Abstract
The multicaloric effect is defined as the adiabatic reversible temperature change in multiferroic materials induced by the application of an external electric or magnetic field, and it was first theoretically proposed in 2012. The multicaloric effects in multiferroics, as well as other similar caloric effects in single ferroics, such as magnetocaloric, elastocaloric, barocaloric, and electrocaloric, have been the focus of much research due to their potential commercialization in solid-state refrigeration. In this short communication article, we examine the thermodynamics of the multicaloric effect for solid-state heating applications. A possible thermodynamic multicaloric heating cycle is proposed and then implemented to estimate the solid-state heating effect for a known electrocaloric system. This work offers a path to implementing caloric and multicaloric effects to efficient heating systems, and we offer a theoretical estimate of the upper limit of the temperature change achievable in a multicaloric cooling or heating effect.
Solid-state caloric effects [1,2,3,4,5,6] manifest as a temperature change within a given physical system in response to adiabatic changes of internal or external variables such as volume, strain, magnetization, or polarization. These temperature changes can be either heating or cooling, depending on the sequence of the applied excitation, i.e., application or removal of the specific control parameter.
There is, in fact, a particular interest in solid-state magnetocaloric or electrocaloric cooling because they offer the prospect of vibration-free, low noise, efficient, and environmentally friendly refrigeration, including room temperature refrigeration applications and ultra-low cryogenics [7]. The ability to develop solid-state cooling technologies is also attractive for integrating cooling devices into electronic and micro-electronic components [8].
Driven by their huge commercialization potential, the research in solid-state caloric effects has accelerated, with most of the efforts concentrated on finding suitable materials that display significant temperature changes, leading to the report of enormous caloric effects [1,9,10]. The research efforts in discovering large caloric effects in single ferroic materials have been aided by parallel research in a class of materials used for caloric effects called multiferroics [11]. Multiferroic materials display simultaneously multiple ferroic order phases. Since each ferroic order phase can facilitate a wide range of applications, it is generally expected that materials displaying multiple combined order phases would offer enhanced capabilities leading to an abundance of applications, including advanced sensors [12,13,14], memories [15,16], magnetic recording readers [17,18], transformers [19], and even energy harvesting devices [20]. Some of the most promising applications of multiferroic materials have been detailed in [21], one of them being the application to solid-state caloric effects. This stimulated the concept of multicaloric effect in multiferroics, first proposed theoretically in 2012 [22] and followed by several other studies revolving around the same concept [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. In [23], the generalized theory of the giant caloric effects was introduced, allowing one to describe all possible caloric and multicaloric effects, including those induced by more exotic means of excitation such as mechanical stress [33,34]. For historical accuracy, it is important to mention that the term “multicaloric” appeared in the public domain the same year, in an earlier article [35]. While Fahler et al. [35] proposed the possibility of an enhanced caloric effect via magnetoelectric coupling in multiferroics, the theoretical justification was presented by Vopson [22] a few months later and was credited by other authors [36].
The original introduction of the multicaloric effect in multiferroics was performed theoretically using a thermodynamic approach. Assuming a multiferroic solid containing electrically and magnetically ordered phases, the differential Gibbs free energy is dG = −S·dT − M·dH − P·dE, where S is the entropy, M is the magnetization, and P the polarization of the system. Under this assumption, the system displays a linear magnetoelectric effect characteristic to multiferroics and is mathematically defined by the α coupling coefficient (∂M/∂E)T,H = (∂P/∂H)T,E = α. Then the electrically (1) and magnetically (2) induced multicaloric effects in a given multiferroic system are expressed as [22]:
where µ0 is the magnetic permeability of vacuum, ε0 is the dielectric permittivity of vacuum, C is the specific heat capacity of the system per unit volume as C = T(∂S/∂T)H,E, and χm and χe are the susceptibilities of the magnetic and polar phase, respectively. The full derivation of relations (1) is given in references [22,23].
Equation (1) indicates that a single excitation field could induce a full multicaloric effect. If the electric field is used to induce the effect, then only Equation (1a) applies, while if a magnetic field is driving the caloric process, only Equation (1b) applies. Hence, a single excitation delivers a multiple caloric response, i.e., multicaloric. This effect is very different from ordinary ferroic systems, where a single excitation induces a single caloric response.
Since M and P of most ferroic and multiferroic materials decrease with the temperature, i.e., ∂M/∂T < 0 and ∂P/∂T < 0, at constant applied fields, then the multicaloric temperature change given by relations (1) can be positive (ΔTE,H > 0) for adiabatic polarization/magnetization, or negative (ΔTE,H < 0) for adiabatic depolarization/demagnetization, respectively. A closer examination of relations (1) indicates that they are very similar to those describing the electrocaloric and magnetocaloric effects, except that the multicaloric effects contain additional terms, (αe/( µ0·χm)·(∂M/∂T) and (αm/(ε0·χe)·(∂P/∂T). These additional terms result from the magnetoelectric coupling in multiferroics, and they can further enhance the thermal effect, especially in strongly coupled multiferroics. For large multicaloric coupling terms, we expect a significant increase in the total temperature change. In fact, according to (1), ΔT can increase indefinitely with increasing the α coupling coefficient. This, of course, is not possible, thus, the following question arises:
What is the maximum predicted temperature change in the multicaloric effect?
In order to answer this question, it is helpful to rewrite Equation (1) in a further simplified manner by expressing the derivatives of the magnetoelectric induced M and P with respect to T as: (∂M/∂T) = αe·(ε0·χe)−1 · (∂P/∂T) and (∂P/∂T) = αm · (µ0 · χm)−1· (∂M/∂T). Using these expressions, we obtained the following simplified relations of the electrically and magnetically induced multicaloric effects:
where ΔE = Ef − Ei and ΔH = Hf − Hi. Equation (2) shows clearly the enhancement of the electrocaloric and magnetocaloric effects in the case of multicaloric effect in multiferroics, with the additional contribution to ΔT given by the magnetoelectric caloric coupling term (α2/(µ0 · ε0 · χmχe) + 1). Indeed, in the particular case of a material that does not display any magnetoelectric coupling, or it is not multiferroic (αe = αm = 0), Equation (2) simply describes the electrocaloric and magnetocaloric effects.
However, the magnetoelectric coupling coefficient has a fundamental thermodynamic limit, which is given by the relation α2 ≤ (µ0 · ε0 · χmχe) [11]. A more recent derivation of this limit was given here [37]. This implies that the magnetoelectric caloric coupling term always takes fractional values, α2/(µ0 · ε0 · χmχe) ≤ 1. Placing this condition in Equation (2), an upper limit can be established for the maximum ΔT expected for the electrically or magnetically induced multicaloric effect, which is twice the temperature change expected for the equivalent electrocaloric or magnetocaloric effects induced by the same excitation fields, in case no magnetoelectric coupling exists. This offers a significant enhancement of the temperature change in a multicaloric effect relative to single caloric effects.
The main focus of all previous studies of single caloric effects in single ferroic systems has been the development of solid-state cooling technologies. Similarly, the recently proposed multicaloric effect in multiferroics is regarded as the most promising candidate for developing efficient solid-state refrigeration systems [22,23], far superior to single caloric effects.
Here we take a different approach, and instead of solid-state cooling, we propose the application of the multicaloric effect in multiferroics to solid-state heating technologies. The proposed operation principle is explained in Figure 1. For clarity, we show the cooling diagram (Figure 1a), and thermodynamic cycle (Figure 1b) (adapted from previously published work [22]), and the newly proposed heating operation principle (Figure 1c,d).
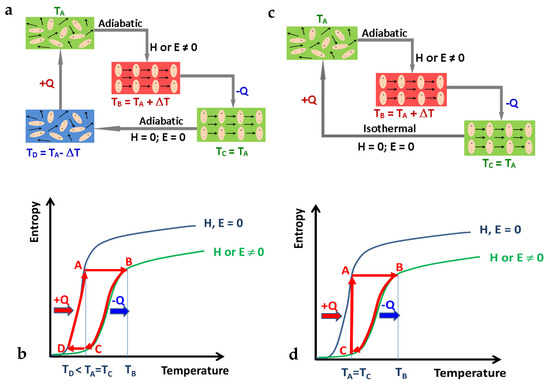
Figure 1.
Diagrams of the proposed cooling (a,b adapted from ref. [22]) and heating cycles of the solid-state multicaloric effect. (a) Schematic of the four stages cooling cycle (A–D) showing the entropy change due to relaxation of the magnetic moments (black arrows) and electric dipoles (ovals); (b) The corresponding Brayton cooling cycle; (c) Schematic of the three stages heating cycle (A–C); (d) The corresponding thermodynamic heating cycle.
We first explain the multicaloric cooling cycle briefly. The system is initially at the operation temperature TA. The system is also initially assumed in thermal equilibrium. Since the operation temperature TA is selected so that the cooling agent is in a para-ferroic state, then at this state, magnetic and electric dipole moments are thermally activated and undergo random fluctuations in a para-multiferroic state (Figure 1a). Imposing an adiabatic state, a single excitation field H or E is applied to the multiferroic system. The effect of the field application is to align the magnetic and electric dipole moments, essentially resulting in a transition from disorder (high entropy state) to ordered multiferroic (low entropy state) (transition A–B, Figure 1b). Hence, the decrease in the entropy of the system under adiabatic conditions will increase the overall temperature of the system to TB = TA + ΔT. This additional temperature could be reduced back to the initial temperature via a heat sink. In this process, the applied E or H field is maintained constant, preventing the magnetic and electric dipoles from reabsorbing heat. The required operating temperature usually dictates the nature of the heat sink, and it is usually a fluid coolant such as water for room temperature operation or a cryogenic liquid for cryogenic cooling. The transition B–C in Figure 1b corresponds to the system returning to the initial equilibrium temperature TA of the heat sink. Using a thermal switch to break the contact with the heat sink, the system returns to adiabatic conditions, and the total entropy remains constant again. Simultaneously, the applied H or E field is switched off, corresponding to transition C–D (Figure 1b). The field removal initiates an adiabatic demagnetization and depolarization process, causing the magnetic and electric moments to absorb heat as they relax back to equilibrium. Since entropy increases again, the adiabatic condition is fulfilled by decreasing the temperature of the refrigerant to a value lower than the temperature of the heat sink, i.e., TD = TA − ΔT. The transition D–A in Figure 1b corresponds to the multiferroic refrigerant being placed in thermal contact with the environment being refrigerated, ending the cooling cycle. The solid-state cooling technology and its thermodynamic cycle are well established and essentially applied identically to all the solid-state caloric effects, with the only difference being the caloric material itself and the corresponding excitation force/field.
Our proposed solid-state heating thermodynamic cycle is very similar to the cooling cycle, except it has three stages instead of four (see Figure 1c,d).
The multicaloric heating cycle begins again with the system at the initial operation temperature TA (Figure 1c,d). Upon applying an H or E field, forcing the magnetic spins and electric dipole moments to align, reducing the entropy of the system, the multiferroic’s temperature increases to TB = TA + ΔT (transition A–B, Figure 1c,d). While the applied excitation field is still on, the excess temperature is transferred to the environment via a heat sink. For room temperature heating applications, the heat exchange/sink is typically water circulated in contact with the multiferroic heating element. In this process, the system returns to the initial equilibrium temperature TA given by the heat sink (transition B–C, Figure 1c,d). Maintaining thermal contact with the heat sink, the applied H or E field is switched off (transition C–A, Figure 1c,d), creating, in effect, an isothermal demagnetization and depolarization process, which causes the spins and electric dipoles to exchange heat with the environment, at constant temperature TA. The multiferroic heating element is then subjected to another field application, and the whole cycle is repeated.
The temperature change ΔT (increase for heating or decrease for cooling) is governed by the set of multicaloric effects, Equation (1) or (2), also applicable for nonmultiferroic materials.
By selecting an active multiferroic material displaying order phase transition temperatures of the magnetic and electric phases at room temperature [38,39] (i.e., Tcm ≈ Tce ≈ 300 K), the ∂M/∂T, ∂P/∂T and the total entropy change are most significant at around 300 K. This property combined with a large enough magnetoelectric coupling coefficient, would result in significant ΔT changes. In terms of room temperature heating applications for domestic use, this is interesting as it suggests that a domestic heating system operating on the proposed multicaloric heating principle would only require a temperature change of around ΔT = 10 K, in order to ensure that it maintains a constant working temperature of the environment ideal for habitation. Assuming that active multiferroic elements displaying large magnetoelectric coupling effects at room temperature are developed, the heating systems operating on this principle would undoubtedly become a reality.
To highlight the potential heating application, we have investigated an idealized heating system comprising the electrocaloric material PbSc0.5Ta0.5 O3 (PST). Using the data presented in Nair et al. [40], we have constructed an idealized model to investigate the potential output heating power, electrical input power, and the resulting coefficient of performance (CoP) for a system operating between 10 °C and 60 °C, these being the respective vales for TA and TB of Figure 1d. As it is typical of currently known electrocaloric materials, the temperature change in the application of an electric field is low; for PST, the maximum is ~4 K at 305 K with 15.8 V µm−1 electric field [40]. In order to increase the temperature differential between points TA and TB (Figure 1d), we have considered a 13 PST multilayer system. The resulting thermal output power and electrical input power are presented in Figure 2 as a function of the speed at which the thermodynamic cycle in Figure 1d can be achieved. The resulting coefficient of performance, i.e., the difference in output power to input power, is ~3, giving an efficiency of ~300%. This result highlights the high efficiency/CoP due to the ability to extract heat from the low-temperature end of the system in the same way that heat pumps extract heat from their surroundings.
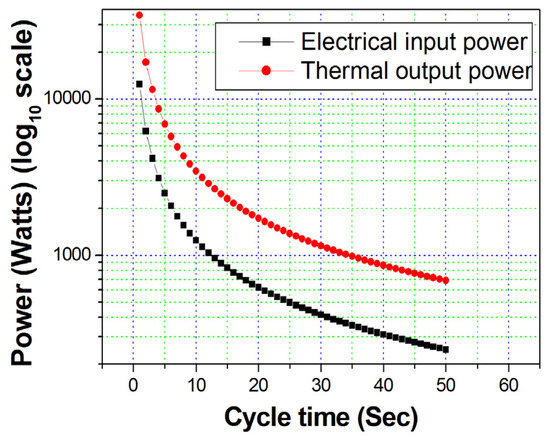
Figure 2.
Thermal output power and electrical input power for our idealized electrocaloric heater.
A cycle time (path A–B–C in Figure 1d) of the order of seconds is not unrealistic considering the subminute magnetocaloric cycle times presented in Bartlett et al. [41] and the relative ease in which an electric field can be generated compared to a magnetic field. When the same heating principle is applied to a suitable multiferroic active element, up to twice the temperature change is expected, leading to even more efficient heating systems.
The purpose of this communication article is to reemphasize the fundamentals of solid-state refrigeration based on the new concept of multicaloric effect in multiferroics and to propose a new possible application of this effect to solid-state heating in addition to the refrigeration. Theoretically, both heating and cooling offer the promise of achieving ultra-efficient temperature changes with predicted cooling/heating rates per cycle of up to double the values achieved in electrocaloric or magnetocaloric materials. We, therefore, hope that this work will stimulate experimental and commercial interest in developing not only solid-state cooling based on the multicaloric effect but also solid-state heating technologies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.V., Y.K.F. and I.H.; methodology, M.M.V.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.V., Y.K.F. and I.H.; Final review and editing, I.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.M.V. and I.H. received no external funding for this research. Research of YF at RTU MIREA was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project No. 17-12-01435-P.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
M.M.V. acknowledges the support received from SMAP, University of Portsmouth to undertake this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mañosa, L.; González-Alonso, D.; Planes, A.; Bonnot, E.; Barrio, M.; Tamarit, J.L.; Aksoy, S.; Acet, M. Giant solid-state baro-caloric effect in the Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape-memory alloy. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnot, E.; Romero, R.; Mañosa, L.; Vives, E.; Planes, A. Elastocaloric Effect Associated with the Martensitic Transition in Shape-Memory Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Tsokol, A.O. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. Electrocaloric Materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2011, 41, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castan, T.; Planes, A.; Saxena, A. Thermodynamics of ferrotoroidic materials: Toroidocaloric effect. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 144429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.S. Oscillating adiabatic temperature change of diamagnetic materials. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, J.; Hardy, G.; Hepburn, I.D.; Brockley-Blatt, C.; Coker, P.; Crofts, E.; Winter, B.; Milward, S.; Stafford-Allen, R.; Brownhill, M.; et al. Improved performance of an engineering model cryogen free double adiabatic de-magnetization refrigerator. Cryogenics 2010, 50, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakouri, A.; Zhang, Y. On-chip solid-state cooling for integrated circuits using thin-film microrefrigerators. IEEE Trans. Components Packag. Technol. 2005, 28, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Giant magnetocaloric effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4494–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischenko, A.S.; Zhang, Q.; Scott, J.F.; Whatmore, R.W.; Mathur, N.D. Gian Electrocaloric Effect in Thin-Film PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3. Science 2006, 311, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, M. Revival of the magnetoelectric effect. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, R123–R152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Gray, D.; Li, J.; Viehland, D. Enhanced sensitivity to direct current magnetic field changes in Metglas/Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3–PbTiO3 laminates. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 074507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopsaroiu, M.; Cain, M.; Sreenivasulu, G.; Srinivasan, G.; Balbashov, A. Multiferroic composite for combined detection of static and alternating magnetic fields. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajek, M.; Bibes, M.; Fusil, S.; Bouzehouane, K.; Fontcuberta, J.; Barthélémy, A.; Fert, A. Tunnel junctions with multiferroic barriers. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibes, M.; Barthélémy, A. Multiferroics: Towards a magnetoelectric memory. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.F. Data storage: Multiferroic memories. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vopsaroiu, M.; Blackburn, J.; Muniz-Piniella, A.; Cain, M.G. Multiferroic magnetic recording read head technology for 1 Tb/in2 and beyond. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07F506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, C.; Ma, J.; Lin, Y.; Nan, C.W. Demonstration of magnetoelectric read head of multiferroic heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 152510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Li, J.F.; Viehland, D. Voltage gain effect in a ring-type magnetoelectric laminate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; Song, Y.; Bhatti, K.; James, R.D. The direct conversion of heat to electricity using multiferroic alloys. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. Fundamentals of Multiferroic Materials and Their Possible Applications. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2015, 40, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. The multicaloric effect in multiferroic materials. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 2067–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. Theory of giant-caloric effects in multiferroic materials. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 345304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Li, B.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z. Coupled caloric effects in multiferroics. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpay, S.P.; Mantese, J.; Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Zhang, Q.; Whatmore, R.W. Next-generation electrocaloric and pyroelectric materials for solid-state electrothermal energy interconversion. Mrs Bull. 2014, 39, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M.; Zhou, D.; Caruntu, G. Multicaloric effect in bi-layer multiferroic composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 182905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, A.; Castan, T.; Saxena, A. Thermodynamics of multicaloric effects in multiferroics. Philos. Mag. 2014, 94, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Janolin, P.E.; Infante, I.C.; Kreisel, J.; Lou, X.; Dkhil, B. Prediction of giant elastocaloric strength and stress-mediated electrocaloric effect in BaTiO3 single crystals. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Chauhan, A.; Vaish, R. Multiple caloric effects in (Ba0.865Ca0.135Zr0.1089Ti0.8811Fe0.01)O3 ferroelectric ceramic. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 042902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. The induced magnetic and electric fields’ paradox leading to multicaloric effects in multiferroics. Solid State Commun. 2016, 231, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Q.; Cao, H.-X. Multicaloric effect in multiferroic EuTiO3 thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5705–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. Multicaloric effect: An outlook. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2017, 513, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Castillo-Villa, P.O.; Soto-Parra, D.E.; Matutes-Aquino, J.A.; Ochoa-Gamboa, R.A.; Planes, A.; Mañosa, L.; González-Alonso, D.; Stipcich, M.; Romero, R.; Ríos-Jara, D.; et al. Caloric effects induced by magnetic and mechanical fields in a Ni 50 Mn 25−x Ga 25 Co x magnetic shape memory alloy. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 174109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Villa, P.O.; Mañosa, L.; Planes, A.; Soto-Parra, D.E.; Sánchez-Llamazares, J.L.; Flores-Zúñiga, H.; Frontera, C. Elasto-caloric and magnetocaloric effects in Ni-Mn-Sn(Cu) shape-memory alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 053506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahler, S.; Roßler, U.K.; Kastner, O.; Eckert, J.; Eggeler, G.; Emmerich, H.; Entel, P.; Muller, S.; Quandt, E.; Albe, K. Caloric Effects in Ferroic Materials: New Concepts for Cooling. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2012, 14, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Fodouop, F.K.; Fouokeng, G.C.; Tsokeng, A.T.; Tchoffo, M.; Fai, L.C. Metamagnetoelectric transitions-enhanced multicaloric effect in multiferroics A2Cu2Mo3O12 (A = Rb and Cs) quantum spin chain. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 128, 114616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M.; Fetisov, Y.K.; Caruntu, G.; Srinivasan, G. Measurement Techniques of the Magneto-Electric Coupling in Mul-tiferroics. Materials 2017, 10, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neese, B.; Chu, B.; Lu, S.-G.; Wang, Y.; Furman, E.; Zhang, Q.M. Large Electrocaloric Effect in Ferroelectric Polymers Near Room Temperature. Science 2008, 321, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.G.; Sun, J.R.; Hu, F.X.; Zhang, H.W.; Cheng, Z.H. Recent Progress in Exploring Magnetocaloric Materials. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4545–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, B.; Usui, T.; Crossley, S.; Kurdi, S.; Guzmán-Verri, G.G.; Moya, X.; Hirose, S.; Mathur, N.D. Large electrocaloric effects in oxide multi-layer capacitors over a wide temperature range. Nature 2019, 575, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, J.; Hardy, G.; Hepburn, I. Performance of a fast response miniature Adiabatic Demagnetisation Refrigerator using a single crystal tungsten magnetoresistive heat switch. Cryogenics 2015, 72, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).