Abstract
In order to break the bottleneck of the integer-order transfer function in vehicle ISD (inerter-spring-damper) suspension design, a positive real synthesis design method of vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension based on the fractional-order biquadratic transfer function is proposed. The emergence of the fractional-order components disrupts the equivalence relationship between the passivity of components and the positive realness of integer-order transfer functions in traditional networks. In this paper, the positive real condition of the fractional-order biquadratic transfer function is given. Then, a quarter dynamic model of the vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension is established, and the parameters of the fractional-order biquadratic transfer function and vehicle suspension are obtained by an NSGA-II multi-objective genetic algorithm. Moreover, the structure of the external circuit and the parameters of the electrical components are obtained by the fractional-order passive network synthesis theory. The simulation results show that under the condition of random road input and vehicle speed of 20 m/s, the root-mean-square (RMS) value of the vehicle body acceleration and the dynamic tire load of the fractional-order ISD suspension are reduced by 7.98% and 18.75% compared with the traditional passive suspension, while under the same condition, the integer-order ISD suspension can only reduce by 5.34% and 16.07%, respectively. The results show that employing a fractional-order biquadratic electrical network in the vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension enhances vibration isolation performance compared with the suspension using an integer-order biquadratic electrical network.
1. Introduction
The vehicle suspension system is an essential component intended to support the weight of the vehicle body while mitigating the effects of uneven road surfaces. It plays a vital role in minimizing vehicle vibrations. Suspension performance has a major impact on vehicle driving safety, operating stability, and riding comfort. The evolution of suspension systems has progressed from traditional passive configurations, consisting of springs and dampers, to semi-active [1,2,3] and active suspensions [4,5,6]. Nonetheless, both semi-active and active suspension systems necessitate precise state and parameter estimation, often employing filter algorithms [7,8]. This complexity increases the challenges associated with their design and introduces drawbacks such as high energy consumption and elevated costs. By comparison, passive suspension still plays an irreplaceable role because of its simple and reliable structure. Traditional passive suspension systems face the challenge of structural solidification, limiting their ability to meet the increasingly demanding performance requirements of vehicle suspension, and the proposal of “inerter” [9] makes the suspension composed of “inerter-spring-damper” attract attention in the realm of engineering.
The application of inerter in fields such as aerospace engineering [10], civil engineering [11], and railway engineering [12] has proved the vibration isolation performance improvement and the application value of the device. Based on the previous research, Professor Smith conducted a further study on vehicle suspensions and found that the application of an inerter can effectively reduce body acceleration and dynamic tire load [13]. Nie [14] realized the passive realization of skyhook damping suspension system by means of the method of reduced-order ISD suspension. Zhang [15] combined a hydro-pneumatic spring with an inerter to reduce the vehicle body and wheel vibration effectively. Wang [16] investigated the influence of an inerter on the multi-directional vibrations. Du [17] explored 21 engineering feasible vehicle ISD suspension structures, identifying 12 configurations that exhibited superior vibration isolation performance compared to traditional passive suspensions. Shen [18] researched a nonlinear fluid inerter-based hydro-pneumatic suspension, and the key parameters of the suspension were optimized by the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II), which was proposed by Srinivas and Deb [19] and has been applied in many fields [20,21,22]. Yang [23] considered an energy-harvesting vehicle suspension with an inerter. The above methods are all from the perspective of structural methods to carry on the structural design of suspension systems. The work is huge, and the suspension structure with excellent vibration isolation performance is easily missed. From the perspective of the impedance method to design the suspension system, we can gain inspiration from passive network synthesis in electricity. This used to be a key issue in circuit theory, and many scholars have studied it [24,25]. However, with the development of integrated circuits, the heat of related research has declined. The birth of the inerter makes the new electromechanical similarity theory correspond perfectly and promotes the development of passive mechanical network synthesis theory. The previous research on the network synthesis theory of electrical systems can be leveraged for the reverse impedance design of suspension systems.
Papageorgiou first proposed the impedance method for passive ISD suspension design [26]. Due to the passive network synthesis for low order transfer function being relatively simple, numerous scholars [27,28,29,30,31,32] mainly focus on the simplest realization of biquadratic and bicubic transfer function. According to the Bott–Duffin circuit synthesis [25], a biquadratic transfer function can be implemented passively using no more than nine components, while a bicubic transfer function requires no more than ten components. Jiang investigated the passive implementations of the biquadratic transfer function using at least six and five components [27,28]. Wang [29] extended this research by exploring sufficient and necessary conditions for passive implementation of the biquadratic transfer function with at least four and three components, respectively. Zhang [30] addressed the network synthesis problem, demonstrating the passive implementation of the bicubic transfer function with at least seven components. Wang and Chen further examined the conditions under which the bicubic transfer function can be passively implemented using at least six and five components [31,32]. However, with the reduction of the number of components in the synthetic passive implementation of the passive network, the constraints of biquadratic and bicubic transfer functions become more and more stringent. Many studies [33,34,35] have found that fractional order can be used to describe more complex system dynamics. Chen [36] presented a design methodology to achieve critical damping by integrating fractional dampers and inerters. Fractional-order mechanical components exhibit more intricate vibration transmission characteristics compared to their integer-order counterparts, offering new design perspectives for mechanical systems. However, implementing fractional-order mechanical elements remains challenging in engineering. At the same time, fractional-order electrical elements have been widely researched in recent years [37,38]. By designing the external circuit of the mechatronic inerter [39], complex impedance outputs can be easily achieved. Shen [40] investigated a shock mitigation system with a three-element electrical network structure comprising a fractional inductor, a fractional capacitor, and a resistor. Subsequently, Shen [41] analyzed the effects of parametric perturbations, including the numerical values and orders of electrical components. However, the exploration of the fractional-order transfer functions remains limited. The emergence of fractional order necessitates a departure from network synthesis conditions tailored for integer order transfer functions, as they are not fully applicable to fractional-order transfer functions. Therefore, this paper concentrates on investigating the influence of the fractional-order biquadratic transfer functions implemented in mechatronic inerters on the vibration suppression effectiveness of vehicle suspension systems. The paper is structured as follows:
In Section 2, the construction of vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension with a fractional-order biquadratic electrical network is given. In Section 3, the NSGA-II multi-objective genetic algorithm is employed to optimize the critical suspension parameters, and the passive network positive real synthesis of fractional-order biquadratic transfer function is given. Section 4 is the dynamic analysis of the suspension system. Some conclusions and discussions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Model of Suspension Dynamics
2.1. Model of Vehicle Mechatronic ISD Suspension
The 2-DOF (degrees of freedom) dynamic model is established to evaluate the vertical vibration of vehicle suspension in Figure 1.
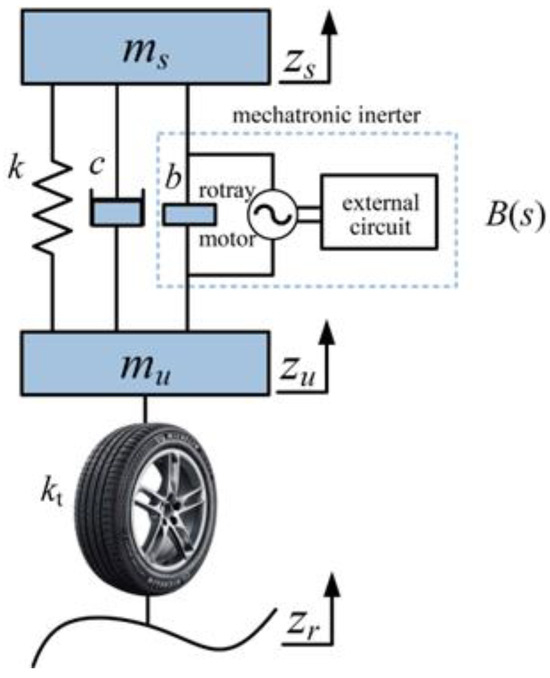
Figure 1.
Model of vehicle suspension.
In Figure 1, ms and mu are the sprung mass and unsprung mass of the vehicle, respectively, zs and zu are the corresponding vertical displacements, k is the stiffness of the suspension support spring, c is the damper coefficient of the suspension, b is the inertance coefficient of inerter, B(s) is the impedance expression of the mechatronic inerter, kt is the equivalent spring stiffness of the tire, and zr is the pavement input. The Laplacian equation of the suspension is obtained:
In the Equation (1), Zs, Zu, and Zr represent the Laplacian transforms of zs, zu, and zr, respectively.
The constructed suspension parameters shown in Table 1 are given according to reference [42].

Table 1.
Parameters of vehicle suspension.
2.2. Fractional-Order Biquadratic Electrical Network
The schematic diagram of the ball-screw mechatronic inerter [40] used in this paper is shown in Figure 2.
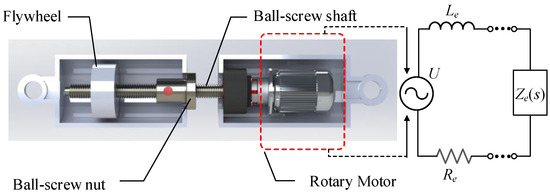
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the mechatronic inerter.
Ignoring the equivalent inductance Le and resistance Re of the rotating motor, we can obtain the impedance function expression B(s) of the mechanical inerter:
where b represents the inertance coefficient of the inerter, s denotes the Laplacian operator, P signifies the lead of ball screw, ke and kt are the induced electromotive force coefficient and the thrust coefficient of the rotary motor, severally, and Ye(s) is the admittance expression of the external circuitry of the rotating motor. The admittance expression of the external circuit is as follows:
In the equation, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H are the coefficients of the biquadratic admittance expression, s is the Laplacian operator, and α and β are the order of the Laplacian operator. According to articles [43,44], when the order of fractional-order inductors and capacitors meet 0 < α, β < 1, passive networks can be formed with passive components.
3. Parameter Optimization
3.1. NSGA-II Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm
NSGA (non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm) is a genetic algorithm based on the Pareto optimization concept. This algorithm improves the selection regeneration method on the basis of the genetic algorithm; each individual is stratified according to its dominant and non-dominant relationship, and then the selection operation is performed. However, the NSGA has some problems, such as high complexity of non-dominated sorting time and lack of elite retention strategy to improve the performance of the algorithm. NSGA-II, therefore, uses an elitism-based non-dominated sorting method for ranking and sorting each individual and uses a crowding distance approach in its section operator for keeping the diversity among the obtained Pareto optimal solutions [45]. The algorithm flow chart is shown in Figure 3.
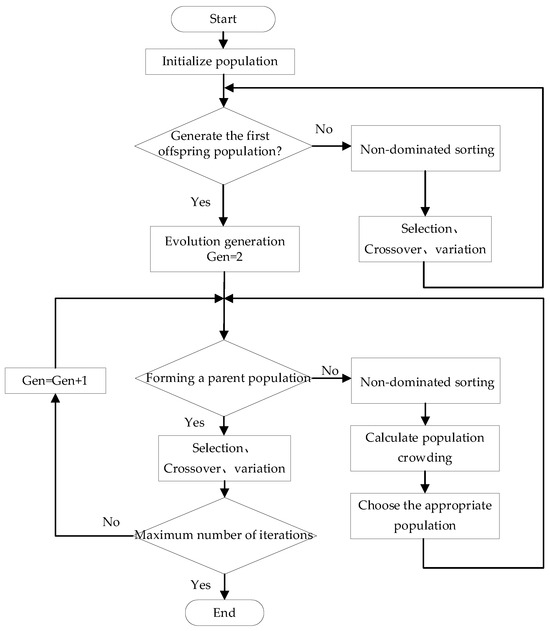
Figure 3.
Flowchart of NSGA-II.
This research mainly focuses on the riding comfort and operating stability of the vehicle. In addition, we still set a hard limit on the suspension working space: ±0.08 m [46]. Since the single-objective optimization algorithm has limitations in determining weight coefficients and handling non-uniform objective dimensions, we adopt a multi-objective optimization algorithm, which exhibits strong global search capability and robustness. The Pareto front generated by this algorithm provides multiple feasible solutions for decision-making. More information can be obtained from the Pareto front for the analysis of the correlation between the targets, and the suspension structure with the best performance can be selected according to the focus. With this in mind, we can consider both the minimum vehicle body acceleration and the dynamic tire load through Equation (4).
where J1 is the minimum RMS value of the vehicle body acceleration to be optimized; J3 is the minimum RMS value of the dynamic tire load.
A kind of passive suspension with a parallel structure composed of the parallel spring and damper elements has been elected as the contrast suspension in this paper. We improved the efficiency of the optimization algorithm by setting E as 1. The optimization variables were selected as follows: damping coefficient c/N∙s∙m−1, inertance b/kg of the mechatronic inerter, and coefficient A, B, C, D, F, G, H of the fractional-order transfer function and order α, β. In the optimization process, the range of variables is set as follows:
In addition, the above variables must satisfy both the nonlinear inequality constraints of theorem 1 and the nonlinear equality constraints of theorem 2 in Appendix A. Theorem 1 makes the fractional-order biquadratic function a positive real function, and theorem 2 makes the numerator and denominator of the fractional-order biquadratic function have common factors.
In the following, we will refer to the fractional-order ISD suspension as FO-ISD suspension and the integer-order ISD suspension as IO-ISD suspension in the text description section. Figure 4 shows the optimized Pareto front. It represents the curve formed by all the Pareto optimal solutions obtained in multi-objective optimization problems in the graph. This curve shows the trade-off relationship between different objectives. Choosing different optimal solutions on the curve means that the corresponding parameters can change the performance tendency of the suspension system. In Figure 4, the optimal parameter solutions for the FO-ISD suspension are represented by red triangles, the IO-ISD suspension is indicated by blue dots, and the black squares represent the optimal parameter solutions for the traditional passive suspension.
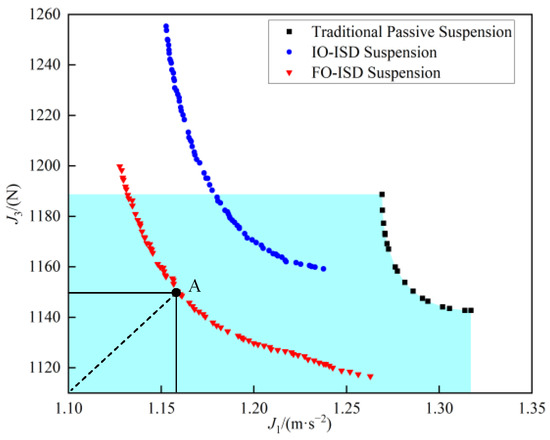
Figure 4.
Pareto front.
It can be seen from the figure that compared with the traditional passive suspension, both the FO-ISD suspension and the IO-ISD suspension have a certain degree of reduction in the two indicators. However, the reduction of J1 in the IO-ISD suspension will lead to a more serious deterioration of J3, which results in fewer available parameters for the IO-ISD suspension. In contrast, the curve formed by the optimal parameter solutions of the FO-ISD suspension is closer to the origin of the coordinate axis, which means that the two performance indicators of the FO-ISD suspension are better than those of the IO-ISD suspension, and there are more available points better than the traditional passive suspension. Therefore, the FO-ISD suspension has more and better parameter options. It can reduce J1 while also reducing J3, thereby comprehensively improving the vehicle’s suspension performance. The optimal normalized weighted sum of the J1 and J3 is selected as the final optimization variable so as to balance and comprehensively improve the performance of the vehicle suspension. Its formula is as follows:
Through comparative calculations, it can be found that the f-value at point A is the smallest, at 0.9479. Therefore, the parameters of the FO-ISD suspension corresponding to point A are selected, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Optimized parameters.
3.2. Positive Real Synthetic Passive Implementation of Fractional-Order Biquadratic Transfer
The positive realness of the transfer function is very important for the determination of passive networks. However, with the arrival of fractional-order components, the equivalence relationship between component passivity and positive real transfer function in traditional networks is broken. Nevertheless, from the study of articles [47,48,49], it is found that the transfer function obtained after appropriate variable substitution for fractional-order network satisfies the positive realness condition.
According to the positive real synthetic passive realization condition of the fractional-order transfer function, the simplest realization condition of two, three, four, and five electrical-element network components is tested according to the simplest principle [50]. In Appendix B, based on the positive real synthetic passive realization conditions of the fractional-order biquadratic transfer function given in the literature, it can be obtained that the A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H optimized in this paper meet the fourteenth condition of the five-element implementation conditions of the transfer function Ye(s), that is, AH + DE − BG − CF = 0, AD − BC = 0, BE > AF and satisfy BH > DF or DF > BH. Thus, the optimized fractional-order biquadratic transfer function Ye(s) meets the conditions of positive real function and satisfies inequalities (7); it can be implemented passively with a five-element structure, as shown in Figure 5, which is composed of three resistors, a fractional-order capacitor, and a fractional-order inductor.
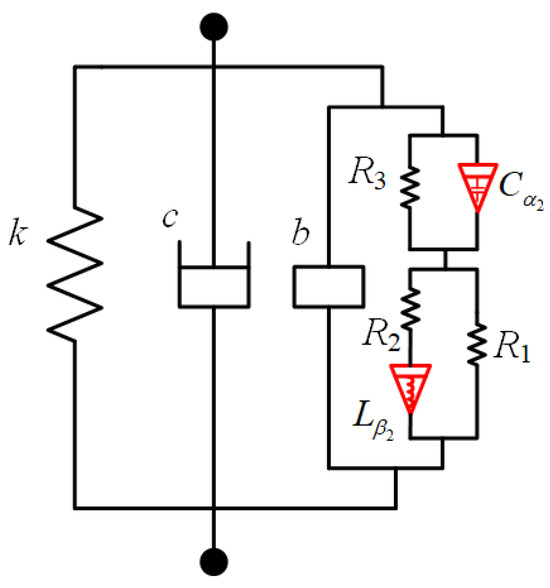
Figure 5.
Optimal electrical structure.
The expression of each parameter component in Figure 5 is as follows:
Table 3 shows that the transfer function coefficients obtained by optimization are substituted into the component expressions of each parameter.

Table 3.
Parameters of the external electrical circuit.
4. Simulation Analysis
4.1. Random Pavement Input
The expression for random pavement input [51] is as follows:
where u is the velocity of vehicle, G0 is the road roughness coefficient, and w(t) represents the Gaussian white noise. Table 4 presents a comparison of performance indexes for each suspension at three different speeds. Figure 6a, Figure 7a and Figure 8a show the comparison of RMS values of performance indicators at speeds ranging from 10 m/s to 30 m/s. Figure 6b, Figure 7b and Figure 8b show the comparison of performance index at the speed of 20 m/s. The formula for calculating the RMS of a performance indicator is as follows:
where ai is the acceleration value at each point in time; Fi is the dynamic tire load at each time point; and n is the total number of time points.

Table 4.
Evaluation indexes at various velocities.
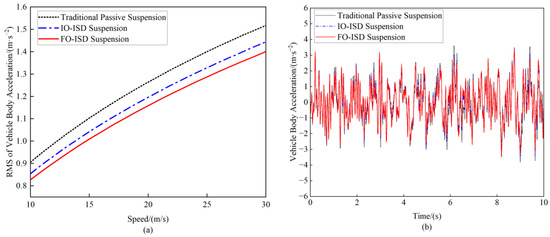
Figure 6.
(a) Comparison of RMS values of vehicle body acceleration at speeds ranging from 10 m/s to 30 m/s. (b) Comparison of vehicle body acceleration at the speed of 20 m/s.
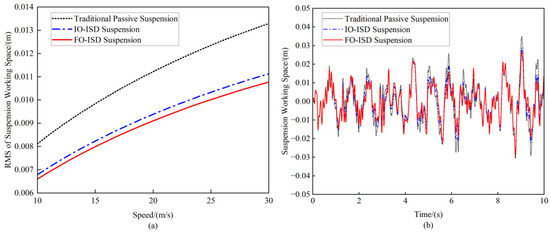
Figure 7.
(a) Comparison of RMS values of suspension working space at speeds ranging from 10 m/s to 30 m/s. (b) Comparison of suspension working space at the speed of 20 m/s.
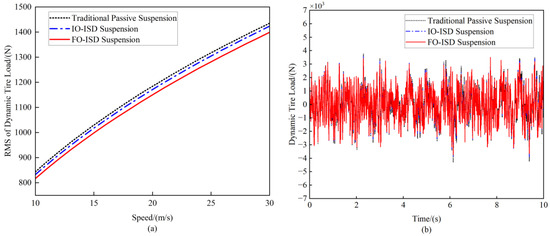
Figure 8.
(a) Comparison of RMS values of dynamic tire load at speeds ranging from 10 m/s to 30 m/s. (b) Comparison of dynamic tire load at the speed of 20 m/s.
It can be seen that the FO-ISD suspension shows excellent advantages compared to the other two suspensions in the three performance indexes. Specifically, for the vehicle body acceleration, the RMS values of IO-ISD suspension decreased by 5.65%, 5.34%, and 4.88% at speeds of 10 m/s, 20 m/s, and 30 m/s, respectively. Meanwhile, the FO-ISD suspension decreased by 8.36%, 7.98%, and 7.41% at the corresponding speeds. Regarding the suspension working space, the IO-ISD suspension reduced by 16.05%, 16.07%, and 16.54% at different speeds, whereas the FO-ISD suspension achieved reductions of 18.52%, 18.75%, and 18.80%. Although the improvement in dynamic tire load was relatively small, IO-ISD suspension showed optimization margins of 1.32%, 1.11%, and 0.79%, while FO-ISD suspension achieved 2.68%, 2.39%, and 2.01%.
The results indicate superior performance of the FO-ISD suspension over the IO-ISD suspension across three key performance metrics. This superiority is attributed to the more intricate vibration transmission characteristics inherent in FO-ISD suspension, which enhances its vibration isolation capabilities.
4.2. Frequency Responses Analysis
For the frequency response to the suspension indexes, sinusoidal road input is given in different frequency domains, and the output amplitude is divided by the input amplitude to obtain the gain value of the corresponding index. Sinusoidal road input is as follows:
In Formula (12), A represents the amplitude of sinusoidal road input, which is 0.01 m; f represents the frequency of the sinusoidal road input, with values ranging from [0.01,15].
The frequency responses of suspension indexes are shown in Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11 and Figure 12.
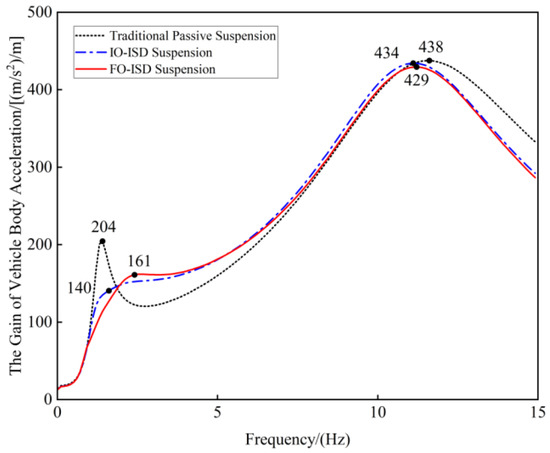
Figure 9.
Frequency responses of vehicle body acceleration.
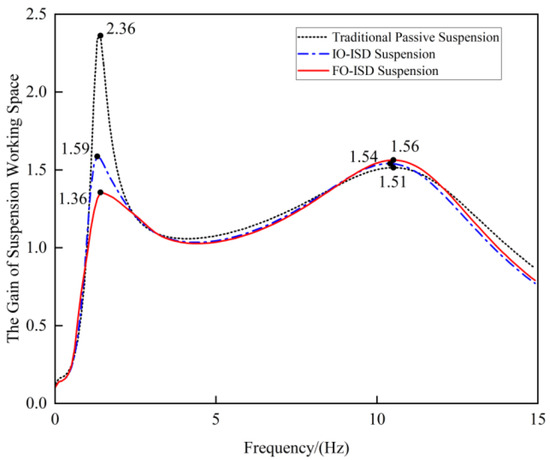
Figure 10.
Frequency responses of suspension working space.
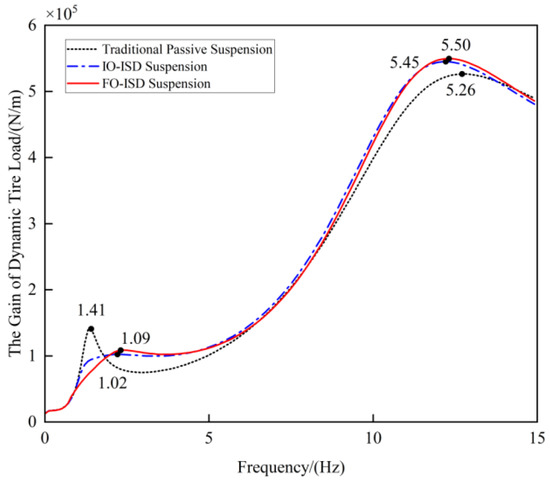
Figure 11.
Frequency responses of dynamic tire load.
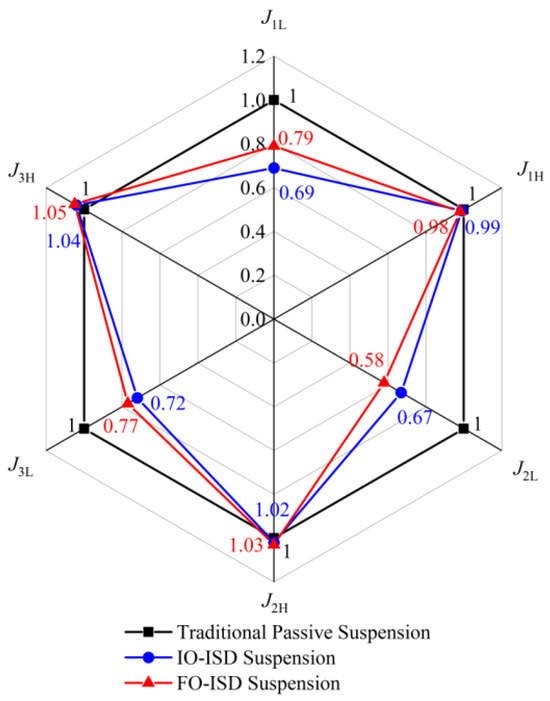
Figure 12.
Radar diagram of low and high-frequency peak of suspensions.
The vehicle body acceleration gain is shown in Figure 9. In the figure, the red line represents the FO-ISD suspension, the blue line represents the IO-ISD suspension, and the black line represents the traditional passive suspension. It can be seen from the figure that in the low-frequency band (0–5 Hz), although the low-frequency peak of the FO-ISD suspension exceeds that of the IO-ISD suspension, it is still better than the traditional passive suspension. In the high-frequency band (10–15 Hz), the differences in the high-frequency peaks of the three types of suspensions are very small. However, the performance of the FO-ISD suspension is always better than that of the traditional passive suspension and the IO-ISD suspension. This indicates that the fractional-order design enhances the energy dissipation capacity of the inerter through the complex impedance characteristics, thereby more effectively suppressing the body vibration.
As can be seen from Figure 10, although both types of ISD suspensions are slightly worse at the high-frequency peak, the low-frequency gain of the suspension working space of the FO-ISD suspension is significantly better than that of the other two types of suspensions, effectively improving the working space of the vehicle suspension when working in the low-frequency band. In Figure 11, although the dynamic tire load at the low-frequency peak of the FO-ISD suspension exceeds that of the IO-ISD suspension, it is still better than the traditional passive suspension. At the high-frequency resonance peak, the FO-ISD and IO-ISD suspensions deteriorate slightly, respectively. Overall, the FO-ISD suspension is slightly worse at the high-frequency peak, but the overall trend is similar to that of the IO-ISD suspension. In the low-frequency range, due to the complex impedance, the FO-ISD suspension fully exerts the advantage of the inerter. Compared with the IO-ISD suspension, the low-frequency amplitude suppression effect is further enhanced in most frequencies.
In Figure 12, the comparison of various indicators can be seen more intuitively. Among them, J1L denotes the low-frequency peak of vehicle body acceleration, while J1H represents its high-frequency counterpart. Similarly, J2L and J2H denote the low and high-frequency peaks of suspension working space, respectively. Meanwhile, J3L and J3H signify the low and high-frequency peaks of the dynamic tire load. In terms of body acceleration, although the J1L of the FO-ISD suspension in the low-frequency band is slightly higher than that of the IO-ISD suspension, it is still 21% lower than that of the traditional passive suspension. The low-frequency peak of the IO-ISD suspension is reduced by 31%. In the case of J1H in the high-frequency band, the performance of the FO-ISD and IO-ISD suspensions is similar. However, the FO-ISD suspension is still slightly better than the IO-ISD suspension and can further reduce body acceleration. In terms of suspension working space, the J2L of the FO-ISD suspension working space is reduced by 42% compared with that of the traditional passive suspension, and the IO-ISD suspension working space is reduced by 33%. This shows that the FO-ISD suspension can maintain the optimal suspension working space when working at low frequency. In the case of J3L in the low-frequency band, although the FO-ISD suspension is slightly higher than the IO-ISD suspension, it is still 23% lower than the traditional passive suspension. This effectively reduces the dynamic tire load of the vehicle and improves driving stability. In the case of J2H and J3H in the high-frequency band, the FO-ISD and IO-ISD suspensions exhibit slight deterioration. However, they are still within the acceptable range.
4.3. Impulse Pavement Input
The vehicle is set to drive through a speed reducer with a height of 0.05 m and a width of 0.3 m at a speed of 10 m/s [52]. The impulse response of dynamic performance indexes is illustrated in Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15; Table 5 shows the corresponding peak-to-peak (PTP) values.
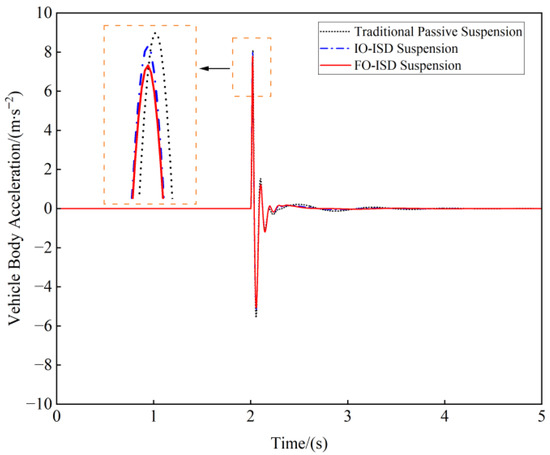
Figure 13.
The impulse response of vehicle body acceleration.
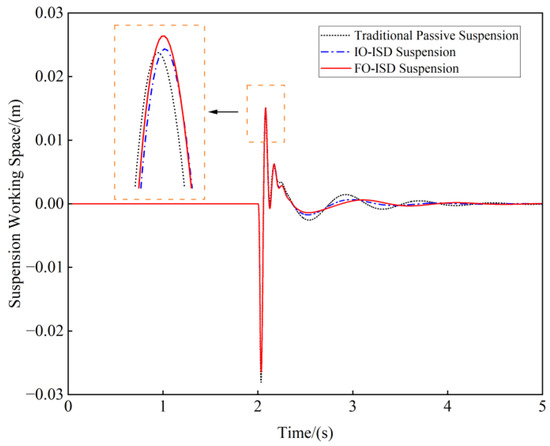
Figure 14.
The impulse response of suspension working space.
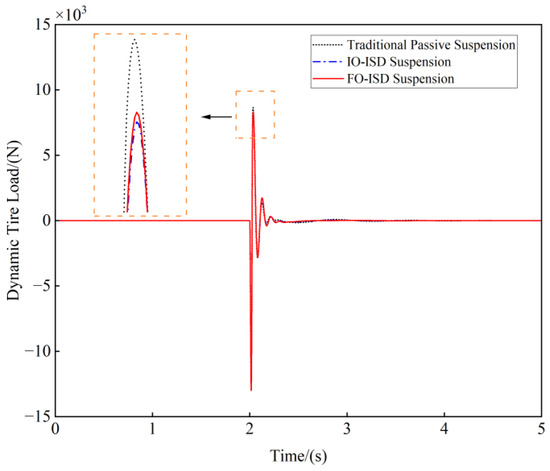
Figure 15.
The impulse response of dynamic tire load.

Table 5.
PTP values comparison between different suspensions.
The FO-ISD suspension optimizes the PTP values of the three suspension performance indexes compared to the traditional passive suspension. Specifically, the vehicle body acceleration shows a reduction of 5.94%, the suspension working space reduces by 2.80%, and the dynamic tire load exhibits marginal improvement. In comparison with IO-ISD suspension, the vehicle body acceleration is optimized by 2.00%, whereas the other two performance indexes exhibit a slight worsening in PTP values.
5. Discussion
This paper employs the fractional-order calculus theory to propose a design methodology for vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension utilizing a fractional-order biquadratic electrical network. A dynamic model of the vehicle suspension is formulated, with suspension parameters to be optimized using NSGA-II. The external network structure is synthesized using the fractional-order passive network design principles. Simulation results validate that the proposed fractional-order ISD suspension exhibits superior vibration isolation effectiveness compared to both integer-order ISD suspension and traditional passive suspension.
It is worth mentioning that the positive real synthetic passive implementation of the fractional-order transfer function can be applied to other vibration isolation fields to obtain better vibration isolation performance. In the future, we will focus on the simplest implementation of fractional-order transfer functions and the engineering implementation of fractional-order electrical components.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S.; methodology, Y.S.; software, Z.L.; investigation, X.T.; data curation, K.J.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L. and K.J.; writing—review and editing, X.T. and X.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.S. and X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 52072157), the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. SJCX23_2084), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (Grant No. 2022QNRC001), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2024T171048, 2024M753653, 2024M761549).
Data Availability Statement
All the pertinent data are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Xiang Tian was employed by the company Chery New Energy Automobile Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| RMS | Root-mean-square |
| ISD | Inerter-spring-damper |
| DOF | Degrees of freedom |
| NSGA | Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithms |
| FO | Fractional-order |
| IO | Integer-order |
| PTP | Peak-to-peak |
Appendix A
The positive real condition of the fractional-order biquadratic transfer function is given by the following theorem [51]:
Theorem 1.
Consider the fractional biquadratic transfer function Ye(s) of the Formula (3), where A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H ≥ 0 and 0 < α, β < 1. Then, the necessary and sufficient condition for a positive real function of fractional order Ye(s):
Theorem 2.
For the fractional-order biquadratic transfer function represented by Formula (3), a necessary and sufficient condition for common factors to exist between its numerator and denominator is met when one of the following conditions holds:
AG − CE = 0 and AH + BG − CF − DE = 0 and BH − DF = 0
AF − BE = 0 and AH + CF − BG − DE = 0 and CH − DG = 0
Appendix B
The following are the positive real synthetic passive realization conditions of the fractional-order biquadratic transfer function [51]. According to the principle of simplicity, the simplest realization conditions of the two, three, four, and five electrical network components are tested in turn. The specific flow chart of its network synthesis process is shown in Figure A1.
Binary implementation conditions of the transfer function Ye(s) (5 coefficients are 0):
1. B > 0, C > 0 and E > 0 or H > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
2. F > 0, G > 0 and A > 0 or D > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
3. A > 0, D > 0 and F > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
4. B > 0, E > 0 and H > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0.
Three-element implementation conditions of the transfer function Ye(s) (in conditions 1–4, 4 coefficients are 0, and in conditions 5–10, 3 coefficients are 0):
1. B > 0, C > 0 and A, E > 0 or D, H > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
2. F > 0, G > 0 and A, E > 0 or D, H > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
3. A > 0, B > 0, D > 0, F > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
4. B > 0, E > 0, F > 0, H > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
5. BG = CF, and A > 0 or D > 0 or E > 0 or H > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
6. CF = DE, and B > 0 or G > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
7. AH = BG, and C > 0 or F > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
8. BG = DE, and A > 0 or H > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
9. AH = CF, and D > 0 or E > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0;
10. AH = DE, and C > 0 or G > 0, the remaining coefficients are 0.
Four-element implementation condition of the transfer function Ye(s) (in conditions 1–7, 2 coefficients are 0, and in conditions 8–15, 1 coefficient is 0);
1. BG = CF, A = E = 0, and satisfy BH > DF or DF > BH or CH > DG or DG > CH;
2. BG = CF, D = H = 0, and satisfy AG > CE or CE > AG or AF > BE or BE > AF;
3. AH = CF, B = D = 0, and satisfy AG > CE or CE > AG;
4. AH = CF, E = G = 0, and satisfy DF > BH or BH > DF;
5. BG = DE, F = H = 0, and satisfy AG > CE or CE > AG;
6. BG = DE, A = C = 0, and satisfy DF > BH or BH > DF;
7. AH = DE, C = G = 0, and satisfy DF > BH or BH > DF;
8. BG = CF + DE, and satisfy AG = CE, H = 0 or DF = BH, A = 0;
9. CF = AH + BG, and satisfy AG = CE, D = 0 or DF = BH, E = 0;
10. AH = BG + CF, and satisfy EH + FG, D = 0 or AD = BC, E = 0;
11. DE = BG + CF, and satisfy AD = BC, H = 0 or EH = FG, A = 0;
12. DE = AH + CF, and satisfy AF = BE, DF > BH, G = 0 or CH = DG, CE > AG, B = 0;
13. AH = BG + DE, and satisfy AF = BE, BH > DF, C = 0 or CH = DG, AG > CE, F = 0;
14. CF = AH + DE, EH = GF, B = 0;
15. BG = AH + DE, AD = BC, F = 0.
Five-element implementation conditions of the transfer function Ye(s) (in conditions 1–6, 1 coefficient is 0, and in conditions 7–14, all coefficients are > 0):
1. 4BC(FG − EH) = (DE − CF − BG)2, A = 0;
2. 4BC(FG − EH) = (AH − CF − BG)2, D = 0;
3. 4FG(BC − AD) = (DE − CF − BG)2, H = 0;
4. 4FG(BC − AD) = (AH − CF − BG)2, E = 0;
5. 4AG(BH − DF) = (DE − BG − AH)2, C = 0;
6. 4CE(DF − BH) = (AH − CF − DE)2, G = 0;
7. AH + BG − CF − DE = 0, BH − DF = 0, CE > AG, and satisfy DE > AH or AH > DE;
8. AH + BG − CF − DE = 0, BH − DF = 0, AG > CE, and satisfy DE > AH or AH > DE;
9. AH + BG − CF − DE = 0, AG − CE = 0, DE > AH, and satisfy BH > DF or DF > BH;
10. AH + BG − CF − DE = 0, AG − CE = 0, AH > DE, and satisfy BH > DF or DF > BH;
11. AH + DE − BG − CF = 0, EH − FG = 0, DG > CH and satisfy AG > CE or CE > AG;
12. AH + DE − BG − CF = 0, EH − FG = 0, AF > BE and satisfy BH > DF or DF > BH;
13. AH + DE − BG − CF = 0, AD − BC = 0, CH > DG and satisfy AG > CE or CE > AG;
14. AH + DE − BG − CF = 0, AD − BC = 0, BE > AF and satisfy BH > DF or DF > BH.
In order to follow the simplest principle of passive implementation of the transfer function, the implementation conditions of six elements and more are not given here.
When all coefficients A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H are positive, a network comprising five series-parallel elements with two fractional-order reactance elements can be implemented. If at least one of the coefficients A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H is zero, the network can be realized using up to four elements.
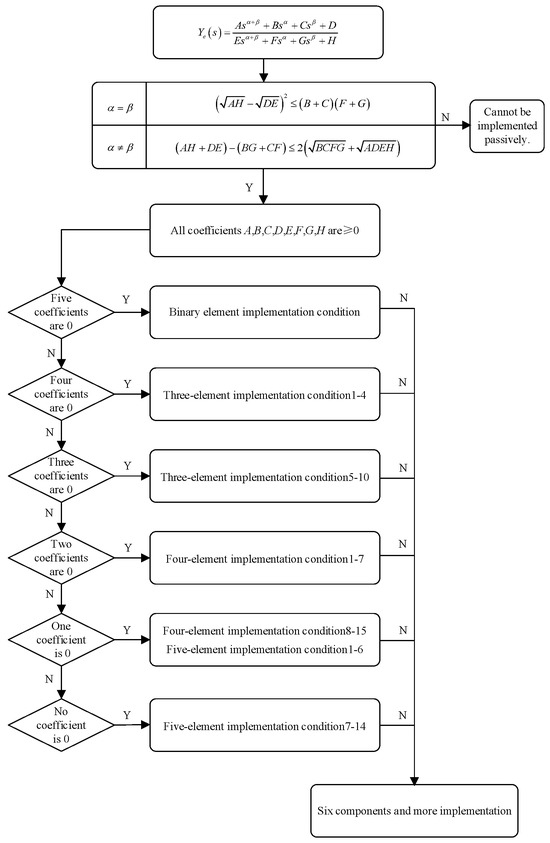
Figure A1.
References.
References
- Sankaranarayanan, V.; Emekli, M.E.; Gilvenc, B.A.; Guvenc, L.; Ozturk, E.S.; Ersolmaz, E.S.; Sinal, M. Semiactive suspension control of a light commercial vehicle. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 13, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.N.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, Y. General theory of skyhook control and its application to semi-active suspension control strategy design. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 101552–101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; Chen, A.; Du, F.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, Y.L.; Chen, L. Performance enhancements of semi-active vehicle air ISD suspension. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2024, 09544070241233024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; Jia, M.Q.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, Y.L.; Chen, L. Vibration suppression using a mechatronic PDD-ISD-combined vehicle suspension system. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 250, 108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Nguyen, T.A.; Dang, N.D. A novel sliding mode control algorithm for an active suspension system considering with the hydraulic actuator. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2022, 19, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. A nonlinear model predictive control for air suspension in hub motor electric vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2025, 239, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, S.E.; Tang, K.; Cao, W.; Wu, W.; Li, H. Approximate optimal filter design for vehicle system through actor-critic reinforcement learning. Automot. Innov. 2022, 5, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, L.; Shan, Z.; Ma, F. Vehicle state and bias estimation based on unscented kalman filter with vehicle hybrid kinematics and dynamics models. Automot. Innov. 2023, 6, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C. Synthesis of mechanical networks: The inerter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2002, 47, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zang, J.; Ni, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L. Dynamic design of a nonlinear energy sink with NiTiNOL-steel wire ropes based on nonlinear output frequency response functions. Appl. Math. Mech. 2019, 40, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Niyitangamahoro, A.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, H. Tuned inerter dampers for civil structures subjected to earthquake ground motions: Optimum design and seismic performance. Eng. Struct. 2019, 198, 109470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Han, S.; Na, J.; Wang, C. Vertical suspension optimization for a high-speed train with PSO intelligent method. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 1526792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Wang, F.C. Performance benefits in passive vehicle suspensions employing inerters. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2004, 42, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, H. Passive skyhook suspension reduction for improvement of ride comfort in an off-road vehicle. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 150710–150719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Liu, J.; Nie, J.; Wei, H.; Chen, L. Simulation analysis and experiment research on hydro-pneumatic isd suspension. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 2095350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Meng, H.; Chen, L.Q. Nonlinear vibration and dynamic performance analysis of the inerter-based multi-directional vibration isolator. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2022, 92, 3597–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Ming, M.; Yijie, C.; Yajun, W.; Yafeng, Z. Structure design and performance analysis of ISD suspension based on dynamic model and parameter optimization. Shock Vib. 2014, 33, 59–65. Available online: https://jvs.sjtu.edu.cn/CN/Y2014/V33/I6/59 (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Shen, Y.; Qiu, D.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, T. Vibration isolation performance analysis of a nonlinear fluid inerter-based hydro-pneumatic suspension. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.; Deb, K. Muiltiobjective optimization using nondominated sorting in genetic algorithms. Evol. Comput. 1994, 2, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.G.; Lan, X.D.; Zhou, M.; Lv, K.X. Performance optimization of flywheel motor by using NSGA-2 and AKMMP. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8103707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q.; Lee, C.H. Multiobjective optimization of a dual stator brushless hybrid excitation motor based on response surface model and NSGA 2. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 6105–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zang, T.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Men, H.; Li, J. An optimized resource allocation approach in limited emergency situations using NSGA-II. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Big Data and Information Analytics (Big DIA), Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 December 2023; pp. 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bui, V.; Qiu, D. Tradeoff analysis of the energy-harvesting vehicle suspension system employing inerter element. Energy 2024, 308, 132841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, O. Synthesis of a Finite Two-Terminal Whose Driving-Point Impedance Is a Function of Frequency. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bott, R.; Duffin, R.J. Impedance synthesis without use of transformers. J. Appl. Phys. 1949, 20, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, C.; Smith, M.C. Positive real synthesis using matrix inequalities for mechanical networks: Application to vehicle suspension. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2006, 14, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Z.; Smith, M.C. Series-parallel six-element synthesis of biquadratic impedances. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2012, 59, 2543–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Z.; Smith, M.C. Regular positive-real functions and five-element network synthesis for electrical and mechanical networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 56, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Implementation of Biquadratic Function in Passive Network Synthesis. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Jiang, J.Z.; Wang, H.L.; Neild, S. Synthesis of essential-regular bicubic impedances. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2017, 45, 1482–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, M.Z.; Liu, F. Series-parallel mechanical circuit synthesis of a positive-real third-order admittance using at most six passive elements for inerter-based control. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 5442–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, M.Z. Passive mechanical realizations of bicubic impedances with no more than five elements for inerter-based control design. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 5353–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.E.; Rosário, J.M.; Tenreiro Machado, J. Fractional order calculus: Basic concepts and engineering applications. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 375858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponetto, R.; Graziani, S.; Pappalardo, F.L.; Sapuppo, F. Experimental characterization of ionic polymer metal composite as a novel fractional order element. Adv. Math. Phys. 2013, 2013, 953695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, N.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Akgül, A.; Younas, U.; Nasreen, S.; Al-Ahmadi, A.N. Propagation of optical pulses in fiber optics modelled by coupled space-time fractional dynamical system. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 73, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Tai, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, N. Critical damping design method of vibration isolation system with both fractional-order inerter and damper. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 1348–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kartci, A.; Elwakil, A.; Bagci, H.; Salama, K.N. Fractional-order inductor: Design, simulation, and implementation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 73695–73702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirimokou, G.; Psychalinos, C.; Elwakil, A.S.; Salama, K.N. Experimental behavior evaluation of series and parallel connected constant phase elements. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 74, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Chan, H.A. Vehicle suspensions with a mechatronic network strut. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 49, 811–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; Hua, J.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, X.F.; Chen, L. Optimal design and dynamic performance analysis of a fractional-order electrical network-based vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 184, 109718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J.; Hua, J.; Hou, Q.H.; Xia, X.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, X.F. Performance analysis of the fractional-order vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension with parameter perturbation. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2022, 60, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Yu, M.; Evangelou, S.A.; Jaimoukha, I.M.; Dini, D. Mu-synthesis PID control of full-car with parallel active link suspension under variable payload. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 72, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Ma, L. Multivariate theory-based passivity criteria for linear fractional networks. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2018, 46, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Huo, X. Synthesis of fractional-order biquadratic immittance functions. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2019, 28, 1950187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhvi, B.; Savsani, V.; Patel, V. Multi-objective optimization of vehicle passive suspension system using NSGA-II, SPEA2 and PESA-II. Procedia Technol. 2016, 23, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, C.; Kucukdemiral, I.B.; Sivrioglu, S.; Yuksek, I.; Cansever, G. LPV gain-scheduling controller design for a non-linear quarter-vehicle active suspension system. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2009, 31, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, V.; Rao, A.S. The real part of a multivariable positive real function and some applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1974, 21, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Z.; Smith, M.C. A note on tests for positive-real functions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, N.K. A criterion to determine if two multivariable polynomials are relatively prime. Proc. IEEE 1972, 60, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X. Passive Synthesis of Fractional Order Biquadratic Impedance Functions. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Loizos, A.; Plati, C. An alternative approach to pavement roughness evaluation. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2008, 9, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Naghdy, F.; Du, H.; Qin, Y. Coupling effect between road excitation and an in-wheel switched reluctance motor on vehicle ride comfort and active suspension control. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 443, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).