Abstract
Wearable biosensors play a critical role in healthcare monitoring. However, the reliance of biosensors on batteries has serious drawbacks. Although the human body’s energy can be converted into electricity with energy harvesters, the hybridisation of multiple energy harvesters is a prominent way of increasing power output. In this work, a hybrid piezoelectric and reverse electrowetting (REWOD) energy harvester is proposed. Its main working principle is based on the presence of an electrical double layer in the REWOD component and coupling with a piezoelectric nanogenerator via an electret. The proposed energy harvester design was tested numerically and in a series of experiments.
1. Introduction
Modern healthcare widely employs implantable and wearable biosensors to continuously monitor patients’ physiological data. Biosensors rely heavily on the use of batteries in their design, which has several drawbacks that can be addressed by using energy harvesters. There are multiple potential sources of energy in the human body that can be effectively exploited by various transducers [1]. As a single targeted energy type might be insufficient or suboptimal in terms of the power output and availability of energy, several energy generators are coupled in one hybrid energy harvester that can target multiple energy sources or scavenge energy from one energy source but with multiple generators. Biomechanical energy produced by the human cardiovascular system represents a reliable source of pulsations produced by the radial artery in particular, which have been successfully used in numerous energy harvesting applications [2,3].
In the present work, a hybrid piezoelectric nanogenerator (PENG) and electrostatic energy harvester that scavenges energy from radial artery pressure variation are presented. Reverse electrowetting on dielectric (REWOD) is implemented through a bubble of conductive liquid which is squeezed in between two electrodes, one of which is coated with a dielectric material [4]. By modulating the distance between the electrodes, the electrical double layer (EDL) formed at the fluid–electrode surface changes, modifying the capacitance of the system and thus allowing it to collect the accumulated charge [5]. The working principle of the designed energy harvester is explained in Figure 1. The electret on the top of the shared electrode biases the REWOD component and therefore prevents ions and counterions in the EDL from changing places [6]. The EDL, which forms on top of the electret, increases the overall capacitance of the system and the maximum charge generation. When pressure is released and the harvester moves back to its initial state, the process repeats itself with electrons moving in the opposite direction.
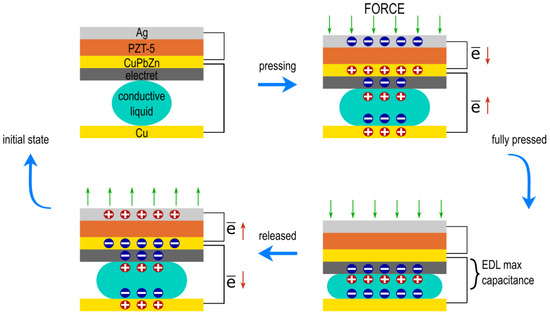
Figure 1.
The hybrid harvester working principle.
2. Materials and Methods
In this project, the hybrid harvester consists of a commercially available piezoelectric disc and a customised printed circuit board (PCB) for the REWOD component. The piezoelectric disk harnesses PZT-5 ceramics that are deposited on top of a brass diaphragm (CuPbZn). The top part of the piezoelectric material is coated with silver (Ag). The REWOD component consists of a shared brass electrode coated with an electret and a counter electrode (Cu). NaCl was used as a conductive liquid.
3. Discussion
The concept of the hybrid piezoelectric/REWOD energy harvester was explored computationally through simulations with the Multiphysics software COMSOL, where finite element analysis was employed to better understand the physical behaviour in solid and liquid phases of the REWOD component. In addition, an experimental setup was designed and constructed. The piezoelectric component was experimentally assessed across the range of practically available frequencies (1–2.5 Hz). The effects of material and geometrical parameters were investigated (Figure 2).
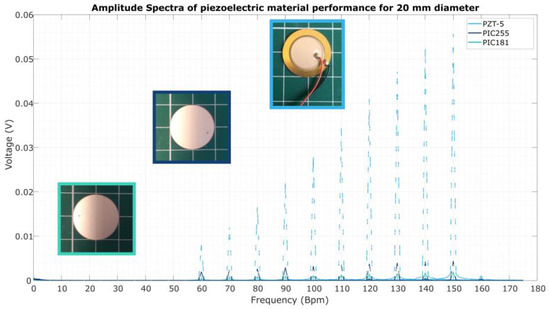
Figure 2.
Empirical data on the influence of piezoelectric material on harvester output.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, I.S. and S.D.P.; methodology, I.S., S.D.P. and A.T.; formal analysis, I.S.; investigation, I.S., S.D.P. and A.T.; resources, S.D.P.; data curation, I.S. and S.D.P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.S. and A.T.; writing—review and editing, I.S., S.D.P. and A.T.; visualisation, I.S., S.D.P. and A.T.; supervision S.D.P. and A.T.; project administration, S.D.P.; funding acquisition, S.D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sobianin, I.; Psoma, S.D.; Tourlidakis, A. Recent Advances in Energy Harvesting from the Human Body for Biomedical Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, B.H.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Simchi, A. Self-Powered Wearable Piezoelectric Sensors Based on Polymer Nanofiber–Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticle Composites for Arterial Pulse Monitoring. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 8742–8752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, R.; Ma, C.; Tang, Z.; Bao, N.; Wu, W.; Fan, F.; Wu, W. Solution-synthesized chiral piezoelectric selenium nanowires for wearable self-powered human-integrated monitoring. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.R.; Tasneem, N.T.; Reid, R.C.; Mahbub, I. Electrode and electrolyte configurations for low frequency motion energy harvesting based on reverse electrowetting. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, D.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, P.; Abeyrathne, C.D.; Hossain, M.S.; Skafidas, E. Environmentally friendly power generator based on moving liquid dielectric and double layer effect. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 26708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Halvorsena, E.; Dong, T. Power generation from conductive droplet sliding on electret film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 213905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).