Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review
Abstract
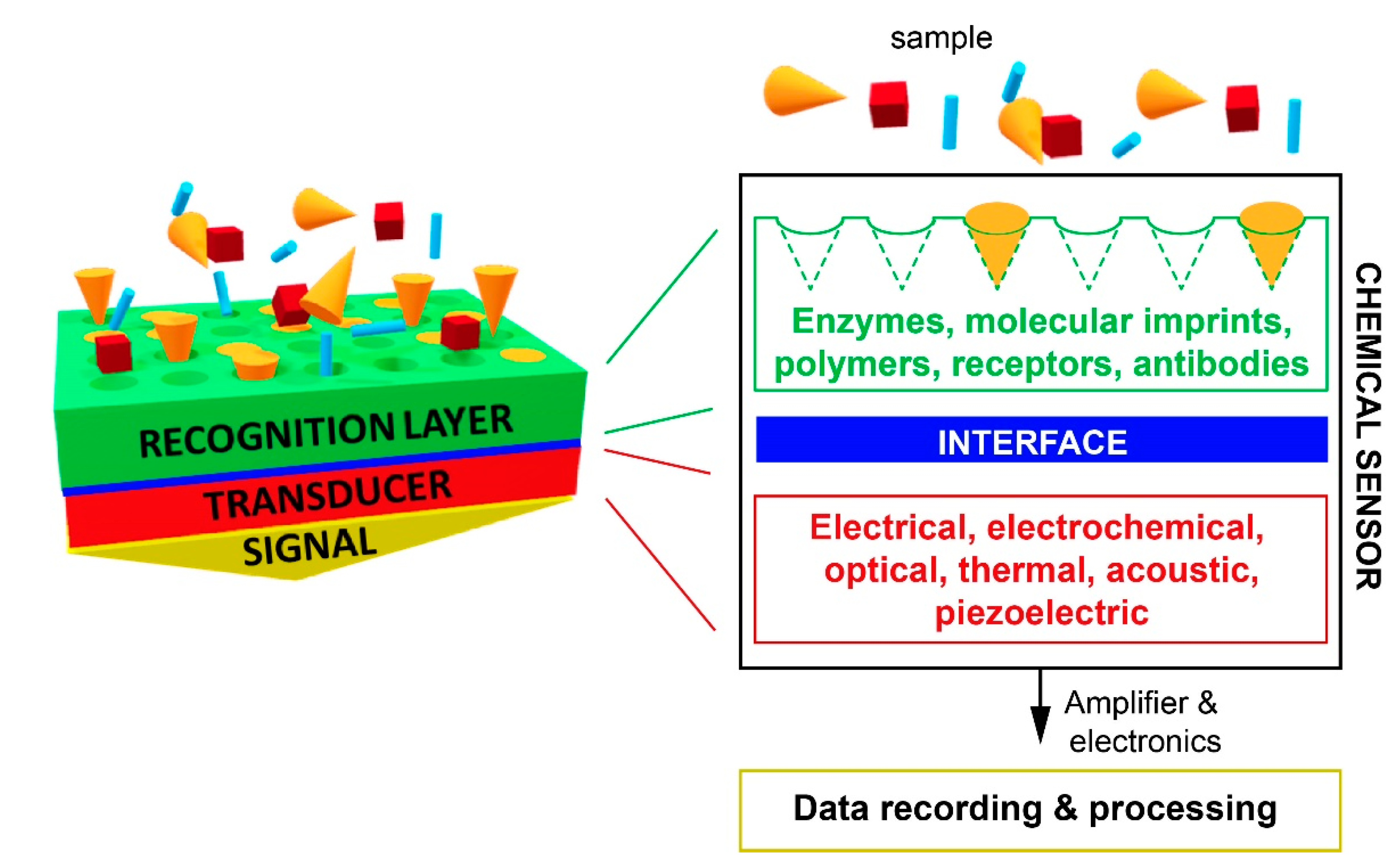
1. Introduction
2. Electrochemical MIP Sensors
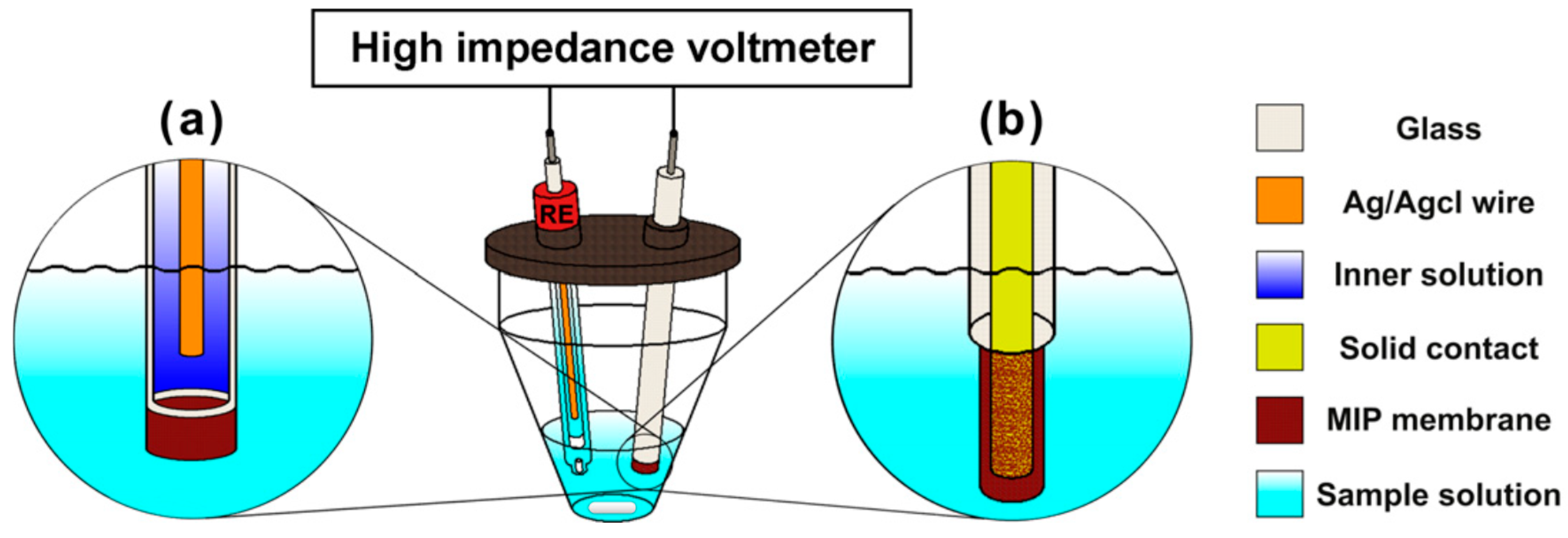
2.1. Potentiometric Sensors
2.2. Conductometric and Impedimetric Sensors
2.3. Voltametric and Amperometric Sensors
3. Mass-Sensitive Sensors
3.1. QCM Sensors
3.2. SAW Sensors
4. Optical Sensors
- (a)
- The inherent optical activity of the target.
- (b)
- The incorporation of a fluorophore or a chromophore into the polymer matrix, which can result either in the quenching or in the enhancement of fluorescence.
- (c)
- A signal generated upon a catalytic reaction, leading to spectroscopically active species.
4.1. UV/Vis and Fluorescence Readout
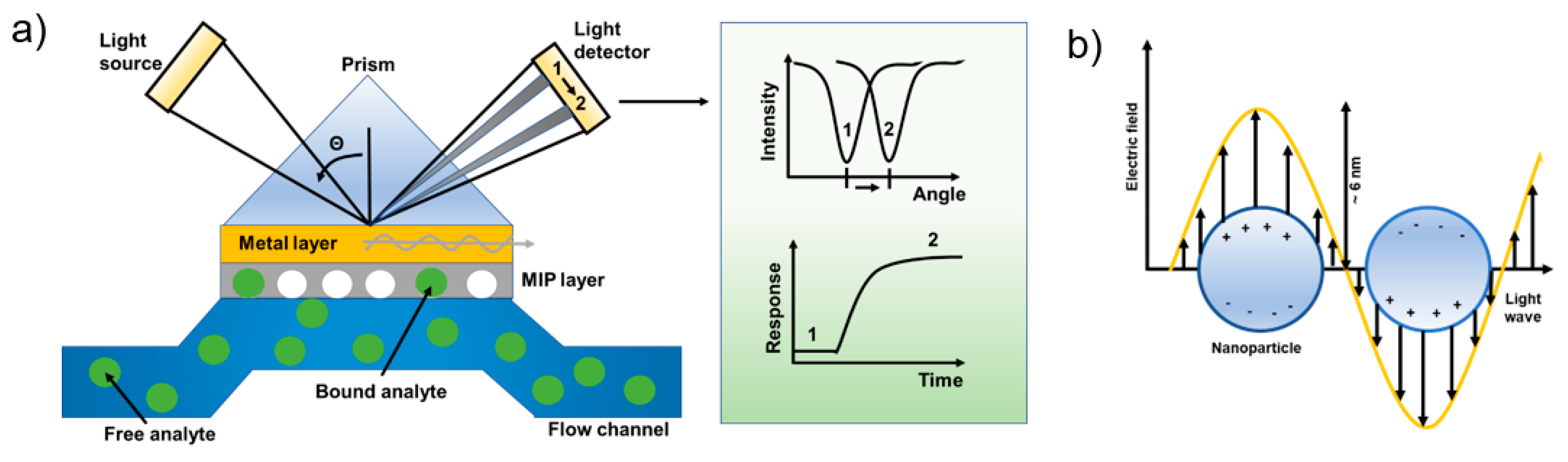
4.2. SPR Readout
4.3. LSPR Readout
4.4. SERS and SERRS Readouts
4.5. Reflectometric Interference Readout
4.6. Colorimetric Readout
5. Interfacing
6. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, L.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers as antibody and receptor mimics for assays, sensors and drug discovery. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Blaas, D.; Dickert, F.L. Artificial antibodies for bioanalyte detection—Sensing viruses and proteins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, O. One binder to bind them all. Sensors 2016, 16, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P.F. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, F.L. Molecular imprinting and functional polymers for all transducers and applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Singla, P.; Peeters, M.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K. MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays – An overview of the current status quo. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Rangel, P.X.M.; Tse, B.; Bui, S. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Antibody mimics for bioimaging and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedwell, T.S.; Whitcombe, M.J. Analytical applications of MIPs in diagnostic assays: Future perspectives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1735–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulanicki, A.; Glab, S.; Ingman, F. Chemical sensors definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1991, 63, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xue, M.; Xu, Z.; Dong, X.; Xue, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the sensing of explosives and chemical warfare agents. Curr. Org. Chem. 2015, 19, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awino, J.K.; Zhao, Y. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles as tailor-made sensors for small fluorescent molecules. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 5752–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Xiao, M.; Fu, Q.; Yu, S.; Shen, H.; Bian, H.; Tang, Y. A portable smart-phone readout device for the detection of mercury contamination based on an aptamer-assay nanosensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baş, D. Sensitive and reliable paper-based glucose sensing mechanisms with smartphone readout using the: L ∗ a ∗ b ∗ color space. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6698–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, N. Smartphone-Based Sensors, Electrochem. Soc. Interface. Available online: https://www.electrochem.org/ecs-blog/25-years-interface-2/ (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Broeders, J.; Croux, D.; Peeters, M.; Beyens, T.; Duchateau, S.; Cleij, T.J.; Wagner, P.; Thoelen, R.; De Ceuninck, W. Mobile application for impedance-based biomimetic sensor readout. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guembe-García, M.; Santaolalla-García, V.; Moradillo-Renuncio, N.; Ibeas, S.; Reglero, J.A.; García, F.C.; Pacheco, J.; Casado, S.; García, J.M.; Vallejos, S. Monitoring of the evolution of human chronic wounds using a ninhydrin-based sensory polymer and a smartphone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 335, 129688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, R.; Qin, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based potentiometric sensors. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudpour, M.; Torbati, M.; Mousavi, M.M.; de la Guardia, M.; Ezzati Nazhad Dolatabadi, J. Nanomaterial-based molecularly imprinted polymers for pesticides detection: Recent trends and future prospects. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 129, 115943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdrachek, E.; Bakker, E. Potentiometric sensing. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 72–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, D.; Mosbach, K. Competitive amperometric morphine sensor based on an agarose immobilised molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 300, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Zhang, R.; Qin, W. Potentiometric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for determination of melamine in milk. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 141, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, K.Y.; M, S.; Reddy, K.K.; Gobi, K.V. Development of highly selective electrochemical impedance sensor for detection of sub-micromolar concentrations of 5-Chloro-2,4-dinitrotoluene. J. Chem. Sci. 2016, 128, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, S.K.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J. Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensor for the electrochemical determination of triacetone triperoxide (TATP). Sensors 2014, 14, 23269–23282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wei, W.Z.; Zeng, J.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Gao, Y.P. Application of a novel electrosynthesized polydopamine-imprinted film to the capacitive sensing of nicotine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Anal. Lett. 2001, 34, 635–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuña-Jiménez, D.; Díaz-Díaz, G.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors: Past, Present, and Future; Li, S., Piletsky, S.A., Ge, Y., Lunec, J., Eds.; ScienceDirect: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780444563316. [Google Scholar]
- Hedborg, E.; Winquist, F.; Lundström, I.; Andersson, L.I.; Mosbach, K. Some studies of molecularly-imprinted polymer membranes in combination with field-effect devices. Sens. Actuators A. Phys. 1993, 37–38, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Turner, A.P.F. Electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical biosensors - Sensor principles and architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasyuk, T.L.; Mirsky, V.M.; Piletsky, S.A.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor layers in capacitive chemical sensors. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4609–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasada Rao, T.; Kala, R. Potentiometric transducer based biomimetic sensors for priority envirotoxic markers-An overview. Talanta 2008, 76, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.; Kala, R.; Prasada Rao, T.; Naidu, G.R.K. Ion imprinted polymer based ion-selective electrode for the trace determination of dysprosium(III) ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 566, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.; Prathish, K.P.; Gladis, J.M.; Naidu, G.R.K.; Rao, T.P. Molecularly imprinted polymer (biomimetic) based potentiometric sensor for atrazine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, R.S.; Bachas, L. Nitrate-selective electrode developed by electrochemically mediated imprinting/doping of polypyrrole. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Almeida, S.A.A.; Sales, M.G.F. Novel potentiometric sensors of molecular imprinted polymers for specific binding of chlormequat. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, J.R.L.; Sales, M.G.F.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Rebelo, T.S.R. Selective recognition in potentiometric transduction of amoxicillin by molecularly imprinted materials. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 232, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.S.; Vardini, M.T.; Azar, P.A.; Husain, S.W. Molecularly imprinted polymer based PVC-membrane-coated graphite electrode for the determination of metoprolol. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Javanbakht, M.; Fard, S.E.; Abdouss, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Safaraliee, L. A biomimetic potentiometric sensor using molecularly imprinted polymer for the cetirizine assay in tablets and biological fluids. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sokolov, J.; Rigas, B.; Levon, K.; Rafailovich, M. A potentiometric protein sensor built with surface molecular imprinting method. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, M.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Katz, O.; Kunitake, T.; Willner, I. Tailored chemosensors for chloroaromatic acids using molecular imprinted TiO2 thin films on ion-sensitive field-effect transistors. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayats, M.; Lahav, M.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Willner, I. Imprinting of specific molecular recognition sites in inorganic and organic thin layer membranes associated with ion-sensitive field-effect transistors. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelova, S.P.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Willner, I.; Sukenik, C.N.; Pizem, H.; Bayer, T. Development of ion-sensitive field-effect transistor-based sensors for benzylphosphonic acids and thiophenols using molecularly imprinted TiO 2 films. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelova, S.P.; Zayats, M.; Bourenko, T.; Kharitonov, A.B.; Lioubashevski, O.; Katz, E.; Willner, I. Analysis of NAD(P)+/NAD(P)H cofactors by imprinted polymer membranes associated with ion-sensitive field-effect transistor devices and Au-quartz crystals. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.H.; Lin, C.F.; Juang, Y.Z.; Wang, I.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, R.L.; Lin, H.Y. Multiple type biosensors fabricated using the CMOS BioMEMS platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 144, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.H.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Liang, R. A paper-based potentiometric sensing platform based on molecularly imprinted nanobeads for determination of bisphenol A. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3890–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, E.; Yang, X. Capacitive detection of glucose using molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y. Capacitive detection of theophylline based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2007, 12, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Prusty, A.; Bhand, S. Molecularly imprinted polyresorcinol based capacitive sensor for sulphanilamide detection. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Akaad, S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Abdelwahab, N.S.; Abdelaleem, E.A.; De Saeger, S.; Beloglazova, N. Capacitive sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers for detection of the insecticide imidacloprid in water. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rycke, E.; Leman, O.; Dubruel, P.; Hedström, M.; Völker, M.; Beloglazova, N.; De Saeger, S. Novel multiplex capacitive sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers: A promising tool for tracing specific amphetamine synthesis markers in sewage water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Piletskaya, E.V.; Elgersma, A.V.; Yano, K.; Karube, I.; Parhometz, Y.P.; El’skaya, A.V. Atrazine sensing by molecularly imprinted membranes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suedee, R.; Intakong, W.; Dickert, F.L. Molecularly imprinted polymer-modified electrode for on-line conductometric monitoring of haloacetic acids in chlorinated water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 569, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C.; Yeh, W.M.; Tung, T.S.; Liao, J.Y. Amperometric detection of morphine based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) immobilized molecularly imprinted polymer particles prepared by precipitation polymerization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 542, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Picca, R.A.; Malitesta, C.; Piletsky, S.A.; Piletska, E.V. Development of a sensor prepared by entrapment of MIP particles in electrosynthesised polymer films for electrochemical detection of ephedrine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, L.; Şahin, Y. Determination of paracetamol based on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Wei, X. A sensitive and selective sensor for dopamine determination based on a molecularly imprinted electropolymer of o-aminophenol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, R.; Takeuchi, T.; Kubo, I. Atrazine sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer-modified gold electrode. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4882–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Sharma, P.S.; Prasad, B.B. Development of a creatinine sensor based on a molecularly imprinted polymer-modified sol-gel film on graphite electrode. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 2102–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Moradi, N.; Pashabadi, A. Coupled electrochemical-chemical procedure used in construction of molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrode: A highly sensitive impedimetric melamine sensor. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2018, 22, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Duma, L.; Gonzato, C.; Haupt, K. Polydopamine-based molecularly imprinted thin films for electro-chemical sensing of nitro-explosives in aqueous solutions. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalvand, A.R.; Zangeneh, M.M.; Jalili, F.; Soleimani, S.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. An elegant technology for ultrasensitive impedimetric and voltammetric determination of cholestanol based on a novel molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2020, 229, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, D.; Kempe, M.; Mosbach, K. Introduction of molecularly imprinted polymers as recognition elements in conductometric chemical sensors. Sens. Actuators B 1996, 33, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, M. Advances in high-resolution microscale impedance sensors. J. Sens. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Xia, J.; Tao, H.; Yang, P. Capacitive biosensor for glutathione detection based on electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer and kinetic investigation of the recognition process. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, T.L.; Zimin, D.; Rahm, M.; Weiss, D.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Mirsky, V.M. Capacitive detection in ultrathin chemosensors prepared by molecularly imprinted grafting photopolymerization. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3220–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbruno, J.J.; Zhang, G.; Gibson, U.J. Capacitive sensing of amino acids in molecularly imprinted nylon films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontimuang, C.; Suedee, R.; Dickert, F. Interdigitated capacitive biosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid detection of Hev b1 latex allergen. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 410, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.J. Composites of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and molecularly imprinted polymers for dopamine recognition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 4849–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yao, S. Novel layer-by-layer assembly molecularly imprinted sol-gel sensor for selective recognition of clindamycin based on Au electrode decorated by multi-wall carbon nanotube. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 344, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xing, X.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Lin, Q.; Lian, W.; Zhu, H. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotube-gold nanoparticle composites and chitosan for the detection of tyramine. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diñeiro, Y.; Menéndez, M.I.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Computational predictions and experimental affinity distributions for a homovanillic acid molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, S.; Turner, A.P.F.; Mosbach, K.; Haupt, K. Imprinted polymer-based sensor system for herbicides using differential-pulse voltammetry on screen-printed electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3698–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curie, J.; Curie, P. Developpement par compression de l’électricité polaire dans les cristaux hemièdres à faces inclinées. Bull. Soc. Fr. Miner. 1880, 3, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayela, C.; Dubourg, G.; Pellet, C.; Haupt, K. All-organic microelectromechanical systems integrating specific molecular recognition—A new generation of chemical sensors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5876–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, C.J.; Stanley, S.; Braithwaite, A.; Newton, M.I.; McHale, G. Molecular imprinted polymer coated QCM for the detection of nandrolone. Analyst 2002, 127, 1024–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.R.; Yau, Z.S.; Tasi, Y.C.; Chou, T.C.; Liu, C.C. Size-selective recognition of catecholamines by molecular imprinting on silica-alumina gel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Noworyta, K.; Kutner, W. Imprinted polymer-based enantioselective acoustic sensor using a quartz crystal microbalance. Anal. Commun. 1999, 36, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Murawaki, Y.; Reddy, P.S.; Abe, M.; Fujii, N. Molecular imprinting of caffeine and its recognition assay by quartz-crystal microbalance. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 435, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, H.; Ng, W.Y.; Lin, X.H.; Li, S.F.Y. Development of a hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer for the detection of hydrophilic targets using quartz crystal microbalance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 300, 127044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Nie, L. A novel molecularly imprinted nanosensor based on quartz crystal microbalance for specific recognition of α-amanitin. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Ahmad, O.S.; Guerreiro, A.; Karim, K.; Sandström, N.; Ostanin, V.P.; van der Wijngaart, W.; Piletsky, S.A.; Ghosh, S.K. Direct detection of small molecules using a nano-molecular imprinted polymer receptor and a quartz crystal resonator driven at a fixed frequency and amplitude. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, K.; Jandas, P.J.; Luo, J.; Fu, C.; Wei, Q. Molecularly imprinted poly(methacrylic acid) based QCM biosensor for selective determination of L-tryptophan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 611, 125859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Kotova, K.; Lieberzeit, A.P. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for formaldehyde sensing with QCM. Sensors 2016, 16, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Peng, H.; Liang, C.; Yao, S. New assay system for phenacetin using biomimic bulk acoustic wave sensor with a molecularly imprinted polymer coating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 73, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretjakov, A.; Syritski, V.; Reut, J.; Boroznjak, R.; Öpik, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer film interfaced with Surface Acoustic Wave technology as a sensing platform for label-free protein detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 902, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Tretjakov, A.; Reut, J.; Boroznjak, R.; Öpik, A.; Rappich, J.; Furchner, A.; Hinrichs, K.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted polymer integrated with a surface acoustic wave technique for detection of sulfamethizole. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazouz, Z.; Rahali, S.; Fourati, N.; Zerrouki, C.; Aloui, N.; Seydou, M.; Yaakoubi, N.; Chehimi, M.M.; Othmane, A.; Kalfat, R. Highly selective polypyrrole MIP-based gravimetric and electrochemical sensors for picomolar detection of glyphosate. Sensors 2017, 17, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidakova, A.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Saarma, M.; Syritski, V. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based SAW sensor for label-free detection of cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor protein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 308, 127708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L.D.C. On waves propagated along the plane surface of an elastic solid. Proc. London Math. Soc. 1886, 17, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Pi, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, F.; Pan, F.; Li, F.; Jia, S.; Shi, J.; Deng, S.; Chen, M. Label-free and high-sensitive detection of human breast cancer cells by aptamer-based leaky surface acoustic wave biosensor array. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyanarayanan, S.; Cywinski, P.J.; Moro, A.J.; Mohr, G.J.; Kutner, W. Chemosensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. In Topics in Current Chemistry: Molecular Imprinting; Haupt, K., Ed.; Molecular Imprinting: Austin, TX, USA, 2012; pp. 165–265. ISBN 9783642284205. [Google Scholar]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Piletska, E.V.; Chen, B.; Karim, K.; Weston, D.; Barrett, G.; Lowe, P.; Turner, A.P.F. Chemical grafting of molecularly imprinted homopolymers to the surface of microplates. Application of artificial adrenergic receptor in enzyme-linked assay for β-agonists determination. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4381–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullett, W.M.; Martin, P.; Pawliszyn, J. In-tube molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase microextraction for the selective determination of propranolol. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Zhang, C.; Yu, F.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Layer-by-layer self-assembly CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymers modified chemiluminescence sensor for deltamethrin detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Lin, J.M. Preparation of surface imprinting polymer capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots and their application for chemiluminescence detection of 4-nitrophenol in tap water. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7380–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Fluorescence sensing. In Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Lakowicz, J.R., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 623–673. ISBN 978-0-387-46312-4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Niu, Q.; Wei, T.; Li, T. Novel thiophene-based colorimetric and fluorescent turn-on sensor for highly sensitive and selective simultaneous detection of Al 3+ and Zn 2+ in water and food samples and its application in bioimaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1049, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, X.A.; Acha, V.; Bonomi, P.; Tse Sum Bui, B.; Haupt, K. A disposable evanescent wave fiber optic sensor coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer as a selective fluorescence probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, H.; Ma, F.; Sun, M.; Yu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, S. Efficient ratiometric fluorescence probe based on dual-emission quantum dots hybrid for on-site determination of copper ions. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6461–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Gao, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Upconversion particles coated with molecularly imprinted polymers as fluorescence probe for detection of clenbuterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Core-shell molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles as synthetic antibodies in a sandwich fluoroimmunoassay for trypsin determination in human serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24476–24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lai, J.P.; Lin, D.S.; Huang, X.X.; Zuo, Y.; Li, Y.L. A novel fluorescent multi-functional monomer for preparation of silver ion-imprinted fluorescent on-off chemosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, X.A.; Tse Sum Bui, B.; Resmini, M.; Bonomi, P.; Dika, I.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K. A versatile fiber-optic fluorescence sensor based on molecularly imprinted microstructures polymerized in situ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8317–8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhani, S.; Nahavandifard, F. Molecular imprinting-based fluorescent optosensor using a polymerizable 1,8-naphthalimide dye as a florescence functional monomer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Hardwick, S.A.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.V. Intrinsic fluorescence-based optical fiber sensor for cocaine using a molecularly imprinted polymer as the recognition element. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Ho, M.H.; Lin, H.Y. Optical recognition of salivary proteins by use of molecularly imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol)/quantum dot composite nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.M.; Narayanaswamy, R. Fluorescence sensor using a molecularly imprinted polymer as a recognition receptor for the detection of aluminium ions in aqueous media. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Fan, C.; Liu, H.; Pan, M.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S. A novel molecularly imprinted polymer on CdSe/ZnS quantum dots for highly selective optosensing of mycotoxin zearalenone in cereal samples. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2764–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; D’Agostino, G.; Porto, G.; Biasiolo, A.; Perri, C.; Arcadio, F.; Zeni, L. A molecularly imprinted polymer on a plasmonic plastic optical fiber to detect perfluorinated compounds in water. Sensors 2018, 18, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurelio, R.D.; Ashley, J.; Rodgers, T.L.; Trinh, L.; Temblay, J.; Pleasants, M.; Tothill, I.E. Development of a NanoMIPs-SPR-based sensor for β -lactoglobulin detection. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. SPR nanosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer film with gold nanoparticles for sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1. Talanta 2020, 219, 121219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Armutcu, C.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer film based plasmonic sensors for detection of ochratoxin A in dried fig. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, J.; Akamatsu, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; Miyoshi, D.; Nawafune, H.; Tamaki, K.; Sugimoto, N. Composite of Au nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, A.; Kitayama, Y.; Takano, E.; Ooya, T.; Takeuchi, T. Supraparticles comprised of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles and modified gold nanoparticles as a nanosensor platform. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25306–25311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompart, M.; De Wilde, Y.; Haupt, K. Chemical nanosensors based on composite molecularly imprinted polymer particles and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Ding, Y.; Li, X. Surface molecular imprinting onto silver microspheres for surface enhanced Raman scattering applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmont, A.S.; Jaeger, S.; Knopp, D.; Niessner, R.; Gauglitz, G.; Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymer films for reflectometric interference spectroscopic sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 3267–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Huang, S.; Xue, F.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Xue, M. Detection of organophosphorus compounds using a molecularly imprinted photonic crystal. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, Y.; Kunath, S.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K.; Mayes, A.G. Molecularly imprinted silver-halide reflection holograms for label-free opto-chemical sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmann, E.; Raether, H. Radiative decay of non radiative surface plasmons excited by light. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. A J. Phys. Sci. 1968, 23, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, A. Excitation of nonradiative surface plasma waves in silver by the method of frustrated total reflection. Physics (College Park. Md.) 1968, 410, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.L.; Bhalla, N.; Rafiee, S.D.; Estrela, P. Localized surface plasmon resonance as a biosensing platform for developing countries. Biosensors 2014, 4, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, L.; Andreetto, E.; Vestri, A.; Bovi, M.; Barozzi, M.; Iacob, E.; Busato, M.; Castagna, A.; Girelli, D.; Bossi, A.M. Surface plasmon resonance based on molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for the picomolar detection of the iron regulating hormone Hepcidin-25. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cennamo, N.; Donà, A.; Pallavicini, P.; D’Agostino, G.; Dacarro, G.; Zeni, L.; Pesavento, M. Sensitive detection of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by tridimensional monitoring of molecularly imprinted polymer with optical fiber and five-branched gold nanostars. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 208, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing - Synthesis, characterisation and application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lépinay, S.; Kham, K.; Millot, M.C.; Carbonnier, B. In-situ polymerized molecularly imprinted polymeric thin films used as sensing layers in surface plasmon resonance sensors: Mini-review focused on 2010–2011. Chem. Pap. 2012, 66, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.I.; Shaikh, H.; Mustafa, G.; Bhanger, M.I. Recent applications of molecularly imprinted polymers in analytical chemistry. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2019, 48, 179–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, P.I.; Pradeep, T. A Textbook of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- McNay, G.; Eustace, D.; Smith, W.E.; Faulds, K.; Graham, D. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and surface-enhanced resonance raman scattering (SERRS): A review of applications. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 65, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompart, M.; Gheber, L.A.; De Wilde, Y.; Haupt, K. Direct detection of analyte binding to single molecularly imprinted polymer particles by confocal Raman spectroscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nopper, D.; Lammershop, O.; Wulff, G.; Gauglitz, G. Amidine-based molecularly imprinted polymers-new sensitive elements for chiral chemosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamra, T.; Chaudhary, S.; Xu, C.; Johansson, N.; Montelius, L.; Schnadt, J.; Ye, L. Covalent immobilization of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles using an epoxy silane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Turco, A.; Chianella, I.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S.A.; Malitesta, C. Solid-phase synthesis of electroactive nanoparticles of molecularly imprinted polymers. A novel platform for indirect electrochemical sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.H.; Mosbach, K.; Haupt, K. A simple method for spin-coating molecularly imprinted polymer films of controlled thickness and porosity. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, G.; Hürttlen, J.; Pontius, H.; Hartlieb, K.; Krause, H. Gas phase detection of explosives such as 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 591, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, N.; Honeychurch, K.C.; Hart, J.P.; Whitcombe, M.J. Voltammetric determination of urinary 1-hydroxypyrene using molecularly imprinted polymer-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horemans, F.; Diliën, H.; Wagner, P.; Cleij, T.J. MIP-Based Sensor Platforms for Detection of Analytes in Nano- and Micromolar Range; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780444563316. [Google Scholar]
- Kamra, T.; Chaudhary, S.; Xu, C.; Montelius, L.; Schnadt, J.; Ye, L. Covalent immobilization of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles on a gold surface using carbodiimide coupling for chemical sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 461, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korposh, S.; Chianella, I.; Guerreiro, A.; Caygill, S.; Piletsky, S.; James, S.W.; Tatam, R.P. Selective vancomycin detection using optical fibre long period gratings functionalised with molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles. Analyst 2014, 139, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Dabrowski, M.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Surface development of molecularly imprinted polymer films to enhance sensing signals. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Deng, F.; Luo, S.; Tu, X.; Yang, L. Grafting of molecularly imprinted polymers from the surface of Fe3O4 nanoparticles containing double bond via suspension polymerization in aqueous environment: A selective sorbent for theophylline. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Z.; Florea, A.; Cristea, C.; Bessueille, F.; Vocanson, F.; Goutaland, F.; Zhang, A.D.; Səndulescu, R.; Lagarde, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. 1,3,5-Trinitrotoluene detection by a molecularly imprinted polymer sensor based on electropolymerization of a microporous-metal-organic framework. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.-P.; Sosnowska, M.; Sobczak, J.W.; KC, C.B.; Nesterov, V.N.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Simultaneous chronoamperometry and piezoelectric microgravimetry determination of nitroaromatic explosives using molecularly imprinted thiophene polymers. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 8361–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskin, M.; Tel-Vered, R.; Bourenko, T.; Granot, E.; Willner, I. Imprinting of molecular recognition sites through electropolymerization of functionalized Au nanoparticles: Development of an electrochemical TNT sensor based on π-donor-acceptor interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9726–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Transducer | Receptor | Analyte | LOD (mol/L) | Response Time (s) | Stability (Weeks) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potentiometric | MIPs | Nitrates | 0.2 × 10−6 | 24 | - | [37] |
| MIPs into membranes | Dy(III) | 2 × 10−6 | 10 | - | [35] | |
| Atrazine | 0.5 × 10−6 | 120 | - | [36] | ||
| Melamine | 5 × 10−6 | 16 | - | [22] | ||
| NAD(P)+/NAD(P)H | 2 × 10−7 | 60 | 4 | [46] | ||
| Thiophenols | 2 × 10−6 | 45 | 2 | [45] | ||
| MIP-covered electrode | Amoxicillin | 0.3 × 10−6 | 20 | - | [39] | |
| Metoprolol | 1.3 × 10−7 | 14 | - | [40] | ||
| MIP TiO2 thin films | Acids | 5 × 10−4 | 300 | - | [43] | |
| 5 × 10−5 | 300 | - | [44] | |||
| AMP 1 GMP CMP | 1.5 × 10−5 1.5 × 10−5 8 × 10−7 | 60 | - | [44] | ||
| Impedimetric | MIP layer on Au electrode | Phenylalanine | 3 × 10−3 | 900 | - | [33] |
| Glucose | 50 × 10−6 | - | <1 | [49] | ||
| MIP film | Nicotine | 0.5 × 10−6 | 600 | 12 | [25] | |
| MIP film | Theophylline | 1 × 10−6 | 600 | - | [50] | |
| MIP on Au electrode | Resorcinol | 0.1 × 10−6 | - | 5 | [51] | |
| MIP particles on Au electrode | Imidacloprid | 4.61 × 10−6 | - | - | [52] | |
| Multiplex MIP on gold electrodes | AMP 2 NFA 3 BMK 4 | 50 × 10−6 20 × 10−6 20 × 10−6 | - | - | [53] | |
| Conductometric | MIPs into membranes | Atrazine | 0.5 × 10−6 | 1800 | 16 | [54] |
| MIPs | Haloacetic acids | 3 × 10−9 | 30 | 12 | [55] | |
| Voltametric | MIP NPs | Morphine | 0.3 × 10−3 | - | - | [56] |
| MIP films | Ephedrine | 0.5 × 10−3 | - | - | [57] | |
| MIP | Paracetamol | 7.9 × 10−7 | - | - | [58] | |
| MIP | Dopamine | 1.98 × 10−9 | 4 | 1 | [59] | |
| MIP | Atrazine | 1 × 10−6 | 600 | - | [60] | |
| MIP Sol–gel film | Creatinine | 1.23 × 10−3 | 120 | <1 | [61] | |
| MIP-based electrode | Melamine | 0.83 × 10−9 | - | 4 | [62] | |
| TATP 5 | 27 × 10−6 | - | - | [24] | ||
| MIp(DA) 6 films | TNT 7 RDX 8 | 0.1 × 10−9 10 × 10−9 | - | - | [63] | |
| MIP-covered electrode | Cholestanol | 1 × 10−12 | - | 7 | [64] |
| Transducer | Receptor | Analyte | LOD (mol/L) | Response Time (s) | Stability (Weeks) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QCM | MIP film | (S)-propranolol | 50 × 10−6 | - | - | [80] |
| MIP membranes | Caffeine | 1 × 10−6 | 720 | - | [81] | |
| Two formats 1 | Catecholamines | - | 150 | - | [79] | |
| MIP film | Trichlorfon | 4.63 × 10−6 | - | 3 | [82] | |
| MIP film | Formaldehyde | 1 × 10−6 | 10 | - | [86] | |
| MIP NPs | N-hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone | 1 × 10−6 | 1800 | - | [84] | |
| MIP film onto QCM crystal | α-Amanitin | 0.052 × 10−12 | 1200 | poor | [83] | |
| L-tryptophan | 0.73 × 10−6 | 5 | - | [85] | ||
| SAW | MIP particles 2 | Phenacetin | 5 × 10−9 | 900 | - | [87] |
| MIP film | IgG | 0.4 × 10−9 | 1020 | - | [88] | |
| MIP film onto SAW chip | Sulfamethizole | 1.7 × 10−9 | 1000 | - | [89] | |
| MIP film onto Au electrode | Glyphosate | 1 × 10−12 | 1800 | - | [90] | |
| MIP film | CDNF protein | 4.2 × 10−6 | 1980 | - | [91] |
| Transducer | Receptor | Analyte | LOD (mol/L) | Response Time (s) | Stability (Weeks) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV/Vis and fluorescence | 3-Aminophenyl boronic acid film | Epinephrine | 9.2 × 10−6 | 1200 | - | [95] |
| Crushed and sieved MIP particles | Propranolol | 0.32 × 10−3 | - | - | [96] | |
| Crushed and sieved MIP particles | Al3+ | 3.62 × 10−6 | 40 | - | [110] | |
| Core shell composite particles | 4-nitrophenol | 76 × 10−9 | - | - | [98] | |
| QDs 1 embedded in MIP films/NPs | Amylase, lipase, lysozyme | 0.1 × 10−3, 0.1 × 10−3, 0.013 × 10−3 | 300 | - | [109] | |
| MIP particles embedded in a PVC 2 matrix | Deltamethrin | 0.018 × 10−3 | 180 | 3 | [97] | |
| MIP tip on an optical fiber | Cocaine | 2 × 10−6 | ~1000 | 4 | [108] | |
| MIP tip on an optical fiber | 2,4-D 3 | 0.25 × 10−9 | 600 | - | [106] | |
| Crushed and sieved MIP particles | Caffeine | 1.22 × 10−3 | 4800 | - | [107] | |
| MIP ionic liquid CdSe/ZnS QDs | Mycotoxin zearalenone | 3.12 × 10−6 | - | - | [111] | |
| MIP NPs embedded in a PVA 4 film, on an optical fiber | 2,4-D 3, Citrinin | 1 × 10−9, 1 × 10−6 | 600 | - | [101] | |
| Core-shell composite MIP particles | Clenbuterol | 0.12 × 10−6 | 300 | - | [103] | |
| MIP NPs | Trypsin | 50 × 10−12 | 7200 | - | [104] | |
| SPR | MIP film spin-coated on the SPR chip | Ammonium perfluorooctanoate | 0.13 × 10−6 | 600 | - | [112] |
| MIP NPs coupled on a SPR chip | β-lactoglobulin | 211 × 10−12 | - | - | [113] | |
| MIP film on a SPR chip | Aflatoxin B1 | 1.04 × 10−9 | 300 | 12 | [114] | |
| MIP film spin-coated on the SPR chip | Ochratoxin A | 0.028 × 10−6 | 600 | - | [115] | |
| LSPR | Au NPs embedded in an MIP gel | Adrenaline | 5 × 10−6 | long | - | [116] |
| Supra-particles between MIP-NPs and BPA-Au-NPs | Bisphenol A (BPA) | <10−9 | 1200 | - | [117] | |
| SERS/SERRS | Core-shell Au@MIP particles | (S)-propranolol | 1 × 10−7 | 1 | - | [118] |
| Mercaptobenzoic acid | 1 × 10−15 | - | - | [119] | ||
| Reflectometric | MIP films | Atrazine | 8 × 10−6 | 2000 | - | [120] |
| Colorimetric | MIPC 5 | Methyl phosphonic acid | 1 × 10−6 | 480 | - | [121] |
| Silver-halide holograms into MIPs films | Testosterone | 1 × 10−6 | long | - | [122] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060123
Leibl N, Haupt K, Gonzato C, Duma L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(6):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060123
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeibl, Nadja, Karsten Haupt, Carlo Gonzato, and Luminita Duma. 2021. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review" Chemosensors 9, no. 6: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060123
APA StyleLeibl, N., Haupt, K., Gonzato, C., & Duma, L. (2021). Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors, 9(6), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9060123








