Biorecognition-Based Nanodiagnostics: Maltotriose-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Bacterial Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
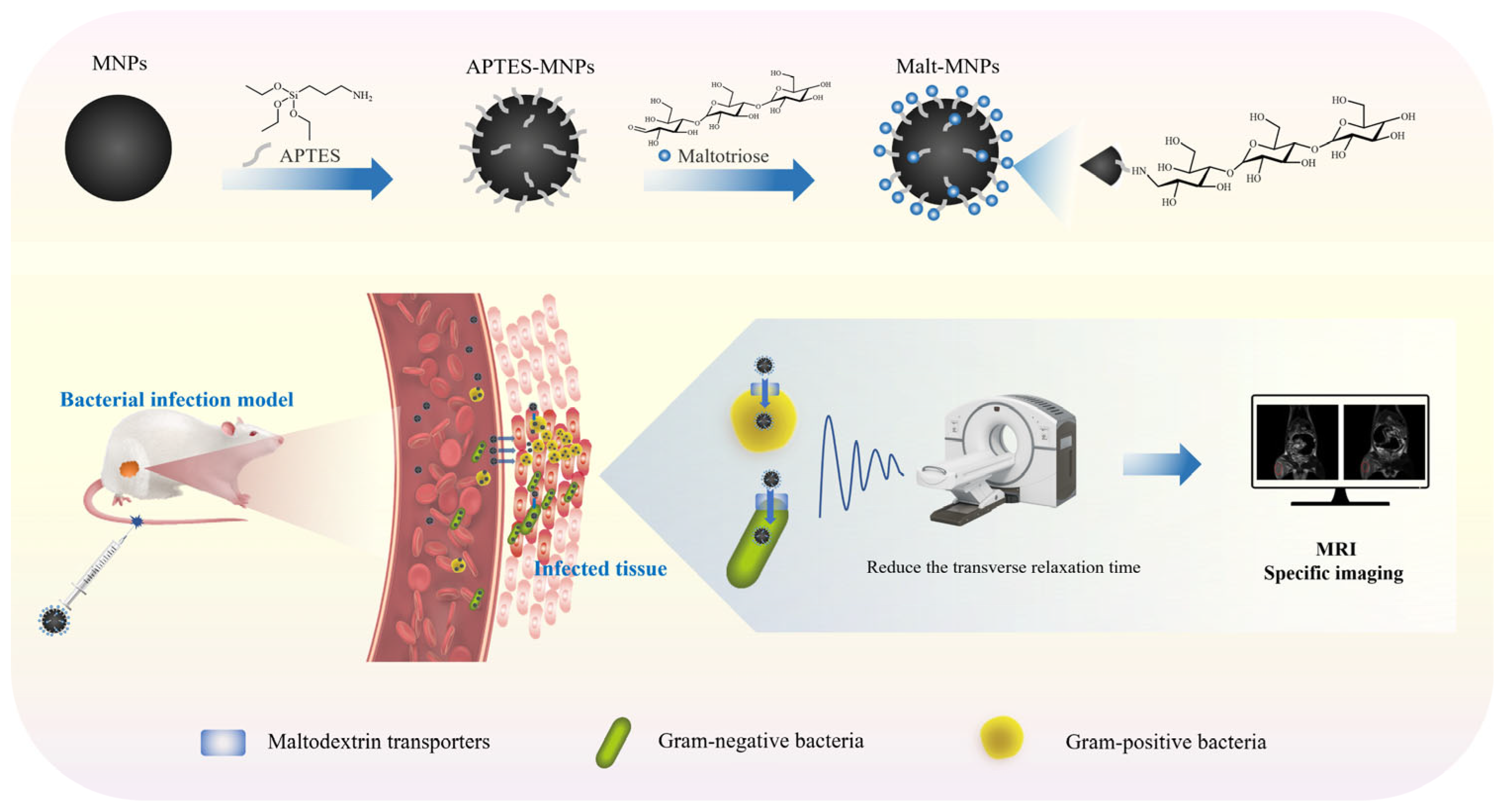
2.1. Synthesis of MNPs
2.2. Synthesis of Malt-MNPs
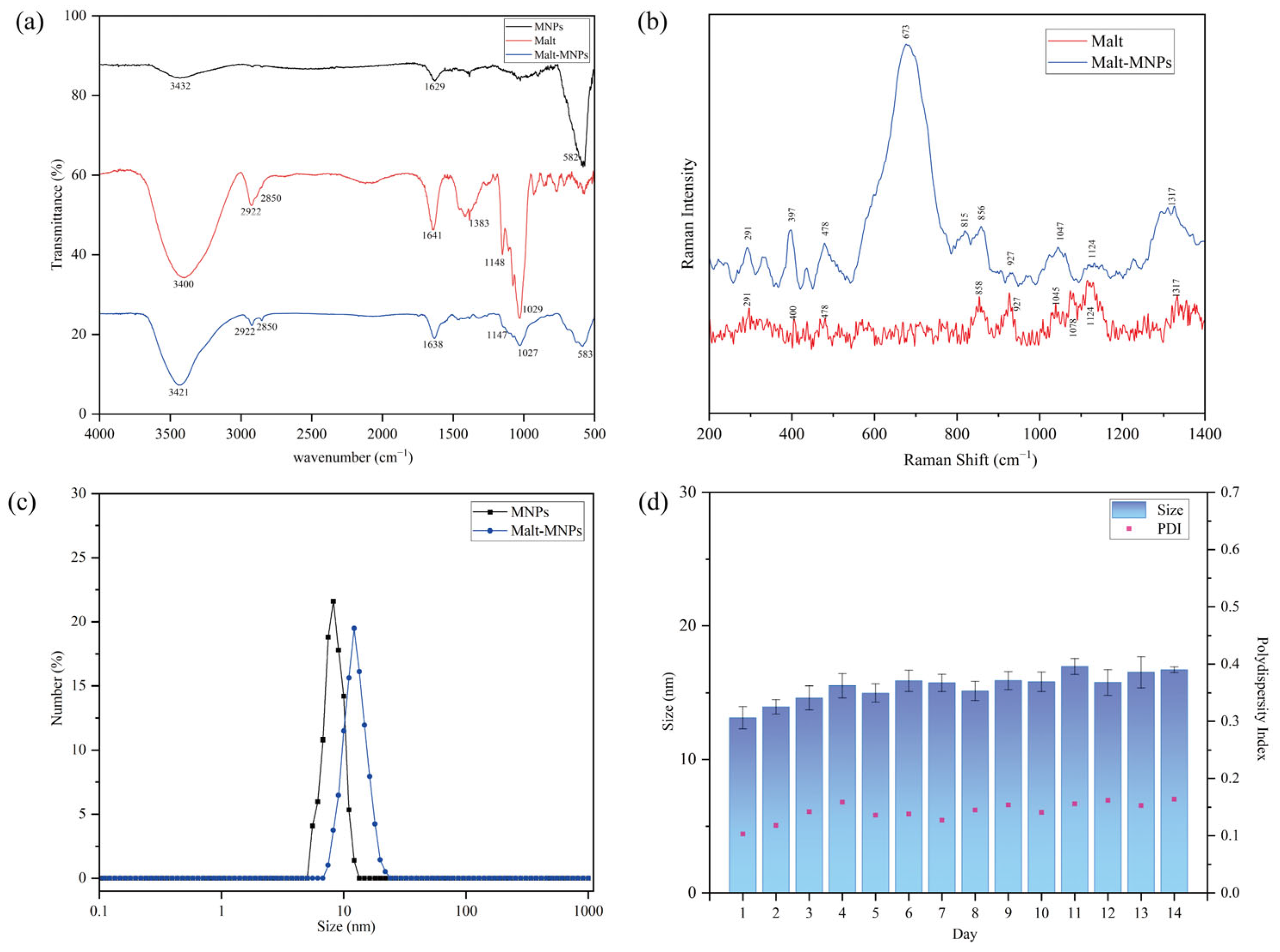
2.3. Characterization of Malt-MNPs
2.4. Bacterial Culture
2.5. In Vitro Imaging of Bacteria
2.6. Infection Animal Models
2.7. In Vivo MRI
2.8. Toxicity Assessment of Malt-MNPs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Malt-MNPs
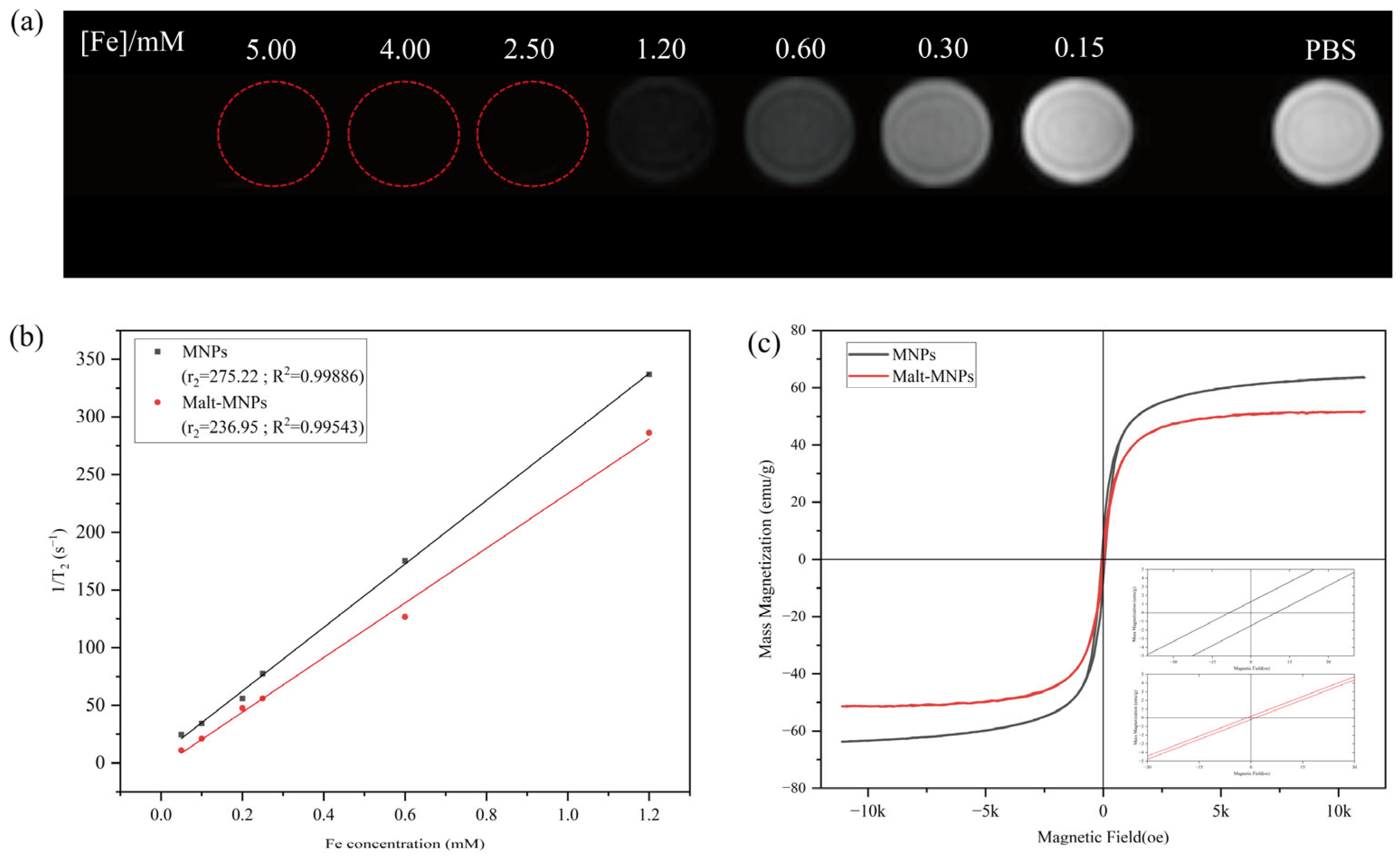
3.2. Magnetic Properties and T2 of Malt-MNPs
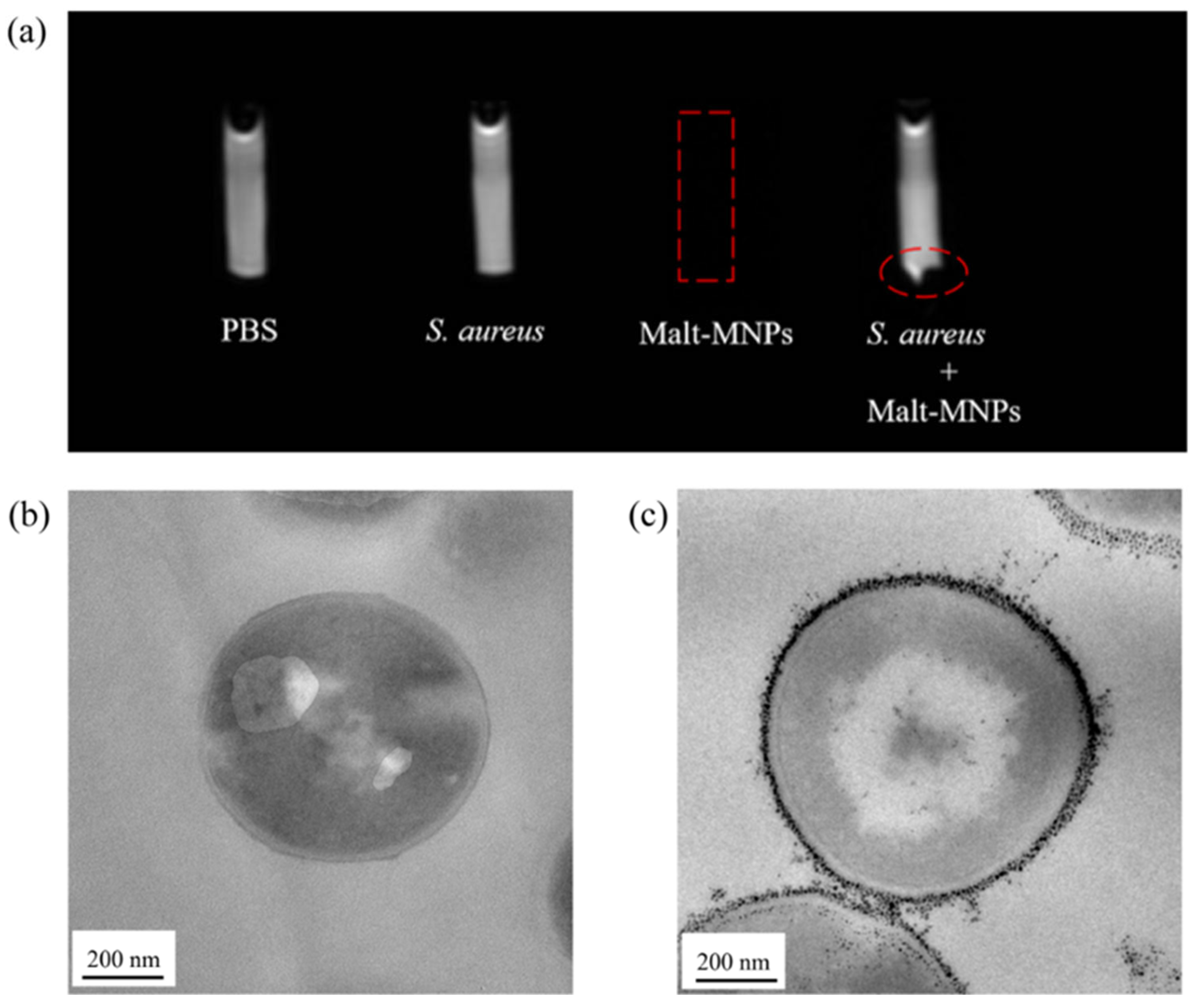
3.3. In Vitro Uptake of Malt-MNPs by Bacteria
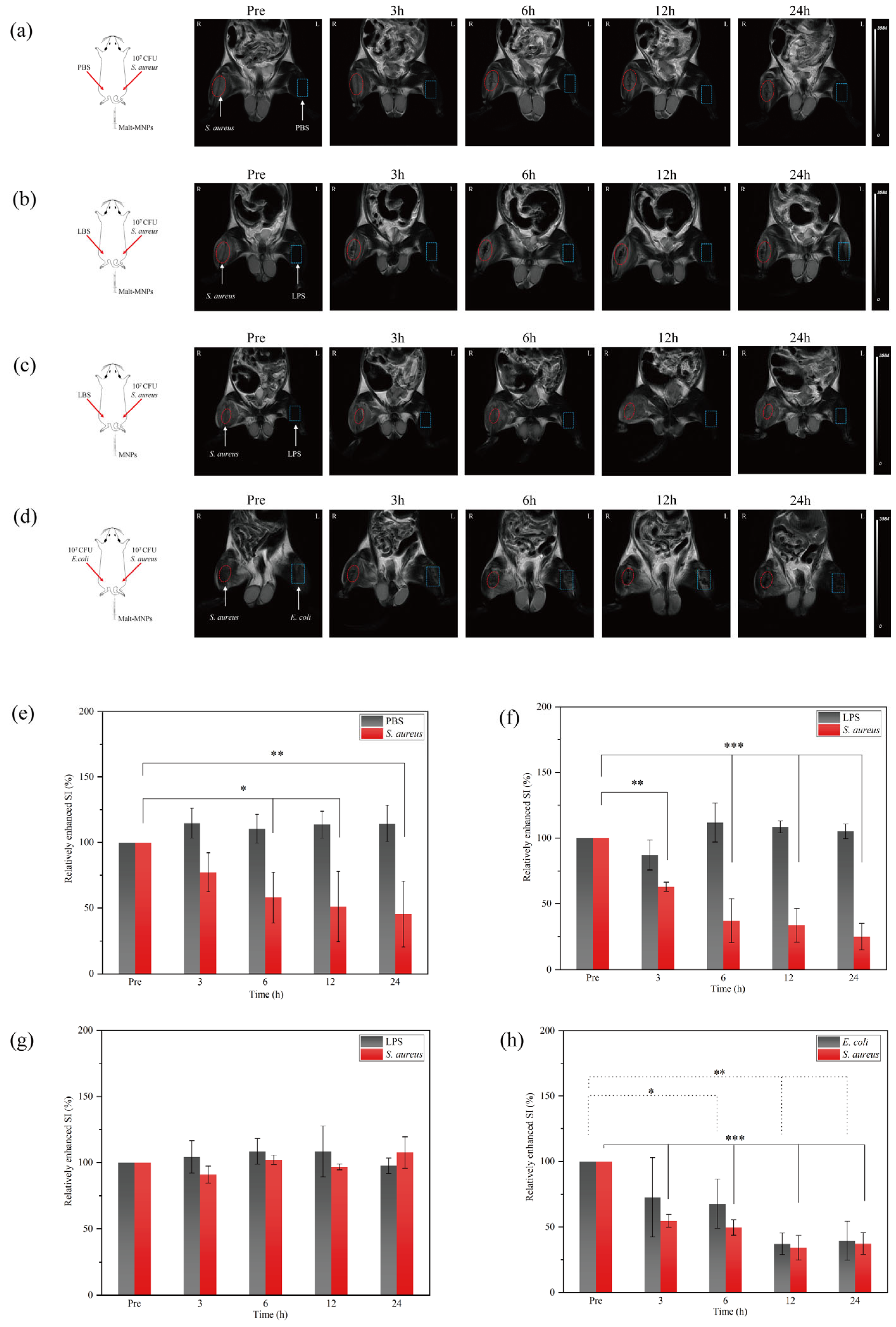
3.4. In Vivo Imaging Capability of Malt-MNPs at Infection Sites
3.5. Toxicity Evaluation of Malt-MNPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Fu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Lin, J.; Li, P.; Yu, Y. Antibiotic susceptibility patterns and trends of the gram-negative bacteria isolated from the patients in the emergency departments in China: Results of SMART 2016–2019. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronald, A. The etiology of urinary tract infection: Traditional and emerging pathogens. Dis. Mon. 2003, 49, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, S.; Soares, S.; Ramos, F.; Moretti, M.; Zavascki, A.P.; Rigatto, M.H. A Cohort Study of the Impact of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infections on Mortality of Patients Presenting with Sepsis. mSphere 2019, 4, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhao, M.; Li, B.; Liu, L.; et al. Risk Factors and Molecular Epidemiology of Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections with Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A Multicenter Study in China. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, S156–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations. Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20cover.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Anderson, D.J. Surgical site infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 25, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterer, G.W.; Kessler, L.A.; Wunderink, R.G. Delayed administration of antibiotics and atypical presentation in community-acquired pneumonia. Chest 2006, 130, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliver on diagnostics to save lives. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 847. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Point-of-care diagnostics for infectious diseases: From methods to devices. Nano Today 2021, 37, 101092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, M.; Brar, N.; Khatib, R.; Fakih, M.G. Misdiagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia and inappropriate utilization of antibiotics: Side effects of the 4-h antibiotic administration rule. Chest 2007, 131, 1865–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trampuz, A.; Zimmerli, W. Diagnosis and treatment of infections associated with fracture-fixation devices. Injury 2006, 37 (Suppl. S2), S59–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, N.; Tabas, J.; Afshar, K.; Silbergleit, R. Blood cultures for community-acquired pneumonia: Are they worthy of two quality measures? A systematic review. J. Hosp. Med. 2009, 4, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, P.; Bryson, A.L.; Binnicker, M.J.; Pritt, B.S.; Patel, R. Syndromic Panel-Based Testing in Clinical Microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.K.; Ali, M.M.; Zhang, K.; Huang, S.S.; Peterson, E.; Digman, M.A.; Gratton, E.; Zhao, W. Rapid detection of single bacteria in unprocessed blood using Integrated Comprehensive Droplet Digital Detection. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-W.; Procop, G.W.; Persing, D.H. Molecular diagnostics of infectious diseases. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 2021–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, C.; Palestro, C.J. Nuclear medicine imaging of bone infections. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bruggen, W.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; Boerman, O.C.; Gotthardt, M.; Oyen, W.J. PET and SPECT in osteomyelitis and prosthetic bone and joint infections: A systematic review. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 40, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yao, S.; Xing, H.; Zhang, H.; Tai, Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, H.; et al. Biodistribution and Radiation Dosimetry of the Enterobacteriaceae-Specific Imaging Probe [18F]Fluorodeoxysorbitol Determined by PET/CT in Healthy Human Volunteers. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, E.A.; Ordonez, A.A.; DeMarco, V.P.; Murawski, A.M.; Pokkali, S.; MacDonald, E.M.; Klunk, M.; Mease, R.C.; Pomper, M.G.; Jain, S.K. Imaging Enterobacteriaceae infection in vivo with 18F-fluorodeoxysorbitol positron emission tomography. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 259ra146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudo, C.; Evangelista, L.; Fraia, A.S.; Lupi, A.; Quaia, E.; Cecchin, D.; Casali, M. Molecular Imaging of Pulmonary Inflammation and Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Mubeen, I.; Ullah, N.; Shah, S.; Khan, B.A.; Zahoor, M.; Ullah, R.; Khan, F.A.; Sultan, M.A. Modern Diagnostic Imaging Technique Applications and Risk Factors in the Medical Field: A Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5164970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. Computed tomography–An increasing source of radiation exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Li, B.; Yang, H.F.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Zheng, H.J.; Gong, Q.Y. Can diffusion-weighted imaging be used to differentiate brain abscess from other ring-enhancing brain lesions? A meta-analysis. Clin. Radiol. 2014, 69, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelreich, U.; Accurso, R.; Malik, R.; Dolenko, B.; Somorjai, R.L.; Gupta, R.K.; Gomes, L.; Mountford, C.E.; Sorrell, T.C. Identification of Staphylococcus aureus brain abscesses: Rat and human studies with 1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2005, 236, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bettegowda, C.; Qiao, Y.; Staedtke, V.; Chan, K.W.; Bai, R.; Li, Y.; Riggins, G.J.; Kinzler, K.W.; Bulte, J.W.; et al. Noninvasive imaging of infection after treatment with tumor-homing bacteria using Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST) MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, M.W.; Grey, M.L. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Overview, risks, and safety measures. AJN Am. J. Nurs. 2002, 102, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustace, S.J.; Nelson, E. Whole body magnetic resonance imaging. BMJ 2004, 328, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, H.; Robinson, D.B.; Raoux, S.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Li, G. Monodisperse MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Mn) nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.L. Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 2005, 1, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Hofmann, H.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Petri-Fink, A. Assessing the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2323–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopiou, E.D.; Pissas, M.; Fibbi, G.; Margheri, F.; Kalska-Szostko, B.; Papanastasiou, G.; Jansen, M.; Wang, J.; Laurenzana, A.; Efthimiadou, K.E. Synthesis and characterization of modified magnetic nanoparticles as theranostic agents: In vitro safety assessment in healthy cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 72, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Han, L.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Song, G.; Rao, J. Engineering of magnetic nanoparticles as magnetic particle imaging tracers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8102–8146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, B.; MacDonald, D.; Jasiński, K.; Cheng, F.Y.; Tomanek, B. Application of H2N-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Prostate Cancer Magnetic Resonance Imaging in an Animal Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, R.A.; Hilt, J.Z. Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine: Synthesis, functionalization and applications. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloag, L.; Mehdipour, M.; Chen, D.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J. Advances in the Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1904385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, S.V.; Navolokin, N.A.; Kuznetsova, N.R.; Zuev, V.V.; Inozemtseva, O.A.; Anis’kov, A.A.; Volkova, E.K.; Bucharskaya, A.B.; Maslyakova, G.N.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; et al. Liposomes loaded with hydrophilic magnetite nanoparticles: Preparation and application as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Gai, S.; Lin, J. Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3679–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.; Parekh, K.; Pandey, B. Influence of crystallite size on the magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 678, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D.; Yoshida, T.; Rincón-Domínguez, T.; Cuñado, J.L.F.; Salas, G.; Bollero, A.; Morales, M.D.P.; Camarero, J.; Teran, F.J. Superparamagnetic-blocked state transition under alternating magnetic fields: Towards determining the magnetic anisotropy in magnetic suspensions. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 8789–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordignon, E.; Grote, M.; Schneider, E. The maltose ATP-binding cassette transporter in the 21st century--towards a structural dynamic perspective on its mode of action. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boos, W.; Shuman, H. Maltose/maltodextrin system of Escherichia coli: Transport, metabolism, and regulation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 204–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeckelmann, J.M.; Erni, B. Transporters of glucose and other carbohydrates in bacteria. Pflug. Arch. 2020, 472, 1129–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axer, A.; Hermann, S.; Kehr, G.; Clases, D.; Karst, U.; Fischer-Riepe, L.; Roth, J.; Fobker, M.; Schäfers, M.; Gilmour, R.; et al. Harnessing the Maltodextrin Transport Mechanism for Targeted Bacterial Imaging: Structural Requirements for Improved in vivo Stability in Tracer Design. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlitni, A.; Gowrishankar, G.; Steinberg, I.; Haywood, T.; Sam Gambhir, S. Maltotriose-based probes for fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging of bacterial infections. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.; Kim, D.; Stubblefield, B.; Gilbert, E.; Murthy, N. Maltodextrin-based imaging probes detect bacteria in vivo with high sensitivity and specificity. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemiya, K.; Ning, X.; Seo, W.; Wang, X.; Mohammad, R.; Joseph, G.; Titterington, J.S.; Kraft, C.S.; Nye, J.A.; Murthy, N.; et al. Novel PET and Near Infrared Imaging Probes for the Specific Detection of Bacterial Infections Associated with Cardiac Devices. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.; Berg, D.; Hagen, N.; Schriefer, E.M.; Stoll, R.; Goebel, W.; Kreft, J. Maltose and maltodextrin utilization by Listeria monocytogenes depend on an inducible ABC transporter which is repressed by glucose. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, R.; Cabuil, V. Synthèse en milieu alcalin de magnétite colloïdale: Contrôle du rendement et de la taille des particules. J. Chim. Phys. 1987, 84, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; He, J.; Deng, L.; Gao, X. Fabrication of cyclodextrin-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4/amino-silane core–shell nanoparticles via layer-by-layer method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 7974–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrahimi, M.; Vasilakaki, M.; Slimani, S.; Ntallis, N.; Varvaro, G.; Laureti, S.; Meneghini, C.; Trohidou, K.N.; Fiorani, D.; Peddis, D. Magnetism of Nanoparticles: Effect of the Organic Coating. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Xue, J.M.; Shuter, B.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Synthesis of PEOlated Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanoparticles via Bioinspired Silification for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, C.; Blank, F.; West, A.; Black, G.; Woodward, R.C.; Carroll, M.R.; Mainka, A.; Kartmann, R.; Brandl, A.; Bruns, H.; et al. Labeling of cancer cells with magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Bhattarai, N.; Sun, C.; Zhang, M. Functionalized nanoparticles with long-term stability in biological media. Small 2009, 5, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, T.; Ninjbadgar, T.; Kapetanakis, A.; Roche, S.; O‘Connor, R.; Kerskens, C.; Heise, A.; Brougham, D.F. Stable aqueous dispersions of glycopeptide-grafted selectably functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 3164–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.D.; Paudel, R.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhou, S.K. MRI contrast agents: Classification and application (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.J. Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: Current status of clinical application. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2011, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, A.; Hosseini, H.R.; Reyhani, S.M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Oghabian, M.A.; Ahmadi, R. Long-term investigation on the phase stability, magnetic behavior, toxicity, and MRI characteristics of superparamagnetic Fe/Fe-oxide core/shell nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzopardi, E.A.; Ferguson, E.L.; Thomas, D.W. The enhanced permeability retention effect: A new paradigm for drug targeting in infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 68, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Laurent, S.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Hosseinkhani, M. Toxicity evaluations of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Cell “vision” versus physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7263–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Jokerst, J.V. A Gold/Silver Hybrid Nanoparticle for Treatment and Photoacoustic Imaging of Bacterial Infection. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5615–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, B.; Bradley, M.; Dhaliwal, K. Optical imaging of bacterial infections. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2016, 4, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, X.; Seo, W.; Lee, S.; Takemiya, K.; Rafi, M.; Feng, X.; Weiss, D.; Wang, X.; Williams, L.; Camp, V.M.; et al. PET imaging of bacterial infections with fluorine-18-labeled maltohexaose. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 14096–14101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, J.; Yin, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Y.; Chang, J.; Wang, T. Biorecognition-Based Nanodiagnostics: Maltotriose-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Bacterial Infections. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030296
Wan J, Yin C, Chen X, Wu K, Zhang C, Zhou Y, Feng Y, Chang J, Wang T. Biorecognition-Based Nanodiagnostics: Maltotriose-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Bacterial Infections. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(3):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030296
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Junshan, Chuqiang Yin, Xiaotong Chen, Keying Wu, Chonghui Zhang, Yu Zhou, Yugong Feng, Jing Chang, and Ting Wang. 2025. "Biorecognition-Based Nanodiagnostics: Maltotriose-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Bacterial Infections" Bioengineering 12, no. 3: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030296
APA StyleWan, J., Yin, C., Chen, X., Wu, K., Zhang, C., Zhou, Y., Feng, Y., Chang, J., & Wang, T. (2025). Biorecognition-Based Nanodiagnostics: Maltotriose-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Bacterial Infections. Bioengineering, 12(3), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12030296





