Abstract
The synthetic jet actuator (SJA) generated high noise which limits the area of its application. In this paper, the five actuators with different types of soundproofing in the cavity were tested and compared to the classic actuator. The resistance and the sound pressure level (SPL) were measured for real power W, and frequency in a range of 20–150 Hz. The resonant frequency of actuators was designed. Only one type of soundproofing had a significant impact on the resonant frequency. The use of soundproofing in the actuator cavity increased or did not affect the generated noise at a frequency below 120 Hz and only the mineral wool significantly decreased the noise at a frequency above 120 Hz– even 7 dBA. The direction for further investigations was set.
1. Introduction
The concept of the synthetic jet (SJ) was proposed in the early 1970s and is still alive and developed [1]. New types of synthetic jet actuators (SJA), new methods of SJ generation, and new applications of SJ are being proposed all the time. The SJ is used in many science areas and also in industrial applications. The most common uses are heat transfer enhancement [2,3,4,5], active flow control and jet vectoring [6,7,8], and mixing enhancement [9,10,11]. Regardless of the application, however, one of the big problems of SJA remains the high level of generated noise, which can be as high as 90 dB or more [12]. According to the EN ISO 9241-6: 2002 [13] standard, in the case of difficult and complex tasks requiring concentration (office work), the sound pressure level (SPL) should not exceed 35–55 dB.
The level of noise in the background has a significant impact on our health and mental condition. Many papers showed that noise has a negative impact on physical and psychological well-being, self-rated fatigue, and causes a disturbance, annoyance, and physiological stress [14,15]. Additionally, environmental noise is one of the causes of cardiovascular disorders such as ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, hypertension, stroke, etc. [16]. For these reasons, the SPL should be reduced if it is possible.
Arick [17] was one of the first to point out the noise problem. However, his proposal to enclose the actuator in a small box with a muffler was impractical. Lasance et al. [18] investigated the impact of the orifice diameter and length on the sound pressure level (SPL). The smaller the diameter and the longer the hole, the lower the SPL. These dependencies have been confirmed by other researchers. Bhapkar et al. [19] and Kanase et al. [20] confirmed that the SPL decreased with the orifice length, and Kanase et al. [20] show also that the SPL increased with the orifice diameter.
Bhapkar et al. [21] postulated that the noise increased with the orifice length. They investigated actuators with a constant aspect ratio orifice. The increase of the orifice length from 2 mm to 5 mm caused the SPL to increase by 3–6 dB (4–10%). However, because the orifices had a constant aspect ratio, the orifice diameter also increased. Based on other studies [18,19,20], it should be noted that Bhapkar et al. [21] made an inference error in the course of their research. While maintaining the same aspect ratio, they assessed that it is the orifice length that influences the generated noise, and not the orifice diameter, which in this case turned out to be the decisive factor. Whereas, Zhang et al. [22] simulated the SJA and investigated the impact of the orifice and cavity parameters on the SPL level. The SPL increased when the orifice diameter increased, and the cavity height decreased. In the case of orifice length and cavity diameter, the dependence is not so clear. The maximal value of the SJ was obtained at the resonant frequency of the actuator. Gil et al. [23] showed that the SPL directly depends on the ratio of the orifice diameter to the cavity diameter and is proportional to the SJ velocity. The other researchers investigated the impact of the orifice shape or number on the SPL [20,21,24,25,26,27].
In this paper, the multi–orifice SJA with one wall replaced by the soundproofing was tested. This idea arose during research carried out on multi-hole actuators with a heat exchanger in the chamber. This type of actuator was first time presented by Gil [28] and generated a relatively low noise level compared to other actuators [29]. Hence, the wall opposite the actuator exciter was replaced by one of five different types of soundproofing materials. Electrical parameters and generated noise were examined for such a constructed actuator.
2. Materials and Methods
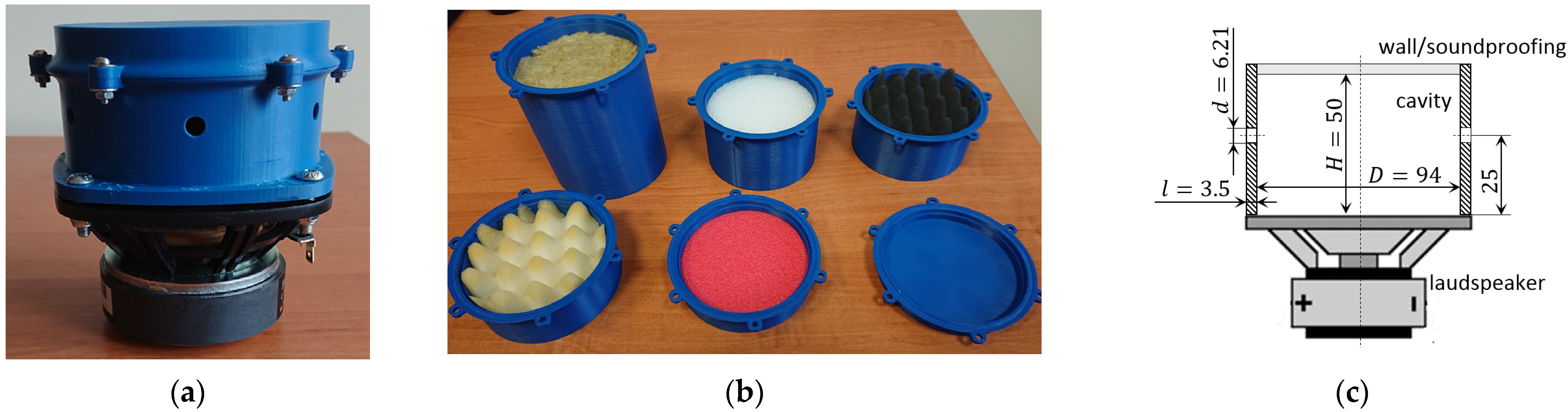
In the paper, the SJ with soundproofing in the cavity was tested. The multi-orifice actuator, used in this investigation, is shown in Figure 1. The actuator body was printed from Z-ULTRAT (material based on ABS—acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) using 3D technology. The wall thickness was 3.5 mm. The cavity diameter was 95 mm, and the cavity height was 50 mm. In the body were six orifices with a diameter of 6.21 mm (value measured on the model). The orifices were arranged symmetrically around the perimeter. The orifices were made halfway between the loudspeaker and the opposite wall (Figure 1c). The mid-range woofer SB Acoustics SB12PAC25-4/4” was used.
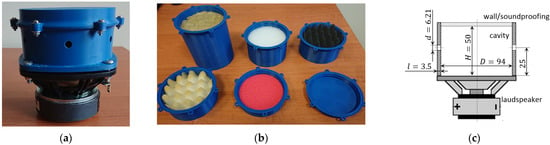
Figure 1.
The synthetic jet actuator: (a) the compound actuator for Case 0; (b) the top part of the actuator body with the soundproofing filling; (c) the schema of the actuator.
The actuator body was made of two parts. The top part of the actuator body was made for each type of filling separately in such a way that the cavity height H was 50 mm (Figure 1b). The connections between the loudspeaker and actuator body and between the top and bottom parts of the actuator body have been sealed with an O-ring. In cases 2 and 3, a cavity height was understood to mean a distance from the loudspeaker to half the height of the ‘pyramids’. The used soundproofing is presented Table 1.

Table 1.
The tested type of the soundproofing.
The SJA was supplied with a sinusoidal signal generator by a Rigol GD4162 and amplified by an HW-447 TPA3116D2 amplifier. The current and voltage drops were measured with Keithley 2701 instruments (6.5 digits, 22-bits) with a 7706 all-in-one I/O module. The current was measured as a voltage drop on a reference resistor (1 Ω, ±0.01%). The measurements were for the frequency range from 20 to 150 Hz with step 5 Hz and at the complex power 1, 2, and 4 VA. It was proved many times that the phase shift between the current and voltage at low frequency is close to 1 [30,31,32]. Therefore, complex power can be identified as real power without serious error. It was used before in other papers [33]. The power was measured with relative accuracy of ±0.25%. The power was calculated as:
where E is an effective voltage [V], and I is an effective current [A].
Additionally in the paper, the resistance of the actuator was calculated as:
The SPL was measured with a testo 816-1 sound level meter compiled with the requirements of the IEC 61672-1 Class2 and ANSI S1.4 Type 2 standards. The measurements range was from 30 to 130 dB and the frequency range was from 20 Hz to 8 kHz. The accuracy of measurements was ±1.4 dB with a resolution of 0.1 dB. The background SPL of the environment was 37.8 dB, and the sound level meter was placed 1 m from the SJA. During the measurements, the A-weighting was used. The measurements were made according to ISO 3746:2010 [34].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Resonant Frequency
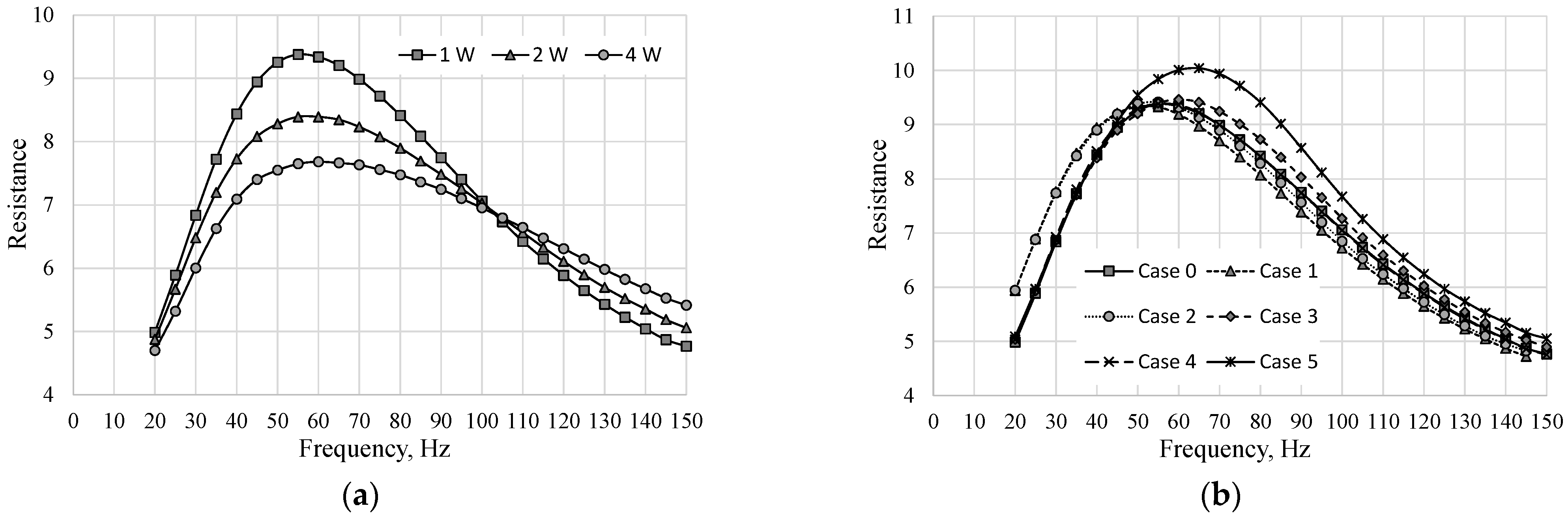
Figure 2 presents the resistance in the function of the actuator frequency at different real power for Case 0 (Figure 2a) and at the real power equal to 1 W for all investigated cases (Figure 2b). The resonant frequency of the actuator can be determined as a local maximum of the actuator resistance. The resonant frequency of Case 0 was determined as 55 Hz at real power 1 W and 2 W and as 60 Hz at 3 W. However, the resonant frequency is independent of the power of the actuator. The difference in the resonant frequency value determined from Figure 2a was caused by the large step of the frequency (5 Hz) and it should be assumed that the real value of the resonant frequency of Case 0 was in the range from 55 to 60 Hz. For the sake of simplicity, the resonance frequencies were determined for the power of 1 W. Based on Figure 2b, the characteristics frequency for subsequent (from 0 to 5) cases was: 55; 55; 60; 60; 55; and 65 Hz.
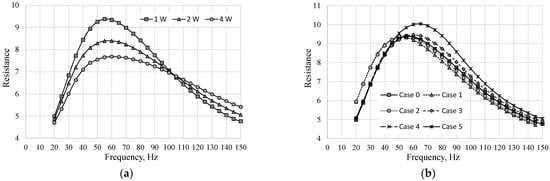
Figure 2.
Resistance vs. frequency: (a) Case 0 at the different real power; (b) different cases at the real power W.
The determined characteristic frequency was the natural frequency. The natural frequency of the synthetic jet actuator is the function of the diaphragm spring constant, the diaphragm mass, the mass of the air in the actuator orifices, and the diameter of the cavity and the orifice [22,33,35]. However, some investigations showed that the natural frequency was dependent also on the cavity volume [30,36] but only to a minor extent. Therefore, the natural frequency should be the same or close to each other in all investigated cases.
The change of characteristic frequency in cases 2 and 3 was not surprising. The pyramid acoustic foam was used in these cases and keeping the same cavity volume was very difficult. This may have influenced the frequency value. The change of the characteristic frequency in case 5 was harder to explain.
The surface of the mineral wool is almost flat, and the cavity volume is the same as in cases 0, 1, and 4. The explanation for this may be the air volume which was closed in the mineral wool. This volume can increase the volume of the air in the actuator cavity. The thickness of the wool is the biggest and the volume of air trapped in the soundproofing (in case 5) was the biggest. Therefore, in this case, it can have an impact on the resonant frequency.
The value of the resistance in case 5 was also much bigger than in other cases. That shows that the operation parameter of the loudspeaker deviated from the parameters in other cases. The pressure in the actuator cavity alternately increased and decreased in a sinusoidal manner [37]. The mineral wool can behave in such conditions as a spring or a damper, which can also influence the obtained characteristics. However, this and previous assumptions should be verified in future research.
3.2. Sound Pressure Level
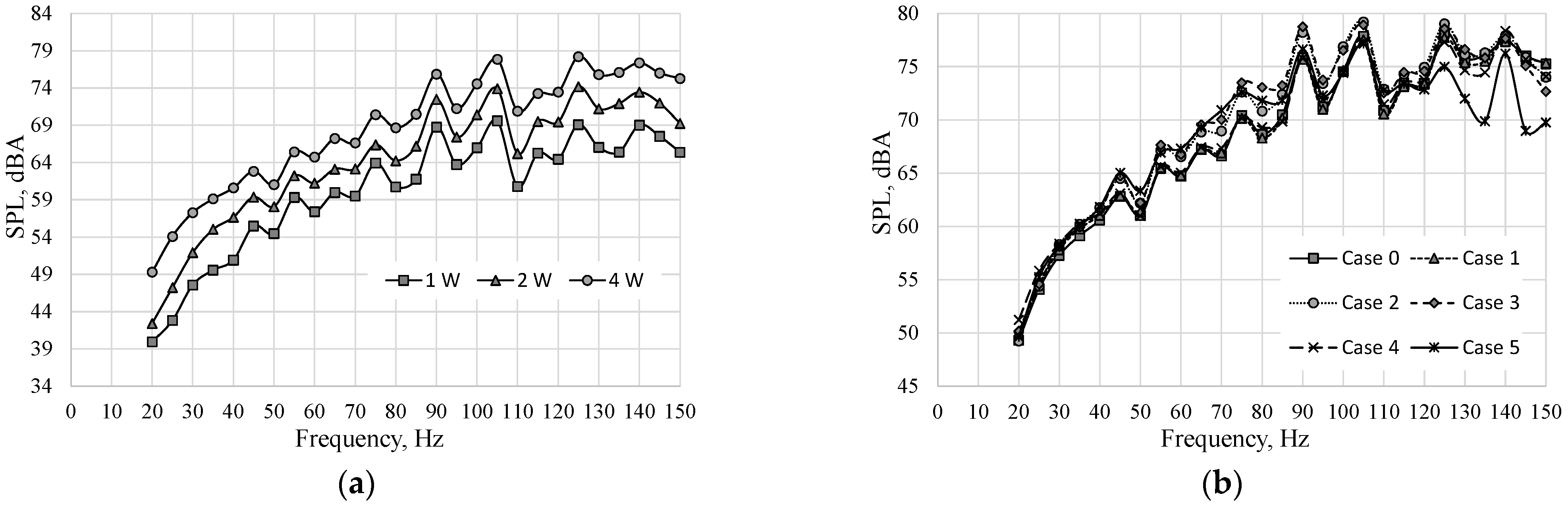
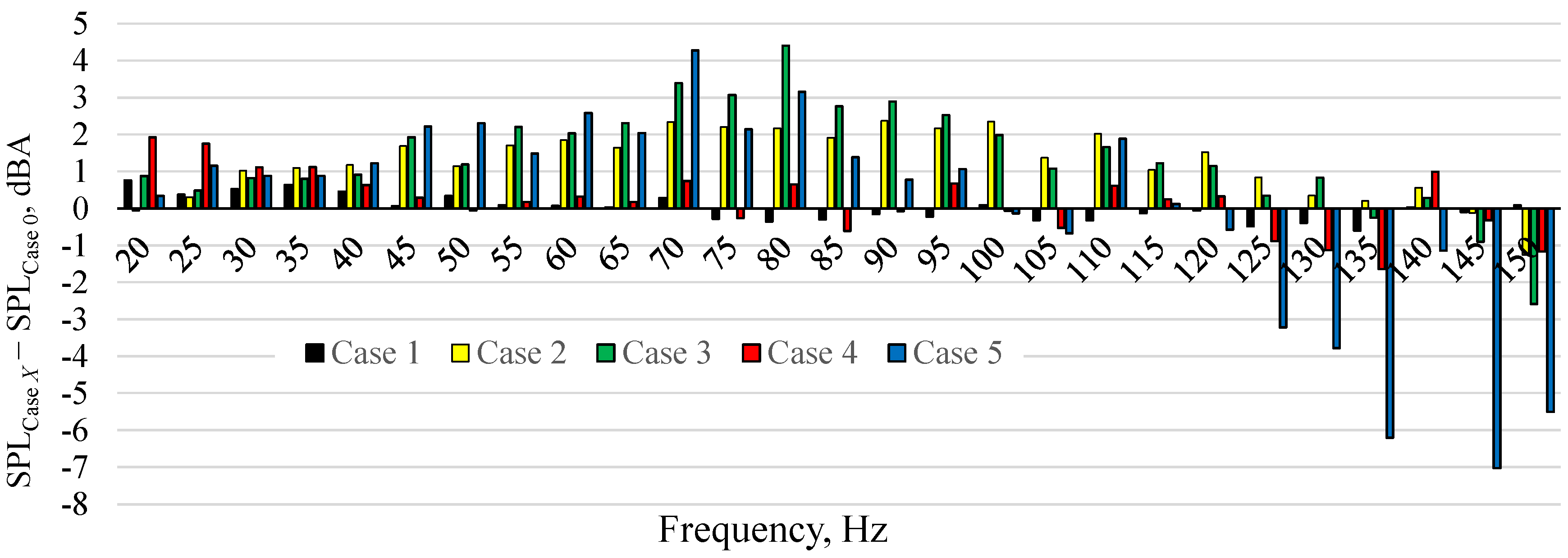
Figure 3 presents the SPL as a function of frequency. The SPL at different real power for case 0 is presented in Figure 3a. The SPL increased with the frequency and the measured curves had the same course regardless of the power. Therefore, only the SPL at the real power of 4 W for all cases is shown in Figure 3b. Figure 3b was hardly legible due to the amount of data presented. For this reason, the SPL for cases 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 decreased by SPL for case 0 is presented in Figure 4. The positive value in Figure 4 means that the SPL generated by the actuator was higher than the SPL for case 0, at the same frequency. The negative value means that the generated noise was lower than in case 0. It should be also noted that the accuracy of measurements was ±1.4 dB.
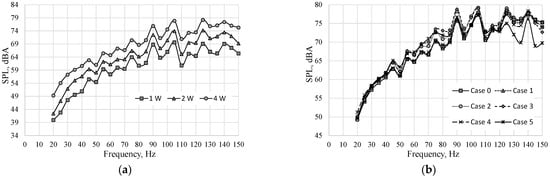
Figure 3.
SPL vs. frequency: (a) Case 0 at the different real power; (b) different cases at the real power W.
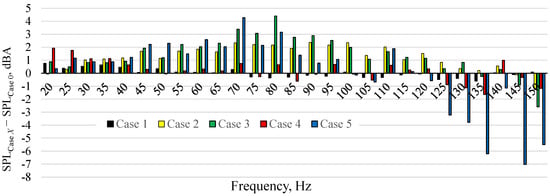
Figure 4.
SPL differences between case 0 and other cases, where .
The SPL generated by the SJA with the soundproofing in the cavity was generally similar to or higher than the SPL generated by the SJA without soundproofing at the frequency in the range of 20 to 120 Hz. The highest difference was obtained for case 5 which generated noise even 7 dBA lower than case 0 at the frequency of 145 Hz. The SJA is operated usually at the resonant frequency and any soundproofing type did not reduce the actuator noise at this frequency. Since the soundproofing at the low frequency can increase the noise generated by the actuator the use of this is discouraged. However, significant noise reduction at the higher frequencies suggests that the use of soundproofing in the actuator cavity may be appropriate at the Helmholtz frequency which is usually higher than the natural frequency. It should be investigated. However, the acoustic SJA operated generally at the natural frequency at which the velocity of SJ is significantly higher than when SJA operated at Helmholtz frequency [30,36,38,39]. Therefore, this investigation should be carried out with the piezoelectrics SJA which operated at Helmholtz frequency [40].
4. Conclusions
In the paper, the SJA with soundproofing in the cavity was tested. Firstly, the resistance of the actuator was determined at constant power and frequency range from 20 to 150 Hz. The resonant frequency was determined. Secondly, the SPL was tested in the same conditions. The impact of the five different types of soundproofing on generated noise was presented.
The soundproofing in the cavity had no impact on the resonant frequency except in case 5, in which the mineral wool was used. The authors believe it could have been caused by the large volume of air closed in the wool or wool susceptibility to pressure changes in the cavity. However, it should be investigated in the future.
The actuators with soundproofing in the cavity generated similar to or higher noise than the classic actuator at a frequency below 120 Hz. Only case 5 with the mineral wool significantly reduced the noise of the actuator even by about 7 dBA at a frequency above 120 Hz. For this reason, the use of soundproofing in the cavity is not recommended in the case of acoustic SJA. However, it should be checked whether this method of noise reduction will work at higher frequencies, e.g., for actuators operating at Helmholtz frequency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, formal analysis, writing—review and editing, E.S. and M.M.; methodology, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, E.S.; software, validation, investigation, resources M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Center for Research and Development, Poland. Grant No.: LIDER/6/0024/L-10/18/NCBR/2019.
Data Availability Statement
Some or all data generated or used during the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Smith, B.L.; Glezer, A. The formation and evolution of synthetic jets. Phys. Fluids 1998, 10, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Upadhyay, P.K. Experimental investigation of the thermal behavior a single-cavity and multiple-orifice synthetic jet impingement driven by electromagnetic actuator for electronics cooling. Exp. Heat Transf. 2022, 35, 132–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Upadhyay, P.K.; Jain, A.K. Experimental investigation on thermal characteristics of hot surface by synthetic jet impingement. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 165, 114596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Wilk, J. Heat transfer coefficients during the impingement cooling with the use of synthetic jet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 147, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelczyk, P.; Gil, P. Properties of velocity field in the vicinity of synthetic jet generator. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 760, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P. Bluff body drag control using synthetic jet. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2019, 12, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-F.; Luo, Z.-B.; Deng, X.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Li, S.-Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.-X. Dual Synthetic Jets Actuator and Its Applications—Part II: Novel Fluidic Thrust-Vectoring Method Based on Dual. Actuators 2022, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Dancova, P.; Lam, J.H.; Timochenko, V.; Reizes, J. Numerical and experimental studies of a channel flow with multiple circular synthetic jets. EPJ Web Conf. 2012, 25, 01094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Zhong, S. Enhancement of laminar flow mixing using a pair of staggered lateral synthetic jets. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 207, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, L.H.; Wang, J.J.; Li, T. Characteristics and mechanism of mixing enhancement for noncircular synthetic jets at low Reynolds number. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2018, 98, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Dong, J. Experimental study of coaxial jets mixing enhancement using synthetic jets. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, M.; Yasir, M.; Ghaffari, O.; Arik, M. Acoustics and Heat Transfer Characteristics of Piezoelectric Driven Central Orifice Synthetic Jet Actuators. Exp. Heat Transf. 2021, 35, 758–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9241-6:1999; Ergonomic Requirements for Office Work with Visual Display Terminals (VDTs)-Part 6: Guidance on the Work Environment. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; p. 32.
- Colenberg, S.; Jylhä, T.; Arkesteijn, M. The relationship between interior office space and employee health and well-being—A literature review. Build. Res. Inf. 2021, 49, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourikas, L.; Gauthier, S.; Khor Song En, N.; Xiong, P. Effect of Thermal, Acoustic and Air Quality Perception Interactions on the Comfort and Satisfaction of People in Office Buildings. Energies 2021, 14, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Muslim, M.; Jehangir, A. Environmental noise-induced cardiovascular, metabolic and mental health disorders: A brief review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arik, M. An investigation into feasibility of impingement heat transfer and acoustic abatement of meso scale synthetic jets. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasance, C.J.M.; Aarts, R.M.; Ouweltjes, O. Synthetic Jet Cooling Part II: Experimental Results of An Acoustic Dipole Cooler. In Proceedings of the 2008 Twenty-Fourth Annual IEEE Semiconductor Thermal Measurement and Management Symposium, San Jose, CA, USA, 16–20 March 2008; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bhapkar, U.S.; Srivastava, A.; Agrawal, A. Acoustic and heat transfer aspects of an inclined impinging synthetic jet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 74, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanase, M.M.; Mangate, L.D.; Chaudhari, M.B. Acoustic aspects of synthetic jet generated by acoustic actuator. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control. 2018, 37, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhapkar, U.S.; Srivastava, A.; Agrawal, A. Acoustic and heat transfer characteristics of an impinging elliptical synthetic jet generated by acoustic actuator. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 79, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Lin, J.; Sun, A.; Gan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Effects of loudspeaker-driven synthetic jet actuator parameters on the characteristics of the synthetic jet. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 197, 108943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Smyk, E.; Gałek, R.; Przeszłowski, Ł. Thermal, flow and acoustic characteristics of the heat sink integrated inside the synthetic jet actuator cavity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 170, 107171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbal, M.; Jeyalingam, J. Towards the noise reduction of piezoelectrical-driven synthetic jet actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 266, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangate, L.D.; Chaudhari, M.B. Heat transfer and acoustic study of impinging synthetic jet using diamond and oval shape orifice. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2015, 89, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangate, L.; Yadav, H.; Agrawal, A.; Chaudhari, M. Experimental investigation on thermal and flow characteristics of synthetic jet with multiple-orifice of different shapes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 140, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyk, E.; Markowicz, M. Acoustic and Flow Aspects of Synthetic Jet Actuators with Chevron Orifices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P. Performance of special type heat sink with an integrated synthetic jet actuator. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 100, 00017. [Google Scholar]
- Smyk, E.; Gil, P.; Gałek, R.; Przeszłowski, Ł. Acoustic and Flow Aspects of Novel Synthetic Jet Actuator. Actuators 2020, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Smyk, E. Synthetic jet actuator efficiency based on the reaction force measurement. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 295, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyk, E.; Przeszłowski, Ł.; Strzelczyk, P.M. Impact of the confinement plate on the synthetic jet. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyk, E.; Smusz, R. Impact of the confinement plate on the velocity of synthetic jet. Actuators 2021, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broučková, Z.; Trávníček, Z. Visualization study of hybrid synthetic jets. J. Vis. 2015, 18, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3746:2010; Acoustics—Determination of Sound Power Levels and Sound Energy Levels of Noise Sources Using Sound Pressure—Survey Method Using an Enveloping Measurement Surface over a Reflecting Plane. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; p. 48.
- Kordík, J.; Trávníček, Z. Optimal diameter of nozzles of synthetic jet actuators based on electrodynamic transducers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2017, 86, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Strzelczyk, P. Performance and efficiency of loudspeaker driven synthetic jet actuator. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2016, 76, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhapkar, U.S.; Srivastava, A.; Agrawal, A. Proper cavity shape can mitigate confinement effect in synthetic jet impingement cooling. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2015, 68, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.; Wilk, J.; Korzeniowski, M. Helmholtz Resonance Frequency of the Synthetic Jet Actuator. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, M.; Verma, G.; Puranik, B.; Agrawal, A. Frequency response of a synthetic jet cavity. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2009, 33, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.; Girfoglio, M.; Chiatto, M.; Coppola, G. Scaling properties of resonant cavities driven by piezo-electric actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).