Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy of Periodontitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenic Roles of BEVs in Periodontitis and Associated Systemic Diseases
3. BEVs and Periodontitis
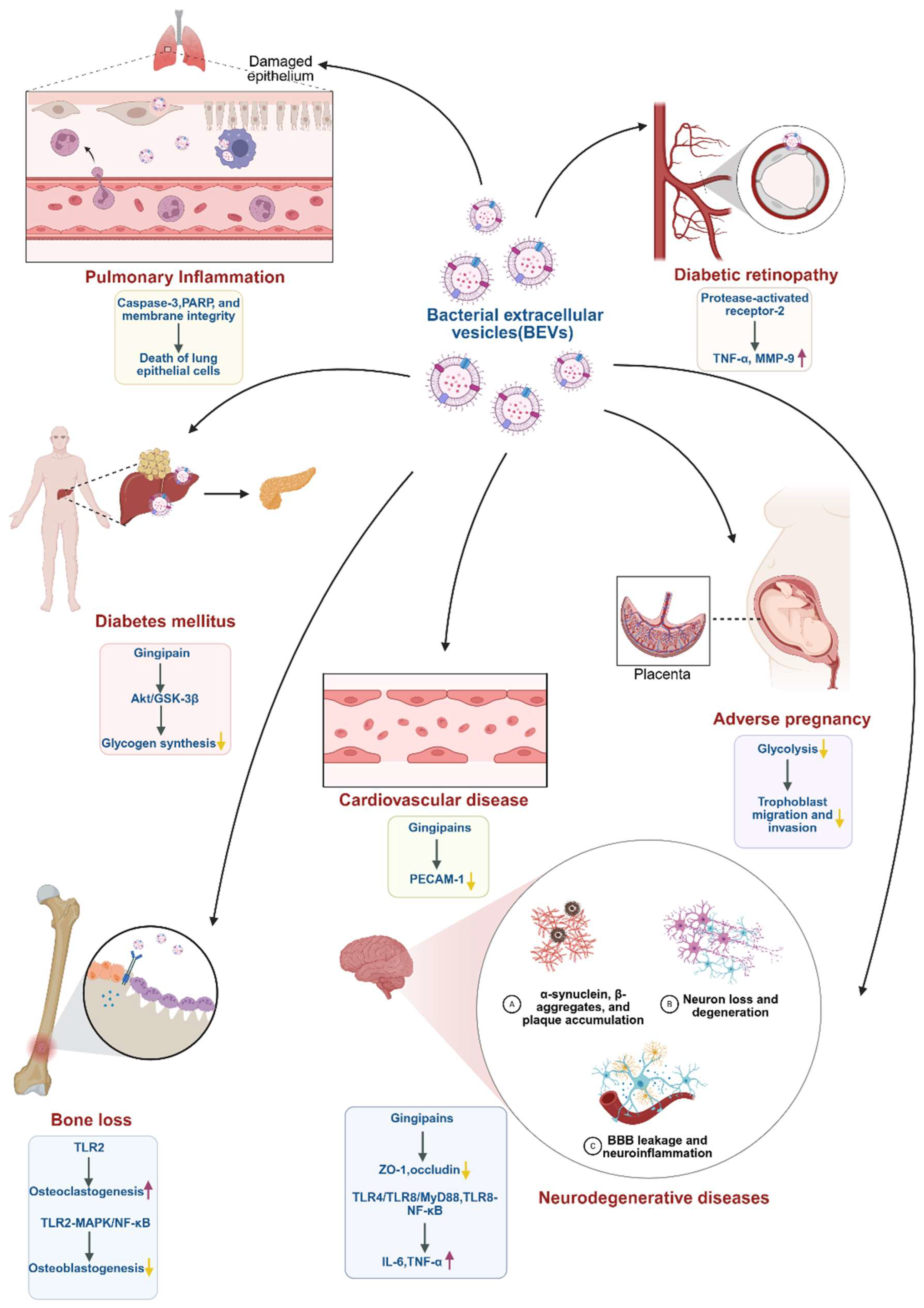
4. BEVs and Associated Systemic Diseases
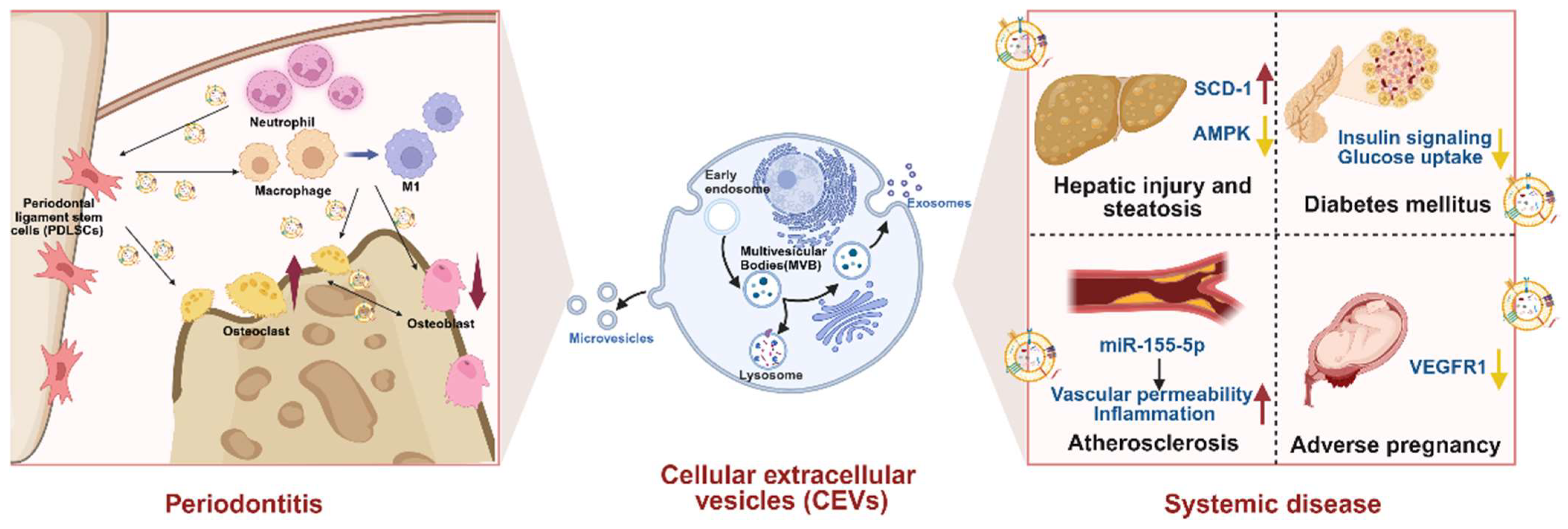
5. Pathogenic Roles of CEVs in Periodontitis and Associated Systemic Diseases
6. CEVs and Periodontitis
7. CEVs and Associated Systemic Diseases
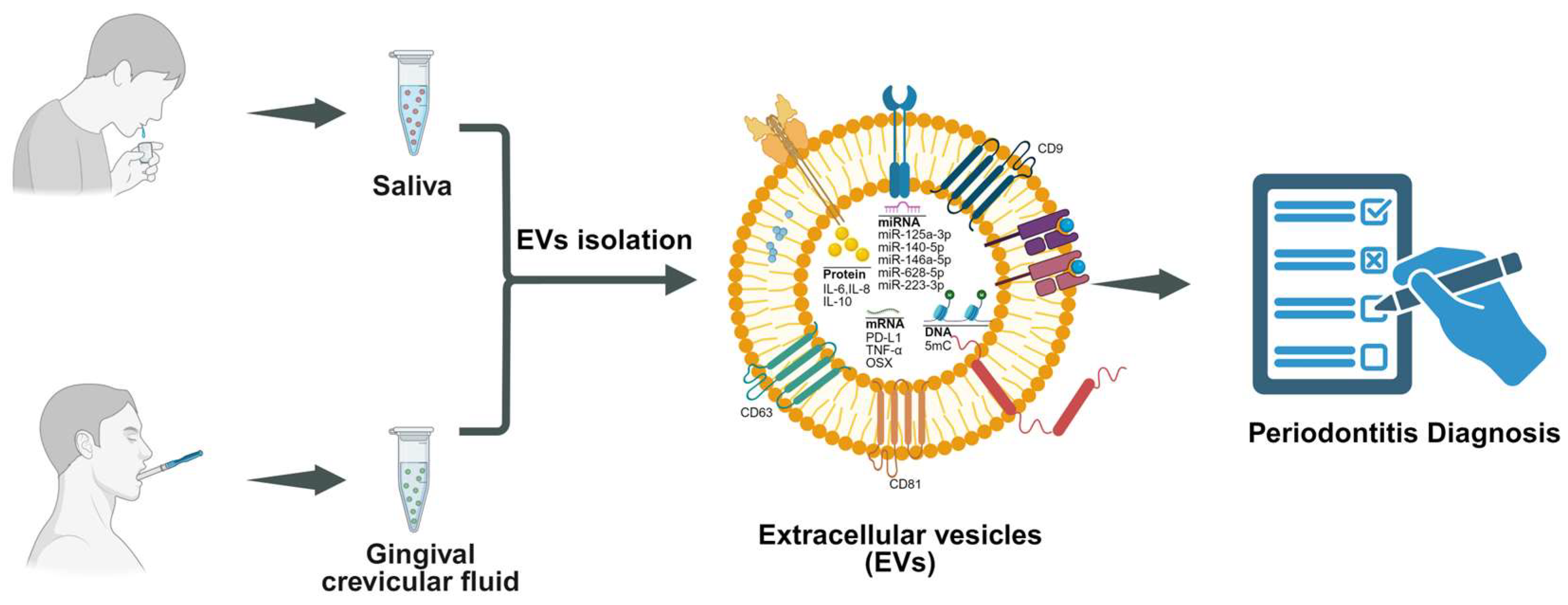
8. Diagnostic Role of EVs in Saliva and GCF
9. EVs in GCF
10. EVs in Saliva
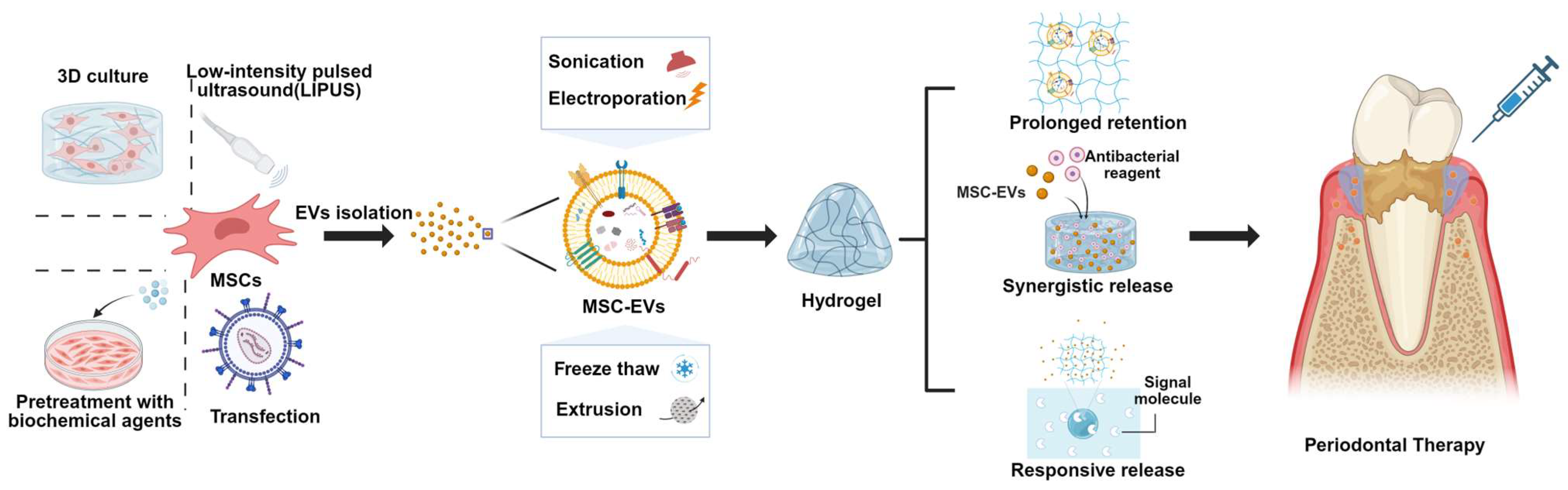
11. Strategies to Improve Therapeutic Function of MSC-EVs in Periodontitis
12. Pretreatment Approaches of Parental Cells
13. Direct Engineering Approaches of EVs
14. MSC-EVs Combined with Biomaterials Promote Periodontal Tissue Regeneration
15. Summary and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EVs | extracellular vesicles |
| GCF | gingival crevicular fluid |
| MSC-EVs | mesenchymal stem cell–derived EVs |
| BEVs | bacterial extracellular vesicles |
| CEVs | cellular extracellular vesicles |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| P. gingivalis | Porphyromonas gingivalis |
| T. forsythia | Tannerella forsythia |
| F. nucleatum | Fusobacterium nucleatum |
| F. alocis | Filifactor alocis |
| A. actinomycetemcomitans | Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans |
| DCs | dendritic cells |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | interleukin-8 |
| CXCL1 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 |
| GM-CSF | granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| TLR2 | toll-like receptor 2 |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| ZO-1 | zonula occludens-1 |
| TLR4 | toll-like receptor 4 |
| TLR8 | toll-like receptor 8 |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| PECAM-1 | platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| MMP-9 | matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| GSK-3β | glycogen synthase kinase-3β |
| CXCR2 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 2 |
| PDLSCs | periodontal ligament stem cells |
| SCD-1 | stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 |
| VEGFR1 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 |
| GDM | gestational diabetes mellitus |
| OSX | osterix |
| IL-10 | interleukin-10 |
| 5mC | 5-methylcytosine |
| PDLCs | periodontal ligament cells |
| FoxO1 | forkhead box protein O1 |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 |
| OXPHOS | oxidative phosphorylation |
| ACSL1 | acyl-CoA synthetase-1 |
| CS | chitosan |
| β-GP | β-sodium glycerophosphate |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
References
- GBD 2021 Oral Disorders Collaborators Trends in the Global, Regional, and National Burden of Oral Conditions from 1990 to 2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 897–910. [CrossRef]
- Trindade, D.; Carvalho, R.; Machado, V.; Chambrone, L.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Prevalence of Periodontitis in Dentate People between 2011 and 2020: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiological Studies. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50, 604–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X. Global Burden of Periodontal Diseases among the Working-Age Population from 1990–2021: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.T.; Babiker, R.; Padmanabhan, V.; Ahmed, A.T.; Chaitanya, N.C.S.K.; Mohammed, R.; Priya, S.P.; Ahmed, A.; El Bahra, S.; Islam, M.S.; et al. The Global Burden of Periodontal Disease: A Narrative Review on Unveiling Socioeconomic and Health Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, R.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Yi, L.; Zeng, M.; Huang, C.; Fu, L. Antibacterial-Osteogenic Integrated Liquid Metal Nanomedicine for Periodontitis Treatment. Cell Biomater. 2025, 1, 100009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.-R.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.-Y.; Gu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yu, X.-Y.; Lai, H.-C.; Tonetti, M.S. Deep Learning Photo Processing for Periodontitis Screening. J. Dent. Res. 2025, 220345251347508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Meng, L.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, X. Development of an Injectable Salicylic Acid-Choline Eutectic Hydrogel for Enhanced Treatment of Periodontitis. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 3788–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y.; Mei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Lai, H.; Tonetti, M.S.; Shen, D. PerioAI: A Digital System for Periodontal Disease Diagnosis from an Intra-Oral Scan and Cone-Beam CT Image. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Fu, L.; Guo, S.; Liang, Y.; Shu, T.; Shao, W.; Xia, H.; Xia, T.; Wang, M. Senescent Fibroblasts Drive FAP/OLN Imbalance Through mTOR Signaling to Exacerbate Inflammation and Bone Resorption in Periodontitis. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2409398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, M.; Masi, S.; Lucenteforte, E.; Bhowruth, D.; Malanima, M.A.; Darbar, U.; Patel, K.; Lim, C.; Curra, C.; Shiehfung, T.; et al. Periodontitis Treatment and Progression of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness: A Randomized Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2025, ehaf555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, J.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, F. Periodontitis-Induced Neuroinflammation Triggers IFITM3-Aβ Axis to Cause Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathology and Cognitive Decline. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhou, W.; Shen, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, R.; Wang, T.; Xie, X.; Hong, B.; Ren, R.; Wang, G.; et al. Profiles of Subgingival Microbiomes and Gingival Crevicular Metabolic Signatures in Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Deng, C.; Niu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S.; Hu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Xu, M.; Huang, Y.; et al. IFN-I-Mediated Neutropoiesis Bias Drives Neutrophil Priming and Inflammatory Comorbidities. Theranostics 2025, 15, 6058–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Fang, C.; Leng, W.-D.; Wu, L.; Li, B.-H.; Wang, X.-H.; Hu, H.; Zeng, X.-T. Oral Microbiota in the Oral-Genitourinary Axis: Identifying Periodontitis as a Potential Risk of Genitourinary Cancers. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Ma, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, W.; Ma, J. Periodontitis Pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis Promotes Pancreatic Tumorigenesis via Neutrophil Elastase from Tumor-Associated Neutrophils. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2073785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinane, D.F.; Bornstein, M.M. Introduction to the Diagnostics in Periodontology and Implant Dentistry Issue. Periodontol 2000 2024, 95, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, D.; Choi, B.-K. Proteome and Immune Responses of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Macrophages Infected with the Periodontal Pathogen Tannerella forsythia. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Tan, M.; Yan, G.; Peng, L. Revolutionizing Lung Cancer Treatment: Harnessing Exosomes as Early Diagnostic Biomarkers, Therapeutics and Nano-Delivery Platforms. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Yu, K.; Niu, Y.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y.; Guo, S.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Essential Roles of Exosome and circRNA_101093 on Ferroptosis Desensitization in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 287–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dou, G.; Zhao, W.; Hu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Impaired Liver Aggravate Alveolar Bone Loss via Shuttle of Fasn in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 33, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.-Q.; Yang, S.; Dong, M.-H.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.-L.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Chu, Y.-H.; Xu, L.-L.; et al. The Foam Cell-Derived Exosomes Exacerbate Ischemic White Matter Injury via Transmitting Metabolic Defects to Microglia. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 1636–1654.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Gao, C.; Jiang, S.; Cai, Q.; Li, R.; Sun, Q.; Xiao, C.; Xu, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhou, H. Fusobacterium nucleatum Outer Membrane Vesicles Activate Autophagy to Promote Oral Cancer Metastasis. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 56, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Long, W.; Yin, Y.; Tan, B.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Ge, S. Outer Membrane Vesicles of Porphyromonas gingivalis: Recent Advances in Pathogenicity and Associated Mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1555868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Ma, Q. SnS2 QDs@MXene Ohmic Junction-Based Surface Plasmon Coupling ECL Sensor to Detect Saliva Exosome for the Diagnosis of Childhood Asthma. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 15878–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Fu, K.; Zhang, Q. Advances of Exosomes-Based Applications in Diagnostic Biomarkers for Dental Disease and Dental Regeneration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 229, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, S.; Guo, S.; Tian, W. Mechanisms and Clinical Application Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontal Regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Ou, Q.; Ren, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Lei, F.; Mao, X.; Shi, S.; Chen, Z.; Teng, W. Engineered Foxp1high Exosomes Ameliorates Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e15712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Xiang, W.; Gong, Y.; Feng, D.; Fang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, R.; et al. Engineering Exosomes Derived from TNF-α Preconditioned IPFP-MSCs Enhance Both Yield and Therapeutic Efficacy for Osteoarthritis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.-K.; Zhang, J.-J.; Gan, D.; Zou, J.-K.; Wu, R.-X.; Tian, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, F.-M.; He, X.-T. Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontal Homeostasis and Their Therapeutic Potential. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, H.B.; Passegger, C.A.; Fleischhacker, D.; Kohl, P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kalawong, R.; Tam-Amersdorfer, C.; Gerstorfer, M.R.; Strahlhofer, J.; Schild-Prüfert, K.; et al. Enrichment of Human IgA-Coated Bacterial Vesicles in Ulcerative Colitis as a Driver of Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Xie, M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Mei, F.; Zhang, K.; Yang, X.; Chen, G.; Yin, Y.; Feng, G.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis Aggravates Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability by Promoting Lipid-Laden Macrophage Necroptosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Kowashi, Y.; Demuth, D.R. Outer Membrane-like Vesicles Secreted by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Are Enriched in Leukotoxin. Microb. Pathog. 2002, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Song, P.; Lin, Q.; Tang, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, J.; Huang, D.; et al. Harnessing Extracellular Vesicles from Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus paracasei for Synergistic Osteoporosis Therapy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 297, 112255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, Q.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Hoecke, L.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. The Tremendous Biomedical Potential of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1173–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, Y.; Hiroshima, Y.; Tada, A.; Murakami, K.; Yoshida, K.; Inagaki, Y.; Kuwahara, T.; Murakami, A.; Fujii, H.; Yumoto, H. Porphyromonas gingivalis Outer Membrane Vesicles Stimulate Gingival Epithelial Cells to Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines via the MAPK and STING Pathways. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lim, Y.; An, S.-J.; Choi, B.-K. Characterization and Immunostimulatory Activity of Extracellular Vesicles from Filifactor alocis. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugsten, H.R.; Kristoffersen, A.K.; Haug, T.M.; Søland, T.M.; Øvstebø, R.; Aass, H.C.D.; Enersen, M.; Galtung, H.K. Isolation, Characterization, and Fibroblast Uptake of Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles from Porphyromonas gingivalis Strains. Microbiologyopen 2023, 12, e1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Teil Espina, M.; Fu, Y.; van der Horst, D.; Hirschfeld, C.; López-Álvarez, M.; Mulder, L.M.; Gscheider, C.; Haider Rubio, A.; Huitema, M.; Becher, D.; et al. Coating and Corruption of Human Neutrophils by Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0075322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Trautwein-Schult, A.; Piersma, S.; Sun, C.; Westra, J.; de Jong, A.; Becher, D.; van Dijl, J.M. Characterization of Outer Membrane Vesicles of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Serotypes a, b and c and Their Interactions with Human Neutrophils. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2025, 319, 151655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitkov, L.; Krunić, J.; Dudek, J.; Bobbili, M.R.; Grillari, J.; Hausegger, B.; Mladenović, I.; Stojanović, N.; Krautgartner, W.D.; Oberthaler, H.; et al. Vesicular Messages from Dental Biofilms for Neutrophils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleetwood, A.J.; Lee, M.K.S.; Singleton, W.; Achuthan, A.; Lee, M.-C.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Cook, A.D.; Murphy, A.J.; Dashper, S.G.; Reynolds, E.C.; et al. Metabolic Remodeling, Inflammasome Activation, and Pyroptosis in Macrophages Stimulated by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Its Outer Membrane Vesicles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.-C.; Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, J.-W.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J. Extracellular RNAs in Periodontopathogenic Outer Membrane Vesicles Promote TNF-α Production in Human Macrophages and Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier in Mice. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 13412–13422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sun, Q.; Cai, Q.; Zhou, H. Outer Membrane Vesicles From Fusobacterium nucleatum Switch M0-Like Macrophages Toward the M1 Phenotype to Destroy Periodontal Tissues in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 815638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, R.; Elashiry, M.; Liu, Y.; El-Awady, A.; Hamrick, M.; Cutler, C.W. Porphyromonas gingivalis Provokes Exosome Secretion and Paracrine Immune Senescence in Bystander Dendritic Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 669989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; An, S.-J.; Choi, B.-K. Activation of Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells and CD4+ T Cell Differentiation by Outer Membrane Vesicles of Periodontal Pathogens. J. Oral Microbiol. 2022, 14, 2123550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-K.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, B.-K.; Kim, H.-H. Filifactor alocis-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inhibit Osteogenesis through TLR2 Signaling. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 35, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Song, M.-K.; Lim, Y.; Jang, J.S.; An, S.-J.; Kim, H.-H.; Choi, B.-K. Effects of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Oral Bacteria on Osteoclast Differentiation and Activation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Shin, Y.-J.; Yoo, J.-W.; Park, H.-S.; Kim, D.-H. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Porphyromonas gingivalis Induce Trigeminal Nerve-Mediated Cognitive Impairment. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 54, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, S.; Kadowaki, T.; Nakanishi, H. Secreted Gingipains from Porphyromonas gingivalis Increase Permeability in Human Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells through Intracellular Degradation of Tight Junction Proteins. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 154, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.Y.; Seok, J.; Kim, S.-J.; Jung, H.-J.; Ryu, K.-Y.; Nakamura, M.; Jang, I.-S.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.-J. Periodontitis Promotes Bacterial Extracellular Vesicle-Induced Neuroinflammation in the Brain and Trigeminal Ganglion. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.Y.; Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J. Delivery of Periodontopathogenic Extracellular Vesicles to Brain Monocytes and Microglial IL-6 Promotion by RNA Cargo. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 596366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, A.; Tomasi, M.; Zanella, I.; Ganfini, L.; Caproni, E.; Fantappiè, L.; Irene, C.; Frattini, L.; Isaac, S.J.; König, E.; et al. Synergistic Protective Activity of Tumor-Specific Epitopes Engineered in Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, C.; Stafford, G.P.; Murdoch, C. Porphyromonas gingivalis Outer Membrane Vesicles Increase Vascular Permeability. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Cao, G.; Dai, D.; Xu, Q.; Ruiz, S.; Shindo, S.; Nakamura, S.; Kawai, T.; Lin, J.; Han, X. Porphyromonas gingivalis Outer Membrane Vesicles Exacerbate Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1167160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Song, M.-K.; Gho, Y.S.; Kim, H.-H.; Choi, B.-K. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from the Periodontal Pathogen Filifactor alocis Induce Systemic Bone Loss through Toll-like Receptor 2. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Shiotsu, N.; Uchida-Fukuhara, Y.; Guo, J.; Weng, Y.; Ikegame, M.; Wang, Z.; Ono, K.; Kamioka, H.; Torii, Y.; et al. Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived from Porphyromonas gingivalis Induced Cell Death with Disruption of Tight Junctions in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 118, 104841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyama, M.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshida, K.; Fujiwara, N.; Ono, K.; Eguchi, T.; Kawai, H.; Guo, J.; Weng, Y.; Haoze, Y.; et al. Outer Membrane Vesicles of Porphyromonas gingivalis Attenuate Insulin Sensitivity by Delivering Gingipains to the Liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, B.; Loureiro, I.; Gliosca, L.; Castagnola, L.; Merech, F.; Gallino, L.; Calo, G.; Sassot, M.; Ramhorst, R.; Vota, D.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis Outer Membrane Vesicles Shape Trophoblast Cell Metabolism Impairing Functions Associated to Adverse Pregnancy Outcome. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 2679–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Chang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, C. Interactions between Extracellular Vesicles and Microbiome in Human Diseases: New Therapeutic Opportunities. iMeta 2023, 2, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.M.; Boulanger, C.M.; Aikawa, E.; Badimon, L.; Barile, L.; Binder, C.J.; Brisson, A.; Buzas, E.; Emanueli, C.; Jansen, F.; et al. Methods for the Identification and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Studies: From Exosomes to Microvesicles. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Chen, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Koutouratsas, V.; Fleishman, J.S.; Huang, C.; Zhang, S. The Uptake of Extracellular Vesicles: Research Progress in Cancer Drug Resistance and Beyond. Drug Resist. Updat. 2025, 79, 101209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixson, A.C.; Dawson, T.R.; Di Vizio, D.; Weaver, A.M. Context-Specific Regulation of Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Cargo Selection. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 454–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadka, Ł.; Eggerstorfer, B.; Buzalewicz, I.; Vraka, C.; Rusak, A.; Godbersen, G.M.; Opalińska, A.; Unterholzner, J.; Ulatowska-Jarża, A.; Philippe, C.; et al. Phenotyping Extracellular Vesicles and Their Serotonin Transporter Cargo in Major Depressive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 389, 119740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, Y.; Hanayama, R.; Akiyoshi, K.; Futaki, S.; Hida, K.; Ichiki, T.; Ishii-Watabe, A.; Kuroda, M.; Maki, K.; Miura, Y.; et al. Quality and Safety Considerations for Therapeutic Products Based on Extracellular Vesicles. Pharm. Res. 2024, 41, 1573–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.-Y.; Zheng, C.-X.; Guo, H.; Fan, S.-Y.; Huang, X.-Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.-X.; Gao, Y.-R.; Liu, A.-Q.; Liu, J.-N.; et al. Inflammation-Triggered Gli1+ Stem Cells Engage with Extracellular Vesicles to Prime Aberrant Neutrophils to Exacerbate Periodontal Immunopathology. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Gao, R.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Xie, Y. Extracellular Vesicles From LPS-Treated PDLSCs Induce NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Periodontitis. Oral Dis. 2025, 31, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fei, D.; Wang, Q. Inflammatory Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Drive M1 Macrophage Polarization via Exosomal miR-143-3p-Mediated Regulation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Signaling. Stem Cells 2023, 41, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, C.; Tang, S.; Zhai, M.; Li, L.; Wei, F.; Ding, G. Small Extracellular Vesicles from Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Primed by Lipopolysaccharide Regulate Macrophage M1 Polarization via miR-433-3p Targeting TLR2/TLR4/NF-κB. Inflammation 2023, 46, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Chou, J.; Wang, Z. Exosomal microRNA-223 from Neutrophil-like Cells Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation of PDLSCs through the cGMP-PKG Signaling Pathway. J. Periodontal Res. 2023, 58, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Yang, T.; Ma, S.; Li, D.; Hu, C.; Tan, J. Macrophage-Derived Mitochondria-Rich Extracellular Vesicles Aggravate Bone Loss in Periodontitis by Disrupting the Mitochondrial Dynamics of BMSCs. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ke, T.; Bian, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Tan, J. Osteoclast-Derived Exosomal miR-5134-5p Interferes with Alveolar Bone Homeostasis by Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 Axis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 3727–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Zheng, W.; Li, S. Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Promotes Osteoclast Differentiation through the Exosomes of Inflammatory Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2022, 40, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Pan, L.; Zhang, H.; Ke, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Tan, J. Osteoblasts-Derived Exosomal lncRNA-MALAT1 Promotes Osteoclastogenesis by Targeting the miR-124/NFATc1 Signaling Axis in Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.-C.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sun, M.-J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Z.-C. Porphyromonas Gingivalis LPS-Stimulated BMSC-Derived Exosome Promotes Osteoclastogenesis via miR-151-3p/PAFAH1B1. Oral Dis. 2025, 31, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L. M2-like Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Inhibit Osteoclastogenesis via Releasing miR-1227-5p. Immunobiology 2025, 230, 152861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Shen, Z.; Xu, R.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.; Fan, C.; Hu, D.; Xing, T. Exosomes Derived from Periodontitis Induce Hepatic Steatosis through the SCD-1/AMPK Signaling Pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, B.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, S.; Duan, D.; Ding, Y. Polymicrobial Infection Induces Adipose Tissue Dysfunction via Gingival Extracellular Vesicles. J. Dent. Res. 2024, 103, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Peng, L.; Gu, F.; Huang, P.; Cheng, B.; Chen, G.; Meng, L.; Bian, Z. Circulating Small Extracellular Vesicles from Patients with Periodontitis Contribute to Development of Insulin Resistance. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1902–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhang, S.-H.; Gao, Z.-R.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Zhang, G.-Y.; et al. miR-124-3p Increases in High Glucose Induced Osteocyte-Derived Exosomes and Regulates Galectin-3 Expression: A Possible Mechanism in Bone Remodeling Alteration in Diabetic Periodontitis. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 14234–14249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-W.; Li, Q.-X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.-R.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wang, M.; Xue, D.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, L. Exosomal miR-155-5p Promote the Occurrence of Carotid Atherosclerosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanai, A.; Fukuhara, Y.; Eguchi, T.; Kawai, H.; Ueda, K.; Ochiai, K.; Ikegame, M.; Okamoto, K.; Okamura, H.P. Gingivalis-Infected Macrophage Extracellular Vesicles Cause Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes. J. Dent. Res. 2025, 104, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xue, Y.; Fan, S.; Hao, J.; Deng, R. Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Macrophages Regulate the Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Exosomes. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; An, J.; Jiao, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y. Novel Insights into the Association of ZJU Index with Periodontitis in US Participants: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2025, 24, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Deng, H.; Sun, K.; Huang, Z.; Wei, S.; Lin, Y.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y. Prevalence of Chronic Periodontitis in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis and Its Correlation with Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Complications. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, N.; Llevenes, P.; Denis, G.V. Exosomes as Novel Biomarkers in Metabolic Disease and Obesity-Related Cancers. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Huo, M.; Chu, H.; Zhuang, X.; Deng, G.; Li, W.; Wei, H.; Zeng, L.; He, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Exosome circATP8A1 Induces Macrophage M2 Polarization by Regulating the miR-1-3p/STAT6 Axis to Promote Gastric Cancer Progression. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, H.; Deng, W.; Lin, W.; Li, K.; Xiong, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, F.; Ma, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Evaluation of Salivary Exosomal Chimeric GOLM1-NAA35 RNA as a Potential Biomarker in Esophageal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3035–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, N. Salivary Exosomes Exacerbate Colitis by Bridging the Oral Cavity and Intestine. iScience 2024, 27, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Zhao, L.; Petrovic, B.; Li, A.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; You, M. Recent Advances of Oral Fluids-Based Point-of-Care Testing Platforms for Oral Disease Diagnosis. Transl. Dent. Res. 2025, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, L.; Durante, K.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. A Signature of Saliva-Derived Exosomal Small RNAs as Predicting Biomarker for Esophageal Carcinoma: A Multicenter Prospective Study. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.; Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Salivary Extracellular MicroRNAs for Early Detection and Prognostication of Esophageal Cancer: A Clinical Study. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 932–945.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro Padilla, A.; Weber Aracena, L.; Realini Fuentes, O.; Albers Busquetts, D.; Hernández Ríos, M.; Ramírez Lobos, V.; Pascual La Rocca, A.; Nart Molina, J.; Beltrán Varas, V.; Acuña-Gallardo, S.; et al. Molecular Signatures of Extracellular Vesicles in Oral Fluids of Periodontitis Patients. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, T.; Khurshid, Z.; Rehman, A.; Imran, E.; Srivastava, K.C.; Shrivastava, D. Gingival Crevicular Fluid (GCF): A Diagnostic Tool for the Detection of Periodontal Health and Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Bartold, P.M.; Ivanovski, S. The Emerging Role of Small Extracellular Vesicles in Saliva and Gingival Crevicular Fluid as Diagnostics for Periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2022, 57, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizgier, M.L.; Nardocci, G.; Ramírez, V.; Bendek, M.J.; Hernández, M.; Rojas, C.; Herrera, D.; Kantarci, A.; Kemp, M.W.; Illanes, S.E.; et al. Proteomic Insights Into Gingival Crevicular Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontitis and Gestational Diabetes: An Exploratory Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2025, 52, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Tsuruya, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Jin, Z.; Yamazaki-Takai, M.; Takai, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Ogata, Y. Changes in the Components of Salivary Exosomes Due to Initial Periodontal Therapy. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2023, 53, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nik Mohamed Kamal, N.N.S.; Awang, R.A.R.; Mohamad, S.; Shahidan, W.N.S. Plasma- and Saliva Exosome Profile Reveals a Distinct MicroRNA Signature in Chronic Periodontitis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 587381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Bartold, P.M.; Salomon, C.; Ivanovski, S. Salivary Small Extracellular Vesicles Associated miRNAs in Periodontal Status—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhou, K.; Sun, M.; Shu, R.; Qian, J.; Xie, Y. The miR-223-3p Regulates Pyroptosis Through NLRP3-Caspase 1-GSDMD Signal Axis in Periodontitis. Inflammation 2021, 44, 2531–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Y.; Xiong, X.; Li, K.; Yao, Z.; Dong, H.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, D.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; Zhang, H. Detection of Exosomal PD-L1 RNA in Saliva of Patients with Periodontitis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Jiao, K.; Moran, C.S.; Liaw, A.; Zhou, Y.; Salomon, C.; Ivanovski, S. TNF-α and OSX mRNA of Salivary Small Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontitis: A Pilot Study. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2023, 29, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of Salivary Exosomal Proteins in Young Adults with Severe Periodontitis. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Seneviratne, C.J.; Palma, C.; Rice, G.; Salomon, C.; Khanabdali, R.; Ivanovski, S.; Han, P. Immunoaffinity-Enriched Salivary Small Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontitis. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids 2023, 4, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Bartold, P.M.; Salomon, C.; Ivanovski, S. Salivary Outer Membrane Vesicles and DNA Methylation of Small Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for Periodontal Status: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobón-Arroyave, S.I.; Celis-Mejía, N.; Córdoba-Hidalgo, M.P.; Isaza-Guzmán, D.M. Decreased Salivary Concentration of CD9 and CD81 Exosome-Related Tetraspanins May Be Associated with the Periodontal Clinical Status. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Huo, F.; Guo, S.; Tian, W. Lipopolysaccharide-Preconditioned Dental Follicle Stem Cells Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Treating Periodontitis via Reactive Oxygen Species/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling-Mediated Antioxidant Effect. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; Cai, Z.; Hou, R.; et al. Giant Panda Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Dermal Fibroblast Proliferation and Wound Healing. Stem Cells 2025, sxaf051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Tang, J.; Dou, L.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Mao, H.; Yang, D. Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Regulate Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenesis in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells and Promote the Repair of Experimental Periodontitis in Rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4683–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Guo, J.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, W.; He, X.; Wu, M.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Zhou, M. SHED Aggregate Derived Exosomes-Shuttled miR-222 Promotes the Angiogenic Properties of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells and Enhances Periodontal Regeneration. Transl. Dent. Res. 2025, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, J.; Li, A.; Li, Y.; Pei, D. BMSC-Derived Exosomal CircHIPK3 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Cells via Mitophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.-J.; Chen, Y.; Deng, D.-K.; Li, X.; Chen, F.-M.; He, X.-T. Critical Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontal Disease and Regeneration. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2025, 14, szae092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, R. Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontitis: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Pang, J.; Ma, C. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontitis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1151322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Liu, T.; Zhao, G.; Liang, Y.; Li, P.; Li, F.; Li, Q.; Fu, J.; Zhong, C.; Zou, X.; et al. A Novel Exosome-Based Multifunctional Nanocomposite Platform Driven by Photothermal-Controlled Release System for Repair of Skin Injury. J. Control. Release 2024, 371, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; You, Z.; Shao, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; et al. PlexinA1 (PLXNA1) as a Novel Scaffold Protein for the Engineering of Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, J.; Pillarisetti, S.; Junnuthula, V.; Saha, M.; Hwang, S.R.; Park, I.-K.; Lee, Y.-K. Hybrid Exosomes, Exosome-like Nanovesicles and Engineered Exosomes for Therapeutic Applications. J. Control. Release 2023, 353, 1127–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liao, C.; Xiao, L.; Xiang, M.; Guan, X.; Liu, J. Metformin Enhances the Therapeutic Effects of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells on Periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Chu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, M.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y. Effect of Psoralen on the Regulation of Osteogenic Differentiation Induced by Periodontal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Hum. Cell 2023, 36, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, Z.; Zheng, W.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Xiao, J.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Huang, W. Gallic Acid Ameliorates the Inflammatory State of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells and Promotes Pro-Osteodifferentiation Capabilities of Inflammatory Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Life 2022, 12, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Song, L.; Wang, Q.; Ding, P.; Tian, W.; Guo, S. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Lipopolysaccharide-Preconditioned Dental Follicle Cells Inhibit Cell Apoptosis and Alveolar Bone Loss in Periodontitis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2024, 162, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Guo, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Huo, F.; Ding, Y.; Tian, W. Small Extracellular Vesicles from Lipopolysaccharide-Preconditioned Dental Follicle Cells Promote Periodontal Regeneration in an Inflammatory Microenvironment. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 5797–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Lin, C.; Yang, S.; Rong, S.; Wei, J.; Zhao, T.; Peng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. FoxO1-Overexpressed Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from hPDLSCs Promote Periodontal Tissue Regeneration by Reducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Regulate Osteogenesis and Inflammation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 8751–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, D.; Li, R.; Li, R.; Teng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zou, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, C. Genetically Engineered CXCR4-Modified Exosomes for Delivery of miR-126 Mimics to Macrophages Alleviate Periodontitis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Tian, B.-M.; Xia, Y.; Xia, Y.-L.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Tan, Y.-Z.; Chen, F.-M. Exosomes Derived from P2X7 Receptor Gene-Modified Cells Rescue Inflammation-Compromised Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells from Dysfunction. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 1414–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Deng, L.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Mu, Y. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Loaded with miR-26a through the Novel Immunomodulatory Peptide DP7-C Can Promote Osteogenesis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 45, 905–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Tang, N.; Guo, J.; Deng, L.; Yuan, L.; Zeng, L.; Yang, L.; Mu, Y. Immunomodulatory Peptide DP7-C Mediates Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miR-21b to Promote Bone Regeneration via the SOCS1/JAK2/STAT3 Axis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 253, 114709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Kuang, S.; He, F.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Z.; Qin, W.; Lin, Z.; Huang, S. Exosomes Derived from 3D-Cultured MSCs Improve Therapeutic Effects in Periodontitis and Experimental Colitis and Restore the Th17 Cell/Treg Balance in Inflamed Periodontium. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, M.; Jing, X.; Xu, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Chen, D.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulated with Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Alleviate Inflammation-Induced Bone Loss in a Mouse Model of Periodontitis. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 1613–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, B.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Xu, W.; Qian, H. Extracellular Vesicles: A Bright Star of Nanomedicine. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, Q.; Chai, Y.; Rong, R.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. An Anti-CD19-Exosome Delivery System Navigates the Blood-Brain Barrier for Targeting of Central Nervous System Lymphoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehryab, F.; Rabbani, S.; Shahhosseini, S.; Shekari, F.; Fatahi, Y.; Baharvand, H.; Haeri, A. Exosomes as a Next-Generation Drug Delivery System: An Update on Drug Loading Approaches, Characterization, and Clinical Application Challenges. Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Hong, S.; Xia, Y.; Li, X.; He, X.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, K.; Mao, L. Melatonin Engineering M2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Mediate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Immune Reprogramming for Periodontitis Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, R.; Da, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, B.; He, X. Aspirin Loaded Extracellular Vesicles Inhibit Inflammation of Macrophages via Switching Metabolic Phenotype in Periodontitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 667, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; He, X.N.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.Z.; Li, B. Study of the methotrexate loaded extracellular vesicles in the treatment of experimental periodontitis in mice. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2024, 59, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Tan, G.; Shi, Y.; Tao, D.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Jin, F.; He, X. Methotrexate Loaded Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Periodontitis by Suppressing ACSL1 and Promoting Anti-Inflammatory Macrophage. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 182, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Kuang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Qin, W.; Shi, X.; Lin, Z. Chitosan Hydrogel Incorporated with Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Alleviates Periodontitis in Mice via a Macrophage-Dependent Mechanism. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, Z.; Huang, L.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Erythropoietin-Stimulated Macrophage-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Chitosan Hydrogel Rescue BMSCs Fate by Targeting EGFR to Alleviate Inflammatory Bone Loss in Periodontitis. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2500554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Su, J. Synergistic Effects of Shed-Derived Exosomes, Cu2+, and an Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel on Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Osteogenic Activity for Periodontal Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 33053–33069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles Laden Oxygen-Releasing Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Enhanced Antibacterial Therapy against Anaerobe-Induced Periodontitis Alveolar Bone Defect. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 932–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarubova, J.; Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Zhang, X.; Ansari, S.; Li, S.; Moshaverinia, A. Engineered Delivery of Dental Stem-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Periodontal Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2102593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elieh-Ali-Komi, D.; Shafaghat, F.; Alipoor, S.D.; Kazemi, T.; Atiakshin, D.; Pyatilova, P.; Maurer, M. Immunomodulatory Significance of Mast Cell Exosomes (MC-EXOs) in Immune Response Coordination. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 68, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Lei, J. The Updated Role of Exosomal Proteins in the Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.-Y.; Xu, J.-L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.-N.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, Y. Exosomal circRHCG Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis via Facilitating M2 Polarization through TFEB Ubiquitination and Degradation. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Zheng, J.; Lu, Y.; Lin, P.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, R.; Mai, Z.; Guo, B.; Zhao, X. New Frontiers in Salivary Extracellular Vesicles: Transforming Diagnostics, Monitoring, and Therapeutics in Oral and Systemic Diseases. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, R.; Houghton, M.J.; Barber, E.; Williamson, G. Structure-Function Relationships in (Poly)Phenol-Enzyme Binding: Direct Inhibition of Human Salivary and Pancreatic α-Amylases. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, J.; Luo, Q.; Luo, H. Sensitive Detection of Multiple Blood Biomarkers via Immunomagnetic Exosomal PCR for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eabm3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, B.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, Z.-L.; Yu, H.; Qin, S.-F.; Lv, L.-L.; et al. Comprehensive Comparison of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cultured with Fetal Bovine Serum and Human Platelet Lysate. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 12366–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Bai, Y.; Wu, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X. PTEN/PI3K/AKT Pathway Activation with Hypoxia-Induced Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell Exosome for Angiogenesis-Based Diabetic Skin Reconstruction. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 32, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Wu, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Yi, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. A New Frontier in Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis Treatment: Exosome-Based Therapeutic Strategy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1074536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, N.; Liu, P.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y. Emerging Technologies towards Extracellular Vesicles Large-Scale Production. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 52, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiest, E.F.; Zubair, A.C. Challenges of Manufacturing Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Regenerative Medicine. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiest, E.F.; Zubair, A.C. Generation of Current Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Automated Bioreactors. Biology 2025, 14, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
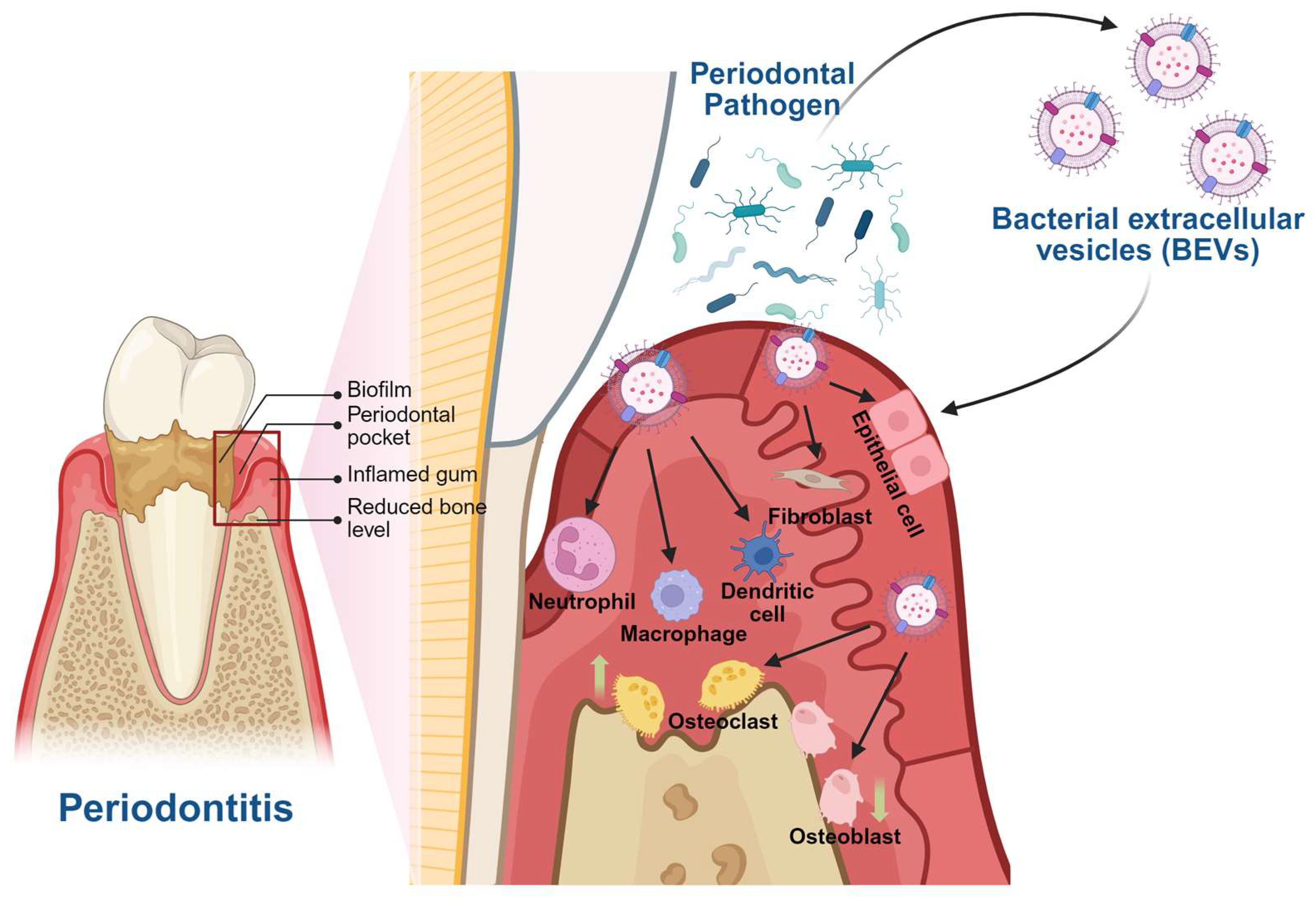
| BEVs and Periodontitis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV Source | Cargo | Target Cell | Pathway | Readouts | Model | Strength of Evidence | Ref. |
| P. gingivalis | Gingipains | Gingival epithelial cells | MAPK(Erk1/2, JNK, p38) and STING | ↑IL-6 and ↑IL-8 | In vitro gingival epithelial cells assay | In vitro | [35] |
| F. alocis | Lipoproteins, FACIN, and autolysins | Monocytes and oral keratinocyte cells | / | ↑CCL1, ↑CCL2, ↑MIP-1, ↑CCL5, ↑CXCL1, ↑CXCL10, ↑ICAM-1, ↑IL-1β, ↑IL-1ra, ↑IL-6, ↑IL-8, ↑MIF, ↑SerpinE, and ↑TNF-α in human monocytes and ↑CXCL1, ↑G-CSF, ↑GM-CSF, ↑IL-6, and ↑IL-8 in human oral keratinocyte cells | In vitro monocytes and oral keratinocyte cells assay | In vitro | [36] |
| P. gingivalis | Gingipains | Oral fibroblasts | / | The internalization of Porphyromonas gingivalis bEVs by oral fibroblasts ↓Fibroblast proliferation and growth | In vitro oral gingival fibroblasts assay | In vitro | [37] |
| P. gingivalis | Gingipains | Neutrophils | / | ↑LL-37, ↑MPO | In vitro neutrophils assay | In vitro | [38] |
| A. actinomycetemcomitans | / | Neutrophils | / | The formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) | In vitro neutrophils assay | In vitro | [39] |
| Dental biofilm | LPS | Neutrophils | LPS/caspase-4/11/Gasdermin D | The formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) | In vitro neutrophils assay Human periodontal tissues, blood, and biofilm samples | In vitro→Human | [40] |
| P. gingivalis | / | Macrophages | Caspase-1 | ↑TNFα, ↑IL-12p70, ↑IL-6, ↑IL-10, ↑IFNβ, ↑nitric oxide, ↑IL-1β, and ↑IL-18 The activation of the inflammasome and pyroptotic cell death pathways | In vitro macrophages assay | In vitro | [41] |
| T. forsythia | BspA, sialidase, GroEL, and various bacterial lipoproteins | Macrophages | TLR2 | ↑Pro-inflammatory cytokines and ↑inflammatory mediators | In vitro macrophages assay | In vitro | [17] |
| F. nucleatum | / | Macrophages and gingival fibroblasts | / | Polarization of macrophages toward the proinflammatory M1 phenotype ↑TNF-α,↑iNOS, and ↑LDH | In vitro macrophages and gingival fibroblasts assay In vivo mouse periodontitis model | In vitro→Animal | [43] |
| Red complex pathogens | / | Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) | / | ↑MHC class II, ↑CD80, ↑CD86, ↑CD40, ↑IL-1, ↑IL-6, ↑IL-23, and ↑IL-12p70 Maturation of BMDCs | In vitro BMDCs assay | In vitro | [45] |
| F. alocis | Bone-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BMSCs) | TLR2 | ↑RANKL/OPG | In vitro BMSCs assay | In vitro | [46] | |
| Periodontal pathogens and oral commensal | Lipoproteins and LPS | Osteoclasts | TLR2 | ↑Expression of osteoclastogenic cytokines ↑Osteoclast differentiation | In vitro osteoclast precursors assay | In vitro | [47] |
| BEVs and Associated Systemic Diseases | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | EV Source | Cargo | Target Cell | Pathway | Readouts | Model | Strength of Evidence | Ref. |
| Neurodegenerative diseases | P. gingivalis | Neurotoxic GPs, inflammation-inducible fimbria protein and LPS | BV2, SH-SY5Y, and peritoneal macrophages | / | ↑TNF-α expression in the periodontal and hippocampus tissues ↑Hippocampal GP+Iba1+, ↑LPS+Iba1+, and ↑NF-κB+Iba1+ cell numbers ↓BDNF, ↓claudin-5, ↓N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor expression, and ↓BDNF+NeuN+ cell number ↑Blood LPS and TNF-α | In vitro BV2, SH-SY5Y, and peritoneal macrophages assay In vivo mouse models of cognitive impairment induced by P.g or pEV | In vitro→Animal | [48] |
| Gingipains | hCMEC/D3 | PAR2 | ↓ZO-1 and ↓occludin ↑Permeability of hCMEC/D3 cell monolayer | In vitro hCMEC/D3 assay | In vitro | [49] | ||
| A. actinomycetemcomitans | RNA | Trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons | TLR4, TLR8, MyD88 | ↑IL-6 and ↑TNF-α | In vivo mouse periodontitis model | Animal | [50] | |
| exRNA | Macrophages | TLR8, NF-κB | ↑TNF-α | In vitro macrophages assay In vivo mouse heart injection OMV model | In vitro→Animal | [42] | ||
| Microglia | NF-κB | ↑IL-6 | In vitro BV2 assay In vivo imaging model after OMV injection in mice | In vitro→Animal | [51] | |||
| Cardiovascular disease | P. gingivalis | Gingipains | Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) | ↓PECAM-1 ↑Vascular permeability | In vitro HMEC-1 cells assay In vivo zebrafish OMV injection model | In vitro→Animal | [53] | |
| Diabetic retinopathy | P. gingivalis | / | Human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMECs) | PAR-2 | ↑HRMECs inflammatory factors and ↑reactive oxygen species production Mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and altered endothelial permeability | In vitro HRMECs assay In vivo mouse diabetes model | In vitro→Animal | [54] |
| Bone loss | F. alocis | / | Committed osteoclast precursors (COCs) | TLR2 | ↑Proinflammatory cytokines, ↑Osteoclastogenesis, and ↑bone resorption | In vivo mice intraperitoneal injection of OMVs model | Animal | [55] |
| / | Bone-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BMSCs) | MAPK, NF-κB | ↑RANKL/OPG | In vitro BMSCs assay | In vitro | [46] | ||
| Pneumonia | P. gingivalis | / | Lung epithelial cells | / | Caspase-3 activation and PARP cleavage ↓Tight junction proteins | In vitro lung epithelial cells | In vitro | [56] |
| Diabetes | P. gingivalis | Gingipains | HepG2 | Insulin-induced Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) | ↓Insulin sensitivity | In vitro HepG2 assay In vivo mouse intraperitoneal injection of OMVs model | In vitro→Animal | [57] |
| Adverse pregnancy | P. gingivalis | / | Trophoblast cells | / | ↓Glycolytic pathways in the placenta, ↓placental, ↓fetal weight and ↓GLUT1 | In vitro the first trimester trophoblast cells assay In vivo mouse pregnancy model | In vitro→Animal | [58] |
| CEVs and Periodontitis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EV Source | Cargo | Target Cell | Pathway | Readouts | Model | Strength of Evidence | Ref. |
| Gli1+ MSCs | / | Neutrophils | CXCL1–CXCR2 axis and NF-κB | ↑ROS Aberrant activation of neutrophils | In vitro neutrophils assay In vivo mouse periodontitis model | In vitro→Animal | [65] |
| Periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) | / | Macrophages and periodontal ligament fibroblasts (PLFs) | / | Polarization of macrophages toward the proinflammatory M1 phenotype NLRP3 inflammasome activation | In vitro macrophages and PLFs assay In vivo mouse periodontitis model | In vitro→Animal | [66] |
| miR-143-3p | Macrophages | PI3K/AKT/NF-κB | Polarization of macrophages toward the proinflammatory M1 phenotype | In vitro macrophages assay In vivo mouse periodontitis model | In vitro→Animal | [67] | |
| microRNA-433-3p | Macrophages | TLR2/TLR4/NF-κB p65 | Polarization of macrophages toward the proinflammatory M1 phenotype | In vitro macrophages assay Human periodontal ligament stem cells isolation | In vitro→Human | [68] | |
| Neutrophils | miR-223 | Periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) | cGMP-PKG | Inhibit osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs | In vitro PDLSCs assay | In vitro | [69] |
| Macrophages | mitochondria | Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) | LCN2/OMA1/OPA1 | ↑LCN2 Mitochondrial morphological changes in BMSCs Osteogenesis impairment in BMSCs | In vitro BMSCs assay In vivo mouse periodontitis model | In vitro→Animal | [70] |
| Osteoclasts | miR-5134-5p | Osteoblasts | JAK2/STAT3 | ↑miR-5134-5p ↓Runx2, ↓p-JAK2, and ↓p-STAT3 ↑Inflammatory factors mRNA expression ↓BV/TV ↑Cementoenamel junction and alveolar bone crest distance Morphological disruption of periodontal tissue Inflammatory cell infiltration | In vitro osteoblasts assay In vivo mouse periodontitis model | In vitro→Animal | [71] |
| Periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) | RANKL, TNF-α | Macrophages | NF-κB | ↑Osteoclast differentiation | In vitro macrophages assay | In vitro | [72] |
| Osteoblasts | lnc-MALAT1 | Macrophages | miR-124/NFATc1 | The acceleration of the progression of osteoclastogenesis | In vitro macrophages assay | In vitro | [73] |
| Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) | miR-151-3p | Macrophages | miR-151-3p/PAFAH1B1 | ↑Osteoclastogenesis | In vitro macrophages assay | In vitro | [74] |
| M2-like macrophages | miR-1227-5p | Osteoclasts | / | ↑miR-1227-5p ↓Osteoclast differentiation | In vitro Osteoclasts assay | In vitro | [75] |
| CEVs and Associated Systemic Diseases | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | EV Source | Cargo | Target Cell | Pathway | Readouts | Model | Strength of Evidence | Ref. |
| Hepatic steatosis | Macrophages and human periodontal ligament fibroblasts (hPDLFs) | / | HepG2 | SCD-1/AMPK | ↑SCD-1 and ↑Hepatocyte adipogenesis ↓AMPK | In vitro HepG2 assay In vivo rat periodontitis model | In vitro→Animal | [76] |
| Adipose tissue dysfunction | Gingival cells | / | Adipocytes | / | WAT dysfunction ↓Levels of AKT phosphorylation, ↓adiponectin, ↓leptin, and ↓genes associated with adipogenesis and lipogenesis | In vivo mouse oral and intraperitoneal injection models | Animal | [77] |
| Diabetes | Plasma | / | HepG2 | Insulin signaling | ↓p-AKT, ↓p-GSK3β, and ↓hepatic glycogen content | In vitro HepG2 assay In vivo rat diabetic model Human blood sample collection | In vitro→Animal→Human | [78] |
| Osteocytes | miR-124-3p, Gal-3, and IL-6 | Osteoblasts | / | The regulation of Gal-3 expression of osteoblasts | In vitro Osteoblasts assay In vivo rat diabetic model and periodontitis model Human saliva collection | In vitro→Animal→Human | [79] | |
| Carotid atherosclerosis | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) | miR-155-5p | Human aortic endothelial cells(HAECs) | / | ↑Angiogenesis and ↑permeability of HAECs ↑Expression of angiogenesis, ↑permeability, and ↑inflammation genes The acceleration of the occurrence of carotid atherosclerosis | In vitro HAECs assay In vivo mouse intravenous injection of OMVs model Human tissue samples | In vitro→Animal→Human | [80] |
| Adverse pregnancy | Macrophages | / | Human umbilical vascular endothelial cells(HUVECs) | / | ↓VEGFR1 Disoriented blood vessel alignment Impaired angiogenesis | In vitro HUVECs assay In vivo mouse intravenous injection of OMVs model | In vitro→Animal | [81] |
| Aspect | What’s New | What’s Controversial |
|---|---|---|
| BEVs | Systematic summary of BEVs promoting periodontitis via epithelial barrier disruption, immune-inflammatory amplification, osteogenesis inhibition, and osteoclastogenesis promotion, as well as their involvement in periodontitis-associated systemic diseases. | Mechanisms of BEVs crossing biological barriers, and their contribution to periodontitis and systemic diseases remain debated. |
| CEVs | Emphasis on periodontal cell derived EVs under inflammatory conditions, which promote periodontitis by aggravating inflammation and disturbing bone homeostasis, and further contribute to systemic disease progression. | Mechanisms of CEVs-mediated effects in periodontitis and related systemic diseases are still insufficiently defined. |
| EVs for Diagnosis | Updated summary of recent studies on GCF- and saliva-derived EVs as non-invasive biomarkers for detection, staging, and risk assessment. | The diagnostic biomarkers derived from GCF and saliva EVs for periodontitis have not yet been clearly identified. |
| EVs for Therapy | Highlight recent engineering strategies (pretreatment of parental cells, direct EV modification, biomaterial-based delivery) to improve EVs’ therapeutic function and achieve targeting and controlled release, thereby enhancing periodontal tissue regeneration. | Clinical translation of EVs is limited by low yield, rapid clearance, poor tissue specificity, and unpredictable cargo loading. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Wang, M.; Teng, R.; Li, A. Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy of Periodontitis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102521
Fu Y, Wang M, Teng R, Li A. Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy of Periodontitis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102521
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yiru, Mengmeng Wang, Rui Teng, and Ang Li. 2025. "Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy of Periodontitis" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102521
APA StyleFu, Y., Wang, M., Teng, R., & Li, A. (2025). Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy of Periodontitis. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102521




