Enzyme has been unique properties due to superior catalytic activity, low toxicity, high substrate specificity. However, their efficient use at industrial application is limited due to some disadvantages such as low stability, difficulty in recovery and reusability, loss of catalytic activity after administration into the reaction. In order to handle these disadvantages, several immobilization approaches have been advanced. Recently, hybrid materials, combining with the advantages of organic and inorganic components have been widely used for enzyme immobilization. Herein, we prepared and characterized a hybrid nanoflowers (hNFs) containing xanthine oxidase (XO) (as organic component) and copper (II) ions (as inorganic component) and were analyzed (Figure 1 and Figure 2). These hybrid nanostructures can be applied on cancer cells in the future.

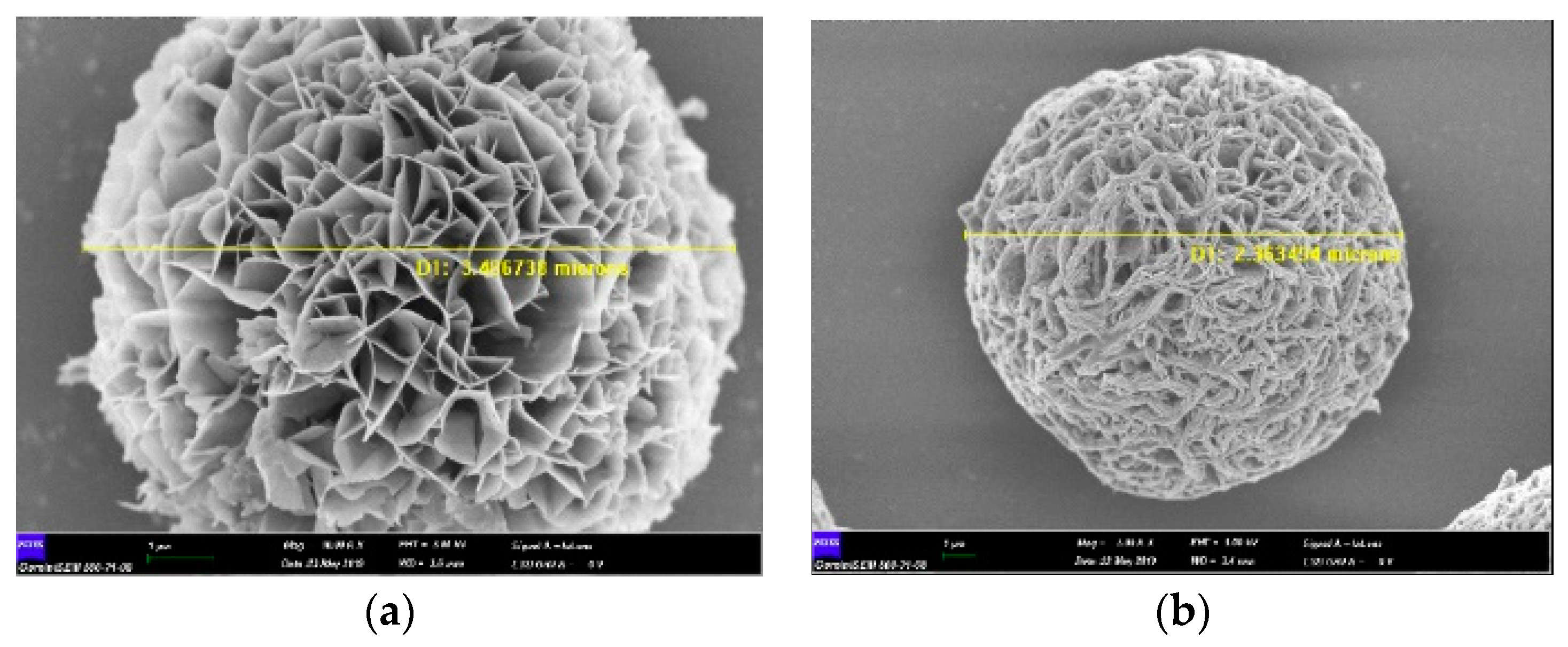
Figure 1.
SEM images of xo-Cu2+ hNFs synthesized at different incubation temperatures (a) +4 °C, (b) Room temperature.
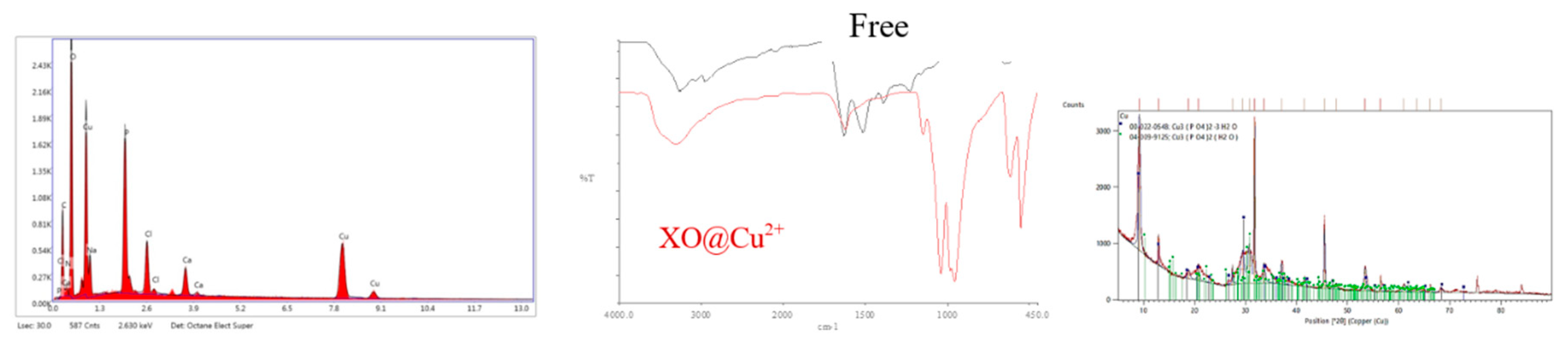
Figure 2.
EDX, FTIR and XRD analysis of xo-Cu2+ hNFs.
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).