Abstract
African Americans have been disproportionately vaccinated at lower rates, which warrants the development of theory-based interventions to reduce vaccine hesitancy in this group. The fourth-generation theories, e.g., multi-theory model (MTM) of health behavior change, are vital in developing behavioral interventions. Therefore, the current study aims to determine recent trends in COVID-19 vaccination rates and to test the MTM model in predicting the initiation of COVID-19 vaccines among vaccine-hesitant Blacks. A sample of 428 unvaccinated African Americans were recruited through a web-based survey using a 28-item psychometric valid questionnaire. Chi-square, independent-samples-t-test or Welch’s t test, and Pearson’s correlation tests were utilized for the analyses. Hierarchical regression modelling was performed to determine the increment in variation accounted for through addition of predictors over a set of models. Nearly 48% of unvaccinated Blacks reported being vaccine-hesitant. The vaccine-hesitant group was relatively younger (40.5 years ± 15.8 vs. 46.2 years ± 17.4, p < 0.001), were Republicans (22.1% vs. 10.0%, p < 0.001), lived in the North-East region (26.0% vs. 11.4%, p < 0.001) and had religious affiliations other than Christianity (21.2% vs. 13.6%, p = 0.04). The mean scores of perceived advantages ((9.01 ± 3.10 vs. 7.07 ± 3.60, p < 0.001) and behavioral confidence (8.84 ± 3.76 vs. 5.67 ± 4.09, p < 0.001) were higher among vaccine non-hesitant group as opposed to the hesitant ones. In a final regression model, all MTM constructs) predicted nearly 65% of variance in initiating COVID-19 vaccination behavior among the vaccine-hesitant group (adjusted R2 = 0.649, F = 32.944, p < 0.001). With each unit increment in MTM constructs (e.g., participatory dialogue and behavior confidence), the initiation of COVID-19 vaccination among vaccine-hesitant Blacks increased by 0.106 and 0.166 units, respectively. Based on the findings of this study a m-health educational intervention to promote COVID-19 vaccine uptake behavior among Blacks is proposed.
1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic is an ongoing public health threat, which accelerated the development of the COVID-19 vaccine to prevent severe illness, hospitalizations, and mortality [1]. In May 2020, a partnership between the Departments of Health and Human Services and Defense established the Operation Warp Speed (OWS) with a projected goal of producing 300 million doses by early 2021 [2]. In the United States, on 11 December 2020, Pfizer’s BioNTech (BNT161b2) vaccine was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as the first vaccine for emergency use for people 16 years and older [3]. Then, a week later, Moderna’s (mRNA-1273) vaccine was approved by the FDA followed by the approval of single-shot Johnson and Johnson’s vaccine (Ad26.COV2. S) on 27 February 2021 for people 18 years and older [3]. In clinical studies, all three vaccines have shown sufficient efficacy in preventing COVID-19 infection [4,5,6]. Given the vaccine was approved on an emergency use authorization (EUA) basis on a fast approval track, there are some concerns and hesitancy among the general public regarding the COVID-19 vaccine uptake behavior. Attitudes of Antivaxxers, myths and misconceptions, conspiracy theories, the unknown nature of long-term side effects, and prevailing skepticism have also been fueling the vaccine hesitancy [7,8,9,10]. As of 25 August 2021, nearly 203 million or 60.1% of the population has been fully or partially vaccinated in the U.S. [11]. This is short of the Biden administration’s projected goal of giving at least one COVID-19 vaccine shot to 70% of the U.S. adult population by 4 July 2021 [12].
Recent studies indicated that COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy is higher among Blacks or African Americans [13]. A pooled analysis of 13 studies found COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy to be 26.3% in all Americans and 41.6% (95%CI: 34.4–48.9) for Blacks [14]. Previous studies have voiced concerns about racial differences in mistrust as a contributing factor of hesitancy among Blacks towards vaccines as well as clinical research [15]. In addition, reduced access to healthcare, less research evidence with African American participants in studies, lower awareness and educational attainment, and history of the Tuskegee Syphilis study’s ethical misconduct were also cited as contributing factors of vaccine hesitancy [16,17,18,19]. This is alarming as Blacks share a disproportionate burden of high morbidity, mortality, and socioeconomic impacts of COVID-19 pandemic [20]. These disparate effects were also existent during the 2009 influenza outbreak and vaccination; the current event (COVID-19 pandemic) is a wake-up call to address this discrepancy and gain trust of communities hit hard by the pandemic [21]. Until today, no theory-based studies have been conducted to understand the correlates of COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among Blacks or African Americans, which will aid in developing evidence-based interventions to promote vaccine acceptability in this group.
A theoretical basis is vital in deciphering why people engage or fail to engage in behaviors that promote health [22]. The theoretical evidence can help designing efficacious, effective and precision interventions [23]. Theory-based health behavior research has evolved over the years from crude knowledge–attitude–practices (KAP) surveys, to skill-based intervention planning, to single theory interventions to the current Fourth-generation multiple theory precision interventions [23]. One such Fourth-generation theory is the multi-theory model (MTM) of health behavior change [23,24], which will be the framework of this proposed study. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to identify sociodemographic and MTM-based differences between vaccine-hesitant African Americans and non-vaccine-hesitant African Americans. Further, the study aimed to utilize MTM in explaining COVID-19 vaccine acceptability behavior among Blacks from data collected during the third quarter of 2021 and proposed an m-health (mobile phone-based) educational intervention for the possible implementation.
1.1. Study Design and Participants
This study was a cross-sectional survey including 28 questions. The survey was conducted during July-August 2021 to recruit unvaccinated African American adults residing in the United States. According to the recent estimates, the African American racial subgroup constitutes 13.5% of the U.S. population [25]. Reportedly, African American subgroups were less willing to take the COVID-19 vaccine than their other race counterparts [26,27].
1.2. Recruitement and Data Collection
A commercial survey sampling and administration company, Qualtrics, was contacted to recruit a nationwide sample of unvaccinated African American U.S. residents [28,29]. The majority of the sample come from the traditional market research panels, however, for hard-to-reach or restrictive sample (such as that used in this study), Qualtrics uses a niche panel through specialized campaigns. Invitation methods include but are not limited to emails and in-app notifications. Panel members can unsubscribe from the emails at any time [28,29]. Screening questions are asked from the potential participants prior to survey entry to ensure eligibility [28,29]. To prevent the self-selection bias, survey invitation was kept general and specific details of the survey were not revealed before the screening questions. The respondents were compensated for their time to take the survey and incentives may include gift cards, redeemable points, cash rewards, vouchers, SkyMiles, etc.
1.3. Ethical Considerations
This study was conducted according to the Helsinki declarations. The research protocol and informed consent forms used in this study were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (IRB Protocol # 1702350-2). A detailed information sheet outlining the objectives, procedures of the study, duration of the survey and expected outcomes including benefits, risks, and dissemination of findings were provided to the participants before taking the survey. The participation in this survey was made completely voluntary by providing options of “agree” or “disagree” to the participants. Adherence to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was maintained during this study. In other words, no personal identifiers were collected to preserve anonymity of the responses. Each participant was allowed to take the survey only once to prevent ballot box stuffing, which was the algorithm used during the data collection. To exclude duplication and ensure validity, Qualtrics uses the unique digital fingerprinting mechanism to retain the integrity of the survey data.
1.4. Survey Instrument
We used a psychometric valid and reliable tool developed/used by a previous study to explain COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among U.S. college students [30]. This tool was based on the Fourth-generation theory called the Multi-theory Model (MTM) framework [23,24]. The MTM has been widely tested in studying or explaining several health behaviors such as physical activity [31], and fruits and vegetables intake [32]. In addition, the MTM has also been used to explain behaviors (e.g., handwashing) and social connectedness during the COVID-19 pandemic [33,34]. The survey tool consisted of 15 demographic questions with 13 questions based on MTM subscales of intention to initiate COVID-19 vaccination behavior. A detailed description of the instrument’s components is provided in Table 1. The two MTM constructs of initiation (e.g., Advantages and Disadvantages) were measured on a 5-point Likert scale, which ranges from “Never” to “Very Often.” As described in the Table 1, the Participatory dialogue score was obtained after subtracting the total disadvantages score from the advantages score of each participant. The other two constructs, i.e., behavioral confidence and changes in the physical environment were measured on a scale of surety, which ranged from “Not at all sure” to “Completely sure” on a 5-point Likert scale (Table 1). Each construct has 3 items and the score ranges from 0–12 units.

Table 1.
Theoretical framework of Multi-level Theory Model explaining the initiation of COVID-19 vaccination.
1.5. Statistical Analysis
All analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS v.26, (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and SAS 9.3 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Descriptive and exploratory analyses were utilized to investigate data distribution, normality, missing values, and outliers. All assumptions of the statistical tests were assessed. Categorical variables were compared among vaccine-hesitant and non-hesitant groups by Chi-square analyses. The follow-up contingency table analysis (post-hoc) was conducted to obtain p-values corresponding to multilevel variables. The observed p-values were Bonferroni-corrected in multiple comparisons to prevent type 1 errors [35]. The values of adjusted residuals (or Z scores) were used to generate Bonferroni-corrected p values. Effect sizes were reported wherever appropriate. Continuous variables, such as age, advantages, disadvantages, participatory dialogue, behavior confidence, and changes in the physical environment were compared among groups using independent-samples t-tests or Welch’s t test where equal variance could not be assumed. A square root transformation was applied to the non-normally distributed variables, which were later back-transformed for the ease of interpretation. A bivariate Pearson’s correlation was also conducted to investigate the relationships between the MTM constructs. We also calculated the proportion of perceived advantages and disadvantages among hesitant and non-hesitant group. Hierarchical regression modelling was performed to determine the increment in variation (by R-square change) accounted for through addition of predictors over a set of models. The details about the model building process is provided in the Figure 1 given below. The statistical significance was set at 5% for all analyses. For polytomous variables (e.g., region, religion, and political affiliation in our dataset), we used dummy coding by converting the polytomous categorical variable into a series of dichotomous variables for each level where a value of 1 was assigned for each observation at that level and zero for all others. The level of categorical variable which was coded zero at all levels was considered a reference category. The algorithm of the dummy coding is described in the Appendix A Table A1. Prior to running analyses, we conducted power analyses to determine whether our sample was sufficient to detect the hypothesized effects. The following formula was used to compute sample size: n = (z)2 p (1 − p)/d2 with a 95% confidence interval (alpha = 0.05, z = 1.96), and a margin of error d = 5%, and the proportion of vaccine hesitancy among Blacks was 18% in May 2021 based on the data reported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation Report [36]. The estimated sample size was 227 and the true sample size was increased to 428 allow group comparisons. We used a Checklist for Statistical Assessment of Medical Papers (CHAMP statement) for our results’ reporting [37].
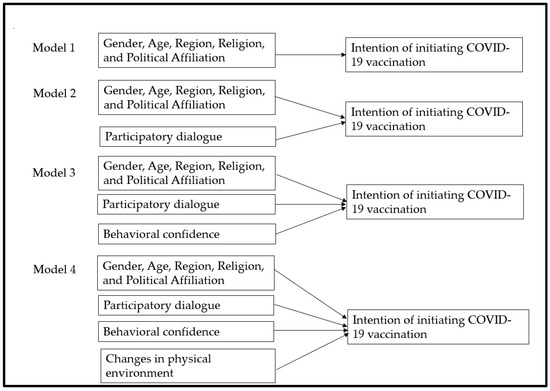
Figure 1.
Regression model building process indicating hierarchical entry of predictors to explain variance in the dependent variable (intention of initiating COVID-19 vaccination).
2. Results
Nearly 48 percent of our sample population (208 out of 428) reported that they are hesitant to take the COVID-19 vaccine (Table 2). The vaccine-hesitant group was relatively younger compared to the vaccine non-hesitant group (40.5 years ± 15.8 vs. 46.2 years ± 17.4, p < 0.001, Table 2). There was no statistically significant differences in the proportion by gender, education, marital status, employment status and location of residence. However, the vaccine-hesitant group had a significantly higher proportion of Republicans (22.1% vs. 10.0%, p > 0.001), those living in the North-East region (26.0% vs. 11.4%, p < 0.001) and belong to religions other than Christianity (21.2% vs. 13.6%, p = 0.04, Table 2). As expected, there were significant differences in the proportions of perceived advantages and disadvantages among vaccine-hesitant and vaccine non-hesitant group (Figure 2). Over 40% of the vaccine non-hesitant group strongly perceived the advantage of the COVID-19 vaccine in protecting them or their family members against SARS-CoV infection compared to nearly 20.0% among the vaccine-hesitant group (Figure 2). Nearly 40% of the vaccine-hesitant group perceived COVID-19 to be unsafe compared to only 16.8% among the vaccine non-hesitant group. The vaccine-hesitant group was more concerned about the lack of long-term studies on the vaccine’s effectiveness (45.7% vs. 13.6%) and the virus’s mutation, which may lead to vaccine breakthrough (30.3% vs. 8.6%, Figure 2). The mean score of perceived advantages was significantly higher among the vaccine non-hesitant group compared to the vaccine hesitant group (9.01 ± 3.10 vs. 7.07 ± 3.60, p < 0.001, Table 3). On the contrary, the mean score of perceived disadvantages was higher among the vaccine-hesitant group compared to the non-hesitant group (8.36 ± 3.02 vs. 5.15 ± 3.12, p < 0.001, Table 3). The vaccine non-hesitant group had a statistically significant higher mean score of the behavior confidence as compared to the hesitant group (8.84 ± 3.76 vs. 5.67 ± 4.09, p < 0.001, Table 3). The results of Pearson’s correlation test indicated a moderate significant positive correlation between the constructs of advantages, behavior confidence and changes in the physical environment (p < 0.001, Table 4). A strong positive correlation was also found between the physical environment and behavior confidence (p < 0.001). In hierarchical regression analysis, the overall regression model (with age and all MTM constructs) predicted nearly 65% of variance in initiating COVID-19 vaccination behavior among the vaccine-hesitant group (Adjusted R2 = 0.649, F = 32.944, p < 0.001, Table 5). With each unit increment in participatory dialogue and behavior confidence, the conditional mean for initiation of COVID-19 vaccination among hesitant Blacks increased by 0.106 and 0.166 units, respectively (Model 4, Table 4). Among the demographic variables, except age, the slope for gender, region, religion, and political affiliation were not significant, indicating no significant differences in the conditional mean change in the initiation among vaccine-hesitant Blacks.

Table 2.
Demographic characteristics of the sample population (n = 428).
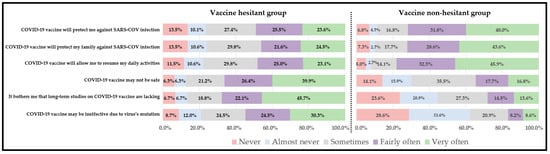
Figure 2.
Perceived advantages and disadvantages of COVID-19 vaccination among hesitant and non-hesitant group.

Table 3.
Comparison of Multi-theory model (MTM) constructs among vaccine-hesitant and non-hesitant groups.

Table 4.
Pearson correlations, and reliability estimates for study variables in the sample population (n = 428).

Table 5.
Hierarchical Multiple Regression (HRM) predicting likelihood for initiation of COVID-19 vaccination among hesitant African Americans (n = 208).
3. Discussion
The purpose of this study was to identify correlates of vaccine hesitancy among African Americans, including those derived from MTM, and upon successful testing of MTM present a framework for the m-health intervention. In our study, 48.6% African Americans had not been vaccinated and expressed vaccine hesitancy. The study found that, among socio-demographic characteristics, age (younger Blacks being more hesitant), being from the Northeast region of the United States, being a Republican as political affiliation, and having a religion other than Christianity or atheist had statistically significant greater proportion of vaccine-hesitant Blacks. Previous reports have indicated that Blacks bear a disproportionate burden of COVID-19-associated morbidity and mortality, which in turn contribute to vaccine hesitancy among this group [38]. Blacks have distrust towards medical profession and research, which might explain hesitancy of this group [38]. While testing MTM constructs, it was noted that all constructs of MTM were statistically significant between vaccine-hesitant Blacks and vaccine non-hesitant Blacks with effect sizes ranging predominantly from medium to large with the exception of participatory dialogue where the effect size was small. The MTM constructs of participatory dialogue and behavioral confidence along with age accounted for a large proportion of variance (64.9%) in explaining the likelihood of getting the COVID-19 vaccination among the hesitant African Americans. Thus, this established MTM as a robust model for m-health intervention planning.
Upon examining our results in the context of existing literature, age was an important determinant of vaccine hesitancy with younger Blacks being more hesitant than their older counterparts. This finding is also supported by the study by Fisher and colleagues (2020), who early on in the pandemic found that younger age was associated with greater vaccine hesitancy [39]. Similar evidence for greater vaccine hesitancy among the younger population was also found by other studies [40,41,42]. This can be explained by the preconceived notion of the younger generations of being ‘invincible’, beliefs of toughness, not enough confidence in vaccines, mistrust with the medical system especially among African Americans [43], carelessness, or a carefree attitude. These findings suggest developing concerted efforts for COVID-19 vaccine promotion among Black youth through diverse channels.
Next, vaccine-hesitant African Americans were clustered in the Northeastern region of the U.S. This was somewhat surprising as the Southern region was presumed to have a greater proportion of vaccine-hesitant groups given the lowest rates of vaccination per previous studies [44]. The reason for this could be that while the Northeastern region has the highest rates of vaccination, this has not still reached total vaccination coverage and the remaining group of people may be laggards, thus driving up the percentage of COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy in this subgroup of African Americans. Further, the Pew Research Center (2021) reported that the Black population in the U.S. is growing and is becoming more diverse [45]. From 2000 to 2019, there was a 29% increase in the African American population [45]. Moreover, nearly 10% of African Americans were foreign-born, with New York (area that lies in Northeast U.S.) having the largest number [45]. A substantial proportion of this Black population that is foreign-born mainly from the Caribbean [45]. Some of the cities in the Northeast have a greater number of such individuals and they may possibly be more reluctant to get vaccinated as they may not have assimilated into the American culture [45]. These findings about greater disparity in the North-East has implications for targeting African Americans residing in the North-East region with proactive educational campaigns and not becoming complacent.
Consistent with previous reports, the Republican political affiliation had greater proportion of vaccine hesitancy as opposed to those being Democrats [13,46,47,48,49]. These findings suggest the need for Republican party leaders and especially African American Republican role models to support openly the COVID-19 vaccine campaigns.
Religion in the African American community other than Christianity and Atheist was found to have higher vaccine hesitancy (21.2%) in comparison to the non-hesitant group (13.6%). The predominant other religion within the African American community is Islam [49]. A majority of these Muslim African Americans live in the Northeast [50]. Our study found a greater proportion of African Americans with vaccine hesitancy living in the Northeast and this could be an attribute related to that distribution.
As expected, our study found all MTM constructs to be statistically significant and having higher scores for the non-hesitant African American population as compared to the hesitant population. Furthermore, the constructs of participatory dialogue and behavioral confidence were statistically significant predictors of the likelihood of taking the COVID-19 vaccine among the hesitant group. No previous study using MTM has been conducted in this regard with the African American community and this was the first study. However, a previous study has been done with college students in which all three constructs of MTM were found to be significant predictors and accounted for 54.8% of variance in the likelihood of taking the COVID-19 vaccine among vaccine-hesitant students [30]. In our study, we did not find changes in the physical environment as significant because the previous study was done when the vaccine was not available, but at present availability is no longer an issue and the COVID-19 vaccine is available to anyone intending to take it. In our sample, 96.6% (201/208) of the vaccine-hesitant group had a cell phone. Based on the results of this study, an m-health (mobile phone based) educational intervention for testing and implementation with Blacks to promote COVID-19 vaccine uptake behavior can be undertaken. Therefore, based on these findings an m-health intervention can be proposed.
3.1. Proposition of a m-Health (Mobile Phone-Based Intervention)
Based on the findings of this survey, m-health (mobile phone-based) interventions can be planned and instituted. This can be a brief and precise intervention. The tentative logic model for the intervention is depicted in Figure 3. For designing and implementing such an intervention, a variety of educational methods would need to be utilized such as scripted, interactive text messaging that would underscore the advantages of the COVID-19 vaccine over the disadvantages and initiate participatory dialogue between the facilitator and the client. This will help the participants sway their decisions towards greater vaccine acceptance. In order to build behavioral confidence, success stories of role models and testimonials would need to be shared with the clients. For instance, messages from leading Black health professionals and community leaders can encourage COVID-19 vaccine uptake behavior among the African American community. For changes in the physical environment, even though the vaccine is available, reminder systems and facilitation of resources would need to be undertaken to ensure that the immunization schedule is completed, including the proposed boosters. It is critical to help the participants overcome logistical barriers in getting the vaccine that can be provided through phone dialogue linking people to resources.
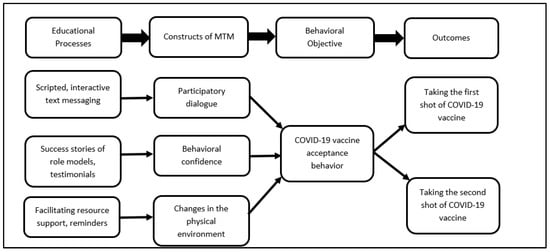
Figure 3.
Diagrammatic depiction of how the multi-theory model (MTM) for health behavior change can be used to improve the COVID-19 vaccine uptake behavior through an m-health intervention.
3.2. Strengths and Limitations
To our knowledge, this study is the first study to utilize a contemporary theoretical paradigm of MTM to explain the correlates of COVID-19 acceptability among a nationally representative sample of African Americans. The study also delved into understanding the differences between COVID-19 vaccine-hesitant African Americans and non-vaccine-hesitant African Americans. The study found evidence in support of MTM and was able to propose a putative m-health intervention for possible implementation in high need areas. However, the study also had some limitations. First, the cross-sectional study design limits the causal inferencing due to measurement of independent and dependent variables at the same point in time. Second, we might expect some residual confounding attributed to unmeasured variables, for example academic performance. Third, self-reports are the only means of gathering information about attitudes, and they suffer from measurement bias in the form of dishonesty, exaggeration, yay saying, nay saying, etc. Moreover, the likelihood of getting the COVID-19 vaccine was measured through self-report as a proxy of actual behavior. Therefore, these limitations need to be considered while interpreting the results for causality.
4. Conclusions
Our study found that a substantial proportion of African Americans who have not yet been vaccinated have a high degree of vaccine hesitancy (48.6%). Our study also found that age (younger Blacks being more hesitant), residence in North-East region of the United States, having a Republican political affiliation, and belonging to a religion other than Christianity or atheist resulted in statistically significant greater proportion of vaccine-hesitant African Americans. Our study found that all the constructs of MTM were statistically significant between vaccine-hesitant African Americans and non-vaccine-hesitant African Americans. The MTM constructs of participatory dialogue and behavioral confidence along with age explained a large proportion of variance in the likelihood of getting COVID-19 vaccination among the hesitant African Americans. The study proposed a framework for an m-health intervention for African Americans.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S. and K.B.; methodology, M.S. and K.B.; software, R.B.; validation, M.S., K.B. and R.B.; formal analysis, K.B., and R.B.; investigation, M.S., K.B. and R.B.; resources, M.S.; data curation, M.S., K.B.; writing—original draft, M.S., K.B. and R.B.; writing—review and editing, M.S., K.B. and R.B.; visualization, M.S., K.B. and R.B.; supervision, M.S. and K.B.; project administration, M.S. and K.B.; funding acquisition, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for the data collection was received from the School of Public Health, University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (1702350-2 dated 6 January 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Dummy coding algorithm of polytomous variables used in the regression.
Table A1.
Dummy coding algorithm of polytomous variables used in the regression.
| Variable | New Variable 1 (X1) | New Variable 2 (X2) | New Variable 3 (X3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | |||
| 1 Midwest | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 West | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 Northeast | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 South | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Religion | |||
| 1 Christianity | 0 | 0 | - |
| 2 Atheist | 0 | 1 | - |
| 3 Others | 1 | 0 | - |
| Political affiliation | |||
| 1 Democrat | 1 | 0 | - |
| 2 Republicans | 0 | 0 | - |
| 3 Others | 0 | 1 | - |
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vaccination Offers Higher Protection Than Previous COVID-19 Infection. 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/s0806-vaccination-protection.html (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- United States Government Accountability Office. Operation Warp Speed. 2021. Available online: https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-21-319.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Vaccines NIH’s Role in Vaccine Development and Vaccine Studies to Prevent COVID-19. 2021. Available online: https://covid19.nih.gov/treatments-and-vaccines/covid-19-vaccines (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.E.; Gargano, J.W.; Scobie, H.; Wallace, M.; Hadler, S.C.; Leung, J.; Blain, A.E.; McClung, N.; Campos-Outcalt, D.; Morgan, R.L.; et al. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ Interim Recommendation for Use of Janssen COVID-19 Vaccine—United States, February 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badur, S.; Ota, M.; Öztürk, S.; Adegbola, R.; Dutta, A. Vaccine confidence: The keys to restoring trust. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P. Anti-vaccine movement could undermine efforts to end coronavirus pandemic, researchers warn. Nature 2020, 581, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, A.A.; Eisenbach, N.; Taiber, S.; Morozov, N.G.; Mizrachi, M.; Zigron, A.; Srouji, S.; Sela, E. Vaccine hesitancy: The next challenge in the fight against COVID-19. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAteer, J.; Yildirim, I.; Chahroudi, A. The VACCINES Act: Deciphering Vaccine Hesitancy in the Time of COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Our World in Data. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccination. 2021. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations?country=USA (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- White House. Fact Sheet: President Biden to Announce Goal to Administer at Least One Vaccine Shot to 70% of the U.S. Adult Population by 4 July. 2021. Available online: https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2021/05/04/fact-sheet-president-biden-to-announce-goal-to-administer-at-least-one-vaccine-shot-to-70-of-the-u-s-adult-population-by-july-4th/ (accessed on 11 August 2021).
- Khubchandani, J.; Sharma, S.; Price, J.H.; Wiblishauser, M.J.; Sharma, M.; Webb, F.J. COVID-19 vaccination hesitancy in the United States: A rapid national assessment. J. Community Health 2021, 46, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khubchandani, J.; Macias, Y. COVID-19 vaccination hesitancy in Hispanics and African-Americans: A review and recommendations for practice. Brain Behav. Immunity-Health 2021, 15, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbie-Smith, G.; Thomas, S.B.; George, M.M. Distrust, Race, and Research. JAMA 2002, 162, 2458–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, M.A.; Giger, J.N.; Powell-Young, Y.; Brannon, C.B. Why African-Americans are hesitant to take the newly proposed COVID-19 vaccines: Tuskegee revisited. J. Natl. Black Nurses Assoc. 2020, 31, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinand, K.C.; Nedunchezhian, S.; Reddy, T.K. The COVID-19 and influenza “twindemic”: Barriers to influenza vaccination and potential acceptance of SARS-CoV2 vaccination in African Americans. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2020, 112, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, F.J.; Khubchandani, J.; Striley, C.W.; Cottler, L.B. Black-White differences in willingness to participate and perceptions about health research: Results from the population-based HealthStreet study. J. Immigr. Minority Health 2019, 21, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woko, C.; Siegel, L.; Hornik, R. An investigation of low COVID-19 vaccination intentions among Black Americans: The role of behavioral beliefs and trust in COVID-19 information sources. J. Health Commun. 2020, 25, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millett, G.A.; Jones, A.T.; Benkeser, D.; Baral, S.; Mercer, L.; Beyrer, C.; Honermann, B.; Lankiewicz, E.; Mena, L.; Crowley, J.S.; et al. Assessing differential impacts of COVID-19 on black communities. Ann. Epidemiol. 2020, 47, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.E.; Reither, E.N.; Mamelund, S.-E.; Lim, S. Black-white disparities in 2009 H1N1 vaccination among adults in the United States: A cautionary tale for the COVID-19 pandemic. Vaccine 2021, 39, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanz, K.; Bishop, D.B. The Role of Behavioral Science Theory in Development and Implementation of Public Health Interventions. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2010, 31, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M. Theoretical Foundations of Health Education and Health Promotion, 4th ed.; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Sudbury, ON, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M. Multi-theory model (MTM) for health behavior change. WebmedCentral Behav. 2015, 6, WMC004982. [Google Scholar]
- United States Census Bureau. Quick Facts. Available online: https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/US/PST045219 (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- NRC Health. Updated COVID Vaccinations Study: Have Consumers’ Opinions about the Vaccine Changed with an Upcoming Release? 2020. Available online: https://nrchealth.com/updated-covid-vaccinations-study-have-consumers-opinions-about-the-vaccine-changed-with-an-upcoming-release/ (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Press Ganey Media. Press Ganey COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy Research Finds Black/African American Patients Far Less Willing Than Asian or White Patients to Get the Vaccine. Business Wire. 2021. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210204005712/en/Press-Ganey-COVID-19-Vaccine-Hesitancy-Research-Finds-BlackAfrican-American-Patients-Far-Less-Willing-Than-Asian-or-White-Patients-to-Get-the-Vaccine/?feedref=JjAwJuNHiystnCoBq_hl-aWOJSq7maz1kUlsOIrkZM4xz5QOdfJiTifxwfmkU5A67fxFuNFTHSunhvli30RlBNXya2izy9YOgHlBiZQk2LPgxNjXHjsNmKaXEz4koEK2KQOELXF1Klv27yoigQe38g= (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- ESOMAR. Data Protection Checklist. Available online: https://www.esomar.org/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Qualtrics Market Research Panel Survey. 2021. Available online: https://www.qualtrics.com/market-research/ (accessed on 22 August 2021).
- Sharma, M.; Davis, R.E.; Wilkerson, A.H. COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptance among College Students: A Theory-Based Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, T.; Sharma, M.; Shahbazi, M.; Sung, J.H.; Bennett, R.; Reese-Smith, J. The evaluation of a fourth-generation multi-theory model (MTM) based intervention to initiate and sustain physical activity. Health Promot. Perspect. 2019, 9, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.L.; Sharma, M.; Mendy, V.L.; Leggett, S.; Akil, L.; Perkins, S. Using multi theory model (MTM) of health behavior change to explain intention for initiation and sustenance of the consumption of fruits and vegetables among African American men from barbershops in Mississippi. Health Promot. Perspect. 2020, 10, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Batra, K.; Davis, R.E.; Wilkerson, A.H. Explaining Handwashing Behavior in a Sample of College Students during COVID-19 Pandemic Using the Multi-Theory Model (MTM) of Health Behavior Change: A Single Institutional Cross-Sectional Survey. Healthcare 2021, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Batra, K.; Flatt, J. Testing the Multi-Theory Model (MTM) to Predict the Use of New Technology for Social Connectedness in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare 2021, 9, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B. The Use of Statistical Significance Tests in Research. J. Exp. Educ. 2014, 61, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation. 2021. Available online: https://aspe.hhs.gov/reports/vaccine-hesitancy-covid-19-state-county-local-estimates (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Mansournia, M.A.; Collins, G.S.; Nielsen, R.O.; Nazemipour, M.; Jewell, N.P.; Altman, D.G.; Campbell, M.J. A Checklist for statistical Assessment of Medical Papers (the CHAMP statement): Explanation and elaboration. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurencin, C.T. Addressing Justified Vaccine Hesitancy in the Black Community. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2021, 8, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.A.; Bloomstone, S.J.; Walder, J.; Crawford, S.; Fouayzi, H.; Mazor, K.M. Attitudes toward a potential SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: A survey of U.S. Adults. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadante, A.R.; Law, A.V. Will they, or won’t they? Examining patients’ vaccine intention for flu and COVID-19 using the health belief model. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2021, 17, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.B.; Bell, R.A. Predictors of intention to vaccinate against COVID-19: Results of a nationwide survey. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, G.; Nardi, A. Vaccine hesitancy in the era of COVID-19. Public Health 2021, 194, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, L.M.; Ojikutu, B.O.; Tyagi, K.; Klein, D.J.; Mutchler, M.G.; Dong, L.; Lawrence, S.J.; Thomas, D.R.; Kellman, S. COVID-19 related medical mistrust, health impacts, and potential vaccine hesitancy among Black Americans living with HIV. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2021, 86, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo Clinic. U.S. COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker: See Your State’s Progress. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/coronavirus-covid-19/vaccine-tracker (accessed on 22 August 2021).
- Pew Research Center. Facts about the U.S. Black Population. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/fact-sheet/facts-about-the-us-black-population/ (accessed on 22 August 2021).
- Agarwal, R.; Dugas, M.; Ramaprasad, J.; Luo, J.; Li, G.; Gao, G.G. Socioeconomic privilege and political ideology are associated with racial disparity in COVID-19 vaccination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107873118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.D.; Feng, W.; Corlin, L.; Porteny, T.; Acevedo, A.; Schildkraut, D.; King, E.; Ladin, K.; Fu, Q.; Stopka, T.J. Why are some people reluctant to be vaccinated for COVID-19? A cross-sectional survey among U.S. Adults in May–June 2020. Prev. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, A.; Gershon, R.; Gneezy, A. COVID-19 and vaccine hesitancy: A longitudinal study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, K.; Bekalu, M.; Dhawan, D.; Pinnamaneni, R.; Lang, J.; McLoud, R. Individual and social determinants of COVID-19 vaccine uptake. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, B.; Diament, J. Black Muslims Account for a Fifth of All U.S. Muslims, and about Half Are Converts to Islam. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/01/17/black-muslims-account-for-a-fifth-of-all-u-s-muslims-and-about-half-are-converts-to-islam/ (accessed on 22 August 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).