Abstract
Ozone is one of the most important pollutant gases. The excellent sensitivity and low limit of detection of gas sensors based on Semiconducting Metal Oxides (SMOXs) make them ideal candidates to accurately monitor outdoor air quality. We present a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture that is trained on the resistance readout of a multi-pixel SMOX gas sensor array operated in temperature modulation. The trained model outperforms a ridge regressor in the quantification of ozone concentrations in real outdoor air.
1. Introduction
Tropospheric ozone (O3) is a reactive trace gas that is tightly linked to other natural and anthropogenic pollutants that act as ozone precursors [1]. To monitor air pollution on a global scale and maintain guidelines, small, cheap, and reliable sensor solutions are needed. Thanks to their low cost, excellent sensitivity, and low limit of detection, sensors based on Semiconducting Metal Oxides (SMOXs) are among the most commonly used in a plethora of applications, such as automotive, medical, safety, and environmental contexts [2]. To quantify analyte gases in a complex matrix, gas sensor arrays have been turned to, combining multiple, ideally orthogonal, sensing materials or sensor types [3]. Additionally, temperature modulation and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been shown to be promising approaches for various analytical tasks [4]. In this work, we demonstrate the superior performance of a temperature-modulated SMOX sensor array in combination with CNNs in the prediction of ozone in real outdoor air.
2. Materials and Methods
An SGP30 (Sensirion AG, Stäfa, Switzerland) sensor array was operated outside of our laboratory on the Morgenstelle Campus in Tübingen, Germany. The operating temperature was cycled continuously, increasing from room temperature to 375 °C and decreasing again, with a dip of the temperature in the middle [4]. For calibration and testing, the ozone concentration, as published by the German Umweltbundesamt (UBA), from the closest air-quality monitoring station (Tübingen Derendingen—DEBW107) was used [5]. The approach is similar to the one described by Mueller et al. for the field calibration of sensor units in Zurich [6]. The complete data set covers two months, and the hourly mean concentration was interpolated using cubic splines to yield concentrations corresponding to the measurement time of the sensor array.
3. Results and Discussion
The predicted ozone concentrations of the test set are plotted against the real ones for the best-performing CNN and ridge regression model in Figure 1.
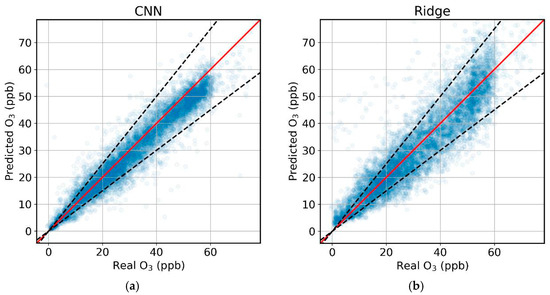
Figure 1.
Predicted vs. real concentrations of ozone for (a) the CNN model and (b) the ridge regression.
The CNN model outperforms the ridge regression with mean relative errors in the test set of 16.1% and 26.9%, respectively. There are significantly fewer outliers for the CNN prediction, and the trend line is closely followed, especially for concentrations above 30 ppm.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.B. and A.K.; data analysis, A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.; writing—review and editing, N.B.; supervision, U.W. and N.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fuhrer, J.; Martin, M.V.; Mills, G.; Heald, C.L.; Harmens, H.; Hayes, F.; Sharps, K.; Bender, J.; Ashmore, M.R. Current and future ozone risks to global terrestrial biodiversity and ecosystem processes. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 8785–8799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izawa, K.; Ulmer, H.; Staerz, A.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Application of SMOX-based sensors. In Gas Sensors Based on Conducting Metal Oxides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 217–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, J.R.; Penrose, W.R. Understanding chemical sensors and chemical sensor arrays (Electronic Noses): Past, Present, and Future. Sens. Update 2002, 10, 189–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobald, A.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N. Regression Model for the Prediction of Pollutant Gas Concentrations with Temperature Modulated Gas Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Aveiro, Portugal, 29 May–1 June 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokumentation|Umweltbundesamt. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/daten/luft/luftdaten/doc (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Mueller, M.; Meyer, J.; Hueglin, C. Design of an ozone and nitrogen dioxide sensor unit and its long-term operation within a sensor network in the city of Zurich. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 3783–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).