Abstract
Glochidion chodoense, a rare and endangered plant endemic to Republic of Korea, is known for containing a wide variety of phytochemicals, including triterpenoid saponins and flavonoids. This study sought to profile the phytochemical composition of the leaves and branches of G. chodoense harvested during three different periods (May, July, and October 2023) using liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization/mass spectrometry (LC-ESI/MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography–photodiode array detection (HPLC/PDA). Plant materials were harvested, authenticated, and subjected to ethanol extraction prior to chemical analysis. LC-ESI/MS and quantitative HPLC/PDA analyses were conducted to identify and quantify nine key phytochemicals: norbergenin (1), bergenin (2), epigallocatechin (3), ethyl gallate (4), orientin (5), epicatechin gallate (6), isovitexin 2″-O-arabinoside (7), ellagic acid (8), and cynaroside (9). Our findings revealed significant seasonal variations in major phytochemicals, with leaves containing higher concentrations than branches. Notably, bergenin (2) showed the highest content in May leaves (43.42 mg/g extract), followed by October (17.60 mg/g extract) and July branches (8.56 mg/g extract). Ethyl gallate (4), which was absent or present in trace amounts in branches, was abundant in leaves, with concentrations of 22.24 mg/g extract in October, 21.75 mg/g extract in May, and 17.48 mg/g extract in July. A similar trend was observed for norbergenin (1). These findings provide valuable insights into the phytochemical composition of G. chodoense, emphasizing its potential applications in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and functional foods, while highlighting the critical importance of conserving this endangered species.
1. Introduction
Glochidion chodoense C. S. Lee & H. T. Im, commonly known as “Cho-do-man-du-na-mu” in Republic of Korea, was first discovered in Jindo-gun, Republic of Korea [1]. According to the Korea National Arboretum, G. chodoense was designated as a critically endangered plant in 2012 [2]. This species belongs to the Glochidion genus, which comprises over 250 species known for their rich content of triterpenoid saponins and flavonoids [3]. The Glochidion genus, predominantly consisting of tree and shrub species, is part of the family Phyllanthaceae [4]. This family, in turn, primarily consists of flowering plants and encompasses approximately 2000 species [5]. Members of the Glochidion genus are widely distributed across tropical Asia, Australia, and Madagascar [6]. The flowers of this genus are typically small and inconspicuous compared to the white or pale-yellow blossoms of many moth-pollinated plants [7].
The Glochidion genus is a group of flowering plants with significant phytochemical diversity [8]. Although research on this genus is limited, studies have identified a variety of phytochemicals, including sterols, terpenoids, flavonoids, and saponins [8]. For example, six types of lupine triterpenes have been isolated from the roots and stem wood of G. sphaerogynum and G. eriocarpum [9]. Additionally, studies have explored the potential of the Glochidion species for tumor prevention and cytotoxic activity [10]. Some species within this genus have also been reported for their medicinal applications in treating conditions such as fever, malaria, diarrhea, and ulcers [11].
Phytochemicals, which are plant-derived compounds, exhibit diverse bioactive properties [12]. They are broadly classified into primary metabolites, such as amino acids and proteins, and secondary metabolites, including saponins, alkaloids, and flavonoids [13]. Investigating bioactive phytochemicals can provide valuable insights into the therapeutic potential of underexplored medicinal plants for treating various diseases and symptoms [14]. Such diseases range from age-related eye conditions to life-threatening illnesses, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and type-2 diabetes [15,16]. Research into the biological activities of phytochemicals can therefore support their application in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries [17].
This study focuses on the chemical composition of the aerial parts of G. chodoense harvested at different times using liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization/mass spectrometry (LC-ESI/MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography–photodiode array detection (HPLC/PDA).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
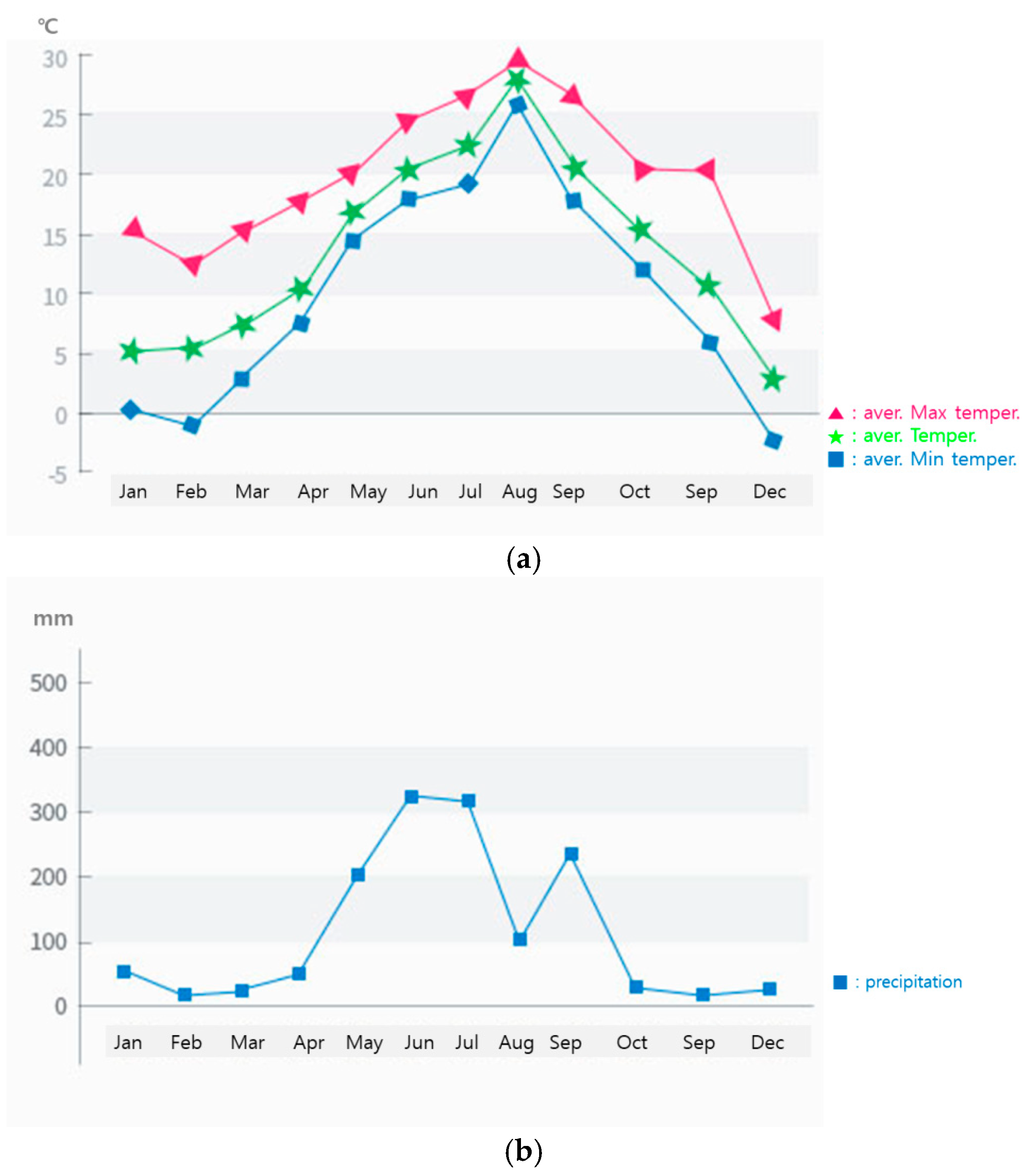
G. chodoense samples were collected from their native habitat in Jindo-gun, Republic of Korea (34.3672398° N, 126.1649026° E). Leaves and branches were harvested at three distinct time points (May, July, and October 2023) to examine seasonal variations in chemical composition. The sample collection site was the natural habitat of G. chodoense, a rare and endemic plant species. Samples were collected from mature trees within this habitat, ensuring that the selected trees were of similar age. Only healthy, undamaged leaves were chosen for analysis (Figure 1). The climatic conditions of the region, including monthly average temperature and precipitation, are presented in Figure 2. Samples were collected from mature trees, and the leaves used for analysis were continuously harvested, starting 30 days after leaf expansion began. The plant materials were authenticated by Dr. Jajung Ku, a co-author of this study, and voucher specimens were deposited in the National Arboretum Herbarium, under the accession number KHB1654521. The collected samples were divided into leaves and branches, air-dried under controlled conditions (25 °C, 50% relative humidity), and subsequently ground into a fine powder for further analysis. While lyophilization preserves thermolabile compounds, air-drying was selected due to its practicality, relevance to natural conditions, and wide use in phytochemical studies. Samples were stored in sealed containers at −20 °C to preserve their chemical integrity prior to experimental analysis.

Figure 1.
Wild G. chodoense within its natural habitat (a) and sampling (b).
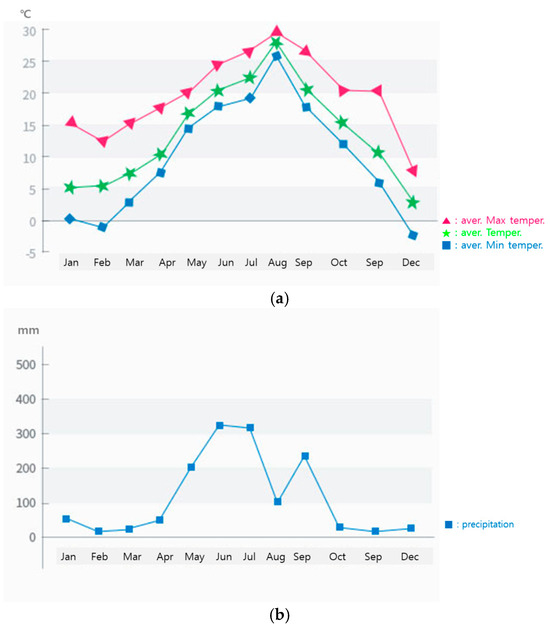
Figure 2.
Monthly average temperature (a) and precipitation (b).
2.2. Instruments and Chemicals
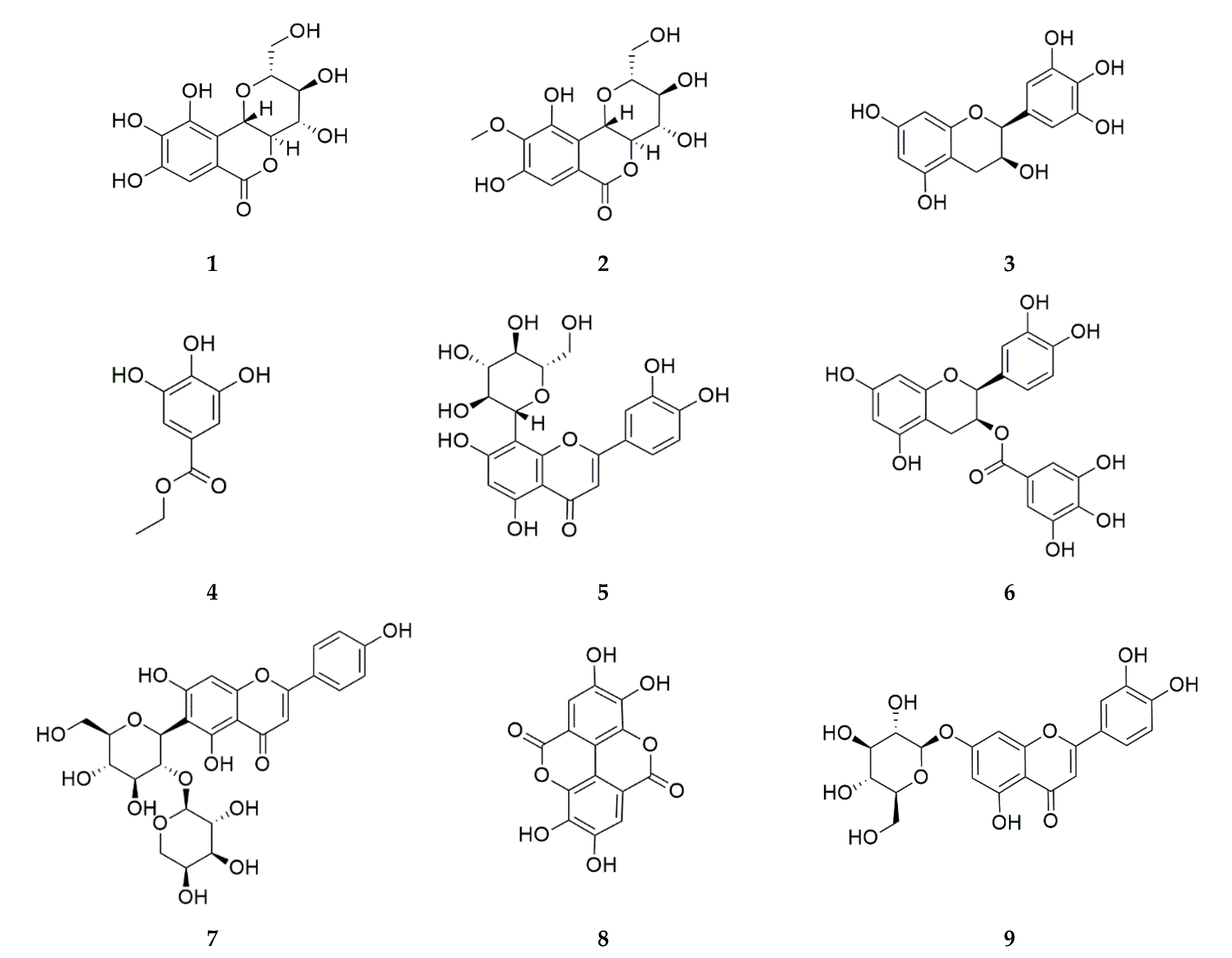
The LC-ESI/MS analysis was performed using a Vanquish Ultra HPLC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with a Triple TOF 5600+ high-resolution LC/MS/MS spectrometer (AB Sciex LLC, Framingham, MA, USA). Separation was conducted using a CORTECS T3 column (150 × 2.1 mm, 1.6 µm particle size, Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA). Quantitative analysis of the samples was performed using an HPLC apparatus, the Waters Alliance 2695 Separations Module (Milford, MA, USA), equipped with a Waters 2998 PDA Detector (Milford, MA, USA). For isolation, an Aegispak C18-L column (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) was purchased from Young Jin Biochrom Co., Ltd. (Seongnam, Republic of Korea). Standards for norbergenin, bergenin, epigallocatechin, ethyl gallate, orientin, epicatechin gallate, isovitexin 2″-O-arabinoside, ellagic acid, and cynaroside were obtained from the Natural Product Institute of Science and Technology (www.nist.re.kr, accessed on 10 November 2024), Anseong, Republic of Korea (Figure 3).
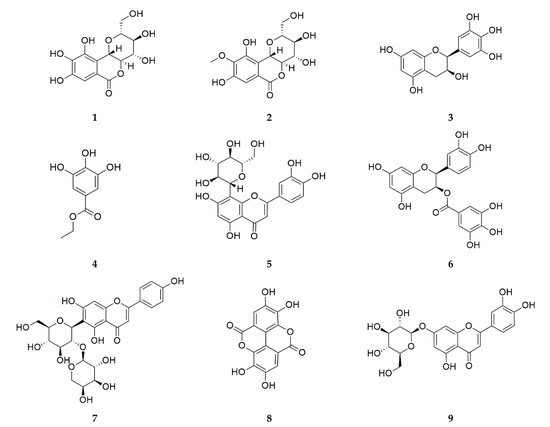
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of norbergenin (1), bergenin (2), epigallocatechin (3), ethyl gallate (4), orientin (5), epicatechin gallate (6), isovitexin 2″-O-arabinoside (7), ellagic acid (8), and cynaroside (9).
2.3. Extraction of Samples
Ten grams of dried G. chodoense samples were ground into a fine powder using a mortar and pestle before extraction. Ethanol (EtOH) was chosen as an extraction solvent due to its lower toxicity compared to methanol, making it safer for potential applications. The samples were extracted with 200 mL of EtOH using a Soxhlet reflux extractor for 3 h. The procedure was repeated three consecutive times for the same sample, and the resulting extracts were combined and dried using a rotary evaporator.
2.4. Preparation for HPLC/PDA Analysis
Prior to HPLC/PDA analysis, 30 mg of dried extracts were dissolved in 80% methanol (MeOH) to create a 20 mg/mL sample solution and filtered using a 0.2 μm polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) filter. One milligram of standards was also dissolved in 80% MeOH and filtered through a 0.2 μm PVDF filter to prepare the standard solutions. Solutions of norbergenin, bergenin, ethyl gallate, orientin, and ellagic acid were then sequentially diluted to concentrations of 7.8125–1000 µg/mL to form a calibration curve for quantitative analysis.
2.5. LC-ESI/MS Conditions
The LC system used for the separation process consisted of an Ultimate 3000 UHPLC system with a Waters Cortex T3 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.6 µm) maintained at a temperature of 45 °C. A mobile phase of water (eluent A: 0.1% formic acid) and ACN (eluent B: 0.1% formic acid) was used to maintain the temperature of the column. The gradient started at 3% B and then increased to 15% B over 15 min. This was followed by a further increase to 100% B over 35 min and maintained for a further 5 min, giving a total running time of 55 min. Finally, the column was re-equilibrated to 3% eluent B for 5 min. The flow rate was adjusted to 0.25 mL/min. The Triple TOF 5600+ (AB SCIEX, Concord) was used to perform MS and MS/MS detection under both positive and negative electrospray ionization conditions. Full scan and information-dependent acquisition (IDA) mode were employed with a mass range of 100–2000 m/z. The experimental parameters included ion spray voltages of 5.5 kV (positive mode) and 4.5 kV (negative mode), gas-1 and gas-2 pressures of 50 psi each, curtain gas at 25 psi, collision gas at 20 psi, and a source temperature of 500 °C. Collision energies were set at 35 ± 15 eV for positive mode and −35 ± 15 eV for negative mode. The identification of compounds was performed by comparing the obtained mass spectra with reference spectra from NIST, MoNA, and an in-house library.
2.6. HPLC/PDA Conditions
Quantitative analysis was performed using an Aegispak C18-L column (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm). The following HPLC conditions were applied: the column temperature was set to 35 °C, the injection volume was 10 μL, the flow rate was 1 mL/min, and the UV wavelength was set to 254 nm. The mobile phases consisted of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in water (A) and acetonitrile (B). A gradient system was used as follows: 92% A from 0 to 10 min, 84% A from 15 to 16 min, 82% A from 23 to 24 min, 75% A at 31 min, 100% B from 36 to 46 min, and 92% A from 51 to 61 min.
2.7. Calibration Curve
Prior to HPLC/PDA analysis, bergenin, ethyl gallate, orientin, and ellagic acid were each dissolved in 80% MeOH to create 1 mg/mL stock solutions. These solutions were then sequentially diluted to seven concentrations to form a calibration curve. The contents of the four compounds (mg/g) were calculated using the following formula:
where C is the concentration of the standard in the sample solution, calculated using the calibration curve equation based on peak areas of the analytes, V is the total volume of the test solution, D is the dilution factor, P is the standard purity, and W is the sample weight. The calibration curves for the phytochemicals are shown in Table 1, demonstrating good linearity with R2 values ranging from 0.9996 to 1.

Table 1.
Calibration curves of compounds 1, 2, 4, 5, and 8.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The mean ± standard deviation represents the experimental results. Using Minitab 16 software (Minitab LLC, State College, PA, USA), statistical significance was evaluated using an analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple range test. All experiments were conducted in triplicate (n = 3, biological replicates).
3. Results
3.1. LC-ESI/MS Analysis
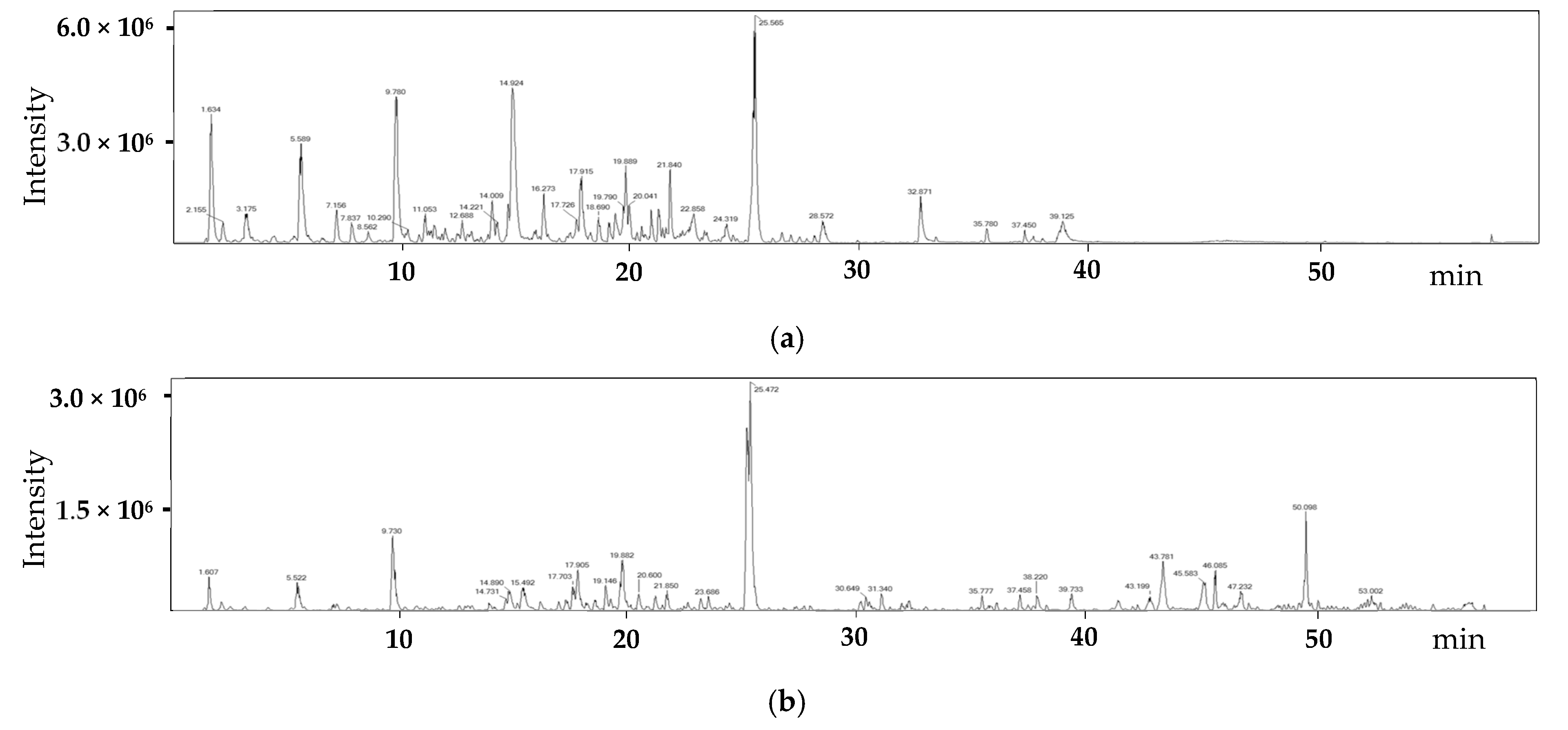
The compounds present in G. chodoense were characterized using LC-ESI/MS analysis. The total ion chromatograms of the EtOH extract of the sample are shown in Figure 4. Ten compounds were selected, and listed in Table 2, based on their peak intensity (indicating relative abundance) and their identification through mass-to-charge ratios, fragmentation patterns, and spectral matching with a spectral database. Identification was further confirmed by comparing MS2 fragmentation patterns with reference spectra from the database. The compounds that had the most significant presence in the sample and a high confidence level in identification were selected.
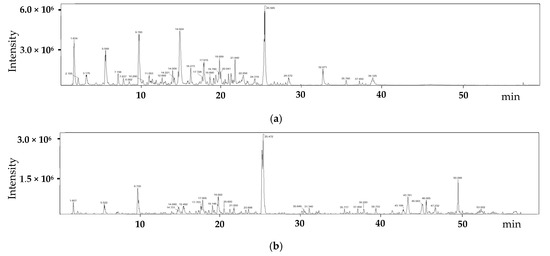
Figure 4.
Total ion chromatograms of EtOH extract from G. chodoense in negative (a) and positive (b) ionization modes using LC-ESI/MS.

Table 2.
LC-ESI/MS profiling of G. chodoense in positive and negative ionization modes.
3.2. HPLC/PDA Analysis
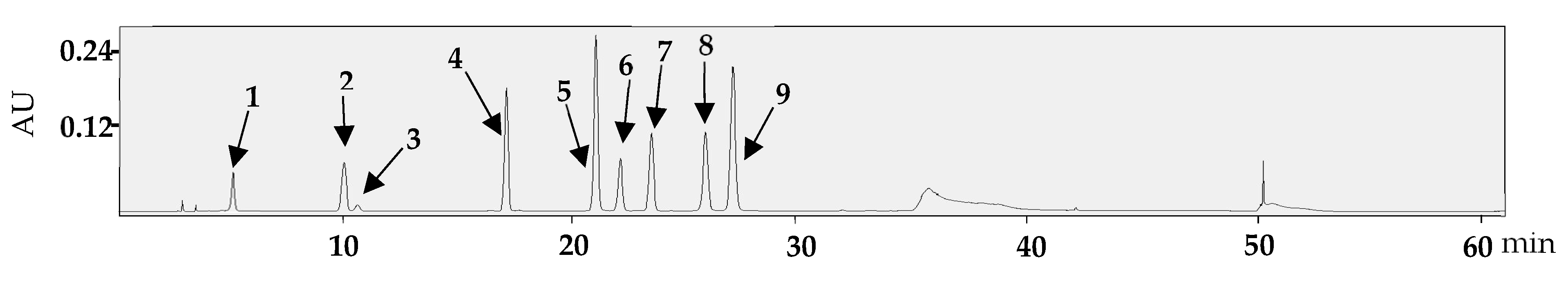
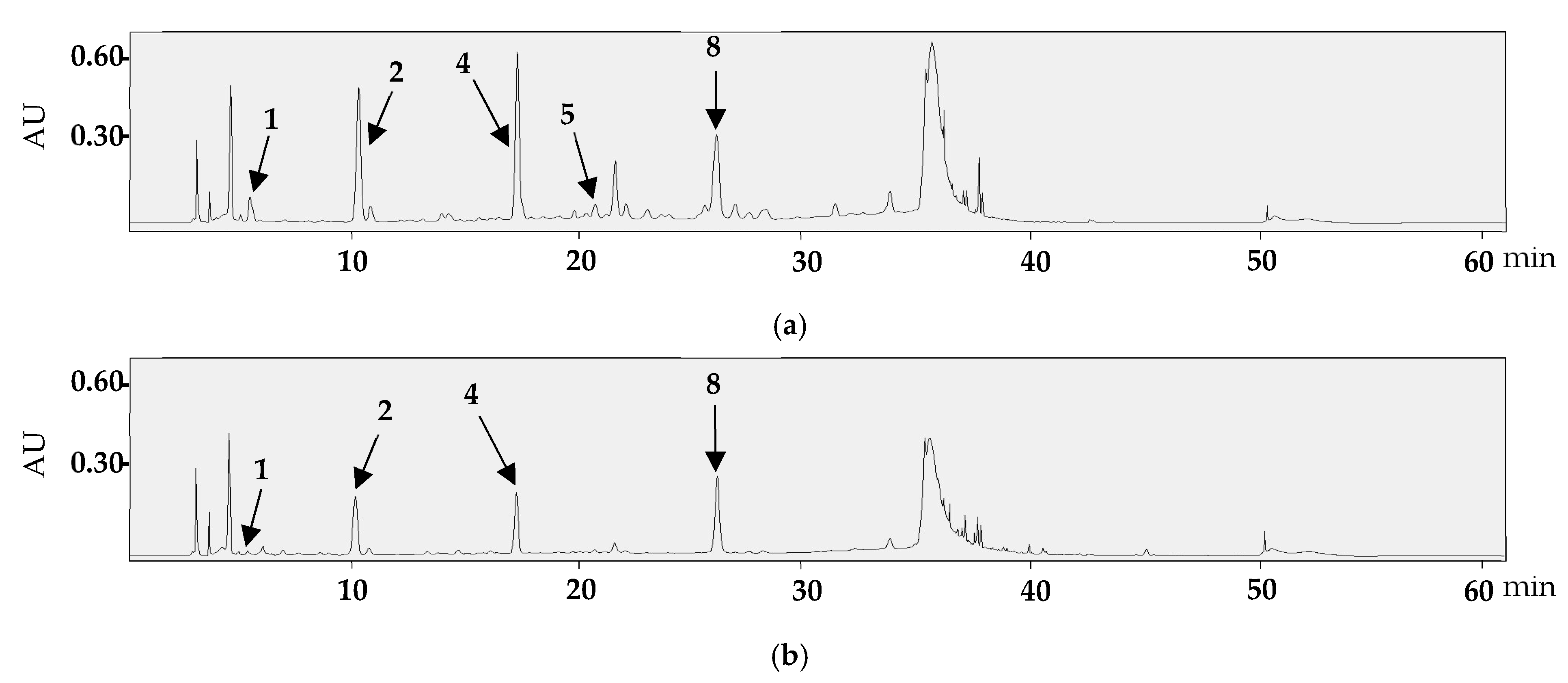
Quantitative analysis revealed the content of compounds 1, 2, 4, 5, and 8 which were quantified based on the calibration curves (Table 1). The calibration curves showed excellent linearity, with R-values ranging from 0.9996 to 1. The HPLC/PDA chromatograms of the standards analyzed simultaneously are presented in Figure 5, while the chromatograms for leaf and branch samples are shown in Figure 6.
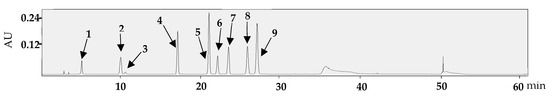
Figure 5.
HPLC/PDA chromatograms of norbergenin (1), bergenin (2), epigallocatechin (3), ethyl gallate (4), orientin (5), epicatechin gallate (6), isovitexin 2″-O-arabinoside (7), ellagic acid (8), and cynaroside (9).
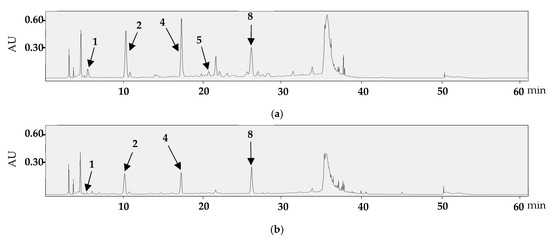
Figure 6.
HPLC/PDA chromatograms of the leaf samples collected in May (a) and the branch samples collected in October (b).
Compounds 3, 6, and 7 were not detected in any of the branch or leaf samples. The total content of compounds 1, 2, 4, 5, and 8 was highest in leaf sample 5 (78.52 mg/g extract), while most compounds were either undetected or detected only in trace amounts in the branch samples collected in May (Table 3).

Table 3.
Content of compounds 1–9.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the chemical composition and biological activities of G. chodoense, a plant that has been rarely studied. Specifically, it focused on seasonal variations in the chemical composition and differences between plant parts (leaves and branches).
Previous research has explored the potential industrial uses of its constituents. Norbergenin (1), an O-demethylated derivative of bergenin, has been reported to exhibit anti-arthritic activities, particularly in relation to Th1/Th2 cytokine balance [18]. Additionally, significant anti-inflammatory effects of norbergenin have been linked to its inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK, and STAT3 pathways [19]. Bergenin (2), a glycosidic secondary metabolite of trihydroxybenzoic acid, was first isolated from the rhizomes of Bergenia crassifolia [20]. Both bergenin and norbergenin have been shown to inhibit tyrosine hydroxylase [21]. Bergenin has been extensively studied for its total synthesis and pharmacological applications, including antifungal and antidiabetic properties, as well as its ability to promote wound healing [22]. Ethyl gallate (4), a phenolic antimicrobial compound abundant in longan, walnuts, and wine, has been shown to induce a dose- and time-dependent reduction in the proliferation of MDA-MB-231/MCF-7 breast cancer cells [23,24,25]. Orientin (5), a C-glycosylflavonoid, has been isolated from Ocimum sanctum and Jatropha gossypifolia [26]. Studies have demonstrated that orientin can reduce blood clot formation and prevent platelet aggregation, both in vitro and in vivo [27]. Ellagic acid (8), commonly found in pomegranate, has demonstrated a range of beneficial effects, including anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties, and the ability to inhibit pigmentation in UV-irradiated human skin [28,29].
However, because G. chodoense is a critically endangered plant, phytochemical research on this species remains limited. Ten compounds, including compounds 1–9, were identified using LC-ESI/MS, and quantitative analysis of the samples was conducted via HPLC/PDA analysis. Significant variations in phytochemical content were observed between different plant structures. For instance, leaves exhibited higher concentrations of phytochemicals compared to branches harvested at the same time. Among all samples, the highest total content was observed in leaves and branches harvested in May. Specifically, the concentration of compound 2 was highest in leaves from May (43.42 mg/g extract), followed by branch samples from October (17.60 mg/g extract) and July (8.56 mg/g extract). Compounds 1 and 4 were either absent or present in low amounts in branch samples compared to leaf samples.
The influence of harvest timing on factors such as phytochemical content, antioxidative functions, and growth patterns in the Lamiaceae species has been previously confirmed through heatmap analysis [30]. Additionally, seasonal variations, including humidity, have been reported to affect total phenolic, flavonoid, and alkaloid content in medicinal plant samples [31]. These variations may be attributed to factors such as reduced nutrient synthesis, decreased photosynthetic activity, and lower nutrient absorption from the soil [32]. Similarly, Tran et al. (2023) analyzed the chemical composition of three different leaf types of Lepidium sativum, suggesting that differences in chemical profiles may correlate with superior biological functions [33].
Further studies are needed to explore the bioactive functions of G. chodoense samples, particularly to understand the synergistic and antagonistic effects of phytochemical mixtures on activities such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions [34,35,36]. Such investigations would also help identify optimal environmental conditions for the mass production of G. chodoense, unlocking its potential for large-scale industrial applications. Also, since the current study focused on quantifying marker compounds of a rarely studied plant, further research regarding the metabolomic aspects and additional analysis is still needed in order to uncover the detailed relationship between plant growth stages and phytochemical variations. Furthermore, future studies will further assess the drying effects on compound stability, to optimize the most efficient method.
5. Conclusions
The chemical composition of the endangered plant species G. chodoense and its possible uses in a variety of industries have not been yet investigated, despite their ecological importance. By examining the relationship between various plant sections and harvesting times in relation to the phytochemical content of G. chodoense, this study sought to provide an initial understanding of its chemical composition. A two-step analytical method was used to accomplish this. The phytochemical components were first identified and characterized using LC-ESI/MS, from which eleven selected compounds have been analyzed by a quantitative evaluation using HPLC/PDA. It enabled a more accurate detection of certain bioactive chemicals. Depending on the plant section and harvest season, the phytochemical concentration varied greatly, according to this study’s findings. In particular, the phytochemical concentrations in the leaves were greater than those in the branches, indicating that the leaves could be a more abundant source of bioactive substances. Furthermore, seasonal variations were found to influence the levels of bergenin (2), highlighting the impact of environmental conditions on the plant’s chemical composition. Additionally, differences between plant parts significantly affected the concentrations of norbergenin (1) and ethyl gallate (4), emphasizing the importance of selecting the appropriate plant material for optimal extraction of valuable compounds. These results underscore the necessity for a more comprehensive investigation of the chemical composition of G. chodoense, as some selected compounds were analyzed in this study. By systematically investigating the bioactivity of these compounds and carefully considering factors such as harvest timing and plant part selection, researchers could validate the practical applications of G. chodoense in a wide range of industries. These include pharmaceuticals, where their bioactive compounds may contribute to drug development, cosmetics, where their natural extracts could enhance skincare formulations, and food production, where it may offer health-promoting properties as a functional ingredient. Ultimately, this study suggests the potential applications of G. chodoense, although further research is needed to fully elucidate its bioactive properties and commercial viability, paving the way for its sustainable utilization in various scientific and industrial fields.
Author Contributions
LC-ESI/MS and HPLC/PDA analysis and writing–original draft, N.Y.; experimental design and funding acquisition, J.K.; sampling and resources, Y.-H.K.; supervision, writing—review and editing, S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Forest Science, Suwon, Republic of Korea (grant number: “FG0802-2020-01-2024”).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This published article contains all the data created or analyzed during this study. Any additional data or information can be made available to the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Forest Recreation Department (Jindo Country Office, Jindo, Republic of Korea) for providing the samples used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.L.; Han, S.H.; Lee, H.; Han, J.E.; Kim, T.S.; Seong, S.H.; Kim, B.R.; Lee, H.N.; Seo, C.; et al. In vitro callus induction and growth for medicinal use of an endangered Korean native plant, Glochidion chodoense C. S. Lee and H. T. Im. Rhizosphere 2024, 29, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Son, S.W. Korean and worldwide research trends on rare plant and endemic plant in Korea. Korean J. Environ. Ecol. 2022, 36, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, S.; Chaintanya, R.S.N.A.K.K.; Vinod, K.R.; Rao, K.N.V.; Banji, D.; Sudhakar, K.; Swetha, R. An updated review on the genus Glochidion plant. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 2, 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Brahma, P.; Baruah, S. Comparative morphological and ethnobotanical assessment of certain taxa of genus Glochidion (Phyllanthaceae) from Assam, India. J. Threat. Taxa. 2023, 15, 24409–24419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Deng, M. Phyllanthaceae. In Identification and Control of Common Weeds: Volume 2; Xu, Z., Deng, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 475–486. ISBN 978-94-024-1157-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M.; Takimura, A.; Kawakita, A. An obligate pollination mutualism and reciprocal diversification in the tree genus Glochidion (Euphorbiaceae). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5264–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Kawakita, A.; Kato, M. Interspecific variation of floral scent composition in Glochidion and its association with host-specific pollinating seed parasite (Epicephala). J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 1065–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, N.N.; Hop, N.Q.; Tuyet, T.; Bich, T.; Son, N.T. Glochidion species: A review on phytochemistry and pharmacology. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2024, 19, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puapairoj, P.; Naengchomnong, W.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M.M.; Pedro, M.; Nascimento, M.S.; Silva, A.M.; Herz, W. Cytotoxic activity of lupane-type triterpenes from Glochidion sphaerogynum and Glochidion eriocarpum two of which induce apoptosis. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thang, T.D.; Kuo, P.C.; Yu, C.S.; Shen, Y.C.; Hoa, L.T.M.; Van Thanh, T.; Kuo, Y.H.; Yang, M.L.; Wu, T.S. Chemical constituents of the leaves of Glochidion obliquum and their bioactivity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, D.; Cheng, R.; Yang, C.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y. A new phloroglucinol glucoside from the whole plants of Glochidion eriocarpum. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, 35, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velavan, S. Phytochemical techniques-a review. World J. Sci. Res. 2015, 1, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Koche, D.; Shirsat, R.; Kawale, M. An overeview of major classes of phytochemicals: Their types and role in disease prevention. Hisiopia 2016, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, M.; Saxena, J.; Nema, R.; Singh, D.; Gupta, A. Phytochemistry of medicinal plants. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2013, 1, 168–182. [Google Scholar]
- Rhone, M.; Basu, A. Phytochemicals and age-related eye diseases. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. Phytochemicals and their role in curing fatal diseases: A review. Pure Appl. Biol. 2018, 7, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawatra, A.; Gupta, S.; Dhankhar, R.; Singh, P.; Gulati, P. Application of phytochemicals in therapeutic, food, flavor, and cosmetic industries. In Phytochemical Genomics; Swamy, M.K., Kumar, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 85–108. ISBN 978-981-19577-8-9. [Google Scholar]
- Nazir, N.; Koul, S.; Qurishi, M.A.; Taneja, S.C.; Ahmad, S.F.; Bani, S.; Qazi, G.N. Immunomodulatory effect of bergenin and norbergenin against adjuvant-induced arthritis—A flow cytometric study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cai, Z.; Schindler, F.; Bahiraii, S.; Brenner, M.; Heiss, E.H.; Weckwerth, W. Norbergenin prevents LPS-induced inflammatory responses in macrophages through inhibiting NFκB, MAPK and STAT3 activation and blocking metabolic reprogramming. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1117638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimo, Z.M.; Yakubu, M.N.; da Silva, E.L.; de Almeida, A.C.G.; Chaves, Y.O.; Costa, E.V.; da Silva, F.M.A.; Tavares, J.F.; Monteiro, W.M.; de Melo, G.C.; et al. Chemistry and pharmacology of bergenin or its derivatives: A promising molecule. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Fang, L.H.; Lee, M.K.; Ku, B.S. In vitro inhibitory effects of bergenin and norbergenin on bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajrocharya, G.B. Diversity, pharmacology and synthesis of bergenin and its derivatives: Potential materials for therapeutic usages. Fitoterapia 2015, 101, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sui, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, B. Stimulation of the production of prostaglandin E2 by ethyl gallate, a natural phenolic compound richly contained in longan. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooshiro, A.; Hiradate, S.; Kawano, S.; Takushi, T.; Fujii, Y.; Natsume, M.; Abe, H. Identification and activity of ethyl gallate as an antimicrobial compound produced by Geranium carolinianum. Weed Biol. Manag. 2009, 9, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yuan, J.; Du, X.; Wang, M.; Yue, L.; Liu, J. Ethyl gallate suppresses proliferation and invasion in human breast cancer cells via Akt-NF-κB signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.Y.; Ling, A.P.K.; Koh, R.Y.; Wong, Y.P.; Say, Y.H. A review on medicinal properties of orientin. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Bae, J.S. Antithrombotic and antiplatelet activities of orientin in vitro and in vivo. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Ghadiri, M.; Ramezani, M.; Askari, V.R. Antiinflammatory and anti-cancer activities of pomegranate and its constituent, ellagic acid: Evidence from cellular, animal, and clinical studies. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 685–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Koga, T.; Arii, M.; Kawasaki, S. Effects of oral administration of ellagic acid-rich pomegranate extract on ultraviolet-induced pigmentation in the human skin. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2006, 52, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, H.Y. Effects of harvest timing on phytochemical composition in Lamiaceae plants under an environment-controlled system. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwamatope, B.; Tembo, D.; Kampira, E.; Mallwichi-Nyirenda, C.; Ndolo, V. Seasonal variation of phytochemicals in four selected medicinal plants. Pharmacogn. Res. 2021, 13, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Park, S.D.; Park, C.H.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.C.; Choi, B.S. Changes of root yield and paeoniflorin content affected by harvesting times in peony (Paeonia lactiflora). Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2000, 8, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, G.H.; Cho, H.; Lee, H.D.; Lee, C.D.; Shim, J.; Ahn, K.H.; Sung, J.S.; Yoo, E.; Lee, S. Analysis of the total polyphenol, flavonoid, and phenolic acid contents in three different leaf types of Lepidium sativum. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2023, 29, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Deng, Z. The synergistic and antagonistic antioxidant interactions of dietary phytochemical combinations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5658–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Virgous, C.; Si, H. Synergistic anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of combined phytochemicals. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 69, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, T.T.M.; Tran, G.H.; Ngyuyen, T.K.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, S. Antioxidant activity of different cultivars of Chrysanthemum morifolium and quantitative analysis of phenolic compounds by HPLC/UV. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).