Improvement in Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Rice Bran Treated with Different Processing Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Rice Bran Using Different Processing Methods
2.2.1. Extruded DRB (EDRB)
2.2.2. Fermented DRB (FDRB)
2.2.3. Fermented–Extruded Defatted Rice Bran (FEDRB)
2.3. Preparation of Insoluble Dietary Fiber (IDF)
2.4. Structural Characterization of IDF
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FT-IR)
2.4.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5. Physicochemical Properties of IDF
2.5.1. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.5.2. Oil-Holding Capacity (OHC)
2.6. Functional Properties of IDF
2.6.1. Sodium Cholate-Binding Capacity (SCBC)
2.6.2. Cholesterol-Binding Capacity (CBC)
2.6.3. α-Amylase-Activity-Inhibitory Ability
2.6.4. Determination of Glucose-Adsorption Capacity (GAC)
2.6.5. Determination of Glucose Dialysis Retardation Index (GDRI)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Composition of IDFs
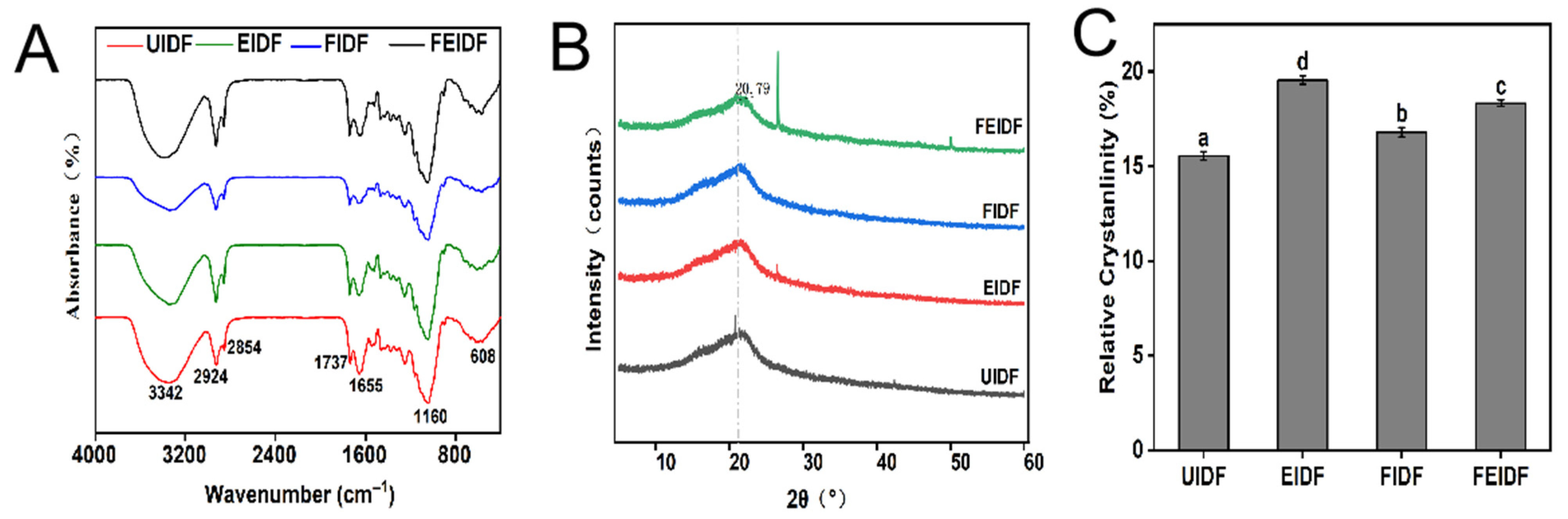
3.2. Structural Properties of IDFs
3.2.1. Microscopic Morphology
3.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
3.2.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
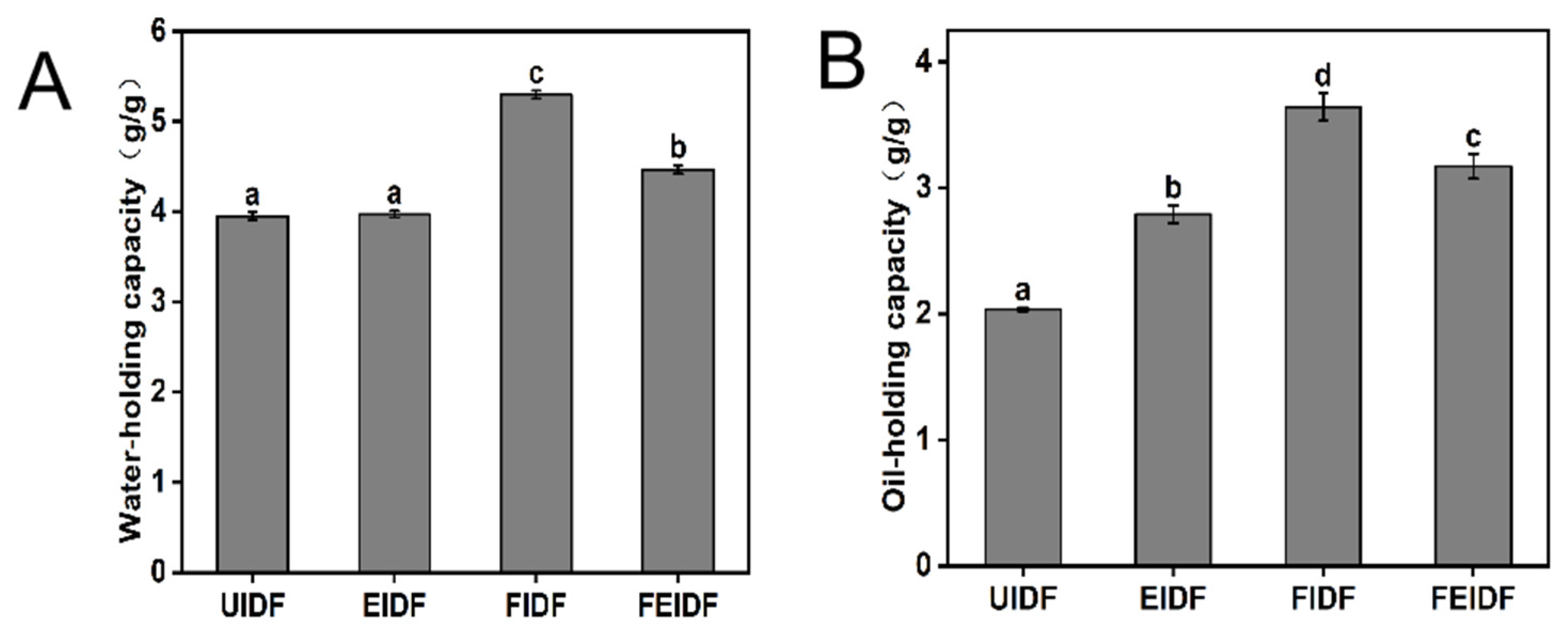
3.3. Physicochemical Properties of IDFs
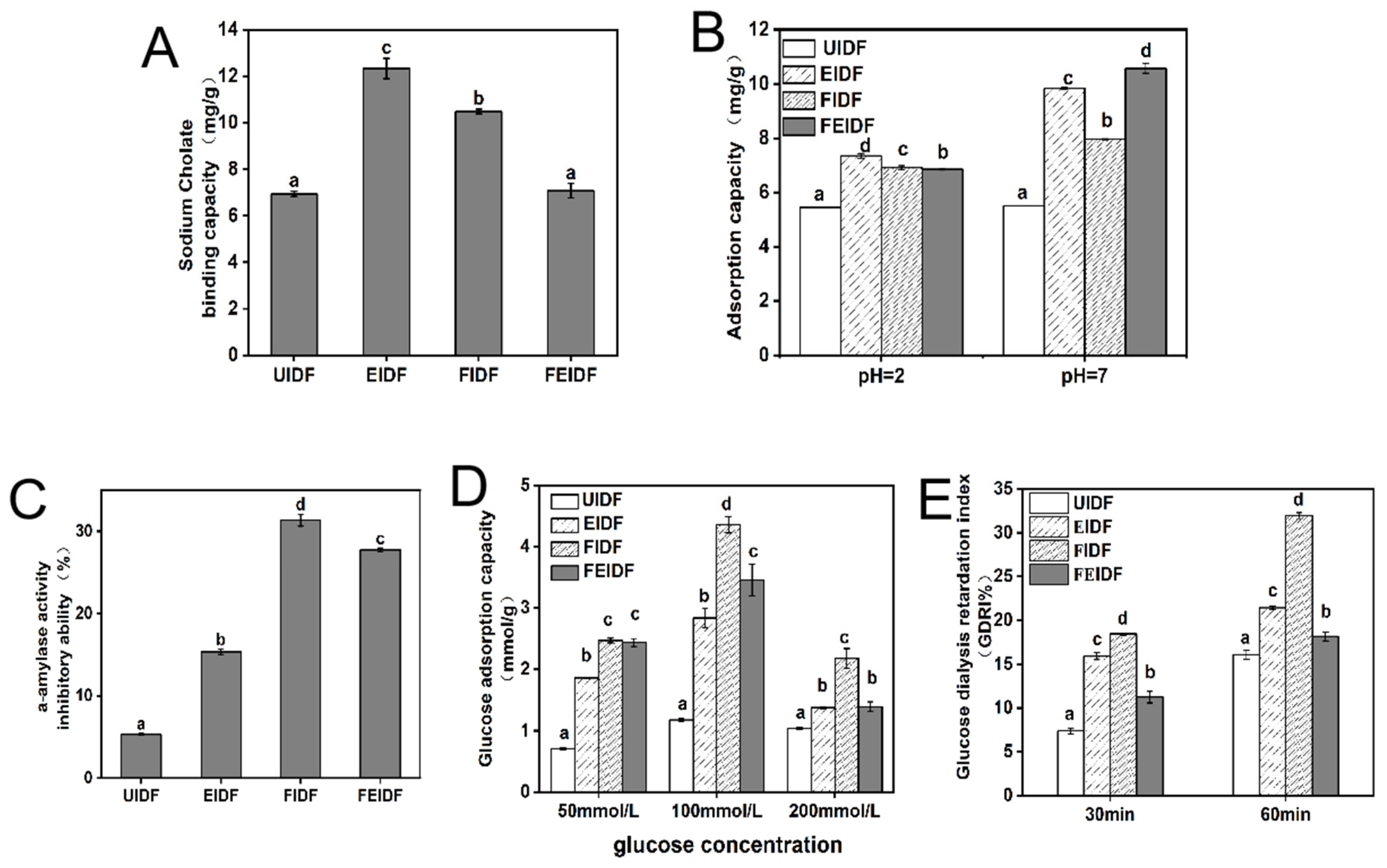
3.4. Functional Properties of IDFs
3.4.1. Sodium Cholate-Binding Capacity
3.4.2. Cholesterol-Binding Capacity
3.4.3. α-Amylase-Activity-Inhibitory Ability
3.4.4. Glucose-Adsorption Capacity (GAC)
3.4.5. Glucose Dialysis Retardation Index (GDRI)
3.5. Industrial Processing Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Ying, D.; Guo, B.; Cheng, L.J.; May, B.; Bird, T.; Sanguansri, L.; Cao, Y.; Augustin, M. Extrusion of apple pomace increases antioxidant activity upon in vitro digestion. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Huang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Peng, G.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Microwave assisted extraction with three modifications on structural and functional properties of soluble dietary fibers from grapefruit peel. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Chau, C. Classification and regulatory perspectives of dietary fiber. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, S.; Kaur, N. Utilization of fruits and vegetable by-products for isolation of dietary fibres and its potential application as functional ingredients. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2022, 27, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, E.S.V.; Lima, G.C.; Naves, M.M.V. Dietary fibers as beneficial microbiota modulators: A proposed classification by prebiotic categories. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Zhao, X.; Ao, T.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Gui, Y.; Gao, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Exploring and comparing the anti-obesity mechanisms of defatted rice bran total dietary fiber, insoluble dietary fiber, and soluble dietary fiber based on multi-omics technologies. Food Front. 2024, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, P.V.P.; Joye, I.J. Dietary fibre from whole grains and their benefits on metabolic health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.; Vasanthan, T. Modification of rice bran dietary fiber concentrates using enzyme and extrusion cooking. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Guo, Q.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.; Sun, T.; Liu, X.; Xiao, C. The effect of ball milling on the structure, physicochemical and functional properties of insoluble dietary fiber from three grain bran. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Q.; Deng, M.; Jia, X.; Huang, F.; Dong, L.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M. Composition, structural, physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from different milling fractions of black rice bran. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 195, 115743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanavanitchakorn, S.; Wansuksri, R.; Chaichoompu, E.; Kamolsukyeunyong, W.; Vanavichit, A. Dietary fibre impacts the texture of cooked whole grain rice. Foods 2023, 12, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Gong, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; You, L. The effects of dietary fibers from rice bran and wheat bran on gut microbiota: An overview. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Effects of modification methods on microstructural and physicochemical characteristics of defatted rice bran dietary fiber. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphosa, Y.; Jideani, V.A. Dietary fiber extraction for human nutrition—A review. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 32, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.G.; Goncalves, L.M.; Prietto, L.; Hackbart, H.S.; Furlong, E.B. Antioxidant activity and enzyme inhibition of phenolic acids from fermented rice bran with fungus Rizhopus oryzae. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Xie, L.; Peng, G.; Xie, J.; Yu, Q. Systematic review on modification methods of dietary fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Long, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.; Qin, W.; Tu, Z. Effects of microbial fermentation and microwave treatment on the composition, structural characteristics, and functional properties of modified okara dietary fiber. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 123, 109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Jia, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Chi, F.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R. Extrusion and fungal fermentation change the profile and antioxidant activity of free and bound phenolics in rice bran together with the phenolic bioaccessibility. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 115, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Luan, G. Effect of extruded soybean okara on the texture, rheology, and structural properties of high-fiber composite dough. Food Chem. 2025, 487, 144722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B. Mechanism and functional activities of dietary fiber-bound polyphenol released from pomegranate pomace in mixed solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus oryzae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 21987–21998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, R.; Dong, L.; Huang, F.; Tang, X. Particle size of insoluble dietary fiber from rice bran affects its phenolic profile, bioaccessibility and functional properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Method 930.15: Moisture in animal feed, cereals, and oilseeds. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Official Method 990.03: Crude protein in animal feed and plant materials. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 593–598. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Official Method 996.11: Total starch in cereals and derived products. J. AOAC Int. 2025, 108, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Official Method 942.05: Total ash in food and agricultural products. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 599–604. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Fang, D.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, C.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, Y. Modification of insoluble dietary fibers from bamboo shoot shell: Structural characterization and functional properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Lin, L.; Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, J. Hydration properties and binding capacities of dietary fibers from bamboo shoot shell and its hypolipidemic effects in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2017, 109, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichamroen, A.; Chavasit, V. In vitro retardation of glucose diffusion with gum extracted from malva nut seeds produced in Thailand. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerajit, P.; Chiewchan, N.; Devahastin, S. Effects of pretreatment methods on health-related functional properties of high dietary fibre powder from lime residues. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daou, C.; Zhang, H. Functional and physiological properties of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fibres derived from defatted rice bran. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 3878–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, P. Effects of carboxymethylation, hydroxypropylation and dual enzyme hydrolysis combination with heating on physicochemical and functional properties and antioxidant activity of coconut cake dietary fibre. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, X.; Zhu, K. Impact of solid state fermentation on nutritional, physical and flavor properties of wheat bran. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Wei, Z. Physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from Bamboo Shoots (Phyllostachys praecox). Emir. J. Food Agric. 2017, 29, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y. Physicochemical and functional properties of coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) cake dietary fibres: Effects of cellulase hydrolysis, acid treatment and particle size distribution. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Ding, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, H. Modification of insoluble dietary fiber from garlic straw with ultrasonic treatment. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, N.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Lei, H. Physical modifications of dietary fibers from kiwifruit pomace: Physicochemical, structural and functional properties. Food Chem. 2025, 484, 144422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; He, Y.; Quan, B.; Xia, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M. Physicochemical properties, structure, and ameliorative effects of insoluble dietary fiber from tea on slow transit constipation. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.; Velez Marques, A.; Domingos, I.; Pereira, H. Chemical changes of heat treated pine and eucalypt wood monitored by FTIR. Maderas Cienc. Y Technol. 2013, 15, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Hussain, S.; Yan, S.; Wang, Q. Effects of extrusion on structural and physicochemical properties of soluble dietary fiber from nodes of lotus root. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 93, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet, A.; Rodríguez-Arcos, R.; Guillén-Bejarano, R.; Chaira, N.; Ferchichi, A.; Jiménez-Araujo, A. Dietary fiber from Tunisian common date cultivars (Phoenix dactylifera L.): Chemical composition, functional properties, and antioxidant capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3658–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, Y. The effect of extrusion processing on the physiochemical properties of extruded orange pomace. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, R.; Sui, W.; Zhang, M. Effect of extrusion, steam explosion and enzymatic hydrolysis on functional properties of wheat bran. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 24, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralet, M.C.; Valle, G.D.; Thibault, J.F. Raw and extruded fibre from pea hulls. Part I: Composition and physico-chemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 1993, 20, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Fang, Z.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Hodgson, J.M.; Johnson, S.K. Extrusion cooking increases soluble dietary fibre of lupin seed coat. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 99, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, S.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Martin, A.; Schuster, M.; Eisner, P. Effects of extrusion processing on the physiochemical and functional properties of lupin kernel fibre. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 111, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C. Improved physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from millet bran fermented by Bacillus natto. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fai, C.; Ling, W.; Ting, W. Effects of micronisation on the characteristics and physicochemical properties of insoluble fibres. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, G.; Ros, G.; Rincón, F.; Periago, M.J.; Martínez, M.C.; OrtuñO, J. Relationship between Physical and Hydration Properties of Soluble and Insoluble Fiber of Artichoke. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Zeng, F.; Wu, N.; Tan, B. Functional, physicochemical and structural properties of soluble dietary fiber from rice bran with extrusion cooking treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 6, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, C.; Ou, S. In vitro binding capacities of three dietary fibers and their mixture for four toxic elements, cholesterol, and bile acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsor-Atindana, J.; Zhong, F.; Mothibe, K.J. In vitro hypoglycemic and cholesterol lowering effects of dietary fiber prepared from cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) shells. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Hu, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, F.; Qin, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Huang, C. A functional dietary fiber composite film developed from grapefruit processing waste: Superior UV-shielding capacity, hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities in vitro, and maintaining the good quality of New Year cakes. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 171, 111793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chu, J.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, H. Physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from foxtail millet (Setaria italic) bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qu, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y. Structure, physicochemical properties and adsorption function of insoluble dietary fiber from ginseng residue: A potential functional ingredient. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, M.; Nie, S.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Yu, Q. Structural characteristics and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from defatted rice bran obtained through Trichoderma viride fermentation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Wang, A.; Qin, W.; Nie, M.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F. The structural and functional properties of dietary fibre extracts obtained from highland barley bran through different steam explosion-assisted treatments. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 135025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, C. Structure, physicochemical properties and effects on nutrients digestion of modified soluble dietary fiber extracted from sweet potato residue. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y. Different micronization methods significantly improve the functionality of carrot insoluble fibre. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, D.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y. Effect of microfluidization process on the functional properties of insoluble dietary fiber. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, Y.; Masamba, K.G.; Shoemaker, C.F.; Zhong, F.; Majeed, H.; Ma, J. The effect of chemical treatment on the In vitro hypoglycemic properties of rice bran insoluble dietary fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Ma, Q.; Guo, Q.; Santhanam, R.K.; Gao, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Physicochemical and functional properties of extruded dietary fiber from mushroom Lentinula edodes residues. Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.; Huang, Y.; Lee, M. In Vitro Hypoglycemic Effects of Different Insoluble Fiber-Rich Fractions Prepared from the Peel of Citrus sinensis L. cv. Liucheng. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6623–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sheraji, S.H.; Ismail, A.; Manap, M.Y.; Mustafa, S.; Yusof, R.M.; Hassan, F.A. Functional properties and characterization of dietary fiber from Mangifera pajang Kort. fruit pulp. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3980–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sun, W.; Swallah, M.S.; Amin, K.; Yu, H. Preparation and characterization of soybean insoluble dietary fiber and its prebiotic effect on dyslipidemia and hepatic steatosis in high fat-fed C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8760–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcrae, M.P. The benefits of dietary fiber intake on reducing the risk of cancer: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. J. Chiropr. Med. 2018, 17, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IDF Content | Protein | Starch | Moisture | Ash | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIDF | 29.17 ± 0.16 a * | 7.25 ± 0.06 a | 4.17 ± 0.02 a | 5.82 ± 0.08 c | 5.13 ± 0.03 b |
| EIDF | 29.75 ± 0.28 ab | 7.69 ± 0.05 b | 4.23 ± 0.05 a | 4.74 ± 0.04 b | 9.23 ± 0.12 d |
| FIDF | 29.45 ± 0.28 ab | 9.75 ± 0.25 d | 4.67 ± 0.02 b | 5.92 ± 0.08 c | 3.42 ± 0.12 a |
| FEIDF | 30.00 ± 0.26 b | 7.50 ± 0.10 ab | 4.24 ± 0.03 a | 4.22 ± 0.04 a | 6.28 ± 0.01 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Huang, F.; Jia, X.; Dong, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R. Improvement in Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Rice Bran Treated with Different Processing Methods. Foods 2025, 14, 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173116
Chen Y, Ma Q, Huang F, Jia X, Dong L, Liu D, Zhang M, Zhang R. Improvement in Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Rice Bran Treated with Different Processing Methods. Foods. 2025; 14(17):3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173116
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yanxia, Qin Ma, Fei Huang, Xuchao Jia, Lihong Dong, Dong Liu, Mingwei Zhang, and Ruifen Zhang. 2025. "Improvement in Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Rice Bran Treated with Different Processing Methods" Foods 14, no. 17: 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173116
APA StyleChen, Y., Ma, Q., Huang, F., Jia, X., Dong, L., Liu, D., Zhang, M., & Zhang, R. (2025). Improvement in Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Insoluble Dietary Fiber from Rice Bran Treated with Different Processing Methods. Foods, 14(17), 3116. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14173116





