Abstract
The use of economic methods to design and fabricate flexible copper sensors decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites for the detection of lead and cadmium in sweat is demonstrated. The flexible copper sensors were constructed with simple and cost-effective materials; namely, flexible and adhesive conductive copper tape, adhesive label containing the design of a three-electrode electrochemical system, and nail polish or spray as a protective layer. The flexible copper device consisted of a working electrode decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites using an electrodeposition technique, a copper pseudo-reference and copper counter electrodes. Under optimal experimental conditions, the flexible sensing platform showed excellent performance toward the detection of lead and cadmium using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPAdSV) in a wide linear range from 2.0 μM to 50 μM with acceptable reproducibility and repeatability, and limits of detection and quantification of 5.36 and 17.9 μM for Cd2+ ions and 0.76 μM and 2.5 for Pb2+ ions. Studies of addition and recovery in spiked artificial sweat sample were performed, with a recovery of 104.6%. The flexible copper device provides a great opportunity for application in wearable perspiration-based healthcare systems or portable sensors to detect toxic metals in biological samples.
1. Introduction
Human body fluids such as saliva, urine, blood, tears, interstitial fluid (IF), and sweat are constituted of electrolytes, hormones, metabolites, salts, and proteins, which are used to noninvasively monitor health conditions of individuals [1,2,3]. Sweat has been extensively used due to ease of sampling, simplicity of operation and obtainment, and the extensive interface of the skin [3]. Several heavy metals can be present in human perspiration, including Zn, Pb, Cu, Cd, Mg, Ni, Ca, Hg, Na, and K ions, and are closely related to human health conditions [4,5,6,7]. Lead (Pb2+) and cadmium (Cd2+) show toxic effects on the systems of human body, including the endocrine, nervous, circulatory, immunological, digestive, and cardiovascular systems [8], due to the accumulation characteristic in tissues; the respiratory system is the main route of intoxication with heavy metals [9]. Exposure to the high levels of cadmium cause inflammatory responses and destructive problems in the respiratory tract, kidney, liver [9]; for example, Fanconi syndrome is associated with severe bone pain [10]. Lead intoxication causes damage to the brain and central nervous system, increased behavioral disorders, irritability, fatigue, intellectual disability, learning difficulties, anemia, infertility, increase in blood pressure, renal impairment and development of chronic kidney disease, decline in mental functioning and cognitive impairment, loss of appetite, and in some cases leads to coma, seizures, and even death [8,10,11]. Therefore, the monitoring of Pb2+ and Cd2+ exposure using human body fluids can provide insight into human health status and inform auxiliar therapeutic and toxicological studies.
Gold standard techniques to detect heavy metals in human biological fluids use unportable and expensive analytical instruments, including inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) [12] and atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) [13], making them difficult to use for on-site detection and continuous monitoring. As an alternative, sensors play a decisive role in transferring biosensing technologies to portable meters for tracking hazardous compounds in decentralized analysis, reflecting advantages such as speed, miniaturization, scalability, low power requirements, and low cost [14]. Moreover, electrochemical devices can be combined with preconcentration or deposition steps, accumulating heavy metals at the working electrode surface, making anodic stripping analysis the most sensitive and effective electroanalytical technique [8]. The most commonly used electrode materials as nonflexible supports are gold [15], carbon paste [16], glassy carbon [17,18], and indium tin oxide [19,20]; however, they are rarely applied in the monitoring of heavy metals in a portable system [21]. The flexible sensing systems are generated by photolithography [22,23], direct laser writing [24], inkjet printing [25], e-beam evaporation [26], wax printing [27], soft lithography [28], plasma etching [29], and electrodeposition [30] techniques. However, most of these methods require fabrication processes with sophisticated and expensive instruments, time-consuming steps, and in some cases, need a clean work space [21]. Wei gao et. al. reported a microsensor array designed to simultaneously detect multiple heavy metals, including Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu, and Hg, using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry (SWASV), in which a microchip array was constructed on a flexible polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate in a protocol involving multiple steps of photolithography, evaporation (Cr/Au, Ag, Bi), and lift off [8]. Alternatively to the exhaustive and expensive protocols, Xig Xuan et. al. reported a flexible graphene-based electrode formed by laser-writing and substrate-transfer techniques for zinc detection in sweat [4]. Due to the toxicity of lead and cadmium and the importance of management, the design and fabrication of flexible sensors using facile, inexpensive, and rapid prototyping methods to produce at a large scale is fundamental for on-site management of individual health states [8,21].
Bismuth-based electrodes have been selected because they are an environmentally friendly alternative to mercury electrodes due to their low toxicity, and their ability to form amalgam (metal alloys) with toxic metals [4,8,31]. The development and use of greener electrode materials is extremely attractive for the routine use of disposable (“one-shot”) metal sensors [31]. Bismuth electrodes display a well-defined, undistorted, and highly reproducible stripping response, exhibiting excellent resolution of neighboring peaks, wide linear dynamic range, with signal-to-background characteristics comparable to those of common mercury electrodes [4,8,31]. While amalgam formation is responsible for the stripping performance of mercury electrodes, the attractive and unique behavior of bismuth film electrodes is attributed to the formation of multicomponent alloys [31]. Bismuth-based electrodes are known to form binary- or multicomponent “fusible” alloys with numerous heavy metals using stripping analysis of elements with standard potentials more negative than bismuth (i.e., Zn, Ga, Cd, In, Tl, Sn, Pb) [31]. The attractive behavior of the “mercury-free” flexible copper sensors, associated with the negligible toxicity of bismuth, hold great promise for “one-shot” decentralized metal detecting. Moreover, Bi micro/nanostructures are a great material for working electrodes, offering biocompatibility, high sensitivity, and wide operational potential range owing to their stability and low influence of dissolved oxygen [8,31]. In this work, we designed a flexible copper electrochemical sensor with an easy, inexpensive, and prototyping method to detect lead and cadmium in sweat samples. The flexible sensory platform contains a full electrochemical system with an auxiliary (AE) and reference (RE) electrode consisting of copper tape, and a working (WE) electrode consisting of copper tape decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites obtained via electrodeposition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
Bismuth(III) nitrate pentahydrate (99%), sodium acetate (99%), acetic acid (95%), lead(II) nitrate (99%), cadmium(II) nitrate (99%), lactic acid (95%), urea (98%), sodium chloride (99%), and potassium chloride (99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Hydrochloric acid and sodium citrate were acquired from Synth. All other reagents were of analytical grade and used as received. Ferric chloride solution (iron(III) chloride solution) was purchased from Suetoku. All solutions were prepared with ultrapure water (resistivity > 18.0 MΩ cm) obtained from a Millipore Milli-Q system (Billerica, MA, USA).
2.2. Instruments
Electrochemical measurements were performed using a PGSTAT204 Autolab (Eco Chemie, Utrecht, The Netherlands) potentiostat/galvanostat controlled by NOVA software, 2.0 version. Electron microscopy images of bismuth micro/nanodentrites were obtained with a Zeiss Sigma (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) scanning electron microscope equipped with a field emission electron gun (SEM–FEG) operating at 20 kV and OXFORD qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis system. The Raman spectra were measured with a micro-Raman spectrometer (LabRAM Horiba Jobin Yvon-model HR 800), equipped with a He–Ne laser at 632.81 nm (17 mW) and a CCD camera. The measurements were performed in backscattering configuration with 50× WD objective (Olympus MPL) by exposing the samples during 30 s of acquisition for three accumulation intervals. The slit width of the Raman spectrometer was 100 μm, and a diffraction grating of 600 lines/mm was used. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) was acquired with a D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer (Bruker) operated at 40 mA and 40 kV, employing Ni-filtered Cu Kα X-ray radiation (λ = 1.540 Å).
2.3. Preparation of Sweat Samples
Analyses of cadmium and lead ions in synthetic sweat samples were prepared as reported by Mathew et al. [32], consisting of 1.0 g·L−1 of urea, 1.0 g·L−1 of KCl, 7.5 g·L−1 of NaCl, and 1.0 mL·L−1 of lactic acid solubilized in 0.1 mol·L−1 of acetate buffer solution.
3. Results
3.1. Design and Fabrication of Flexible Copper Sensor Decorated with Bismuth Micro/Nanodentrites
The flexible copper sensors decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites were fabricated on a flexible polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate using a procedure with simple steps and inexpensive materials, as demonstrated in Figure 1. A flexible, conductive copper adhesive tape (thickness of 40 µm) was cut in pieces of 5 × 4 cm (Figure 1(Ai)) and glued onto PET, as depicted in Figure 1(Aii). Copper surfaces were cleaned with paper towels and acetone. A template containing the design of electrochemical devices was generated on an adhesive label sheet (Pimaco®) with a Silhouette Cameo model 3 cutting machine, and glued onto the copper adhesive tape, as shown in Figure 1(Aiii). The rectangular shape of electrodes was chosen to facilitate the Silhouette Cameo cutting machine work. The entire surface was covered with a polymer layer using nail polish (Figure 1(Aiv,Av)), transferring the design of the devices contained in the template for the copper adhesive surface after removing the mask, as can be seen in Figure 1(Avi). The exposed copper was removed by a corrosion step through the immersion of devices in inexpensive concentrated ferric chloride solution for 20 min, followed by a wash step with distilled water (Figure 1(Avii)). The corrosion step should be not too long to avoid the side erosion phenomenon, which can affect the area of working electrodes. The polymer layer was removed with acetone-soaked paper towels and then the flexible copper sensors were ready to use, as shown in Figure 1(Aviii). The procedure described here is generic, and can be used for others metallic surface, e.g., gold and nickel, alternatively to the expensive photolithography process. Figure 1(Bi) depicts a detailed representation of a flexible copper sensor with a complete electrochemical system containing auxiliary (AE), pseudo-reference (RE), and working electrodes (WE). An insulation tape (Scotch, 3M) of flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC) was used to delimit the area of the working electrodes. Figure 1(Bii) depicts the working electrode decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites electrochemically deposited in a solution containing 0.02 mol·L−1 of bismuth(III) nitrate, 1.0 mol·L−1 of hydrochloric acid, and 0.15 mol·L−1 of sodium citrate at a constant potential of −0.18 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) for 60 s [33]. The layer of micro/nanodentrites was selectively deposited on the working electrode using the electrodeposition technique, in which the WE are polarized cathodically, reducing the bismuth ions on the copper surface. The formation of bismuth micro/nanodentrites is controlled by the applied potential and time of the applied potential. Different applied potential will produce structures without specific morphology, and the time will control the amount of electrodeposited bismuth. The flexible copper sensor can be connected to a potentiostat using any commercial or lab-built connector for screen-printed electrodes, e.g., DropSens connectors ref. CAC4MMH or DSC4MM. Figure 1(Biii) shows a schematic representation of the preconcentration step of lead and cadmium analysis of a sweat sample.
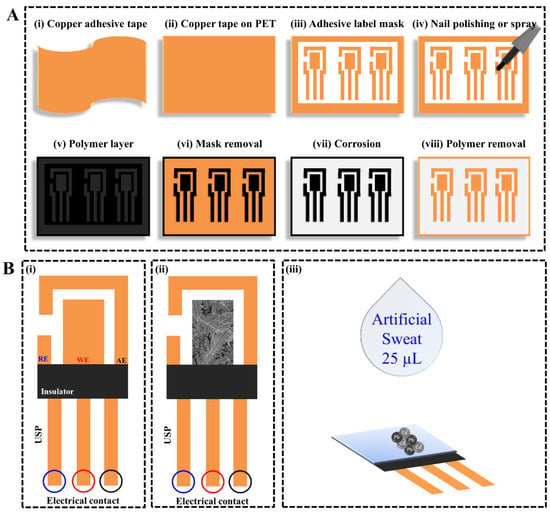
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the design and fabrication of a flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites. (A): (i) conductive copper adhesive tape; (ii) copper adhesive tape glued onto PET substrate; (iii) adhesive tape mask glued onto copper; (iv) the surface is painted with nail polish or spray; (v) a polymer layer covered the surface; (vi) the adhesive tape mask is removed from the surface; (vii) the copper is corroded; (viii) the polymer layer is removed with acetone and then the flexible copper sensors are ready to use. (B): (i) Detailed representation of flexible copper sensor with a complete electrochemical system containing auxiliary (AE), pseudo-reference (RE), and working electrodes (WE); (ii) working electrode decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites; (iii) analysis of lead and cadmium in artificial sweat sample. USP refers to the University of Sao Paulo.
The structural morphology of bismuth micro/nanodentrites was inspired by rime ice from cold areas, as illustrated in Figure 2A,B. The conductive flexible copper substrate acts as a tree branch because the bismuth micro/nanodentrites are grown electrochemically similarly to the ice. Initially, the bismuth structures seeds onto the flexible copper surface, and they are continuously electrodeposited on the seed producing rime-ice-like micro/nanostructures, as depicted in Figure 2A,B. Figure 2C depicts the Raman spectra containing five peaks located at 64, 93, 124, 308, and 464 cm−1 of the bismuth micro/nanodentrites deposited on flexible copper sensor. The two peaks at 66 and 92 cm−1 are indicative of the rhombohedral bismuth structure [34]. The three weak Raman peaks centered at 124, 308, and 464 cm−1 are attributed to the β-Bi2O3 (tetragonal) phase [34,35]. No significant change in the bare flexible copper sensor and flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites after Pb2+ and Cd2+ ion sensing was detected by EDS or XRD, as depicted in Figure 2D,E, indicating that there was no corrosion after the sensing step. This high catalytic stability is therefore attributed to the physical and chemical stability of bismuth micro/nanodentrites. The XRD pattern of the flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites (top, in gray) shows six diffraction peaks at 22.7°, 26.5°, 27°, 37.8°, 39.7°, 47.3°, and 48.7° attributed to the (003), (111), (012), (104), (110), (024), (116), and (112) planes of Bi2O3 [PDF#41-1449] [36]. The XRD pattern of bare flexible copper sensor (bottom, in orange) depicts three diffraction peaks at 43°, 50.5°, and 74.3° attributed to the (111), (200), and (220) planes of the FCC copper phase [JCPDS# 65–9026] [21]. The flexible copper sensor was successfully decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites using an easy preparation process with which it is also quite simple and efficient to detect Cd2+ and Pb2+ in sweat.
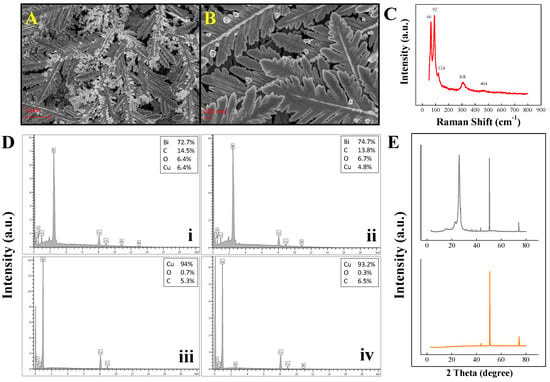
Figure 2.
SEM–FEG image for flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites under different magnifications of 20,000× in (A) and 50,000× in (B). Raman spectra of flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites in (C). Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy for flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites before (D(i)) and after (D(ii)) sensing, and for bare flexible copper sensor before (D(iii)) and after (D(iv)) sensing. XRD patterns of flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites (top, in gray) and bare flexible copper sensor (bottom, in orange) in (E).
3.2. Analytical Performance
Bismuth is a promising electrode material for lead, cadmium, and zinc detection; however, it is not appropriate for the anodic stripping of copper and mercury ions due to its lower oxidation potential (~−0.2 V). Hence, a flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites can only be used for cadmium and lead detection, because zinc can react with chloride ions from sweat, forming chloro complexes with different oxidation states, leading to competition with cadmium and lead ions. Taking into account that the focus of this work is to demonstrate the design and fabrication of flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites, the deposition potential and deposition time were strategically chosen to be −1.0 V, due to the fact that zinc ions can interfere, for which the oxidation peak is centered between −1.4 V and −1.0 V; they can also form chloride complexes with different oxidation state, and due to strong hydrogen evolution [4,8]. Similarly to the zinc ions, the copper ions were not selected because the reoxidation of Cu2+ can occur in the potential range between −0.2 V and 0.2 V (vs. Bi), in which the copper from the electrode can be oxidized, decreasing the accuracy of the analysis. The deposition time was 60 s, indicating a rapid method using devices fabricated with low-cost materials. Figure 3A depicts voltammograms (DPASV) with two distinct oxidation peaks at −0.5 V and −0.35 V for simultaneous detection of cadmium and lead in artificial sweat obtained in the concentration ranges between 2.0 and 50 μM for Pb2+ and 0.5 and 10 μM for Cd2+. The metallic ions in solution are reduced on the flexible copper sensor decorated with a bismuth micro/nanodentrites surface (M+n + ne− → M(Bi)) followed by reoxidation initiated with anodic stripping. The anodic peak potential was shifted due to copper reference electrode, which can be addressed using silver ink. The anodic current peak increased linearly with the concentration in agreement with DPASV, as demonstrated in Figure 3A. The equations of linear regression of the analytical curves shown in Figure 3B,C are: I (A) = 2.6 × 10−7 + 1.0 Ccadmium (mol·L−1) with r = 0.997 and I (A) = −1.8 × 10−5 + 6.4 Clead (mol·L−1) with r = 0.995. The detection limits were 5.36 μM for Cd2+ and 0.76 μM for Pb2+.
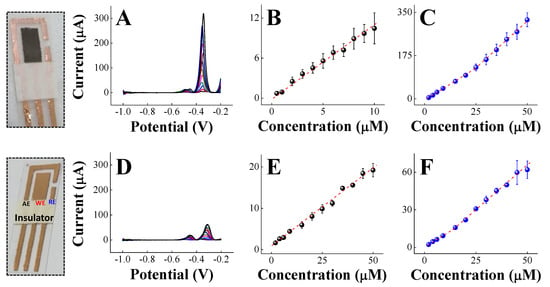
Figure 3.
Differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry in (A) and analytical curves for Cd2+ in (B) and Pb2+ in (C) obtained for flexible copper sensors decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites. Differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry in (D) and analytical curves for Cd2+ in (E) and Pb2+ in (F) obtained for bare flexible copper sensor. Conditions: simultaneous detection of heavy metals with the concentration varying from 2.0 μM to 50 μM in artificial sweat.
The simultaneous detection of cadmium and lead was also performed with bare flexible copper sensors, as shown in Figure 3D. All DPAS voltammograms were well-defined with well-separated oxidation peaks and a narrow linear concentration range from 2 to 50 µM. The current signals at −0.45 V and −0.30 V generated analytical curves with linear regressions of I (A) = −7.4 × 10−7 + 0.4 Ccadmium (mol·L−1), r = 0.999, and I (A) = −1.8 × 10−6 + 1.3 Clead (mol·L−1), r = 0.996, for cadmium and lead, respectively. The limits of detection were 4.2 μM and 3.7 μM for cadmium and lead, respectively. The sensitivity (slope of the analytical curve) for the bare flexible copper sensor was higher than for the flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites for Cd2+ detection, while for Pb2+ ions, the highest slope was obtained with the flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites, demonstrating that the detection system is versatile and able to detect cadmium and lead with either a bare sensor or flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites. The sensitivity and wider detection range is superior with bismuth micro/nanodentrites due to the ability of bismuth to form alloys with heavy metals, and to its insensitivity to dissolved oxygen [37,38].
Additionally, Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions were detected individually in sweat, as illustrated in Figure 4. The current signals at anodic peak potential at −0.47 V and −0.32 V increased linearly with concentrations in the range of 2.0 × 10−6 mol L−1 to 50 μM, as depicted in A for Cd2+ ions and in C for Pb2+ ions. The regression line of analytical curve obtained in B for Cd2+ ions was I (A) = −4.1 × 10−6 + 1.5 Ccadmium (mol·L−1), and the analytical curve obtained in C for Pb2+ ions was −4.03 × 10−5 + 18.8 Ccadmium (mol·L−1). The detection limits were 6.6 μM for Cd2+ ions and 2.6 μM for Pb2+ ions. The slopes for individual detection were close to those of simultaneous detection, indicating that the flexible copper is versatile and can be used to detect Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions simultaneously or individually.
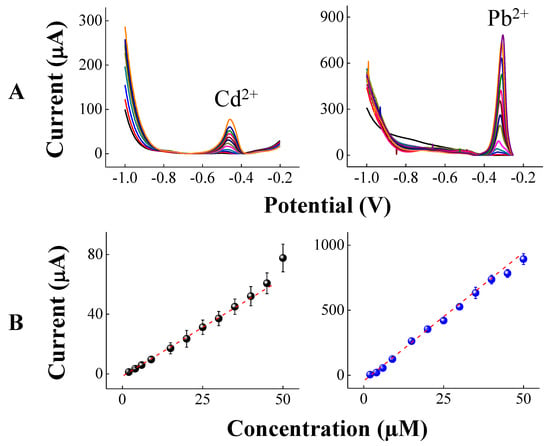
Figure 4.
Differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry in (A) and respective analytical curves in (B) for detection of Cd2+ and Pb2+ ions using flexible copper sensors decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites. Conditions: individual detection of heavy metals with the concentration varying from 2.0 μM to 50 μM in artificial sweat.
The physiological levels of toxic metals in sweat are low (<1 mg/L); in the cases of Cd2+ and Pb2+ the concentrations are 100 μg/L [8]. The flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites was used to determine Cd2+ and Pb2+ levels in fortified sweat samples to simulate contaminated sweat. The average recovery ranged from 97.8% to 104.6%. The satisfactory results demonstrate that the flexible copper sensor decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites has a high accuracy and potential for Cd2+ and Pb2+ sensing in biofluids.
The selectivity of flexible copper sensor decorated with decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites was generated with 2.5 µM of glucose, cholesterol, ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid in artificial sweat. Voltammograms obtained for DPASV in Figure 5 indicate a maximum percentage of interference of 10% for dopamine due to a biofouling effect, which could be addressed using a thin layer of Nafion [39]. Copper ions can compete with lead and cadmium for the bismuth active sites on the electrode surface [39]. Zinc ions were not added in the interference study because the oxidation peak is centered between −1.4 V and −1.0 V, leading to strong hydrogen evolution, and Zn2+ can form chloride complexes with different oxidation states [4,8]. Considering that the flexible device was fabricated with inexpensive flexible copper tape, the results shown in this work are satisfactory; however, they can be enhanced with the use of a high-quality flexible copper tape and a Nafion layer on the bismuth micro/nanodentrites [39].
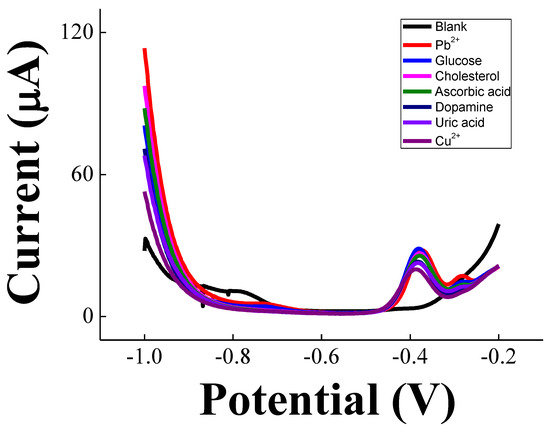
Figure 5.
Interferent study with glucose, cholesterol, ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. The concentration for lead and interferents was 2.5 µM in artificial sweat.
Table 1 depicts a list of sensors to detect Pb2+ and Cd2+ in different matrices using stripping voltammetry. We could not find any report on the use of flexible copper sensors decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites to detect toxic metals (i.e., Pb2+ and Cd2+) in sweat. The LOD of this work is higher than in previous studies using different matrices, which may be attributed to the reason that the nature of the copper layer composition is unfavorable when compared to the carbonaceous electrode materials. However, flexible copper sensors decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites are highly adaptable to wearable microfluid devices with inexpensive materials. Our method involves simple steps with non-sophisticated materials and an apparatus that can be easily acquired in any local market, such as adhesive label sheets (Pimaco®), Silhouette Cameo model 3 cutting machine, and copper adhesive tape. They are cheaper than copper inks, providing an alternative method for copper flexible electrode production to be adapted for microfluidics and wearable devices.

Table 1.
Figures of merit for Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions detection using devices functionalized with bismuth. Due to the limited studies on sensors modified with bismuth micro- nano-structures for determination of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions on relevant biological fluids, figures of merit are also included for environmental purposes.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we have developed a simple and low-cost method for the design and fabrication of flexible copper sensors through a patterned label on copper adhesive tape, nail polish, and corrosion technique with ferric chloride. The flexible copper sensor with a complete electrochemical system consisted of a pseudo-reference (RE) and working (WE) and auxiliary (AE) electrodes. The working electrode was decorated with bismuth micro/nanodentrites prepared by an easy electrodeposition method on the flexible copper surface. The flexible sensors were used for lead and cadmium detection by DPASV, with a wide linear range between 2.0 μM and 50 μM in artificial sweat samples, high sensitivity of 1.0 A·M−1 and 6.4 A·M−1, and a low limit of detection (LOD) of 5.36 μM and 0.76 μM for Cd2+ and Pb2+, respectively. The determination of toxic metals in artificial sweat showed an easy, fast, inexpensive method for on-site in noninvasive biological samples and environmental analysis.
The advantages of the flexible copper sensor are related to mass production and low cost, and they can be used in organic solvents, e.g., analysis of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in fuels, in comparison with screen-printed carbon electrodes. Despite the advances, important challenges remain for the production of flexible copper sensors via an entirely ecofriendly procedure. In future works, effort is required to design systems using the cutting machine to produce sensors without a corrosion step to avoid waste production and environmental pollution.
Author Contributions
A.M.d.C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Writing—Review and Editing. R.R.S.: Resources, Writing—Review and Editing. M.L.C.: Methodology, Investigation, Writing—Review and Editing. P.A.R.-P.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing—Original Draft, Visualization, Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Processes number 2016/01919-6, 2022/02164-0 and 2016/06612-6; Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico–CNPq (164569/2020-0, 151200/2022-0, and 423952/2018-8).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support granted by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Processes number 2016/01919-6 and 2016/06612-6; Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico–CNPq (164569/2020-0, 151200/2022-0 and 423952/2018-8).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anastasova, S.; Crewther, B.; Bembnowicz, P.; Curto, V.; Ip, H.M.; Rosa, B.; Yang, G.-Z. A wearable multisensing patch for continuous sweat monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, D.; Khorsandian, Y.; Pelusi, J.; Mirabella, A.; Pirrotte, P.; Zenhausern, F. Molecular and physical technologies for monitoring fluid and electrolyte imbalance: A focus on cancer population. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J. Wearable Biosensors for Non-Invasive Sweat Diagnostics. Biosensors 2021, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Hui, X.; Yoon, H.; Yoon, S.; Park, J.Y. A rime ice-inspired bismuth-based flexible sensor for zinc ion detection in human perspiration. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jia, W.; Wang, J. Tattoo-Based Wearable Electrochemical Devices: A Review. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Benzigar, M.R.; Subramony, J.A.; Lovell, N.H.; Liu, G. Advances in Sweat Wearables: Sample Extraction, Real-Time Biosensing, and Flexible Platforms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34337–34361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, T.R.; Choi, J.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Krishnan, S.; Gutruf, P.; Tian, L.; Ghaffari, R.; Rogers, J.A. Bio-Integrated Wearable Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5461–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Shahpar, Z.; Fahad, H.M.; Chen, K.; Emaminejad, S.; Gao, Y.; Tai, L.-C.; Ota, H.; Wu, E.; et al. Wearable Microsensor Array for Multiplexed Heavy Metal Monitoring of Body Fluids. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Ceccato, A.D.; Ramos, E.M.C.; de Carvalho, L.C.S.; Xavier, R.F.; Teixeira, M.F.D.S.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Proença, C.D.A.; de Toledo, A.C.; Ramos, D. Short terms effects of air pollution from biomass burning in mucociliary clearance of Brazilian sugarcane cutters. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1766–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Lucchini, R.; Kotelchuck, D.; Grandjean, P. Principles for Prevention of the Toxic Effects of Metals. In Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, 4th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.; Ebdon, L.; McWeeny, D.J. Application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for trace metal determination in foods. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1986, 1, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohnadel, D.C.; Sunderman, F.W.; Nechay, M.W.; McNeely, M.D. Atomic Absorption Spectrometry of Nickel, Copper, Zinc, and Lead in Sweat Collected from Healthy Subjects during Sauna Bathing. Clin. Chem. 1973, 19, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel, V.R.-V.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Vargas, E.; Bailey, E.; May, J.; Bulbarello, A.; Düsterloh, A.; Matusheski, N.; Wang, J. Decentralized vitamin C & D dual biosensor chip: Toward personalized immune system support. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 194, 113590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, G.; Nguyen, T.D.; Piro, B. Modified Electrodes Used for Electrochemical Detection of Metal Ions in Environmental Analysis. Biosensors 2015, 5, 241–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudelkova, Z.; Syrovy, T.; Ambrozova, P.; Moravec, Z.; Kubac, L.; Hynek, D.; Richtera, L.; Adam, V. Determination of Zinc, Cadmium, Lead, Copper and Silver Using a Carbon Paste Electrode and a Screen Printed Electrode Modified with Chromium(III) Oxide. Sensors 2017, 17, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.-K.; Choi, E.; Piao, Y. Voltammetric determination of trace heavy metals using an electrochemically deposited graphene/bismuth nanocomposite film-modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 766, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.M.; Gaber, S.E.; Altahan, M.F.; Azzem, M.A. Single and simultaneous voltammetric sensing of lead(II), cadmium(II) and zinc(II) using a bimetallic Hg-Bi supported on poly(1,2-diaminoanthraquinone)/glassy carbon modified electrode. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 2020, 29, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshoria, S.; Narula, A.K. Bare indium tin oxide electrode for electrochemical sensing of toxic metal ion. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 13858–13863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohari, N.A.; Siddiquee, S.; Saallah, S.; Misson, M.; Arshad, S.E. Optimization and Analytical Behavior of Electrochemical Sensors Based on the Modification of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Using PANI/MWCNTs/AuNPs for Mercury Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshroo, A.; Sadrjavadi, K.; Taran, M.; Fattahi, A. Electrochemical system designed on a copper tape platform as a nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.C.; Soares, A.C.; Rodrigues, V.C.; Oiticica, P.R.A.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Bott-Neto, J.L.; Buscaglia, L.A.; de Castro, L.D.C.; Ribas, L.C.; Scabini, L.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 sequence with genosensors using data analysis based on information visualization and machine learning techniques. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 5658–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Shimizu, F.M.; Coelho, D.; Piazzeta, M.H.; Gobbi, A.L.; Machado, S.A.; Oliveira, O.N. A Nanostructured Bifunctional platform for Sensing of Glucose Biomarker in Artificial Saliva: Synergy in hybrid Pt/Au surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasraoui, S.; Ameur, S.; Al-Hamry, A.; Ben Ali, M.; Kanoun, O. Development of an Efficient Voltammetric Sensor for the Monitoring of 4-Aminophenol Based on Flexible Laser Induced Graphene Electrodes Modified with MWCNT-PANI. Sensors 2022, 22, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.W.; White, I.M. Inkjet-printed paper-based SERS dipsticks and swabs for trace chemical detection. Analyst 2012, 138, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannoor, M.S.; Tao, H.; Clayton, J.D.; Sengupta, A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Naik, R.R.; Verma, N.; Omenetto, F.G.; McAlpine, M. Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scordo, G.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F. A reagent-free paper-based sensor embedded in a 3D printing device for cholinesterase activity measurement in serum. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, W.; Harada, S.; Arie, T.; Akita, S.; Takei, K. Wearable, Human-Interactive, Health-Monitoring, Wireless Devices Fabricated by Macroscale Printing Techniques. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Nguyen, T.; Shen, W. Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices by Plasma Treatment. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9131–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazaca, L.C.; Imamura, A.H.; Gomes, N.O.; Almeida, M.B.; Scheidt, D.T.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Janegitz, B.C.; Machado, S.A.S.; Carrilho, E. Electrochemical immunosensors using electrodeposited gold nanostructures for detecting the S proteins from SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5507–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Stripping Analysis at Bismuth Electrodes: A Review. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.; Ariza, E.; Rocha, L.; Fernandes, A.; Vaz, F. TiCxOy thin films for decorative applications: Tribocorrosion mechanisms and synergism. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo-Filho, L.C.; Baccarin, M.; Janegitz, B.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. A disposable and inexpensive bismuth film minisensor for a voltammetric determination of diquat and paraquat pesticides in natural water samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Pérez, A.J.; Camacho-López, M.; Morales-Luckie, R.A.; Sánchez-Mendieta, V. Structural evolution of Bi2O3 prepared by thermal oxidation of bismuth nanoparticles. Soc. Mex. Cienc. Tecnol. Superf. Mater. 2005, 18, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, T.; Shi, S. Study of nanostructural bismuth oxide films prepared by radio frequency reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 472, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Bismuth nanodendrites as a high performance electrocatalyst for selective conversion of CO2to formate. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13746–13753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torma, F.; Kádár, M.; Tóth, K.; Tatár, E. Nafion®/2,2′-bipyridyl-modified bismuth film electrode for anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 619, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyo, S.; Apiluk, A.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. High sensitivity and specificity simultaneous determination of lead, cadmium and copper using μPAD with dual electrochemical and colorimetric detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, G. Synthesis of a three-dimensional (BiO)2CO3@single-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite and its application for ultrasensitive detection of trace Pb(II) and Cd(II) by incorporating Nafion. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2019, 288, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legeai, S.; Vittori, O. A Cu/Nafion/Bi electrode for on-site monitoring of trace heavy metals in natural waters using anodic stripping voltammetry: An alternative to mercury-based electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 560, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Filho, L.C.S.; Janegitz, B.C.; Fatibelilo-Filho, O.; Marcolino-Junior, L.H.; Banks, C.E. Inexpensive and disposable copper mini-sensor modified with bismuth for lead and cadmium determination using square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadara, R.O.; Jenkinson, N.; Banks, C.E. Disposable Bismuth Oxide Screen Printed Electrodes for the High Throughput Screening of Heavy Metals. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 2410–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, R.C.; Cornejo, L.; Bertotti, M.; Brett, C.M.A. Electrochemical determination of Cd(ii) and Pb(ii) in mining effluents using a bismuth-coated carbon fiber microelectrode. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3624–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosolina, S.M.; Chambers, J.Q.; Lee, C.W.; Xue, Z.-L. Direct determination of cadmium and lead in pharmaceutical ingredients using anodic stripping voltammetry in aqueous and DMSO/water solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 893, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riman, D.; Jirovsky, D.; Hrbac, J.; Prodromidis, M.I. Green and facile electrode modification by spark discharge: Bismuth oxide-screen printed electrodes for the screening of ultra-trace Cd(II) and Pb(II). Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 50, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Fernández-Sánchez, C.; Gich, M.; Navarro-Hernández, C.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Roig, A. Screen-printed electrodes made of a bismuth nanoparticle porous carbon nanocomposite applied to the determination of heavy metal ions. Mikrochim. Acta 2015, 183, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakhova, N.A.; Mysik, A.A.; Saraeva, S.Y.; Stozhko, N.; Uimin, M.A.; Ermakov, A.E.; Brainina, K.Z. A voltammetric sensor on the basis of bismuth nanoparticles prepared by the method of gas condensation. J. Anal. Chem. 2010, 65, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promphet, N.; Rattanarat, P.; Rangkupan, R.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. An electrochemical sensor based on graphene/polyaniline/polystyrene nanoporous fibers modified electrode for simultaneous determination of lead and cadmium. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of an Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid Detection of Lead(II) in Blueberries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).