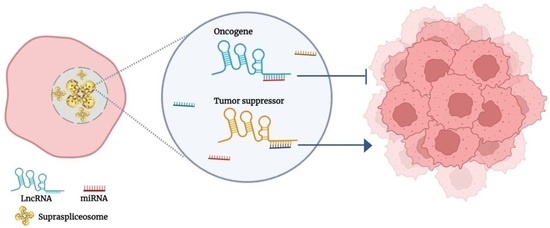
Crosstalk between Long Non-Coding RNA and Spliceosomal microRNA as a Novel Biomarker for Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ncRNA in Cancer
2.1. MicroRNA (miRNA)
2.2. miRNA in the Supraspliceosome
2.3. Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA)
2.3.1. Genomic Localization
2.3.2. Function
2.3.3. Structure
2.4. Competing Endogenous RNA (ceRNA) Networks and Regulation
2.5. lncRNA in Cancer
3. lncRNA: Spliceosomal miRNA Crosstalk in Breast and Cervical Cancer Cells
| miRNA | Reads | miRNA Strand | lncRNA b | lncRNA Strand | miRNA Annotation Relative to lncRNA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF10A (% Mature) a | MCF7 (% Mature) | MDA (% Mature) | Name | Genomic Coordinates c | Accession No. | ||||
| Antisense direction (lncRNA and miRNA) | |||||||||
| * has-mir-7704 | 1167 (100) | 80 (100) | 94 (100) | + | HAGLR | chr2:176173189-176188958 | NR_033979.2 | − | exon |
| hsa-mir-99b | 23 (95.65) | 37 (94.59) | 69 (100) | + | SPACA6P-AS1 | chr19:51685363-51693456 | NR_108100.1 | − | Splice junction |
| hsa-let-7e | 66 (19.7) | 24 (91.67) | 23 (100) | + | exon | ||||
| hsa-mir-125a | 25 (84) | 10 (100) | 16 (87.5) | + | exon | ||||
| hsa-let-7i | 76 (97.37) | 138 (98.55) | 661 (99.09) | + | LINC01465 | chr12:62601751-62603690 | ENST00000408887.3 | − | Part of exon (first 5 nt) |
| hsa-mir-29a | 27 (11.11) | 0 | 39 (87.18) | − | LINC00513 | chr7:130853732-130930680 | ENST00000653887.1 | + | intron |
| LINC-PINT | chr7:130791264-131107928 | ENST00000642963.1 | − | intron/exon | |||||
| hsa-mir-16-2 | 0 | 0 | 14 (100) | + | TRIM59-IFT80 | Isoform 1: chr3:160227454-160449838 | NR_148401.1 | − | intron |
| Isoform 2: chr3:160256986-160449838 | NR_148402.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 3: chr3:160256986-160485747 | NR_148403.1 | ||||||||
| * has-mir-1246 | 1814 (100) | 189 (100) | 144 (100) | − | LINC01117 | chr2:176495255-176655967 | ENST00000652995.1 | + | intron |
| hsa-let-7d | 0 | 0 | 24 (83.33) | + | LINC02603 | Isoform 1: chr9:94176569-94204566 | NR_046163.1 | − | intron |
| Isoform 2: chr9:94176570-94204566 | NR_046165.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 3: chr9:94176569-94259311 | NR_160773.1 | ||||||||
| Sense direction (lncRNA and miRNA) | |||||||||
| hsa-mir-92b | 0 | 0 | 26 (100) | + | THBS3-AS1 | Isoform 1: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183234.1 | + | exon |
| isoform 2: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183235.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 3: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183236.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 4: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183237.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 5: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183238.1 | ||||||||
| * has-mir-612 | 1494 (0.47) | 0 (0) | 20 (0) | + | NEAT1 | chr11:65422798-65445540 | NR_131012.1 | + | exon |
| hsa-mir-30c-2 | 0 | 0 | 39 (100) | − | LINC00472 | Isoform 1: chr6:71343427-71420130 | ENST00000651778.1 | − | intron/exon |
| * hsa-mir-30a | 19 (100) | 0 | 473 (97.67) | − | Isoform 2: chr6:71373251-71420148 | ENST00000625013.2 | intron | ||
| hsa-mir -4712 | 21 (90.48) | 0 | 0 | + | GABPB1-AS1 | Isoform 1: chr15:50355476-50372158 | ENST00000648591.1 | + | intron/exon |
| Isoform 2: chr15:50355467-50372202 | ENST00000499624.3 | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-16-1 | 0 | 0 (0) | 13 (76.92) | − | DLEU2 | Isoform 1: chr13:49982549-50125541 | NR_152566.1 | − | intron |
| Isoform 2: chr13:50043436-50082041 | NR_152567.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 3: chr13:50043436-50082041 | NR_152568.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 4: chr13:50049189-50082041 | NR_152569.1 | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-15a | 42 (0) | 27 (3.7) | 33 (3.03) | − | Isoform 5: chr13:50026695-50082041 | NR_152571.1 | intron/part of exon | ||
| Isoform 6: chr13:50049189-50082041 | NR_152570.1 | ||||||||
| Isoform 7: chr13:50026695-50082041 | NR_152572.1 | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-1204 | 22 (0) | 0 | 0 | + | PVT1 | chr8:127794533-128101253 | NR_003367.3 | + | intron |
| hsa-mir-545 | 10 (0) | 0 | 0 | − | FTX | chrX:74028136-74293574 | NR_028379.1 | − | intron |
| hsa-mir-6516 | 10 (0) | 0 | 0 | + | SNHG20 | chr17:77088643-77094986 | NR_027058.1 | + | intron |
| SCARNA16 | chr17:77089307-77089493 | NR_003013.1 | exon | ||||||
| hs-mir-6840 | 85 (0) | 21 (0) | 13 (0) | + | STAG3L5P-PVRIG2P-PILRB | Isoform 1: chr7:100336065-100367831 | NR_036569.1 | + | intron |
| Isoform 2: chr7:100336065-100367831 | NR_036570.1 | ||||||||
| miRNA | Reads | miRNA Strand | lncRNA d | lncRNA Strand | miRNA Annotation Relative to lncRNA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF HeLa a (% Mature) c | CE HeLa b | Name | Genomic Coordinates e | Accession No. | ||||
| Antisense direction (lncRNA and miRNA) | ||||||||
| ^ hsa-mir-7704 | 2798 (100) | 0 | + | HAGLR | chr2:176173189-176188958 | NR_033979.2 | − | exon |
| hsa-mir-99b | 366 (97.5) | 25,823 | + | SPACA6P-AS1 | chr19:51685363-51693456 | NR_108100.1 | − | Splice junction |
| hsa-mir-125a | 209 (99.5) | 7587 | exon | |||||
| hsa-let-7e | 532 (99.8) | 5326 | exon | |||||
| hsa-mir-3615 | 46 (95.65) | 646 | + | SLC9A3R1-AS1 | chr17:74747319-74748912 | ENST00000585285.1 | − | exon |
| ^ hsa-let-7i | 16,229 (99.75) | 243,109 | + | LINC01465 | chr12:62601751-62603690 | ENST00000408887.3 | − | Part of exon (first 5 nt) |
| hsa-mir-196b | 27 (100) | 959 | − | HOXA10-AS | chr7:27168899-27171915 | NR_046609.1 | + | exon |
| HOXA10-HOXA9 | chr7:27162438-27180261 | NR_037940.1 | - | intron | ||||
| hsa-mir-29a | 57 (89.47) | 3818 | − | LINC00513 | chr7:130853732-130930680 | ENST00000653887.1 | + | intron |
| LINC-PINT | chr7:130791264-131107928 | ENST00000642963.1 | − | intron/part of exon | ||||
| ^ hsa-mir-1246 | 3365 (100) | 1025 | − | LINC01117 | chr2:176495255-176655967 | ENST00000652995.1 | + | intron |
| hsa-let-7d | 285 (97.54) | 5172 | + | LINC02603 | Isoform 1: chr9:94176569-94204566 | NR_046163.1 | − | intron |
| Isoform 2: chr9:94176570-94204566 | NR_046165.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 3: chr9:94176569-94259311 | NR_160773.1 | |||||||
| hsa-mir-196a-1 | 389 (98.71) | 4663 | − | HOXB-AS4 | Isoform 1: chr17:48628698-48634932 | NR_046611.1 | + | intron |
| Isoform 2: chr17:48629521-48634932 | NR_170224.1 | |||||||
| hsa-mir-149 | 10 (100) | 431 | + | GPC1-AS1 | chr2:240449379-240456700 | NR_161169.1 | − | intron |
| hsa-mir-10a | 146 (100) | 17,518 | − | HOXB-AS3 | chr17:48549630-48602332 | ENST00000465846.6 | + | intron |
| hsa-mir-15b | 14 (85.71) | 800 | + | TRIM59-IFT80 | Isoform 1: chr3:160227454-160449838 | NR_148401.1 | − | intron |
| hsa-mir-16-2 | 30 (80) | 3123 | Isoform 2: chr3:160256986-160449838 | NR_148402.1 | ||||
| Isoform 3: chr3:160256986-160485747 | NR_148403.1 | |||||||
| Sense direction (lncRNA and miRNA) | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-612 | 15 (0) | 0 | + | NEAT1 | chr11:65422798-65445540 | NR_131012.1 | + | exon |
| hsa-mir-30c-2 | 192 (99.48) | 19,157 | − | LINC00472 | Isoform 1: chr6:71343427-71420130 | ENST00000651778.1 | − | intron/exon |
| ^ hsa-mir-30a | 2311 (98.91) | 79,239 | − | Isoform 2: chr6:71373251-71420148 | ENST00000625013.2 | intron | ||
| hsa-mir-92b | 235 (100) | 4963 | + | THBS3-AS1 | Isoform 1: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183234.1 | + | exon |
| isoform 2: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183235.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 3: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183236.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 4: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183237.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 5: chr1:155194997-155205489 | NR_183238.1 | |||||||
| hsa-mir-143 | 12 (100) | 704 | + | CARMN | Isoform 1: chr5:149406845-149432836 | NR_105059.1 | + | exon |
| Isoform 2: chr5:149406845-149432836 | NR_105060.1 | |||||||
| hsa-mir-15a | 13 (30.77) | 20 | − | DLEU2 | Isoform 1: chr13:49982549-50125541 | NR_152566.1 | − | intron |
| Isoform 2: chr13:50043436-50082041 | NR_152567.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 3: chr13:50043436-50082041 | NR_152568.1 | |||||||
| hsa-mir-16-1 | 11 (100) | 1196 | Isoform 4: chr13:50049189-50082041 | NR_152569.1 | intron | |||
| Isoform 5: chr13:50026695-50082041 | NR_152571.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 6: chr13:50049189-50082041 | NR_152570.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 7: chr13:50026695-50082041 | NR_152572.1 | |||||||
| hsa-mir-421 | 15 (0) | 207 | − | FTX | chrX:74028136-74293574 | NR_028379.1 | − | intron |
| hsa-mir-374a | 42 (85.71) | 2070 | intron | |||||
| hsa-mir-374b | 16 (93.75) | 1941 | intron | |||||
| hsa-mir-4449 | 74 (0) | 1 | + | LINC01618 | chr4:52,712,394-52,866,821 | ENST00000650700.1 | + | intron |
| DANCR | Isoform 1: chr4:52712394-52714138 | NR_024031.2 | ||||||
| Isoform 2: chr4:52712394-52720697 | NR_145129.1 | |||||||
| Isoform 3: chr4:52712394-52720696 | NR_145130.1 | |||||||
3.1. Antisense lncRNA and Spliceosomal miRNA Interaction in Breast and Cervical Cancer Cells
3.1.1. HAGLR (HOXD Antisense Growth-Associated Long Non-Coding RNA)
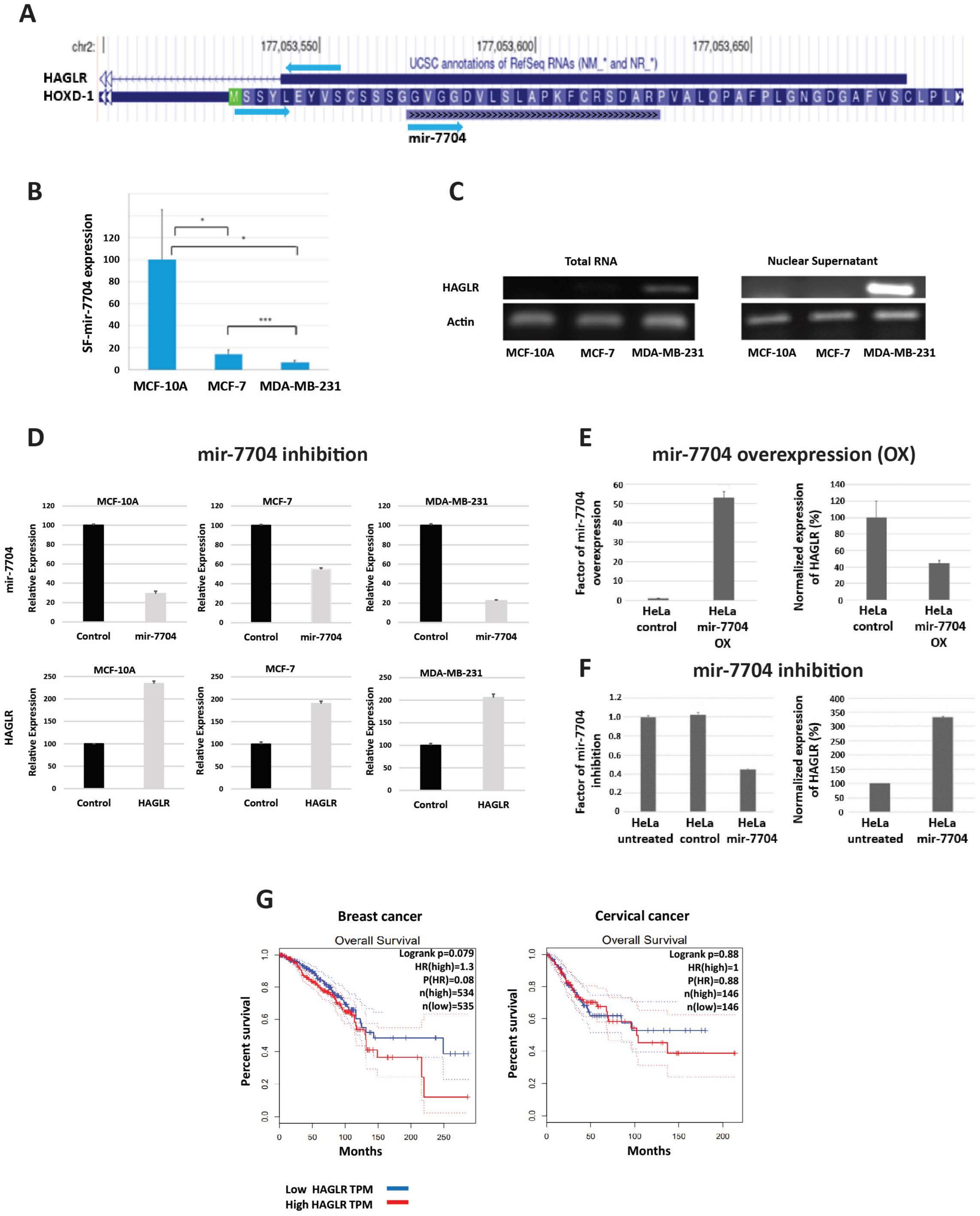
3.1.2. SPACA6P-AS (SPACA6 Antisense RNA 1)

3.1.3. LINC01465 (Long Intergenic Non-Protein-Coding RNA 1465)
3.1.4. LINC01117 (Long Intergenic Non-Protein-Coding RNA 1117)
3.1.5. TRIM59-IFT80: Located on Chromosome 3q25.33
3.2. Antisense lncRNA and Spliceosomal miRNA Interaction in Cervical Cancer Cells
3.2.1. HOXB-AS3 (HOXB Cluster Antisense RNA 3)
3.2.2. HOXA10-AS (HOXA Cluster Antisense RNA 4)
3.3. Sense Spliceosomal miRNA and lncRNA Crosstalk in Breast and Cervical Cancer Cells
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhan, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mandal, S.S. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, B.T.; Fearon, E.R. Abeloff’s Clinical Oncology, Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations in Cancer, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2020; pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Mitelman, F.; Johansson, B.; Mertens, F. The impact of translocations and gene fusions on cancer causation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R. Small non-coding RNA within the endogenous spliceosome and alternative splicing regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlab-Aviv, S.; Zohar, K.; Cohen, Y.; Peretz, A.R.; Eliyahu, T.; Linial, M.; Sperling, R. Spliceosome-associated microRNAs signify breast cancer cells and portray potential novel nuclear targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. Long noncoding RNAs: Emerging stars in gene regulation, epigenetics and human disease. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1932–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnal, S.C.; López-Oreja, I.; Valcárcel, J. Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer—Implications for care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ule, J.; Blencowe, B.J. Alternative splicing regulatory networks: Functions, mechanisms, and evolution. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, L.E.; Kornblihtt, A.R. The physiology of alternative splicing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Charenton, C.; Nagai, K. RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R. The nuts and bolts of the endogenous spliceosome. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, M.; Sperling, R. A Quality Control Mechanism of Splice Site Selection Abrogated under Stress and in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, J.; Azubel, M.; Sperling, R. Structure and function of the Pre-mRNA splicing machine. Structure 2008, 16, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agranat-Tamir, L.; Shomron, N.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R. Interplay between pre-mRNA splicing and microRNA biogenesis within the supraspliceosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4640–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Falaleeva, M.; Agranat-Tamir, L.; Pages, A.; Eyras, E.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R.; Stamm, S. The 5’ untranslated region of the serotonin receptor 2C pre-mRNA generates miRNAs and is expressed in non-neuronal cells. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 230, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaleeva, M.; Pages, A.; Matuszek, Z.; Hidmi, S.; Agranat-Tamir, L.; Korotkov, K.; Nevo, Y.; Eyras, E.; Sperling, R.; Stamm, S. Dual function of C/D box small nucleolar RNAs in rRNA modification and alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1625–E1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlab-Aviv, S.; Boulos, A.; Peretz, A.R.; Eliyahu, T.; Carmel, L.; Sperling, R.; Linial, M. Small RNA sequences derived from pre-microRNAs in the supraspliceosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 11014–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan micrornas. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavast, C.J.; Erkeland, S.J. The non-canonical aspects of microRNAs: Many roads to gene regulation. Cells 2019, 8, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Ma, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shao, P.; Chen, Y.; Qu, L. Deep sequencing of human nuclear and cytoplasmic small RNAs reveals an unexpectedly complex subcellular distribution of miRNAs and tRNA 3′ trailers. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, C.; He, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, D.; Tao, Y. Nuclear functions of mammalian MicroRNAs in gene regulation, immunity and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucci, E.; Patella, F.; Waage, J.; Holmstrøm, K.; Lindow, M.; Porse, B.; Kauppinen, S.; Lund, A.H. microRNA-9 targets the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 for degradation in the nucleus. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, K.; Nishi, A.; Nagasawa, T.; Ui-Tei, K. Human TNRC6A is an Argonaute-navigator protein for microRNA-mediated gene silencing in the nucleus. RNA 2013, 19, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younger, S.T.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Corey, D.R. Predicting potential miRNA target sites within gene promoters. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3791–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Schwartz, J.C.; Chu, Y.; Younger, S.T.; Gagnon, K.T.; Elbashir, S.; Janowski, B.A.; Corey, D.R. Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs at sequences downstream from 3′ gene termini. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, S.; Xie, H.; Peng, X.; Yin, W.; Tao, Y.; et al. miRNA-based biomarkers, therapies, and resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, N.; Ulitsky, I. Regulation of gene expression by cis-acting long non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, M.; Mafra, A.C.P.; Dias, S.M.G.; Vasilescu, C.; Calin, G.A. Using microRNA networks to understand cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.J.; Tay, Y. Noncoding RNA: RNA regulatory networks in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connerty, P.; Lock, R.B.; de Bock, C.E. Long non-coding RNAs: Major regulators of cell stress in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Gao, L.; Ma, X.; Huang, J.J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, L.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Zou, C.; Chen, Z.S. Long non-coding RNAs regulate drug resistance in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarte, M. The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Diao, Y.; Yin, H.; Liu, H. Long non-coding RNA HOXD-AS1 in cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 487, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yi, L.; Paizula, X.; Xu, W.; Wu, X. HOXD antisense growth-associated long noncoding RNA promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression by activating Wnt signaling pathway. J. Breast Cancer 2021, 24, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xiao, G.-R.; Wu, C.-L.; Xu, Y.-Q. HAGLR promotes neuron differentiation through the miR-130a-3p-MeCP2 axis. Open Med. 2021, 16, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-C.; Wang, A.-M.; Lu, J.-K.; Cen, R.; Liu, L.-L. Long noncoding RNA HOXD-AS1 regulates proliferation of cervical cancer cells by activating Ras/ERK signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 5049–5055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Corey, D.R. The 10th oligonucleotide therapy approved: Golodirsen for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiriboga, C.A. Nusinersen for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. Expert Rev. Neurothe. 2017, 17, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilton, S.D.; Fall, A.M.; Harding, P.L.; McClorey, G.; Coleman, C.; Fletcher, S. Antisense oligonucleotide-induced exon skipping across the human dystrophin gene transcript. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Zhang, S.; Qu, J. A seven-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis in breast carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 4033–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Palo, A.; Siniscalchi, C.; Mosca, N.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. A novel ceRNA regulatory network involving the long non-coding antisense RNA SPACA6P-AS, miR-125a and its mRNA targets in hepatocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgundkar, S.H.; Abdullah Hassan, N.; Al Badi, H.; Gupta, I.; Burney, I.A.; Al Hashami, Z.; Al Barwani, H.; Al Riyami, H.; Al Kalbani, M.; Lakhtakia, R.; et al. Identification and validation of a novel long non-coding RNA (LINC01465) in ovarian cancer. Hum. Cell 2023, 36, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shu, L.; Niu, N.; Zhao, C.; Lu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zou, T.; Zou, J.; et al. Novel lncRNAs with diagnostic or prognostic value screened out from breast cancer via bioinformatics analyses. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Jia, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Cong, Y.; Lv, M.; Xu, J.; Ruan, H.; Jia, X.; Xu, P.; et al. LncRNA HOXB-AS3 promotes growth, invasion and migration of epithelial ovarian cancer by altering glycolysis. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Li, C.; Lu, P.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Gong, J. HTR1D functions as a key target of HOXA10-AS/miR-340-3p axis to promote the malignant outcome of pancreatic cancer via PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 3777–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Z.; Chen, M.; Chen, D.; Gao, X.-C.; Zhu, S.; Huang, H.; Hu, M.; Zhu, H.; Yan, G.-R. A Peptide Encoded by a Putative lncRNA HOXB-AS3 Suppresses Colon Cancer Growth. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 171–184.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, D.; Petri, A.; Dovey, O.M.; Terreri, S.; Wang, E.; Collins, F.A.; Woodward, L.A.; Walker, A.E.; Nicolet, D.; Pepe, F.; et al. The long non-coding RNA HOXB-AS3 regulates ribosomal RNA transcription in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Avino, M.; Wellinger, R.J.; Laurent, B. Distinct regulatory functions and biological roles of lncRNA splice variants. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 32, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Nie, P.; Zhu, D. LncRNA HOXA10-AS Activated by E2F1 Facilitates Proliferation and Migration of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells Through Sponging miR-582-3p to Upregulate RAB31. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2022, 36, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemson, C.M.; Hutchinson, J.N.; Sara, S.A.; Ensminger, A.W.; Fox, A.H.; Chess, A.; Lawrence, J.B. An architectural role for a nuclear noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA is essential for the structure of paraspeckles. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, E.; Harris, A.L.; Perander, M. Expression and functions of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 and isoforms in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, T.; Souquere, S.; Chujo, T.; Kobelke, S.; Chong, Y.S.; Fox, A.H.; Bond, C.S.; Nakagawa, S.; Pierron, G.; Hirose, T. Functional domains of NEAT1 architectural lncRNA induce paraspeckle assembly through phase separation. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 1038–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Hu, H.; Zhang, T.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Kong, Q.; Lu, H.; Lu, Z. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes breast cancer proliferation and metastasis by binding miR-128-3p and UPF1. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Loo, L.W.; Ni, Y.; Jia, W.; Fei, P.; Risch, H.A.; Katsaros, D.; Yu, H. LINC00472 expression is regulated by promoter methylation and associated with disease-free survival in patients with grade 2 breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 154, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, Z. Comprehensive Analysis of Regulatory Network for LINC00472 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Health Eng. 2021, 2021, 3533608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Lv, X.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Song, J.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Ai, Y. LINC00472 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-4311/GNG7 axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 6371–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arafat, M.; Sperling, R. Crosstalk between Long Non-Coding RNA and Spliceosomal microRNA as a Novel Biomarker for Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040042
Arafat M, Sperling R. Crosstalk between Long Non-Coding RNA and Spliceosomal microRNA as a Novel Biomarker for Cancer. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(4):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleArafat, Maram, and Ruth Sperling. 2023. "Crosstalk between Long Non-Coding RNA and Spliceosomal microRNA as a Novel Biomarker for Cancer" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 4: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040042
APA StyleArafat, M., & Sperling, R. (2023). Crosstalk between Long Non-Coding RNA and Spliceosomal microRNA as a Novel Biomarker for Cancer. Non-Coding RNA, 9(4), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040042