Residual-Free Micro–Nano Titanium Surfaces via Titanium Blasting and Single Acid-Etching: A Cleaner Alternative
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Surface Characterization Method
2.2.1. Surface Topography and Morphology Method
2.2.2. Contact Angle Test
2.3. In Vitro Cell Culture Test
2.3.1. Proliferation Assay
2.3.2. Cytotoxicity Method
2.3.3. Cell Morphology Test
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Surface Characterization Results
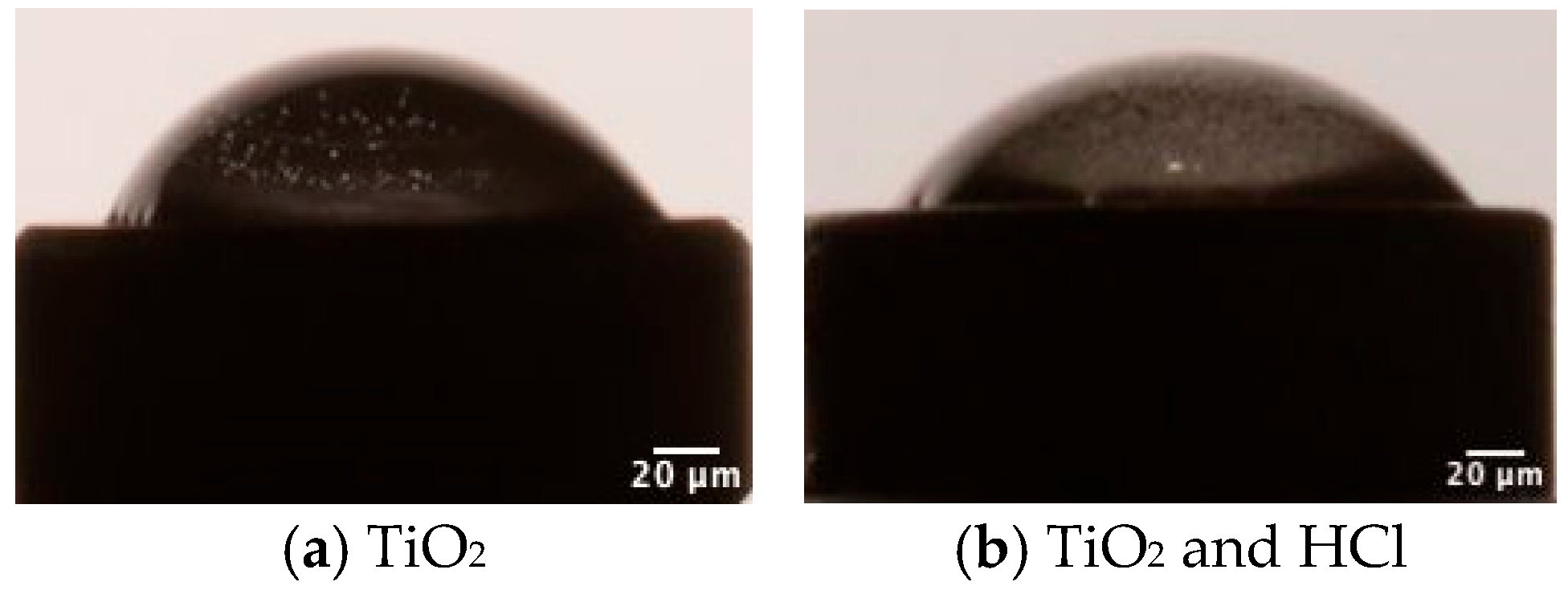
3.1.1. Surface Topography and Morphology Results
3.1.2. Contact Angle Results
3.2. In Vitro Cell Culture Results
3.2.1. Proliferation Results
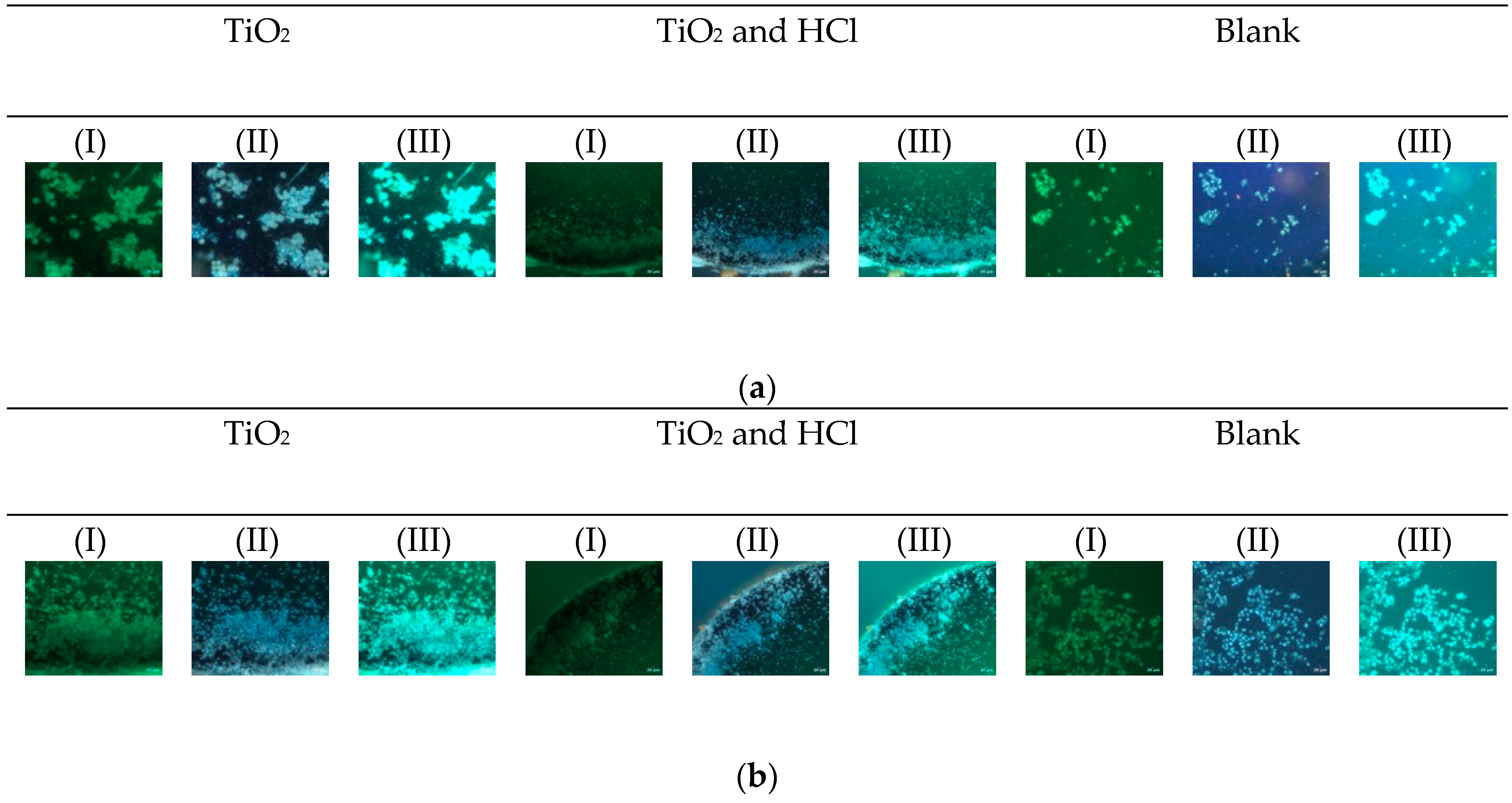
3.2.2. Cytotoxicity Results
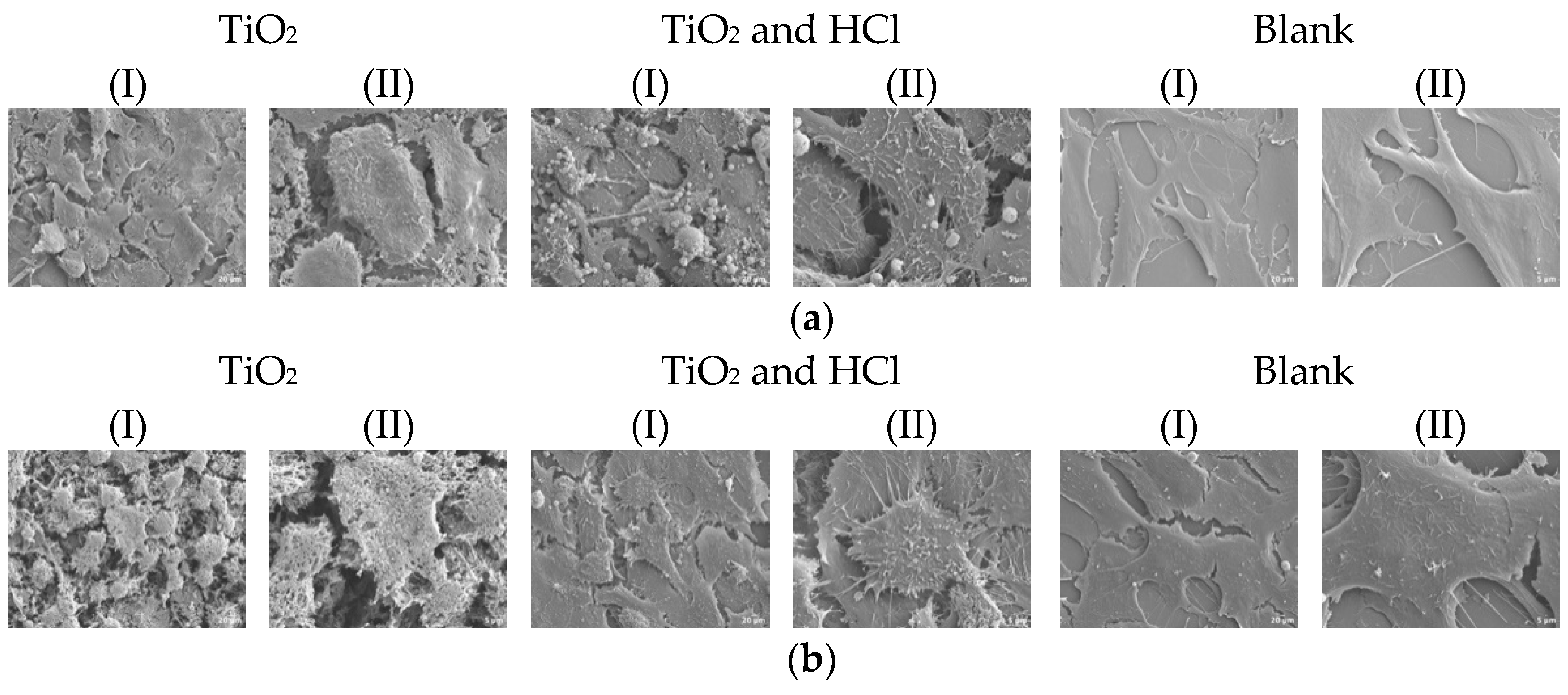
3.2.3. Cell Morphology Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SP | Stylus profilometer |
| hFOB | Human osteoblasts |
References
- Kim, J.C.; Lee, M.; Yeo, I.L. Three interfaces of the dental implant system and their clinical effects on hard and soft tissues. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1387–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Bijit, V.; Inostroza, N.C.; Orellana, R.; Rivera, A.; Von Marttens, A.; Cortez, C.; Covarrubias, C. Influence of Topography and Composition of Commercial Titanium Dental Implants on Cell Adhesion of Human Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.G.S.; Bertolini, M.M.; Costa, R.C.; Nagay, B.E.; Dongari-Bagtzoglou, A.; Barão, V.A.R. Targeting implant-associated infections: Titanium surface loaded with antimicrobial. iScience 2020, 24, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Walker, M.; Xiao, Y.; Donnelly, H.; Dalby, M.J.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M. The influence of nanotopography on cell behaviour through interactions with the extracellular matrix—A review. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 15, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Xing, Y.; Jia, S.; Mo, Z.; Gong, H. Effect of microtopography on osseointegration of implantable biomaterials and its modification strategies. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 981062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majhy, B.; Priyadarshini, P.; Sen, A.K. Effect of surface energy and roughness on cell adhesion and growth–facile surface modification for enhanced cell culture. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15467–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.R.; Hong, M.H. Improved Biocompatibility and Osseointegration of Nanostructured Calcium-Incorporated Titanium Implant Surface Treatment (XPEED®). Materials 2024, 17, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Ortiz-Garcia, I.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Núñez-Márquez, E.; Moreno-Muñoz, J.; Rondón-Romero, J.L.; Cabanillas-Balsera, D.; Gil, J.; Muñoz-Guzón, F.; Monsalve-Guil, L. Osseointegration of Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Implant Surfaces. A Histological and Histomorphometric Study in the Rabbit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Patel, S.; Girgis, W.; Ahmed, W.; Barrak, F. A systematic assessment of the stability of SLA(R) vs. SLActive(R) implant surfaces over 12 weeks. Evid. Based Dent. 2025, 26, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Ge, X.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y. Microarray analysis reveals that lncRNA PWRN1-209 promotes human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation on microtopography titanium surface in vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2020, 108, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, G.M.; Almeida, T.C.S.; Oliveira, F.P.; Azzi, P.C.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Souza, R.L.; Lacerda, S.M.S.N.; Lages, F.S.; Martins, M.D. Comparative Study of Acid Etching and SLA Surface Modification for Titanium Implants. Materials 2025, 18, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupbach, P.; Glauser, R.; Bauer, S. Al2O3 Particles on Titanium Dental Implant Systems following Sandblasting and Acid-Etching Process. Int. J. Biomater. 2019, 2019, 6318429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, J.S.; David, S.R.N.; Zulhilmi, N.R.; Dhaliwal, S.K.S.; Knights, J.; De Albuquerque, R.F. Contamination of titanium dental implants: A narrative review. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Ortiz-García, I.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Muñoz-Guzón, F.; Perez, R.A.; Gil, F.J. Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.; Tumedei, M.; Panda, S.; Goker, F.; Depalma, C.M.; Pande, T.; Del Fabbro, M. The Biological Impact of Residual Aluminum Particles on Sand-Blasted Dental Implant Surfaces: A Systematic Review of Animal Studies. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Padros, A.; Gil, F.J. In vivo evaluation of micro-rough and bioactive titanium dental implants using histometry and pull-out tests. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deppe, H.; Wolff, C.; Bauer, F.; Ruthenberg, R.; Sculean, A.; Mucke, T. Dental implant surfaces after insertion in bone: An in vitro study in four commercial implant systems. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Ramirez-Fernandez, M.P.; Marín, J.M.G.; Salles, M.B.; Del Fabbro, M.; Guirado, J.L.C. A comparative evaluation between aluminium and titanium dioxide microparticles for blasting the surface titanium dental implants: An experimental study in rabbits. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, L.; Mercadé, M.; Torrent, S.; Punset, M.; Pérez, R.A.; Delgado, L.M.; Gil, F.J. Double acid etching treatment of dental implants for enhanced biological properties. J. Appl. Biomater. Func. Mater. 2018, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Wan, K.M.; Lu, J.H.; Yuan, C.Y.; Cui, Y.W.; Duan, R.Q.; Yu, J. Research Progress on Surface Modification of Titanium Implants. Coatings 2025, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowska, A.; Zielinski, A. The Mechanisms of Degradation of Titanium Dental Implants. Coatings 2020, 10, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; da Costa, E.M.; Junior, J.A.; Eilers Treichel, T.L.; Del Fabbro, M.; Scarano, A. Comparison Between Micro- and Micro-Nano Surface Texturization in the Initial Osseointegration Process: An Experimental In Vitro and In Vivo Preclinical Study. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Volume Section 13: Medical Devices; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Adhitya, K.; Mustika, T.; Manawan, M.; Ulfah, I.M.; Hanafi, R.; Setyadi, I.; Suryadi; Hidayat, A.; Wibisono, M.; Sah, J.; et al. Optimizing surface properties in pure titanium for dental implants: A crystallographic analysis of sandblasting and acid-etching techniques. Powder Diffr. 2024, 39, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, K.; Wennerberg, A.; Wroblewski, J.; Hultenby, K.; Lopez, B.S.; Arvidson, K. Deter-mining optimal surface roughness of TiO2 blasted titanium implant material for attachment, proliferation and differentiation of cells derived from human mandibular alveolar bone. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20 (Suppl. 4), 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.G.; De Oliveira, P.T.; Nanci, A.; Hawthorne, A.C.; Rosa, A.L.; Xavier, S.P. Treatment of a commercial, machined surface titanium implant with HSO/HO enhances contact osteogenesis. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Ide-Ektessabi, A.; Hatkamata, S.; Sawase, T.; Johansson, C.; Albrektsson, T.; Martinelli, A.; Södervall, U.; Odelius, H. Titanium release from implants prepared with different surface roughness: An and study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stich, T.; Alagboso, F.; Krenek, T.; Kovarik, T.; Alt, V.; Docheva, D. Implant-bone-interface: Reviewing the impact of titanium surface modifications on osteogenic processes in vitro and in vivo. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, e10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.M.; Moon, H.J.; Kwon, Y.D.; Yoo, J.Y.; Pae, A.; Kwon, I.K. Osteoblastic and osteoclastic differentiation on SLA and hydrophilic modified SLA titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Ra (nm, AFM) | Rz (nm, AFM) | Rq (nm, AFM) | Rmax (nm, AFM) | Ra (nm, SP) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 850.9 ± 133.2 | 7.7 ± 3.7 | 1.1 ± 3.2 | 10.1 ± 12.1 | 922 ± 134.0 |
| TiO2 and HCl | 921.2 ± 143.0 * | 8.1 ± 2.8 | 1.2 ± 4.1 * | 10.5 ± 16.2 | 1.315 ± 165.0 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lijnev, A.; Maté Sánchez de Val, J.E.; Elango, J.; Pérez-Albacete Martínez, C.; Marín, J.M.G.; Scarano, A.; Gehrke, S.A. Residual-Free Micro–Nano Titanium Surfaces via Titanium Blasting and Single Acid-Etching: A Cleaner Alternative. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070735
Lijnev A, Maté Sánchez de Val JE, Elango J, Pérez-Albacete Martínez C, Marín JMG, Scarano A, Gehrke SA. Residual-Free Micro–Nano Titanium Surfaces via Titanium Blasting and Single Acid-Etching: A Cleaner Alternative. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070735
Chicago/Turabian StyleLijnev, Artiom, José Eduardo Maté Sánchez de Val, Jeevithan Elango, Carlos Pérez-Albacete Martínez, José Manuel Granero Marín, Antonio Scarano, and Sergio Alexandre Gehrke. 2025. "Residual-Free Micro–Nano Titanium Surfaces via Titanium Blasting and Single Acid-Etching: A Cleaner Alternative" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070735
APA StyleLijnev, A., Maté Sánchez de Val, J. E., Elango, J., Pérez-Albacete Martínez, C., Marín, J. M. G., Scarano, A., & Gehrke, S. A. (2025). Residual-Free Micro–Nano Titanium Surfaces via Titanium Blasting and Single Acid-Etching: A Cleaner Alternative. Bioengineering, 12(7), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070735









