Abstract
Background/Objectives: Retinal ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury is a common mechanism in glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusion, leading to progressive loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). This study investigates the regulatory role of miR-21-5p and its interaction with Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) in retinal I/R injury. Methods: An acute intraocular hypertension (AIH) rat model was used to induce retinal I/R. The interaction between miR-21-5p and STAT3 was examined by dual-luciferase reporter assays. miR-21-5p and STAT3 expression were quantified by qRT-PCR and Western blotting. Retinal morphology, microglial polarization, and RGC survival were assessed by H&E staining and immunofluorescence. In vitro, microglia and RGCs were subjected to oxygen–glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R), and microglial-conditioned media (MCM) were applied to RGCs. Results: (1) miR-21-5p ameliorated AIH-induced retinal damage in vivo. (2) Overexpression of miR-21-5p inhibits M1 polarization of RM cultured in vitro. (3) MCM from miR-21-5p-overexpressing microglia attenuated OGD/R-induced RGC death. (4) miR-21-5p downregulates STAT3 expression to inhibit RM M1 polarization. (5) miR-21-5p down-regulation of STAT3 levels inhibits M1 polarization and reduces apoptosis of RGCs in retinal microglia of AIH rats. Conclusions: miR-21-5p alleviates retinal I/R injury by restraining microglial M1 polarization through direct repression of STAT3, thereby promoting RGC survival. These findings identify the miR-21-5p/STAT3 axis as a potential therapeutic target for ischemic retinal diseases.
1. Introduction
Retinal ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) leads to loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and neuroinflammation, which is an important pathophysiological basis for various retinal diseases like glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusion, potentially leading to irreversible vision loss or blindness [1,2]. Neuroinflammation is a key driver of ischemic retinal pathology, wherein glial cells respond to injury by producing inflammatory factors that adversely affect RGC function and viability [3,4,5].
Microglia, the resident macrophages of the central nervous system (CNS), maintain homeostasis and, upon activation, release inflammatory mediators that drive optic nerve inflammation [6,7]. Microglia can polarize into either M1 or M2 phenotypes depending on external stimuli. M1 polarization, typically induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or interferon-γ (IFN-γ), activates Toll-like receptor signaling and promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide (NO), and reactive oxygen species (ROS), ultimately leading to neuronal injury [8,9,10,11]. M2 polarization is typically induced by interleukin-4 (IL-4) or interleukin-13 (IL-13) and is characterized by the upregulation of anti-inflammatory mediators such as IL-10 and reparative factors including Arg-1, which contribute to extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, debris clearance, and tissue repair [12,13]. Previous studies have demonstrated that retinal I/R injury drives M1 polarization of retinal microglia, which in turn amplifies retinal inflammation and contributes to the loss of RGCs [14]. Therefore, elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of microglial polarization and developing strategies to suppress M1 polarization under I/R conditions are crucial for preventing retinal inflammation and treating ischemic retinal diseases.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous single-stranded non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by binding to the 3′ untranslated regions (3′-UTRs) of target mRNAs, thereby participating in diverse biological processes including apoptosis, inflammation, and cell polarization [15,16,17]. miR-21-5p, one of the earliest identified microRNAs, is markedly upregulated in models of neural injury and has been shown to play a pivotal regulatory role in the progression of neurological diseases. In traumatic nerve injury, neuronal extracellular vesicles are enriched with miR-21-5p, which promotes neuroprotection by inhibiting autophagy, enhancing neuronal survival, supporting axonal growth, and facilitating regeneration [18,19,20,21,22]. In retinal I/R injury and glaucoma models, miR-21-5p has been reported to facilitate aqueous humor outflow by activating the eNOS/MMP9 signaling pathway in trabecular meshwork (TM) and Schlemm’s canal (SC) cells, thereby lowering intraocular pressure [23]. Furthermore, miR-21-5p has been shown to attenuate I/R-induced pyroptosis of RGCs by inhibiting activation of the NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway, thereby mitigating inflammation and preserving visual function [4,24]. Moreover, evidence indicates that miR-21-5p facilitates M2 polarization of macrophages by targeting PDCD4 and modulating the SPRY2/ERK signaling pathway [25,26]. Although miR-21-5p has been implicated in alleviating retinal I/R injury [27], the underlying mechanisms remain insufficiently defined. In particular, whether it exerts protective effects by modulating retinal microglial polarization and thereby regulating neuroinflammation has not been systematically examined.
This study established rat models of acute intraocular hypertension (AIH) and cellular oxygen–glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) to investigate miR-21-5p expression in retina and rat microglia (RM). TargetScan prediction and dual-luciferase reporter assays identified Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) as a direct target of miR-21-5p. STAT3 is a transcription factor that regulates proliferation, survival, differentiation, and metabolism [28]. Upon activation, STAT3 induces the expression of cell cycle- and survival-related genes, including Cyclin D1, Survivin, and c-Myc, while driving the transcription of downstream inflammation-related genes such as IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and COX-2, thereby amplifying inflammatory cascades during I/R injury [28,29,30,31]. STAT3 activation is regulated by phosphorylation, which is markedly elevated under I/R conditions; phosphorylated STAT3 (p-STAT3) translocates into the nucleus and promotes the transcription of downstream target genes, thereby amplifying inflammatory responses and aggravating tissue injury [32,33,34]. Inhibition of STAT3 signaling has been demonstrated to attenuate neuronal injury and restrain macrophage activation [35], thereby identifying STAT3 as a promising therapeutic target in I/R.
To test causality, RM were transfected with an miR-21-5p mimic or treated with the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201, and, in vivo, rats received intravitreal delivery of an miR-21-5p agomir or S3I-201 before AIH-induced retinal I/R. These complementary gain- and loss-of-function manipulations demonstrate that miR-21-5p alleviates retinal I/R injury by restraining STAT3-dependent pro-inflammatory signaling, nominating the miR-21-5p/STAT3 axis as a potential therapeutic target.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rat Model of AIH
Male Sprague Dawley rats (6–8 weeks; 200–250 g) obtained from the Experimental Animal Centre of Central South University were used. Animals were housed in a temperature- and humidity-controlled room on a 12 h light/dark cycle with ad libitum access to food and water.
Rats were randomly divided into two groups: the normal control group (without I/R surgery) and the AIH group. The acute intraocular hypertension (AIH) model was established as described previously [36]. Rats were anesthetized via intraperitoneal injection of 2% pentobarbital sodium (0.2 mL/100 g). The periocular skin was cleaned with povidone–iodine, followed by topical anesthesia with proparacaine ophthalmic solution and pharmacologic mydriasis with tropicamide/phenylephrine. Intraocular pressure was raised to 120 mmHg for 1 h via anterior chamber cannulation with a 30-gauge saline-connected needle under general anesthesia, followed by reperfusion; rats were euthanized 3 days post-reperfusion.
2.2. Intravitreal Injection
A total of 40 male SD rats (6–8 weeks old, 200–250 g) were randomly assigned to five groups (n = 8 per group): normal control (CON), AIH, miR-21-5p agomir+AIH, miR-21-5p agomir negative control (NC)+AIH, and S3I-201+AIH.
miR-21-5p agomir (chemically modified miR-21-5p mimic, 2 µL at 50 µM per eye) and its negative control (scrambled sequence) were synthesized by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). S3I-201(0.2 mg/kg) was purchased from Selleck Chemicals (Houston, TX, USA). Intravitreal injections were performed 30 min before AIH induction. Injections were made 1 mm posterior to the limbus between two vortex veins using a 30-gauge needle, as described previously [37].
2.3. Tissue Preparation
Following euthanasia, both globes were enucleated and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) at 4 °C for 24 h, followed by graded ethanol dehydration (70%, 80%, 90%, 95%, and 100%; 1 h each), clearing in ethanol–xylene and xylene, and paraffin infiltration according to standard histological protocols [38]. Paraffin blocks were sectioned at 5 µm, mounted on glass slides, labeled, and stored at room temperature (RT). Retinal sections adjacent to the optic nerve head were used for subsequent histological analyses.
In a separate cohort, retinas were rapidly dissected after euthanasia, placed into pre-chilled microcentrifuge tubes on ice, and stored at −80 °C until use.
2.4. Cell Culture and Transfection
Rat microglia (RM; BNCC360237) were obtained from BeNa Culture Collection (BeNa Culture Collection, Beijing, China). Rat retinal precursor cells (R28) were obtained from the Affiliated Eye Hospital of Nanchang University (Nanchang, China). RM were maintained in high-glucose DMEM (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco). R28 cells were cultured in low-glucose DMEM (Gibco) containing 10% FBS. All cells were incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2.
RM at 70–80% confluence were transfected using Advanced Series High-Efficiency Transfection Reagent with miR-21-5p mimic (50 nM) or mimic NC (50 nM); for gain-of-function, a STAT3 overexpression plasmid (Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was used. S3I-201 (30 µM) was applied for pharmacologic inhibition. Vendors for the miRNA reagents and S3I-201 are as described above. Cells were harvested 24 h after treatment.
2.5. Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion (OGD/R) and Conditioned Medium Transfer
RM and R28 cells were switched to glucose-free DMEM (Gibco) and placed in a hypoxia chamber (1% O2, 5% CO2, 94% N2) at 37 °C for 4 h (RM) or 3 h (R28). After OGD, cultures were returned to normoxia (humidified 5% CO2 at 37 °C) for reperfusion. Microglia-conditioned media (MCM; CON, OGD/R, miR-21-5p mimic NC+OGD/R, miR-21-5p mimic+OGD/R) were collected from RM after the indicated treatments and immediately applied to R28 at the end of OGD; R28 were then incubated with the indicated MCM for 2 h under standard culture conditions.
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol (TSP401; DynaTech Biotechnology, Shanghai, China). For miRNA quantification, miR-21-5p was reverse-transcribed with a stem-loop RT primer; for mRNA analysis, STAT3 and β-actin (Actb) were reverse-transcribed using the RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (K1622; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Primers (miR-21-5p stem-loop/forward/reverse; U6; Actb; STAT3) were synthesized by DynaProbiotics (Shanghai, China). U6 served as the endogenous control for miRNA assays, and β-actin served as the endogenous control for mRNA assays. Relative expression was calculated by the 2^−ΔΔCt method. Primer sequences (5′→3′): miR-21-5p, stem-loop RT: GTCGTATCCAGTG-CAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATAC-GACTCAACA, forward: GCGCGTAGCTTATCAGACTGA, reverse: AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT; U6, forward: CTGTGGAGAAGGGAGGGTGAGAG, reverse: AGGTGAGAAGGAGGTGCAGACTG; β-actin (Actb), forward: TACTGCCCTGGCTCCTAGCA, reverse: TGGACAGTGAGGCCAGGATAG; STAT3, forward: AGGGCTTCTCGTTCTGGGTCTG, reverse: CTCCCGCTCCTTGCTGATGAAAC; IL-1β, forward: GACTTCACCATGGAACCCGT, reverse: GGAGACTGCCCATTCTCGAC; TNF-α, forward: CATCCGTTCTCTACCCAGCC, reverse: AATTCTGAGCCCGGAGTTGG; IL-6, forward: GCCCACCAGGAACGAAAGTC, reverse: ACTGGCTGGAAGTCTCTTGCG.
2.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
Paraffin-embedded retinal sections (5 µm) were deparaffinized in xylene (2 × 10 min), rehydrated through graded ethanol (100%, 95%, 70%, 5 min each) to water, stained with hematoxylin (5 min) and eosin (2 min), then dehydrated through 95% and 100% ethanol (5 min each), cleared in xylene (2 × 5 min) and coverslipped [39]. Images were acquired under a light microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan), and retinal morphology was evaluated in a blinded manner.
2.8. Immunofluorescence
2.8.1. Immunofluorescence of Retinal Paraffin Sections
Deparaffinization and rehydration were performed as described in Section 2.7 (H&E), followed by transfer to distilled water. Sections were then subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval in sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) and blocked with 5% goat serum for 1 h at RT [40]. Sections were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibodies: Iba1 (mouse, 1:1000, Huabio, Hangzhou, China, Cat# RT1316, RRID: AB_3698022), CD206 (rabbit, 1:500, Proteintech, Wuhan, China, Cat# 18704-1-AP, RRID: AB_10597232), CD86 (rabbit, 1:500, Proteintech, Cat# 83523-4-RR, RRID: AB_3671150), and RBPMS (rabbit, 1:500, Abcam, Cambridge, UK, Cat# ab152101, RRID: AB_2923082). After PBS washes (3 × 5 min), sections were incubated 1 h at RT with FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Servicebio, Wuhan, China, Cat# GB21303) and Cy3-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Servicebio, Cat# GB22301). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (10 µL, 5 min, RT), and sections were mounted with antifade mounting medium (Beyotime, Shanghai, China, Cat# P0126). Images were acquired on a Nikon fluorescence microscope. Microglial polarization was quantified as the percentage of Iba1+ cells co-expressing CD86 (M1) or CD206 (M2). Fluorescence intensity and cell counts were measured with ImageJ (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA). At least three fields per coverslip and three independent experiments were analyzed.
2.8.2. Cellular Immunofluorescence
Cells were washed with PBS, fixed in 4% PFA for 20 min, washed again with PBS, permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 20 min, and blocked with 5% goat serum for 1 h at RT [41]. Cells were incubated overnight at 4 °C with CD206 and CD86 (same primary antibodies and dilutions as in Section 2.8.1), followed by the same secondary antibodies, DAPI counterstain, and mounting procedures as described above.
2.9. TUNEL Staining
Apoptosis in retinal sections and R28 cells was assessed using a TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China, Cat# C1090) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Images were acquired on a Nikon fluorescence microscope. TUNEL-positive cells and total nuclei (DAPI) were quantified per field by blinded observers using ImageJ (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA), and the percentage of apoptotic cells was calculated as TUNEL+/DAPI × 100%.
2.10. PI Staining
Cells were fixed in 4% PFA for 15 min, washed with PBS, and incubated with propidium iodide (PI; Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany, Cat# P4170) working solution for 15 min protected from light. After PBS washes, cells were counterstained with DAPI (5 min, RT), mounted with antifade medium, and imaged using a Nikon fluorescence microscope [42]. PI-positive cells and total nuclei were quantified with ImageJ by blinded observers.
2.11. Western Blotting (WB)
Retinal tissues were homogenized on ice in RIPA buffer (Beyotime, Shanghai, China, P0013B) supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Cwbio, Beijing, China, CW2200S; CW2383S), centrifuged (12,000× g, 20 min, 4 °C), and the supernatants were collected for protein quantification by BCA (Beyotime, P0010S). Cultured cells were washed with ice-cold PBS, lysed on ice in the same RIPA buffer with inhibitors, centrifuged under identical conditions, and supernatants were quantified by BCA. Equal amounts of protein (20 µg per lane) were resolved on 10% SDS–PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Membranes were blocked with 5% nonfat milk for 1 h at room temperature (RT), incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4 °C, washed with TBST (3 × 10 min), and then incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies (1:4000; Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, PA, USA, 315-005-003 and 211-009-109) for 2 h at RT. Signals were developed by chemiluminescence and quantified with ImageJ; target proteins were normalized to actin and expressed relative to control.
Primary antibodies: CD206 (Rabbit, 1:1000, Proteintech, Wuhan, China, Cat# 18704-1-AP, RRID: AB_10597232), CD86 (Rabbit, 1:2000, Huabio, Hangzhou, China Cat# ET1606-50, RRID: AB_3069745), Arg-1 (Rabbit, 1:5000, Proteintech, Wuhan, China, Cat# 16001-1-AP, RRID: AB_2289842), IL-1β (Rabbit, 1:2000, G-Biosciences, St. Louis, MO, USA, Cat# ITT5201, RRID: AB_3662796), Bcl-2 (Rabbit, 1:500, WanLeiBio, Shenyang, China, Cat# WL01556, RRID: AB_2904235), Bax (Rabbit, 1:500, WanLeiBio Cat# WL01637, RRID: AB_2904236), STAT3 (Rabbit, 1:1000, WanLeiBio Cat# WL01836, RRID: AB_3665484), Phospho-Stat3 (Rabbit, 1:2000, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA, Cat# 73533, RRID: AB_3675996), actin (Mouse, 1:10000, Cohesion Biosciences, London, UK, Cat# CPA9100, RRID: AB_3697272), TNF-α (Rabbit, 1:2000, Proteintech Cat# 80258-6-RR, RRID: AB_3670472), IL-6 (Rabbit, 1:2000, Proteintech Cat# 21865-1-AP, RRID: AB_11142677).
2.12. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
HEK293T cells were co-transfected with STAT3 3′-UTR reporter plasmids—wild type (WT) or mutant (MUT)—together with miR-21-5p mimic or mimic negative control (NC). After 24 h, luciferase activity was measured using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Firefly luciferase signals were normalized to Renilla luciferase to control for transfection efficiency. Data are presented as relative luciferase activity (Firefly/Renilla). Each condition was tested in technical triplicates, and the experiment was repeated in at least three independent biological replicates.
2.13. Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SD. For comparisons between two groups, unpaired two-tailed t-tests were used. For ≥3 groups, one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test was performed. n denotes independent biological replicates (typically n = 3 per group; technical triplicates where indicated). Analyses were conducted in GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. miR-21-5p Ameliorated AIH-Induced Retinal Damage In Vivo
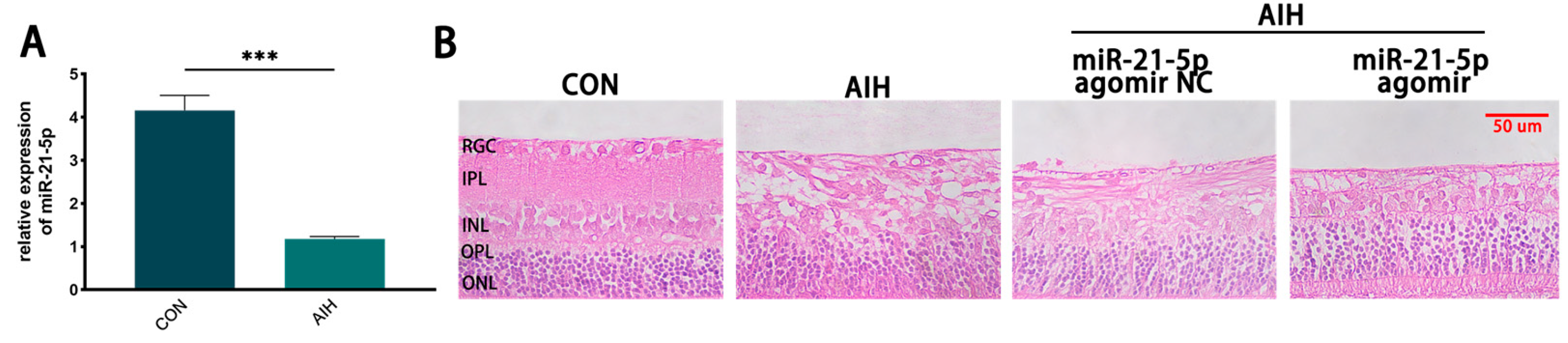
Using an AIH model to induce retinal I/R injury, intraocular pressure was elevated to 120 mmHg for 1 h. Rats were euthanized 3 days after reperfusion, and retinal miR-21-5p levels were quantified by qRT–PCR. Compared with the CON group, miR-21-5p expression was significantly decreased in AIH retinas (p < 0.001; Figure 1A). H&E staining showed marked retinal structural damage in the AIH group, which was mitigated by pretreatment with miR-21-5p agomir (miR-21-5p agomir + AIH; Figure 1B). Collectively, these data indicate that miR-21-5p exerts a protective effect in AIH-induced retinal I/R injury.
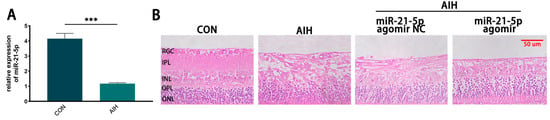
Figure 1.
miR-21-5p alleviates AIH-induced retinal damage in rats. (A) qRT–PCR analysis of retinal miR-21-5p under AIH; expression was significantly reduced versus CON (*** p < 0.001; unpaired two-tailed t-test; n = 3; data = mean ± SD). (B) H&E staining of rat retina. Scale bar = 50 μm. AIH and miR-21-5p agomir NC + AIH showed marked structural disruption relative to CON, whereas miR-21-5p agomir + AIH exhibited attenuated histopathological damage.
3.2. Overexpression of miR-21-5p Inhibits M1 Polarization of RM Cultured In Vitro
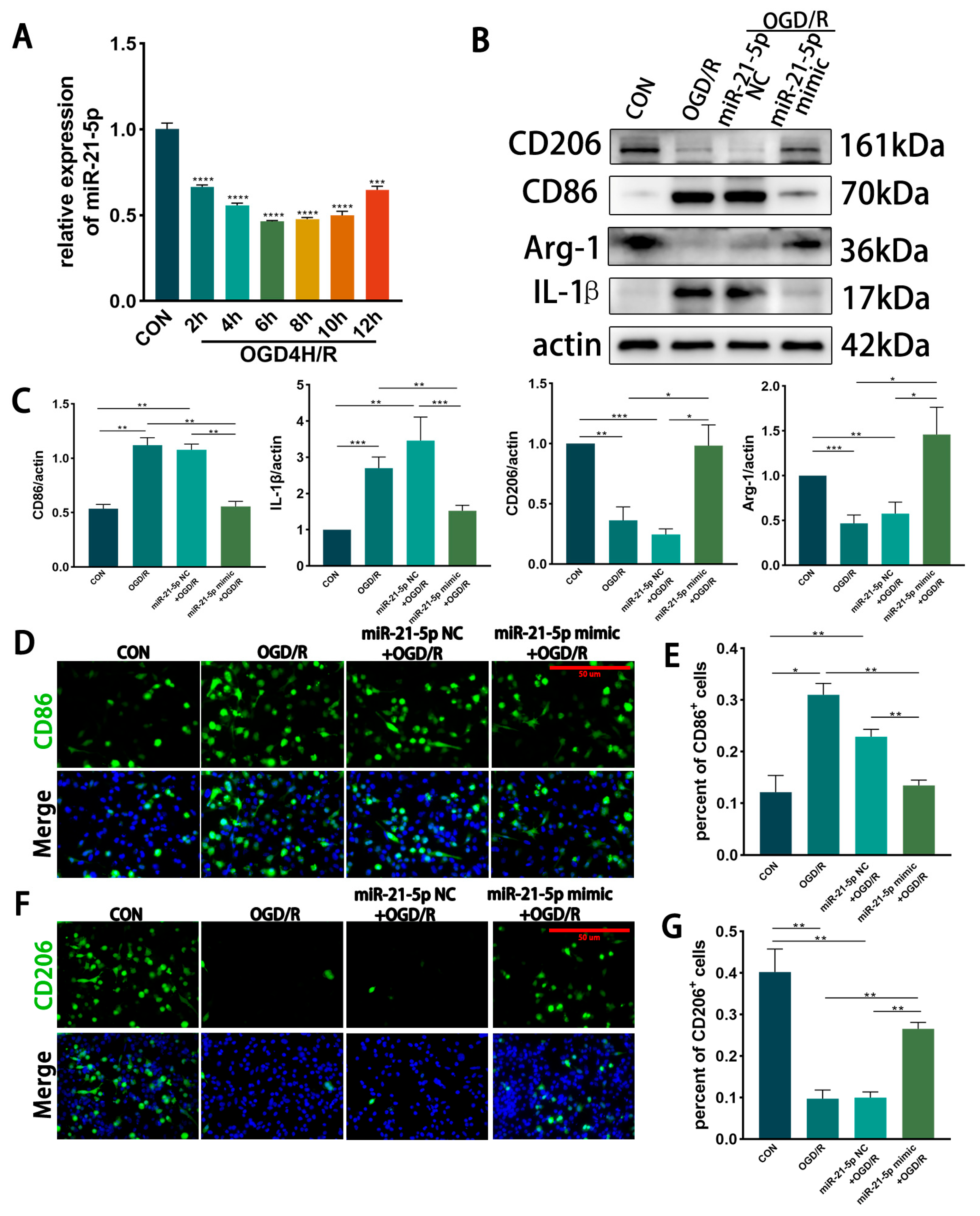
In vitro time course of miR-21-5p under OGD/R. RM were subjected to OGD for 4 h followed by reoxygenation, and miR-21-5p expression was measured at different recovery time points by qRT-PCR. Expression levels progressively decreased during reoxygenation, reaching a nadir at 6 h and 8 h (p < 0.001 vs. CON). By 12 h, expression partially rebounded but remained significantly lower than control levels (Figure 2A). These in vitro kinetics were consistent with the in vivo findings. Based on this profile, we selected OGD4 h/R6 h for subsequent experiments, as it represented the time point with the most pronounced reduction.
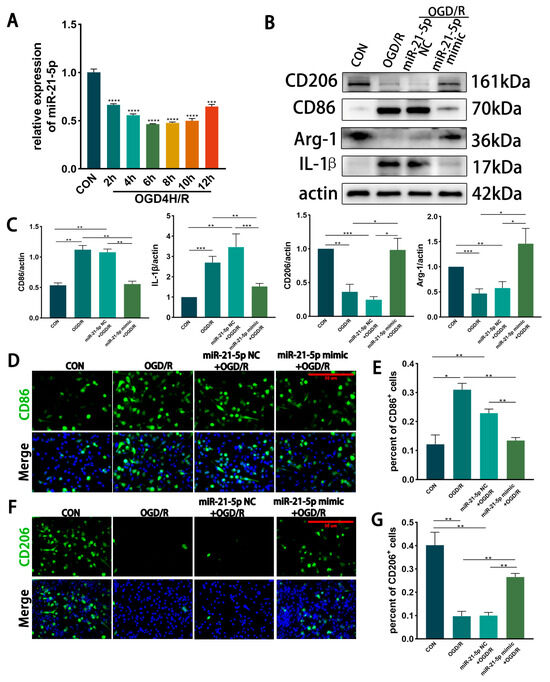
Figure 2.
Overexpression of miR-21-5p inhibits M1 polarization of RM under OGD/R conditions. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of miR-21-5p expression in RM at different recovery time points after 4 h OGD. Expression decreased progressively, reaching the lowest levels at 6 h and 8 h, and partially rebounded at 12 h but remained below CON (*** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA; n = 3). (B,C) WB detection and densitometric quantification of polarization-associated proteins. Compared with CON, the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups showed elevated CD86 and IL-1β and reduced CD206 and Arg-1. In contrast, the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group exhibited reduced CD86 and IL-1β and increased CD206 and Arg-1 (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA; n = 3). (D–G) Immunofluorescence analysis of RM polarization. (D,E) CD86+ RM (M1-like, green) and nuclei (DAPI, blue). (F,G) CD206+ RM (M2-like, green) and nuclei (DAPI, blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. Quantification shows a higher proportion of CD86+ and a lower proportion of CD206+ RM in the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups compared with CON. The miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group displayed a lower percentage of CD86+ RM and a higher percentage of CD206+ RM relative to both OGD/R controls (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA; n = 3).
Effect of miR-21-5p overexpression on RM polarization under OGD/R. RM cells were transfected with miR-21-5p mimics, with scramble mimics serving as negative controls. After OGD4 h/R6 h, WB and immunofluorescence analyses were performed. Compared with CON, both the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups showed markedly increased expression of the M1 marker CD86 and the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β, along with reduced expression of the M2 marker CD206 and the anti-inflammatory factor Arg-1 (Figure 2B,C). In contrast, the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group exhibited significantly lower protein levels of CD86 and IL-1β while CD206 and Arg-1 expression were upregulated (Figure 2B,C).
Immunofluorescence results further confirmed that the proportion of CD86+ (M1-like) RM was higher and the proportion of CD206+ (M2-like) RM was lower in the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups compared with CON, whereas the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group displayed a lower percentage of CD86+ RM and a higher percentage of CD206+ RM relative to both OGD/R controls (Figure 2D–G). Together, these results demonstrate that miR-21-5p overexpression inhibits M1 polarization while promoting M2 polarization of RM under OGD/R conditions, thereby downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulating anti-inflammatory factors.
3.3. MCM from miR-21-5p-Overexpressing Microglia Attenuated OGD/R-Induced R28 Death
Building on the observation that miR-21-5p suppresses M1 polarization of RM under OGD/R, we next examined its impact on neuronal survival. R28 cells were subjected to OGD for 3 h [43], after which the culture medium was replaced with MCM collected from the groups described in Result 2 (CON, OGD/R, miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R, and miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R), followed by 2 h of reoxygenation.
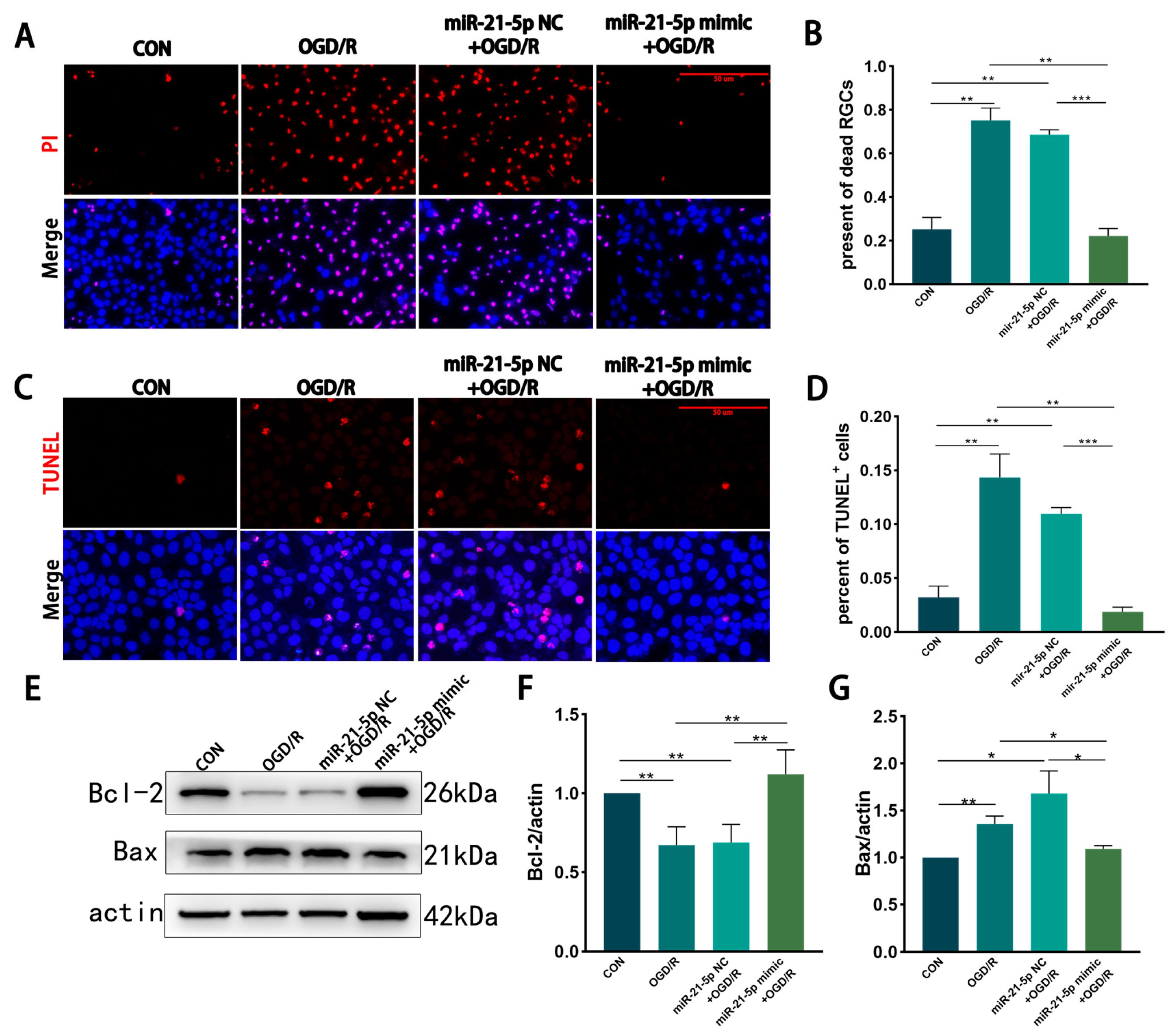
PI and TUNEL staining revealed that, compared with MCM from CON RM, MCM from the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups significantly increased necrosis and apoptosis of R28 cells (Figure 3A–D). In contrast, MCM from the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group markedly reduced necrotic and apoptotic cell percentages compared with both OGD/R control groups (Figure 3A–D). WB analysis further showed that R28 cells exposed to MCM from the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group displayed higher expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and lower expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax than those treated with MCM from the OGD/R or miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups (Figure 3E–G). Collectively, these results indicate that RM overexpressing miR-21-5p alleviate OGD/R-induced necrosis and apoptosis in R28 cells, thereby exerting a neuroprotective effect.
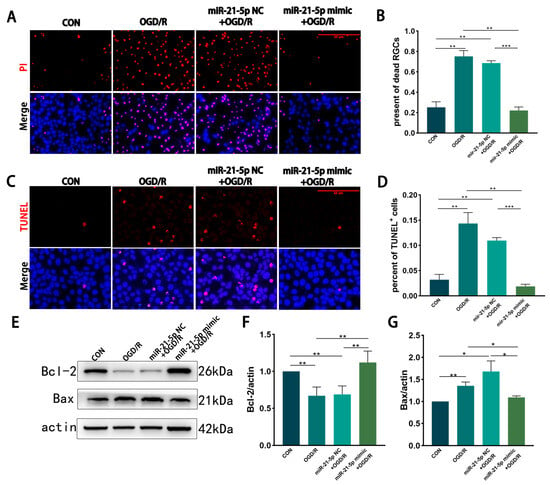
Figure 3.
RM-conditioned medium with miR-21-5p overexpression under OGD/R conditions promotes R28 cells survival in vitro. (A,B) PI staining showing necrosis of R28 cells after OGD (3 h) and reoxygenation (2 h) in different RM-conditioned media. PI (red), nuclei (DAPI, blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. Quantification indicates increased PI+ cells in the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups compared with CON, whereas the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group showed fewer PI+ cells (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA; n = 3). (C,D) TUNEL staining of apoptotic R28 cells. TUNEL (red), nuclei (DAPI, blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. Quantification shows elevated TUNEL+ cells in the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups versus CON, while the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group exhibited a lower proportion (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA; n = 3). (E–G) WB analysis of apoptosis-related proteins. Representative blots and densitometry of Bcl-2 and Bax. Compared with CON, the OGD/R and miR-21-5p NC + OGD/R groups showed reduced Bcl-2 and increased Bax, whereas the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group displayed higher Bcl-2 and lower Bax (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA; n = 3).
3.4. miR-21-5p Downregulates STAT3 Expression to Inhibit RM M1 Polarization
In summary, overexpression of miR-21-5p under OGD/R conditions suppressed M1 polarization while promoting M2 polarization of RM, thereby reducing RGC necrosis and apoptosis. To clarify the mechanism, we next examined whether this effect involves STAT3 signaling.
3.4.1. STAT3 Is the Direct Target Gene of miR-21-5p
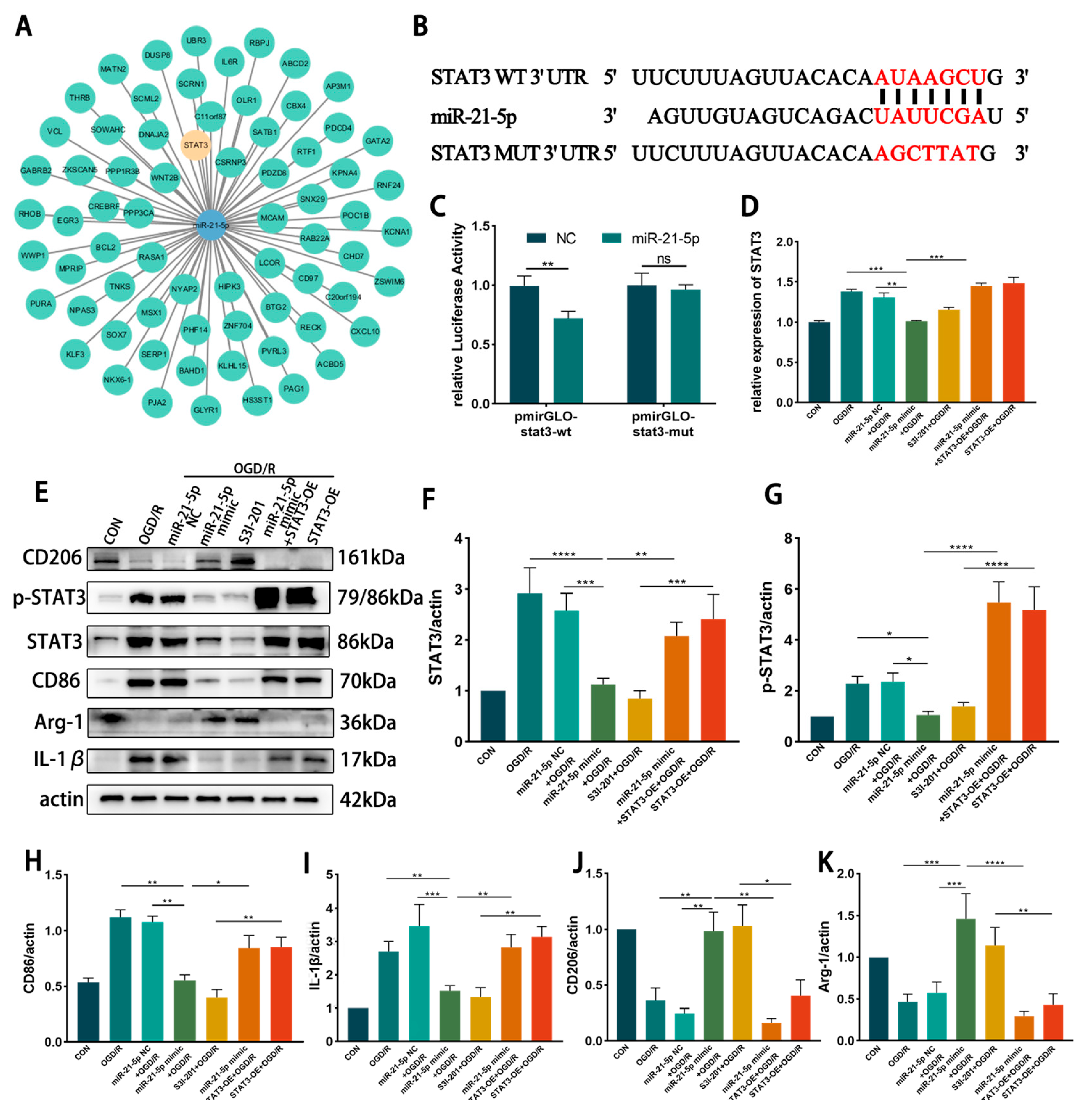
To explore potential downstream targets of miR-21-5p in RM, TargetScan analysis was conducted and predicted STAT3, a transcription factor linked to inflammation, as a candidate (Figure 4A). A dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed direct binding between miR-21-5p and the 3′-UTR of STAT3 (p < 0.001; Figure 4B,C). qRT-PCR revealed that STAT3 mRNA levels were significantly decreased in the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group compared with the OGD/R group and the NC + OGD/R group (Figure 4D). Consistently, WB analysis demonstrated that total STAT3, phosphorylated STAT3 (p-STAT3), and the downstream inflammatory protein IL-1β were markedly reduced in the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group relative to both control groups (Figure 4E–G,I). Moreover, qRT-PCR showed decreased mRNA levels of STAT3 downstream inflammatory mediators, including IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 (Figure A1). Collectively, these findings identify STAT3 as a direct functional target of miR-21-5p and demonstrate that miR-21-5p suppresses its expression and downstream pro-inflammatory signaling.
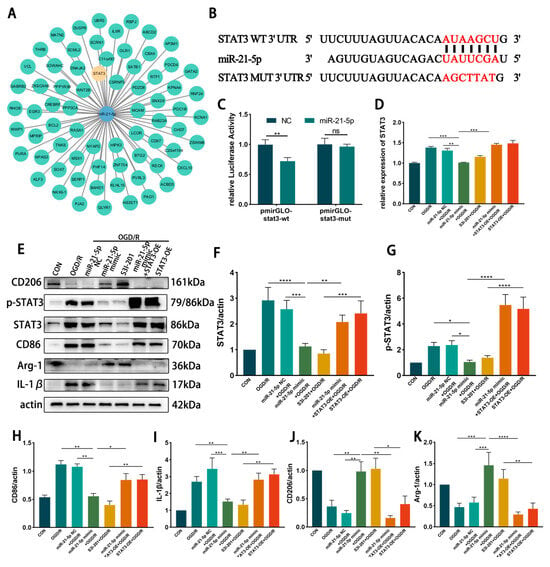
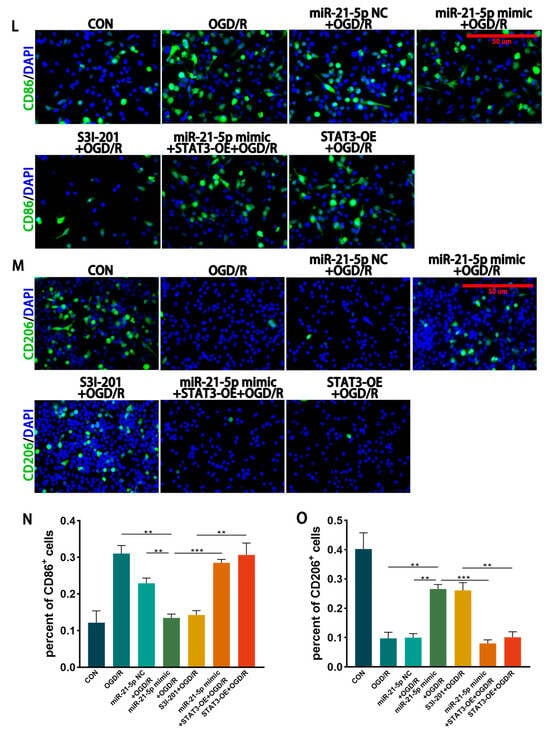
Figure 4.
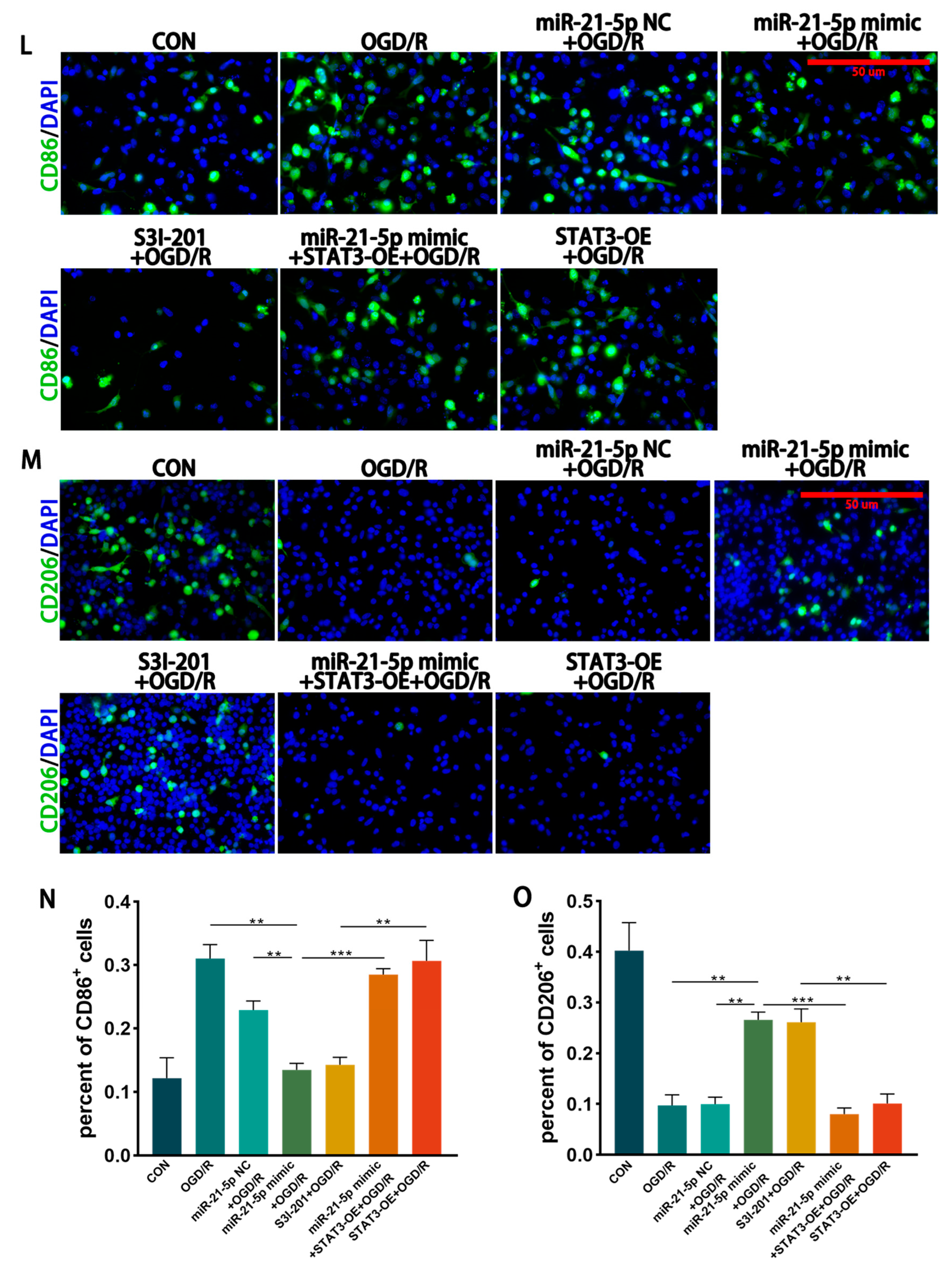
miR-21-5p directly targets STAT3 and regulates RM polarization under OGD/R conditions. (A) TargetScan prediction of miR-21-5p target genes. (B) Binding site between miR-21-5p and the STAT3 3′-UTR. (C) Dual-luciferase reporter assay confirming direct binding between miR-21-5p and STAT3 (** p < 0.01). (D) qRT-PCR analysis of STAT3 expression in RM (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA, n = 3). STAT3 mRNA was reduced in the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group compared with the OGD/R and NC groups, but increased with STAT3-OE co-transfection. (E–K) WB analysis and quantification of STAT3, p-STAT3, and polarization-related proteins (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA, n = 3). p-STAT3, STAT3, CD86, and IL-1β were decreased, whereas CD206 and Arg-1 were increased, in the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R and S3I-201 + OGD/R groups compared with OGD/R, NC, and STAT3-OE groups. (L–M) Immunofluorescence staining of RM polarization. (L) CD86 (green), DAPI (blue); (M) CD206 (green), DAPI (blue). Quantification (N,O) showed fewer CD86+ RM and more CD206+ RM in the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R and S3I-201 + OGD/R groups compared with OGD/R, NC, and STAT3-OE groups (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA, n = 3).
3.4.2. Inhibition of STAT3 Reduces M1 Polarization of RM Cultured In Vitro
To further investigate the regulatory role of STAT3 in RM polarization in vitro, RM were transfected with either a STAT3 overexpression plasmid (STAT3-OE) or treated with the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201, followed by induction of the OGD 4 h/R 6 h model. WB analysis showed that STAT3 and p-STAT3 protein levels were markedly reduced in the S3I-201 + OGD/R group compared with the OGD/R group, whereas STAT3 protein expression was not significantly altered in the STAT3-OE + OGD/R group (Figure 4E–G). WB results further demonstrated that, relative to the OGD/R and STAT3-OE + OGD/R groups, the S3I-201 + OGD/R group exhibited lower expression of CD86 and IL-1β, while CD206 and Arg-1 levels were increased (Figure 4E–K). Immunofluorescence confirmed these findings, showing decreased percentages of CD86+ RM and increased percentages of CD206+ RM in the S3I-201 + OGD/R group compared with controls (Figure 4L–O). Together, these results indicate that inhibition of STAT3 activity suppresses M1 polarization of RM and attenuates pro-inflammatory responses in vitro.
3.4.3. miR-21-5p Downregulates STAT3 Levels to Inhibit M1 Polarization of RM
To determine whether miR-21-5p inhibits M1 polarization of RM by downregulating STAT3, RM were co-transfected with an miR-21-5p mimic and a STAT3 overexpression plasmid (STAT3-OE), followed by induction of the OGD 4 h/R 6 h model. qRT-PCR confirmed that STAT3 mRNA levels were significantly higher in the miR-21-5p mimic + STAT3-OE + OGD/R group than in the miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R group (Figure 4D). WB analysis further showed that STAT3 overexpression reversed the effects of miR-21-5p, with increased CD86 and IL-1β expression and decreased CD206 and Arg-1 expression (Figure 4E–K). Immunofluorescence results were consistent, showing a higher percentage of CD86+ RM and a lower percentage of CD206+ RM in the co-transfection group compared with the miR-21-5p mimic group (Figure 4L–O). Together, these results demonstrate that miR-21-5p inhibits M1 polarization of RM and alleviates inflammatory responses by negatively regulating STAT3 expression.
3.5. miR-21-5p Down-Regulation of STAT3 Levels Inhibits M1 Polarization and Reduces Apoptosis of RGCs in Retinal Microglia of AIH Rats
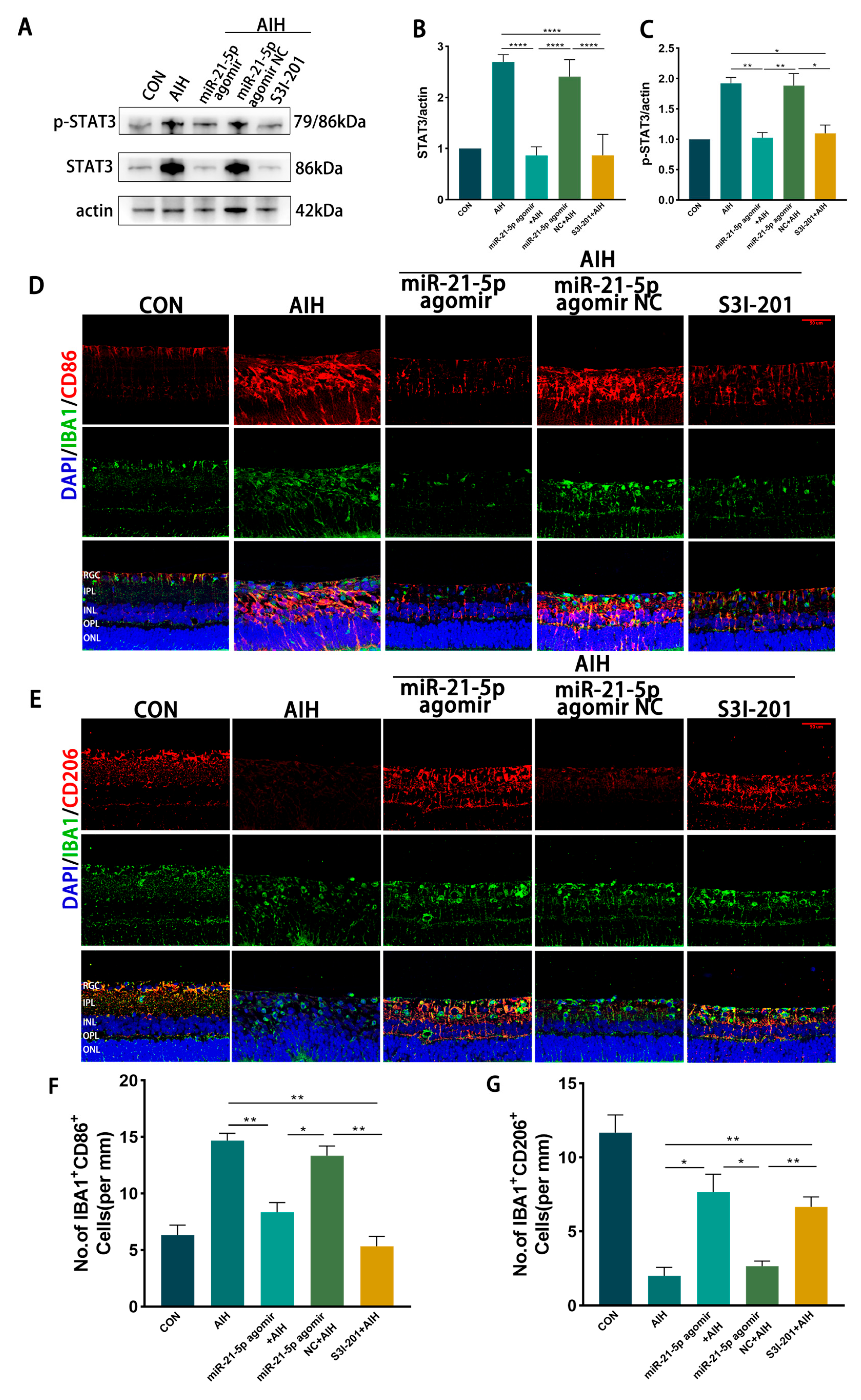
In vivo effects of miR-21-5p on retinal I/R injury. Rats received intravitreal injections of miR-21-5p agomir, scramble agomir (miR-21-5p agomir NC), or the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201, followed by induction of the AIH model. After 3 days, eyeballs were enucleated, and retinas were dissected for analysis. WB analysis revealed that protein levels of STAT3 and p-STAT3 were significantly lower in the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH group compared with the AIH and NC + AIH groups (Figure 5A–C). Similar reductions in STAT3 and p-STAT3 expression were observed in the S3I-201 + AIH group. In addition, both mRNA and protein levels of STAT3 downstream inflammatory mediators, including IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6, were decreased in the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH group (Figure A2).
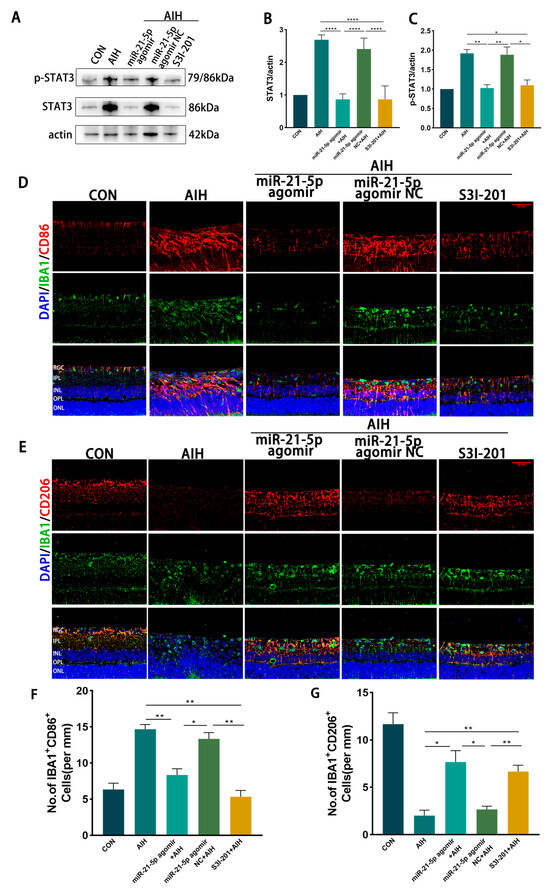
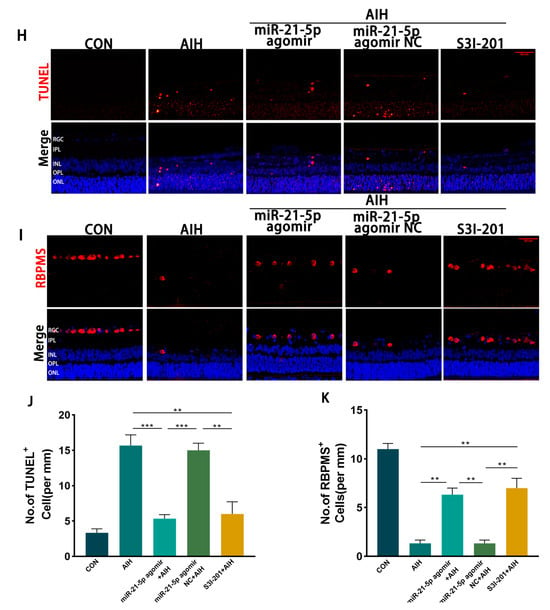
Figure 5.
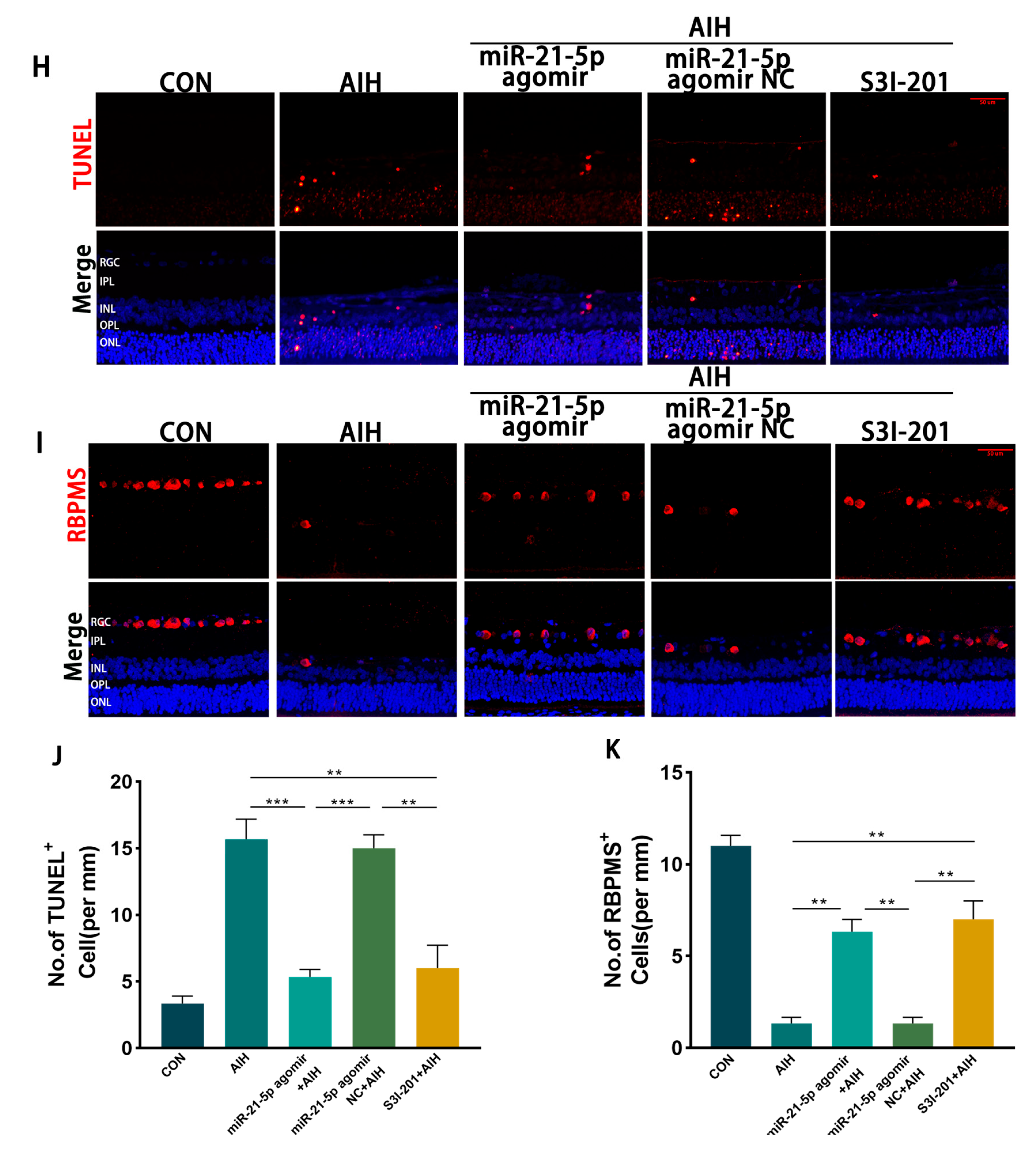
miR-21-5p downregulates STAT3 expression in vivo to inhibit M1 polarization of retinal microglia and reduce RGCs apoptosis. (A–C) WB analysis of STAT3 and p-STAT3 expression in rat retinas, with quantification (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA, n = 3). STAT3 and p-STAT3 levels were elevated in the AIH and miR-21-5p agomir NC + AIH groups compared with CON, whereas both were reduced in the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH groups. (D–G) Immunofluorescence staining of retinal microglial polarization. (D) IBA1 (green), CD86 (red), DAPI (blue); (E) IBA1 (green), CD206 (red), DAPI (blue). Quantification showed that IBA1+CD86+ (M1-like) microglia were increased and IBA1+CD206+ (M2-like) microglia were decreased in the AIH and NC groups compared with CON. In contrast, the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH groups exhibited reduced numbers of IBA1+CD86+ and increased numbers of IBA1+CD206+ cells (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; one-way ANOVA, n = 3). (H) TUNEL staining of RGC apoptosis (red), with DAPI (blue). The number of TUNEL+ RGCs was higher in the AIH and NC groups but reduced in the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH groups. (I) RBPMS staining of RGC survival (red), with DAPI (blue). Compared with AIH and NC groups, RBPMS+ RGCs were significantly increased in the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH groups. (J,K) Quantitative analysis of TUNEL+ apoptotic RGCs and RBPMS+ surviving RGCs, respectively (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA, n = 3).
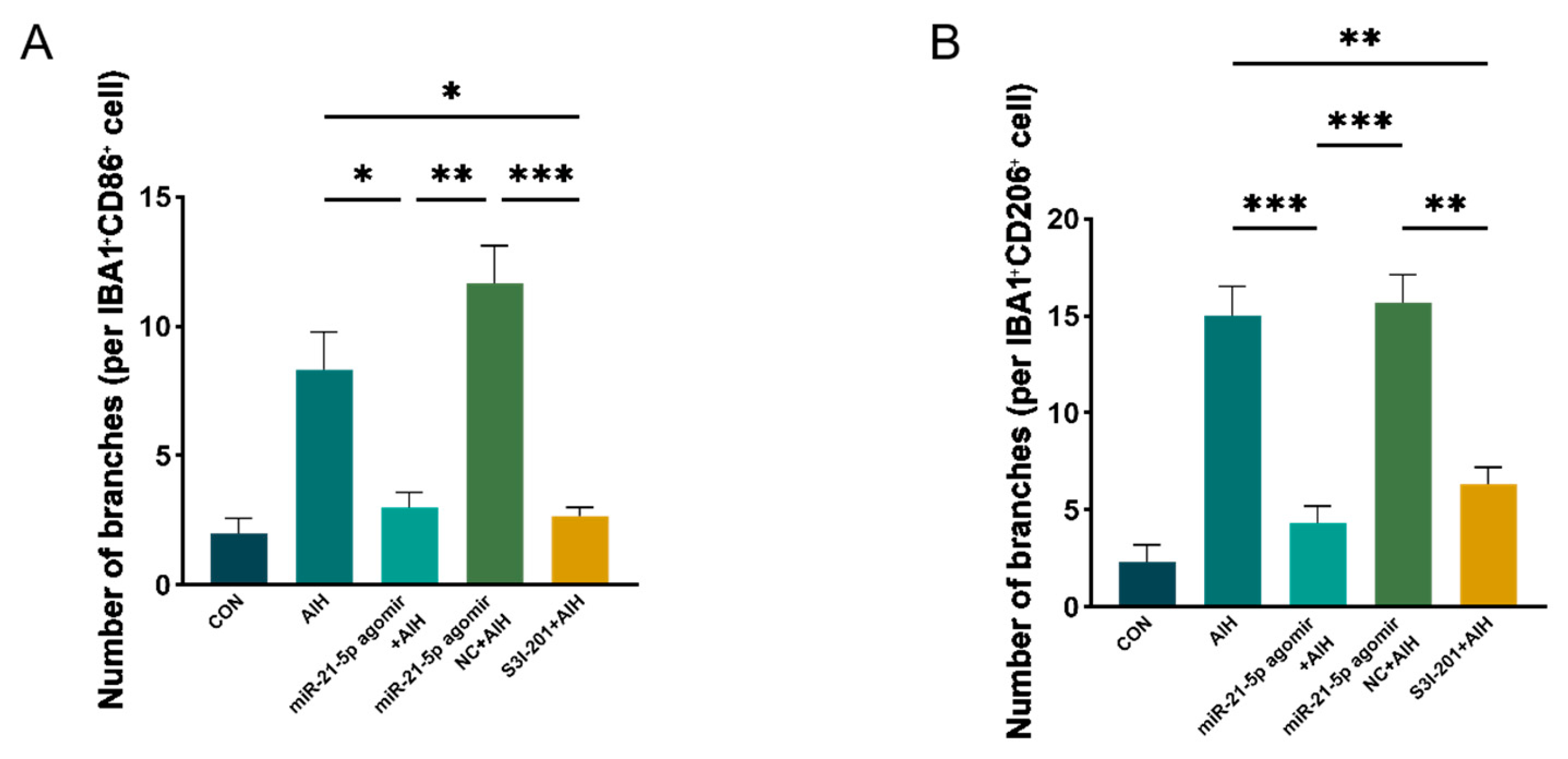
Immunofluorescence staining showed that the proportion of IBA1+CD86+ (M1-like) microglia was reduced and that of IBA1+CD206+ (M2-like) microglia was increased in both the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH groups compared with the AIH and NC groups (Figure 5D–G). Using skeleton analysis on IBA1+ microglia, the AIH group displayed a marked increase in the number of branches per cell, whereas both the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH groups significantly reduced the number of branches per cell toward CON levels (Figure A3). However, the soma area of microglia did not show a significant difference among groups. Cell survival assays demonstrated that the number of TUNEL+ RGCs was significantly reduced and the number of RBPMS+ RGCs was increased in the miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH groups relative to the AIH and NC groups (Figure 5H–K). Together, these in vivo experiments demonstrate that miR-21-5p overexpression attenuates retinal I/R injury by downregulating STAT3 signaling, inhibiting M1 polarization of microglia, and protecting RGCs from apoptosis.
4. Discussion
Our data suggest that miR-21-5p mitigates retinal I/R injury by downregulating STAT3, which in turn inhibits M1-like and favors M2-like microglial polarization, ultimately limiting loss of RGCs. Collectively, these results support a critical role of miR-21-5p in tuning microglial polarization and neuroinflammation, pointing to the miR-21-5p/STAT3 axis as a potential therapeutic target in ischemic retinal pathology.
Accumulating evidence indicates that miRNAs serve as key regulators of neuroinflammatory processes [44]. miR-21 is a highly conserved miRNA that is widely expressed in the brain and actively involved in CNS diseases [45,46,47]. miR-21 exerts neuroprotective effects in models of cerebral ischemia, subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), and traumatic brain injury (TBI), primarily by targeting p53, PTEN, or Rab11a and modulating the PI3K/AKT and Bcl-2/Bax pathways, thereby suppressing neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress [19,48,49]. In retinal injury, a study found that increasing endogenous miR-21 levels can alleviate photoreceptor apoptosis and attenuate retinal structural and functional degeneration in an N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU)-induced photoreceptor loss model [50]. Another study reported that miR-21-5p also exerts anti-inflammatory effects in retinal I/R injury by rebalancing NLRP3/6 inflammasome function and inhibiting microglial pyroptosis [4]. In this study, retinal miR-21-5p was downregulated in AIH rats, and miR-21-5p intervention mitigated AIH-induced retinal injury. Consistently, our data show that miR-21-5p overexpression enhances RGCs survival in I/R retinas and under OGD/R conditions. Together, our results indicate that increasing miR-21-5p may exert neuroprotective effects in retinal I/R pathology. However, chronic ocular hypertension (OHT)-induced glaucoma models do not show a clear upregulation of miR-21-5p [51,52]. The divergence may stem from differences in injury context: acute I/R entails robust inflammatory cascades and apoptotic responses, whereas chronic glaucoma is dominated by sustained mechanical loading and progressive neurodegeneration [53,54]. In light of our data, miR-21-5p may preferentially confer benefit in acute ischemic settings.
Microglial polarization critically shapes neuroinflammatory outcomes. The M1 phenotype produces pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) that aggravate neuronal damage, while the M2 phenotype secretes IL-4, IL-10, and neurotrophic factors, fostering tissue repair [6]. Microglial polarization plays a critical role in neuroinflammation, tissue repair, and neurodegenerative diseases, and its regulation involves multiple factors and pathways [55,56,57,58]. miRNAs critically shape microglial polarization. Notably, miR-9-5p targets and downregulates suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2), relieving its inhibitory constraint on JAK/STAT3 signaling, which in turn drives M1 microglial polarization [59]. By inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB pathway and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, miR-216a-5p promotes the transition of microglia from a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype to an anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype [60]. Across in vivo and in vitro settings, upregulation of miR-21-5p attenuated M1 and favored M2 microglial polarization under I/R or OGD/R conditions, with concomitant reductions in pro-inflammatory mediators and increases in anti-inflammatory mediators, which collectively enhanced the survival of RGCs. In line with our findings, previous reports indicate that miR-21 attenuates inflammatory responses in retinal I/R through PDCD4 or TLR4-dependent mechanisms, and in brain ischemia fosters M2 polarization of microglia with concomitant neuroprotection by engaging the PI3K/AKT signaling axis [61,62,63]. Collectively, these data suggest that miR-21 may coordinately modulate microglial polarization through multiple targets, representing a promising target for regulating microglial polarization in retinal I/R injury and offering a new avenue for retinal protection.
miR-21-5p regulates several validated targets—BTG2, MELK, PDCD4, and STAT3—thereby influencing apoptosis and ferroptosis [64,65,66,67]. Notably, STAT3 is a key mediator of neuroinflammation, typically activated within the JAK/STAT axis to drive inflammatory gene expression [68]. Bioinformatic screening (TargetScan) coupled with dual-luciferase reporter assays, WB, and qRT-PCR demonstrated that STAT3 is a direct effector target of miR-21-5p. In the context of retinal I/R, enforced miR-21-5p expression reduced p-STAT3 and downregulated STAT3-responsive pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), corroborating previously published findings [69,70]. STAT3 is a pleiotropic transcription factor that, upon JAK-mediated phosphorylation, translocates to the nucleus to regulate downstream gene expression, thereby participating in immune responses, cell growth, and apoptosis [71,72]. Our data indicate that pharmacologic inhibition of STAT3 dampens M1-like and favors M2-like microglial polarization, with concomitant decreases in pro-inflammatory and increases in anti-inflammatory mediators. Consistently, in vivo STAT3 inhibition under I/R conditions was associated with improved RGC survival. We further provide evidence that miR-21-5p directly targets STAT3, leading to lowered STAT3 phosphorylation and repression of STAT3-responsive inflammatory mediators, thereby mitigating retinal I/R damage. Consistent with our findings, previous studies have shown that reducing STAT3 activity in in vitro and in vivo models markedly attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α [73]. Complementing these disease-context data, recent chemical-biology advances have yielded azetidine-based covalent STAT3 inhibitors that selectively and irreversibly engage STAT3 and demonstrate in vivo efficacy [33]. Structure–activity work further identifies the azetidine ring and salicylic-acid/bioisosteric motifs as key determinants of STAT3 engagement [34]. Meanwhile, in a neonatal mouse hypoxia–ischemia (HI) model, Xin et al. reported that elevating miR-21a-5p (the murine ortholog of miR-21-5p) downregulated p-STAT3 and biased microglia toward an M2-like phenotype, thereby conferring neuroprotection [74]. Taken together, lines of evidence from miRNA-based modulation and pharmacologic suppression of the signaling cascade support STAT3 as a pivotal node that orchestrates microglial polarization and neuroinflammation.
Our investigation centers on miR-21-5p in microglia, and we did not comprehensively assess its effects in astrocytes or neurons. Because miR-21-5p may exhibit cell-type-specific targeting, future studies combining single-cell transcriptomic/proteomic approaches with protein–protein interaction mapping are warranted to resolve its intercellular specificity and STAT3-related activation mechanisms.
Taken together, our data indicate that miR-21-5p, via STAT3 downregulation, suppresses M1-like while favoring M2-like microglial polarization, thereby dampening inflammatory responses and preserving RGCs in retinal I/R injury. This work strengthens the mechanistic framework for miRNA-driven regulation in ischemic retinal pathology and highlights STAT3 as a promising, potentially translatable therapeutic target.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this research indicates that miR-21-5p mitigates retinal I/R injury by downregulating STAT3, which suppresses M1-like and favors M2-like microglial polarization, thereby dampening inflammatory responses and limiting loss of RGCs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Q. and C.T.; methodology, L.Q. and W.S. and C.L. and J.L.; formal analysis, L.Q. and J.L.; investigation, C.L.; resources, D.C.; data curation, L.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Q.; writing—review and editing, L.Q. and J.L.; visualization, L.Q.; supervision, D.C.; project administration, D.C.; funding acquisition, D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China, grant number 2025JJ50478. The APC was funded by the Graduate Student School-Enterprise Joint Innovation Program of Central South University, China (Grant No. 2023XQLH016).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by Chinese government animal protection regulations and management laws, and were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Animal Experimentation Centre of Central South University (Ethics Review Number: XMSB-2022-0002-01).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge researcher L.S. (Affiliated Eye Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China) for generously providing the rat retinal precursor cells (R28). We would also like to thank the Department of Human Anatomy and Neurobiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Central South University (Changsha, China) for their technical support in animal experiments. In addition, we thank all contributors to this work for their valuable suggestions regarding data analysis and experimental procedures.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| I/R | Ischemia-reperfusion |
| RGCs | Retinal ganglion cells |
| AIH | Acute intraocular hypertension |
| OGD/R | Oxygen and glucose deprivation/reperfusion |
| MCM | Microglial-conditioned media |
| RM | Rat Microglia |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| Arg-1 | Arginase-1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| 3′-UTR | 3′ Untranslated Region |
| TM | Trabecular Meshwork |
Appendix A
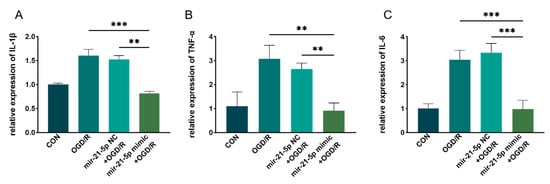
Figure A1.
qRT–PCR analysis of STAT3 downstream inflammatory mediators in rat microglia (RM) under OGD/R with the indicated treatments. Relative mRNA levels of (A) IL-1β, (B) TNF-α, and (C) IL-6 were quantified across CON, OGD/R, miR-21-5p mimic NC + OGD/R, and miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R groups. Values were normalized to β-actin and calculated by the 2^−ΔΔCt method. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). Statistical comparisons were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. indicated controls. These results show that miR-21-5p overexpression significantly reduces STAT3-responsive pro-inflammatory transcripts following OGD/R.
Figure A1.
qRT–PCR analysis of STAT3 downstream inflammatory mediators in rat microglia (RM) under OGD/R with the indicated treatments. Relative mRNA levels of (A) IL-1β, (B) TNF-α, and (C) IL-6 were quantified across CON, OGD/R, miR-21-5p mimic NC + OGD/R, and miR-21-5p mimic + OGD/R groups. Values were normalized to β-actin and calculated by the 2^−ΔΔCt method. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). Statistical comparisons were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. indicated controls. These results show that miR-21-5p overexpression significantly reduces STAT3-responsive pro-inflammatory transcripts following OGD/R.
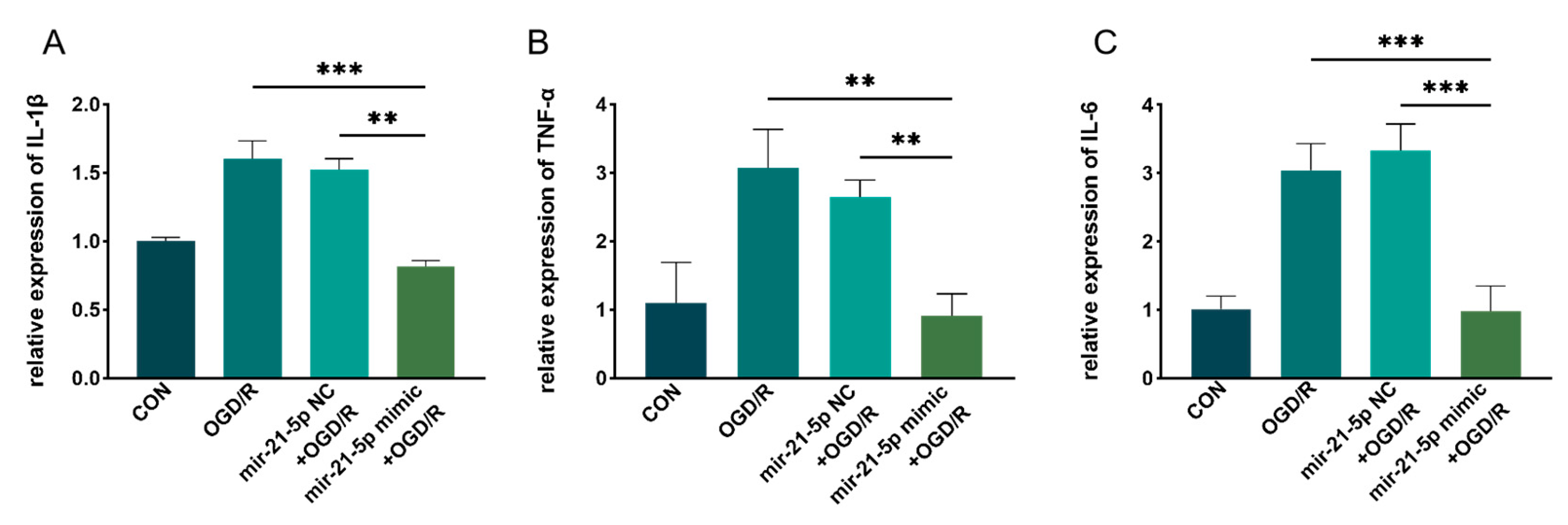
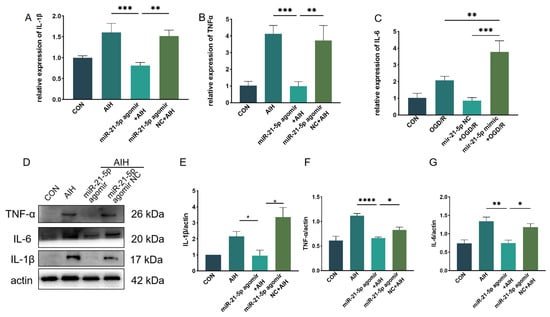
Figure A2.
miR-21-5p attenuates STAT3-responsive inflammatory mediators in vivo after retinal I/R (AIH model). (A–C) qRT-PCR of IL-1β (A), TNF-α (B) and IL-6 (C) mRNA in rat retinas from CON, AIH, miR-21-5p agomir NC + AIH, and miR-21-5p agomir + AIH groups (3 d after AIH). Values were normalized to β-actin and calculated by the 2^−ΔΔCt method. (D) Representative same-membrane immunoblots of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 (sequentially reprobed after stripping) with ACTB as the loading control. (E–G) Densitometric quantification of protein levels for IL-1β (E), TNF-α (F) and IL-6 (G), normalized to ACTB. Data are presented as mean ± SD (mRNA: n = 3 independent biological samples per group; protein: n = 3 blots from independent animals). Statistics: one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 vs. indicated com-parisons.
Figure A2.
miR-21-5p attenuates STAT3-responsive inflammatory mediators in vivo after retinal I/R (AIH model). (A–C) qRT-PCR of IL-1β (A), TNF-α (B) and IL-6 (C) mRNA in rat retinas from CON, AIH, miR-21-5p agomir NC + AIH, and miR-21-5p agomir + AIH groups (3 d after AIH). Values were normalized to β-actin and calculated by the 2^−ΔΔCt method. (D) Representative same-membrane immunoblots of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 (sequentially reprobed after stripping) with ACTB as the loading control. (E–G) Densitometric quantification of protein levels for IL-1β (E), TNF-α (F) and IL-6 (G), normalized to ACTB. Data are presented as mean ± SD (mRNA: n = 3 independent biological samples per group; protein: n = 3 blots from independent animals). Statistics: one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 vs. indicated com-parisons.
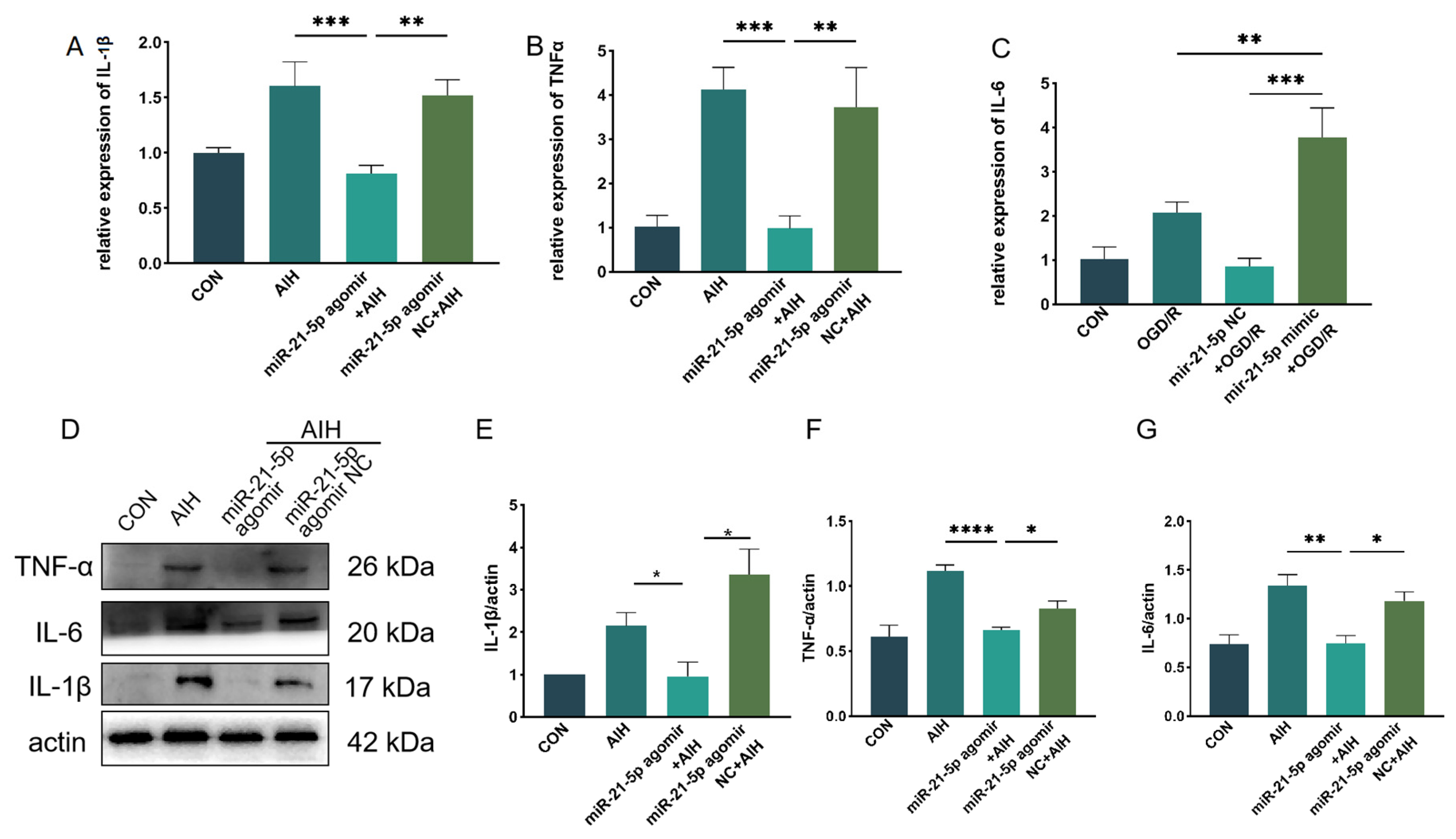
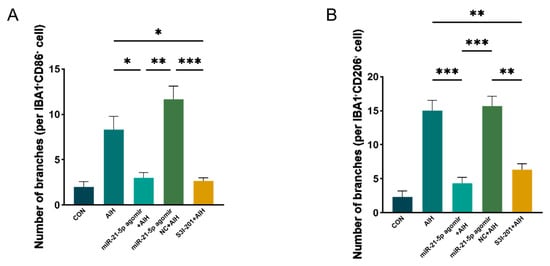
Figure A3.
Branching of double-positive retinal microglia assessed by skeleton analysis. (A) IBA1+/CD86+ microglia (retina, in vivo). Double-positive cells were identified by IBA1/CD86 colocalization. Single-cell ROIs were binarized and skeletonized; the number of branches per cell was obtained with Analyze Skeleton (2D/3D) and averaged per animal. AIH increased the number of branches per cell compared with CON, and the agomir NC + AIH group showed a similar increase. In contrast, both miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH reduced branching toward CON levels. (B) IBA1+/CD206+ microglia analyzed with the same pipeline showed a concordant pattern. Bars represent mean ± SD (animals as the statistical unit, n = 3 per group). One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test was used; * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Figure A3.
Branching of double-positive retinal microglia assessed by skeleton analysis. (A) IBA1+/CD86+ microglia (retina, in vivo). Double-positive cells were identified by IBA1/CD86 colocalization. Single-cell ROIs were binarized and skeletonized; the number of branches per cell was obtained with Analyze Skeleton (2D/3D) and averaged per animal. AIH increased the number of branches per cell compared with CON, and the agomir NC + AIH group showed a similar increase. In contrast, both miR-21-5p agomir + AIH and S3I-201 + AIH reduced branching toward CON levels. (B) IBA1+/CD206+ microglia analyzed with the same pipeline showed a concordant pattern. Bars represent mean ± SD (animals as the statistical unit, n = 3 per group). One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test was used; * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
References
- Jayaram, H.; Kolko, M.; Friedman, D.S.; Gazzard, G. Glaucoma: Now and Beyond. Lancet 2023, 402, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Fang, W.; Hu, F.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, C. A High-Salt Diet Aggravates Retinal Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 188, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Zhao, G.-L.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.-L. Activation of Retinal Glial Cells Contributes to the Degeneration of Ganglion Cells in Experimental Glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2023, 93, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.; Su, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, N.; Huang, S.; Long, E.; Zhuo, Y. LncRNA H19 Initiates Microglial Pyroptosis and Neuronal Death in Retinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Yu, N.; Gu, Y.; Ke, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, M. Inhibiting Multiple Forms of Cell Death Optimizes Ganglion Cells Survival after Retinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, K.; Dumas, A.A.; Prinz, M. Microglia: Immune and Non-Immune Functions. Immunity 2021, 54, 2194–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkar, A.; Wall, R.V.; Basavarajappa, D.; Chitranshi, N.; Parilla, G.E.; Mirzaei, M.; Yan, P.; Graham, S.; You, Y. Glial Cell Activation and Immune Responses in Glaucoma: A Systematic Review of Human Postmortem Studies of the Retina and Optic Nerve. Aging Dis. 2024, 15, 2069–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-P.; Chen, S.-Y.; Pang, Q.-M.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X.-C.; Wan, X.; Wan, W.-H.; Ao, J.; Zhang, T. Advances in the Research of the Role of Macrophage/Microglia Polarization-Mediated Inflammatory Response in Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1014013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Qu, X.; Chen, W.; Sang, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, C.; Zhu, K.; et al. CD36 Deletion Prevents White Matter Injury by Modulating Microglia Polarization through the Traf5-MAPK Signal Pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Kumari, S.; Dhapola, R.; Sharma, P.; Beura, S.K.; Singh, S.K.; Vellingiri, B.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. Shedding Light on Microglial Dysregulation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Exploring Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Avenues. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 679–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Li, X.-Q.; Deng, J.; Ye, Q.-B.; Li, D.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Hu, Y.; He, X.-F.; Wen, J.; et al. Modulating the Polarization Phenotype of Microglia—A Valuable Strategy for Central Nervous System Diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 93, 102160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, C.; Zhan, H.; Li, S.; Zeng, K.; Xu, C.; Zou, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Yin, S.; et al. Targeting the HSP47-Collagen Axis Inhibits Brain Metastasis by Reversing M2 Microglial Polarization and Restoring Anti-Tumor Immunity. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, M.; Yang, D.; Xie, Q. Huanglian Wendan Decoction Improves Insomnia in Rats by Regulating BDNF/TrkB Signaling Pathway Through Gut Microbiota-Mediated SCFAs and Affecting Microglia Polarization. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 1047–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.; Yu, S.; Song, G.; Liu, Q.; Gong, P. Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C) Reduces Apoptosis and Improves Neurological Function after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Modulating Microglia Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Yang, B.; Liu, W.; Tan, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Neuroinflammation Mediated by Microglia and Astrocytes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ding, L.; Ding, S.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Du, P. miRNA Dosage Control in Development and Human Disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, C.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Emerging Concepts of miRNA Therapeutics: From Cells to Clinic. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, S.; Zhu, J.; Hu, T.; Han, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, F.; Lei, P. Exosomes from MiR-21-5p-Increased Neurons Play a Role in Neuroprotection by Suppressing Rab11a-Mediated Neuronal Autophagy In Vitro After Traumatic Brain Injury. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1871–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Q.; Han, M.; Shan, D.; Yang, G.; Zhang, S.; Xin, D.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of miR-21-5p from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Neurons Alleviates Early Brain Injury to Improve Cognitive Function via the PTEN/Akt Pathway after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Hu, J.-J.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.-L.; Sun, X.-T.; Wang, L.-T.; Wu, X.; Zhu, L.-J.; Yang, X.-J.; He, Q.-R.; et al. miRNA-21-5p Is an Important Contributor to the Promotion of Injured Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Using Hypoxia-Pretreated Bone Marrow-Derived Neural Crest Cells. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinders, M.; Üçeyler, N.; Thomann, A.; Sommer, C. Aberrant microRNA Expression in Patients with Painful Peripheral Neuropathies. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 380, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Cai, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, L. Neuroinflammation Signatures in Dorsal Root Ganglia Following Chronic Constriction Injury. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Hu, C.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Fan, W.; Xie, J.; Lei, Y. Reduction-Responsive Polymeric Micelles for Trans-Corneal Targeted Delivery of microRNA-21-5p and Glaucoma-Specific Gene Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 10433–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Li, Y.; Jiang, N.; Huang, S.; Su, W.; Zhuo, Y. Interleukin-35 Suppresses Pyroptosis and Protects against Neuronal Death in Retinal Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 220, 109109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Luan, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. IL-4-Primed Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Facilitate Recovery in Spinal Cord Injury via the miR-21-5p/PDCD4-Mediated Shifting of Macrophage M1/M2 Polarization. Life Sci. 2025, 364, 123441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Wu, E.; Chen, H.; Yao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, C.; Li, Y.; et al. MSCs-Exosomes Can Promote Macrophage M2 Polarization via Exosomal miR-21-5p through Mesenteric Injection: A Promising Way to Attenuate Murine Colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2024, 18, jjae110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Jia, F.; Zhang, P.; Sun, X.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lei, Y. A miRNA Stabilizing Polydopamine Nano-Platform for Intraocular Delivery of miR-21-5p in Glaucoma Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 3335–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Tang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y. The Effects of STAT3 Acetylation on the Transcriptional Activity and Tumorigenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 240, 117076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tošić, I.; Frank, D.A. STAT3 as a Mediator of Oncogenic Cellular Metabolism: Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, Y.; Manolopoulou, M.; Ivanova, A.V.; Vartanian, N.; Mignemi, M.P.; Kern, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, H.; Fogo, A.B.; Zhang, M.; et al. Blocking Cell Cycle Progression through CDK4/6 Protects against Chronic Kidney Disease. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e158754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Hu, S.; Jian, Y. siRNA Nanodelivery Systems in the Treatment of Skin Diseases: Research Progress and Clinical Translation Prospects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 1005, 178075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wan, H.; Yang, J. Formononetin Protects against Inflammation Associated with Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Targeting the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Zhu, Y.; Brotherton-Pleiss, C.; Fu, W.; Verma, N.; Chen, J.; Nakamura, K.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Alonso-Valenteen, F.; et al. Novel Potent Azetidine-Based Compounds Irreversibly Inhibit Stat3 Activation and Induce Antitumor Response against Human Breast Tumor Growth In Vivo. Cancer Lett. 2022, 534, 215613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhai, N.; Zhu, Y.; Yue, P.; Verma, N.; Brotherton-Pleiss, C.; Fu, W.; Nakamura, K.; Chen, W.; Kawakami, J.; et al. Azetidine Ring, Salicylic Acid, and Salicylic Acid Bioisosteres as Determinants of the Binding Characteristics of Novel Potent Compounds to Stat3. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2024, 97, 129565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Rao, Z.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, L.; Liu, Q.; Weng, X.; Wang, C.; Bi, Y.; Zeng, T. Naoqing Formula Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Induced Inflammatory Injury by Regulating Csf3 Mediated JAK/STAT Pathway and Macrophage Polarization. Phytomedicine 2025, 140, 156626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Xue, F.; Tan, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, D. Melatonin Alleviates Pyroptosis of Retinal Neurons Following Acute Intraocular Hypertension. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 20, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wen, T.; Fang, X.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Jonas, J.B.; Zhang, X. MicroRNA-93/STAT3 Signalling Pathway Mediates Retinal Microglial Activation and Protects Retinal Ganglion Cells in an Acute Ocular Hypertension Model. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotnala, A.; Anderson, D.M.G.; Patterson, N.H.; Cantrell, L.S.; Messinger, J.D.; Curcio, C.A.; Schey, K.L. Tissue Fixation Effects on Human Retinal Lipid Analysis by MALDI Imaging and LC-MS/MS Technologies. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yue, Y.; Sun, D. Mechanism of the AMPK/SIRT1 Pathway in Gut Dysbiosis-Mediated Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction in Aged Mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2025, 28, pyaf066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Li, F.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, L.-Y.; He, H.-Y.; Yan, X.; He, W.-B.; Sun, H.-S.; Feng, Z.-P.; et al. Neuronal Chemokine-like-Factor 1 (CKLF1) up-Regulation Promotes M1 Polarization of Microglia in Rat Brain after Stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yi, J.; Wang, X.; Luo, M.; et al. Treg-Microglia Partnership in the Injured Spinal Cord Preserves Treg Cell Function and Regulates Microglial Cholesterol Metabolism. Neuron, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dai, L.; Wang, M.; Feng, F.; Xiao, Y. Tunicamycin Induces Hepatic Stellate Cell Apoptosis Through Calpain-2/Ca2 +-Dependent Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 684857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; You, M.; Fan, C.; Rong, R.; Li, H.; Xia, X. Pathologically High Intraocular Pressure Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction through Drp1 and Leads to Retinal Ganglion Cell PANoptosis in Glaucoma. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; He, X.; Luo, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; et al. Transcranial Focused Ultrasound Stimulation Alleviates NLRP3-Related Neuroinflammation Induced by Ischemic Stroke via Regulation of the Nespas/miR-383-3p/SHP2 Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 144, 113680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Huang, S.; Gao, H.; Han, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Kang, C.; Jiang, R.; Yue, S.; et al. miR-21-5p Alleviates Leakage of Injured Brain Microvascular Endothelial Barrier in Vitro through Suppressing Inflammation and Apoptosis. Brain Res. 2016, 1650, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Han, Z.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, R.; Lei, P.; Zhang, J. MiR-21 Alleviates Secondary Blood-Brain Barrier Damage after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats. Brain Res. 2015, 1603, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.-T.; Lei, P.; Wang, H.-C.; Zhang, A.-L.; Han, Z.-L.; Chen, X.; Li, S.-H.; Jiang, R.-C.; Kang, C.-S.; Zhang, J.-N. miR-21 Improves the Neurological Outcome after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Wang, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Hu, T.; Guo, M.; Lei, P. Hydrogen Exerts Neuroprotection by Activation of the miR-21/PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Pathway in an in Vitro Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 4061–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Huang, W.; Rao, J.; Yuan, J. miR-21 Regulates Ischemic Neuronal Injury via the P53/Bcl-2/Bax Signaling Pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 22242–22255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.-L.; Hu, C.-B.; Ling, S.-T.; Zhao, N.; Bao, L.-H.; Zhou, F.; Xiong, Y.-C.; Chen, T.; Sui, B.-D.; Yu, X.-R.; et al. Photoreceptor Protection by Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Identifies Exosomal MiR-21 as a Therapeutic for Retinal Degeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1041–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, B.; Tomarev, S. The Role of miRNA in Retinal Ganglion Cell Health and Disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaram, H.; Cepurna, W.O.; Johnson, E.C.; Morrison, J.C. MicroRNA Expression in the Glaucomatous Retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 7971–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abcouwer, S.F.; Shanmugam, S.; Muthusamy, A.; Lin, C.-M.; Kong, D.; Hager, H.; Liu, X.; Antonetti, D.A. Inflammatory Resolution and Vascular Barrier Restoration after Retinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou Ghanem, G.O.; Wareham, L.K.; Calkins, D.J. Addressing Neurodegeneration in Glaucoma: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Treatments. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2024, 100, 101261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Liu, S.; Gao, L.; Xin, N.; Shang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ma, R.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Long-Term Minocycline Treatment Exhibits Enhanced Therapeutic Effects on Ischemic Stroke by Suppressing Inflammatory Phenotype of Microglia Through the EMB/MCT4/STING Pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2025, 31, e70328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, F. The Immunomodulatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Neurogenerative Diseases and Ischemic Stroke Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1525623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, F. METTL3/IGF2BP2/IκBα Axis Participates in Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease by Regulating M1/M2 Polarization of Microglia. Neurochem. Int. 2025, 186, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, A.; He, Q.; Xiao, F.; Zhan, J. Cannabinoid Receptor-2 Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Neuroinflammation by Modulating Microglia M1/M2 Subset Polarization Through Inhibiting Nogo-B Expression. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 9258–9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.; Cai, L.-L.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.-C.; Xu, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Xie, Y.-H.; Zhu, X.-L.; Li, Y.-F. Neuron Secrete Exosomes Containing miR-9-5p to Promote Polarization of M1 Microglia in Depression. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Rong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ge, X.; Ji, C.; Jiang, D.; Gong, F.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; et al. Exosome-Shuttled miR-216a-5p from Hypoxic Preconditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury by Shifting Microglial M1/M2 Polarization. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, N.; Li, Z.; Guan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, C.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, S.G.; Zhu, Y.; et al. TNF-α Stimulation Enhances the Neuroprotective Effects of Gingival MSCs Derived Exosomes in Retinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via the MEG3/miR-21a-5p Axis. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Bian, Z. MicroRNA-21 Is a Versatile Regulator and Potential Treatment Target in Central Nervous System Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 842288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.; Pinto, S.; Ferreira, S.; Lopes, D.; Serrador, M.J.; Fernandes, A.; Vaz, A.R.; Mendonça, A.d.; Edenhofer, F.; Malm, T.; et al. Emerging Role of miR-21-5p in Neuron-Glia Dysregulation and Exosome Transfer Using Multiple Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, J.; Li, L. miR-21-5p Inhibits Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Regulating the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway through MELK. J. Immunol. Res. 2023, 2023, 8929525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Hu, M.; Lv, Y.; Duan, Y.; Fang, W.; Ding, R.; Qiu, Y. miR-21-5p Prevents Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy by Downregulating BTG2. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewalle, V.; Essaghir, A.; Bollaert, E.; Lenglez, S.; Graux, C.; Schoemans, H.; Saussoy, P.; Michaux, L.; Valk, P.J.M.; Demoulin, J.-B.; et al. miR-15a-5p and miR-21-5p Contribute to Chemoresistance in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukaemia by Targeting PDCD4, ARL2 and BTG2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, J.; Yang, M.; Peng, Y. Exosomes Derived from Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Wound Healing by miR-21-5p/STAT3 Axis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 11257–11273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abroumand Gholami, A.; Tahmasebi, F.; Haghir, H.; Babaloo, H. Targeting JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway by Curcumin: Implications for Spinal Cord Injury Neuroprotection. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 4377–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-W.; Zeng, H.-S. Regulation of JAK/STAT Signal Pathway by miR-21 in the Pathogenesis of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, T.; Zhang, X.; Pan, T.; Peng, F.; Feng, J.; Sun, Q.; Song, N.N.; Ding, X.; Jia, P. MiR-21 Suppression in Macrophages Promotes M2-like Polarization and Attenuates Kidney Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e70251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Rashidi, M.; Amini, N.; Talebi Anaraki, K.; Motahhary, M.; Khalilipouya, E.; Harif Nashtifani, A.; Shafiei, S.; Ramezani Farani, M.; et al. STAT3 as a Newly Emerging Target in Colorectal Cancer Therapy: Tumorigenesis, Therapy Response, and Pharmacological/Nanoplatform Strategies. Environ. Res. 2023, 233, 116458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmer, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.S.; Watowich, S.S. STAT3 Signaling in Immunity. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2016, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.Y.; Nam, J.H.; Yoon, G.; Lee, J.-Y.; Nam, Y.; Kang, H.-J.; Cho, H.-J.; Kim, J.; Hoe, H.-S. Ibrutinib Suppresses LPS-Induced Neuroinflammatory Responses in BV2 Microglial Cells and Wild-Type Mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, D.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Li, T.-T.; Ke, H.-F.; Gai, C.-C.; Guo, X.-F.; Chen, W.-Q.; Liu, D.-X.; Wang, Z. The Delivery of miR-21a-5p by Extracellular Vesicles Induces Microglial Polarization via the STAT3 Pathway Following Hypoxia-Ischemia in Neonatal Mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).