Abstract
One of the more problematic textile wastewaters to manage is dyeing wastewater, especially methylene-blue-containing wastewater. Its release has a significant negative impact on ecosystems, which could harm the environment. Adsorption techniques are still an efficient technology to eliminate and remove the coloring agent. Tailing ash, obtained from the floatation process, was selected as an adsorbent in the present study. The purpose of this study was to analyze the performance of tailing ash (TA) for MB removal. The effects of operating parameters investigated were pH (2–10), stirring speed (50–150 rpm), initial dye concentration (20–100 mg/L), contact time (120 min), adsorbent dosage (0.5–2.5 g), and temperature (25–45 °C). The performance of TA pretreated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and thermal tailing ash were also investigated. The experimental results for batch adsorption indicated that 96.23% removal of methylene blue took place at the optimum condition (pH = 10, initial adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, 45 °C). The results showed that the dye adsorption capacity increased with contact time and adsorbate dosage. The adsorption data were then fitted to kinetic models and isotherm models. The pseudo-second-order model was the most suitable model for the kinetic of adsorption and the Freundlich isotherm was the best-fitted isotherm model. This research provides a feasible approach to reusing tailing ash as an effective low-cost adsorbent for water quality improvement.
1. Introduction
Despite being a major CO2 emitter, power generation using coal is still important from an economic point of view. Annually, more than 780 million metric tons of coal conversion ash are produced worldwide [1,2]. Coal is still being used significantly in energy production [3]. Power generation using coal as fuel produces fly ash and bottom ash. In Malaysia, fly ash can be used in cement factories [4]. Coal bottom ash is of limited use due to its high carbon content.
A large area is required to dispose of the large amount of bottom ash, which eventually becomes a source of pollution. From the viewpoint of a circular economy, coal bottom ash could be utilized as a resource. In the European Project CHARPHITE under the scope of the “Third ERA-MIN Joint Call (2015) on Sustainable Supply of Raw Materials in Europe” [5], unburned carbon was recovered to be utilized as graphite material. After the unburned carbon is recovered, a large quantity of tailing is left behind. It is important to find use for the tailing. Adsorption is a widely applied method for the removal of color in textile wastewater. Compared to methods such as biotreatment, flocculation–coagulation, photocatalytic degradation, Fenton chemical oxidation, cation exchange membranes, and electrochemical degradation, adsorption has the advantages of the availability of material and simple design and operation [6]. The literature shows that a significant number of waste products have been utilized as adsorbents. These include coal, peat, fly ash, bagasse, iron slag, shale oil ash, zeolites, magnesium chloride, maize cob, and wool [6].
The present paper is an attempt to investigate the possibility of utilizing waste material tailing ash derived after the flotation of coal bottom ash to remove the well-known dye methylene blue. The aims of this paper are to report the effect of various process parameters on the removal of the dye, to optimize the process parameters, and to apply several adsorption isotherms and kinetic equations to the adsorption rate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The tailing ash used here is a by-product derived after the recovery of unburned carbon from coal bottom ash, which was acquired from TNB Janamanjung. This material was taken directly from the bottom of a combustion chamber. Methylene blue was purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30%) was acquired from Merck. The 1000 mg/L methylene blue dye stock solution was prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of methylene blue (MB, C16H18ClN3S, structure shown in Figure 1) in 1000 mL distilled water. The distilled water was used throughout the experiment to prepare the desired concentration range of the solutions. The 0.1 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) and 0.1 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solutions were used to adjust the pH.
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of methylene blue.
2.2. Analytical Method
A UV–visible spectrophotometer (HITACHI U-2010) was used to monitor the adsorption process and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) nitrogen adsorption method was used to determine the surface area of the tailing ash. The tailing ash’s basic elemental composition was analyzed using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) (ZSX Primus IV) and the salt titration method was used to measure the point of zero charge (PZC). The pHpzc was measured using the pH drift method.
The adsorbent was first acquired from the floatation process to obtain 63 µm sized powder. It was washed successfully with distilled water and then dried at 100 °C to remove the moisture. The adsorbent was stored in desiccators until use.
2.3. Floatation Process
The column flotation was carried out at pH of 6, 7.5, and 9 with the air flowrate injected at 4 to 10 L/min for 10 min of conditioning time. Additionally, 1000, 3000, and 5000 g/ton kerosene and 1400, 1600, and 1800 g/ton MIBC were used as the reagent. Kerosene and MIBC act as a collector and frother, respectively. The flotation experiment was carried out in a glass column with a 6 cm diameter and 2.0 L capacity. The size of the bottom ash was fixed at 63 μm and loaded at 50 g/L. Each sample was conditioned in water for 5 min to ensure complete wetting at the desired pH before the addition of reagents. The conditioning period for the kerosene was 2 min and for MIBC was 30 s. The kerosene and MIBC were added in droplets. The conditioning period for each test was 10 min. At the end of the experiment, the flotation products (called concentrates) were filtered, dried, and weighed.
2.4. Methylene Blue Concentration Determination
Using a UV–visible spectrophotometer (HITACHI U-2010), the concentration of methylene blue was determined spectrophotometrically by taking measurements at the absorbance maximum. A calibration curve was plotted between the absorbance and the concentration of the methylene blue solution to obtain the absorbance concentration profile. The amount of methylene blue uptake per unit of adsorbent was calculated using the following equation:
where C0 (mg/L) and Ct (mg/L) are the methylene blue concentration initially and at time t, respectively; Ce (mg/L) is the methylene blue concentration at the adsorption equilibrium; qe and qt are the adsorption capacity at equilibrium and at time t, respectively; V (L) is the volume of methylene blue solution; and m (g) is the weight of the tailing ash.
2.5. Adsorption Study
The adsorption studies were conducted in batches. A conical flask solution containing 100 mL of MB solution at 20 mg/L was used as a control sample in this study. A fixed amount of tailing ash was added to a conical flask solution containing 100 mL of MB solution at 20–100 mg/L.
The flasks were then mechanically agitated intermittently at room temperature to achieve equilibrium. The supernatant was carefully filtered through a 0.45 µm syringe filter when equilibrium was reached within 75 to 120 min. Then the samples were analyzed spectrophotometrically by measuring the absorbance at the maximum wavelength of 660 nm. All of the experiments were conducted in triplicate. A schematic diagram of the adsorption study is shown in Figure 2.
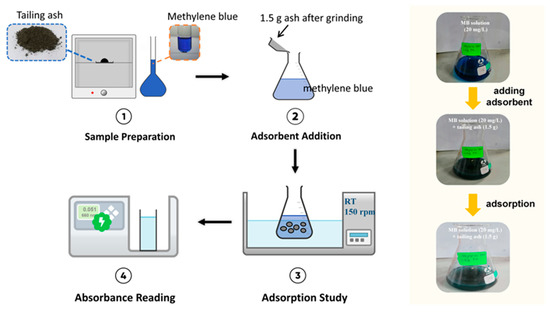
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of adsorption study.
The dye removal efficiency (%R) was calculated using Equation (3).
2.6. Material Development
2.6.1. Tailing Ash Pretreated with H2O2
After about 24 h, the small-sized granules of tailing ash were immersed into a hydrogen peroxide solution (30% w/v) to oxidize all undesired organic impurities from it. The solution was then filtered and washed again several times by doubly distilled water. The material was then kept in an oven at 100 °C to remove the moisture for about 15 min. It was then stored in vacuum desiccators until further use.
2.6.2. Thermal Tailing Ash
Further heat treatment was required to produce the thermal tailing ash. This was accomplished by heating the dried material in a furnace at 500 °C for about 30 min. The product was then stored in a vacuum desiccator until further use.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization
According to Gupta and Suhas [7], low-cost adsorbents can be employed to remove dyes where adsorption capacities depend on their surface area or micro/meso porosity, pore size distribution, and particle size. The results of the characterization of the tailing ash are shown below.
3.1.1. XRF Analysis Results
Table 1 shows the results of the XRF analysis of the tailing ash. It is noted that the main composition of the tailing ash is SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, CaO, and the residual carbon from coal burning. Silica, alumina, iron, and calcium oxide were the major contents of the bottom ash. The highest was SiO2 (wt 32.52%), followed by CaO (wt 16.93%), Fe2O3 (wt 15.95%), and Al2O3 (wt 10.96%), which had the possibility to remove dye from wastewater.

Table 1.
Results of XRF analysis of tailing ash.
3.1.2. SEM Analysis Results
The morphology of the tailing ash samples was influenced by the combustion temperature and cooling rate during the incineration process [8]. Figure 3 shows the morphology of the tailing ash, showing the pores and surface texture. High surface porosity was observed in the pieces, and this decreased their thermal conductivity. The samples consisted of irregularly shaped, hollow, and spherical particles (ceno-spheres), which had also been reported in other studies [9]. Moreover, the irregularly shaped and dark particles seen in the tailing ash were likely related to carbon.

Figure 3.
SEM micrograph of tailing ash.
3.1.3. BET Analysis Results
Table 2 shows the results of the BET analysis. The surface areas of three samples were found to be 3.5420 m2/g for tailing ash, 4.0471 m2/g for tailing ash pretreated H2O2, and 3.2220 m2/g for thermal tailing ash. Moreover, activating the tailing ash with H2O2 caused an increase in the surface area. The larger surface area of H2O2 tailing ash will give an improved and effective contact area for adsorption. Figure 4 shows the BET nitrogen isotherm for the tailing ash, tailing ash pretreated H2O2, and thermal tailing ash. This result shows that the isotherms displayed the presence of a narrow hysteresis loop, which is a characteristic assigned to type IV isotherms [10].

Table 2.
Results of BET analysis.
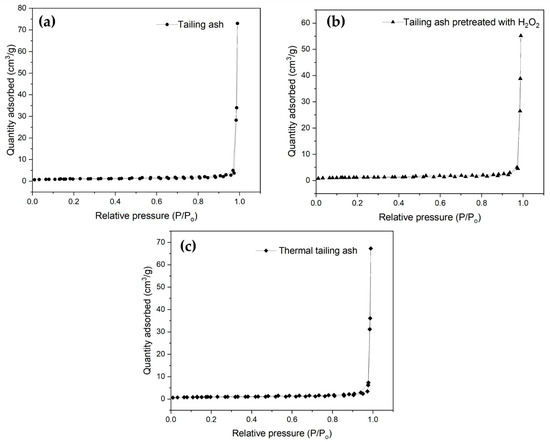
Figure 4.
BET nitrogen isotherm plot for (a) tailing ash, (b) tailing ash pretreated with H2O2, and (c) thermal tailing ash.
3.2. Adsorption Study
3.2.1. Effect of pH and Determination of pH Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc) of Tailing Ash
The pH effect on the adsorption of methylene blue is one of the important factors of controlling the adsorption of dyes. Figure 5 shows the effect of pH on MB removal. The uptake of dyes increased with the increase in the pH, achieving about 89.9% removal at pH 10. This indicated that the more alkaline the solution, the more methylene blue was adsorbed. From Figure 2, it was observed that the adsorption capacity qe increased from 0.9 mg/g to 1.2 mg/g, with the increasing pH value from 2 to 10. Similarly, a previous study reported that the adsorption capacity of dye increased with the increase in the initial pH [11]. When the pH of the solution is increased, the number of negatively charged sites in the adsorbent increases, while the number of positively charged sites decreases. Because of electrostatic forces, negatively charged surface areas on the adsorbent can promote cationic dye adsorption [12]. In the lower pH range, the low adsorption of methylene blue also exhibited the potential for the growth of a neutral or weakened charge at the porous biochar surface, which decreased the electrostatic motivation for the methylene blue adsorption onto it [13]. Hence, all of the following studies were conducted at pH 10.0 as the optimal pH.
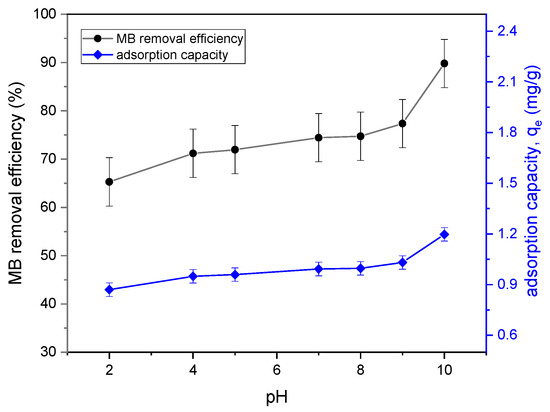
Figure 5.
Effect of pH on the removal efficiency and qe of MB adsorption onto tailing ash (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, RT (25 °C)).
When the charge in the adsorbent surface is zero, the pH is known as pHpzc. The pHpzc of tailing ash has been deducted from figures where the initial pH is equal to the final pH (intersection of curves). From Figure 6, it can be seen that the pHpzc of the tailing ash was 7.7. At the pH of 7.7, the surface becomes positively charged (+ve), while at a pH greater than 7.7, it becomes negatively charged (−ve). The literature reported that the cations uptake is favorable to a pH > pHpzc, whereas the uptake of anions is encouraged to a pH < pHpzc of sorbent [14].
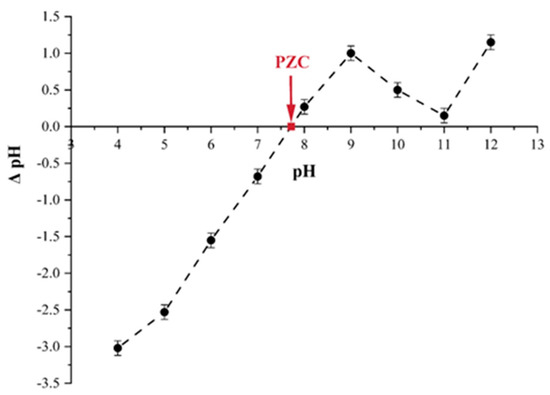
Figure 6.
Determination of pH point of zero charge (pHpzc) of tailing ash.
3.2.2. Effect of Stirring Speed
Figure 7 shows the effect of stirring speed on MB removal. A stirring speed from 50 to 150 rpm was applied for this study. It was revealed that an increase in the stirring speed from 50 to 150 rpm resulted in an increase in the MB removal efficiency (76.24%) and qe (1.01 mg/g). The thickness of the adsorbent boundary layer tended to decrease due to an increase in the speed of agitation of the solution [15]. The highest adsorption capacity (qe) was about 0.999 mg/g at 150 rpm.
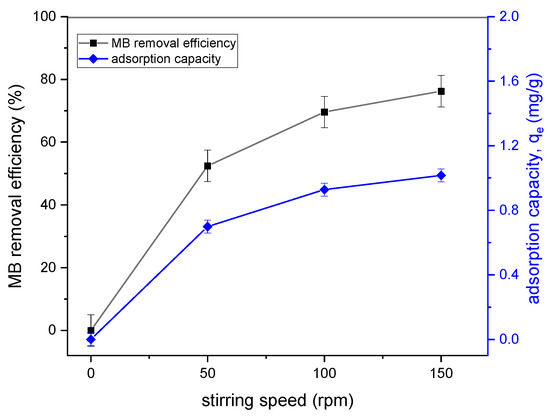
Figure 7.
Effect of stirring speed on the removal efficiency and qe of MB adsorption onto tailing ash (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, contact time = 120 min, pH = 10, RT (25 °C)).
3.2.3. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration and Contact Time
Figure 8a illustrates the effect of initial dye concentration and contact time on MB removal using tailing ash. As can be observed, the MB removal efficiency dropped as the initial concentration increased from 20 to 100 mg/L, resulting in a decrease in the percentage of the dye adsorbed from 74.82% to 49.6%. Within the first 15 min, over 60% removal of MB occurred. It also demonstrated that increasing the contact duration resulted in a significant increase in the dye adsorbed until equilibrium (75 min contact time) for all initial concentrations ranging from 20 to 100 mg/L. The initial fast adsorption or uptake rate was due to the increased number of vacant sites available for adsorption at the initial stage [16]. Figure 8b shows the adsorption capacity, qe, of MB at various initial concentration values. The adsorption capacity was 0.99, 1.63, 2.25, 2.64, and 3.48 mg/g. It is clearly seen that the adsorption capacity increased with the initial concentrations of MB.
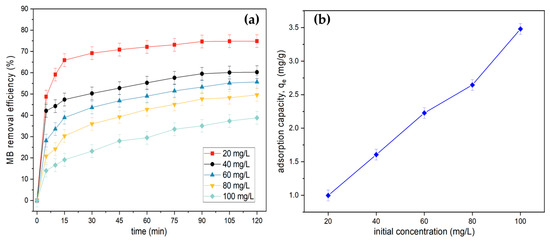
Figure 8.
(a) Effect of contact time and initial MB concentration and on MB adsorption onto tailing ash (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, pH = 10, RT). (b) Effect of initial MB concentration.
3.2.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
The effect of adsorbent dosage for MB removal was studied to determine the most appropriate amount of adsorbent at various MB concentrations. The investigation was carried out by varying the amount of tailing ash from 0.5 g to 2.5 g. The result is presented in Figure 9. This study found that when the amount of adsorbent was increased, the removal efficiency increased. The dye uptakes with tailing ash increased excessively from 1 g to 1.5 g, which is from 65.8% to 84.7%. It could also be noticed that qe increased with an increase in the adsorbent dose until the optimum dose of 1.5 g and remained almost constant even with an increase in the adsorbent dosage. This suggested that for dye adsorption, an appropriate adsorbent should be used to lower the adsorbent cost. Additionally, the higher adsorbent dose provided more adsorption sites for the adsorbate, but it was commonly found that, when the adsorbent concentration was too high, some adsorption sites may be blocked by spatial or physical hindrance that can cause a decrease in the availability of some sorption sites [15].
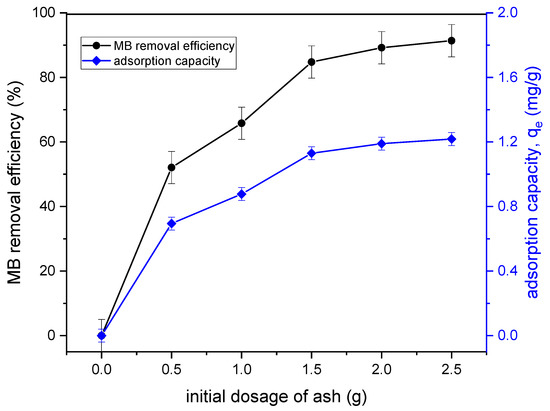
Figure 9.
Effect of adsorbent dosage of TA on the removal efficiency and qe of MB adsorption onto tailing ash (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, pH = 10, RT (25 °C)).
3.2.5. Effect of Temperature
The effect of the initial adsorbate concentration on temperature for MB removal efficiency was investigated at temperatures of 25 °C, 35 °C, and 45 °C at initial concentration ranges from 20 to 100 mg/L (Figure 10). The experiments were carried out with a fixed adsorbent dose of 1.5 g of tailing ash adsorbent at pH 10. The results indicated that the uptake of methylene blue was favored at high temperatures. Figure 10 shows that the uptake is 96% at low concentrations and the adsorption capacity increases with the increase in the concentration of the dye. These results also signify the good efficacy of the adsorbents towards MB. Adsorption may increase due to an increase in the rate of diffusion of the adsorbate molecules over the surface boundary layer and the presence of internal pores in the adsorbent particles [17].
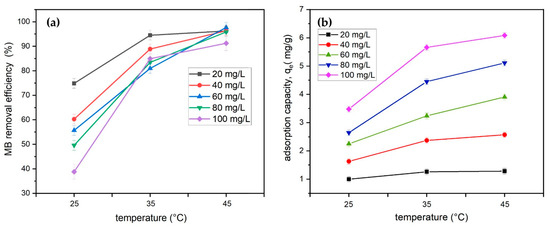
Figure 10.
(a) Effect of temperature of TA on the removal efficiency and (b) qe of MB adsorption onto tailing ash (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, pH = 10, 25–45 °C).
3.3. Modification of Adsorbent
Figure 11 shows the MB removal by thermal TA, TA, and TA pretreated with H2O2. As we can see, the highest removal of 83.0% is promoted by TA pretreated with H2O2 compared with the separate tailing ash of 61.4% and thermal TA with 55.78% of removal. Involving H2O2 in the modification of the adsorbent can increase the number of surface active sites by providing it with a wider surface available for the adsorption [18]. Previous studies reported that acid treatment produced increased numbers of various surface oxygen complexes, which enhanced the active adsorbent sites [19].
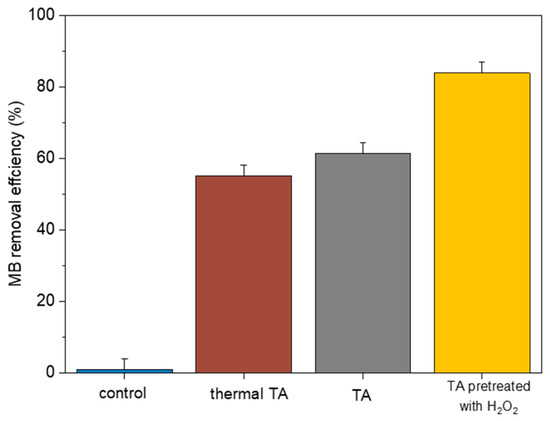
Figure 11.
MB removal by thermal TA, TA, and TA pretreated with H2O2 (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, pH = 3, RT (25 °C)).
According to Figure 12a, thermal TA and TA had a lower adsorption for MB dye when compared to TA pretreated with H2O2. The small surface area and poor adsorption selection efficiency resulted in a low cationic MB adsorption capability. TA pretreated with H2O2 had the highest removal efficiency with 83.0% removal. The adsorption capacity of thermal TA, TA, and TA pretreated with H2O2 are presented in Figure 12b, in which TA pretreated with H2O2 gave a higher capacity (1.045 mg/g). In addition, the adsorption of all tailing ash attained equilibrium between 90 and 120 min of contact. Since adsorption is a surface phenomenon, the higher adsorption rate was attributed to the greater accessibility to pores and the larger surface area [8].
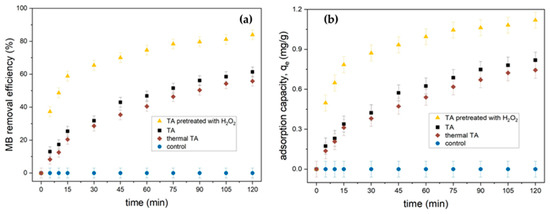
Figure 12.
(a) Effect of contact time on MB removal by thermal TA, TA, and TA pretreated with H2O2 (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, pH = 3, RT). (b) Adsorption capacity, qe, of thermal TA, TA, and TA pretreated with H2O2.
3.4. Functioning of H2O2
In order to clarify the potential combining effects of HTA on MB removal, the original tailing ash was employed for a comparative investigation with the involvement of hydrogen peroxide of different percentages. The result is shown in Figure 13. The graph shows the highest removal was obtained using 3% of H2O2 tailing ash (HTA). The results indicated that hydrogen peroxide involvement significantly promoted their removal efficiency to 74.18% compared with the separate tailing ash of 59.96% and separate hydrogen peroxide of 28.99%, respectively. It can be concluded that H2O2 can react as a catalyst to remove MB, which can help decompose the MB. Existing transition metals (shown in Table 1), such as Fe, Co, Ni, and Mn, in the biomass can trigger the Fenton-like reaction to release the hydroxyl radicals [20].
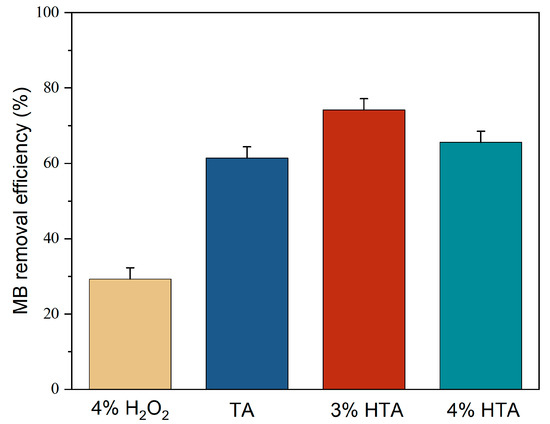
Figure 13.
MB removal by H2O2, TA, and HTA (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, pH = 3, RT).
Effect of Contact Time by TA, H2O2, and HTA for MB Removal
Figure 14 shows the effect of contact time on MB removal by the three samples, namely, tailing ash (TA), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and tailing ash with hydrogen peroxide (HTA). In acidic conditions, tailing ash with hydrogen peroxide (HTA) has the greatest removal efficiency of 77.2% and adsorption capacity of 1.03 mg/g (Figure 15) when compared to tailing ash and H2O2 alone. The adsorption capacity of methylene blue by the tailing ash with hydrogen peroxide increased as the contact time increased, and then reached a maximum value. Tailing ash is a low-cost adsorbent that can react to remove the MB. It can be concluded that H2O2 can react as a catalyst to remove and help decompose the MB. Existing transition metals (shown in Table 1), such as Fe, Co, Ni, and Mn, in the biomass can trigger the Fenton-like reaction to release the hydroxyl radicals [20].
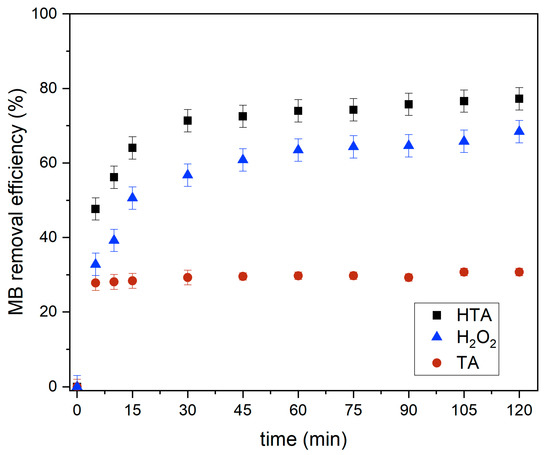
Figure 14.
Effect of contact time on MB removal using TA, H2O2, and HTA (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, pH = 3, RT).
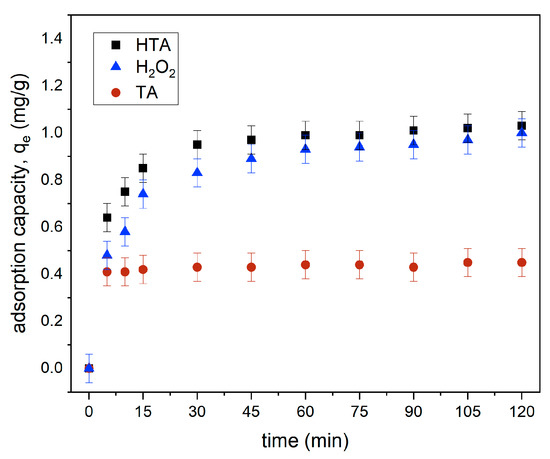
Figure 15.
Effect of contact time on adsorption capacity (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, pH = 3, RT).
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm
3.5.1. Adsorption Kinetics
The reaction rate between the adsorbents and adsorbates and the factors affecting the reaction rate were studied using adsorption kinetics. A discussion of the results was made according to the fitting of the adsorption data by the kinetic models and the adsorption mechanism [11]. The consistency between the experimental results and the theoretical values of the model was evaluated on the basis of the coefficient of determination (the R2 value was close to or equal to 1) [11].
The pseudo-first-order equation is:
where k1 is the rate constant of adsorption (1/min), qe is the quantity of dye adsorbed at equilibrium (mg/g), and qt is the equilibrium concentration at various times t (in mg/g). The rate constant in this model was determined by the slope of the plot of ln (qe − qt) over time (t).
The pseudo-second-order equation is:
where k2 is the second-order rate constant (g/mg/min) that can be determined for different MB concentrations according to the linear plots of t/qt versus t, as shown in Figure 16b.
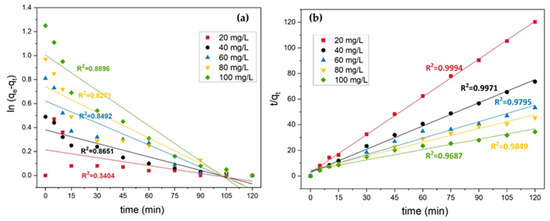
Figure 16.
(a) Pseudo-first-order kinetic (initial MB concentration = 20 mg/L, adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, stirring speed = 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, pH = 10, RT). (b) Pseudo-second-order kinetic.
From Figure 16b, it was found that the pseudo-second-order model fitted better than the pseudo-first-order model (Figure 16a) to explain the adsorption process of MB on the tailing ash. The calculated correlation coefficients (R2) were found to be close to 1 (0.099) and the experimental qe that differ from the calculated ones are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Pseudo-first-order model and pseudo-second-order model form.
3.5.2. Adsorption Isotherm Study
The adsorption mechanisms of the tailing ash in the removal of the methylene blue dye solutions were analyzed using Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin adsorption isotherm models. It is important to establish the most appropriate correlation for the equilibrium curves to optimize the design of an adsorption system for the adsorption of adsorbates [21]. The equilibrium adsorption of methylene blue dye solutions by TA were used to determine the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin isotherm models. The Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin adsorption isotherm can be written as follows:
where KL is the Langmuir adsorption constant (L/mg) related to the energy of adsorption and qmax is the Langmuir constants that are related to the adsorption capacity (mg/g); KF is the Freundlich constant (L/mg) and 1/n is the heterogeneity factor; B is a constant related to the heat of adsorption and is defined by the expression B = RT/b; b is the Temkin constant (J/mol); T is the absolute temperature (K); R is the gas constant (8.314 J/mol K); and A is the Temkin isotherm constant (L/g). The Langmuir isotherm model determines the adsorption of ions on the surface of the adsorbent on the monolayer and specific homogeneous surface [14,17]. The Freundlich isotherm model assumes that multi-layer adsorption processes occur on heterogeneous surfaces. The Temkin isotherm model assumes that the adsorption heat of all molecules decreases linearly with the increase in the coverage of the adsorbent surface, and that adsorption is characterized by a uniform distribution of binding energies, up to maximum binding energy [22,23].
Figure 17a–c show the Langmuir (Ce/qe versus Ce) plot, Freundlich (ln qe versus ln Ce), and Temkin (ln Ce versus qe), respectively, for the removal of MB with TA. The high value of R2 obtained from the linear graph of ln qe versus ln Ce was 0.9934, which demonstrated that the adsorption process meets the Freundlich isotherm model, as shown in Figure 12b. Tailing ash is made up of heterogeneous, multi-layered surfaces, which are available for adsorption, as demonstrated by the Freundlich isotherm, the governing equilibrium model [8]. The obtained parameters for each model are summarized in Table 4.
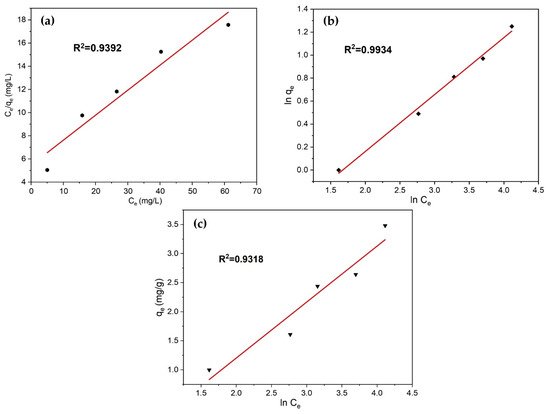
Figure 17.
(a) Langmuir, (b) Freundlich, and (c) Temkin isotherm plots for adsorption of MB on tailing ash.

Table 4.
Isotherm parameters of the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models.
The adsorption data were also analyzed according to the nonlinear form of the Langmuir isotherm, as shown in Figure 18. In all cases, all error values for any of the parameter sets are lower than the same errors determined for the linear form of the isotherm. The comparatively lower magnitudes of the error values together with the lower range of variation in the isotherm parameters [24] suggests that the Langmuir isotherm does provide a good model for the adsorption of MB onto tailing ash.
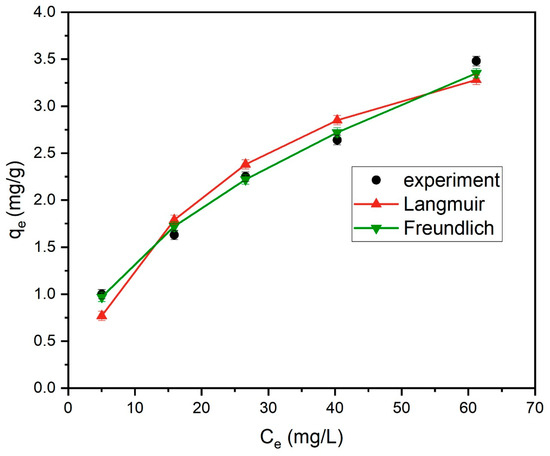
Figure 18.
Nonlinear regression fitting of Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms of MB adsorption by tailing ash.
3.5.3. Thermodynamic Parameters
The thermodynamic parameters were verified using the data from the adsorption isotherms. The changes in standard free energy (ΔG°), enthalpy (ΔH°), and entropy (ΔS°) of adsorption for methylene blue were calculated. The values are given in Table 5. The negative free energy value indicates the feasibility of the process and spontaneous process nature of adsorption. Moreover, the result showed that by increasing the adsorption temperature, the ΔG° values gradually decreased. This phenomenon reveals that the adsorption process is more favorable at high temperatures. The negative enthalpy value implies that the process is an exothermic removal of energy from the reaction [25]. The values of ΔH° and ΔS° can be determined from the slopes and the intercepts of the linear graph of ln (KL) versus 1/T, as shown in Figure 19.

Table 5.
Thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of MB by tailing ash at different temperatures.
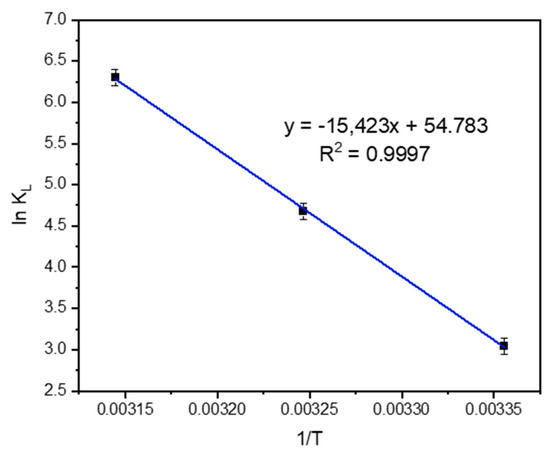
Figure 19.
Van’t Hoff plot for adsorption of MB by tailing ash.
Table 6 compares the adsorption capacity, qe (mg/g), of MB on different adsorbents. As with the data reported in the literature, the adsorption capacity of the MB on ash obtained in this study is rather low [26]. The MB is a cationic dye that produces positively charged ions when dissolved in water, and the positive surface charge of the adsorbent tends to oppose the adsorption of cationic species, leading to low adsorption capacity [27]. The adsorption capacity could be enhanced via surface modifications or extracting adsorptive material from waste material [27,28]. In the future, we plan to synthesize synthetic zeolite from coal bottom ash for the more effective removal of MB [29].

Table 6.
Comparison of low-cost adsorbents for MB.
4. Conclusions
The present study showed that tailing ash can be used as an adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Tailing ash is a more cost-effective adsorbent than commercially available adsorbents. The tailing ash was derived from the floatation of bottom ash, which is a freely available waste material with no additional cost and is usually dumped in landfill areas. The adsorption of methylene blue onto tailing ash adsorbents was conducted under several experimental parameters such as pH, stirring speed, adsorbent dosage, initial dye concentration, contact time, and temperature. The adsorbents were characterized using XRF, SEM, and BET. The SEM image shows that the adsorbents consist of porous particles. The XRF results show that the adsorbent consists mainly of SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3. The experimental results for batch adsorption showed that up to 96.23% MB removal was achieved under optimum conditions (pH = 10, initial adsorbent dosage = 1.5 g, 150 rpm, contact time = 120 min, 45 °C). The kinetic modeling study showed that the experimental data followed the pseudo-second-order model, and for isotherms, the data followed the Freundlich model with correlation coefficient values (R2) equal to 0.993. This study demonstrated that tailing ash can be used as an excellent adsorbent and the developed method is quite inexpensive.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.Y.C.; methodology, T.S.Y.C. and S.N.A.M.J.; validation, T.S.Y.C., W.A.W.A.K.G., F.N.A.A.A. and S.N.A.M.J.; formal analysis, T.S.Y.C., C.J.F.b.Y. and F.L.; investigation, C.J.F.b.Y.; resources, C.J.F.b.Y.; data curation, C.J.F.b.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, C.J.F.b.Y.; writing—review and editing, T.S.Y.C. and F.L.; visualization, T.S.Y.C., C.J.F.b.Y. and F.L.; supervision, T.S.Y.C., W.A.W.A.K.G., F.N.A.A.A. and S.N.A.M.J.; funding acquisition, T.S.Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universiti Putra Malaysia via the Graduate Research Fellowship program (GRF) (GS51339).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on demand from the corresponding author or the first author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Universiti Putra Malaysia for financial support via the Graduate Research Fellowship program (GRF), and TNB Janamanjung power plant for providing the coal bottom ash for this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Heidrich, C.; Feuerborn, H.; Weir, A. Coal Combustion Products: A Global Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2013 World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference, Lexington, KY, USA, 22–25 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds-Clausen, K.; Singh, N. South Africa’s Power Producer’s Revised Coal Ash Strategy and Implementation Progress. Coal Combust. Gasif. Prod. 2019, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.; Ehsan, M.; Islam, M. Issues relating to energy conservation and renewable energy in Bangladesh. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2003, 7, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelgasim, R.; Rashid, A.S.; Bouassida, M.; Shien, N.; Abdullah, M.H. Geotechnical Characteristics of Tanjung Bin Coal Bottom Ash. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 932, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenhorst, C.; Wagner, N.; Valentim, B.; Santos, A.C.; Guedes, A.; Białecka, B.; Mozco, J.C.; Popescu, L.; Cruceru, M.; Predeanu, G.; et al. Char from Coal Ash as a Possible Precursor for Synthetic Graphite—Recent Developments of the Charphite Project. In Proceedings of the World of Coal Ash (WOCA), St. Louis, MO, USA, 13–16 May 2019; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Carrott, M.M.L.R. Suhas Low-Cost Adsorbents: Growing Approach to Wastewater Treatment—A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 783–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K. Suhas Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorme, J.B.; Maniquiz, M.C.; Kim, S.-S.; Son, Y.-G.; Kim, Y.-T.; Kim, L.-H. Characterization of Bottom Ash as an Adsorbent of Lead from Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Eng. Res. 2010, 15, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Kong, S.-H.; Rhee, S.-W.; Lee, W.-K. The adsorption characteristics of heavy metals by various particle sizes of MSWI bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Poulopoulos, S.G.; Kazemian, H. Insights into the S-shaped sorption isotherms and their dimensionless forms. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 272, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmiyati, K.; Listyanto, P.A.; Vitasary, D.; Indra, R.; Islamica, D. Hadiyanto Coal Bottom Ash and Activated Carbon for Removal of Vertigo Blue Dye in Batik Textile Waste Water: Adsorbent Characteristic, Isotherms, and Kinetics Studies. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 427–439. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, N.I.R.R.; Shahidan, S.; Ali, N.; Maarof, M.Z. A Comprehensive Review on the Properties of Coal Bottom Ash in Concrete as Sound Absorption Material. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 103, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumediene, M.; Benaïssa, H.; George, B.; Molina, S.; Merlin, A. Effects of PH and Ionic Strength on Methylene Blue Removal from Synthetic Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Orange Peel and Desorption Study. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Altaher, H.; Khalil, T.E.; Abubeah, R. The effect of dye chemical structure on adsorption on activated carbon: A comparative study. Color. Technol. 2014, 130, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworanti, A.; Agarry, S.E. Kinetics, Isothermal and Thermodynamic Modelling Studies of Hexavalent Chromium Ions Adsorption from Simulated Wastewater onto Parkia Biglobosa-Sawdust Derived Acid-Steam Activated. Appl. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 3, 58–76. [Google Scholar]
- Idan, I.J.; Abdullah, L.C.; Choong, T.S.; Jamil, S.N.A.B.M. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic adsorption studies of acid dyes on adsorbent developed from kenaf core fiber. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2017, 36, 694–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Mittal, A.; Jhare, D.; Mittal, J. Batch and bulk removal of hazardous colouring agent Rose Bengal by adsorption techniques using bottom ash as adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8381–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Jang, Y.-S. Pore Structure and Surface Properties of Chemically Modified Activated Carbons for Adsorption Mechanism and Rate of Cr(VI). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 249, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tian, D.; Hu, J.; Shen, F.; Long, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; et al. Functionalizing bottom ash from biomass power plant for removing methylene blue from aqueous solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K. Removal of Orange-G and Methyl Violet dyes by adsorption onto bagasse fly ash—Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Dyes Pigments 2006, 69, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, J.; Jhare, D.; Vardhan, H.; Mittal, A. Utilization of bottom ash as a low-cost sorbent for the removal and recovery of a toxic halogen containing dye eosin yellow. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 52, 4508–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyinbor, A.A.; Adekola, F.A.; Olatunji, G.A. Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic modeling of liquid phase adsorption of Rhodamine B dye onto Raphia hookerie fruit epicarp. Water Resour. Ind. 2016, 15, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarry, S.; Ogunleye, O. Chemically treated kola nut pod as low-cost natural adsorbent for the removal of 2,4-dinitrophenol from synthetic wastewater: Batch equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic modelling studies. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2014, 38, 11–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, T.; Rohendi, D.; Mohadi, R.; Lesbani, A. Congo red dye removal from aqueous solution by acid-activated bentonite from sarolangun: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Arab. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2019, 26, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleşoğlu, S.; Kes, M.; Sütçü, L.; Polat, H. Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution on High Lime Fly Ash: Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, R.; Muntean, S.-G.; Nistor, M.-A.; Putz, A.-M.; Almásy, L.; Săcărescu, L. Highly efficient and fast removal of colored pollutants from single and binary systems, using magnetic mesoporous silica. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esa, Y.A.M.; Sapawe, N. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using silica nanoparticle extracted from skewer coconut leaves. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, M. Synthetic zeolite from coal bottom ash and its application in cadmium and nickel removal from acidic wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 26089–26100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.T.; Vo, L.N.H.; Tran, N.T.T.; Phan, T.D.; Nguyen, D.B. Enhancing the removal efficiency of methylene blue in water by fly ash via a modified adsorbent with alkaline thermal hydrolysis treatment. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 20292–20302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsami, J.N.; Mbadcam, J.K. The Adsorption Efficiency of Chemically Prepared Activated Carbon from Cola Nut Shells by ZnCl2 on Methylene Blue. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelifajri, L.; Rahmi, R.; Supriatno, S.; Susilawati, S.; Indarum, A.S. Study on methylene blue dye adsorption in aqueous solution by heat-treated Gnetum gnemon shell waste particles as low-cost adsorbent. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2243, 020012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).