A 65-year-old woman presented to the Pulmonary Clinic for evaluation after Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (PET/CT), which was obtained for assessment of a 12 mm right middle lobe solitary pulmonary nodule. She denied shortness of breath, fever, arm swelling, or breast masses. The PET/CT showed intensely FluoroDeoxyGlucose (FDG) avid right axillary lymph nodes (The largest of which measured 30 mm) and the right deltoid muscle (Figure 1 and Figure 2). There was no FDG uptake in the right lung or breast. The enlarged right axillary lymph nodes were not visualized on Computed Tomography imaging obtained two weeks prior to PET/CT. A mammogram performed ten days prior also showed benign findings. The patient reported receiving the first dose of a COVID-19 vaccine one day prior to PET/CT. Right axillary ultrasonography was performed four weeks later and showed complete resolution of lymphadenopathy. The PET/CT findings were thought to be secondary to the COVID-19 vaccination [1,2].
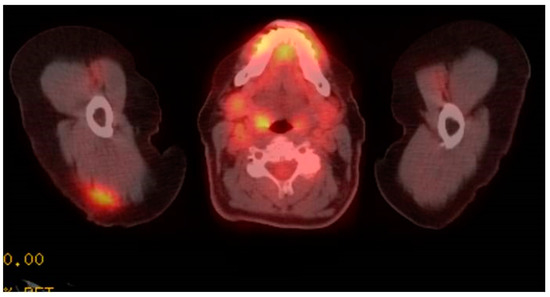
Figure 1.
PET/CT imaging shows increased FDG avidity in right deltoid muscle.
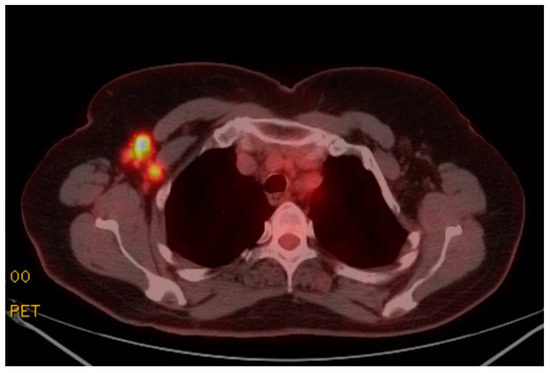
Figure 2.
PET/CT imaging shows increased FDG avidity in right axillary lymph nodes.
Funding
This manuscript received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The project also does not involve individuals who would receive a test article (drug or device) as participants and therefore the FDA regulations do not apply. Thus, this project does not require review or approval by the Wayne State University Institutional Review Board. IRB Administration Office no. 2022 125.
Informed Consent Statement
This project does not constitute human participant research according to the definition codified in the Common Rule at 45 CFR 46 and FDA regulations. This means that IRB review and oversight is not required for this project.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- McIntosh, L.J.; Bankier, A.A.; Vijayaraghavan, G.R.; Licho, R.; Rosen, M.P. COVID-19 Vaccination-Related Uptake on FDG PET/CT: An Emerging Dilemma and Suggestions for Management. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Wagner, T.; Nathan, M.; Szyszko, T. COVID-19 vaccine-related lymph node activation—Patterns of uptake on PET-CT. BJR Case Rep. 2021, 7, 20210040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).