analysis for selected elements and (b) k-means plot of two principal components PC1 (35.5%) and PC2 (17.8%) of PCA.
The best results of the k-means cluster method were obtained by setting up a four-cluster search for the observations because the mean silhouette value is 0.4234. A two-dimensional graph was again chosen based on PC1 and PC2 to best compare the results obtained from the two methods.
In the plot of the k-means method (Figure 8b), the blue group (cluster 1) consists of the XRF measurement characterized by a dark red coloration with a higher Hg and K content. Point 6 belongs to this group for high K counts but differs from the others in the Sr and Fe intensities: iron could be related to the use of a red ochre, a thesis supported by the absence of mercury. In the red group (cluster 4), there are points characterized by the colors black, yellow-black and light blue. They are in the same cluster because they have a high copper content; hence, they are characterized by a copper-based pigment (counts between 97,740 and 428,496 for Cu-Kα): points 23, 34 have a black coloration, 1 and 22 yellow–black, while 43 and 50 are light blue.
Points 1 and 22 are distant from the others because their black coloration is affected by the presence of tin (the pigment giallolino, composed of lead stannate, is probably present); therefore, they are closer to the Sn variable. Point 34 is another black point of the painting but is not included in red group because it has traces of gold (it is placed within the golden halo of Saint Clare).
The green group (cluster 2) is composed of points strongly characterized by the presence of lead. Among them, points 2 and 3 are influenced by the Sn variable, suggesting that the pigment is giallolino and points 30, 31, 32 (on the bishop’s hat) have cinnabar to which giallolino has been added. Point 45 appears to be characterized only by lead white due to its visibly white coloration. The other points of the cluster are characterized by cinnabar, to which a lead pigment has been added (a possible sign that minium or white lead has been used to obtain light and dark shades as skin tones).
In the pink group (cluster 3), there are points characterized by the presence of Ca, Fe and Au. The variables connected to these three elements are correlated with each other because the preparatory layer (Ca and Fe in traces) was often covered with bolus (containing Fe) before the application of the gold leaf (Au) [48]. Points 10, 14, 20, 35 are included in the plane formed by Ca-Fe and are related to the golden background of the painting. The red color of point 17 is not made with cinnabar because mercury is absent. It is in the cluster 3 because the area where it is located is probably made with an enamel composition undetectable through XRF investigation; for this reason, only the nature of the preparatory layers and surrounding gilding emerge. Point 15 located on the brown habit of San Bernardino is very rich in Fe; therefore, it is very close to the Fe vector; here, traces of Mn could be related to iron and suggest the use of an earth pigment [20]. Points 16, 18 and 33 are gold and placed on the haloes (hence, closer to the Au variable vector): they differ from other gold points that are in the same group but characterize the background of the table. This separation, due to their larger amounts of copper, suggests a greater application of drying pigment on the haloes [47] compared to the golden background or a lower purity of gold leaf for the haloes.
The fifty spectra obtained from measurements on Saint Francis delivering the Rule were used to implement the PCA analysis. In this case, the loading plot was calculated to understand which fluorescence peak contributed the most on each principal component. The best clustering among the spectra was obtained by considering the first two principal components and the fourth one.
The loading plot (Figure 9) shows that the Cu-Kα, Pb-Lα, Au-Lα and Ca-Kα peaks predominate on PC1 (56%), PC2 (40%) and PC4 (2%), respectively.
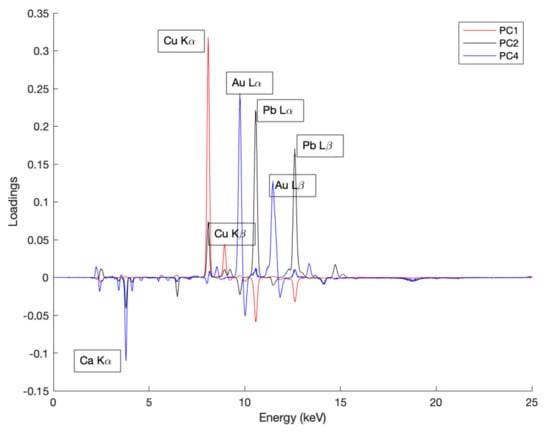
Figure 9.
Loading plot of PC1, PC2 and PC4 obtained from spectra.
The high intensity of the Cu-Kα fluorescence peak at points 23, 34, 43, and 50 (circled in red, Figure 10) indicates that a copper-based pigment is present (same result shown by the k-means method, Figure 8b). The contribution of the variables Au-Lα and Ca-Kα along PC4 direction (Figure 9), is evident in the score plot (Figure 10). Here, the points (circled by blue) belong to the haloes of the saints, while the green circle contains points taken on the gold background of the painting (except point 13, which has less gold since the gold leaf is partly missing). The two clusters show a division between the gilding of the haloes and the background or at least a correlation between the gildings made for the same purpose.
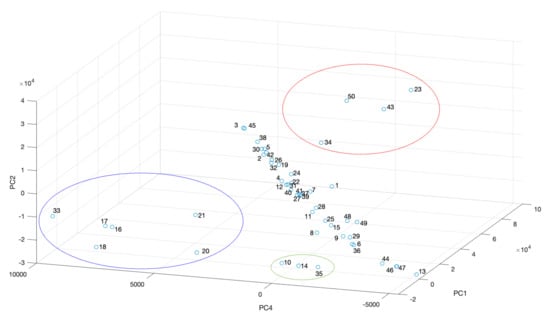
Figure 10.
Score plot of PC1, PC4 and PC2 obtained from spectra. Points (circled in red) have high intensity of the Cu-Kα fluorescence peak, points (circled in blue) belong to the haloes of the saints and points (circled in green) belong to the gold background of the painting.
The other points in the graph (Figure 10) are distributed along a straight line according to the Pb-Lα counts: those with higher coordinates along PC2 direction are the same as those found in the green group in Figure 8b, while points with a lower coordinate along PC2 direction could have Pb as a characteristic element of the preparatory layer and not a pigment.
The choice of two types of observation for the multivariate analysis provided useful information and highlighted different characteristics at the measurement points. The intensities (counts) of single fluorescence lines helped to identify the pigments used by the artist, while the full spectra provided information on the techniques of execution, which helps to support hypotheses made since the individual intensities.
XRF data of Saint Jerome in the studio were also analyzed with PCA. Counts of the main fluorescence lines of the elements Ca, Sr, Cu, K, Hg, Sn, Fe, Pb were used (see Supplementary Materials, Table S2). The principal components considered for the analysis are PC1 and PC3, whose explained variability is 30% and 26%.
The biplot (Figure 11a) shows a close correlation between Ca and Sr because their vectors have the same direction and length. Furthermore, in the score plot (Figure 11b), it is visible that the coordinate in abscissa of point 23* (where there is only the preparatory layer) is strongly influenced by these two variables. It corroborates the thesis that calcium and strontium constitute the material of the first preparatory layer. In the same quadrant, the plan formed by the variables K and Hg contains five points of the painting whose coloring is red (in the score plot, the name labels of the points are shown in different colors according to the color in the visible, except 22* and 23*, which are white). This highlights the fact that the red colorations are in cinnabar and red lake. In detail, points 1*, 2*, 3* and 4* belong to the galero and are characterized by the presence of Sn (among them, the highest counts of Sn-Kα are in point 2*).
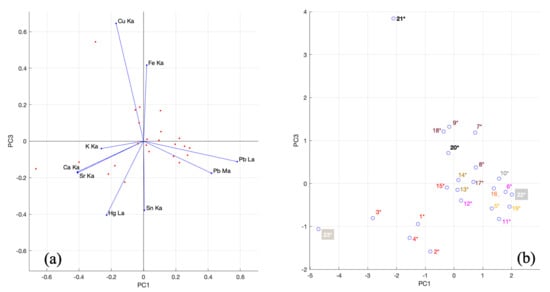
Figure 11.
(a) Biplot and (b) score plot PC1-PC3 of twenty-three points of Saint Jerome in the studio. In (b), name labels of the points are shown in different colors according to the color in the visible, except 22* and 23* which are white.
Point 15* is less saturated red than the others. Its higher counts for the Pb-Mα line emphasize that maybe a lead-based pigment was used to make the coloring less bright. The points included in the plane formed by the variables Pb-Mα and Pb-Lα and near these vectors have a high lead content. As can be seen from the score plot, the points have different coloration (white, grey, pink, orange, yellow and gold): the presence of the Sn variable in the same quadrant of the Pb lines corroborates the fact that these colorations are characterized by giallolino. Points 11* and 12* are of a different pink coloration from point 6* and are, therefore, not close to it (they have a higher Sn-Kα counts). Gold colorations on the halo of Saint Jerome (point 13*, 14*) are also characterized by the presence of tin. Points 7*, 9*, 18*, 20* form a subgroup because of their higher Fe-Kα counts, while points 8* and 17* have a positive ordinate because of the Fe-Kα variable (brown coloration) but are distant because they are influenced by the amounts of Pb. The score plot shows high Fe counts for point 20* because its coloration is black. Point 21* is strongly influenced by the presence of copper; in fact, the Cu Kα counts are the 481446, while the average value of Cu Kα counts in the other points of the painting is 1200.
Elements attributable to pigments of modern origin have been revealed in some points, signaling the possible presence of repainting and restoration.
In Saint Francis of Assisi delivering the Rule, a selected point on the face of Saint Clare (point 37) appears to have been retouched (according to visual and IR analysis); XRF analysis shows high counts of K lines of titanium (Ti). In fact, point 38 (located on the saint’s face) presents 367 counts of Ti-Kα; in contrast, point 37 has 5407 counts of the Ti-Kα and 741 count sat Kβ line. This difference suggests the presence of a titanium white-containing pigment, a material historically observed after the period of the work’s realization. Titanium is present in all investigated points of the painting, but its counts are low and related only to the Kα line: it is possible that titanium is an impurity of earths and ochres diffused in the mixture or associated with an iron-based pigment (bolus) used in the preparatory layer of the gilding areas on the background of the panel [40,48]. Chromium (Cr) was detected in points 47, 48 and 49 located on a tile feature: in our case this element indicates the use of anachronistic materials because Cr was introduced into pigments in the 19th century [20]. Point 47 also shows traces of the element cadmium (Cd), a good tracer for restoration treatments [49]. Point 39 on Saint Francis’ dress could also have been retouched because of Ti-Kα’s anomalous counts, a possibility that also emerges in the infrared-acquired image [37].
Some peculiarities emerge from the point XRF analysis of Saint Jerome in the studio. For example, in points 8* and 9* (located on the lion’s mane and on the saint’s habit), there is zinc (Zn), which is generally present in modern pigments [50]; however, IR analysis does not trace a restoration to these two points. The similarity between the two brown colorations in the visible and the high Fe counts suggest that the same pigment was used. Analysis of more measurement points on the painting could be helpful to associate Zn with the predominant presence of Fe (thus, the use of a zinc-rich ochre) or with another element (thus, the presence of another pigment or material). The coloration of the ampulla (point 20*) and the capital letter of the book (point 21*) appear visibly black: their high copper content suggests the use of a copper-based pigment to achieve such a dark shade. The first point presents traces of Zn that may be related to copper (if a green copper pigment was used [40]) and high counts of Fe that could be related to the pigment used for the yellow–brown coloration of the furniture placed on the back of the ampulla. Point 21* is characterized by much higher counts of Cu Kα than the point 20* and by the element barium (Ba). The counts of Ba, especially of its L lines, could indicate the presence of this element in the surface layers and that it therefore belongs to the composition of a pigment (a lake? Han blue?), rather than indicating an impurity of a copper mineral [40].
In Saint Jerome in the studio, Sn was identified in the two points that belong to the saint’s halo (points 13* and 14*). This element could be related to the use of a lake, such as yellow lake reseda (weld) that exhibited a large Sn signal, which could be indicative that a tin chloride mordant is present [39]. The Pb-Mα counts are lower than the same counts for points 5* and 19* (which have a yellow color, identified as giallolino due to the presence of Pb and Sn) to assume the use of giallolino; the application of tin leaf in combination with gold leaf should be excluded since gilding is not applied to a wall surface or a fresco [51]. A curtain visibly appears on the right margin of the painting, which the painter later overpainted by making other objects. The investigation on the chemical composition of the curtain was carried out by choosing two measuring points (17* and 18*) placed, respectively, where the curtain is present and where it is not. Both points are characterized by Hg; therefore, cinnabar was used to paint the cover of the book but the higher Hg La counts for point 17* suggest that the curtain was also made using cinnabar. Point 17* is also characterized by the presence in traces of Sn.
An overview of main elements detected by XRF analysis and color palette in the two paintings is reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Overview of elements detected by XRF analysis and color palette in the two paintings. It summarizes what emerged from the XRF data analysis and multivariate analysis (PCA, k-means).
The mapping acquisition mode was performed on an area of Saint Jerome in the studio that contains the shaded area of the cardinal’s hat placed on the desk (white box, Figure 12). At the end of the scan, the Elio instrument provides a visualization of the fluorescence spectrum of analyzed points and the stitched image (Figure 12).

Figure 12.
Photo of the cardinal’s hat in Saint Jerome in the studio. The white box shows the area scanned by MA-XRF analysis.
MA-XRF maps were processed through the PyMca software. They allow the visualization of the distribution of chemical elements emerged from the sum spectrum (specifically, the intensity distribution of the selected fluorescence characteristic lines for each element).
The MA-XRF map of Hg-Lα (Figure 13) shows that the whole area is characterized by mercury with varying amounts (cinnabar, HgS).
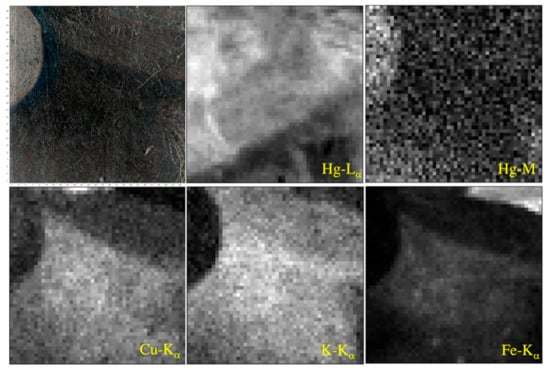
Figure 13.
Stitched image of the investigated area with MA-XRF. It is processed using ELIO software, which creates a montage with the pixel images captured by the instrument’s internal camera at each point on the map [52]. Elemental distribution maps of Hg-Lα, Hg-M, K-Kα, Cu-Kα and Fe-Kα in linear intensity scale obtained by PyMca software.
In general, the M fluorescence line allows us to determine the presence of an element placed more on the surface: in our case, the Hg-M map underlines that the highest counts of this line are present in the upper left part, which presents a brighter and more intense red color than all the rest of the investigated area (see inside the white box, Figure 12)
In the investigated area of the hat, there is a dark red part due to a shadow created. Here, the copper content is particularly evident (Figure 13); therefore, a copper pigment was probably added to obtain a darker shade of red. Along with copper, potassium also appears to be present in this same part, suggesting the use of a lake [36,43]. Comparison of the maps of Hg-Lα, Hg-M, K-Kα, Cu-Kα shows that in the same area where Cu and K are present, the Hg-M line counts are lower than its Hg-L line because the cinnabar is covered by other pigments.
An interesting result is also obtained from the analysis of the distribution of the Fe-Kα fluorescence line: the corresponding map shows a high iron content in the upper right part of the investigated area. From the visible, this area is actually external to the hat and its yellow–brown coloration is related to the presence of the furniture placed near the table on which the hat is placed. This indication could suggest the use of an earth or ochre as a pigment. In smaller amounts, iron is also present in the central area (the dark red one): comparison with the Cu-Kα map suggests that here, too, the iron belongs to a pigment used to create the hat shade.
4. Conclusions
IR reflectography and XRF technique were used to analyze two panel paintings of the artist Colantonio, an important Renaissance painter of south Italy, who painted in Naples, the cultural center in Mediterranean Europe, in the central decades of the 15th century. He worked at the service of Aragonese court and the main Neapolitan churches in the period of transition from tempera to oil painting, with higher results of transparency and lightness deriving from the use of oil as a medium for applying glazed color. Two non-invasive techniques have provided important results. The IR analysis brought to light the underdrawings (including the pentimenti). Therefore, it was ascertained that the underdrawings are constant in Colantonio’s pictures (this data emerges not only from the analysis of the two panels of the ‘Cona degli Ordini’ but also in the other two paintings attributed to him and equally preserved in the Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte). The underdrawings were made almost entirely with a brush, as evidenced by the liquid line in infrared, while some parts were made with a charcoal. Reflectography also helped to detect distinct perspective settings and to describe the painter’s early production. In Saint Francis delivering the Rule, no traces from a drawing transfer have emerged, but repeating modules clearly referring to the use of the patrons and, in some cases, the lines of the drawing made almost entirely with a brush while the hatching, made with a charcoal, built the shading according to the Flemish technique.
The XRF technique was able to suggest the composition of the preparatory layer and some pigments used. The preparatory layer is composed of Ca and Sr, but XRF analysis could not confirm whether it is gypsum or chalk. Some pigments of the color palette have been hypothesized due to the chemical elements revealed but further investigations, with other techniques, could clarify their identity. Chemical elements, known in the literature to be non-original pigments, but introduced in later periods, were identified. The gilded parts are indeed composed of gold: in Saint Francis delivering the Rule, PCA analysis (Figure 10) shows two clusters for the golden points of the haloes and the background (a cluster for the haloes and one containing the background points are evident), while in Saint Jerome in the studio, the halo is characterized by Sn. The MA-XRF application was useful to determine the elemental composition of the dark part of the galero. As the hat, other dark red areas of the paintings were made of cinnabar, a copper-based pigment and a lake. Regarding lakes, in some cases, their presence was hypothesized and stands as an opportunity to carry out investigations capable of revealing them.
The campaign to investigate these paintings by Colantonio is still ongoing, but the study carried out helps to better understand his technique and working method.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/heritage6020095/s1, Table S1: Counts of the main fluorescence characteristic line detected in the measurement points of Saint Francis delivering the Rule; Table S2: Counts of the main fluorescence characteristic line detected in the measurement points of Saint Jerome in the studio.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C., A.Z. and A.C.; methodology and software, M.C., P.I., J.B. and E.S.; validation, M.C., A.Z. and C.S.; resources, A.C. and A.R.; data curation, P.I., E.S. and J.B.; writing—original draft preparation, E.S. and P.I.; writing—review and editing, M.C., A.Z., A.C., A.R., J.B. and C.S.; supervision, A.C., A.Z. and C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author, subject to authorization by the Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte and Università degli Studi della Campania.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the director of the Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte in Naples, Sylvain Bellenger and museum staff for making this work possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nicolini, F.; Summonte, P.; Michiel, M. L’arte napoletana del Rinascimento. In Napoli Nobilissima; Arte tipografica: Napoli, Italy, 1923; Volume 3, pp. 42–59, 68–79, 98–105, 121–146, 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- De Rinaldis, A. Pinacoteca del Museo Nazionale di Napoli Catalogo di Aldo De Rinaldis; Nuova Edition; Richter: Napoli, Italy, 1928; pp. 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Bologna, F. Il Maestro di San Giovanni da Capestrano. In Proporzioni; Sansoni: Firenze, Italy, 1950; Volume 3, pp. 86–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bologna, F. Napoli e le Rotte Mediterranee Della Pittura, da Alfonso il Magnanimo a Ferdinando il Cattolico; Società Napoletana di Storia Patria: Napoli, Italy, 1977; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- De Castris, P. Museo e Gallerie Nazionali di Capodimonte. Dipinti dal XIII al XVI secolo. In Le Collezioni Borboniche e Post-unitarie; Electa: Napoli, Italy, 1999; pp. 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Bologna, F. Il Polittico di Colantonio a San Lorenzo; Electa: Napoli, Italy, 2001; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sottili, L.; Giuntini, L.; Mazzinghi, A.; Massi, M.; Carraresi, L.; Castelli, L.; Czelusniak, C.; Giambi, F.; Mandò, P.A.; Manetti, M.; et al. The Role of PIXE and XRF in Heritage Science: The INFN-CHNet LABEC Experience. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.; Cotte, M.; Vanmeert, F.; de Nolf, W.; Janssens, K. X-ray Diffraction Mapping for Cultural Heritage Science: A Review of Experimental Configurations and Applications. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrieli, F.; Dooley, K.A.; Facini, M.; Delaney, J.K. Near-UV to mid-IR reflectance imaging spectroscopy of paintings on the macroscale. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocchieri, J.; de Viguerie, L.; Sabbarese, C.; Boyer, M. Combination of noninvasive imaging techniques to characterize pigments in Buddhist thangka paintings. X-Ray Spectrom. 2021, 50, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, F.; Burnstock, A.; Van den Berg, K.J.; Miliani, C.; Brunetti, B.G.; Sgamellotti, A. A non-invasive XRF study supported by multivariate statistical analysis and reflectance FTIR to assess the composition of modern painting materials. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Bottura-Scardina, S.; Bottaini, C.; Valadas, S.; Candeias, A.; Bilou, F. The Power of Combining MA-XRF, Infrared Reflectography and Digital Microscopy to Unveil the Production of the 16th Century Illuminated Charter of Évora: What May Be Hidden under a Painted Surface? Heritage 2022, 5, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, C.M. Invited Article: High resolution digital camera for infrared reflectography. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 071301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffara, C.; Fontana, R. Multispectral infrared reflectography to differentiate features in paintings. Microsc. Microanal. 2011, 17, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, P.A.M. Manuale Pratico di Documentazione e Diagnostica per Immagine per i BB. CC.; Il Prato: Saonara, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bellaria, M.; Bertani, D. La riflettografia infrarossa. In I Trattati di Tecniche Artistiche Medievali; CUSL: Milano, Italy, 2006; pp. 115–137. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali, M.; De Ruggieri, M.B.; Falcucci, C. Diagnostica Artistica. Tracce Materiali per la Storia Dell’arte e per la Conservazione; Palombi Editori: Roma, Italy, 2007; pp. 120–135. [Google Scholar]
- Alfeld, M.; De Viguerie, L. Recent developments in spectroscopic imaging techniques for historical paintings-a review. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2017, 136, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musílek, L.; Čechák, T.; Trojek, T. X-ray fluorescence in investigations of cultural relics and archaeological finds. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, H.C.; Caliri, C.; Pappalardo, L.; Catalano, R.; Orlando, A.; Rizzo, F.; Romano, F.P. Real-time MA-XRF imaging spectroscopy of the Virgin with the Child painted by Antonello de Saliba in 1497. Microchem. J. 2018, 140, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojek, T.; Trojkova, D. Several approaches to the investigation of paintings with the use of portable X-ray fluorescence analysis. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 116, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, B.; Grifoni, E.; Hidalgo, M.; Legnaioli, S.; Lorenzetti, G.; Pagnotta, S.; Poggialini, F.; Ripoll-Seguer, L.; Palleschi, V. Multi-technique characterization of madder lakes: A comparison between non-and micro-destructive methods. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 33, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitko, R.; Zawisza, B. Quantification in X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. In X-Ray Spectroscopy; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocchieri, J.; Scialla, E.; Manzone, A.; Graziano, G.O.; Sabbarese, C. Gouache gilding on lead and wood objects studied by multivariate and graph analyses applied to XRF spectra. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2022, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcaida, I.; Maguregui, M.; Fdez-Ortiz de Vallejuelo, S.; Morillas, H.; Prieto-Taboada, N.; Veneranda, M.; Castro, K.; Madariaga, J.M. In situ X-ray fluorescence-based method to differentiate among red ochre pigments and yellow ochre pigments thermally transformed to red pigments of wall paintings from Pompeii. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castris, P.L. La riscoperta di Colantonio. Confronto 2019, 2, 42–65. [Google Scholar]
- Museo e Real Bosco di Capodimonte. Available online: https://capodimonte.cultura.gov.it (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Opus Instruments. Available online: www.opusinstruments.com (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Brocchieri, J.; Scialla, E.; Manzone, A.; Graziano, G.O.; D’Onofrio, A.; Sabbarese, C. An analytical characterization of different gilding techniques on artworks from the Royal Palace (Caserta, Italy). J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 57, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likas, A.; Vlassis, N.; Verbeek, J.J. The global k-means clustering algorithm. Pattern Recognit. 2003, 36, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, V.A.; Papillon, E.; Cotte, M.; Walter, P.; Susini, J. A multiplatform code for the analysis of energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectra. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinisgalli, R. Il nuovo De pictura di Leon Battista Alberti; Kappa: Roma, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sinisgalli, R. Piero della Francesca. In De Prospectiva Pingendi; Silvana Editoriale: Cinisello Balsamo, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aceto, F. Spazio ecclesiale e pale di “primitivi” in San Lorenzo Maggiore a Napoli: Dal “San Ludovico” di Simone Martini al “San Girolamo” di Colantonio (II). In Prospettiva; Centro Di: Firenze, Italy, 2012; pp. 2–61. [Google Scholar]
- Bremenkamp, A. Ars Nova Translata: Altniederländische Malerei in Neapel und der Krone Aragon; Hirmer Verlag GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2021; pp. 157–225. [Google Scholar]
- Scialla, E.; Improda, P.; Brocchieri, J.; Cardinali, M.; Cerasuolo, A.; Rullo, A.; Zezza, A.; Sabbarese, C. Study of Colantonio’s paintings in the Capodimonte Museum using IR and XRF analyses. In Proceedings of the AIAr (Italian Association of Archaeometry) Thematic Conference entitled “Sustainability in Cultural Heritage”, Padua, Italy, 29 June–1 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinali, M.; Improda, P.; Zezza, A.; Cerasuolo, A.; Rullo, A.; Brocchieri, J.; Sabbarese, C.; Scialla, E. La tecnica pittorica di Colantonio attraverso l’analisi del corpus di opere conservate a Capodimonte: Primi risultati e alcune riflessioni. Polygraphia 2022. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Bellucci, R.; Bonanni, P.; Brunetti, B.G.; Calusi, S.; Castelli, C.; Ciatti, M.; Doherty, B.; Fontana, R.; Frosinini, C.; Giuntini, L.; et al. Il restauro del Ritratto Trivulzio di Antonello da Messina. OPD Restauro 2010, 22, 15–54. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, R.; Coluzzi, N.; Cosentino, A. Free XRFSpectroscopy Database Of Pigments Checker. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Seccaroni, C.; Moioli, P.; Fluorescenza, X. Prontuario per L’analisi XRF Portatile Applicata A Superfici Policrome; Nardini: Firenze, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Križnar, A.; Muñoz, M.D.V.; Paz, F.D.L.; Respaldiza, M.A.; Vega, M. Non-destructive XRF analysis of pigments in a 15th century panel painting 2008. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on NDT of Art 2008, Jerusalem, Israel, 25–30 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Snickt, G.; Miliani, C.; Janssens, K.; Brunetti, B.G.; Romani, A.; Rosi, F.; Wittermann, R. Material analyses of ‘Christ with singing and music-making Angels’, a late 15th-C panel painting attributed to Hans Memling and assistants: Part, I. non-invasive in situ investigations. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 2216–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.O. Marika Spring, Catherine Higgitt. The technology of red lake pigment manufacture: Study of the dyestuff substrate. Natl. Gallery Tech. Bull. 2005, 26, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, B.G.; Seccaroni, C.; Sgamellotti, A. The Painting Technique of Pietro Vannucci Called Il Perugino: Proceedings of the LabS Tech Workshop; Nardini: Firenze, Italy, 2004; pp. 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lutzenberger, K.; Stege, H.; Tilenschi, C. A note on glass and silica in oil paintings from the 15th to the 17th century. J. Cult. Herit. 2010, 11, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, K.A.; Conover, D.M.; Glinsman, L.D.; Delaney, J.K. Complementary standoff chemical imaging to map and identify artist materials in an early Italian Renaissance panel painting. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 13995–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A. Artists’ Pigments: A Handbook of Their History and Characteristics; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 1993; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Brocchieri, J.; Scialla, E.; Manzone, A.; Graziano, G.O.; D’Onofrio, A.; Sabbarese, C. The gilding technique on lead objects of the Royal Palace in Caserta (Italy) studied using XRF analysis. Mediterr. Archeol. Archeometry 2022, 22, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Alfeld, M.; Wahabzada, M.; Bauckhage, C.; Kersting, K.; Wellenreuther, G.; Falkenberg, G. Non-negative factor analysis supporting the interpretation of elemental distribution images acquired by XRF. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Borgia, I.; Brunetti, B.G.; Miliani, C.; Sgamellotti, A.; Seccaroni, C.; Passalacqua, P. The Perugino’s palette: Integration of an extended in situ XRF study by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinwandmalerei, T.U. Mapping gold leaf in Gentile da Fabriano’s paintings: A case study. Burlingt. Mag. 2019, 161. [Google Scholar]
- A Non-Invasive Portable XRF Small Spot Mapping System for Cultural Heritage Studies and its Application. Available online: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5de134ef5511bf790e2a9442/t/5e0df9ded2e3413f647bb408/1577974244339/precise+positioning+and+elio+mapping.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).