Abstract
In this work, we studied a disease outbreak that affected meagre (Argyrosomus regius) at a temperature of 14–15 °C, and that reached a mortality rate of 45% in one week. Moribund fish showed neither external nor internal signs of disease. However, a large number of bacteria, phenotypically similar and in pure culture, were recovered from the liver and kidney. A further phenotypic, genotypic and serological characterization of a selection of three isolates (a828, a834 and a842) allowed the identification of them as Vibrio tapetis. Phylogenetic analysis placed the isolates within the subspecies tapetis, being clearly differentiated from the subspecies britannicus and quintayensis. Nevertheless, all the isolates showed some phenotypic discrepancies with the type strain CECT 4600T; also, they proved to belong to a different O-serotype and genogroup (according to REP-PCR analysis) than the type strain. A virulence evaluation performed in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) by intraperitoneal injection using isolate a828 in two different doses (1 × 105 and 3 × 108 cfu/fish) led to mean mortality rates of 30% and 60%, respectively, corroborating its potential to cause significant mortalities in fish. To our knowledge, this is the first evidence of pathogenic Vibrio tapetis isolates associated with disease outbreaks in meagre.
1. Introduction
Vibrio tapetis [1,2] is a bacterial pathogen primarily known to be the etiologic agent of brown ring disease (BRD), a disease that especially affects Manila clams (Ruditapes philippinarum). The disease, first described in 1987, caused massive mortalities in this species in Brittany (France), and was subsequently detected in other species of bivalve mollusks (Ruditapes decussatus, Venerupis aurea, Tapes rhomboides, etc.), in a growing geographical area (Spain, United Kingdom, Italy, Korea, Norway, etc.) [3,4,5,6]. Despite being a pathogen primarily associated with bivalve disease, V. tapetis has also been isolated in an increasing number of marine fish species, both wild and farmed. Thus, it has been associated with disease outbreaks in Corkwing wrasse Symphodus melops in Norway [7], Atlantic halibut Hippoglossus hippoglosus in Scotland [8], Wedge sole Dicologlossa cuneata in Spain [9], Dover sole Solea in Belgium [10], in several species of wrasse (Corkwing wrasse S. melops, Ballan wrasse Labrus bergylta, Goldsinny wrasse Ctenolabrus rupestris) in Norway [11], in Fine flounder Paralichthys adspersus and red conger eel Genypterus chilensis in Chile [12] and in Common dab Limanda in the North Sea [13]. The possible involvement of this bacterium as a pathogen also in meagre (Argyrosomus regius) has been indicated by Cardenas et al. [14], who obtained an isolate identified as V. tapetis from a single specimen that presented lesions. However, the relationship between this bacterium and mortality is not clear since, in many cases, the isolates recovered from sick fish have been unable to cause mortality in experimental challenges [8,9,11,12,14]. Although V. tapetis was initially considered a homogenous taxon, obtaining isolates from different hosts and geographical origins has shown that there are intraspecific variations at the biochemical, serological and genetic levels. Thus, three different subspecies have been described based on phenotypic and genetic criteria (subsp. tapetis, subsp. britannicus and subsp. quintayensis) [12,15], and at least 5 serotypes [11].
In this work, we report the isolation of V. tapetis from an outbreak of high mortality in meagre (A. regius), a candidate species for diversification of marine aquaculture in southern Europe. The characterization, typing and pathogenic potential evaluation of these isolates are presented.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation
Meagre juveniles (80 g average body weight) were kept at the IFAPA Centro Agua del Pino experimental facilities (Huelva, Spain) in re-circulating 600 L fiberglass tanks (24 fish/tank) with natural photoperiod and a flow rate of 2 m3 h−1. Values of physicochemical parameters were <0.04 mg L−1 for total ammonia, <0.02 mg L−1 for total nitrite, 6.7 mg L−1 for dissolved oxygen, and 33 PSU. Water temperature was 18–20 °C until a sharp drop to 14–15 °C occurred. Moribund fish were killed with phenoxyethanol and aseptically necropsied. For bacterial isolation, tissue samples (liver and kidney) were streaked onto Flexibacter maritimus medium (FMM) [16] and aerobically incubated at 15 °C. For long-term preservation, isolates were frozen at −80 °C in sterile seawater supplemented with 20% (v/v) glycerol.
2.2. Phenotypic Characterization
Phenotypic characterization was performed according to López et al. [17], including the following tests: gram staining, glucose fermentation/oxidation test (OF), cytochrome oxidase activity, catalase production, growth at different temperatures (4, 15, 25, 30, 35, 40 and 45 °C), tolerance of salinity (0, 3, 6, 8, 10 and 12% NaCl), growth on TCBS agar, hydrolysis of starch, tween 20, tween 80, casein and lecithin. Hemolysis activity was assayed on FMM agar with 5% gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) blood. Drug susceptibility (presence/absence of halo, according to Buller [18]) to antimicrobial compounds was determined on Mueller Hinton and FMM by the disc diffusion method for novobiocin (30 µg/disc) and the vibriostatic agent O/129 (150 µg/disc) (Oxoid). Antibiogram readings were performed after 48 h incubation at 20 °C.
All tests were incubated aerobically at 20 °C. Commercial miniaturized API 20E galleries (bioMerieux, Madrid, Spain) and Biolog GN2 Micro-Plates (BIOLOG, CA, USA) were also utilized according to the manufacturer’s instructions, but sterile seawater was used as a diluent and 20 °C as the incubation temperature (48 h). The type strains of the three recognized V. tapetis subspecies (V. tapetis subsp. tapetis CECT 4600T, V. tapetis subsp. britannicus HH6087T and V. tapetis subsp. quintayensis QL-9T) were characterized together with the isolates under study with the same methodology.
Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) from isolate a828 and CECT 4600T, grown at 20 °C on Marine Agar plates, was performed in CECT (Universitat de Valencia) according to the instructions of the Microbial Identification System (MIDI) as described by Sasser [19]. FAMEs were analyzed by gas chromatography in an Agilent 6850 system using the MIDI operating system and the aerobic bacteria library TSBA6 [20].
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
DNA extraction from pure cultures was performed using the boiling method (5 min in distilled water, spin for 2 min at 13,200 rpm). DNA concentration and purity were calculated from measurements of absorbance at 260 and 280 nm, using a NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Partial 16S rRNA, gyrB, rpoD and rpoA gene sequences were obtained as previously described [21,22,23,24]. PCRs were basically performed as indicated in the literature: in each case in a total reaction volume of 25 µL, using the commercial kit MyTaqTM DNA Polymerase (Bioline, Cincinnati, OH, USA). PCR products were purified with the commercial kit illustra ExoProStar 1-step (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Direct sequencing of purified PCR products was performed by Secugen, S.L. (Madrid, Spain). The sequences were analyzed using Chromas LITE 2.1 (Technelysium Pty Ltd, Brisbane, Australia) and BioEdit 7.2 [25] programs and subjected to BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 17 October 2022), and EzTaxon (http://www.ezbiocloud.net/eztaxon, accessed on 17 October 2022) searches to retrieve the most closely related sequences. Concatenated gene sequences were constructed by joining the in-frame sequences in the following order: 16S-rpoD-rpoA-gyrB (911, 768, 756 and 513 nt, respectively). Sequence similarities were calculated using SIAS software (imed.med.ucm.es/Tools/sias.html, accessed on 24 October 2022). DNA sequences were aligned with others from related species using Clustal Omega software (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo, accessed on 24 October 2022), and phylogenetic trees were constructed according to the neighbor-joining method [26] by using the program MEGA X [27]. The accuracy of the resulting tree was measured by bootstrap resampling of 1000 replicates.
2.4. Serological and Molecular Typing
Three isolates were subjected to serological typing using the dot-blot technique, according to [28]. Heat stable O antigens of the V. tapetis isolates and antisera against V. tapetis subsp. tapetis CECT 4600T, V. tapetis subsp. tapetis GR0202RD, and V. tapetis subsp. britannicus HH6087T were prepared following the protocols of Magariños et al. [29].
In order to analyze intraspecific genetic variability between the meagre isolates, molecular typing was performed using the repetitive extragenic palindromic (REP)-PCR technique. Analysis was performed as previously described [30] using the commercial kit MyTaqTM DNA Polymerase (Bioline) in a Veriti 96 well Thermal Cycler (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) and using a 100 ng DNA template for each strain. PCR products were electrophoresed on a 2% agarose TBE gel stained with SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). A 100 bp DNA gtP-Ladder molecular weight marker (gTPbio) was included as a molecular weight marker.
Reproducibility was assessed by two independent assays. The similarity between isolates and the V. tapetis type strain was estimated using the Dice similarity coefficient (SD) [31] with the software FAMD [32].
2.5. Pathogenicity Assays
In order to evaluate the pathogenic potential of the bacteria recovered from meagre, a representative isolate (a828) was selected to perform two experimental infections by intraperitoneal injection, using two different doses of bacteria (1 × 105 cfu/fish and 3 × 108 cfu/fish). The challenges were carried out with European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) (n = 10) of 4 (±0.4) g and 12 (±1.2) g weights for the low and high dose, respectively. Each assay was made in duplicate. Bacteria were grown in FMM at 15 °C for 24 h, and bacterial concentration was estimated by absorbance of bacterial cultures at 600 nm wavelength. After recovery by centrifugation, bacteria were washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and finally resuspended in PBS. Doses were confirmed with total viable counts after spreading 0.1 mL volumes of each dose over the surface of duplicate plates of FMM. A control group (challenged with PBS only) of 10 fish was included in each virulence assay. After the bacterial challenge, experimental and control fish were kept without feeding on 18 L tanks at 15 °C in continually flowing seawater, and mortalities were recorded daily for an 11 d period. Dead fish were removed and subjected to bacteriological examination.
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Isolation
During February 2017, an epizootic outbreak occurred in juvenile meagre reared in fiberglass tanks as previously described. The outbreak took place at a water temperature of 14–15 °C and reached a mortality rate of 45% (11 dead) in a week. Although dying, affected fish showed no external or internal signs of disease (Figure 1). The gills of the affected fish were observed under a microscope to detect parasites, obtaining, in all cases, negative results (data not shown). However, numerous cream colonies appeared in pure culture in the culture plates from the liver and kidney of all the sampled fish. A selection of 16 isolates from the 8 sampled fish was made, and a preliminary characterization showed that all these isolates shared a similar phenotypic profile. Then, three isolates from different fish (a828 and a834, recovered from the liver; and a842, recovered from the kidney) were subjected to further biochemical, serological, and molecular characterization to identify the apparent etiological agent of the mortalities.

Figure 1.
Juvenile meagre naturally infected by V. tapetis. No macroscopic external or internal signs of disease were apparent.
3.2. Phenotypic Characterization
The colonies of the isolates under study were cream in color, not luminescent, not adhering to agar, and consisting of gram-negative, fermentative rods. All isolates were cytochrome oxidase and catalase positive. Growth was observed at 4 and 25 °C, but not at 30 °C. All isolates grew in 3% NaCl, but none in 0% or 6–12% NaCl. All isolates were able to grow in TCBS, displaying green colonies. Arginine dihydrolase, lysine decarboxylase and ornithine decarboxylase tests were negative. Hydrolysis of starch, tween 20, tween 80, casein and lecithin were positive, but hemolytic activity was not observed. In API 20E galleries, all isolates showed positive results for indole and acetoin (Voges-Proskauer test) production, beta-galactosidase (weak positive), gelatinase, acid production from glucose, and nitrate reduction. Drug susceptibility tests revealed the presence of clear halos in all the isolates with both novobiocin and O129, both in FMM and Mueller Hinton. Similar results were displayed by the type strain of V. tapetis CECT 4600T, except for the Voges-Proskauer test. The type strains of V. tapetis subsp. britannicus (HH6087T) and V. tapetis subsp. quintayensis (QL-9T) showed a higher number of discrepancies with the meagre isolates, mainly in API 20E profile (both strains were positive for acid production of mannitol, saccharose, melibiose and amygdalin). Biolog GN2 Micro-Plates were utilized with the isolates a828, a834 and a842, together with the type strain CECT 4600T. All utilized 15 carbon sources (α-cyclodextrin, dextrin, glycogen, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, D-fructose, α-D-glucose, maltose, D-mannose, β-methyl-D-glucoside, D-trehalose, succinic acid, L-aspartic acid, inosine, glycerol and D-glucose-6-phosphate). Variable results were found for 16 carbon sources (Table 1), whereas all isolates were negative for the remaining 63 tests. V. tapetis type strain can be clearly differentiated from the meagre isolates with the following six tests: N-acetyl-D-galactosamine, D-cellobiose, D-galactose, citric acid, D, L-lactic acid and bromosuccinic acid. The fatty acids analysis was performed for the type strain CECT 4600T, not available in the literature, and the isolate a828. Both bacteria showed similar FAME profiles. The major cellular fatty acids (> 4% of the total) in strain CECT 4600T and a828 were C16:0 (16.16% and 23.60%, respectively) and sum in features 2 (4.49%, 5.07%), 3 (59.31%, 48.40%), and 8 (10.96%, 10.37%).

Table 1.
Differences in carbon compound utilization between the V. tapetismeager isolates a828, a834 and a842, and V. tapetis CECT 4600T, determined using the BIOLOG GN system.
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
Partial sequences were obtained from isolates a828, a834 and a842 for 16S rRNA, gyrB, rpoD and rpoA genes (GenBnk/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers LR701177- LR701179, LR736249- LR736251, LT736266- LT736268, LR736276- LR736278). EzTaxon homology searches with 16S rDNA sequences placed the meagre isolates clearly within V. tapetis, although it did not allow discriminating between the three subspecies (isolates shared 99.7–100% similarity with the three V. tapetis subspecies type strains—tapetis CECT 4600T, britannicus HH6087T and quintayensis QL-9T, whereas values were below 98% with other related Vibrio species). Individually, gyrB, rpoD and rpoA genes showed a much higher resolving power than 16S, allowing both interspecies and subspecies discrimination. The gyrB sequences of the three isolates showed a similarity percentage of 99.8% with CECT 4600T but only 96.29% with QL-9T, 88.49% with HH6087T, and below 85% with other related species. Quite similar results were obtained with rpoD and rpoA genes. According to these results, multilocus sequence analysis using these genes clearly grouped the isolates recovered from meagre with the V. tapetis clade and, more concretely, with the subspecies tapetis (Figure 2). Concatenated partial sequences of the genes 16S rRNA, gyrB, rpoD and rpoA (2948 nt) shared 99.21–99.38% similarity with V. tapetis subsp. tapetis strains (meagre isolates shared 99.25–99.38%), but only 97.11% with V. tapetis subsp. quintayensis QL-9T and 96.16% with V. tapetis subsp. britannicus HH6087T. Similarity values with the type strains of other Vibrio species were always below 88%.
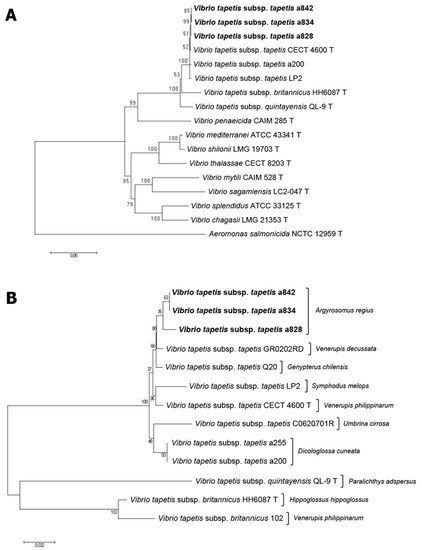
Figure 2.
(A): Phylogenetic tree based on concatenated sequences of four housekeeping genes (16S rDNA, rpoD, rpoA and gyrB; 2948 nt) by the neighbor-joining method, showing the relationships between the isolates recovered from meagre (in bold), and related species of the genus Vibrio. (B): Phylogenetic tree based on concatenated sequences of three housekeeping genes (16S rDNA, rpoD and rpoA; 2435 nt), showing the relationships between Vibrio tapetis strains recovered from meagre and other host species. The numbers at the nodes indicate the levels of bootstrap based on 1000 replicates.
3.4. Serological and Molecular Typing
No positive reaction was obtained in the dot-blot assay with any of the antiserum employed with the meagre isolates. Positive and negative control samples displayed the expected reactions.
In REP-PCR analysis, a unique profile (SD 1) was observed for all the meagre isolates (Figure 3). The most closely related profiles were that of the V. tapetis subsp. tapetis strains CECT 4600T (0.889) and a200/a255 recovered in the same facilities from wedge sole (0.632), whereas V. tapetis subsp. quintayensis QL-9T and V. tapetis subsp. britannicus HH6087T showed quite different profiles (SD of 0.421 and 0.235, respectively).
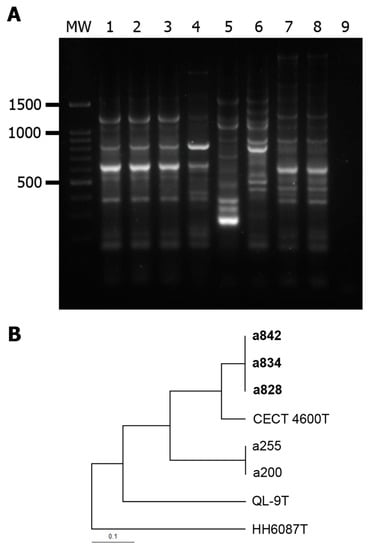
Figure 3.
(A): REP-PCR patterns of Vibrio tapetis strains. MW: 100 bp DNA Ladder; lanes 1 to 9: a828, a834, a842, V. tapetis subsp. tapetis CECT 4600T, V. tapetis subsp. britannicus HH6087T, V. tapetis subsp. quintayensis QL-9T, V. tapetis subsp. tapetis isolates a255 and a200 (recovered from wedge sole Dicologoglossa cuneata), and negative control. The numbers on the left indicate the position of the molecular size marker (in bp). (B): UPGMA dendrogram obtained using distance based on Dice coefficients from the REP profiles.
3.5. Pathogenicity Tests
Mortalities of 20–40% and 50–70% were registered in the groups of fish infected with two different doses of bacteria (1 × 105 and 3 × 108 cfu/fish, respectively). In most cases, mortalities took place within the first 4 days after exposure to the pathogen. As observed in the natural outbreak, dead fish did not show evident external or internal symptoms of the disease. However, the inoculated bacterium was recovered from all the dead fish. None of the control fish died during the assays.
4. Discussion
This paper describes the occurrence of Vibrio tapetis for the first time associated with a disease outbreak in meagre Argyrosomus regius, an economically important species that is being cultivated in southern Spain in a context of diversification of marine aquaculture. High mortality of 45% was observed in a week, and pure cultures were obtained from the internal organs of all the sampled fish. Two previous stressors could have triggered the appearance of the disease outbreak: a recent transfer of the fish between tanks in the fish farm and, on the other hand, the sharp drop in water temperature to 14–15 °C. In this regard, it is well-known that temperature plays an important role in the development of BRD, to the point that temperatures above 21 °C can prevent the disease in clams [4]. In fact, mortalities in fish associated with V. tapetis seem to take place mainly between 12 and 17 °C [8,9,12,13]. Despite the high mortality observed, any dead or moribund fish showed neither internal nor external signs of disease. This contrasts with that observed in other outbreaks involving V. tapetis affecting fish since, in most cases, the hosts showed skin discoloration and/or ulcers [9,10,12,13]. This lack of symptoms could be due to the concurrence of environmental (temperature), host (stress) or pathogen (virulence) factors that led the disease to follow an acute or per-acute course. In pathogens such as Aeromonas salmonicida or Flavobacterium columnare, it has been shown that factors such as the virulence of the strain, the age of the fish, etc., can lead to a chronic course of the disease (with the appearance of gross lesions before death), or to an acute course (with fulminant infections that cause death before macroscopically visible signs appeared) [33,34].
Bacteria identification was made, taking into account both phenotypic and genotypic data. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of the isolates were found to match with those previously reported for V. tapetis [18]. On the basis of these tests, the isolates belonging to the subspecies tapetis are easily differentiated from the subspecies britannicus and quintayensis. The phenotypic profile was basically similar to that of the type strain CECT 4600T, although some discrepancies were detected, mainly in API 20E and Biolog GN results. Interestingly, all the meagre isolates were found to be positive for the Voges-Proskauer test, a characteristic that seems to be unique to these isolates and that differentiates them from the strains described to date, including also other isolates previously recovered in the same place from wedge sole.
Analysis of different housekeeping gene sequences corroborated the preliminary identification of the meagre isolates. Their 16S rDNA sequences showed similarity values clearly above the limit of intraspecific variability (98.7%) proposed by [35] between them and with the V. tapetis subspecies type strains, whereas these values were below 98% with other Vibrio species. Phylogenetic analysis based on concatenated genes was even more discriminating at the species level and also clearly placed these isolates within the subspecies tapetis strains cluster.
Phylogenetic affiliation of the V. tapetis strains usually matches with their O-serotype. Nevertheless, this is not always the case. Gulla et al. [11] proposed the existence of at least five different serotypes in this species (O1, O2, O3, O4, O5), all of them present among the representatives of the subspecies tapetis; on the other hand, other strains, including the type strain of the subspecies britannicus (HH6087T), probably represent one or more additional serotype(s). Nevertheless, these authors found that there is not an exact correlation between subspecies and serotypes since some strains in subspecies britannicus proved to belong to serotypes O2 and O3. In this work, we tested the meagre isolates using antisera against strains CECT 4600T (O1), GR0202RD (O2) and HH6087T, with negative results in all the cases. Further assays would be necessary to elucidate if they belong to the novel serotypes described by Gulla et al. [11] or represent a novel serotype within the species. On the other hand, molecular typing using REP-PCR showed a homogeneous group with a unique band profile. This was clearly different from that of the three type strains tested, but differences were much more relevant with the subspecies britannicus and quintayensis, which showed Dice´s coefficients much lower than that of CECT 4600T. In agreement with the differences previously observed in phenotypic and genotypic characterization, meagre isolates also showed a different profile to that of the wedge sole isolates a200 and a255, recovered in the same facilities [9].
Finally, virulence assays performed in seabass by intraperitoneal injection corroborated the pathogenicity of the isolates, although future works should still elucidate its pathogenicity for other fish species, including meagre. In these assays, both low and high doses caused significant mortality rates (mean values of 30% and 60%, respectively). Previous works made with V. tapetis strains have recorded contradictory results in the virulence of the species. Thus, Bergh & Samuelsen [36] and Gulla et al. [11] reported high mortalities in experimental infection tests carried out with V. tapetis isolates and different species of wrasses. However, the degree of pathogenicity of the bacterium remained to a certain point unclear since, in the first case, the authors reported relatively high mortalities in the negative control group, and in the second case the authors believed that the mortalities were due to acute toxicity because of the high bacterial concentration used. On the contrary, other works that involved different fish species and strains of subspecies britannicus [8], subspecies tapetis [9], and subspecies quintayensis [12], using bacterial doses in the same range as those used in this work reported no mortalities. These results could be due to different degrees of virulence of the strains employed and/or the susceptibility of the hosts [36]. Water temperature probably also played a role, affecting one or both of these factors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R.L., J.I.N. and J.L.R.; methodology, J.R.L. and J.L.R.; investigation, J.R.L., J.L.R. and M.L.-S.; resources, J.I.N. and J.L.R.; data curation, J.R.L. and J.L.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.R.L.; writing—review and editing, J.R.L., J.L.R., M.L.-S. and J.I.N.; project administration, J.I.N.; funding acquisition, J.I.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the program POCTEP (0433_BONAQUA_5_E POCTEP). J.R.L. held a postdoctoral grant from IFAPA supported by the European Union FEDER program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Andalusian Institute of Agricultural and Fisheries Research and Training (IFAPA) Junta de Andalucía (Spain) (Approval Code: NA; Date: 28 September 2018) and complied with the Guidelines of the European Union Council (2010/63/EU) for the use of laboratory animals.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Borrego, J.J.; Castro, D.; Luque, A.; Paillard, C.; Maes, P.; Garcia, M.T.; Ventosa, A. Vibrio tapetis sp. nov., the causative agent of the brown ring disease affecting cultured clams. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, C.; Maes, P. Etiologie de la Maladie de L’anneau Brun Chez Tapes Philippinarum: Pathogénicité d’un Vibrio sp. Available online: https://pascal-francis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=6656228 (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Allam, B.; Paillard, C.; Howard, A.; Le Pennec, M. Isolation of the pathogen Vibrio tapetis and defense parameters in brown ring diseased manila clams Ruditapes philippinarum cultivated in England. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2000, 41, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillard, C. A Short-Review of Brown Ring Disease, a vibriosis affecting clams, Ruditapes philippinarum and Ruditapes decussatus. Aquat. Living Resour. 2004, 17, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, C.; Korsnes, K.; Le Chevalier, P.; Le Boulay, C.; Harkestad, L.; Eriksen, A.; Willassen, E.; Bergh, Ø.; Bovo, C.; Skår, C.; et al. Vibrio tapetis-like strain isolated from introduced Manila clams Ruditapes philippinarum showing symptoms of Brown Ring Disease in Norway. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 81, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-I.; Paillard, C.; Le Chevalier, P.; Choi, K.-S. Report on the occurrence of Brown Ring Disease (BRD) in Manila clam, Ruditapes philippinarum, on the West Coast of Korea. Aquaculture 2006, 255, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.; Samuelsen, O.; Andersen, K.; Torkildsen, L.; Lambert, C.; Choquet, G.; Paillard, C.; Bergh, Ø. Characterization of strains of Vibrio splendidus and V. tapetis isolated from corkwing wrasse Symphodus melops suffering vibriosis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2003, 53, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, H.I.; Duncan, H.L.; Laidler, L.A.; Hunter, D.; Birkbeck, T.H. Isolation of Vibrio tapetis from cultivated Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.). Aquaculture 2003, 221, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.R.; Balboa, S.; Núñez, S.; de la Roca, E.; de la Herran, R.; Navas, J.I.; Toranzo, A.E.; Romalde, J.L. Characterization of Vibrio tapetis strains isolated from diseased cultured wedge sole (Dicologoglossa cuneata Moreau). Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, A.; Chiers, K.; Soetaert, M.; Lasa, A.; Romalde, J.; Polet, H.; Haesebrouck, F.; Decostere, A. Vibrio tapetis Isolated from vesicular skin lesions in Dover sole Solea solea. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 115, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulla, S.; Rønneseth, A.; Sørum, H.; Vågnes, Ø.; Balboa, S.; Romalde, J.; Colquhoun, D. Vibrio tapetis from wrasse used for ectoparasite bio-control in salmon farming: Phylogenetic analysis and serotyping. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 125, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Levican, A.; Lasa, A.; Irgang, R.; Romalde, J.L.; Poblete-Morales, M.; Avendaño-Herrera, R. Isolation of Vibrio tapetis from two native fish species (Genypterus chilensis and Paralichthys adspersus) reared in Chile and description of Vibrio tapetis subsp. quintayensis subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercauteren, M.; De Swaef, E.; Declercq, A.; Bosseler, L.; Gulla, S.; Balboa, S.; Romalde, J.L.; Devriese, L.; Polet, H.; Boyen, F.; et al. First Isolation of Vibrio tapetis and an atypical strain of Aeromonas salmonicida from skin ulcerations in common dab (Limanda limanda) in the North Sea. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, S. Cultivo de Corvina (Argyrosomus regius); Cuadernos de Acuicultura; Fundacion Observatorio Español de Acuicultura, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas: Madrid, Spain, 2011; ISBN 978-84-00-09291-7. [Google Scholar]
- Balboa, S.; Romalde, J.L. Multilocus Sequence Analysis of Vibrio tapetis, the causative agent of Brown Ring Disease: Description of Vibrio tapetis Subsp. britannicus subsp. nov. System. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 36, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazos, F.; Santos, Y.; Macias, A.R.; Nunez, S.; Toranzo, A.E. Evaluation of media for the successful culture of Flexibacter maritimus. J. Fish Dis. 1996, 19, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.R.; Lorenzo, L.; Alcantara, R.; Navas, J.I. Characterization of Aliivibrio fischeri strains associated with disease outbreak in brill Scophthalmus rhombus. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 124, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, N.B. (Ed.) Bacteria and Fungi from Fish and Other Aquatic Animals: A Practical Identification Manual, 2nd ed; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-84593-805-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sasser, M. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newsl. 1990, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- MIDI Sherlock Microbial Identification System Operating Manual v. 6.12. 2012. Available online: http://midi-inc.com/pdf/Sherlock_MIS_Operating_Manual.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S Ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Labbate, M.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Alam, M.; Darling, A.; Melvold, J.; Holmes, A.J.; Johura, F.T.; Cravioto, A.; Charles, I.G.; et al. Indigenous Vibrio cholerae strains from a non-endemic region are pathogenic. Open Biol. 2013, 3, 120181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Harayama, S. Phylogenetic relationships of Pseudomonas putida strains deduced from the nucleotide sequences of gyrb, rpod and 16s rRNA genes. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.L.; Gevers, D.; Thompson, C.C.; Dawyndt, P.; Naser, S.; Hoste, B.; Munn, C.B.; Swings, J. Phylogeny and Molecular identification of vibrios on the basis of multilocus sequence analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5107–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A User-Friendly Biological Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriano, R.C.; Pyle, J.B.; Starliper, C.E.; Pyle, S.W. Detection of Vibrio anguillarum antigen by the dot blot assay. J. Wild. Dis. 1985, 21, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magariños, B.; Romalde, J.L.; Bandín, I.; Fouz, B.; Toranzo, A.E. Phenotypic, antigenic, and molecular characterization of Pasteurella piscicida strains isolated from fish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 3316–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.; López-Romalde, S.; Beaz, R.; Alonso, M.; Castro, D.; Romalde, J.L. Molecular fingerprinting of Vibrio tapetis strains using three PCR-based methods: ERIC-PCR, REP-PCR and RAPD. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 69, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluter, P.M.; Harris, S.A. Analysis of multilocus fingerprinting data sets containing missing data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R. Patologia de los Peces; Ediciones Mundi-Prensa: Madrid, Spain, 1981; ISBN 84-7114-104-3. [Google Scholar]
- Declercq, A.M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van den Broeck, W.; Bossier, P.; Decostere, A. Columnaris disease in fish: A review with emphasis on bacterium-host interactions. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Ebers, J. Taxonomic parameters revisited: Tarnished gold standards. Microbiol. Today 2006, 8, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bergh, Ø.; Samuelsen, O.B. Susceptibility of corkwing wrasse Symphodus melops, goldsinny wrasse Ctenolabrus rupestis, and Atlantic salmon Salmo salar smolt, to experimental challenge with Vibrio tapetis and Vibrio splendidus isolated from corkwing wrasse. Aquacult. Int. 2007, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).