Abstract
The structural determination of ultrasmall clusters remains a challenge due to difficulties in crystallisation. Often the atomically precise clusters undergo structural change under the influence of the environment. X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) can be an attractive tool to study the electronic and geometric properties of such clusters deposited onto various supports under in situ conditions. Herein, [Au6(dppp)4](NO3)2, [Au9(PPh3)8](NO3)3, [Au13(dppe)5Cl2]Cl3, and Au101(PPPh3)21Cl5 clusters were studied using XAS. The clusters exhibited distinct features compared to bulk gold. XANES results show a systematic increase in the absorption edge energy and white line intensity, with a decrease in cluster nuclearity. The EXAFS of clusters are sensitive to nuclearity and ligands and were fitted with their known crystal structures. This study advances the understanding of the phosphine-ligated metal clusters relevant to practical applications in catalysis and sensing.
1. Introduction
Metal clusters constitute a unique class of materials which bridge the gap between single atoms or ions and large nanoparticles with many properties similar to bulk metals [1]. Clusters have interesting optical, magnetic, biomedical, etc., properties, and show exciting performance in sensing and catalysis [2]. The properties and performance of the clusters are strongly affected by their size and composition, offering unique opportunities to fine-tune such materials for a specific application [3,4]. Clusters are typically made either under UHV conditions via size-selection [5,6] or using chemical synthesis in the liquid phase, with the latter approach requiring ligands to cap the surface of the metal core [7,8].
Chemically synthesised clusters, in some cases, can be made at a large scale, and more importantly, in most cases, such species can be crystallised [7]. Crystallisation is an excellent tool for purification, yet more importantly, it enables the solving of crystal structures of clusters using a well-established single-crystal X-ray diffraction technique, with hundreds of structures being reported to date [9].
Gold clusters, in particular, have shown interesting catalytic performance in numerous and diverse reactions, such as oxidation [10,11,12], hydrogenation [13,14], the ester-assisted intermolecular hydration of alkynes, bromination of arenes [15,16] etc., which is in stark contrast to the well-known inertness of bulk gold.
In the case of many applications, such as heterogeneous catalysis and sensing, clusters must be deposited onto solid supports. Cluster-based catalysts can have issues with cluster aggregation, which is often related to specific reaction conditions, be that gas phase [17] or liquid phase [18] heterogeneous catalysis [19].
Hence, a detailed characterisation of cluster-based materials is of paramount importance, ideally under operando conditions that are relevant to industrial application. Aberration-corrected high-resolution HAADF-STEM is capable of imaging supported clusters thanks to recent advances in environmental instruments and stages, allowing for operando studies [20]. However, such facilities are rare as operando experiments are often limited to the gas phase, with liquid phase capabilities only recently emerging [21]. Importantly, only a tiny part of the sample is studied under the high magnification needed for imaging.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) can be used to exclusively study the surface of such materials across large areas easily, making such studies representative of the whole sample, and can be utilised to monitor cluster aggregation [22,23]. However, typically, such studies require a high vacuum, with environmental XPS instruments needed for the operando studies only recently emerging. Similarly to electron microscopy, liquid phase studies can be even more challenging for XPS [24].
X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS) is a well-established synchrotron-based technique suitable for the representative studies of the bulk of cluster-based materials. Most scientifically advanced nations have such facilities, which are typically operated in a multi-user fashion, and many synchrotrons also accept proposals from international researchers. The downside here is the time delay between the beam time proposal and the experiment. Highly sensitive XAS allows for operando studies under both liquid and gas phase heterogeneous catalytic conditions, enabling photocatalytic and electrocatalytic studies as well [25,26].
Herein, we report a detailed XAS investigation of a wide range of ultra-small atomically precise gold clusters capped by phosphine ligands, which highlights changes in the spectra as a function of size. The fitting of the XAS data benefitted from the availability of crystal structures and the application of fuzzy degeneracy in the fitting methodology used in our study of the range of gold clusters. The obtained results suggest that XAS shows promise for future studies (including operando) of the changes in the cluster structure in response to external factors such as temperature, solvation, interaction with the support, complete and/or partial removal of phosphorus-donor ligands, and during the catalytic application.
2. Results and Discussion
Prepared using the aforementioned synthesis methods [27,28,29,30,31,32], Au6, Au9, and Au13 clusters are truly atomically precise (i.e., with known crystal structure) and capped with phosphine ligands (Figure S1), whereas the Au101 clusters correspond to ca. 1.5 nm Au nanoclusters with a narrow particle size distribution (with an estimated formulae Au101(PPh3)21Cl5) and were synthesised using the previously reported method. These clusters were studied using XAS; the details of the acquisition of the X-ray absorption spectra and data analysis are given in the Supplementary Information. The full XAS spectra of the clusters are shown in Figure S2; the spectra were resolved in two parts (XANES and EXAFS) for ease of analysis.
2.1. XANES of Phosphine-Capped Au Clusters
XANES is sensitive to electronic structure (density of unoccupied states), local atomic arrangement, and geometry around the element of interest, making it an important tool for comparing clusters with bulk gold (Figure 1). The absorption edge is shifted to a higher energy for the Au clusters in comparison to the bulk gold, and importantly, the shift increases with a decrease in the cluster size. If we estimate the edge energy as the point of inflection in the rising edge (determined by the position of the maxima of dI/dE), the edge shift compared to the bulk gold systematically increases with a decrease in size. Au6 has a shift of ~2.2 eV, Au9 has a shift of ~1.7 eV, and Au13 has a shift of ~1.5 eV, while Au101 has an absorption edge nearly 0.2 eV above the bulk gold (Figure 1, inset). This observation is consistent with the previous report on related gold−thiolate nanoparticles [33]. The shift in absorption edge compared to the bulk metal is the combined effect of the difference in energy levels [34,35], surrounding environment [36], bond length and strength [37,38], geometry [39,40], the effect of shielding of the core-level holes [41], and charge on absorbing atoms [42,43,44]. These parameters are strongly interrelated; thus, it is difficult to disentangle their individual contributions [37]. For example, the UV-vis spectra of clusters generally interpreted in light of the electronic transitions in the clusters suggest that the electronic transitions in the Au clusters are significantly different from the bulk-like gold nanoparticles (Figure S4).
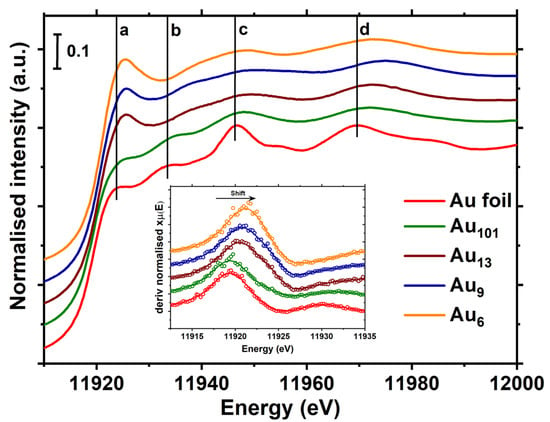
Figure 1.
The normalised XANES spectra of Au clusters and gold foil. The inset shows the first derivative of the XANES spectra.
The surrounding ligands contribute to the rearrangement of energy levels of clusters and can influence the density of the unoccupied d-states of Au atoms [45]. Zhang and Sham reported that the d-charge (hole) distribution of ~2 nm Au nanoparticles could be tailored via changing the capping ligands. It was found that Au NPs lose d electron density when capped with thiol ligands and gain electron density when capped with weakly interacting dendrimer [46], and the effect is more pronounced when the particle size is decreased due to an increase in the surface to volume ratio [47]. All the clusters studied here have phosphine ligands, which are reported to have a very small contribution to XANES features due to the weak Au–P interactions [48,49]. The effect of charge on edge shift can be explained by assuming that an X-ray absorbing atom is surrounded by a spherical shell of charge q and radius R. From the electrostatic interactions theory, we know that the energy levels of an atom inside this shell will be shifted by q/R; thus, the core energy levels will be shifted relative to their initial positions [37]. A partial charge on the absorbing atom can be induced by chemical bonding with an electron-withdrawing or electron-donating ligand, resulting in the shift of an edge. Furthermore, all of the clusters studied here have a formal charge: the pure Au6 cluster has +2, the Au9 clusters have +3, and Au13 has a total charge of +3. Such formal charges are compensated by the counter ions, which are not directly coordinated to the cluster metal core according to the single-crystal X-ray diffraction data. The Au101 has 5 Cl− ligands directly bonded to the gold core according to its formulae (Au101(PPPh3)21Cl5), yet the effect on charge of individual Au atoms within the core is probably significantly diluted due to the much larger size of other ultra-small clusters studied here. The shift in XANES absorption edge to the higher energy with a decrease in cluster size is somewhat similar to the higher Au 4f7/2 binding energies for smaller clusters [22,50,51,52].
Au foil has four distinct near-edge features, shown as a-d in Figure 1, in the first 60 eV past the edge. The first resonance above the edge (labelled as a) corresponds to the characteristic “white line” of transition metals, arising from 2p3/2 → 5d5/2,3/2 dipole transitions [46,49]. The “white line” intensity is related to the unoccupied d-states; thus, it is strong for the transition metals with partially filled d-bands. Although the 5d orbitals of Au atoms are nominally full ([Xe] 4f145d106s1), due to the s-p-d hybridisation, a small white line is observed in the XANES of the bulk gold [53].
The “white line” for the Au clusters is both more intense and shifted to the higher energy compared to bulk gold (Figure 1), in line with the previous reports on thiol-capped Au clusters [45,54,55,56,57]. Moreover, the smaller clusters exhibit the “white line” with higher intensity and at higher energy than the larger clusters, as can be clearly seen in Figure S3, where XANES spectra are superimposed. The Au101 clusters have a much smaller white line, closely resembling bulk metal, which is consistent with the formal charge of +5 shared over 101 Au atoms. It is also worth noting that the width of the peak (FWHM) at the “white line,” which is related to the density of occupied d states [58], is larger for the smaller clusters. The increase in FWHM is similar to the increase in FWHM for the Au 4f7/2 binding energy in XP spectra of the smaller Au clusters of bulk gold [22,50].
The other XANES features peaks b-d (Figure 1), which correspond to the resonances characteristic of the extended local structure of the fcc Au metal [59,60]. The oscillations beyond the “white line” in XANES spectra are broadened for the atomically precise clusters related to lower coordination numbers, higher structural disorder, and difference in the bond distances compared to the bulk gold, in line with the known crystal structures of these clusters [28,29,30,61]. Unlike the other clusters studied here, the Au101 clusters possess all of the XANES features of bulk gold, but these are less intense; this is due to the smaller size of the Au101 clusters (~1.5 nm), which makes the multiple scattering less probable, resulting in the attenuation of the resonance features [48,60].
2.2. EXAFS of Phosphine-Capped Au Clusters
The individual atoms in the atomically precise clusters exhibit dissimilar first shell coordination numbers (Figure S1), unlike the “ideal” fcc metallic gold, where all the Au atoms have 12 neighbouring atoms in their first coordination shell. Since different clusters exhibit different scattering environments from neighbouring gold atoms and peripheral ligands, their experimental EXAFS features are significantly different (Figure 2). The XAS spectra were resolved in the oscillation of χ(k) using Athena software, and fitting was performed by only considering the single scattering paths using Artemis software [62]. To minimise the number of path parameters in such disordered materials, the fuzzy degeneracy approach was used, allowing us to group some Au–Au scattering paths to minimise the fitting variables [63]. Previously, the approach to group the bond distances in the disordered materials [64,65,66] and clusters [54,67,68,69] had been used. Full details describing the fitting procedure are provided in the materials and methods section. The contribution of smaller hydrogen atoms in the EXAFS spectra is expected to be very weak due to the low scattering power of this species; thus, it is ignored in the FEFF calculations [64].
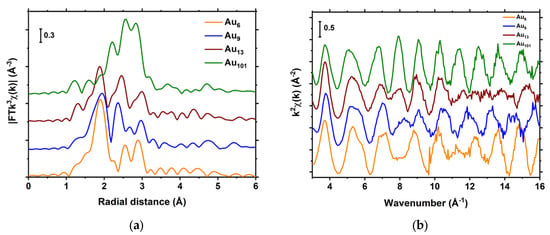
Figure 2.
EXAFS of a series of phosphine-capped gold clusters: (a) Magnitude of Fourier transform; (b) in k-space.
2.2.1. EXAFS of Au9 Clusters
Chemically synthesised [Au9(PPh3)8](NO3)3 clusters consist of one central gold atom bonding with eight peripheral Au atoms, which are bonded to triphenylphosphine ligands (Figure 3 and Figure S1b) [28]. These clusters are highly disordered compounds in the sense that bond lengths vary significantly within the cluster (Table S1). Based on the bonding behaviour with neighbouring atoms from the known crystal structure, Au atoms in the Au9 clusters can be categorised into three types (shown as Au(1) to Au(3) in Figure 2a and Table S1). The Au atoms in one category have a similar scattering environment, but each type of Au atom experiences significantly different scattering environments; for example, the Au(3) type atom, i.e., central Au atom, is bonded with only Au atoms (eight atoms), whereas both Au(1) and Au(2) type atoms are bonded with four Au atoms and one P atom. However, the bond distances between the neighbouring Au atoms are significantly different (Table S1 and Figure 3). In addition, Au(1) and Au(2) type atoms experience more pronounced scattering from carbon atoms in the phosphine ligands compared to central, i.e., Au(3) type atoms (Figure 3c).
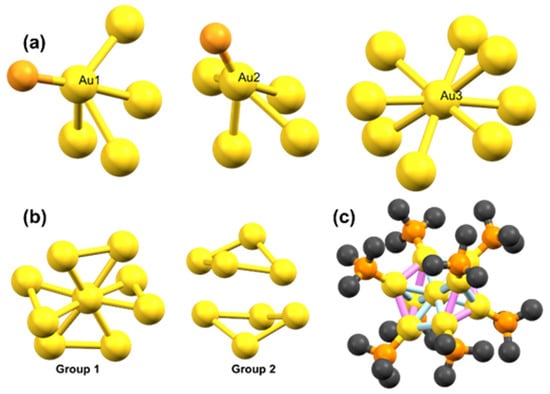
Figure 3.
(a) Different types of Au atoms in Au9 clusters; (b) two groups of bonds with similar features; and (c) Au9 clusters with different groups of atoms; light blue colour represents bonds in group 1, and violet colour represents bonds in group 2. The atomic colour scheme is gold (Au), orange (P), and black (C). All the carbon atoms in Au9 clusters are shown in Figure S1.
In EXAFS analysis, Au–Au interatomic distances were grouped to reduce the number of fitted parameters while preserving as many scattering paths as possible without compromising the overall fit (Figure 3 and Table S2). In this case, the bond distances were grouped into bins of 0.18 Å width, which yields one group of Au–P scattering paths, two Au–Au bond distance groups based on the bond length, and several Au–C single scattering paths (Figure 3 and Table S2). We obtained a satisfactory fit of the Au9 clusters (Figure 4 and Table 1) for the window of R from 1.3 to 3.4 Å (dotted line boxes within corresponding figures highlight such windows); the peaks beyond that range are mainly due to the scattering from Au–C single and multiple scattering paths and large distance Au–Au single scattering and multiple scattering paths [29].
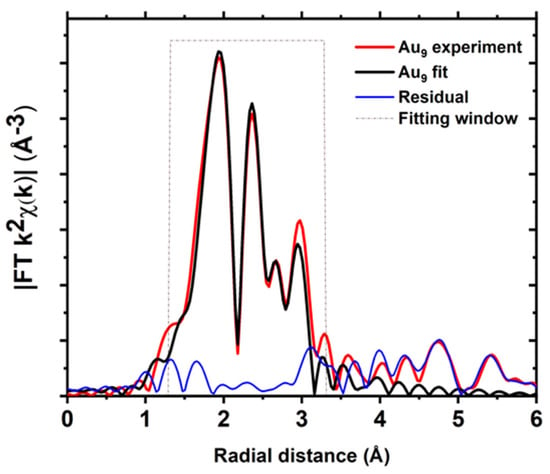
Figure 4.
Fits of the magnitude of Fourier transform of Au L3−edge EXAFS of Au9 clusters.

Table 1.
Structural characteristics of Au9 clusters (with ΔEo = 3.63 eV).
Based on the structural understanding of the Au9 clusters, EXAFS analysis of the Au9 clusters can be divided into several distinct bonding domains (Figure 4 and Figure S5). The first peak in the EXAFS spectrum is attributed to the nearest neighbour P atoms; the following peak is due to the scattering of the neighbouring Au atoms; the peaks at higher R values are due to scattering from distant Au atoms and the carbon atoms (Figure 4). It can be seen that the contribution of carbon atoms cannot be ignored; scattering from the carbon atoms can modify both the magnitude and phase of the photoelectron wave, and the inclusion of one more carbon single scattering path improves the fit at the expense of the additional parameters (Figures S6 and S7). So, it is a matter of having to use the available information from the XAS data, as per the Nyquist criterion, to assign a fit as the final fit [63]; the value of the reduced chi-square and R-factor could be used to describe the better model. In this study, we have synthesised and rigorously characterised atomically precise [Au9(PPh3)8](NO3)3 clusters using the previously reported method; hence, we could fix the coordination number. A similar approach to group the Au–Au scattering environment was previously reported by MacDonald et al. for thiol-capped Au clusters [65]. In order to investigate the supported clusters or submixture of different size clusters in a system, the model can be relaxed to allow the coordination number to vary.
2.2.2. EXAFS of Au6 Clusters
Based on the structural understanding of crystalline Au6 clusters [29], Au atoms in the clusters can be assumed to be of two distinct types (Figure S8a). There are two type (i) gold atoms bonded to two phosphine ligands and two gold atoms, and four type (ii) atoms bonding with one phosphine ligand and two gold atoms (Figures S1a and S8a). The bond distance between neighbouring Au atoms varies from 2.63 to 2.923 Å, and there is also a less significant variation in the Au–P bond length (Table S5). The first shell bonding with the nearest gold atom can be grouped into two groups for EXAFS fitting in order to minimise the fitting variables (Figure S8b). Group one consists of shorter bond distances between the neighbouring Au atoms, while group two was assigned to larger bond distances between neighbouring Au atoms. Grouping of the Au–Au scattering paths results in a satisfactory fit of the EXAFS spectrum of Au6 clusters (Figure 4 and Table S5).
The EXAFS spectra of the Au6 clusters have two main regions (Figure 5 and Figure S9); it is clear the first peak is due to the Au–P bond, and the following peaks are attributable to scattering from Au–Au bonds and contributions from the carbon atoms in the phosphine ligands (Figure S10). Moreover, due to the lower Au–Au coordination numbers in the Au6 clusters compared to the Au9 clusters, the relative contribution from the Au–carbon scattering paths becomes more significant. Here, the fitting of EXAFS data was done by assuming contributions from one aggregate shell of carbon and incorporating more Au–C paths can improve the fit at the expense of additional parameters.
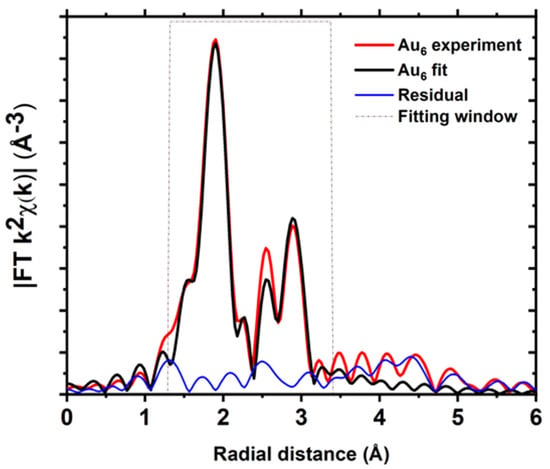
Figure 5.
Fits of the magnitude of Fourier transform of Au L3−edge EXAFS of Au6 clusters.
2.2.3. EXAFS of Au13 Clusters
In the case of the crystalline Au13 clusters [30], all of the Au atoms possess distinct bond distances with the neighbouring atoms. The crystal structure of the Au13 cluster suggests that it has one central gold atom coordinated with twelve peripheral Au atoms [30]. Two of these peripheral Au atoms are bonded to Cl, and the other ten Au atoms are bonded to phosphorus (Figure S1c), and each peripheral Au atom is bonded to four other Au atoms in the periphery. All the bond distances between neighbouring Au and P/Cl atoms are slightly different (Table S7). In order to minimise the number of fitting parameters, the bond distance between the neighbouring Au atoms can be classified into two main groups: the first group involves bonds of the central Au atom with the Au atom in the outer periphery, while the second group have the bonds between Au atoms within the outermost periphery of the metallic core (Figure S11). Hence, the EXAFS data were fitted using the fuzzy degeneracy approach previously performed, grouping the bond distances in the bins of width 0.15 Å, which resulted in a reasonably good fit (Figure 6 and Figure S12).
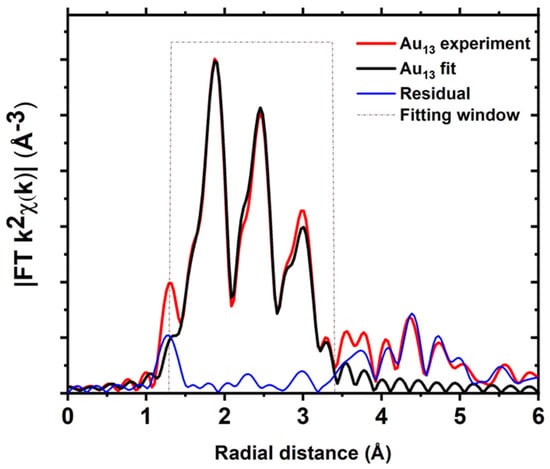
Figure 6.
Fits of the magnitude of Fourier transform of Au L3−edge EXAFS of Au13 clusters.
This grouping of Au–Au bond distances allowed for the fitting EXAFS of Au13 clusters without having to assign different parameters for each scattering path (Figure 6 and Table S6). Moreover, this breakdown of the Au13 clusters into different bonding domains can shed light on the alteration in bonding behaviour of the surface and/or the central atom under the influence of external stimuli.
The EXAFS spectrum of Au13 has three visibly distinguishable regions, with the first coming from the binding of Au with P and Cl, the second one corresponding to the bonds with the central atom, and the surface Au–Au bonds make a major contribution to the third peak—with a minor contribution from carbon atoms (Figure S13). Magnitude-wise, the contribution of carbon spectra are very small but enough to influence the phase of the photoelectron wave.
2.2.4. EXAFS Analysis of Au101 Clusters
Unlike Au6, Au9, and Au13 clusters, Au101 clusters are not atomically precise; these are ultra-small Au nanoparticles capped with triphenylphosphine ligands with a narrow particle distribution. Here, The EXAFS fitting of Au101 clusters was attempted by assuming the Au–P scattering environment was similar to that in AuPPh3Cl, and the overall Au–Au scattering environment for the FEFF calculation was estimated from the Au102 clusters with the known crystal structure (Figure 7 and Figure S14 and Table S9) [9].
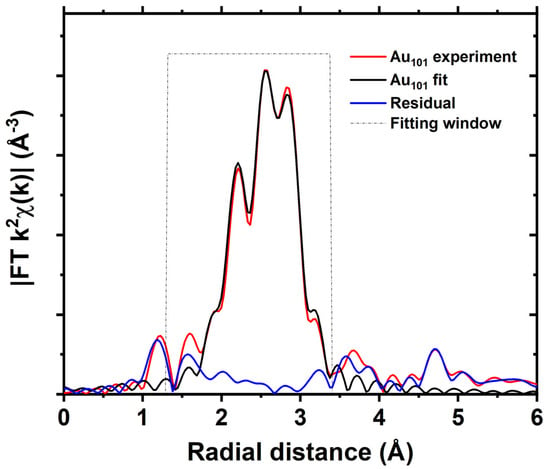
Figure 7.
Fits of the magnitude of Fourier transform of Au L3−edge EXAFS of Au101 clusters.
Only one path for Au–P and one scattering path of Au–Au scattering were considered. As a result, the fitting yields a very low coordination number for Au–P coordination (Table S9), which suggests that, due to a relatively large number of Au atoms in Au101 clusters, the contribution from the Au–P scattering is very much diminished compared to other clusters studied here (Figure S15). The lower coordination number of Au atoms in Au101 clusters compared to the bulk gold (CN = 12) is due to the smaller size of Au101 clusters; this is consistent with the lower coordination number obtained for Au55 clusters [48,66] and ion beam synthesised small Au clusters onto SiO2 [67].
The fitting of Au101 clusters was also performed by fixing the Au–P coordination number to the empirical formula (Figure S16 and Table S10). The fitting looks similar, suggesting that Au–P contribution is indeed very small in the EXAFS. Therefore, fitting was attempted without Au–P scattering paths, which yielded a good fit (Figure S17 and Table S11), suggesting that the Au–P contribution in Au101 clusters is relatively insignificant, which is likely due to its larger size and higher scattering ability of heavier gold atoms compared to phosphorous atoms.
It is clear that the Au clusters show a systematic increase in first shell coordination number from Au6 (1.333 and 2.000) to Au9 (1.778 and 2.667), to Au13 (1.846 and 4.615), and finally to Au101 (~7.5), for which the differentiation of the Au atoms into two groups with different coordination numbers is not needed. Finally, it is noteworthy that the use of scattering contributions by carbon atoms, though relatively distant from the Au absorber, was important in order to achieve better quality fits for the atomically precise ultra-small clusters (Au6 to Au13). Meanwhile, despite having only ca. 10 times larger Au101, the Au metal core completely dominates, with there only being a small contribution by Au–P and no need to include scattering by carbon. Hence, the successful deposition of the intact clusters onto supports for use in catalysis, sensing, etc., can be confirmed by the match in XAS spectra of the pure crystalline clusters. While changes to the adsorption edge, the “white line,” and the appearance of the typical fcc features in XANES, as well as an increase in coordination number in EXAFS coinciding with a reduction in or disappearance of the features due to ligand contribution, can indicate, among other things, cluster aggregation during the cluster deposition of supports, activation of obtained materials, and use of them in sensing and catalysis.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Purification of Au Clusters
Atomically precise [Au6(dppp)4](NO3)2, [Au9(PPh3)8](NO3)3, [Au13(dppe)5Cl2]Cl3 and ultra-small Au nanoclusters (i.e., Au101(PPPh3)21Cl5) were synthesised, and their identity was confirmed following previously reported methods [27,28,29,30,31].
3.2. X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Measurement and Processing
The crystallised clusters were dissolved in dichloromethane and precipitated by adding an excess of diethyl ether; the precipitated powder was dried in a vacuum and mixed with cellulose to make a homogenous powder. X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) measurements on clusters were carried out in fluorescence mode at the Australian Synchrotron in Clayton, Victoria, Australia using multipole wiggler XAS beamline (12-ID), operating with an electron beam energy of 3.0 GeV and a beam current of 200 mA (maintained using the top up mode). The Au-L3 data were collected using a Si(111) monochromator and focusing optics, and the measurements were performed at a 10 K helium cryostat.
Raw data obtained at the beamline were converted using Sakura software [68] and processed using Athena software [62] by extracting the EXAFS oscillation χ(k) as a function of the photoelectron wave number k, following standard procedures. For all of the clusters, the k-range was chosen from 2.5 to 15 Å−1. Fittings of EXAFS were performed using a fuzzy degeneracy approach, which allowed us to group the path lengths in a bin of user-defined width [63,69]. The contribution of smaller hydrogen atoms in the EXAFS spectra was expected to be very weak due to the low scattering power of this species. Thus, it is ignored in the FEFF calculations [64].
Fuzzy Degeneracy Approach for EXAFS Fitting
The FEFF program is quite particular about finding the degenerated path; two similar paths with a difference in path length as low as 1 fm (femtometer) were not grouped as a degenerated path in FEFF calculations [63]. The bond length between the neighbouring atoms in clusters was not always the same [70]; sometimes, the difference in path length was as low as 0.02 Å (Tables S1, S5 and S7)—the FEFF program considered them as two non-degenerate paths. Assigning the individual value of the Debye–Waller factor (σ2) and the shift in the radius parameters (ΔR) makes the total number of variables more than the information available from the Nyquist criterion; thus, the fitting was performed via a fuzzy degeneracy scheme [63]. The fuzzy degeneracy scheme allowed us to group the scattering paths into bins of user-defined width. The paths within the margin were considered to be degenerated, and the path length of each bin was averaged [63,69]. This approach has been previously used for disordered material [63,69,71,72,73,74], and results are close to those of the strict degeneracy approach [63]. Artemis software was used to refine the fitting parameters using only the single scattering paths and modelled each sample in R-space until a satisfactory model describing the system was obtained.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the structures of a wide series of ultra-small, phosphine-capped Au clusters were studied using XAS for the first time. XANES of the clusters show a progressive shift in the adsorption edge to the higher energy within the series of clusters studied (from the largest Au101 to the smallest Au6) and the higher intensity of the white line for the clusters studied (compared to bulk gold). The XANES features of the largest Au101 are the closest to those observed for the bulk gold, while the atomically precise clusters differ from the bulk gold. The EXAFS spectra of clusters were fitted using the fuzzy degeneracy approach, and the results fit closely with the experimental data. Coordination numbers of Au atoms systematically increase across the series from the smallest Au6 to the largest for Au101. Contributions by P and even C atoms of the ligands are important for ultra-small clusters (Au6 to Au13), which may offer a way to study the removal of such ligands (de-ligation). Phosphorus-donor ligands bind to Au less strongly compared to widely studied thiol ligands, offering easier pathways for the supported clusters with partially or fully removed ligands, which is unusual for the crystalline state structures. We believe that this in-depth XAS study of a wide range of ultra-small phosphine-capped Au clusters will provide an excellent starting reference point for the XAS analysis of Au clusters deposited on various supports, studies of their de-ligation, and potential aggregation during thermal activation, pre-treatments, and while applications in sensing and catalysis. Additionally, the breakdown of the clusters into different bonding domains can provide insight into the dependence of site-specific bonding interactions with the reagents or analytes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics11050191/s1, Figure S1: Crystal structures of (a) [Au6(dppp)4](NO3)2, (b) [Au9(PPh3)8](NO3)3, and (c) [Au13(dppe)5Cl2]Cl3. The atomic colour scheme: gold (Au), orange (P), green (Cl), and black (C); hydrogen is omitted for clarity; Figure S2: XAS spectra of Au foil and Au clusters; Figure S3: XANES spectra Au foil and Au clusters overlaid directly for comparison of the intensity; Figure S4: UV-Vis spectra of (a) [Au6(dppp)4](NO3)2, (b) [Au9(PPh3)8](NO3)3, (c) [Au13(dppe)5Cl2]Cl3, and (d) Au101(PPPh3)21Cl5 in methanol; Figure S5: Contribution of individual scattering paths in EXAFS of Au9 clusters (a) in R-space, and (b) in k-space; Figure S6: Fitting of Au9 clusters without using scattering paths from carbon (a) in R-space, and (b) in k-space; Figure S7: Fits of Au9 clusters using two aggregated shells of scattering paths from carbon (a) R-space, and (b) k-space; Figure S8: (a) Different types of Au atoms in Au6 clusters, (b) groups of bonds with similar features, and (c) Au6 clusters with different groups of atoms; light blue colour represents bonds in group 1 and violet colour represent bonds in group 2. The atomic colour scheme: gold (Au), orange (P), and black (C). All the carbon atoms are shown in Figure S1; Figure S9: Fits to the Au L3-edge EXAFS of Au6 clusters in k-space; Figure S10: Contribution of individual scattering paths in EXAFS of Au6 clusters in R-space; Figure S11: The classification of bonds with similar features in the Au13 cluster, and (b) Au13 clusters with different groups of atoms; light blue represents bonds in group 1, and violet colour represents bonds in group 2. The crystal structure of the clusters is shown in Figure S1; Figure S12: Fits the Au L3-edge EXAFS of Au13 clusters in k-space; Figure S13: Contribution of individual scattering paths in EXAFS of Au13 in R-space. Figure S14: Fits to the Au L3-edge EXAFS of Au101 clusters in k-space; Figure S15: Contribution of individual scattering paths in EXAFS of Au101 (a) in R space; Figure S16: EXAFS spectra with fixing Au–P coordination based on the empirical formula of Au101 (a) fitted EXAFS, and (b) individual contribution from different scattering paths; Figure S17: Fits of EXAFS of Au101 clusters without Au–P scattering path; Table S1: Bond distances between neighbouring Au–Au atoms in Au9 clusters; Table S2: Bond distance and coordination numbers for bonds in each selected group of Au atoms in Au9 clusters; Table S3: Structural characteristics of Au9 clusters with no Au–C scattering path (ΔEo = 3.812 eV); Table S4: Structural characteristics of Au9 clusters with two Au–C scattering paths (ΔEo = 3.716 eV); Table S5: Bond distances between neighbouring Au–Au atoms in Au6 clusters; Table S6: Structural characteristics of Au6 clusters (ΔEo = 2.737 eV); Table S7: Bond distances between neighbouring Au–Au atoms in Au13 clusters; Table S8: Structural characteristics of Au13 clusters (ΔEo = 4.574 eV); Table S9: Structural characteristics of Au101 clusters (ΔEo = 4.204 eV); Table S10: Structural characteristics of Au101 clusters after fixing Au–P coordination number (ΔEo = 4.221 eV; Table S11: Structural characteristics of Au101 clusters without Au–P scattering path (ΔEo = 4.67).
Author Contributions
S.K.S.: Investigation, validation, methodology, visualisation, project administration, provision of study materials, writing—original draft preparation, and leading the manuscript writing; V.B.G.: supervision and manuscript review and editing; B.J.: manuscript review and editing; A.T.M.: supervision, manuscript review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was undertaken on the X-ray absorption spectroscopy beamline at the Australian Synchrotron, part of ANSTO, grant M16325. Shailendra Kumar Sharma thanks the University of Canterbury for the UC Connect Ph.D. scholarship.
Data Availability Statement
Most of the data are available in the main text or Supplementary Materials. Any additional data can be requested by contacting the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Rosalie Hocking, Brittany S. Kerr, and Jaydon Meilak for their help in carrying out the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, L.; Corma, A. Metal Catalysts for Heterogeneous Catalysis: From Single Atoms to Nanoclusters and Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4981–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard-Fabretto, L.; Andersson, G.G. Metal Clusters on Semiconductor Surfaces and Application in Catalysis with a Focus on Au and Ru. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, H.; Yoon, B.; Landman, U.; Li, X.; Zhai, H.-J.; Wang, L.-S. On the Electronic and Atomic Structures of Small AuN-(N = 4−14) Clusters: A Photoelectron Spectroscopy and. Density-Functional Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 6168–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, T.; Häkkinen, H. Protected Metal Clusters: From Fundamentals to Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Castleman, A., Jr.; Khanna, S.N. Reactivity of metal clusters. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14456–14492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negreiros, F.R.; Halder, A.; Yin, C.; Singh, A.; Barcaro, G.; Sementa, L.; Tyo, E.C.; Pellin, M.J.; Bartling, S.; Meiwes-Broer, K.-H.; et al. Bimetallic Ag-Pt Sub-nanometer Supported Clusters as Highly Efficient and Robust Oxidation Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Chen, T.; Yuan, X.; Xie, J. Toward Total Synthesis of Thiolate-Protected Metal Nanoclusters. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.; Akola, J.; Lopez-Acevedo, O.; Jadzinsky, P.D.; Calero, G.; Ackerson, C.J.; Whetten, R.L.; Grönbeck, H.; Häkkinen, H. A unified view of ligand-protected gold clusters as superatom complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9157–9162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadzinsky, P.D.; Calero, G.; Ackerson, C.J.; Bushnell, D.A.; Kornberg, R.D. Structure of a Thiol Monolayer-Protected Gold Nanoparticle at 1.1 Å Resolution. Science 2007, 318, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Akita, T.; Faye, J.; Fujitani, T.; Takei, T.; Haruta, M. Propene Epoxidation with Dioxygen Catalyzed by Gold Clusters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7862–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.; Golovko, V.B.; Vaughan, O.P.; Abdulkin, P.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Tikhov, M.S.; Johnson, B.F.; Lambert, R.M. Selective oxidation with dioxygen by gold nanoparticle catalysts derived from 55-atom clusters. Nature 2008, 454, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.; Häkkinen, H.; Landman, U.; Wörz, A.S.; Antonietti, J.-M.; Abbet, S.; Judai, K.; Heiz, U. Charging Effects on Bonding and Catalyzed Oxidation of CO on Au8 Clusters on MgO. Science 2005, 307, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Qian, H.; Drake, B.A.; Jin, R. Atomically Precise Au25(SR)18 Nanoparticles as Catalysts for the Selective Hydrogenation of α,β-Unsaturated Ketones and Aldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Jiang, D.-e.; Kumar, S.; Chen, Y.; Jin, R. Size Dependence of Atomically Precise Gold Nanoclusters in Chemoselective Hydrogenation and Active Site Structure. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2463–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Meseguer, J.; Cabrero-Antonino, J.R.; Domínguez, I.; Leyva-Pérez, A.; Corma, A. Small Gold Clusters Formed in Solution Give Reaction Turnover Numbers of 107 at Room Temperature. Science 2012, 338, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Falletta, E.; Della Pina, C.; Teles, J.H.; Pagliaro, M. Industrial Applications of Gold Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14210–14217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Gu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.-D.; Zou, X.; Chen, J.-S. Corrosion engineering towards efficient oxygen evolution electrodes with stable catalytic activity for over 6000 h. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoeva, B.G.; Ovoshchnikov, D.S.; Golovko, V.B. Establishing a Au Nanoparticle Size Effect in the Oxidation of Cyclohexene Using Gradually Changing Au Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2986–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Corma, A. Evolution of Isolated Atoms and Clusters in Catalysis. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zakharov, D.N.; Arenal, R.; Concepcion, P.; Stach, E.A.; Corma, A. Evolution and stabilization of subnanometric metal species in confined space by in situ TEM. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashin, A.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Monitoring chemical reactions in liquid media using electron microscopy. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.P.; Adnan , R.H.; Alvino , J.F.; Shipper, O.; Donoeva , B.; Ruzicka, J.-Y.; Al Qahtani, H.; Harris, H.H.; Cowie , B. Chemically-synthesised, atomically-precise gold clusters deposited and activated on titania. Part II. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 14806–14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, J.-Y.; Abu Bakar, F.; Hoeck, C.; Adnan, R.; McNicoll, C.; Kemmitt, T.; Cowie, B.C.; Metha, G.F.; Andersson, G.G.; Golovko, V.B. Toward Control of Gold Cluster Aggregation on TiO2 via Surface Treatments. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 24465–24474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonio, E.A.; Velasco-Velez, J.-J.; Schlögl, R.; Knop-Gericke, A. Perspective—Outlook on Operando Photoelectron and Absorption Spectroscopy to Probe Catalysts at the Solid-Liquid Electrochemical Interface. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 054509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshenko, J.; Roldan Cuenya, B. In Situ/Operando Electrocatalyst Characterization by X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 882–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chiu, S.-Y.; Pai, H.-T.; Liao, T.-Y.; Hsu, C.-S.; Chiang, W.-H.; Tsai, M.-K.; Chen, H.M. Operando time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy reveals the chemical nature enabling highly selective CO2 reduction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K. Synthesis and Activation of Metal Cluster-Based Electrocatalysts for CO2 Reduction. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cantebury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, F.; Englert, U.; Gutrath, B.; Simon, U. Crystal Structure, Electrochemical and Optical Properties of [Au9(PPh3)8](NO3)3. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, M.A.; Sugiuchi, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Shichibu, Y.; Konishi, K. Hydrogen bonds to Au atoms in coordinated gold clusters. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichibu, Y.; Konishi, K. HCl-induced nuclearity convergence in diphosphine-protected ultrasmall gold clusters: A novel synthetic route to “magic-number” Au13 clusters. Small 2010, 6, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.P.; Alvino, J.F.; Gentleman, A.; Qahtani, H.A.; Thomsen, L.; Polson, M.I.; Metha, G.F.; Golovko, V.B.; Andersson, G.G. Chemically-synthesised, atomically-precise gold clusters deposited and activated on titania. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3917–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weare, W.W.; Reed, S.M.; Warner, M.G.; Hutchison, J.E. Improved Synthesis of Small (dCORE ≈ 1.5 nm) Phosphine-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 12890–12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.A.; Zhang, P.; Qian, H.; Jin, R. Site-Specific and Size-Dependent Bonding of Compositionally Precise Gold−Thiolate Nanoparticles from X-ray Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1821–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, H. Atomic and electronic structure of gold clusters: Understanding flakes, cages and superatoms from simple concepts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1847–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, H. Electronic shell structures in bare and protected metal nanoclusters. Adv. Phys. X 2016, 1, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cartes, C.; Rojas, T.C.; Litrán, R.; Martínez-Martínez, D.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Penadés, S.; Fernández, A. Gold Nanoparticles with Different Capping Systems: An Electronic and Structural XAS Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 8761–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, G. Introduction to XAFS: A Practical Guide to X-ray Absorption Fine Structure Spectroscopy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, M.; Farges, F.o.; Partzsch, G.M.; Schmidt, C.; Behrens, H. Speciation of Fe in silicate glasses and melts by in-situ XANES spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2007, 92, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waychunas, G.A. Synchrotron radiation XANES spectroscopy of Ti in minerals; effects of Ti bonding distances, Ti valence, and site geometry on absorption edge structure. Am. Mineral. 1987, 72, 89–101. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, P.; Berry, A.J.; Schofield, P.; Mosselmans, J. The effect of site geometry, Ti content and Ti oxidation state on the Ti K-edge XANES spectrum of synthetic hibonite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 187, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankudinov, A.L.; Ravel, B.; Rehr, J.J.; Conradson, S.D. Real-space multiple-scattering calculation and interpretation of X-ray-absorption near-edge structure. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 7565–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggal, H.; Rajput, P.; Alperovich, I.; Asanova, T.; Mehta, D.; Jha, S.N.; Gautam, S. XANES spectroscopic studies at L3 edge of 79Au in its various chemical forms. Vacuum 2020, 176, 109294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, G.R.; Yafet, Y.; Eisenberger, P.; Blumberg, W.E. Observations and interpretation of X-ray absorption edges in iron compounds and proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, J.; Teramura, K.; Shishido, T.; Hitomi, Y.; Kato, K.; Tanida, H.; Uruga, T.; Tanaka, T. In Situ Au L3 and L2 edge XANES spectral analysis during growth of thiol protected gold nanoparticles for the study on particle size dependent electronic properties. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 507, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Miller, J.T.; Stellwagen, D.; Sanampudi, A.; Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Spivey, J.J. Synthesis, characterization, and testing of supported Au catalysts prepared from atomically-tailored Au38(SC12H25)24 clusters. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sham, T.K. Tuning the electronic behavior of Au nanoparticles with capping molecules. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sham, T. X-ray studies of the structure and electronic behavior of alkanethiolate-capped gold nanoparticles: The interplay of size and surface effects. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 245502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M.A.; Andrews, M.P.; Zegenhagen, J.; Bommannavar, A.S.; Montano, P. Structure and vibrations of chemically produced Au55 clusters. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 3312–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yao, T.; Sun, Z.; Yan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Hexane-Driven Icosahedral to Cuboctahedral Structure Transformation of Gold Nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17997–18003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Peredkov, S.; Neeb, M.; Eberhardt, W.; Al-Hada, M. Size-dependent XPS spectra of small supported Au-clusters. Surf. Sci. 2013, 608, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Qahtani, H.S.; Higuchi, R.; Sasaki, T.; Alvino, J.F.; Metha, G.F.; Golovko, V.B.; Adnan, R.; Andersson, G.G.; Nakayama, T. Grouping and aggregation of ligand protected Au9 clusters on TiO2 nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110765–110774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, H.; Yin, Y.; Howard-Fabretto, L.; Sharma, S.K.; Golovko, V.; Andersson, G.G.; Shearer, C.J.; Metha, G.F. Au101–rGO nanocomposite: Immobilization of phosphine-protected gold nanoclusters on reduced graphene oxide without aggregation. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfield, R.E.; Grandjean, D.; Kröll, M.; Pugin, R.; Sawitowski, T.; Schmid, G. Structure and Bonding of Gold Metal Clusters, Colloids, and Nanowires Studied by EXAFS, XANES, and WAXS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, D.M.; MacDonald, M.A.; Chatt, A.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Z.; Jin, R. Sensitivity of Structural and Electronic Properties of Gold–Thiolate Nanoclusters to the Atomic Composition: A Comparative X-ray Study of Au19(SR)13 and Au25(SR)18. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25137–25142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, D.M.; Chatt, A.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, C.; Jin, R. Unique Bonding Properties of the Au36(SR)24 Nanocluster with FCC-Like Core. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 3186–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, D.M.; Zeng, C.; Jin, R.; Chatt, A.; Zhang, P. Role of Au4 Units on the Electronic and Bonding Properties of Au28(SR)20 Nanoclusters from X-ray Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, G.A.; Padmos, J.D.; Zhang, P. Structural and electronic properties of protein/thiolate-protected gold nanocluster with “staple” motif: A XAS, L-DOS, and XPS study. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 214703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padalia, B.D.; Gupta, S.N. White line in the L-absorption spectra of 72Hf to 79Au. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1972, 2, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, G.N.; Durham, P.J.; Diakun, G.; Quinn, P. Near-edge X-ray absorption spectra for metallic Cu and Mn. Nature 1981, 294, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balerna, A.; Bernieri, E.; Picozzi, P.; Reale, A.; Santucci, S.; Burattini, E.; Mobilio, S. Extended X-ray-absorption fine-structure and near-edge-structure studies on evaporated small clusters of Au. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Krishna, K.S.; Losovyj, Y.B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Lozova, N.; Miller, J.T.; Spivey, J.J.; Kumar, C.S.S.R. Ligand-Stabilized and Atomically Precise Gold Nanocluster Catalysis: A Case Study for Correlating Fundamental Electronic Properties with Catalysis. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 10201–10208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. Athena, Artemis, Hephaestus: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B. Path degeneracy and EXAFS analysis of disordered materials. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2014, 21, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, P.; Barone, V.; Chillemi, G.; Sanna, N.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Pavel, N.V. Hydrogen and Higher Shell Contributions in Zn2+, Ni2+, and Co2+ Aqueous Solutions: An X-ray Absorption Fine Structure and Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, M.A.; Chevrier, D.M.; Zhang, P.; Qian, H.; Jin, R. The Structure and Bonding of Au25(SR)18 Nanoclusters from EXAFS: The Interplay of Metallic and Molecular Behavior. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15282–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, M.C.; Benfield, R.E.; Newport, R.J.; Schmid, G. An EXAFS study of the cluster molecule Au55(PPh3)12Cl6. Solid State Commun. 1990, 73, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluth, P.; Johannessen, B.; Giraud, V.; Cheung, A.; Glover, C.J.; Azevedo, G.d.M.; Foran, G.J.; Ridgway, M.C. Bond length contraction in Au nanocrystals formed by ion implantation into thin SiO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3561–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappen, P.; Ruben, G. Sakura; Australian Synchrotron: Clayton, Australia, 2013; Available online: https://sakura.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Ma, F.; Zhou, R.; Su, F.; Ou, Y.; Liang, H. The stability of coordination polyhedrons and distribution of europium ions in Ca6BaP4O17. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 22096–22106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, K. Phosphine-coordinated pure-gold clusters: Diverse geometrical structures and unique optical properties/responses. In Gold Clusters, Colloids and Nanoparticles I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 49–86. [Google Scholar]
- Elbers, M.; Sternemann, C.; Julius, K.; Paulus, M.; Surmeier, G.; König, N.; Nase, J.; Bolle, J.; Wagner, R.; Irifune, T.; et al. Pressure stability of the first hydration shell of yttrium in aqueous YCl3 solution. High Press. Res. 2020, 40, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhu, H.; Dong, J.; Jia, Q.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; An, P.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Local structural changes during the disordered substitutional alloy transition in Bi2Te3 by high-pressure XAFS. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 065901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbolaghy, M. Catalytic Ozonation of Acetone and Toluene on Alumina-Supported Manganese Oxide. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aghbolaghy, M.; Soltan, J.; Chen, N. Low Temperature Catalytic Oxidation of Binary Mixture of Toluene and Acetone in the Presence of Ozone. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 3431–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).