Abstract
We aimed to investigate the occurrence, phylogeny, and virulence of E. coli in the uterine contents and urine of female dogs with pyometra, through the presence of virulence genes and their genetic similarity. Uterine secretions and urine samples from 52 female dogs with pyometra were collected and cultured. Strains identified as E. coli from 25 uterine and 7 urine samples were tested for virulence genes by PCR. Genetic similarity between the isolates was studied using RAPD-PCR. E. coli was observed in 48.07% uterine samples with pyometra and 20.0% urine samples. The strains showed high percentages for the presence of virulence genes: 96.9% had the gene sfa, 59.4% afa, 46.9% pap, 53.1% hly, and 68.75% cnf. Even with the high prevalence of virulence genes, the samples were not submitted to DNA sequencing to confirm the results. Analysis showed high genetic diversity in E. coli, however, strains isolated from the same animal indicate that cystitis and pyometra could be related. Our study indicated the association between E. coli in dogs with pyometra and cases of urinary tract infection and the pathogenic potential of strains increasing with animal age.
1. Introduction
Canine pyometra, also known as a cystic endometrial hyperplasia-pyometra complex, is a disease characterised in the adult dog by uterine inflammation and exudate accumulation. This disease is caused mainly by opportunistic bacteria, and high levels of hormones in the body, such as progesterone and oestrogen, may be preconditioning factors [1,2,3,4]. The incidence of pyometra in female dogs is high, and this disease can be potentially fatal [5].
The most commonly isolated bacteria from the uterine secretions of female dogs with pyometra are Escherichia coli [6,7]. The genetic similarity between E. coli strains isolated from female dogs with simultaneous urinary tract infection (UTIs) and pyometra, showing that the same bacterium infects both sites, has already been demonstrated [8].
E. coli isolates from dogs with pyometra and/or cystitis may have virulence characteristics that include the presence of the pap (P-fimbriae encoding), afa (adhesin afimbrial), sfa (S-fimbriae), hly (α-haemolysin), and cnf (cytotoxic necrotic factor) genes. The presence of these genes demonstrates the invasive potential of the strains [9,10,11,12,13].
Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the occurrence of E. coli in both the uterine secretions and urine of female dogs with pyometra and to analyse these isolates regarding the presence of virulence factors and genetic similarity.
2. Material and Methods
Fifty-two uterine and 35 urine samples were collected from female dogs (Canis familiaris) with pyometra. Samples were collected in 2013 from female patients at the Veterinary Hospital of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Federal University of Uberlândia (FAMEV-UFU), Uberlândia, Minas Gerais, Brazil. The project was approved by the University’s Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals with the number 046/13.
A diagnosis of pyometra was made based on physical examination, haemogram results, and ultrasound [14]. At the time of ovariohysterectomy surgery, the uterus was removed from the animal, kept in a cooler, and sent immediately to the Laboratory of Molecular Epidemiology of FAMEV–UFU [15]. The uterine secretion was aspirated with a sterile needle gauge 40 × 12 mm coupled to a sterile 20 mL syringe. Urine collection was performed using the cystocentesis technique [16]. Both uterine secretions and urine were subjected to bacterial culture to search for the presence of E. coli.
Microbiological analyses were performed [6], with the culture media Sheep Blood Agar 5% (Oxoid, SP, Brazil Ltd.a), MacConkey agar (Oxoid, SP, Brazil Ltd.a), and BHI (Brain and Heart Infusion Broth; Oxoid, SP, Brazil Ltd.a; incubation at 37 °C for 24 h under aerobic conditions). A commercial kit was used for the identification of E. coli by biochemical profiling (tryptophan production, glucose fermentation, gas production from glucose, hydrogen sulphide production, lysine use, ornithine use, motility, indole production, rhamnose, and citrate use) (Laborclin, Pinhais, Paraná, Brazil). E. coli strain ATCC 25922 (MicroBioLogics, St. Cloud, MN, USA) was used as a positive control in phenotypic tests.
Strains identified as E. coli were subjected to the identification of virulence genes. We first assessed DNA extraction by thermal lysis. For DNA extraction, 2 mL cultures were transferred to microtubes (Bio express, SP, Brazil) and centrifuged (Cientec®, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil) at 12,000× g for 5 min to form a pellet. The supernatant was discarded and 200 µL of phosphate buffer plus 2.5 µL of the protease solution (DuPont™ PCR Reagent, Wilmington, Delaware, EUA) were added to the pellet. This mixture was heated at 37 °C for 20 min and at 95 °C for 10 min in a thermocycler (Eppendorf®, SE, Germany). It was then transferred to a cooling block (2 °C to 8 °C) for 5 min to obtain the DNA. An aliquot of the supernatant was used as a DNA template in the PCR [17] and quantification in the Nanodrop device (Thermo Fisher Scientific, SP, Brazil) [18]. Primer pairs and references to the amplification protocol and positive controls are shown in Table 1. The negative control was composed of sterile ultrapure water, which was added to the reaction mixture instead of DNA.

Table 1.
Primers for identification of virulence genes pap, hly, cnf, sfa, and afa in Escherichia coli.
For amplification of the sfa, pap, hly, and cnf genes, the final volume of the reaction (50 µL) contained 50 ng of the bacterial DNA solution and the following reagents: 10 mM of Tris-HCL; 50 mM KCl; 200 µM of each deoxynucleotide triphosphate (DNTP); 1.5 mM MgCl2; 20 picomoles of the sfa, pap, and cnf primers and 30 picomoles of the hly primers, along with 0.2 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Invitrogen®, São Paulo, Brazil). Each gene was studied separately in the reactions. Amplification was performed in a thermocycler (Eppendorf®, Hamburg, Germany), with the following cycles: an initial cycle at 95 °C for 5 min, 35 amplification cycles, consisting of denaturation at 95 °C for 1 min, annealing at 55 °C for 1 min, extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and a final cycle of extension at 72 °C for 5 min [17]. For the afa gene, the amplification solution consisted of 10 mM of Tris-HCL, 50 mM KCl, 2.0 mM MgCl2, 200 µM of each deoxynucleotide triphosphate (DNTP), 30 picomoles of primer, 1 U of Taq, and 70 ng of DNA in a final volume of 30 µL. Amplification was performed in a thermocycler (Eppendorf®, Hamburg, Germany) with the following cycles: an initial cycle at 94 °C for 10 min, 30 amplification cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing at 63 °C for 1 min, extension at 72 °C for 2 min, and a final cycle of extension at 72 °C for 7 min [22].
The genetic similarity between E. coli isolates was assessed using Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA PCR (RAPD-PCR) with the primers 1247 (5′AAGAGCCCG3′) and 1290 (5′GTGGATGCGA3′) [10]. Gels containing the amplified products were taken to capture images (Loccus Biotechnology, SP, Brazil) and computational analysis was performed using the GelCompar II Program (https://www.applied-maths.com/gelcompar-ii—Comparative Analysis of Electrophoresis Patterns. Accessed on 8 November 2016). Bands of weak, medium, and strong intensity captured by the program were considered in the analysis. A similarity matrix was obtained by comparing pairs of strains using the Dice similarity coefficient, adopting 1% tolerance for each primer separately. The final analysis was based on the average of experiments. The unweighted pair group method with the arithmetic mean (UPGMA) method was used for the construction of dendrograms comprising all of the studied strains.
All results were tabulated and analysed for descriptive statistics, calculating the percentage of isolation and presence of virulence genes in isolates identified as E. coli.
3. Results
Bacterial isolation was achieved in 36/52 (69.2%) uterine secretion samples of studied dogs. Of the 35 urine samples collected from the pyometra dogs, only 10 (28.6%) showed bacterial growth.
Regarding E. coli positivity, it was observed that 25/52 (48.07%) uterine secretion samples and 7 of the 35 (20.0%) urine samples contained the bacteria, totalling 32 strains. It showed that animals with positive urine samples for E. coli also showed positive uterine secretions, except in one animal where the agent was isolated in the urine only. Thus, we characterised 32 strains of E. coli from 26 animals of 9 different breeds with ages varying from 1 to 14 years (Table 2).

Table 2.
Age and breed of dogs with pyometra that was positive for E. coli.
The presence of the sfa gene was found in 31/32 E. coli isolates (96.9%) of which 24 were from uterine samples and 7 from urine. The results of the present study were also higher than other studies [23,24] about the afa gene, which was present in 19/32 of the isolates (59.4%), with 15 being from uterine samples and 4 from urine. The pap gene was detected in 15/32 strains (46.9%), of which 11 were derived from uterine secretion and 4 from urine. For the hly gene, positivity was found in 17/32 isolates (53.1%), of which 13 were from uterine secretion and 4 from urine. The last reported gene cnf was detected in 22/32 isolates (68.75%), of which 17 were from uterine secretions and 5 from urine. Of the total strains, 11/32 (34.4%) had all of the virulence genes (V10) investigated and therefore a greater pathogenic potential (Table 3).

Table 3.
Prevalence of virulence genes and profile of virulence of E. coli from female dogs with pyometra.
Four distinct groups (1–4) were identified (Figure 1), with proximity between 51% and 64%, which indicates high variability within the groups. In addition, four genotypes can be observed with genetic similarity lower than 50%, corresponding to the isolates from the uterine secretions of animals 12, 14, 18, and 23. In Group 1, with 53.8% homology, we determined the presence of two clusters “a” and “b” with similarities of 88.9% and 93.8%, respectively. Each cluster consisted of two strains originating from the same animal (05 and 01, respectively) and distinct samples of the uterine secretions and urine. In Group 2, with 55.9% homology, two clusters “c” and “d” were detected with a genetic similarity of 90.0% and 88.9%, respectively. Both clusters also presented two strains isolated from the same animal (02 and 06, respectively). Compared to Group 3, with 56.4% homology, we identified only one cluster “e” with a genetic similarity of 87.3%, consisting of two strains from female dog number 04. Group 4, with the homology of 63.9%, was composed of two strains with a distinct pattern.
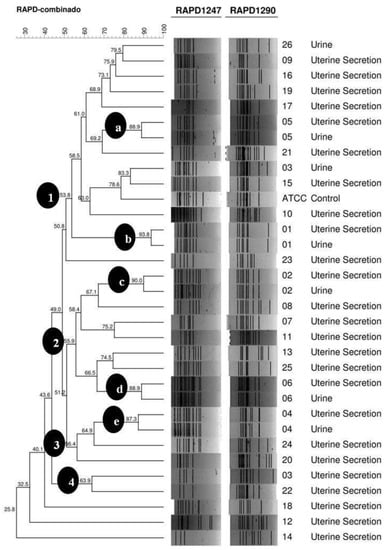
Figure 1.
Dendrogram of 32 E. coli isolates originated from female dogs with pyometra Uberlândia—MG, by RAPD-PCR with primers 1247 and 1290, using the average of experiments with a tolerance of 1.5% and UPGMA method with optimisation of 85% at GelCompar II program, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium. Profile 1—a group with 53.8% homology, consisting of two clusters (a and b) with 88.9% and 93.8% of similarity, respectively. Profile 2—a group with 55.9% homology, consisting of two clusters (c and d) with 90.0% and 88.9% similarity, respectively. Profile 3—a group with 56.4% homology, composed of the cluster (e) with 87.3% similarity. Profile 4—a group with 63.9% homology.
4. Discussion
The complex pathogenesis of pyometra is not fully understood, but it involves hormonal and bacterial factors. Regarding factors related to bacterial pathogens, we can include the species and characteristics of virulence [25].
Our study found E. coli positivity was observed in 25/52 (48.07%) uterine secretion samples and 7/35 (20.0%) urine samples contained the bacteria, totaling 32 strains. A high rate of isolation of this pathogen has been previously reported in female dogs with pyometra in 43/48 (90.0%) of samples [2]. On the prevalence of E. coli, researchers from Brazilian veterinary hospitals [14,21,26,27,28,29,30,31,32] and the United States [31] found percentages close to those found here, between 57.0% and 73.0% for E. coli isolation.
In relation to the virulence factors, the sfa gene, our findings were higher compared to a previous study [33]. These authors reported positivity for this gene in 22/51 (43.1%) of the E. coli isolates from UTIs in female dogs and 24/52 (46.1%) of the uterine secretion samples of animals with pyometra. Studies conducted in Brazil demonstrated the presence of this gene in 19/33 (56.0%) and 120/151 (79.5%) strains of E. coli isolated from female dogs with pyometra [6,32]. S-fimbriae, encoded by the sfa gene, is composed of several subunits that are extremely important in the interaction of the bacteria with the epithelial cells of the kidneys and bladder [34]. These fimbriae are often found in isolates involved in sepsis. Thus, with septicemia being one of the consequences of pyometra, the presence of this virulence factor may contribute to the dissemination and generalisation of infectious conditions [6].
The presence of the afa gene in our research was also higher than that reported by other authors [6], who observed this gene in only 5/151 (3.3%). E. coli isolates has found that the adhesin encoded by this gene plays a small role in uterine colonisation. This low frequency was also reported [27], with 1/52 (1.9%) of the pyometra and 1/51 (2.0%) of the UTI isolates presenting afa.
The afa gene is not often found in E. coli isolated from uterine secretions of female dogs with pyometra [35]. This gene is more associated with uropathogenic E. coli isolated from humans [36]. According to previous work, the high percentage of afa positivity is associated with contact between humans and dogs [37]. These authors observed a 95% genetic similarity in E. coli isolated from samples of canine faeces and their owners.
The pap gene is of great clinical importance because it is involved in the synthesis of pili P, which is the most important adhesin in those strains that cause renal infections [38]. The pap gene was found in 87/151 (57.6%) strains of E. coli isolated from female dogs with pyometra [6].
The synthesis of haemolgysin is regulated by the hly gene. This cytolysin is capable of damaging erythrocytes, leukocytes, and endothelial cells of the kidneys, which favours infection [35,36,39]. During erythrocyte lysis, there is the absorption of exogenous iron, an essential element for bacterial metabolism. This is possible through the synthesis of exoproteins, recognised as siderophores by microorganisms [38].
For the hly gene, positivity was found in 17/32 (53.1%) isolates. Lower results were found in Brazil [34], where it was observed in 17/51 (33.3%) and 18/52 (34.6%) positive isolates in UTI and pyometra from dogs, respectively. In other countries, this gene has been reported in 13/23 (52.0%) strains of E. coli derived from female dogs with pyometra in Australia and 7/30 (23.3%) strains of E. coli isolated from the urine of dogs in Italy [27,35].
The “cytotoxic necrotising factor” produced by the cnf gene was only associated with uropathogenicity due to epidemiological findings [27]. However, culture studies of human neutrophils have indicated that this toxin may influence the immune response of the host since it seems to allow bacterial death by neutrophils [30]. This gene encodes an important cytotoxin that facilitates the spread of bacteria from the lumen of the bladder and intestinal tract into the bloodstream [36]. Considering the importance of this gene in the invasive potential of E. coli, its presence can facilitate infections in different places, including uterine infections. Studies in Brazil and countries such as the United States and Italy found low percentages of cnf in E. coli isolated from the uterine secretions of female dogs with pyometra. The level of variation was 21.6–57.0% in Brazil and 41.0–53.3% elsewhere [6,32,33,40]. Our study shows high prevalence rates identified for the virulence genes in the samples evaluated and encourages the importance of confirmation using the genomic sequencing technique.
The analysis of genetic similarity presented in the dendrogram (Figure 1) of E. coli isolates demonstrates high genetic diversity, possibly due to the different environments, management, and age of the animals in the study. The genotypic diversity demonstrated suggests the possibility of genetic changes in different lineages and the probability of the emergence of a new genotype in the region [12,41]. Several factors enable the evolution of bacteria, such as horizontal transfer, which facilitates adaptation to new environments. This contributes to the acquisition of virulence factors directly involved in infections and the development of different clusters [7].
The relationship between urine isolates and uterine secretion from the same animal (Table 2) was shown by the genetic similarity of the E. coli strains (Figure 1). Most of the strains present in the same animal were of the same genotype (5/6 83.3%). Thus, it can be inferred that cystitis and pyometra in animals 01, 02, 04, 05, and 06 had a direct relationship and that these microorganisms probably showed tropism to both organs (the bladder and uterus).
Moreover, this pattern of high proximity between strains isolated from the same animal was also evidenced by the similarity of the genotypic characteristics between strains. For animal 4 (cluster “e”), it was observed that both strains were positive for all virulence genes tested (sfa, afa, pap, hly, and cnf). The sfa, pap, hly, and cnf genes were present in the bacteria of animal 02, and the sfa gene in the E. coli of animal 06. For animal 01 (cluster “b”) the strains were possessed in the cnf, sfa, and afa genes, while for dog 05, cluster (“a”), the E. coli isolates showed the sfa gene.
This genetic similarity observed between urinary bacteria and uterine secretion of the same animal had already been observed [31]. In a previous study, 14/16 (87.5%) E. coli strains isolated from UTIs have been reported to be identical or similar to those isolated from the infected uterus. They also identified similarities between uterine and faecal bacteria [42]. Interestingly, these authors concluded that E. coli associated with canine pyometra would originate from the faecal microbiota and that UTIs would [43] have occurred from the same E. coli clone observed in the uterus, considering that the isolates were similar but not identical. Any disequilibrium of microflora residing around the urethral ostium of the vagina, especially Lactobacilli, would be a good opportunity for the colonisation of the urinary tract by E. coli or other potentially pathogenic agents [38].
Future work should be performed to determine the actual zoonotic importance of E. coli isolated from female dogs by investigating their similarity to human isolates. The studies should determine whether they have common characteristics, such as resistance to antimicrobials and the presence of resistance genes, to verify whether there is a transfer of virulence to the E. coli strains of humans. Such research could bring greater insight and could help more comprehensible actions to prevent risks to humans and animals.
The monitoring of E. coli isolates from female dogs for virulence genes is important because the same strains that cause infections in dogs can also infect humans, thus indicating their importance for public health.
5. Conclusions
This study corroborated the importance of E. coli as one of the major aetiologic agents of canine pyometra. The genotypic diversity observed in E. coli isolated from different animals demonstrated that canine uterine and urinary infections arise from many, not interconnected sources. However, the genetic similarity between strains from the same animal indicates a relationship between the two types of infection. The presence of several virulence factors, and the high prevalence of these genes, demonstrate the pathogenic potential of these strains.
Author Contributions
R.P.O., R.T.M., D.A.R. and J.P.E.S. conceived, designed, and performed the experiments; B.F.S., G.P.M., L.R.M.C., and S.D.C.D. analysed the data and wrote the paper. The manuscript was extensively reviewed by all co-authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received financial assistance of Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—Brazil CNPq—(Universal 480473/2013-7) to implement the research. This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The project was approved by the University’s Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals with the number 046/13.
Data Availability Statement
All data are included in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no potential conflict of interest concerning the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Dam, T.; Das, P. Plasmids—Potential tool for the investigation of the gene transfer in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egenvall, A.; Hagman, R.; Bonnett, B.N.; Hedhammar, A.; Olson, P.; Lagerstedt, A.S. Breed risk of pyometra in insured dogs in Sweden. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2001, 15, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fransson, B.; Lagerstedt, A.S.; Hellmen, E.; Jonsson, P. Bacteriology findings, blood chemistry profile and plasma endotoxin levels in bitches with pyometra or other uterine diseases. J. Vet. Med. 1997, 44, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Hagman, R.; Kühn, I. Escherichia coli strains isolated from the uterus and urinary bladder of bitches suffering from pyometra: Comparison by restriction enzyme digestion and pulsed- field gel electrophoresis. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 84, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, D.J.; Kengeri, S.S.; Maras, A.H.; Suckow, C.L.; Chiang, E.C. Life course analysis of the impact of mammary cancer and pyometra on age-anchored life expectancy in female Rottweilers: Implications for envisioning ovary conservation as a strategy to promote healthy longevity in pet dogs. Vet. J. 2017, 224, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Coggan, J.A.; Melville, P.A.; Oliveira, C.M.D.; Faustino, M.; Moreno, A.M.; Benites, N.R. Microbiological and histopathological aspects of canine pyometra. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2008, 39, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, N.; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F.A.; Taniwaki, M.H.; Gomes, R.A.R.; Okazaki, M.M. Escherichia coli O157:H7. In Manual De Métodos De Análise Microbiológica De Alimentos e Agua, 5th ed.; Manual of Methods for Microbiological Analysis of Food and Water; Blucher: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017; pp. 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hagman, R. Clinical and molecular characteristics of pyometra in female dogs. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, 323–325. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, K.; Okada, E.; Shimizu, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Sawada, T.; Takahashi, T. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence profiles and phylogenetic groups of faecal Escherichia coli isolates: A comparative analysis between dogs and their owners in Japan. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 35, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, S.; Silva, E.; Lemsaddek, A.; Lopes-da-Costa, L.; Mateus, L. Genotypic and phenotypic comparison of Escherichia coli from uterine infections with different outcomes: Clinical metritis in the cow and pyometra in the bitch. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Hilton, A.C. Optimisation of random amplification of polymorphic DNA analysis for molecular subtyping of Escherichia coli O157. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.R.; Kaster, N.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Ling, G.V. Identification of urovirulence traits in Escherichia coli by comparison of urinary and rectal E. coli isolates from dogs with urinary tract infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhnert, P.; Boerlin, P.; Frey, J. Target genes for virulence assessment of Escherichia coli isolates from water, food and the environment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, A.D.R.V.C. Antibioresistência Em Piometra (In Portuguese) Canina Anti-Bioresistance in Canine Pyometra. Master’s Thesis, Lusofona Veterinary Medicine of University of Humanities and Technologies, Lisboa, Portugal, November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Slatter, D.H. Manual De Cirurgia De Pequenos Animais Small Animal Surgery Handbook, 3rd ed.; Manole: São Paulo, Brazil, 2007. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Chew, D.J.; DiBartola, S.P.; Schenck, P. Canine and Feline Nephrology and Urology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Saunders: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sidjabat, H.E.; Chin, J.J.C.; Chapman, T.; Wu, K.; Ulett, G.C.; Ong, C.Y.; Schembri, M.A.; Johnson, J.R.; Trott, D.J. Colonisation dynamics and virulence of two clonal groups.s of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from dogs. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borsoi, A.; Santin, E.; Santos, L.R.; Salle, C.T.P.; Moraes, H.L.S.; Nascimento, V.P. Inoculation of newly hatched broiler chicks with two Brazilian isolates of Salmonella Heidelberg strains with different virulence gene profiles, antimicrobial resistence and pulse field gel electrophoresis patterns to intestinal changes evaluation. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Terai, A.; Yuri, K.; Kurazono, H.; Takeda, Y.; Yoshida, O. Detection of urovirulence factors in Escherichia coli by multiple polymerase chain reaction. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1995, 12, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Stenske, K.A.; Bemis, D.A.; Gillespie, B.E.; Oliver, S.P.; Draughon, F.A.; Matteson, K.J.; Bartges, J.W. Prevalence of urovirulence genes cnf, hlyD, sfa/foc and papGIII in faecal Escherichia coli from healthy dogs and their owners. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Tarchouna, M.; Ferjani, A.; Ben-Selma, W.; Boukadida, J. Distribution of uropathogenic virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolated from patients with urinary tract infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e450–e453. [Google Scholar]
- De Medici, D.; Croci, L.; Delibato, E.; Di Pasquale, S.; Filetici, E.; Toti, L. Evaluation of DNA extraction methods for use in combination with SYBR green I real-time PCR to detect Salmonella enterica serotype enteritidis in poultry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3456–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Von Sydow, G.A.C.M.O.N. Avaliação Da Ocorrência De Fatores De Virulência Em Estirpes De Escherichia coli Em Fezes De Cães Errantes. Master’s Thesis, University of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, August 2005. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Coggan, J.A. Estudo Microbiológico De Conteúdo Intra-Uterino E Histopatológico De Utero De Cadelas Com Piometra E Pesquisa De Fatores De Virulência Em Cepas De E. coli E O Potencial Risco à Saúde Humana. Master’s Thesis, University of Veterinary Medicine and Animal Science of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, September 2005. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Hagman, R. Canine pyometra: What is new? Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Berl, C.A.; Franco, C.R.; Baltazar, F.N.; Cortez, M.B.X.; Trevisan, R.; Cirillo, T.; Júnior, W. Perfil de suscetibilidade a antimicrobianos de bactérias isoladas da secreção uterina de cadelas com piometra atendidas em hospital veterinário localizado em São Paulo, SP, Brasil, no período de 2010 a 2015. Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of bacteria isolated from uterine secretion of bitches with pyometra treated at a veterinary hospital located in São Paulo, SP, Brazil, from 2010 to 2015. Rev. MV Z 2018, 16, 36–42. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, L.; Xia, Z. Increasing prevalence of ESBL-producing multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli from diseased pets in Beijing, China from 2012 to 2017. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2852. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Wright, P.J.; Lee, C.S.; Browning, G.F. Uropathogenic virulence factors in isolates of Escherichia coli from clinical cases of canine pyometra and faeces of healthy bitches. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 96, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.C.P.; Woerther, P.L.; Bouvet, M.; Andremont, A.; Leclercq, R.; Canu, A. Escherichia coli as reservoir for macrolide resistance genes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1648–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Osugui, L.; de Castro, A.P.; Iovine, R.; Irino, K.; Carvalho, V.M. Virulence genotypes, antibiotic resistance and the phylogenetic background of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from urinary tract infections of dogs and cats in Brazil. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Pretzer, S.D. Clinical presentation of canine pyometra and mucometra: A review. Theriogenology 2008, 70, 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- Rippere-Lampe, K.E.; O’Brien, A.D.; Conran, R.; Lockman, H. A Mutation of gene encoding cytotoxic necrotizing factor type 1 (cnf1) attenuates the virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3954–3964. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, A.K.; Ribeiro, M.G.; Leite, D.D.S.; Tiba, M.R.; de Moura, C.; Lopes, M.D.; Prestes, N.C.; Salerno, T.; da Silva, A.V. Virulence factors in Escherichia coli strains isolated from urinary tract infection and pyometra cases and from faeces of healthy dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2009, 86, 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- Sandholm, M.; Vasenius, H.; Kivistö, A. Pathogenesis of canine pyometra. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1975, 167, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Maluta, R.P.; Borges, C.A.; Beraldo, L.G.; Cardozo, M.V.; Voorwald, F.A.; Santana, A.M.; Rigobelo, E.C.; Toniollo, G.H.; Ávila, F.A. Frequencies of virulence genes and pulse field gel electrophoresis fingerprints in Escherichia coli isolates from canine pyometra. Vet. J. 2014, 202, 393–395. [Google Scholar]
- Trabulsi, L.R.; Alterthum, F. Microbiologia, 4th ed.; Atheneu: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tramuta, C.; Nucera, D.; Robino, P.; Salvarani, S.; Nebbia, P. Virulence factors and genetic variability of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from dogs and cats in Italy. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 12, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hagman, R. Pyometra in small animals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 639–661. [Google Scholar]
- Sary, K.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Arsenault, J.; de Lagarde, M.; Boulianne, M. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence gene profiles among Escherichia coli isolates from retail chicken carcasses in Vietnam. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tiba, M.R. Genotypic Determination of Virulence Factors in Samples of Escherichia coli Isolated from Cystitis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2008, 50, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos Filho, J.C.B. Research of Bacteria and Their Sensitivity to Antimicrobials in Dogs with Pyometra, with Special Interest in the Characterization of Extra-Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC). Master’s Thesis, Veterinary Medicine of University of São Paulo (UNIP), São Paulo, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey, M.A. Adhesion and entry of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Cell Microbiol. 2002, 4, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wadas, B.; Kühn, I.; Lagerstedt, A.S.; Jonsson, P. Biochemical phenotypes of Escherichia coli in dogs: Comparison of isolates from bitches suffering from pyometra and urinary tract infection with isolates from faeces of healthy dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 1996, 52, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).