Abstract
Wood is a versatile resource within the circular economy, widely used across various applications. However, in the European Union, demand for wood continues to rise, leading to increased reliance on imports. The pulp and paper industry, closely linked to wood production, is also experiencing supply shortages. To address these challenges, this study explores the use of wood waste (WW) as an alternative feedstock for pulp and glucose production. WW was collected from a mechanical treatment plant in Perugia, Italy, and processed using the organosolv method. This approach yielded a cellulose pulp with improved quality compared to previous research, achieving a cellulose content of 79.33% and a cellulose recovery rate of 94.59%. The optimized pulp was then subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis, producing 20.66 g of glucose per 100 g of initial WW, corresponding to a glucose concentration of 44.08 g/L and a cellulose digestibility of 51.03%. Additionally, a simulation model of a pilot-scale process was developed using Aspen PLUS software, assuming an annual processing capacity of approximately 5500 t of wood waste—equivalent to the quantity managed annually by a local waste treatment company in Perugia. This study highlights the potential of wood waste as a sustainable raw material for pulp and glucose production, supporting circular economy goals and laying the groundwork for future scale-up investigations.
1. Introduction
Wood is a renewable and versatile natural resource with significant physical and chemical properties, making it suitable for diverse applications, from construction and furniture to energy and chemicals [1]. As a material aligned with the principles of the bioeconomy and circular economy, its use has expanded beyond traditional purposes to include emerging sectors such as bioenergy, green construction, and biobased chemical production [2,3]. However, increasing demand, particularly within the European Union, has raised concerns over future supply constraints. It is projected that by 2030, demand for wood could surpass Europe’s domestic supply, intensifying the urgent need for alternative sourcing strategies [4]. For example, an undersupply of softwood has been reported in the Czech Republic, Germany, and Norway [5].
One such strategy involves the enhanced recovery and valorization of wood waste (WW), which is a growing byproduct of industrial processes, construction, households, and waste management systems. In 2022, the EU-27 treated approximately 41.40 Mt of WW [6]. The dominant pathways were energy recovery (51.38%) and recycling/backfilling (47.87%).
The three major producers of WW in EU are Germany, France, and Italy. They treated 10.61 Mt, 8.51 Mt, and 4.75 Mt, respectively. Germany predominantly uses energy recovery, accounting for 73.47% of its total treated WW. France employs a more balanced approach, with energy recovery at 48.52% and recycling at 51.24% of its treated WW. Italy, in contrast, prioritizes WW recycling, which constitutes 82.05% of its total treated WW [6].
Among recycling pathways, particleboard manufacturing has emerged as a leading example of cascading utilization, with some European countries such as Italy achieving a 95% use rate of recycled WW in panel production [7,8].
Despite this progress, WW remains a heterogeneous and often contaminated feedstock, presenting challenges to its integration into high-value recycling streams [9]. While incineration remains the most common form of recovery, alternative pathways such as composting, mulching, refuse-derived fuel, and pulp production are gaining interest [10,11,12]. In particular, the potential for producing pulp from WW offers a promising opportunity for industrial symbiosis, especially with the paper industry facing rising demand for recycled fibers and increased containerboard consumption [13]. Europe is still facing a significant undersupply of pulp, as evidenced by a negative trade balance of market pulp totaling 2.16 Mt [14].
Traditional pulp production, dominated by the kraft process, is associated with high environmental impacts, notably the emission of sulfur compounds [15]. In contrast, the organosolv process—especially ethanol-based variants—presents a cleaner alternative, yielding high-purity cellulose and lignin, and offering the potential for solvent recovery and reduced particulate emissions [16,17]. Ethanol organosolv has been successfully employed in some studies for pulping different types of wood, including softwood [18,19,20].
An ethanol-based organosolv process offers significant environmental benefits over traditional kraft methods, notably by eliminating sulfur compound emissions into the atmosphere. Beyond its ecological advantages, ethanol itself is an attractive solvent choice due to its lower cost compared to other organic alternatives, its straightforward recovery, and the excellent quality of its co-products, especially lignin [21].
This study aimed to confirm the feasibility of using WW as a feedstock for ethanol-based organosolv pulping, as shown in our preliminary work [22]. It further investigated the production of glucose from the resulting pulp and assessed the presence of heavy metals in the final products. Through a case study in Perugia, Italy, WW samples from municipal treatment plants were characterized and pulped to produce a cellulose pulp (CP) solid and technical lignin. Organosolv process parameters were optimized using design of experiments (DoE), following the results obtained in the previous work [22]. Subsequently, the CP was hydrolyzed to obtain glucose, thus evaluating this alternative recycling approach.
Finally, by integrating laboratory experimentation, a simulation model of a pilot-scale process was generated using Aspen PLUS, which provides the basis for future detailed research on process optimization and environmental assessment. This work aims to contribute to the development of a sustainable, high-value valorization pathway for WW within a circular bioeconomy framework.
2. Results and Discussion
The chemical characterization of WW was taken from Pazzaglia et al. [22] and is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Wood waste chemical composition.
As discussed in our previous work [22], this WW shows potential for use in cardboard production. However, the focus of this paper is to assess improvements in organosolv conditions to produce higher-quality pulp and evaluate its suitability for glucose production via enzymatic hydrolysis (EH), which relies on a WW pre-treatment to separate cellulose from lignin and hemicellulose. The results of these analyses are presented in the following section.
2.1. Organosolv Results and DOE Analysis
The chemical characterization of CP is shown in Table 2 for all 15 runs of DoE. In particular, cellulose, lignin, hemicellulose content, and cellulose recovery (CR) are displayed. Each run was characterized in triplicate, and the average values are reported. Table 2 shows the results.

Table 2.
Chemical characterization of cellulose pulp and cellulose recovery for all runs of the experiment.
The aim is to maximize CR and cellulose content, and on the other hand minimize lignin content, which could be an obstacle for the following EH [23]. Many runs show a lignin percentage higher than that of the initial biomass. This can be explained by the severe treatment conditions affecting several runs. Under these conditions, cellulose is also solubilized, leading to a higher lignin percentage. Considering this, runs #1 and #4 exhibit the most interesting results. These runs are the only ones that show a cellulose content over 70%, a CR over 85%, and a lignin content less than 22%.
Using these data, an optimum point was determined with Minitab 17 software (Minitab, Coventry, UK), yielding conditions of 175 °C, a 0.65 ethanol-to-water ratio (w/w), and 1.3% sulfuric acid (w/w). Table 3 presents the application of these conditions to all three samples (A, B, and C).

Table 3.
Characterization of cellulose pulp for samples A, B, and C after organosolv treatment under optimum conditions. CR and precipitated lignin with respect to their initial content in the raw material.
The optimization of the treatment yielded better results compared to those presented in our previous study [22]. The cellulose content increased to 79.33%, compared to 75.85% in the previous study. Additionally, the solubilization of hemicellulose and lignin improved, leaving 3.02% and 18.15%, respectively, in the final pulp. The CR and precipitated lignin figures also improved slightly, increasing to 94.59% from 93.24% and to 68% from 62%, respectively. Overall, these results demonstrate a general improvement in the CP using this optimum point, enhancing the feasibility of CP production and lignin recovery through organosolv.
2.2. Enzymatic Hydrolysis Results
The results of EH performed on the optimum point of sample A after organosolv treatment are reported in Table 4. Measurements of hydrolyzed cellulose (CD) were conducted in triplicate. The average values obtained for each sample over time are provided below. The table presents data on the percentage of CD, collected at regular intervals of 24 h, up to a total of 168 h, for each sample. These results reflect the progression of hydrolysis over time for each combination of enzyme and buffer solution parameters.

Table 4.
Enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose pulp samples over time as %CD. The first number in the sample name indicates the enzyme loading, while the second indicates the solid loading.
From 120 h onward, the system tended to stabilize. From the reported data, it is evident that samples “30_10” and “30_15,” characterized by a high enzyme content, showed the highest percentages of CD. These samples reached significant levels of hydrolysis within the first 48 h, with a steady increase until reaching a plateau around 120 h, where CD exceeded 90%. However, hydrolysis performed with such high enzyme percentages is not economically viable due to the high cost of the enzyme. Therefore, the remaining samples are of interest, particularly the “6_10” combination, which reached a peak of 51.03% CD at 120 h. While it did not reach the maximum value of the samples with 30% enzyme, it could represent a more sustainable solution in terms of cost–benefit balance.
Another key parameter for evaluating EH is the glucose yield (GY), which indicates the amount of glucose produced per 100 g of WW. Table 5 presents the data on GY for each sample.

Table 5.
Glucose yield and glucose concentration in the liquid fraction at 120 h. The first number in the sample name indicates the enzyme loading, while the second indicates the solid loading.
The sample “6_10” exhibited a GY of 20.66 g/100 g and a CD of 51.03%. While it did not achieve the high percentages observed in samples with high enzyme concentrations, it maintained GY without significantly compromising economic efficiency. It is notable that the sample “6_15”, with a CD of 34.06% and a GY of 13.79 g/100 g, achieved a lower GY despite using the same amount of enzyme.
The reduction in enzymatic efficiency can be attributed to the phenomenon known as the “high solid effect,” which refers to the decline in cellulose conversion yields as the solids loading increases. In this context, this effect might result from the high lignin content, approximately 20% of the total CP (Table 3), and limitations in mass transfer. Lignin likely contributes to enzyme adsorption through both charged and uncharged interactions, potentially restricting enzymatic activity [23].
Mass transfer limitations, caused by the limited amount of free water within the biomass fibers and their tendency to form bonds, negatively impact the hydrolysis process by hindering effective contact between enzymes and the substrate, thereby reducing hydrolysis efficiency [24]. To address this issue, employing a more effective agitation system, such as a mixer designed for viscous liquids, could enhance GY and glucose concentration [25].
To evaluate the hydrolysis process under investigation against other technologies, a comparison with existing studies on EH was conducted. This analysis examined parameters such as CD and glucose GY under varying experimental conditions, including enzyme types, temperatures, substrate concentrations, and reaction times.
Organosolv pretreatment, as used by Gelosia et al. [26] and Loustau-Cazalet et al. [27], demonstrated high CR and cellulose purity, enhancing enzymatic accessibility. Gelosia et al. reported a CD of almost 100% and a GY of 30.17 g per 100 g of biomass, while Loustau-Cazalet achieved a CD of 98% and a GY of 38 g per 100 g of biomass. These methods obtained high CD and GY thanks to the high purity of CP, low solid loading, and high enzyme loading.
Fabbrizi et al. [24], using CP with a cellulose content higher than 90%, extended hydrolysis times to 120 h to overwhelm the “high solid effect” that occurs when a low enzyme loading is employed. Using a solid loading of 20% w/w and two different enzyme loadings (10 FPU/g cellulose and 20 FPU/g cellulose), a GY of 26.89 g per 100 g of biomass and 31.52 g per 100 g of biomass was obtained.
Coupled mechanical and chemical pretreatments were explored by Liu et al. [28], Chen et al. [29], and Ishiguro et al. [30]. These techniques achieved CDs of 87–98% and GYs of 35.3–38.4 g per 100 g biomass within shorter reaction times. For instance, Liu reached peak GY in just 24 h, while Ishiguro reported a 90% CD within 48 h. Nevertheless, these studies used a low solid loading and coupled pretreatments, which, on one hand, accelerated EH, but on the other hand, reduced economic feasibility.
It is evident that the studies analyzed for comparison tend to use relatively high enzyme dosages and low solid loading, generally exceeding the levels adopted in this study, to rapidly enhance cellulose digestibility and GY, while minimizing processing time.
Additionally, this study also included a test with a high enzyme loading, equivalent to 30% of the cellulose to be hydrolyzed (corresponding to about 60 FPU/g cellulose), and low solid loading (10% w/w). This configuration resulted in a GY of 38.24 g per 100 g of initial biomass, closely aligning with outcomes reported in studies using similar enzyme dosages. This makes the EH of WW a promising method for treating this waste.
2.3. Heavy Metals Analysis Results
The results of the heavy metals analysis are shown in Table 6. All measurements were performed in triplicate, and the average results are presented.

Table 6.
Heavy metal concentrations in wood waste, cellulose pulp and residual solid fraction from enzymatic hydrolysis.
Arsenic, cadmium, and mercury were below the detection limit of the instrument. For the other metals, it is noteworthy that their concentrations increased after each treatment, except for lead, where the concentration in the solid fraction from EH was lower than that in the WW and CP. Despite this increase, all the measured values for CP were below the legal limits specified for packaging materials, as outlined in Directive 94/62/EC [31]. According to this directive, the combined concentration of lead, chromium, mercury, and cadmium must not exceed 100 ppm in materials used for packaging.
For the heavy metal concentrations in the residual solid fraction from EH, there is no specific regulation. However, these values can be compared to the legal limits for hazardous waste as defined by Commission Regulation (EU) No 1357/2014 [32]. Notably, the analyzed waste was not classified as hazardous for any of the measured heavy metals.
2.4. Simulation Model Results
The Aspen PLUS simulation was developed to design a potential pilot plant for processing WW collected by GESENU, the company responsible for waste management in the municipality of Perugia. The simulation considers an annual processing capacity of approximately 5500 t of WW, reflecting the quantity collected and managed annually by GESENU. This volume is deemed suitable for evaluation within a pilot-scale valorization process using organosolv treatment and EH. For pilot-scale operations, this quantity was considered appropriate to design a small-scale system that could be benchmarked against large-scale industrial configurations. Since WW is already collected as part of the public waste management system, no additional environmental or economic impacts arise from the production or transportation of the raw material to the plant. Unlike many large-scale facilities that rely on virgin biomass, this system does not require biomass cultivation. This simulation explores the feasibility of using such waste to produce cellulose and lignin, aligning with the principles of circular resource recovery.
Assuming continuous operation for a total of 8000 h per year [33], the biomass input corresponds to 687.5 kg/h. This represents the flow of pre-shredded WW fed into the plant. Energy consumption analysis revealed that the total power required to keep the plant operational is approximately 2409.3 kW (3.50 kWh/kg of biomass). The most energy-intensive steps are the pretreatment reactor, the distillation column, and the lignin drying unit, which together account for the highest energy requirements. Specifically, the organosolv reactor, operating under high temperature and pressure conditions, requires approximately 502 kW (0.73 kWh/kg of biomass). The EH reactor, which converts cellulose into glucose, has a significantly lower power demand of about 6.9 kW (0.01 kWh/kg of biomass). The distillation column, used for solvent recovery, is one of the most energy-consuming units, requiring 1415.2 kW (2.06 kWh/kg of biomass) to achieve the necessary ethanol purity by separating it from water and other mixture components. This confirms the results of the author’s previous research [34]. The lignin drying step required another 485.2 kW (0.66 kWh/kg of biomass), ensuring the final product met quality specifications (moisture content below 10%). While essential for sustainability and recycling, the distillation process significantly impacts the overall energy costs, highlighting the need for optimization. Future improvements, such as energy-saving techniques or enhanced heat recovery, could reduce the process’s energy demand, making the organosolv approach more competitive.
To preliminarily assess the system’s energy sustainability and evaluate its efficiency in converting WW into valuable products, specific energy consumption indicators were calculated for the key products of lignin, CP, and glucose. Lignin production requires about 18 kWh/kg of lignin. CP production consumes approximately 5.9 kWh/kg of CP, a relatively modest figure due to the absence of a pulp-drying step. This value mainly reflects the combined energy demands of pretreatment and distillation necessary to obtain a lignin-free cellulose fraction suitable for further conversion. The pulp proceeds directly to EH. Glucose production has an energy demand of approximately 13.5 kWh/kg of glucose, encompassing both pretreatment and hydrolysis but excluding lignin-drying processes, as they are unrelated to glucose production. The simulation also generated essential data for mass balance calculations of the main products: dry CP (323.5 kg/h), lignin (133.3 kg/h), and glucose (142 kg/h). The energy consumption distribution and recovery efficiency for cellulose and lignin highlight that most energy is concentrated in the distillation and pretreatment phases, with hydrolysis being comparatively less energy-intensive. Overall, the process requires about 3.5 kWh/kg of biomass processed. The further optimization of pretreatment and distillation could reduce the specific energy requirements for lignin and glucose production. To contextualize these results, the Aspen PLUS model was compared with other studies on lignocellulosic biomass valorization through organosolv pretreatment and EH. The selected references provide insights into varying solvent–water ratios, thermal conditions, and reaction times, enabling comparisons of product yields, energy consumption, and functional units.
Garcia et al.’s [35] study examines two biorefinery processes, one of which involves organosolv pretreatment using a 60:40 ethanol–water mixture at 160 °C for 90 min with a liquid-to-solid ratio of 6:1. For a biomass input of 1 Mg/h, this process yields 495 kg/h of CP, 130 kg/h of lignin, and 250 kg/h of hemicellulosic sugars (the latter excluded here). The total power demand for the organosolv process is 9.2 MW, equivalent to 9.2 kW/kg of biomass. The specific energy consumption is 70.77 kWh/kg of lignin and 18.59 kWh/kg of CP. In comparison, assuming a biomass input of 1 Mg/h, the pilot-scale model in this study would produce 470.6 kg/h of CP, 193.8 kg/h of lignin, and 206.6 kg/h of glucose. Despite differences in solvent ratios and operational parameters, the results show comparable performance in terms of CP. However, the energy consumption per hour for CP and lignin in the pilot-scale model proposed is 3–4-fold lower than that of Garcia et al., due to a shorter organosolv reaction time (15 min vs. 90 min) and higher lignin production per hour.
Herry’s report [36] details the energy consumption of a distillation column operating continuously at 120 °C over a 3 h cycle. For a biomass input of 5.7 t per cycle, the specific energy consumption was calculated as 2.48 kWh/kg of biomass. This value closely aligns with the simulation’s energy demand for the distillation column (2.06 kWh/kg of biomass). Regarding product yields, Herry’s process produced 451 kg/h of lignin and 665 kg/h of CP. The current model would achieve better performance under identical biomass input conditions (368.3 kg/h of lignin and 894.1 kg/h of CP), with differences attributed to organosolv process efficiency and operational conditions. Although the limited data on specific energy requirements for individual units (e.g., organosolv reactor or drying) restrict direct comparisons, the distillation column remains the dominant energy consumer in both systems. Overall, the pilot plant model demonstrates competitive performance compared to benchmarks in the literature, with room for further optimization to enhance energy efficiency and for the design of a real pilot plant.
3. Materials and Methods
The study analyzed WW collected at the mechanical treatment plant located in Perugia, Italy. This WW came from four different codes in the European Waste Catalogue (EWC) [37], each collected in separate containers to ensure correct classification. The quantities were reported for the year 2021: 150,103—wood packaging, approximately 367.5 t; 170,201—wood from construction and demolition, approximately 21.3 t; 191,207—WW produced by waste treatment plants, approximately 299.3 t; 200,138—WW from municipal collection, approximately 4728.2 t.
These EWC codes were shredded and mixed at the mechanical treatment plant, resulting in a homogeneous waste labeled with the code 191207*. This waste sample underwent a detailed analysis to verify its physical and chemical composition, with particular attention to the presence of impurities, both physical (non-wood materials) and chemical. To ensure adequate material representativity, the homogenized waste sample was processed according to UNI 10802:2013 guidelines. Specifically, about 1 ton of WW was collected from the main pile using an excavator, and then the sample was reduced through the coning and quartering method to obtain a representative fraction of the material. This procedure yielded a subsample of approximately 10 kg, designated for laboratory analysis.
The variability in the chemical composition of the 191207* sample necessitated the application of the aforementioned sampling procedure on three distinct batches collected in different periods—March, May, and August 2022. These samples, labeled as A, B, and C, were sent to the laboratory at the University of Perugia as raw material for further analyses. Before analysis, the raw material was manually pretreated to remove any small metal impurities. Other impurities, such as plastic objects, were retained, although they represented less than 5% of the total weight of the samples. Subsequently, the material was ground using two types of mills, as follows: a rotary blade mill to produce fragments of 4 mm in diameter (SM 2000, RETSCH, Haan, Germany), intended for the organosolv process; a laboratory ultracentrifuge mill to produce particles of 0.5 mm in diameter (ZM 200 RETSCH, Haan, Germany), intended for chemical characterization.
The moisture contents of the samples were determined using a HB43-S Halogen Classic Plus halogen analyzer (Mettler Toledo, Columbus, OH 43240, USA), ensuring the samples were prepared in optimal conditions for the organosolv process.
3.1. Organosolv Treatment
An “Ethos One” microwave digestion system (Milestone S.r.l., Sorisole (BG), Italy) was used for the treatment, with deionized water and ethanol as solvents. Sulfuric acid was used as an acid catalyst. The deionized water was obtained from an ELGA Purelab Option R system (ELGA LabWater, High Wycombe, UK), while the ethanol and sulfuric acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA). A simple distillation system was used to recover the ethanol.
The samples, both treated and untreated, were characterized following the guidelines of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory NREL [38]. The pulp underwent chemical hydrolysis to release monosaccharides, allowing the estimation of cellulose and hemicellulose contents. The residual lignin content was determined by gravimetric analysis. Monosaccharide concentrations were analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a “Dionex UltiMate 3000” (Thermo-Scientific, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), equipped with a “Bio-Rad Aminex HPX-87H” (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) column and a refractive index detector. Analyses were conducted at a temperature of 50 °C, with a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min and a mobile phase consisting of a 0.01 N sulfuric acid solution.
The biomass sample, ground to 4 mm particle size, was placed in a PTFE container along with a solution composed of ethanol, deionized water, and a small amount of sulfuric acid. The treatment was set for an effective duration of 15 min, preceded by a 5 min heating phase to reach the pre-established process temperature. After the reaction phase, the mixture was gradually cooled for about 40 min using an internal fan integrated into the reactor. Subsequently, the resulting mixture was subjected to vacuum filtration using a Büchner flask, thus separating the ethanolic/aqueous solution from the enriched CP. The CP obtained was thoroughly washed with deionized water to remove any residues and impurities, and then dried in a thermostatic chamber at a controlled temperature of 50 °C overnight. At the end of the drying process, the pulp was weighed and analyzed to determine its cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin contents, as described above. The ethanolic/aqueous solution, recovered through filtration, was subjected to a distillation process, allowing the recovery of an aqueous fraction containing sugars derived from hemicellulose and precipitated lignin, as well as ethanol with a purity level of approximately 95% (v/v). The precipitated lignin was dried, and its mass was gravimetrically quantified. The ethanol and monosaccharide concentrations in the various fractions were analyzed and quantified using HPLC.
The results obtained from the tests were used to determine the contents of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, as well as the CR. The calculation of CR was performed using the following Equation (1):
where CCP represents the cellulose content in grams in the CP obtained after the organosolv treatment, while CRM corresponds to the cellulose content in grams present in the raw material, i.e., the WW entering the process. This calculation allows the evaluation of the efficiency of cellulose separation, a key parameter in assessing the overall effectiveness of the treatment.
CR = CCP/CRM
3.2. Design of Experiment
The DoE focused on three key factors: temperature (°C), sulfuric acid (H2SO4) concentration (% w/w), and ethanol concentration in water (w/w). These factors were chosen based on a prior study by the authors [22]. As suggested in the previous study, the low and high levels for acid concentration and temperature were increased in this work.
The DoE was created using Minitab 17 statistical software (Minitab, Coventry, UK) and employed a Box–Behnken design with three levels (−1, 0, +1), resulting in a total of 15 experimental runs, as listed in Table 7. The condition (−1, −1, −1) represents the least intense settings, while (+1, +1, +1) represents the most intense. Sample A was consistently used across all experimental runs.

Table 7.
Design matrix with all possible levels for each input factor in uncoded and coded units.
The data obtained from these runs served as the basis for developing mathematical models to predict the contents of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and CR.
3.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
After pretreatment, CP was subjected to EH, which was conducted in 50 mL flasks with the presence of a commercial enzyme CTec2 (Novozymes, Copenhagen, Denmark) in buffer solutions at an optimal pH of 5–5.5 for enzymatic activity. The buffer was prepared by adding 3.657 g of citric acid and 7.633 g of sodium citrate to 1 L of deionized water. To prevent bacterial growth, 0.2 g of 5% sodium azide solution was added to each flask.
The enzyme concentration varied between 3%, 6%, and 30% by weight relative to the cellulose introduced into the reaction. The 3% and 6% concentrations are the typical enzyme loads recommended for investigating the scalability of the EH process, as suggested by the enzyme supplier. The 30% enzyme load is the amount typically used to assess CD in the presence of an enzyme excess, which is useful for understanding the maximum hydrolyzable cellulose fraction.
The mass ratio between dry pulp and the buffer solution varied from 1:10 to 1:15 by weight, up to a total of 10 g of mixture between the buffer solution and dry pulp. EH was monitored at regular intervals of 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, and 168 h, through the sampling of a 0.1 mL aliquot of solution from each flask. This aliquot was diluted into a 20 mL volumetric flask and analyzed by UHPLC to determine the glucose concentration in solution and, accordingly, the amount of CD. Hydrolysis was conducted in a thermostatic chamber at 50 °C under horizontal mechanical agitation through an IKA™ KS 4000 i control orbital shaker set at 180 rpm.
CD was calculated using Equation (2),
where GHY is the glucose detected by UHPLC in grams, 0.9 is the correction factor associated with the loss or addition of water molecules in the conversion from cellulose to glucose during the EH phase, and COV represents the cellulose present in the pulp exiting the organosolv.
CD = GHY ∗ 0.9/COV
In addition, GY was calculated, expressed as grams of glucose per 100 g of initial WW, using Equation (3),
where %CRM is the percentage of cellulose present in the initial raw material, with CD and CR previously defined.
GY = (%CRM ∗ CR ∗ CD/0.9) ∗ 100
3.4. Heavy Metals Analysis
WW, CP and the residual solid fraction from EH initially undergo a mineralization phase, during which the entire organic component is converted to CO2, and metals within the matrix are oxidized and dissolved. The mineralization process uses acidic solutions under elevated temperatures and pressures within specialized vessels. These vessels are placed inside a Milestone Ethos-One microwave reactor (MILESTONE Srl, Sorisole, Italy), which supplies the necessary energy to heat the solutions. After mineralization, the resulting solution is analyzed using ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry) on a PerkinElmer Optima-8000 model (AMP Tech Instruments, Longwood, FL, USA). Metals are ionized or atomized via an argon gas plasma torch operating at approximately 7000 °C; upon returning to their elemental states, the metals emit radiation detected by a CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) sensor (ONSEMI, Munich, Germany). Each test was conducted in triplicate, and the standard deviation was determined. Metal concentration is expressed in mg/kg.
3.5. Simulation Model
A preliminary simulation model of the process described in the previous chapter was developed. Its objective, using Aspen PLUS, was to replicate the main stages of the WW valorization process—through organosolv and EH, as previously described—to scale up the laboratory setup to a pilot plant. The flowsheet of the modeled process has been presented, including all its blocks. All input data are derived from previous processes previously described. The modeled process begins with the loading of biomass into the system, followed by organosolv treatment, which separates the material into a solid pulp and a liquid fraction. The pulp is washed to remove residual substances, while the liquid fraction is sent to a distillation unit, where ethanol is separated from the water streams and recovered. The remaining liquid fraction is then dried to isolate lignin. The cleaned pulp subsequently undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis, converting cellulose into glucose. All the simulated equipment is described hereunder, and also additional data are provided in a Supplementary Materials file.
Block B1 receives biomass at ambient conditions (25 °C and 1 atm). It is configured to output a mass flow with a composition reflecting Sample A, as detailed in Table 3. The B1 block, functioning as a mixer, performs a simple mass flow summation and recalculates the output temperature, setting the final pressure to the lowest value among the inlets. The wet biomass is then sent to mixer B3, where specific quantities of water, ethanol, and sulfuric acid are added (0.65 ethanol-to-water ratio (w/w), and 1.3% sulfuric acid (w/w)). The liquid-to-solid ratio is set as 4.5:1 [39].
The solid–liquid suspension moves to heat exchanger B13, pressurized to 10 atm by pump B4. Heat exchanger B13 utilizes thermal energy from one of the distillation process outputs to raise the suspension temperature to approximately 67 °C. This preheated suspension then proceeds to the stoichiometric reactor B5, where organosolv reactions occur at 175 °C and 20 atm. The reactor output, at the same temperature and pressure, contains substantial recoverable thermal energy. To enhance energy efficiency, heat from the reactor effluent is transferred to the liquid feed for distillation via heat exchanger B21. This step reduces the energy required by the distillation column B12 while cooling the reactor output to ambient conditions (25 °C, 1 atm). Final cooling occurs in heat exchanger B6, a configurable component capable of adjusting both temperature and pressure.
Once cooled, the suspension undergoes initial filtration in separator B16, which isolates liquids from solids without washing. The solid fraction, slightly moist and containing traces of ethanol, sulfuric acid, and water, represents the first major separation of the mass flows in the plant. Since residual acidic solvents adversely affect EH, the solids undergo a water wash in separator B9. Using a 2:1 water-to-solid ratio [40] ensures that the ethanol and sulfuric acid contents in the solids are reduced to 1% each, without adding excessive liquid to the distillation stream. The washing liquid rejoins the previous liquid streams, heading to distillation. After washing, the moist pulp contains 77.5% water.
For EH in reactor B17, the pulp is combined with enzymes and a buffer solution (as described in Section 3.3). This mixture is preheated to 50 °C using heat exchanger B18, which captures heat from the hot air and vapor streams generated during lignin drying. Inside the stoichiometric reactor B17, EH proceeds under simplified assumptions due to the lack of detailed enzymatic kinetics. Based on laboratory data, cellulose conversion to glucose is estimated at 51.03%.
The liquids from both filtration and pulp washing are combined in mixer B27 to form a single stream. Preheated by recovering heat from the organosolv reactor effluent, this liquid reaches 90 °C, reducing the workload for the reboiler in distillation column B12. Distillation outputs include ethanol recovered at 98.6% purity (at ~78 °C) and a secondary liquid stream containing dissolved lignin, sugars, and 1.4% residual ethanol. The recovered ethanol is reused in the pre-treatment process, with minimal replenishment required to compensate for losses.
The secondary liquid stream proceeds to separator B15, where additional washing water is used to promote lignin precipitation. The residual liquid—containing sugars, ethanol, and washing water—is currently considered waste, but could be utilized in future developments. The precipitated lignin, with a moisture content of 77.5%, is dried in dryer B14 to achieve 10% residual moisture. The dryer uses hot air, supplied by a fan simulated through compressor B10 and heated in heater B11. Figure 1 illustrates all the blocks described above.
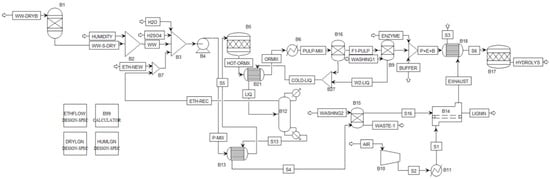
Figure 1.
Flowsheet of the modeled process for glucose production and solvent and lignin recovery.
To provide a preliminary assessment of the energy sustainability of the system and to determine the conversion efficiency of wood waste into valuable products, specific energy consumption indicators were calculated for each key product of the process, namely, lignin, cellulose pulp and glucose. The simulation was designed to supply the essential data required to establish the mass balance of the main output streams, including the amount of pulp obtained through organosolv treatment, the glucose produced via enzymatic hydrolysis, and the lignin recovered. Furthermore, the specific energy consumption for the production of each product was determined, expressed in kWh per kilogram of product (kWh/kg), together with the overall energy demand per kilogram of biomass processed (kWh/kg). These operational parameters provide a useful framework for evaluating the efficiency and scalability of the modeled system.
4. Conclusions
This paper examined a new DoE on 4 mm WW, identifying the following optimal treatment conditions: 175 °C, an ethanol-to-water ratio of 0.65 (w/w), and 1.3% sulfuric acid (w/w). These optimized parameters yielded improved results compared to those in the author’s previous study [22]. The cellulose content increased to 79.33%, up from 75.85% in the previous study. Hemicellulose and lignin solubilization also improved, reaching 3.02% and 18.15%, respectively, in the final pulp. CR showed a slight increase, rising to 94.59% from 93.24%. The obtained pulp is suitable for containerboard production, as also reported by Pazzaglia et al. [22], but with improved values. EH has also been investigated as an alternative use of WW. This process yielded 20.66 g of glucose per 100 g of initial WW, with a glucose concentration of 44.08 g/L and a cellulose digestibility of 51.03%. While these results are encouraging, they may not yet be economically viable. Further studies should explore alternative pre-treatments to reduce lignin content in the CP, thereby minimizing enzyme adsorption and improving overall process efficiency. Heavy metal analysis of the solids revealed that all fractions are safe and within the limits specified by Directive 94/62/EC on packaging materials and Commission Regulation (EU) No 1357/2014 on hazardous waste.
Another key aspect of this research is the simulation model, which considered an annual processing capacity of approximately 5500 t of WW—matching the quantity collected and managed annually by a waste treatment company based in Perugia. The biomass input was set at 687.5 kg/h, yielding dry CP (323.5 kg/h), lignin (133.3 kg/h), and glucose (142 kg/h). Energy consumption analysis showed that the distillation column required 1415.2 kW, the organosolv reactor required 502 kW, and lignin drying required 485.2 kW.
This study provides a foundation for the further evaluation of the environmental and economic impacts of the process, especially in comparison to conventional pathways for producing glucose and CP, and current WW use in particleboard production. Future research should adopt a life cycle assessment and life cycle costing approach to assess the broader implications of scaling up this process.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/recycling10050191/s1, Figure S1: Components selected within the simulation environment. The IDs have been chosen arbitrarily; Figure S2: Structural components present in the BIOFEED database. (Source: Aspen PLUS); Figure S3: Input of reactor RYield B1; Figure S4: Biocomponents constituting, MWASTE-020. Values are non-editable, predefined by the BIOFEED database; Figure S5: Stoichiometric reactions indicated within B5; Figure S6: Reactions present in the pretreatment reactor of the internal Aspen PLUS example. Reactor M207, within the HERARCHY block “BMFRAC”; Figure S7: Configuration of the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction in block B17; Table S1: Possible reactions to be modeled in Aspen Plus for organosolv pretreatment.
Author Contributions
A.P.: Conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; supervision; validation; visualization; writing—original draft; and writing—review and editing. G.F.: Data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology. M.G.: Data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; writing—review and editing. T.G. (Tiziano Galmacci): Data curation; formal analysis; investigation. T.G. (Tommaso Giannoni): Data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology. A.I.: Data curation; formal analysis; investigation. A.N.: Supervision; resources; writing—review and editing. B.C.: Conceptualization; investigation; methodology; funding acquisition; project administration; resources; supervision; writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Fondazione Perugia for supporting the experimental activities and GESENU SpA for the availability and support given in the sampling process, and in sharing data related to samples’ composition analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| WW | Wood waste |
| EH | Enzymatic hydrolysis |
| DoE | Design of experiment |
| CP | Cellulose pulp |
| CR | Cellulose recovery |
| CD | Hydrolyzed cellulose |
| GY | Glucose yield |
| EWC | European Waste Catalogue |
References
- Parham, R.A.; Gray, R.L. Formation and Structure of Wood. In The Chemistry of Solid Wood; Advances in Chemistry; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1984; Volume 207, pp. 3–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cherubini, F. The biorefinery concept: Using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besserer, A.; Troilo, S.; Girods, P.; Rogaume, Y.; Brosse, N. Cascading recycling of wood waste: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höglmeier, K.; Weber-Blaschke, G.; Richter, K. Utilization of recovered wood in cascades versus utilization of primary wood—A comparison with life cycle assessment using system expansion. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzolan, N.; Mohren, F.; Grassi, G.; Schelhaas, M.-J.; Staritsky, I.; Stern, T.; Peltoniemi, M.; Šebeň, V.; Hassegawa, M.; Verkerk, P.J.; et al. Preliminary evidence of softwood shortage and hardwood availability in EU regions: A spatial analysis using the European Forest Industry Database. For. Policy Econ. 2024, 169, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Statistics and Data on Europe. 2025. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Mantau, U.; Saal, U.; Prins, K.; Steierer, F.; Lindner, M.; Verkerk, H.; Eggers, J.; Leek, N.; Oldenburger, J.; Asikainen, A. Methodology Report. Real Potential for Changes in Growth and Use of EU Forests; Uwood: Hamburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Faraca, G.; Boldrin, A.; Astrup, T. Resource quality of wood waste: The importance of physical and chemical impurities in wood waste for recycling. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykidis, C.; Grigoriou, A. Hydrothermal recycling of waste and performance of the recycled wooden particleboards. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, A.; Gelosia, M.; Cavalaglio, G.; Barbanera, M.; Giannoni, T.; Tasselli, G.; Nicolini, A.; Cotana, F. Production of carbohydrates from cardoon pre-treated by acid-catalyzed steam explosion and enzymatic hydrolysis. Energies 2019, 12, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.; Godina, R.; Azevedo, S.G.; Matias, J.C.O. A comprehensive review of industrial symbiosis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, A.; Castellani, B. A Decision Tool for the Valorization of Wood Waste. J. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2023, 27, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, T. Fibre supply, sustainability and the packaging explosion: Market session: Focus on fibre for boxes and sustainable fibre supplies. Appita Mag. 2021, 4, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Confederation of European Paper Industries. Key Statistics 2023—European Pulp & Paper Industry [PDF]. 2023. Available online: https://www.cepi.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Key-Statistics-2023-FINAL-2.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Hoffman, E.; Guernsey, J.R.; Walker, T.R.; Kim, J.S.; Sherren, K.; Andreou, P. Pilot study investigating ambient air toxics emissions near a Canadian kraft pulp and paper facility in Pictou County, Nova Scotia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20685–20698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofani, G.; Jasiukaitytė-Grojzdek, E.; Grilc, M.; Likozar, B. Organosolv biorefinery: Resource-based process optimisation, pilot technology scale-up and economics. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei Kit Chin, D.; Lim, S.; Pang, Y.L.; Lam, M.K. Fundamental review of organosolv pretreatment and its challenges in emerging consolidated bioprocessing. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2020, 14, 808–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, M.; Kirci, H. An environmentally friendly organosolv (ethanol-water) pulping of poplar wood. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 735. [Google Scholar]
- Manfredi, M.; Gomide, J.L.; Barcelos, T.T.; Faria, B.d.F.H.; Colodette, J.L.; Silva, C.M. Washing, bleaching and characterization of eucalyptus pulp from ethanol pulping. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2014, 29, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, A.A.; Murton, K.D.; Smith, D.A.; Dedual, G. A review on organosolv pretreatment of softwood with a focus on enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 12, 5427–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; Chang, J. Novel Method for Production of Phenolics by Combining Lignin Extraction with Lignin Depolymerization in Aqueous Ethanol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, A.; Gelosia, M.; Giannoni, T.; Fabbrizi, G.; Nicolini, A.; Castellani, B. Wood waste valorization: Ethanol based organosolv as a promising recycling process. Waste Manag. 2023, 170, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.S.A.; Espinheira, R.P.; Teixeira, R.S.S.; de Souza, M.F.; Ferreira-Leitão, V.; Bon, E.P.S. Constraints and advances in high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass: A critical review. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrizi, G.; Giannoni, T.; Lorenzi, L.; Nicolini, A.; Iodice, P.; Coccia, V.; Cavalaglio, G.; Gelosia, M. High solid and low cellulase enzymatic hydrolysis of cardoon stems pretreated by acidified γ-valerolactone/water solution. Energies 2022, 15, 2600. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtusik, M.; Zurita, M.; Villar, J.C.; Ladero, M.; Garcia-Ochoa, F. Influence of fluid dynamic conditions on enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass: Effect of mass transfer rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelosia, M.; Bertini, A.; Barbanera, M.; Giannoni, T.; Nicolini, A.; Cotana, F.; Cavalaglio, G. Acid-assisted organosolv pre-treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of Cynara cardunculus L. For glucose production. Energies 2020, 13, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loustau-Cazalet, C.; Sambusiti, C.; Buche, P.; Solhy, A.; Bilal, E.; Larzek, M.; Barakat, A. Innovative deconstruction of biomass induced by dry chemo-mechanical activation: Impact on enzymatic hydrolysis and energy efficiency. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-l.; Fang, Z.; Tian, X.-f.; Miao, Z.-D. Effect of alkali salt-coupled ball milling pretreatment of wheat straw on improving enzymatic hydrolysis and energy efficiency. Fuel 2023, 340, 127336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Wei, W.; Yuan, Z. Enhancing bagasse enzymatic hydrolysis through combination of ball-milling and LiCl/DMSO dissolution and regeneration. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, M.; Endo, T. Effect of the addition of calcium hydroxide on the hydrothermal–mechanochemical treatment of Eucalyptus. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and Council Directive 94/62/EC of 20 December 1994 on Packaging and Packaging Waste. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/1994/62/oj/eng (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Replacing Annex III to Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. 2014. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2014/1357/oj/eng (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Nitzsche, R.; Budzinski, M.; Gröngröft, A. Techno-economic assessment of a wood-based biorefinery concept for the production of polymer-grade ethylene, organosolv lignin and fuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, A.; Romagnoli, F.; Castellani, B. Environmental Assessment of Cellulose Pulp Production from Wood Waste using Organosolv Treatment. J. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2024, 28, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Alriols, M.G.; Llano-Ponte, R.; Labidi, J. Energy and economic assessment of soda and organosolv biorefinery processes. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herry, A. Large Scale Lignin Organosolv Extraction. Bachelor’s Thesis, Chemical Engineering, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2020. Available online: https://fse.studenttheses.ub.rug.nl/22380/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Eurostat. European Waste Classification for Statistics (EWC-Stat Rev. 4) (Version 2010) [Data Set]; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2024; Available online: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/classifications/Family/Detail/1065 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Sluiter, J.; Sluiter, A. Summative mass closure. Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP) Review and Integration. In Technical Report NREL/TP-510-48087; National Renewable Energy Laboratory, U.S. Department of Energy: Golden, CO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, G.C.; Lora, J.; Pye, E. Autocatalyzed organosolv pulping of hardwoods: Effect of pulping conditions on pulp properties and characteristics of soluble and residual lignin. Tappi J. 1992, 75, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, A.R.G.; Errico, M.; Rong, B.-G. Process alternatives for bioethanol production from organosolv pretreatment using lignocellulosic biomass. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Chemical and Process Engineering, Milan, Italy, 28–31 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).