Abstract
As part of the work, studies of the quality of wastewater from alcohol production were carried out; the main characteristics were determined, such as the charge of dispersed particles and the content of organic compounds and fats. A comparison is made of the effectiveness of titanium salts, traditional aluminum, and iron-containing coagulants. It has been established that titanium salts are much more effective than traditional reagents, but their high cost significantly limits the scope of their application. The possibility of increasing the efficiency of traditional coagulants by adding various titanium salts in an amount of up to 10% of the mass has been proved. It has been established that the addition of titanium compounds to aluminum or iron-containing coagulants makes it possible to increase the cleaning efficiency by an average of 10–20% while a significant reduction in the dose of reagents is possible, which will have a positive effect on the cost of the cleaning process. It was found that the addition of titanium salts to a coagulant based on aluminum sulfate allows not only an increase in the cleaning efficiency but also further intensifies the processes of sedimentation and filtration of coagulation sludge, which will significantly reduce the size of the treatment equipment and reduce capital costs.
1. Introduction
Population growth necessitates the increase in capacity of the food industry and related industries. An increase in the volume of manufactured food products, the development of new formulations and products, and innovations in the field of food biotechnology have led to an increase in the environmental impact of enterprises. Most of the food industry’s waste can be easily recycled using the biological methods (biocomposition, fermentation, etc.); the atmospheric emissions have almost no serious consequences, except for the dryers’ emissions. However, treatment and disposal of the wastewater generated as a result of various food production processes remains an unresolved problem.
The processes related to the generation of large volumes of highly contaminated organic wastewater components are typical for all areas of the food industry, including the production of alcohol-containing products (alcohol, beer, and wine), the milk treatment processes, and the manufacturing of the byproducts (butter, cheese) in confectionery enterprises [1,2,3].
The food industry wastewater treatment is a comprehensive and extremely urgent task. The anaerobic digestion methods for highly concentrated effluents have become widespread when the total amount of dissolved and undissolved organic compounds, in terms of the COD, is more than 30,000–40,000 mg(O)/L, with the production of flammable hydrocarbons. However, this technology cannot be used for the effluents with a relatively low content of organic substances, at a COD of up to 10,000 mg(O)/L [4].
The traditional treatment method for such wastewater includes the stage of physicochemical clarification from suspended solids, undissolved organic compounds, partially emulsified fats, etc., followed by biological purification.
The coagulants (polyelectrolyte) and flocculants are used as the reagents at the stage of physicochemical purification. The most common coagulants are aluminum and iron salts. Aluminum sulfate and oxychloride are widely used in the drinking water treatment processes; however, due to their relatively high cost, they are less often used in the wastewater treatment processes. In addition, despite their high efficiency and versatility, the aluminum compounds are effective in a very limited pH range (6.0–7.5) and are subject to a strict standard for the residual aluminum content in water. Moreover, aluminum sulfate is also inefficient at low water temperatures. The iron compounds, such as ferric chloride (FeCl3) and ferrous sulfate (FeSO4), are quite effective reagents and have a wide applicable pH range compared to the coagulants based on aluminum compounds. However, they also have certain disadvantages, such as significant volumes of difficult-to-filter precipitate and the possible generation of complexes with organic ligands [5,6].
A new field of reactant wastewater purification is the use of coagulants based on titanium compounds. The research teams from China [7,8,9,10,11], Russia [12,13], and Ukraine [14] noted the high efficiency of titanium-containing coagulants as well as the absence of most disadvantages inherent in the conventional reagents. The similar results were obtained as a result of the international collaboration of institutions from France, Australia, China, Korea, and other countries [15,16,17,18,19,20].
The collaborating author team from Great Britain confirmed the high efficiency of titanium compounds in the process of removing dissolved organic substances from water [21].
The research groups from Russia proved the possible increase in the efficiency of conventional reagents based on aluminum or iron compounds by introducing a few hydrolysis products of titanium compounds into their composition (up to 10–15% by weight) that made it possible to expand the effective pH range and increase the purification efficiency and sedimentation specifications of the generated sediments [12,22].
Based on the literature review, it can be seen that data of the titanium compounds used as coagulants for the wastewater purification of the alcohol industry are not currently presented, which determines the scientific and practical novelty of the research.
The main purpose of this paper is to assess the possible use of titanium-containing coagulants in the wastewater purification processes at the alcohol industry enterprises.
2. Materials and Methods
The production of alcohol-containing products was selected as the study object. The fermentation tanks as well as separation and distillation shops are located on the site. The manufacturing department produces various types of alcoholic beverages, such as beer, wine, kvass, etc. and is standardized for all similar enterprises in the territory of the Russian Federation (over 70 entities). The production process wastewater was taken from the sewer pipes of the relevant company.
Wastewater samples were taken by averaging the 20 L capacitances and delivered to the laboratory within 4 h.
Samples of the comprehensive titanium-containing coagulants were obtained by adding hydrolysis products of titanium compounds (titanium sulfate or chloride) as well as titanium dioxide in an amount of up to 10 wt% to the conventional reagents based on aluminum and iron salts [23].
The particle size was determined by the dynamic light diffusion method using a Photocor Compact-Z device (Russia).
The zeta potential of colloidal particles was determined with a Zetasizer Nano by Malvern (Great Britain).
The pH value was determined using a digital meter pHHQ11B by HACH (Loveland, CO, USA).
The chromaticity value was determined using a DR 6000 spectrophotometer by HACH (USA).
The chemical oxygen demand was determined by the reference method with dichromate according to the procedure [24].
The biochemical oxygen demand was determined according to the applicable method (APHA 1986) [25].
The content of the suspended solids was determined by the gravimetric method using the HANNA 98703 portable turbidimeter.
The content of the fats and oils was determined gravimetrically (Soxhlet method) [26].
Titanium dioxide (TiO2 99.8%), titanyl sulfate (TiOSO4 ∙ xH2O—99.9%), and titanium tetrachloride (99.9%, TiCl4) were made by Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
Aluminum sulfate, aluminum polyoxychloride, and ferric chloride were produced by Kemira (Helsinki, Finland).
Coagulant solutions were obtained by dissolving (magnetic stirring) a 10 g sample of powdered reagents in 100 mL of water for 60 min.
The jar test was carried out using the portable laboratory flocculator JLT 4 VELP (Italy). Wastewater samples of a given volume (500 mL) were divided into measuring cups, followed by setting it in a laboratory flocculator. With a pipet dispenser, predetermined individual dosages of preprepared complex reagents were injected into the treated water. The pH correction was adjusted using an appropriate volume of 0.05 mol/L NaOH.
During the experiments, coagulants were added at the beginning of mixing at 150 rpm for 2 min, known as the fast coagulation stage (mixing reagent with water and the formation of primary aggregates). Then, the solution underwent slow mixing at 10 rpm for 8 min, which is the flocculation and adsorption phase. This was followed by 30 min of sedimentation (quiescent settling). The samples of water after sedimentation were collected from 5 cm below the water surface.The filtration rate was determined by the passage of 100 mL of liquid through a filter with a pore size of 15 microns and by measuring the volume of the filtrate obtained in 60 s.
The clarified water was analyzed according to the methods described above.
The efficiency of treatment (EffTR) was calculated by equipment:
CBAS—concentration suspended solids (indicator value COD) before treatment, mg/L; CTR—concentration suspended solids (parameter value COD) after treatment, mg/L.
3. Results and Discussion
The results of the particle sizes analysis demonstrate that the wastewater is specified by the availability of two particle peals, namely the rapid settling particles with a size of more than 10 microns and the slow settling particles with a size of about 100 nm. The zeta potential at the particle surface was (−6 mV).
The chemical composition of wastewater samples was examined at the next experimental stage (Table 1).

Table 1.
Chemical composition of the wastewater samples.
Table 1 shows that the priority pollutant in the water composition is the dissolved organic matter as well as the colloidal particles. The supply of such water to the urban facilities for deep biological treatment is impossible due to the prohibitively high rates of chemical and biological oxygen demand.
Among many indicators of wastewater quality (and purification efficiency) analyzed, the most common ones were selected: chemical oxygen consumption and suspended solids content. These indicators are used to correct the operation of purification facilities (dose of coagulant, flotation time, etc.) at most enterprises.
At the first stage, we have made a comparison of the efficiency of conventional reagents and coagulants based on the titanium compounds in the purification process for the actual alcohol industry effluents from the suspended solids (Figure 1) and the chemical oxygen demand index (COD) (Figure 2).
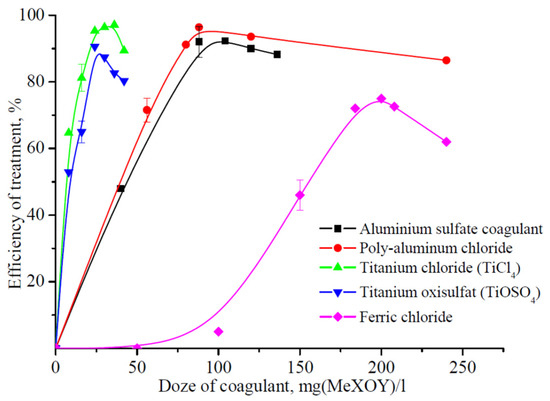
Figure 1.
Dependence of the alcohol industry wastewater treatment efficiency from the suspended solids by various coagulants on the coagulant dose.
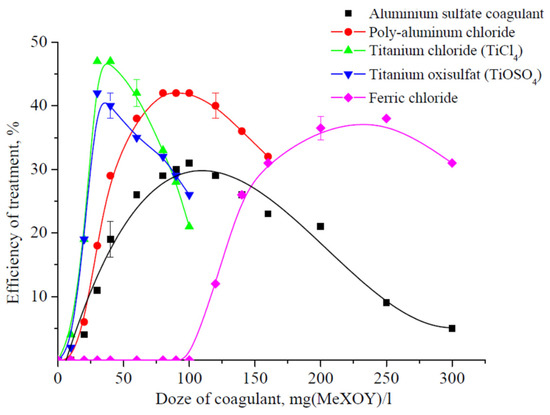
Figure 2.
Dependence of the alcohol industry wastewater treatment efficiency from the organic compounds (COD index) by various coagulants.
The diagrams in Figure 1 and Figure 2 demonstrate that the conventional coagulants based on aluminum compounds can effectively remove the suspended solids and organic compounds from water while the iron compound efficiency in this process is much lower.
The zero efficiency of ferric chloride until dose 100 mg/L can be explained by the formation of complex compounds of iron with organic ligands (for example, citrates or tartrates), which is typical for such coagulants [5,6]. The difference in effective dosages of coagulants for the COD index and suspended solids content can be explained by the cleaning mechanism. Therefore, for colloidal (suspended) particles, this is the charging neutralization and the formation of floccules, and for the COD index (content of organic substances), it is the adsorption on the surface of the hydrolysis products of titanium compounds.
The effective coagulant dose is expressed in mg (MeXOY)/L. The maximum possible treatment efficiency was achieved with the following doses of conventional reagents:
- Aluminum sulfate—88 mg (MeXOY)/L;
- Aluminum oxychloride—80 mg (MeXOY)/L;
- Iron chloride—200 mg (MeXOY)/L.
During the purification process, the titanium compounds were not inferior to the conventional reagents in their efficiency while the minimum effective dose was, on average, 2.5–3.0 times lower and amounted to 20 and 24 mg (MeXOY)/L for titanyl sulfate and titanium tetrachloride, respectively. In addition, the efficiency of titanium compounds during the process of organic compound removal, namely a decrease in the COD index, was, on average, 5–7% higher, which should have a positive effect on further biological treatment. In addition, it should be noted that when the titanium salts are used as the coagulants, the final treatment products will be titanium dioxide that has a much lower toxicity compared to the aluminum compounds [27].
The next experimental stage was to evaluate the effect of adding titanium compounds to the conventional reagents on the overall purification efficiency according to the above indicators.
The diagram in Figure 3 and Figure 4 presents data on the effect of adding various titanium compounds on the alcohol industry wastewater treatment efficiency in terms of the content of the suspended solids and dissolved organic compounds (COD). The basic coagulant dose was 50 mg (Al2O3/L) for aluminum sulfate and oxychloride and 150 mg (Fe2O3/L) for ferric chloride (Figure 3 and Figure 4), and the addition of titanium compounds for TiO2 was 10 wt%.
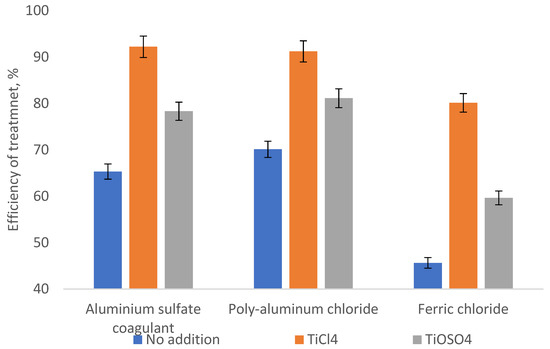
Figure 3.
Efficiency of removing suspended solids from the alcohol industry wastewater by various coagulants.
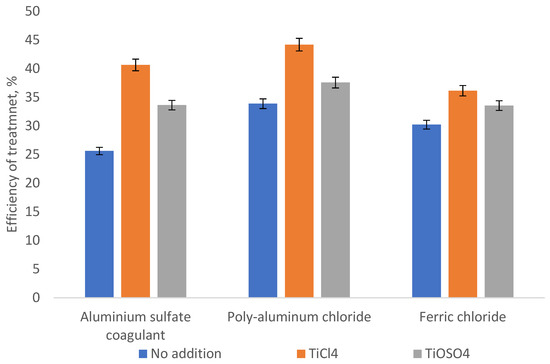
Figure 4.
Efficiency of removing organic compounds (COD) from the alcohol industry wastewater by various coagulants.
The diagrams in Figure 3 and Figure 4 demonstrate that the addition of titanium compounds in an amount of up to 10 wt% allows an increase of the wastewater treatment efficiency from the suspended solids and organic compounds. It should be noted that the greatest positive effect is made by the addition of titanium dioxide that is explained primarily by the primary nucleation processes (neutralizing coagulation) on the surface of negatively charged particles [28,29] as well as by the specific hydrolysis processes [30]. Having considered the relatively low addition (less than 10%) of titanium compounds and a decrease in the effective basic reagent dose by an average of 25–30%, the cost of the purification process can decrease by about 5–8%, depending on the wholesale price for titanium compounds.
Another feature of the food industry wastewater treatment is the low filtration rate of the generated sediments at the additional treatment stage after sedimentation. During the experiments with complex reagents, a change in the structure and shape of the resulting coagulation sludge was noted, to which the authors evaluated the filtration and sedimentation process efficiency when using the pure and complex reagents. A comparison of the precipitation filtration rate is shown in Figure 5.
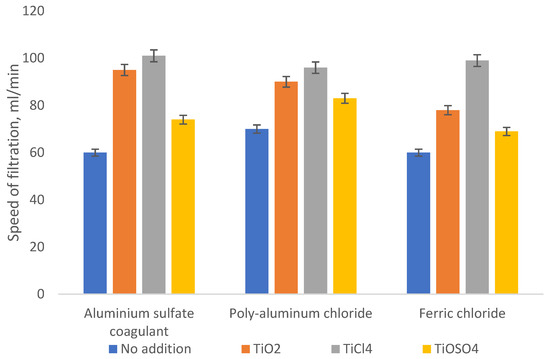
Figure 5.
Filtration rate of coagulation sludge of the alcohol industry wastewater.
Based on the diagram, the availability of titanium compounds in an amount of up to 10 wt% of the conventional coagulant makes it possible to intensify the filtration processes of coagulation sludge by 20–40%. For the iron-containing coagulants, it could be increased by almost 2 times.
Based on the data obtained, the complete efficiency verification of the complex reagents required a reference standard in the form of aluminum sulfate at a dosage of 50 mg (Al2O3/L) with the addition of titanium dioxide (5.0 mg (TiO2/L) as the cheapest reagent option [31]. The cost-based selection of the reagent is primarily due to the significant volumes of wastewater accepted for treatment, and, hence, the operating costs during the arrangement of the reagent facilities, the value of which will be included in the final product cost. The results of coagulation water purification in relation to all studied indicators are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Residual concentrations and treatment efficiency.
Table 2 demonstrates that the use of aluminum sulfate modified with titanium compounds makes it possible to increase the alcoholic industry wastewater treatment efficiency in relation to all the studied parameters that will have a positive effect on the further deep biological treatment process.
The increased efficiency of coagulants containing titanium compounds is explained by the following phenomena:
The adsorption processes on the surface of hydrolysis products of titanium compounds. Therefore, hydroxides (orta- and metatitanic acids) and partially hydrated titanium oxide (xerogel) have a developed surface and are capable of efficient adsorption of organic pollutants during the coagulation process [28,30].
The polycondensation processes and polymerization of highly active polytitanates [15,16] have not only high coagulation activity but also a flocculating effect with the formation of gel-like structures.
The charge neutralization processes on the surface of colloidal particles of pollutants and positively charged forms of aluminum hydroxides leads to the destabilization of the colloidal system and its exit from equilibrium, with quick aggregation and precipitation of the forming structures.
4. Conclusions
According to the studies performed, we obtained information on the possible use of titanium-containing coagulants in the wastewater treatment processes at the enterprises with an alcoholic fermentation stage.
It has been proved that the coagulants based on titanium salts are significantly superior in efficiency to the conventional reagents. The effect of various added titanium compounds on the purification efficiency of the conventional reagents has been established. A positive effect of titanium compounds on the processes of removing insoluble impurities and dissolved organic substances from water has been found. It has been proved that the addition of titanium compounds in an amount of up to 10 wt% allows not only an increase in the treatment efficiency but also a significant reduction of the total coagulant demand that will significantly reduce the treatment process cost. The sludge obtained during the water treatment process, with the complex titanium-containing coagulants, has a voluminous structure that both gives off moisture and is filtered easily.
The resulting hydrolysis products of titanium compounds can be removed from water not only by settling but also by more up-to-date technologies of sediment separation, such as flotation [32,33].
The results obtained will make it possible to reduce the total coagulant demand and further expand the scope of application of titanium-containing reagents in the water treatment processes [34].
Author Contributions
V.B.—systematization of the data obtained, writing an article. E.K.—obtaining samples of complex coagulants, conducting laboratory experiments on water treatment, writing an article, discussing the results. N.K.—study of the initial composition of water, development of the experimental methodology, substantiation of the type of reagents used and dosage of agulants, discussion of the results, writing an article. A.K.—analytical control of the main indicators of water quality before and after treatment, intermediate studies of water in the process of selecting optimal dosages, discussing the results. Y.A.—statistical processing of experimental results, preparation of a literary review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Altech Environmental Consulting Ltd. A Review of Wastewater Management & Best Practices for Dischargers in the Food Processing Sector; Ontario Centre for Environmental Technology Advancement: North York, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Simate, G.S.; Cluett, J.; Iyuke, S.E.; Musapatika, E.T.; Ndlovu, S.; Walubita, L.F.; Alvarez, A.E. The treatment of brewery wastewater for reuse: State of the art. Desalination 2011, 273, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farizoglu, B.; Uzuner, S. The investigation of dairy industry wastewater treatment in a biological high performance membrane system. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 57, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falletti, L.; Conte, L.; Zaggia, A.; Battistini, T.; Garosi, D. Food Industry Wastewater Treatment Plantbased on Flotation and MBBR. Modern Environ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 1, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussas, P.; Tzoupanos, N.; Zouboulis, A. Advances in coagulation/flocculation field: Al- and Fe-based composite coagulation reagents. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 33, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.w.; Kang, L.S. Comparison of Al(III) and Fe(III) Coagulants for Improving Coagulation Effectiveness in Water Treatment June. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2015, 37, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhao, Q. Enhanced algae removal by Ti-based coagulant: Comparison with conventional Al- and Fe-based coagulants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 13147–13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, B.; Cao, B.; Yang, Z.; Yue, Q.; Shon, H.; Kim, J.-H. Comparison of coagulation behavior and floc characteristics of titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) and polyaluminum chloride (PACl) with surface water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, G.; Qi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Phuntsho, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Shon, H.; Yue, Q.; Li, Q. Coagulation and sludge recovery using titanium tetrachloride as coagulant for real water treatment: A comparison against traditional aluminum and iron salts. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gao, B.; Zhang, G.; Phuntsho, S.; Wang, Y.; Yue, Q.; Li, Q.; Shon, H. Comparative study of floc characteristics with titanium tetrachloride against conventional coagulants: Effect of coagulant dose, solution pH, shear force and break-up period. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shon, H.; Phuntsho, S.; Gao, B. Removal of natural organic matter by titanium tetrachloride: The effect of total hardness and ionic strength. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 134, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzin, E.N.; Kruchinina, N.E. Titanium-containing coagulants for found rywaste water treatment. CIS Iron Steel Rev. 2020, 20, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernoberezhsky, J.M.; Minejev, D.J.; Dyagileva, A.B.; Lorenzson, A.V.; Belova, J.V. Isolation of sulphate lignin from aqueous solutions by oxo-titanium sulphate, aluminium sulphate and composite coagulant on their basis. J. Appl. Chem. (Zhurnal Prikladnoy Khimii) 2002, 75, 1730–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Mamchenko, A.V.; Gerasimenko, N.G.; Deshko, I.I.; Pakhar’, T.A. The investigation of the efficiency of coagulants based on titanium when purifying water. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2010, 32, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekli, L.; Eripret, C.; Park, S.; Tabatabai, S.; Vronska, O.; Tamburic, B.; Kim, J.; Shon, H. Coagulation performance and floc characteristics of polytitanium tetrachloride (PTC) compared with titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) and ferric chloride (FeCl3) in algal turbid water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 175, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloux, J.; Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Tijing, L.; Jeong, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, B.; Park, S.; Shon, H. Coagulation performance and floc characteristics of polytitanium tetrachloride and titanium tetrachloride compared with ferric chloride for coal mining wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 152, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Rosli, M.Y.B.; Amr, S.S.A.; Hussain, S. Potential use of titanium tetrachloride as coagulant to treat semi aerobic leachate treatment. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 9, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, K.-J.; Ahn, J.-H. Evaluation of titanium tetrachloride and polytitanium tetrachloride to remove phosphorus from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpalatha, T.N.; Lokeshappa, B. The Use of Alum, Ferric Chloride and Titanium tetrachloride as Coagulants in Treating Landfill Leachate. Int. J.Sci. Eng. Technol. Res. (IJSETR) 2015, 4, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Mashia, M.; Taguchi, Y.; Ohizumi, M.; Koyanagi, S.; Harigai, T. Removal of phosphates from wastewater by titanium(IV) sulfate with precipitation method. Jpn. J. Water Pollut. Res. 1985, 8, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Awad, J.; Sarkar, B.; Chow, C.W.; Duan, J.; van Leeuwen, J. Coagulation of dissolved organic matter in surface water by novel titanium (III) chloride: Mechanistic surface chemical and spectroscopic characterisation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzin, E.N.; Krutchinina, N.E. Purification of circulating and waste water in metallurgical industry using complex coagulants. CIS Iron Steel Rev. 2019, 18, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, H.K.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Zareie, M.H.; Kim, J.B.; Cho, D.L. Preparation and Characterization of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) from Sludge produced by TiCl4 Flocculation with FeCl3, Al2(SO4)3 and Ca(OH)2 Coagulant Aids in Wastewater. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1525–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- ISO 15705:2002. Water Quality—Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand Index (ST-COD)-SMALL-Scale Sealed-Tube Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Waters and Wastewater, 21th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-87553-047-8. [Google Scholar]
- APHA-AWWA-WPFC. Métodos Normalizados Para el Análisis de Agua Potable y Aguas Residuales, 17th ed.; Editorial Díaz de Santos: Madrid, Spain, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zeynalov, O.A.; Kombarova, S.P.; Bagrov, D.V. On the effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on the physiology of living organisms. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2016, 14, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanova, N.A.; Popov, V.V.; Sarkisov, P.D. The Chemistry and Technology of Nanodispersed Oxides; Learner’s Guide; IKTs “Akademkniga”: Moscow, Russia, 2007; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Draginskiy, V.L.; Alekseeva, L.P.; Getmantsev, S.V. Natural Water Treatment Methods and Coagulation; Nauchnoeizdatelstvo: Moscow, Russia, 2005; p. 576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.-H.; Navarrete-López, A.M.; Li, S.; Dixon, D.A.; Gole, J.L. Hydrolysis of TiCl4: Initial Steps in the Production of TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 7561–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzin, E.N.; Kruchinina, N.E.; Gromovykh, P.S.; Tyaglova, Y.V. Coagulants in the Processes of Waste Water Treatment in Dairy Complex Industry. Chem. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikov, A.V.; Savel’ev, D.S.; Kolesnikov, V.A.; Davydkova, T.V. Electroflotation extraction of highly disperse titanium dioxide TiO2 from water solutions of electrolytes. Glass Ceram. 2018, 75, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshalkin, V.P.; Kolesnikov, A.V.; Saveliev, D.S. Analysis of physicochemical efficiency of electroflotation process for removing titanium chloride hydrolysis products from the anthropogenic effluents. Deport Acad. Sci. 2019, 486, 680–684. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Huang, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, S. Potential of titanium coagulants for water and wastewater treatment: Current status and future perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).