Abstract
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a highly selective and sensitive analytical tool with a myriad of applications, but such techniques are typically used in laboratory settings due to the handling and preparations that are necessary. The merging of two streams of robust research, portable MS systems and next-generation ambient ionization methods, now provides the ability to perform high-performance chemical screening in an on-site and on-demand manner, with natural applications in disciplines such as forensic science, where samples of interest are typically found in field environments (i.e., traffic stops, crime scenes, etc.). Correspondingly, investigations regarding the suitability and robustness of these methodologies when they are utilized for authentic forensic evidence processing are prudent. This work reports critical insights into the role that choice of spray solvent system plays regarding analytical performance of two spray-based ambient ionization sources, paper spray ionization (PSI) and filter cone spray ionization (FCSI), when employed for evidence types containing emerging synthetic cannabinoids. The systematic characterization studies reported herein show that the applied spray solvent can dramatically affect both spectral intensity and signal duration, and in some circumstances, yield deleterious false negative responses. Overall, acetonitrile-based systems are shown to strike a balance between analyte solubility concerns and spray ionization dynamics of the novel ion sources employed on portable MS systems.
1. Introduction
Synthetic cannabinoids (SCs) are a family of compounds synthetically manufactured to mimic the effects of naturally derived cannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), the primary psychoactive constituent of marijuana [1,2,3]. These compounds were originally developed to have a similar structure and functionality to Δ9-THC but with a higher pharmacological efficacy and potency, and underground laboratories have further developed them for illicit use as a substitute for marijuana [4]. The growing concerns over the abuse of SCs has necessitated the regulation of their use in many countries. However, clandestine drug manufactures constantly modify said structures, resulting in new designer analogues that find their way into abused drugs. The abuse of SCs poses a global health threat due to their ease of accessibility; they are often spray-deposited on dried plant material [5] to be smoked, added to electronic cigarette formulations (i.e., e-liquids) [6] to be inhaled, and incorporated into other products branded as “not for human consumption” in convenience stores and online marketplaces [7]. With the current and growing market for SCs and their continued presence in forensic evidentiary seizures, it is important to develop sensitive, yet robust, analytical methods for both presumptive identification and confirmation. Conventional hyphenated mass spectrometric (MS) methods [8,9], such as gas chromatography (GC-MS) [10,11,12] and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) [13,14], have been used for the processing of SC-related evidence. However, these traditional technologies are time consuming due to the considerable number of preparative steps and lengthy chromatographic separations, which can result in a backlog of evidence in forensic laboratory systems. Hence, new methods aimed at increasing throughput and ease-of-use method for rapid SC evidence processing are desirable.
To address the limitations of conventional techniques, various ambient ionization mass spectrometry (AIMS) techniques, such as desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) [15] and direct analysis in real-time (DART) [16,17,18], have been used for the identification of SC-class compounds. Ambient ionization techniques generally allow for a direct analysis of raw samples with minimal preparation [19], and these methods have been widely explored for the forensic screening of drugs of abuse [8,20,21,22,23]. DART falls within a subclass of ambient ion sources that utilize hot gases for the thermal desorption of target analytes from samples and gas-phase reagent ions at atmospheric pressure to induce secondary ionization processes [24]; it should be noted here that these methods do not rely on the solvent-borne extraction of analytes from samples, instead relying on thermal mechanisms. The field of ambient ionization has also grown to include “substrate spray” techniques, where materials are used for sample holding/collection and the ionization medium, including techniques like paper spray ionization (PSI) [25], sandpaper spray ionization (SPS) [26], filter cone spray ionization (FCSI) [27], and, more recently, 3D-printed cone spray ionization (3D-PCSI) [28,29], which utilizes additive manufacturing to produce electrically conductive vessels from carbon nanotube-infused filaments. Many of these ionization methods have also been demonstrated on portable MS systems [23,29,30,31,32,33,34], further increasing the overall sample throughput by offering “on-demand” sample screening.
PSI-MS is a low-cost, ambient ion source that has attracted much interest for its use in the rapid analysis of illicit drugs like SCs. This technique utilizes a triangular piece of paper onto which a raw sample is deposited for direct generation of ions upon application of a solvent and high voltage for MS detection [35]. FCSI-MS is akin to a 3-dimensional PSI source, where a conical piece of paper is used to house solid samples. Here, the solvent is applied into said vessel, which initiates extraction and ionization after a high voltage is applied; mock-ups of both of these homebuilt ion sources can be seen herein, and designs have been reported in a past article in Instruments [30]. Both PSI and FCSI fall under the umbrella of spray-based ambient techniques, where an employed solvent is required for analysis, performing critical roles in both analyte extraction from sampled matrices and allowing the underlying molecular ionization mechanisms to proceed. Correspondingly, the choice of solvent system is highly important in terms of overall analytical performance with said ion sources, including sensitivity and signal stability [36]. Said solvents can also compromise the overall integrity of substrates employed for ambient ionization, as shown by Brown et al. [28] who systematically examined how harsher organic solvents degraded both structure and performance of the polymeric cones used for generating ions via 3D-PCSI-MS.
Since the early days of electrospray ionization (ESI) research [37], methanol (MeOH)-based solvent systems (which can also include systems with various proportions of water, as well as low levels of acidic or basic species to induce positive or negative ionization of molecules, respectively) have been considered the precedent for spray-based ionization for MS analysis. Ideally, each individual method would be optimized in terms of target analyte solubility and ionization efficiency, but utilizing a singular solvent system (e.g., 1:1 MeOH:H2O with 0.1% formic acid, which was one of the first reported systems employed for PSI-MS [28]) simplifies the overall method development and decreases the need for decision making by non-scientist operators. However, other factors such as human exposure to toxic organic solvents and waste management should also be considered. Water-based spray solvents rectify these issues, but typically result in a low ionization efficiency due to its high surface tension (which interferes with the generation of stable sprays) and a lack of charge carriers/reagent ions. For ion sources that utilize substrates (like triangular-cut paper via PSI), viscous solvent systems featuring a high percentage of water (>50%) reduce the mobility of extracted analytes through the employed medium [27]. Several groups have reported alternate compositions that target other analyte physicochemical properties (e.g., polarity) as a means of enhancing mass spectral information [38,39,40,41,42], such as Manicke and co-workers who demonstrated acetonitrile (ACN)-based systems for SC determination via PSI-MS [43]. There have also been reports of utilizing additional sample preparation steps [44,45] or derivatization of the employed paper substrate [46] as a means to increase analytical sensitivity via PSI-MS, but such processes increase the overall cost and complexity of the technique.
The demand for cannabinoid screening continues to grow, in both forensic drug evidence processing and in quality control processes for legalized marijuana and associated products (e.g., edibles, personal care products) in countries like the U.S. where legalization is taking place. In this work, we report a systematic investigation of common spray solvent systems and their effect on spectra data collected from synthetic cannabinoids and cannabinomimetics utilizing next-generation, spray-based ion sources like PSI-MS and FCSI-MS. We also present a highly pertinent case study involving authentic forensic evidentiary seizures, showing how improper solvent systems can increase the propensity for false negative responses from MS methods. The scope of this this work includes novel mass spectrometry (MS)-based instrumental approaches to chemical analysis, corresponding method development with innovative sample ionization strategies, and applications aimed towards interdisciplinary scientific arenas like forensic science.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Standards and Stock Solution Preparation
For the study, target cannabinoids were acquired as analytical standards from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, MI, USA); these analytes were selected to represent a variety of structural classes of cannabinoids as defined by the United Nations Office of Drugs and Crime (UNODC) [35]. Molecular structures for the selected cannabinoids (i.e., Δ9-THC, HU-210, (C8)-CP 47,497, XLR-11, JWH-018, ADB-Fubinaca, and AB-Fubinaca) can be seen in Figure 1. LC-MS grade methanol or acetonitrile (Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ, USA) and deionized water from an in-house Barnstead/Thermolyne Nanopure system (18.0 MΩcm) were used to create spray solvents, with formic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) added as the source of cannabinoid protonation. Stock solutions of each cannabinoid were prepared by serial dilution of cannabinoid standards in methanol and/or ACN. Varying compositions (1:0, 9:1, 3:1and 1:1, v/v%) of MeOH-H2O and ACN-H2O systems with 0.1% formic acid added by volume were prepared for use as spray solvents.
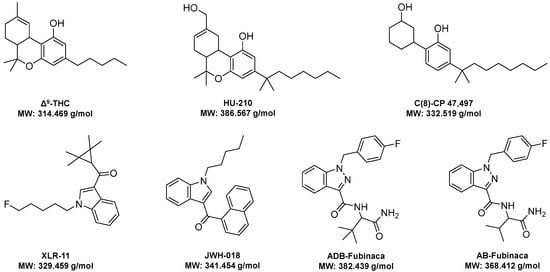
Figure 1.
Molecular structures of naturally occurring and synthetic cannabinoids (SC) of interest to this study.
2.2. Portable Mass Spectrometer Utilized for Spectral Determination
All mass spectral data in this work were collected using a FLIR Systems AI-MS 1.2 cylindrical ion trap (CIT) mass spectrometer (FLIR Mass Spectrometry, West Lafayette, IN, USA). We have reported the use of this portable MS system coupled with ambient ionization methods previously [9,23,27,28,29,30,34]. This instrument features a weight (~45 kg) and overall dimensions (60 cm × 50 cm × 40 cm, LWH) that are well-suited for field-based applications. Incorporated into the design are multiple input power options (120/110/24 V), onboard helium gas to promote fragmentation for tandem MS experiments, and high voltage necessary to induce ionization in employed ion sources. Ion sampling occurs via a continuous atmospheric inlet system in either positive and negative ion mode, and tandem MS (MS/MS) spectra allow for structural determination for unknown analyte identification. All reported experiments were conducted in positive ion mode. Measurements were performed in triplicate for each cannabinoid in each employed solvent system, with a blank sample analyzed between each trial to ensure no sample-to-sample carryover was observed.
2.3. Spray-Based, Ambient Ionization Methods
For PSI-MS analysis, MQuant chromatographic paper strips (EMD Millipore Corp., Billerica, MA, USA), pre-cut into isosceles triangles (7 mm × 5 mm × 5 mm), were used as the employed substrate, which featured a plastic backing; a complete breakdown of this ion source has been previously reported [23,30], and a mock-up can be seen in Figure 2A. The triangular tip with rigid plastic backing plays an important role in spray quality and duration during PSI-MS analysis. Each substrate was spotted with a 1 μL aliquot of stock solution of each cannabinoid under study and allowed to dry completely before analysis—this in turn produced a drug residue of known deposited mass. Each strip was both mounted and exposed to high voltage through a shielded, clamping-style electrode that in conjunction with applied solvent allowed for a plume of charged droplets to be emitted from the triangular egress of the paper. An x–y–z translational stage allowed for fine adjustment in relation to the MS inlet, position at a tip-to-inlet distance of ~3 mm. Ions were generated under ambient conditions by applying high voltage (~4.0 kV) across the triangular paper substrate after they had been saturated with a 3.0 μL aliquot of the desired spray solvent system.
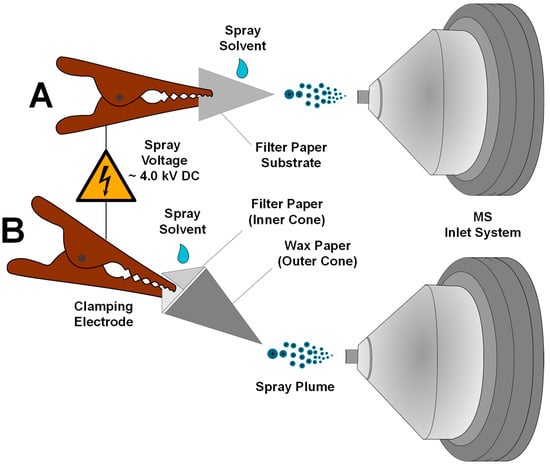
Figure 2.
(A) Schematic and overall mechanistic approach to the (A) PSI-MS and (B) FCSI-MS ion source for mass spectral analysis of unprepared samples.
For FCSI-MS analysis, a triangular pyramidal structure was generated from hand folded cones comprising wax weighing paper and filter paper, creating a reservoir for holding solid/bulk samples, onto which spray solvent can be directly applied. Here, extracted analytes migrated to the pyramidal egress after onboard filtration, where they underwent similar spray-based mechanisms to those seen in PSI-MS; this disposable, low-cost ion source operates akin to a 3-dimensional PSI-MS source. The methodology for hand folding this ion source was described by Fatigante et al. [27], but a summary is provided herein. The hydrophobic outer cone and filter paper-based inner cone (Grade 40 Whatman® filter paper, MilliporeSigma, Burlington, MA, USA) were both hand-folded from 90° quadrants cut from 5 cm circles of each material. Each quadrant was folded into four equal sections relative to the apex, which when folded onto itself created a triangular pyramidal-shaped cone. Then, the filter paper cone was placed with the outer wax paper cone, generating an onboard filtration stage, as seen in Figure 2B. Solid sample and employed spray solvent alike were added into the conical reservoir, and high voltage was applied similarly to PSI-MS. FCSI-MS requires ~150 μL of spray solvent to allow for proper wetting of the sampled material and analyte extraction, and spray-based ionization occurs at the egress with application of 4.0 kV via the clamping electrode. Solvent systems examined in this work consisted of MeOH:H2O and ACN:H2O mixtures in concentrations of 1:0, 9:1, 3:1, and 1:1 (v/v), each doped with 0.1%, v/v formic acid to favor protonation of SC analytes, which were monitored in positive ion mode.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Case Study: Observations Made during Authentic Synthetic Cannabinoid Evidence Screening via FCSI-MS
Over the past decade, we have utilized both PSI and FCSI-MS ion sources coupled to the FLIR AI-MS 1.2 portable MS system for the direct identification of illegal drug analytes from seized contraband. Here, the overarching goal was to provide non-scientist operators, such as law enforcement and crime scene technicians, with better performing tools for on-demand and on-site drug evidence confirmation. To simplify the method, a singular “gold standard” solvent system was always implemented (i.e., 1:1 MeOH:H2O with 0.1% formic acid), which has worked admirably for various traditional drugs of abuse (e.g., cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine), emergent analogues (e.g., synthetic cathinones, desomorphine [47], fentanyls [23], α-PVP [27], and adulterated/abused pharmaceutical tablets [27,28].
Recent collaborative work with local law enforcement departments provided an opportunity to screen contraband acquired via drug buys during vice operations; here, the intent was to quickly provide a presumptive identification prior to the time-delayed results from the state forensic laboratory in an effort to expedite policing. Interestingly, an examination of the purported synthetic cannabinoid (i.e., “spice”) evidence helped to show the potential weaknesses of this gold standard spray solvent system. The initial screening of the plant-based evidence directly with FCSI-MS was inconclusive in regard to known spectral signatures and appreciable ion intensities. As the forensic intelligence provided by the vice operations suggested that these samples should indeed contain contraband, efforts were taken to enhance the data through noise filtering, producing the mass spectra obtained in Figure 3A. Here, the spectral signatures for m/z 330 and 352 were observed after 20× magnification, suggesting the presence of protonated XLR-11 and its sodiated adduct, respectively; similar signatures for XLR-11 have been reported in the literature [27]. As the spectral intensity was near noise-level, an alternate spray solvent system was employed on said evidence, guided by recent reports of ACN-based compositions from Manicke and co-workers [43]. Figure 3B shows FSCI-MS spectra collected from the same evidentiary seizure utilizing 9:1 ACN:H2O w/0.1% (v/v) formic acid (FA), which obtained signal intensities for the protonated, sodiated, and potassiated (m/z 369) forms ~200 times that obtained with the MeOH-based solvent, definitively showing the presence of the controlled synthetic cannabinoid. This case study elucidates potential issues with MeOH-based spray solvents used with spray-based MS ionization methods for cannabinoid-class forensic evidence types, as it leads to a high propensity for deleterious false positive responses with such methods. A corresponding systematic comparison of such solvent systems is indeed prudent.
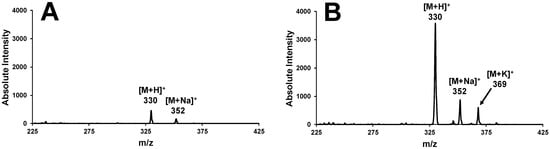
Figure 3.
Positive-mode FCSI-MS spectra generated for synthetic cannabinoid evidence containing XLR-11 with spray solvents comprising (A) 1:1 MeOH:H2O w/0.1% FA (with spectral magnification of 20× applied for visualization) and (B) 9:1 ACN:H2O w/0.1% FA.
3.2. Comparison of MeOH and ACN-Based Spray Solvent Systems for Spray-Based Ambient Ionization Methods Employed for Cannabinoid-Class Evidence Types
The work presented herein examined how differing solvent compositions comprising MeOH and ACN affect the sensitivity of cannabinoid analysis when utilizing spray-based ambient ionization methods. Specifically, we utilized compositions comprising MeOH:H2O or ACN:H2O at proportions corresponding to 1:0, 9:1, 3:1, and 1:1 (by volume), all of which were acidified with 0.1% (v/v) formic acid as a means of increasing the protonation of the target species. These compositions were selected as they are similar to those commonly used in LC and LC-MS mobile phases, as well as other reports utilizing spray-based ionization methods. As the proportion of organic solvent to pure water changes, so does the physicochemical properties of the overall composition, including its ability to dissolve analytes, polarity, and surface tension, all of which can affect the performance of PSI, 3D-PCSI, and other spray-based ion sources. Here, all target cannabinoids (as seen in Table 1) were analyzed in triplicate with PSI-MS, utilizing an analyte mass of 100 ng that was deposited on each paper substrate to test the solvent system. For each replicate, both MS and MS/MS spectra were collected to confirm the presence of the target cannabinoid; MS/MS refers to the ability of the ion trap mass analyzer to isolate an ion of interest (e.g., the protonated molecule of a target cannabinoid), induce low-energy fragmentation via collision-induced dissociation (CID) with a helium damping gas, and produce corresponding mass spectra from the structural fragment ions produced. MS and MS/MS transitions observed, the anticipated formulas for the fragments generated, and the instrumental setting for CID can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
MS and MS2 transitions with possible formula losses for investigated cannabinoid analytes, as well as characteristic instrument settings for fragmentation studies.
Representative PSI-MS and MS/MS spectra collected during this systematic study are presented in Figure 4, showing expected ion signatures for ∆9-THC, HU-210, (C8)-CP 47, 497, XLR-11, JWH-018, ADB-Fubinaca, and AB-Fubinaca. For comparison purposes, said spectra were all collected with 100 ng residues of the target analyte. As observed, all cannabinoid species produced spectral data marked by a base peak representing the protonated molecule, [M+H]+. This is typical for “soft” ionization methods like ESI, PSI-MS, etc., that exhibit little to no fragmentation during the ionization event, although it is not uncommon for alkali earth metal adducts (e.g., [M+Na]+ and [M+K]+) to also be observed in unprepared sample matrices. Each analyte was subjected to optimized MS/MS parameters for fragmentation of the protonated molecule, generating the characteristic fragmentation patterns observed in the insets. Generally, the patterns observed on the FLIR System AI-MS 1.2 match well with those contained in tandem mass spectral databases.
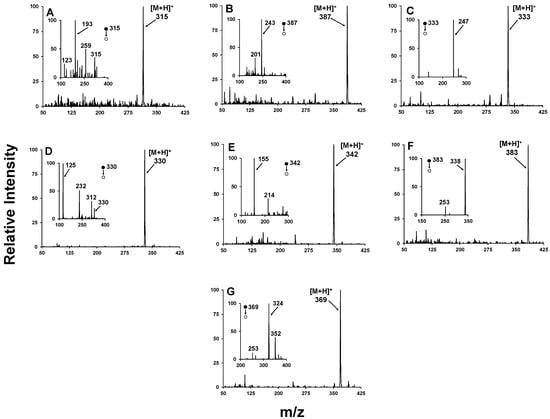
Figure 4.
Positive-mode PSI-MS spectra generated for investigated cannabinoids, including (A) ∆9-THC, (B) HU-210, (C) (C8)-CP 47, 497, (D) XLR-11, (E) JWH-018, (F) ADB-Fubinaca, and (G) AB-Fubinaca using the optimum spray solvent systems as indicated by systematic characterization (seen in Figure 5 and Figure 6). Corresponding MS2 spectra are presented in the inset.
Of specific importance to this work was establishing the relative ionization efficiency of our next-generation, spray-based ion sources for cannabinoid evidence types when employing these variable spray solvent systems. For this, the ionization efficiency can be inferred from the corresponding mass spectral ion signals collected and averaged from replicate measurements from a static deposited mass of cannabinoid analyte (i.e., 100 ng deposited). PSI-MS signal intensities obtained for each cannabinoid using the target compositions (1:0, 9:1, 3:1 and 1:1, v/v) of the MeOH:H2O and ACN:H2O solvent systems acidified with formic acid (0.1%, v/v) are compared in Figure 5. Note that the maximum ion signal intensity obtained on the MS employed is 4000 arbitrary units (AU). For a better visualization, as well as to serve as quick reference guide for future method operators, heat maps were created, as seen in Figure 6. Here, the red-to-green transition corresponds to ion signal intensities ranging from 0 to 4000 AU. Across both graphs, it is apparent that the 9:1 proportion produced the highest ionization efficiency for both solvent systems. Correspondingly, this shows that the level of organic solvent is critical, but also needs to be cut with some amount of water; this is supported by the fact that the 1:0 compositions performed relatively poorly compared to the 9:1 mixtures. When comparing both spray solvent systems, the ACN:H2O compositions were the highest performing, with the 9:1 ACN:H2O w/0.1% FA producing admirable results for all cannabinoids tested. These cumulative results support the observations carried out on the authentic cannabinoid-based evidence (Figure 3).
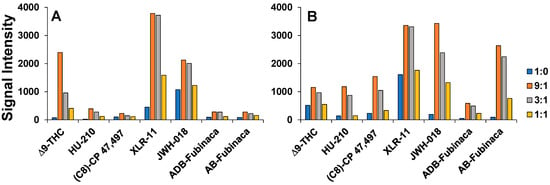
Figure 5.
Bar chart comparison of cannabinoid analyte signal obtained via PSI-MS using various (A) MeOH:H2O and (B) ACN:H2O systems. Concentrations of organic–aqueous solvent systems are 1:0, 9:1, 3:1, 1:1, by volume, with 0.1% formic acid added to assist analyte protonation. Maximum signals obtainable are 4000.

Figure 6.
Heat maps visually representing signal intensity of synthetic cannabinoid detection using different solvent systems during PSI-MS analysis.
3.3. Relation of Experimental Observations to Physicochemical Aspects Related to PSI-MS of Cannabinoids
The observation that the 9:1 ACN:H2O system produced the most efficient and broadly applicable data from target cannabinoids can be explained by both aspects of the PSI-MS ionization mechanism and the physicochemical properties of this analyte class. Generally, the efficiency of PSI-MS ionization will depend on the properties of the paper substrate [35,48] employed and the prowess of the spray solvent [49] used for both extracting and moving the analyte to the triangular tip and generating sustainable spray-based ionization. The application of a spray solvent initiates analyte transport through the paper substrate by capillary action after the substrate has been appreciably dissolved; hence, solubility and wettability are both critical here. The paper substrates employed consist of a framework of cellulosic molecules which are hydrogen bonded and have pore sizes that depend on the type of material used; this, correspondingly, establishes the pore size and filtering ability of the filter paper. In PSI-MS, the analyte is spotted, swabbed, or dabbed onto said paper, whereby it can bind to the cellulosic porous material through several physicochemical mechanisms. This binding can affect signal intensity [41], with a lower intensity suggesting stronger binding between the analyte and the paper substrate and hence slower diffusion upon application of the spray solvent [50]. Solvents play a crucial role in the extraction, transportation, and ionization of the analyte from or on the paper substrate, directing generated ions into the MS inlet system for analysis [51]. When considering spray solvents for both spray-based ion sources and LC-MS methods (which utilize ESI-MS for ionization), crucial criteria include overall eluent strength and the efficient generation of electrospray plumes. Said plume, referred to as the Taylor cone, which emanates from the emitter employed (e.g., ESI capillary, triangular paper, etc.), can be dramatically affected by the solvent’s attributes such as surface tension, dielectric constant, polarity, and boiling point [52]. Correspondingly, the solvent mixtures of MeOH or ACN with H2O examined here affect such parameters, enhancing or attenuating signal intensities, depending on the proportions employed.
Further, completely wetting the paper substrate with the deposited spray solvent is critical, as it is the solvent bridge that allows for the conduction of a high voltage to the triangular tip to produce said Taylor cone plume. A high potential of ~4.0 kV applied via a clamping electrode generates an electric field between the triangular egress and the MS inlet, resulting in charge accumulation at the apex of the paper cone, owing to the deformation of bulk liquid (comprising both the spray solvent and extracted analytes that have properly migrated) found in this region. As this occurs, the surface of the liquid attempts to retain its original shape to minimize unfavorable energetic conditions, all while the columbic repulsive force of the accumulated charges also increases. Once this force reaches a magnitude equivalent to the surface tension of the solvent (i.e., when the Rayleigh stability limit is attained), a Taylor cone forms, thus initiating the electrospray process [53]. This causes the bulk liquid to erupt into a spray of charged droplets which undergo cycles of solvent evaporation and further columbic fission to eventually release desolvated, gas-phase analyte ions sampled via the vacuum inlet for mass analysis. This process, which occurs in ambient conditions, is partially depicted in Figure 2. As anticipated, any change to the employed solvent system can cause corresponding performance changes to any of these aspects of these mechanisms.
Taylor cone generation is a combined effect of the surface tension and the dielectric constant of the spray solvent employed, with lower values reducing the onset voltage of the electrospray and the onset voltage of discharge (which can occur between the emitter used and the MS inlet), respectively [54,55]. Hence, MeOH with slightly lower values for these parameters [54,55] would be expected to produce slightly higher signal intensities. Contrary to this, higher intensities were observed for the ACN:H2O system. The key difference between MeOH and ACN is that the former is a polar-protic and the latter is a polar-aprotic solvent. Hence, the positive ions of interest in this analyte class will be preferentially solvated in ACN, while MeOH favors negative ion solvation [56]. Furthermore, due to the hydrophobic nature of most cannabinoids [57], the migration rate of these compounds through the paper substrate would be highest when utilizing the least polar of the solvent systems (9:1 ACN:H2O) [56]. The lower polarity and aprotic nature of ACN, combined with its higher boiling point (i.e., slower evaporation rate from the paper substrate) compared to MeOH provides sufficient time for the analytes to be extracted at higher relative concentrations into the solvent [54], which also accounts for the higher ion signal intensities observed for ACN-H2O systems. However, the lowest intensities are observed with the 1:0 anhydrous compositions of the solvent systems, indicating that a slight amount of H2O is necessary for spray-based ion sources. All ESI-like mechanisms involve the generation of a Taylor cone to produce an efficient spray, which operates with a balance between the onset voltage and the surface tension of the solvents involved; hence, the presence of some water, with its higher surface tension, is critical for producing stable spray plumes [58]. Further, the addition of water increases the surface tension of the spray solvent to facilitate the formation of a Taylor cone with a concomitant concentration of positive charges (at the tip when like voltage is applied), increasing the probability of protonation through the charge residue model (CRM) that is generally accepted for small molecule analysis via ESI-like ionization mechanisms. While said charged materials, particularly free protons and alkali earth metals, can come from the added water, the majority of protonation is the result of the acid added for preferential positive ionization (i.e., 0.1% formic acid).
4. Conclusions
The systematic characterization studies reported herein show that the spray solvent applied to induce ionization in spray-based ambient MS ion sources can dramatically affect both spectral intensity and signal duration, and in some circumstances, can lead to deleterious false negative responses. As the use of such methods in forensic science settings often involves the presumptive identification of broad evidence types, as well as the inherent persecutorial impact of the data obtained, the reliability of contraband detection with any employed technology is paramount. Further, examining every potential combination of drug analyte/ionization method/solvent system through systematic experimentation is overly burdensome, given the ever-growing population of novel psychoactive substances and new synthetic analogues. In this way, better guidance on entry-level spray solvent systems for the general screening of the common classes of evidence and/or contraband is informative. This work helps to provide such guidance for naturally occurring and synthetic cannabinoid evidence types, which supports the broad use of acetonitrile-based systems to strike a balance between analyte solubility concerns and the spray ionization dynamics of spray-based MS ion sources. More granular guidance is found in the heat maps provided for specific synthetic analogues and/or structural functionalities. With the continued reports of novel synthetic cannabimimetics and the prevalence of young adults using unregulated products containing Δ8-THC, it is anticipated that such studies involving next-generation instrumental techniques [59,60,61] could prove to be useful for forensic science practitioners and public health decision makers alike.
Author Contributions
S.M. and E.H.B. led manuscript creation, as well as the development of the FCSI-MS methodology reported in this work. S.M., S.E.B. and C.D. conducted all evidentiary investigations and solvent optimization studies on the FLIR Systems AI-MS 1.2 and the corresponding data analysis. C.C.M. was the primary investigator for this work, and all instrumentation development and applications were conducted in his laboratory. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This project was supported by Award No. 2015-IJ-CX-K011, awarded by the National Institute of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice. The opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Department of Justice.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Bloomington (IL) Police Department for their assistance with experiments involving authentic forensic evidence containing synthetic cannabinoids.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- May, B.; Naqi, H.A.; Tipping, M.; Scott, J.; Husbands, S.M.; Blagbrough, I.S.; Pudney, C.R. Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists detection using fluorescence spectral Fingerprinting. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12971–12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, E.; Tabrizchi, R.; Daneshtalab, N. Pharmacognosy and effects of cannabinoids in the vascular system. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 1034–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bills, B.; Manicke, N. Using sesame seed oil to preserve and preconcentrate cannabinoids for paper spray mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSohly, M.A.; Gul, W.; Wanas, A.S.; Radwan, M.M. Synthetic cannabinoids: Analysis and metabolites. Life Sci. 2014, 97, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Baggi, T.R. Analytical methods for herbal products containing synthetic cannabinoids: A review. Forensic Chem. 2022, 27, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Liu, W.; Xiang, P.; Zhao, J. Quantitative analysis of three synthetic cannabinoids MDMB-4en-PINACA, ADB-BUTINACA, and ADB-4en-PINACA by thermal-assisted carbon fiber ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 34, 2316–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Pirard, S.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids: Epidemiology, pharmacodynamics, and clinical implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 144, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.M.; McDaniel, T.J.; Fedick, P.W.; Mulligan, C.C. The current role of mass spectrometry in forensics and future prospects. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 3974–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Nguyen, K.; Stelmack, A.R.; Clowser, P.C.; Holtz, J.M.; Mulligan, C.C. Fieldable mass spectrometry for forensic science, homeland security and defense applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2021, 40, 628–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umebachi, R.; Saito, T.; Aoki, H.; Namera, A.; Nakamoto, A.; Kawamura, M.; Inokuchi, S. Detection of synthetic cannabinoids using GC-EI-MS, positive GC-CI-MS, and negative GC-CI-MS. Int. J. Legal Med. 2017, 131, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutsu, M.; Sugie, K.-I.; Saito, K. Analysis of 62 synthetic cannabinoids by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with photoionization. Forensic Toxicol. 2017, 35, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerace, E.; Seganti, F.; Di Corcia, D.; Vincenti, M.; Salomone, A. GC-MS identification and quantification of the synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-4en- PINACA in cannabis-derived material seized in the Turin metropolitan area (Italy). Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 2618–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabenauer, M.; Krol, W.L.; Wiley, J.L.; Thomas, B.F. Analysis of synthetic cannabinoids using high-resolution mass spectrometry and mass defect filtering: Implications for nontargeted screening of designer drugs. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5574–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet, C.T.; Tarifa, A.; DeCaprio, A.P. Comprehensive analysis of synthetic cannabinoids and metabolites in oral fluid by online solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 7937–7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorensen, M.D.B.B.; Hayat, S.Y.; Wellner, N.; Bjarholt, N.; Janfelt, C. Leaves of cannabis sativa and their trichomes studied by DESI and MALDI mass spectrometry imaging for their contents of cannabinoids and flavonoids. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, R.A.; Domin, M.A.; Walling, M.A.; Shepard, J.R.E. Rapid identification of synthetic cannabinoids in herbal samples via direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiak, A.D.; Musah, R.A.; Domin, M.A.; Shepard, J.R.E. DART-MS as a preliminary screening method for “Herbal Incense”: Chemical analysis of synthetic cannabinoids. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 59, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habala, L.; Valentová, J.; Pechová, I.; Fuknová, M.; Devínsky, F. DART—LTQ ORBITRAP as an expedient tool for the identification of synthetic cannabinoids. Leg. Med. 2016, 20, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-H.; Hsieh, H.-Y.; Hsu, C.-C. Clinical application of ambient ionization mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 6, S0060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirro, V.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Vincenti, M.; Cooks, R.G. Direct drug analysis from oral fluid using medical swab touch spray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida de Paula, C.C.; Lordeiro, R.A.; Piccin, E.; Augusti, R. Paper spray mass spectrometry applied to the detection of cocaine in simulated samples. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 9145–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, R.R.; Larson, R.L. Validation of the direct analysis in real time source for use in forensic drug screening. J. Forensic Sci. 2009, 54, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, Z.E.; Traub, A.; Fatigante, W.L.; Mancias, J.; O’Leary, A.E.; Hall, S.E.; Wieland, J.R.; Oberacher, H.; Gizzi, M.C.; Mulligan, C.C. Analytical validation of a portable mass spectrometer featuring interchangeable, ambient ionization sources for high throughput forensic evidence screening. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, A.; Nefliu, M.; Cooks, G.R. Ambient desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Bai, H.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Rapid analysis of synthetic cannabinoids using a miniature mass spectrometer with ambient ionization capability. Talanta 2015, 142, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasecolo, L.; Dabija, L.G.; Shouk, R.; Shouk, D.; Augusti, R.; Ifa, D.R. Application of sandpaper spray ionization mass spectrometry to comprehensively examine maple leaves infected with distinct fungi. J. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 59, e5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatigante, W.L.; Mukta, S.; Lawton, Z.E.; Bruno, A.M.; Traub, A.; Gasa, A.J.; Stelmack, A.R.; Wilson-Frank, C.R.; Mulligan, C.C. Filter cone spray ionization coupled to a portable MS system: Application to on-site forensic evidence and environmental sample analysis. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.M.; McDaniel, T.J.; West, C.P.; Bondzie, E.H.; Aldeman, M.R.; Molnar, B.T.; Mulligan, C.C.; Fedick, P.W. Characterization and optimization of a rapid, automated 3D-printed cone spray ionization-mass spectrometry (3D-PCSI-MS) methodology. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 474, 116781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.M.; McDaniel, T.J.; Doppalapudi, K.; Mulligan, C.C.; Fedick, P.W. Rapid, in-situ detection of chemical warfare agent simulants and hydrolysis products in bulk soils by low-cost 3D-printed cone spray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 2021, 146, 3127–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedick, P.W.; Fatigante, W.L.; Lawton, Z.E.; O’Leary, A.E.; Hall, S.E.; Bain, R.M.; Aryton, S.T.; Ludwig, J.A.; Mulligan, C.C. A low-cost, simplified platform of interchangeable, ambient ionization sources for rapid, forensic evidence screening on portable mass spectrometric instrumentation. Instruments 2018, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.T.; Pulliam, C.J.; Ouzang, Z.; Cooks, G.R. Miniature and fieldable mass spectrometers: Recent advances. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmack, A.R.; Mukta, S.; Fatigante, W.L.; Clowser, P.C.; Holtz, J.M.; Mulligan, C.C. Assessing the environmental ruggedness of paper spray ionization (PSI) coupled to a portable mass spectrometer operated under field conditions. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 472, 116776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, T.J.; Holtz, J.M.; Bondzie, E.H.; Overfelt, M.; Fedick, P.W.; Mulligan, C.C. Rapid screening of high priority N-nitrosamines in pharmaceutical, forensic, and environmental samples with paper spray ionization and filter cone spray ionization-mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondzie, E.H.; Adehinmoye, A.; Molnar, B.T.; Fedick, P.W.; Mulligan, C.C. Application of a modified 3D-PCSI-MS ion source to on-site, trace evidence processing via integrated vacuum collection. J. Am. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 35, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Manicke, N.E.; Lin, J.-M.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Development, characterization, and application of paper spray ionization. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, E.M.; Mach, P.M.; Dhummakupt, E.S.; Dowling, S.; Carmany, D.O.; Demond, P.S.; Rizzo, G.; Manicke, N.E.; Glaros, T. Paper spray ionization: Applications and perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomou, M.G.; Blades, A.T.; Kebarle, P. Electrospray mass spectrometry of methanol and water solutions suppression of electric discharge with SF6 gas. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1991, 2, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badu-Tawiah, A.K.; Eberlin, L.S.; Ouyang, Z.; Cooks, R.G. Chemical aspects of the extractive methods of ambient ionization mass spectrometry. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2013, 64, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.; Kim, S. Optimization and application of paper-based spray ionization mass spectrometry for analysis of natural organic matter. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12027–12034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, M.; Krieger, A.; Wygant, B.R.; Garza, K.Y.; Mullins, C.B.; Eberlin, L.S. Spatially controlled molecular analysis of biological samples using nanodroplet arrays and direct droplet aspiration. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsihuay, D.; Qiu, J.; Swaroop, S.; Nagornov, K.O.; Kozhinov, A.N.; Tsybin, Y.O.; Kuang, S.; Laskin, J. Imaging of triglycerides in tissues using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization (Nano-DESI) mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 448, 116269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberlin, L.S.; Ferreira, C.R.; Dill, A.L.; Ifa, D.R.; Cheng, L.; Cooks, R.G. Nondestructive, histologically compatible tissue imaging by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 2129–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bills, B.J.; Kinkade, J.; Ren, G.; Manicke, N.E. The impacts of paper properties on matrix effects during paper spray mass spectrometry analysis of prescription drugs, fentanyls and synthetic Cannabinoids. Forensic Chem. 2018, 11, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Manicke, N.E. Development of a paper spray mass spectrometry cartridge with integrated solid phase extraction for bioanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6212–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, D.E.; Davis, K.M.; Moreira, C.R.; Capone, P.; Cruttenden, R.; Badu-Tawiah, A.K. Direct biofluid analysis using hydrophobic paper spray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1878–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, S.A.; Saatchi, A.; Palaty, J.; Gill, C.G. A Direct mass spectrometry method for cannabinoid quantitation in urine and oral fluid utilizing reactive paper spray ionization. Analyst 2022, 147, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.E.; O’Leary, A.E.; Lawton, Z.E.; Mulligan, C.C. Trace level screening of chemicals related to clandestine desomorphine production with ambient sampling, portable mass spectrometry. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 8571928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z. A Silica coated paper substrate: Development and its application in paper spray spectrometry for rapid analysis of pesticides in milk. Analyst 2015, 140, 8048–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Manicke, N.E.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Silica coated paper substrate for paper-spray analysis of therapeutic drugs in dried blood spots. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, E.L.; Kulyk, D.S.; Ansu-Gyeabourh, E.; Sahraeian, T.; Pezza, H.R.; Badu-Tawiah, A.K. Direct analysis of doping agents in raw urine using hydrophopic paper spray mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; McLuckey, M.N.; Ouyang, Z. Analysis of biological sample using paper spray mass spectrometry: An investigation of the impacts by the substrate, solvents and elution methods. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboni, N.; Quaranta, A.; Motwani, H.V.; Osterlund, N.; Graslund, A.; Bianchi, F.; Ilag, L.L. Solvent assisted paper spray ionization mass spectrometry (SAPSI-MS) for the analysis of biomolecules and biofluids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G. Disintegration of water drops in an electric field. Proc. R. Soc. A 1964, 280, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.W.; Tipple, C.A.; Yost, R.A. Application of paper spray ionization for explosive analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.N.; Flagan, R.C.; Beauchamp, J.L. Droplet evaporation and discharge dynamics in electrospray ionization. J. Phys. Chem. 2002, 106, 9957–9967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, T.; Juhler, R.K.; Svensmark, B.; Chec, N.B. The relative influence of acidity and polarity on responsiveness of small organic molecules to analysis with negative ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, V.; O’Dwyer, R.; Laur, D.; Tan, J.; Consta, S. Relation between ejection mechanism and ion abundance in electric double layer of droplets. J. Phys. Chem. 2021, 14, 2954–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebarle, P.; Verkerk, U.H. A Brief Overview of the Mechanisms Involved in Electrospray Mass Spectrometry. Available online: https://application.wiley-vch.de/books/sample/3527323511_c01.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Mulligan, C.C.; O’Leary, A.E. Assessing the Probative Value of Physical Evidence at Crime Scenes with Ambient Mass Spectrometry and Portable Instrumentation, Technical Report for NIJ Grant No. 2011-DN-BX-K552; Doc. No. 248884; National Institute of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 1–128. Available online: https://www.ojp.gov/library/publications/accessing-probative-value-physical-evidence-crime-scenes-ambient-mass (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Mulligan, C.C.; Wieland, J.R.; Gizzi, M.C. Analytical Validation and Impact Assessment of On-Site Evidence Screening via Ambient Sampling, Portable Mass Spectrometry, Technical Summary for NIJ Grant No. 2015-IJ-CX-K011; Doc. No. 251910; National Institute of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 1–10. Available online: https://www.ojp.gov/library/publications/analytical-validation-and-impact-assessment-site-evidence-screening-ambient (accessed on 29 May 2024).
- Mulligan, C.C.; Driskell, J.D.; Kim, J.-H.; Wieland, J.R. Coupling Raman Spectroscopy with Ambient Sampling, Portable Mass Spectrometry for On-site, High-Throughput Evidence Confirmation on a Single Instrumental Platform, Technical Summary for NIJ Grant No. 2017-R2-CX-0022; Doc. No. 255670; National Institute of Justice: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 1–20. Available online: https://www.ojp.gov/ncjrs/virtual-library/abstracts/coupling-raman-spectroscopy-ambient-sampling-portable-mass (accessed on 29 May 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).