Abstract
Despite being present in minimal amounts, vitamin B2 (VB2), vitamin C (VC), and vitamin B6 (VB6) each play indispensable roles in human metabolisms. Given that VB2, VC, and VB6 cannot be synthesized by the human body, detections of these three vitamins both in fermentation liquid where vitamins are industrially manufactured and in human serum where vitamin concentrations could be clinically controlled are of significant importance. Here, a nanoporous gold (NPAu) modified screen-printed electrode (NPAu/SPE) was fabricated to detect VB2, VC, and VB6 based on NPAu’s electro-oxidation towards vitamins. Owing to the wide separation of peak potentials among VB2, VC, and VB6, the simultaneous detection of these three vitamins was achieved by the NPAu/SPE within a potential range from −0.8 V to 0.8 V. The achieved limits of detection (LOD) for VB2, VC, and VB6 were 0.46, 6.44, and 1.92 μM, with sensitivities of 68.58, 4.77, and 15.94 μA/μM, respectively. Subsequent reliability experiments suggested that the NPAu/SPE exhibited solid anti-interference capability and repeatability. Additionally, the real-sample detection of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 was achieved both in human serum and in fermentation liquid with comparable accuracy (the recovery rates were from 89.8% to 111.7%) as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Moreover, the portable NPAu/SPE showed comparable performance in terms of the LOD and linear dynamic range when compared to glassy carbon electrodes (GCE) limited to laboratory detection. The proposed NPAu/SPE possesses various advantageous properties including portability, easy fabrication, high sensitivity, and cost-efficiency, making it a potential candidate for clinical and industrial multi-vitamins analysis.
1. Introduction
Vitamins, as a group of organic compounds that are present in the human body in minimal amounts, are indispensable for maintaining good health. Among all of them, vitamin B2 (VB2), vitamin C (VC), and vitamin B6 (VB6) are three water-soluble vitamins essential for maintaining human health. VB2 (riboflavin) is crucial for maintaining the human body’s energy supply such as the decomposition of fats and carbohydrates by directly promoting the formation of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and flavin mononucleotide (FMN) [1]. As a coenzyme, VB6 (pyridoxine) is involved not only in more than 100 metabolic reactions but also in red blood cells production, brain development during pregnancy and infancy, and nervous and immune systems maintenance [1]. VC (ascorbic acid), a necessary nutrient, is especially important for the prevention and treatment of multiple diseases such as scurvy, infertility, cancer, mental illness, and oxidative stress [1].
The absence or deficiency of any of the three vitamins could lead to various diseases. For instance, a deficiency of VB6 may lead to symptoms of psychiatric disorders such as dementia and cognitive impairment [2]. The absence of VB2 could interrupt a myriad of enzymatic syntheses including FAD and FMN, which are enzymes involved in important oxidative metabolisms [3,4]. Last but not least, VC deficiency could result in cardiovascular diseases like scurvy and anemia [5]. Unfortunately, VB2, VC, and VB6 cannot be synthesized inside the human body, so obtaining them from dietary sources becomes necessary [1,6]. In addition to natural sources, VB2, VC, and VB6 are produced industrially by microbial fermentation in bulk amounts [7]. Therefore, the detection towards VB2, VC, and VB6 has received significant attention due to the high detection demands in recent years [8]. Moreover, on-going vitamin detection works target various practical fields including clinical diagnostics, industrial production, and nutrition tests [9].
Given the importance of vitamin detection, various methods of detection have been proposed and developed. The most commonly recognized ones are fluorescence-, spectroscopic-, or chromatographic-based methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [10,11,12]. While these traditional methods of vitamin detection feature high sensitivity and selectivity, they suffer from complex instrumentation, well-trained personnel, large sample sizes, and long-time analysis [13,14,15]. Moreover, the immovability of the detection instrumentation has significantly limited the applicability of these detection methods in home-use medical scenarios.
Compared with the traditional vitamin detection methods above, electrochemical sensors are known for their simple instrumentation, small sample size, and short-time analysis [16]. Some electrochemical sensors even exhibit a higher sensitivity towards vitamins than traditional detection methods [17]. Among various types of electrochemical sensors, screen-printed electrodes (SPE) stand out with their portability, cost-efficiency, and simple fabrication [18]. More importantly, the high adaptability of SPE has enabled it to be modified by a variety of nanomaterials to further improve its detection performance. Several works have proposed that a nanomaterial named nanoporous gold (NPAu) could be used as a candidate to be attached to a thin, free-standing electrode [19,20]. Later experiments showed that, owing to its excellent electric conductivity and structural integrity, NPAu can be easily integrated into detection platforms such as SPE [20]. The electrochemical properties of NPAu are rooted within its topologically and morphologically equivalent gold ligaments and nanopore channels, together with its hidden, internal bi-continuous nanostructure, and the source of the catalytic capability of NPAu is still under debate, with some suggesting that an interplay among many factors during catalysis has rendered NPAu’s catalytic ability [21,22]. Moreover, a high surface-to-volume ratio may also contribute to the remarkable catalytic capability of NPAu by enhancing interactions between the analyte and NPAu catalytic sites. Additionally, NPAu’s particular fabrication method of dealloying (also called alloy corrosion) a gold alloy endows it with a cleaner surface and eliminates the possible poisoning or passivating effects from unwanted molecules or ions such as polymer surfactants and Cl−, commonly found in other Au nanocatalysts [21,22], which indicates that NPAu has good chemical stability. The electrocatalytic activity of NPAu exhibits good temperature stability; for example, it displays exceptional catalytic performance for CO oxidation, even at temperatures as low as −30 °C [21,22]. These unique properties guarantee the NPAu-based electrochemical sensors have excellent sensing characteristics such as temperature and chemical stability, high sensitivity, repeatability, etc.
In this study, an NPAu-modified SPE (NPAu/SPE) was constructed for VB2, VC, and VB6 detection by coating NPAu films to the surface of the working electrode area of SPE (Scheme 1A). The resulting NPAu/SPE’s oxidation behavior, impedance, linear detection range, and selectivity towards VB2, VC, and VB6 were analyzed. Furthermore, the simultaneous detection of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 was achieved, and the anti-interference capability and repeatability of the NPAu/SPE were analyzed and discussed in detail. The practical performance of the NPAu/SPE was then validated by detecting VB2, VC, and VB6 in real samples (human serum and fermentation liquid). A comparison between the NPAu/SPE and other electrochemical sensors developed previously in terms of accuracy of the limit of detection (LOD), linear dynamic range, and sensitivity was discussed.
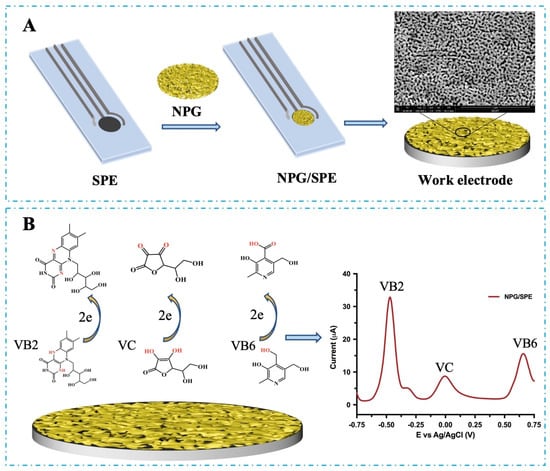
Scheme 1.
Schematic description for the fabrication of the portable NPAu/SPE (A) and the electrochemical catalysis of VB2, VC, and VB6 by the portable NPAu/SPE (B).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
VB2, VC, and VB6 were purchased from Aladdin Chemistry Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). HNO3 and other chemical reagents were purchased from Beijing Dingguo changsheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Nafion perfluorinated solution with a concentration of 0.5% (v/v) was purchased from Kunshan Sunlaite Co., Ltd. (Jiangsu, China). All chemicals were of an analytically pure grade. The ultrapure water (ρ > 18 MΩ cm) used throughout this paper was prepared by Millipore’s Direct-Q 3 UV (Boston, MA, USA). The SPE (0.4 in. × 1.333 in.) incorporating a three-electrode system was purchased from Redmatrix China Limited (Beijing, China).
Sodium acetate buffer (NAAC, 100 mM, pH 5.0) was used as an electrolyte in the electrochemical analysis of VB2, VC, and VB6. Sodium acetate (12.5 g) was dissolved in 500 mL of ultrapure water to form NAAC. The stock solutions of VB2 (10 mM), VC (10 mM), and VB6 (10 mM) were prepared with ultrapure water.
The human serum used in the real samples testing in this study has been ethically approved (Ethical code No. D202111Ab). The ethical clearance ensured that the research was conducted in an acceptable manner, free from any negative effects on other people, animals, or the environment, and was carried out within expected boundaries.
2.2. Construction and Characterization of NPAu/SPE
First of all, NPAu films were prepared and characterized by dealloying white gold sheets with a thickness of 100 nm (Au50Ag50 wt%, Sepp Leaf Products, New York, NY, USA) in concentrated HNO3 at 40 °C for 60 min, as described in a previously reported method [20].
Next, the NPAu films prepared by the dealloying method were washed to neutral pH with ultrapure water and stored at room temperature before modifying the working electrode of the SPE (0.4 in. × 1.333 in.) with a tiny three-electrode system composed of a carbon-made working electrode together with a reference electrode made of Ag/AgCl and a counter electrode made of carbon. The dimensions and electrode materials of the SPE are shown in Figure S1 (Supplementary Material). The NPAu/SPE was fabricated by coating one NPAu film to the working electrode area of the SPE in ultrapure water. When the NPAu loaded on the working electrode surface of the SPE was dry, the NPAu film beyond the working electrode area was removed. Then, 1.5 μL of Nafion solution (0.1%, wt%) was dripped on the surface of the loaded NPAu to stabilize the constructed NPAu/SPE, which was then repeatedly cleaned electrochemically in 0.5 M H2SO4 within a potential range from +0.35 V to +1.55 V.
2.3. Electrochemical Experiments Using NPAu/SCE
To perform electrochemical detection experiments, 100 μL of the sample solution was dropped onto the modified working electrode surface of the constructed NPAu/SPE, and then electrochemical detection was carried out at room temperature by a CHI 760E electrochemical workstation (Chenhua Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). In comparing the electrochemical characteristics of the NPAu/SPE with SPE, cyclic voltammetry (CV) was used in a potential range from –0.6 V to +1.2 V. CV was used again when analyzing the electrochemical reaction kinetics of the three vitamins at their appropriate potential ranges. For the individual detection of VB2, VC, and VB6, differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) was used at appropriate potential ranges in accordance with their respective oxidation peak potentials. The solutions with various concentrations of VB2, VC, and VB6 were prepared by diluting their stock solutions with appropriate amounts of NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0). For the simultaneous detection of multi-vitamins, appropriate amounts of VB2, VC, and VB6 stock solutions were added to 5.0 mL NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0) to form mixtures containing corresponding concentrations of the three vitamins. The calibration curves were obtained by plotting the peak currents against substrate concentrations. The limit of detection (LOD) was determined using Equation (1):
where σ and S present the standard deviation and the slope of the calibration plot [23].
LOD = 3δ/S
The detections of VB2, VC, and VB6 by the NPAu/SPE in human serum and fermentation liquid were performed using DPV in a potential range from –0.8 V to +0.8 V. First, a human serum sample was diluted by NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0) with a ratio of 1:19. Then, vitamin mixtures with different concentrations were added to the diluted human serum, respectively, to form human serum samples one, two, and three. The fermentation liquid samples were prepared in the same way as the human serum samples but without dilution. The fermentation liquid (500 mL, pH 6.9) was composed of glucose (15 g), MgSO4 (0.5 g), KH2PO4 (0.5 g), K2HPO4 (0.5 g), and (NH4)2SO4 (5.0 g). The detections of VB2, VC, and VB6 were carried out at room temperature by dropping 100 μL of the real samples onto the modified working electrode surface of the NPAu/SPE.
2.4. HPLC Analysis in Human Serum and Fermentation Liquid
The HPLC detections of VB2, VC, and VB6 in human serum and fermentation liquid were carried out using HPLC (LC-20AT, refractive index detector RID-20A, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with an SPD-20A ultraviolet detector (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and a C18 column (150 mm in length, 4.6 mm inner diameter, and 5 mm particle size, Thermo, Waltham, MA, USA), as described in a previously published study [24]. To compare the detection accuracy of the NPAu/SPE and HPLC, three real samples (human serum or fermentation liquid) containing spiked concentrations of VB2, VC, and VB6 were analyzed both by the NPAu/SPE and HPLC.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of the Portable NPAu/SPE
In the current work, Au/Ag sheets (Au50Ag50, wt%) were chemically etched with concentrated HNO3 for 60 min at 40 °C. The resultant NPAu sheets with an average pore diameter of 35 nm were then attached to the working electrode on SPE to create a modified NPAu/SPE, as depicted in Scheme 1A. The constructed NPAu/SPE was predicted to effectively catalyze the oxidations of VB2, VC, and VB6 through its catalytic active surface, therefore increasing the rate of electron generation during the oxidation process, as shown in Scheme 1B. The electrochemical behavior of the constructed NPAu/SPE was first evaluated in comparison to bare SPE in the absence of the targeted vitamins. Figure 1A depicts the current signal from CV of the NPAu/SPE and bare SPE in an NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0) at a scan rate of 50 mV/s. The bare SPE exhibited no redox peaks. In contrast, the NPAu/SPE exhibited distinct redox peaks for NPAu, with an oxidation peak at +0.75 V and a reduction peak at +0.33 V vs. Ag/AgCl, which confirms the successful construction of the NPAu-modified biosensing platform.
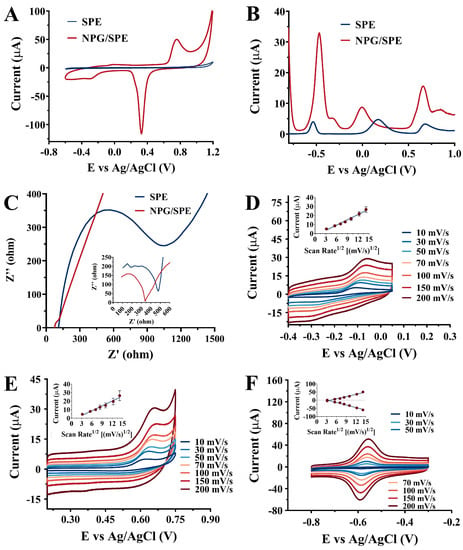
Figure 1.
(A) The CVs of SPE and NPAu/SPE in NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0); (B) The DPVs of SPE and NPAu/SPE in NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0) with VB2 (700 μM), VC (1500 μM), and VB6 (700 μM); (C) The Nyquist plots of SPE and NPAu/SPE; the CVs of the NPAu/SPE in NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0) containing 500 μM VC (D), 200 μM VB6 (E), and 200 μM VB2 (F) at different scan rates. The inserted pictures show the linear relationships between the peak current and the square root of the scan rate.
The initial viability of the simultaneous and selective quantification of VB2, VC, and VB6 deploying the constructed NPAu/SPE was then examined. Figure 1B shows the DPV results of the NPAu/SPE and bare SPE in the presence of VB2 (700 µM), VC (1500 µM), and VB6 (700 µM). The oxidation peaks at –0.52 V, –0.07 V, and +0.66 V were obtained, corresponding to VB2, VC, and VB6, respectively. For each of the three oxidation peaks, the NPAu/SPE exhibited a higher peak current signal compared to the bare SPE. This result confirms that the NPAu/SPE possesses better oxidation capability towards VB2, VC, and VB6. The better oxidation capabilities of NPAu towards VB2, VC, and VB6 are attributed to its distinctive microstructural configuration (Scheme 1A), which endows NPAu with a significantly enhanced specific surface area as well as excellent electrical conductivity and abundant active catalytic sites [21,22]. These features are crucial for the superior catalytic performance exhibited by the NPAu/SPE compared to bare SPE. Moreover, the separation between the peak potentials of VB2 and VC is 450 mV, and that between VC and VB6 is 730 mV, which solves the potential problem of the overlap of the oxidation peaks of these three vitamins. These DPV results suggest that the NPAu/SPE may provide a possibility for multi-vitamins (VB2, VC, and VB6) detection.
The NPAu/SPE and bare SPE were further characterized by electro-chemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in a phosphate buffer solution (50 mM, pH 6.5) containing 5.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]4−/3−. Figure 1C shows the impedance curves (the Nyquist plots) for the NPAu/SPE and bare SPE, with the inset of Figure 1C depicting the equivalent circuit diagram of the Nyquist plot. The diameters of the semicircles of the two impedance curves are directly proportional to the charge transfer resistances (Rct) of the NPAu/SPE and bare SPE [25]. The determined Rct for the NPAu/SPE and bare SPE are 14.4 Ω and 848.3 Ω, respectively, which indicates that the modified NPAu/SPE exhibited significantly decreased electric impedance compared to the bare SPE. Therefore, the NPAu/SPE has enhanced oxidation behavior towards VB2, VC, and VB6.
Further investigation of the electrochemical oxidation behavior of VB2, VC, and VB6 at a modified biosensing platform surface (NPAu/SPE) was carried out by recording the CV curves of the NPAu/SPE under different scan rates ranging from 10 to 200 mV/s in an NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0) containing VB2 (200 μM), VC (500 μM), and VB6 (200 μM), respectively. Figure 1D,E show that, as the scan rate increases, the oxidation peak currents of VC and VB6 exhibit a positively correlated relationship in magnitude together with a slight positive shift in the oxidation peak potential. This relationship was further visualized by plotting the oxidation peak current against the square root of the scan rate, as shown in the inset of Figure 1D,E. The linear relationships between the oxidation peak current and the square root of the scan rate were obtained for VC and VB6, with regression coefficients of 0.9828 and 0.9695, respectively. In addition, the irreversibility of the oxidation processes of VC and VB6 can be suggested by the lack of any reduction peaks on their CV curves. In contrast, as shown in Figure 1F, it is observed that there was a reduction peak corresponding to every oxidation peak, demonstrating the reversibility of the oxidation process of VB2. The inset of Figure 1F depicted the result of visualizing the redox peak current against the square root of the scan rate. The linear relationships between the redox peak currents and the square roots of the scan rate from 10 mV/s to 200 mV/s were obtained with correlation coefficients of 0.9651 and 0.9751 for oxidation and reduction peaks, respectively. Notably, the ratio of the reduction and the oxidation peak current (Ipc/Ipa) approximates to one, and the formal potential remained nearly unchanged, which were both typical characteristics confirming that the electron transfer process is a diffusion-controlled reversible process.
The kinetics analysis of these electrochemical reactions on the surface of NPAu demonstrated that VB2, VC, and VB6 have different catalytic mechanisms, which is determined by their different electrochemical behaviors intrinsically routed in their different structures. According to previous reports [25,26], the electrocatalytic reaction of VB2 involves a two-electrons transfer process. The electron transfer occurs in the isoalloxazine moiety of VB2 in the N1 and N5 positions during the forward scan. In the reverse scan, the reduced form (hydroquinone) at the N1 and N5 positions of the isoalloxazine moiety is oxidized to form riboflavin. The reduced and oxidized form of VB2 is in semiquinone form with a fast equilibrium, as shown in Scheme 1B and Figure 1F. For the electrooxidation of VB6 [27,28], NPAu catalyzes the hydroxyl group of VB6 for a carboxyl group, which also involves a two-electrons transfer process, as shown in Scheme 1B. For VC, its hydroxyl group could be actively oxidized to a carbonyl group on the surface of NPAu and become dehydroascorbic acid by releasing two electrons, as shown in Scheme 1B [26]. These structural and resulting reaction mechanism differences, together, allow for the simultaneous and sensitive analysis of VB2, VC, and VB6.
3.2. Amperometric Quantification of Multi-Vitamins Using the Portable NPAu/SPE
3.2.1. The Individual Detection of Multi-Vitamins by the Portable NPAu/SPE
The electrochemical responses for the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 were investigated individually using the DPV technique. The three vitamins were added as a substrate starting from low concentrations, and detection followed each addition, as shown in Figure 2. The DPV curves for VB2, VC, and VB6, shown in Figure 2A,C,E, respectively, indicated that the peak currents of the NPAu/SPE also increased proportionally as the substrate concentration increased. Moreover, for each of the three vitamins, the peak current detected by the NPAu/SPE as a function of the substrate concentration exhibited linear relationships within the corresponding detection range. The linear relationships between the peak current and substrate concentration are shown in Figure 2B,D,F for VB2, VC, and VB6, respectively. The LOD and sensitivity for VB2, VC, and VB6 were 0.26, 2.03, and 1.50 μM, with sensitivities of 114.90, 15.00, and 20.32 μA/μM, respectively, as summarized in Table 1. For VB2, the linear relationship was j(μA) = 0.0943(±0.0290) × CVB2 + 2.4782(±0.9979) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9983 and a linear dynamic range from 5 μM to 250 μM. Table S1 presented the comparison of the linear dynamic range, LOD, and sensitivity between the NPAu/SPE and other electrochemical sensors developed previously. The NPAu/SPE exhibited a significantly higher sensitivity towards VB2 than α-Fe2O3/GCE [29], Bi2O3@MWCNT@g-C3N4/GCE [30], AZA/NiHCF/GCE [31], ZnO-MnO/GCE [32], and Fe3O4 NPs-ePAD/SPE [33]. Furthermore, the LOD and linear dynamic range of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2 were comparable to those of the electrochemical sensors developed previously, as shown in Table S1. For VC, the linear relationship was j(μA) = 0.0151(±0.0031) × CVC + 2.6570(±0.9426) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9954 and a linear dynamic range from 5 μM to 3000 μM. As shown in Table S2, in terms of detection sensitivity and LOD, the NPAu/SPE out-performed most other electrochemical sensors developed in previous studies, such as CFYM/OCPE [34], Ce2(SO4)3/rGO/SPCE [35], and Au-Pd/MXene/LSG/SPE [36]. Moreover, the linear dynamic range of the NPAu/SPE towards VC was wider than those of PMR/Zn-Al LDH/GCE [37] and S/NP-Au wire electrodes [38]. For VB6, the linear relationship was j(μA) = 0.0173(±0.0045) × CVB6 + 3.5537(±0.0032) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9880 and a linear dynamic range from 5 μM to 3000 μM. As summarized in Table S3, the NPAu/SPE possessed the highest sensitivity towards VB6 among all six electrochemical sensors, such as ZnFe2O4/SPGE [39], the pencil graphite electrode [40], Fe3O4 NPs-ePAD/SPE [33], TiO2/SnO2/GCE [41], and CuO-PLL/GrE [42]. Additionally, the NPAu/GCE also exhibited a lower LOD in the detection of VB6 compared to CuO-PLL/GrE [42], Fe3O4 NPs-ePAD/SPE [33], and the pencil graphite electrode [40]. In general, the NPAu/SPE exhibited outstanding characteristics towards the individual detection of VB2, VC, and VB6 in terms of the linear dynamic range, LOD, and sensitivity.
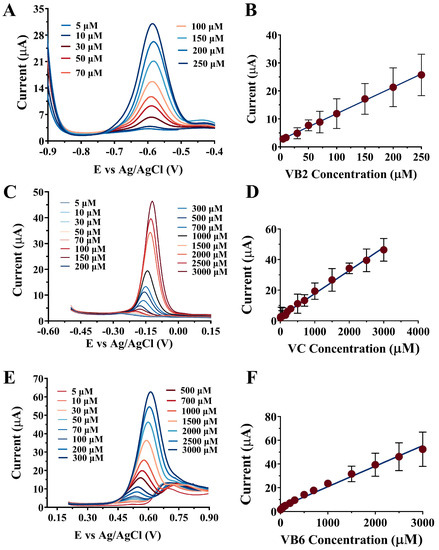
Figure 2.
The individual detection of multi-vitamins by the NPAu/SPE using DPV. (A) VB2 with a range of 5–250 μM; (C) VC with a range of 5–3000 μM; (E) VB6 with a range of 5–3000 μM. Peak current as a function of the substrate concentration for (B) VB2, (D) VC, and (F) VB6.

Table 1.
The LOD and sensitivity of the NPAu/SPE under different conditions.
3.2.2. The Simultaneous Detection of Multi-Vitamins by the Portable NPAu/SPE
In terms of the applied and specific recognition of vitamins, both the simultaneity and specificity of the NPAu/SPE are important characteristics to be explored and developed. Considering the wide separation between the peak potentials of VB2, VC, and VB6, the simultaneity and specificity of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 were examined by using a mixture of the three vitamins as the substrate. The electrochemical behavior of the NPAu/SPE towards all three vitamins was simultaneously investigated using the DPV technique in NAAC buffer (100 mM, pH 5.0) in a potential window from −0.8 V to 0.8 V, as illustrated in Figure 3A. The oxidation peaks of VB2, VC, and VB6 were obtained at distinct potentials (−0.52 V, −0.07 V, and +0.66 V, respectively), which all agreed with their oxidation potentials when detected individually, as shown in Figure 2. This suggests the feasibility of the simultaneous detection towards VB2, VC, and VB6 by the NPAu/SPE. Further regression analysis showed the linear relationships between the peak current and substrate concentration, as shown in Figure 3B,C,D for VB2, VC, and VB6, respectively. For VB2, the linear relationship was j(μA) = 0.0866(±0.0254) × CVB2 − 0.6933(±0.1717) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9234 and a linear dynamic range from 30 μM to 250 μM. For VC, the linear relationship was j(μA) = 0.0045(±0.0001) × CVC + 2.5310(±0.5501) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9664 and a linear dynamic range from 50 μM to 1500 μM. For VB6, the linear relationships was j(μA) = 0.0179(±0.0028) × CVB6 + 4.2245(±0.2242) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9602 and a linear dynamic range from 30 μM to 1100 μM. The LODs for VB2, VC, and VB6, summarized in Table 1, were 0.46, 6.44, and 1.92 μM, and the sensitivities were 68.58, 4.77, and 15.94 μA/μM, respectively. Table S4 presents the comparison of the linear dynamic range and LOD between the NPAu/SPE and other electrochemical sensors developed previously. Compared to the screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) [43], the NPAu/SPE exhibited a similar LOD yet a wider linear dynamic range towards the multi-vitamin detection of VB2, VC, and VB6. Moreover, the NPAu/SPE had comparable performances in terms of the LOD and linear dynamic range when compared to Zn-TiO2/GCE [44], ƒ-MWCNTs-Cu2O-Ag2O/GCE [45], Ag-PLA/GCE [26], and PEDOT/ZrO2NPs/GCE [46], which suggests that the portable, convenient NPAu/SPE’s detection performance matches those of the bioelectrodes limited to the laboratory.
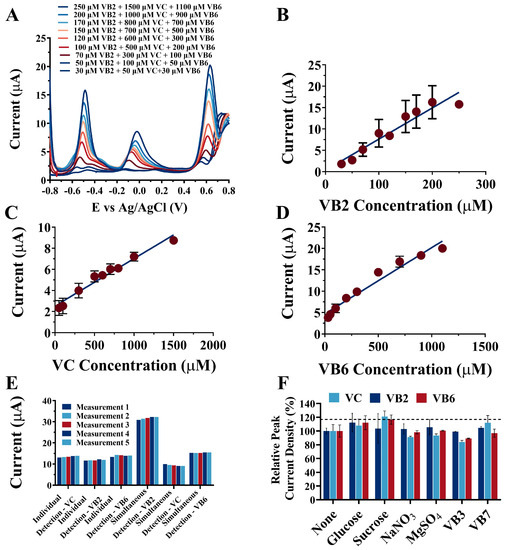
Figure 3.
(A) The simultaneous detection of multi-vitamins by the NPAu/SPE using DPV. The calibration curves between the peak current and the target vitamin concentration: (B) for VB2 from 30 μM to 250 μM, (C) for VC from 50 μM to 1500 μM, and (D) for VB 6 from 30 μM to 1100 μM; (E) The repeatability of the NPAu/SPE in the individual and simultaneous detections of multi-vitamins; (F) The anti-interference of the NPAu/SPE to common ions, vitamins, and carbohydrates.
3.2.3. Anti-Interference and Repeatability of the Portable NPAu/SPE
The repeatability and anti-inference capability of detection methods are of significant importance, especially when it comes to practical detection. In order to test the repeatability of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6, the peak currents of five detections were recorded and compared both when detecting each vitamin alone and simultaneously with the other two, as shown in Figure 3E. Further examination of the anti-interference capability of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 was carried out by adding common metallic ions, vitamins, and carbohydrates such as glucose and sucrose into the detecting environment to mimic a practical detection scenario, as shown in Figure 3F.
For the individual repeatability detection of VB2 (Figure 3E), the peak currents of five detections at a substrate concentration of 200 μM were recorded and compared, and a standard deviation of 2.41% was calculated out of the five peak currents. The same detection processes were applied to VC at 1.0 mM and VB6 at 500 μM, with standard deviations of 3.35% and 3.50%, respectively. The three low values of the standard deviation together suggested that the NPAu/SPE has a reliable repeatability towards VB2, VC, and VB6 when detecting one of them alone. In the multi-vitamins repeatability quantification (Figure 3E), a mixture of VB2, VC, and VB6 at final concentrations of 500 μM, 1.5 mM, and 500 μM was used as the substrate. For the simultaneous repeatability detection of VB2, the peak currents of five detections occurring at −0.52 V were recorded and compared, and a standard deviation of 6.04% was obtained. The detection processes were applied to VC and VB6, and the peak currents were collected at −0.07 V and +0.66V, with standard deviations of 3.71% and 1.30%, respectively. The repeatability of the simultaneous detection of VB2, VC, and VB6 was proved by the low values of the standard deviations.
For the anti-interference ability of the NPAu/SPE, VB2, VC, and VB6 were first detected simultaneously, and the peak currents of VB2, VC, and VB6 were recorded and used as the control group values. Then, the common interferents in the fermentation medium of vitamin production and human serum, such as glucose (200 μM), sucrose (200 μM), NaNO3 (100 μM), MgSO4 (100 μM), VB3 (100 μM), and VB7 (100 μM), were added separately into the vitamin mixture, and the simultaneous detection towards VB2, VC, and VB6 was performed to obtain the peak currents, which were compared to the control peak currents. As demonstrated in Figure 3F, the peak currents in the presence of all six interferents showed high accordance with the peak currents of the control group, with the highest deviation being 4.46% when detecting VB6 in the presence of VB3. Thus, the NPAu/SPE exhibited a substantial anti-interference capability in the presence of common ions, vitamins, and carbohydrates, proving its reliability in practical detection scenarios.
3.3. The Application of the Portable NPAu/SPE in Real Sample Detection
Given the satisfactory repeatability and anti-interference capability of the NPAu/SPE, the practical performance of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 was further evaluated by directly detecting real-world samples of human serum obtained from clinics and fermentation liquid produced by the laboratory. Through the results of the NPAu/SPE detection towards VB2, VC, and VB6 in human serum samples, the implemental possibility of the proposed sensor in clinical vitamin detection opened opportunities for the development of putative diagnosis techniques. Moreover, the NPAu/SPE detection performances over VB2, VC, and VB6 in the fermentation liquid are of significant importance in the field of the industrial production of vitamins, which at present faces the challenge of finding an alternative, cost-efficient, and convenient method for vitamin detection.
3.3.1. The Detection of Multi-Vitamins in Human Serum
In order to visualize the linear correlation between the peak current and vitamin concentration in human serum for all three vitamins, the electrochemical response of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 was investigated using the DPV technique in human serum (diluted 20) within a potential window from −0.8 V to 0.8 V, as shown in Figure 4A. As the vitamin concentrations were elevated, changes in the peak current were recorded and plotted against corresponding vitamin concentrations, as shown in Figure 4B for VB2, Figure 4C for VC, and Figure 4D for VB6. For VB2, the calibration curve was featured by a linear equation j(μA) = 0.1090(±0.0144) × CVB2 + 2.4775(±1.4057) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9939 and a linear dynamic range from 30 μM to 130 μM. For VC, the calibration curve was featured by a linear equation j(μA) = 0.0025(±0.0002) × CVC + 3.3449(±0.4578) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9660 and a linear dynamic range from 50 μM to 1300 μM. For VB6, the calibration curve was featured by the linear equation j(μA) = 0.0189(±0.0006) × CVB6 + 4.9655(±1.5211) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9924 and a linear dynamic range from 30 μM to 500 μM. The LODs for VB2, VC, and VB6 were 0.17, 9.43, and 2.48 μM, with sensitivities of 98.86, 2.47, and 18.50 μA/μM, respectively (Table 1). The three calibration curves were then used to compute for VB2, VC, and VB6 concentrations in three human serum samples by detecting the peak current. The results of the NPAu/SPE-detected vitamin concentrations, along with the results of the commonly used HPLC-detected vitamin concentrations, are shown in Table 2 in comparison with the spiked vitamin concentrations as standards. The recovery rates with respect to the spiked vitamin concentrations are also shown for the results of the NPAu/SPE and HPLC detections. In general, compared to HPLC, with recovery rates from 88.3% to 111.2%, the NPAu/SPE showed similar performances in the quantification of VB2, VC, and VB6 in human serum, with recovery rates from 92.5% to 111.7%. In addition, because of the protein binding properties of VB2 as a critical component of the enzyme cofactor and the presence of undesirable matrix effects in human serum, both methods have significant errors in the determination of VB2 in human serum samples at low concentrations. These results suggested that the NPAu/SPE out-performed HPLC in terms of detection accuracy. Thus, the NPAu/SPE was technically qualified as one of the potential tools in the future of clinical vitamin detection.
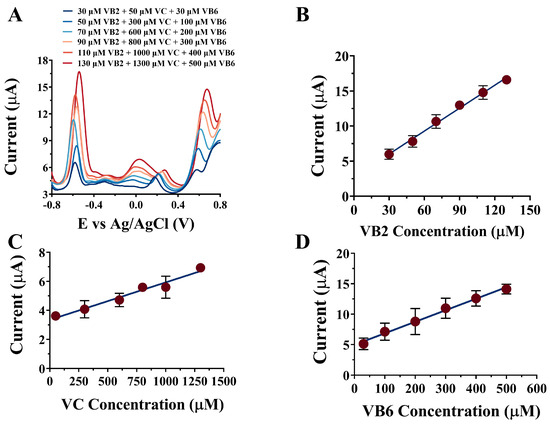
Figure 4.
(A) The simultaneous detection of multi-vitamins in human serum; the linear relationships between the peak current and the target vitamin concentration: (B) for VB2 from 30 μM to 130 μM, (C) for VC from 50 μM to 1300 μM, and (D) for VB6 from 30 μM to 500 μM.

Table 2.
Real sample analysis of VB2, VC, and VB6 by the NPAu/SPE in human serum and fermentation liquid.
3.3.2. The Detection of Multi-Vitamins in Fermentation Liquid
The electrochemical response of the NPAu/SPE towards VB2, VC, and VB6 was investigated using the DPV technique in fermentation liquid within a potential window range from −0.8 V to 0.8 V, as shown in Figure 5A. The resulting peak currents were recorded and plotted against corresponding vitamin concentrations as shown in Figure 5B for VB2, Figure 5C for VC, and Figure 5D for VB6. For VB2, the calibration curve was featured by the linear equation j(μA) = 0.1746(±0.0006) × CVB2 + 4.884(±0.3420) (μM) with a correlation coefficient of 0.9857 and a linear dynamic range from 50 μM to 120 μM. For VC, the calibration curve was featured by the linear equation j(μA) = 0.0033(±0.0002) × CVC + 3.718(±0.0750) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9955 and a linear dynamic range from 100 μM to 1500 μM. For VB6, the calibration curve was featured by the linear equation j(μA) = 0.0122(±0.0006) × CVB6 + 7.116(±0.0874) (μM), with a correlation coefficient of 0.9882 and a linear dynamic range from 100 μM to 1500 μM. For VB2, VC, and VB6, the LODs were 0.3, 11.97, and 1.58 μM, with sensitivities of 174.60, 3.31, and 12.21 μA/μM, respectively (Table 1). The three calibration curves were then used to compute for VB2, VC, and VB6 concentrations in three fermentation samples by detecting the peak currents. Table 2 summarized the results of vitamin concentrations from both HPLC and NPAu/SPE detection, together with their recovery rates from the spiked concentration. Again, the NPAu/SPE showed comparable performances in the detection of VB2, VC, and VB6 in fermentation liquid, with the recovery rates from 89.8% to 110%, suggesting that the NPAu/SPE out-performed HPLC (recovery rates from 95.6% to 106.6%) in terms of detection accuracy. The above results strongly suggest that the NPAu/SPE could be a potential alternative to the existing detection techniques in the vitamin production industry.
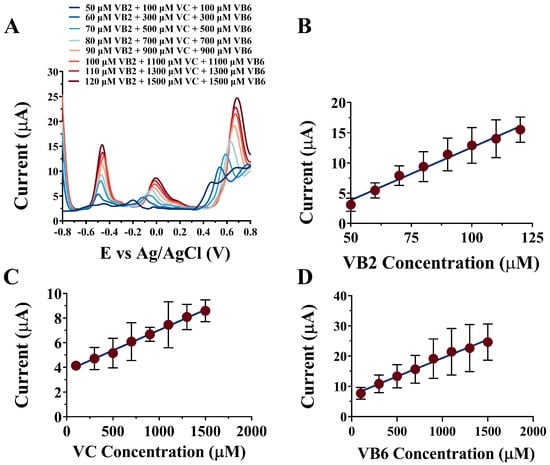
Figure 5.
(A) The simultaneous detection of multi-vitamins in fermentation liquid; the linear relationships between the peak current and the target vitamin concentration: (B) for VB2 from 50 μM to 120 μM, (C) for VC from 100 μM to 1500 μM, and (D) for VB6 from 100 μM to 1500 μM.
4. Conclusions
Taken together, a portable multifunctional electrochemical sensor (the NPAu/SPE) was successfully constructed for the reliable and simultaneous detection of VB2, VC, and VB6 under multiple conditions. Owing to its unique three-dimensional nanoporous structure and electrochemical catalytic activity, NPAu achieved the electro-oxidation of VB2, VC, and VB6 with a wide separation of peak potentials. The constructed NPAu/SPE exhibited satisfactory electrochemical responses in terms of the LOD and sensitivity both when individually and simultaneously detected compared with the existing electrochemical sensors for VB2, VC, and VB6 detection. Moreover, the remarkable reliability of the NPAu/SPE towards multi-vitamins detection was validated by examining the repeatability and anti-interference capability. Based on the solid anti-interference characteristics and repeatability of the NPAu/SPE, the simultaneous detection of VB2, VC, and VB6 was achieved both in human serum samples and fermentation liquid samples. The NPAu/SPE showed comparable detecting performances in terms of LOD, sensitivity, and accuracy when compared to the commonly used HPLC method, indicating the NPAu/SPE’s qualification as one of the potential candidates for clinical and industrial multi-vitamins analysis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors11090502/s1, Figure S1: The dimensions and electrode materials of the SPE used in this study; Table S1: Performance comparison of electrochemical sensors for VB2 detection; Table S2: Performance comparison of electrochemical sensors for VC detection; Table S3: Performance comparison of electrochemical sensors for VB6 detection; Table S4: Performance comparison of electrochemical sensors for the simultaneous detection of multi-vitamins. References [26,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
X.G.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—original draft. S.C.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization. X.W. (Xiaolei Wang): Investigation, Validation. H.L.: Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. X.W. (Xia Wang): Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91951202 and 32070097) and the National Key Research and Development Pro-gram of China (2019YFA0904800).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Ethics Committee of Jinan Central Hospital (protocol code No. D202111Ab and 2/18/2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Huanjie Li from the Second Hospital of Shandong University. The experiments of vitamin detection in human serum samples were carried out with the help of Huanjie Li.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Vaishnavi Sharma, V.; Jayaprakash, G.K. Fabrications of electrochemical sensors based on carbon paste electrode for vitamin detection in real samples. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 12, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen, K.; Stojanovska, L.; Apostolopoulos, V. The effects of vitamin B in depression. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 4317–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, E.C.; Santana, E.R.; Spinelli, A. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dot-modified electrode for monitoring of multivitamins in energy drinks. Talanta 2023, 252, 123836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Li, H.; Shang, M.; Sun, D.; Liu, C.; Che, G. Recent analytical methodologies and analytical trends for riboflavin (vitamin B2) analysis in food, biological and pharmaceutical samples. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2021, 143, 116412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, G.; Yu, K.; Chai, H.; Tian, M.; Qu, L.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Smartphone light-driven zinc porphyrinic MOF nanosheets-based enzyme-free wearable photoelectrochemical sensor for continuous sweat vitamin C detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tian, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, K.; Guo, J. Electrochemical vitamin sensors: A critical review. Talanta 2021, 222, 121645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappenberger, G.; Hohmann, H.P. Industrial production of L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and D-isoascorbic acid. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2013, 143, 143–188. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, T.; Xu, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, K.; Bai, L.; Wen, Y. Electroactive species-doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) films: Enhanced sensitivity for electrochemical simultaneous determination of vitamins B2, B6 and C. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimen, D.; Denizli, A. Development of rapid, sensitive, and effective plasmonic nanosensor for the detection of vitamins in infact formula and milk samples. Photonic Sens. 2020, 10, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollard, D.C.; Bensch, A.; Indyk, H.; Mcmahon, A. Determination of vitamin A and vitamin E esters in infant formulae and fortified milk powders by HPLC: Use of internal standardisation. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziomba, S.; Kowalski, P.; Baczek, T. Field-amplified sample stacking–sweeping of vitamins B determination in capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1267, 224–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Yang, X. Ovalbumin-directed synthesis of fluorescent copper nanoclusters for sensing both vitamin B1 and doxycycline. J. Lumin. 2018, 196, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, L.; Favero, G.; Tortolini, C.; Di Fusco, M.; Romagnoli, E.; Minisola, S.; Mazzei, F. Several approaches for vitamin D determination by surface plasmon resonance and electrochemical affinity biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L. Recent advances in synthesis of three-dimensional porous graphene and its applications in construction of electrochemical (bio)sensors for small biomolecules detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Sadowska, M.; Krasnodebska-Ostrega, B.; Nowicka, A.M. Selective and sensitive electrochemical device for direct VB2 determination in real products. Talanta 2017, 163, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Q.; Khan, R.A.; Alsalme, A.; Ahmad, K.; Kim, H. Design and fabrication of α-MnO2-nanorods-modified glassy-carbon-electrode-based serotonin sensor. Biosensor 2022, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, H. Sensitive and selective determination of riboflavin in milk and soymilk powder by multi-walled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquid [BMPi]PF6 modified electrode. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 10, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, C.; Soriano, M.L.; Villaseñor, M.J.; Ríos, A. Carbon-based nanodots as effective electrochemical sensing tools toward the simultaneous detection of bioactive compounds in complex matrice. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 878, 114573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Kim, Y.; Erlebacher, J. Nanoporous gold leaf: “ancient tecnology”/advanced material. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1897–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shang, K.; Gao, X.; Wang, X. The development of NAD+-dependent dehydrogenase screen-printed biosensor based on enzyme and nanoporous gold co-catalytic strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 211, 114376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Chen, M. Nanoporous metals for catalytic and optical applications. MRS Bull. 2009, 34, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ding, Y. Carbon-free nanoporous gold based membrane electrocatalysts for fuel cells. Prog. Nat. Sci.-Mater. 2020, 30, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Meng, F.; Cui, S.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.; Zou, Z. Effective and rapid electrochemical detection of hydrazine by nanoporous gold. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 661, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xiao, S.; Ma, H.; Wang, X. Multianalyte electrochemical electrode for the determination of vitamins B2 and B6 in complex biosystem. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, R.; Koventhan, C.; Chen, S.; Hung, W. A portable Ru-decorated cobalt phosphide on graphitic carbon nitride sensor: An effective electrochemical evaluation method for vitamin B2 in the environment and biological samples. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Y.M.; Sun, D.M. Simultaneous determination of vitamins B2, B6 and C using silver-doped poly(L-arginine)-modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 71, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkar, P.K.; Ganesan, V.; Gupta, S.K.S.; Yadav, D.K.; Gupta, R.; Yadav, M. Highly dispersed multiwalled carbon nanotubes coupled manganese salen nanostructure for simultaneous electrochemical sensing of vitamin B2 and B6. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 807, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitollahi, H.; Nejad, F.G. Voltammetric determination of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) at a graphite screen-printed electrode modified with graphene oxide/Fe3O4@SiO2 nanocomposite. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2018, 6, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribata, L.C.; Babautab, J.T.; Beyenalb, H.; Walla, N.A. New rotating disk hematite film electrode for riboflavin detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 798, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Pratibha, V.; Rajput, J.K.; Singh, D.; Jigyasa, K.N. Bi2O3@MWCNT@g-C3N4 ternary nanocomposite for the efficient electrochemical determination of Riboflavin in pharmaceutical samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, N.S.; Narayanan, S.S. Effective electrochemical detection of riboflavin and butylated hydroxy anisole based on azure A and nickel hexacyanoferrate framework on graphite electrode. Chem. Data Collect. 2020, 30, 100544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesamurthi, J.; Shanmugam, R.; Chen, S.M. Electrochemical evaluation of vitamin B2 through a portable electrochemical sensor based on binary transition metal oxide in various biological and vegetable samples. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 096505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.F.; Santana, E.R.; Spinelli, A. Electrochemical paper-based analytical devices containing magnetite nanoparticles for the determination of vitamins B2 and B6. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, H.; Bahadori, Y. Chicken feet yellow membrane/over-oxidized carbon paste electrodes: A novel electrochemical platform for determination of vitamin C. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil Subash, S.; Manjunatha, C.; Sudeep, M.; Chandresh, K.R.; Vishal, C.; Girish, K.S.; Praveen, S. Development of a non-enzymatic vitamin-C electrochemical sensor based on rGO/Ce2(SO4)3 hierarchical nanocomposite. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 037504. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Gao, B.; Yuan, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Self-reduction of bimetallic nanoparticles on flexible MXene-graphene electrodes for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Microchem. J. 2023, 185, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Xu, T.; Yan, H.; Zhao, F. A flexible and self-supported nanoporous gold wire electrode with a seamless structure for electrochemical ascorbic acid sensor. Microchem. J. 2023, 186, 108259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-bakr, A.M.; Abd-Elsabour, M.; Abou-Krisha, M.M. An efficient novel electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of vitamin C and aspirin based on a PMR/Zn-Al LDH/GCE. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 2476–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahani, P.M.; Jafari, M.; Ahmadi, S.A. Voltammetric determination of vitamin B6 in the presence of vitamin C based on zinc ferrite nano-particles modified screen printed graphite electrode. ADMET DMPK 2023, 11, 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Buleandră, M.; Popa, D.E.; Popa, A.; Codreanu, N.A.M.; Davidz, I.G. Multi-analyte sensor based on pencil graphite electrode for riboflavin and pyridoxine determination. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 017517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, D.; Rajendran, S.; Qin, J.; Sundaravadivel, E.; Yola, M.L.; Necip Atar, N.; Gracia, F.; Boukherroub, R.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.A.; Gupta, V.K. Heterostructures of mesoporous TiO2 and SnO2 nanocatalyst for improved electrochemical oxidation ability of vitamin B6 in pharmaceutical tablets. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 542, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; Long, Y.; Li, A.; Yang, B. In situ detection of melatonin and pyridoxine in plants using a CuO−poly(L-lysine)/graphene-based electrochemical sensor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19537–19545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomthiangthae, P.; Takeshi Kondo, T.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. The effects of the supporting electrolyte on the simultaneous determination of vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and vitamin C using a modification-free screen-printed carbon electrode. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 12603–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, D.; Rajendran, S.; Gracia, F.; Naushad, M.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Soto-Moscoso, M.; Gracia-Pinilla, M.A. Engineering ZnO nanocrystals anchored on mesoporous TiO2 for simultaneous detection of vitamins. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 186, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puangjan, A.; Suwan Chaiyasith, S.; Taweeporngitgul, W.; Keawtep, J. Application of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes supporting cuprous oxide and silver oxide composite catalyst on copper substrate for simultaneous detection of vitamin B2, vitamin B6 and ascorbic acid. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, T.; Zhang, K.; Xu, J.; Lu, L.; Bai, L. A facile one-pot strategy for the electrochemical synthesis of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/Zirconia nanocomposite as an effective sensing platform for vitamins B2, B6 and C. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 717–718, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).