Abstract
Background/Objectives: Long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) represent a significant advancement in the treatment of schizophrenia (SCZ), particularly for improving adherence and long-term outcomes. This study aimed to assess the clinical outcomes of patients receiving atypical LAIs compared to those on various oral antipsychotics over a one-year follow-up in a naturalistic setting. Methods: Sixty patients with SCZ were subdivided in two groups, those receiving LAIs (n = 25) and those receiving oral antipsychotics (n = 35). The groups were comparable for age, gender, educational attainment, employment status, marital status, smoking habits, and baseline SCZ severity, with no differences in baseline chlorpromazine equivalent dosages. Results: Over the follow-up period, patients in the LAI group discontinued treatment less frequently (χ2 = 4.72, p = 0.030), showed fewer suicide attempts (χ2 = 5.63, p = 0.018), fewer hospitalizations (χ2 = 4.95, p = 0.026), and fewer relapses (χ2 = 6.61, p = 0.010). Significant differences also emerged on the Drug Attitude Inventory (DAI-10) scores (F = 8.76, p = 0.005) and Body Mass Index (BMI) values (F = 8.32, p = 0.007), with the LAI group showing more favorable outcomes. Conclusions: LAIs, compared to oral antipsychotics, may promote treatment adherence, as shown by decreased hospitalization; furthermore, their use is related with better outcomes, like fewer relapses and less suicide attempts in individuals with SCZ in real-world settings.
1. Introduction
Schizophrenia (SCZ) is a severe and debilitating disorder that frequently follows a lifelong course [1]. Hallmarks of SCZ include recurrent relapses and deteriorating psychopathology and social functioning [2]. While some patients with SCZ recover well enough to achieve good daily functioning, take proper care of themselves, and have little or no symptoms, this subgroup is a tiny minority [3]. Naturalistic studies indicate that approximately 80% of patients experience relapse within a 5-year period [4,5], which ensues in negative consequences, regardless of illness stage [6]. Among these consequences, suicide is a leading cause of mortality among patients with SCZ [7], with an almost 3-fold higher risk during the first 5 years following their initial hospitalization [8].
Antipsychotic drugs (APs) are pivotal in the treatment of SCZ. APs have shown efficacy in reducing relapse rates in both first-episode and multiple-episode patients. The risk of relapse is reduced 2–6-fold when compared to the absence of AP therapy [4,9,10,11]. Compared to placebo or no treatment, APs are linked to lower all-cause mortality [12,13]. Despite their proven efficacy, adherence to AP treatment remains a major clinical challenge. Following first hospitalization, discontinuation rates escalate rapidly, from 36% within 30 days to nearly 50% within 60 days after discharge [14]. A subset of patients continues treatment with suboptimal adherence, with nearly half of them adhering to less than 70% of their prescribed oral medications [15]. Given the well-established link between non-adherence and risk of relapse (not to mention inefficacy), long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) have emerged as a strategy to enhance adherence and reduce relapse rates [16,17,18]. However, their use in everyday clinical practice is still limited, often being limited to patients with chronic SCZ with the aim to maintain adherence, while oral APs are still preferred during the early phases of the illness [19,20].
LAIs are delivered by healthcare professionals at regular intervals, thus ensuring that patients return to their scheduled visits; this facilitates treatment adherence. Switching from oral antipsychotics to LAIs seems an appropriate way to enhance adherence and thereby reduce the risk for relapse [21]. However, evidence on the comparative effectiveness of LAIs vs. oral formulations are inconsistent, with some studies endorsing their superiority over oral formulations [22,23], while others do not [24,25,26]. A 2021 meta-analysis comprising randomized controlled trials (RCTs), observational, and retrospective or prospective studies found LAIs to be linked with a lower risk of relapse and hospitalization [15]. An updated meta-analysis of 137 studies proved a small but consistent benefit of LAIs across RCTs, cohort, and retrospective or prospective studies [27]. Though discontinuation due to inefficacy or non-adherence was postponed, and hospitalization rates were lower in RCTs, a systematic review by the same group of investigators [28] confirmed a small benefit of LAIs in relapse prevention or all-cause discontinuation focusing on early-phase schizophrenia. This larger study indicated lower relapse risk in early illness, especially in newly diagnosed individuals [28]. Though hospitalization rates were comparable, a cluster-randomized trial found LAIs to be related to increased time to first hospitalization [29].
Long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) were first introduced in the mid-1960s as oil-based formulations of first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs). From the early 2000s, second-generation LAIs (SGAs) became available, based on aqueous formulations [30]. The SGAs approved for used in patients with SCZ and other disorders, including the psychotic spectrum and bipolar disorder, were intramuscular risperidone microspheres, paliperidone (9-hydroxyrisperidone) palmitate (PP), olanzapine pamoate, and aripiprazole monohydrate and dodecanoate (Lauroxil). The first risperidone LAI used microspheres, an innovative technology, but its use was limited by high costs and the need for injections every two weeks [31]. To overcome these limitations, risperidone’s drug manufacturers produced PP, a monthly formulation now also available as 3-month and 6-month injections; the last two are of doubtful cost-effectiveness [32]. Almost simultaneously with PP, olanzapine pamoate has been introduced, but its associated post-injection syndrome (sedation and confusion, and even delirium, which limit patient’s autonomy and are incompatible with driving back home for some time) [33] and the need to let the patient resting for 2–3 h at the outpatient unit or other healthcare facilities [34], limited its popularity among clinicians, not to mention the cardiometabolic side effects of this drug, which are similar to those of the oral formulation [35]. A 2013 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) investigation [36], further added to the mistrust for this formulation. In 2013 and 2015, aripiprazole monohydrate and Lauroxil became available on the market, but only the former has received approval in the European Union [37]. More recently, risperidone LAI formulations were enriched by subcutaneous formulations [38], one of which showed good efficacy in once monthly and 2-month injections [39]. Such formulations have still to be introduced in Europe. In our service, we mostly use PP and aripiprazole monohydrate along of sorts of oral AP formulations.
LAIs have been compared with oral APs in terms of outcomes like relapses, rehospitalizations (length of hospital stay and number), and emergency room accesses. One study used a mirror design, i.e., one in which data in the same patient after the introduction of a LAI were compared to those before its introduction, when the patient was on oral APs, and found that the numbers of both emergency room accesses and hospitalization dropped after LAI prescription, as did the total time of hospital stay [40]. Another longitudinal study tested the FGA haloperidol oral vs. LAI in a randomized prospective 12-week study of patients with first-episode schizophrenia and found similar efficacy on the PANSS, but better Quality of Life (QoL), increased treatment adherence and less side effects [41]. However, the duration of this study was relatively limited. While the occurrence of less adverse events with LAIs compared oral might be surprising at a first glance, it was confirmed by two meta-analyses, although differences between molecules were recognized [42,43]; in contrast, another meta-analysis found more extrapyramidal and prolactin-related adverse events in LAIs compared to oral APs [44]. LAI APs were found to possess lower risk of all-cause and non-suicidal mortality in people with schizophrenia compared to oral APs, with better treatment adherence partly explaining this difference [45]. There is a dearth in the literature of comparisons of LAI AP to its own oral counterpart; only one study compared aripiprazole LAI to oral aripiprazole in acute episodes of psychosis in Chinese patients and found the two formulations to be comparable for efficacy and safety, but this study was a noninferiority study [46]. Summarizing the evidence, there is design heterogeneity and inconsistency of findings in LAI vs. oral AP comparisons [15,43].
Given the current uncertainty over the comparative efficacy of LAIs over oral antipsychotics, especially in naturalistic settings where real-world variables like treatment adherence and clinical complexity come into play, we aimed to assess the clinical outcomes of patients diagnosed with DSM-5 schizophrenia [47] receiving LAIs (i.e., aripiprazole or paliperidone) compared with those treated with oral APs, over a 12-month follow-up period in a naturalistic setting. This study compared treatment modalities rather than individual molecules or their respective formulations. The primary outcomes of interest were relapse, psychiatric hospitalization, suicidal ideation, treatment discontinuation, and BMI change. Our hypothesis was that LAIs would be associated with improved long-term outcomes compared to oral antipsychotic therapy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Patients were recruited from the outpatient clinics of the Psychiatry Department of the Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS in Rome, Italy, between January 2022 and December 2023. The study enrolled 60 patients diagnosed according to DSM-5 criteria with schizophrenia, multiple episodes, currently in acute episode [47]. Patients were treated either with long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs; n = 25) or with second-generation oral antipsychotics (n = 35). The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Research Version (SCID-5-RV [48]) was used to diagnose SCZ and to identify psychiatric comorbidities. Additionally, we screened patients for Personality Disorders with the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Personality Disorders (SCID-5-PD; [49]). Diagnostic interviews were conducted by senior psychiatrists with acceptable inter-rater reliability (Cohen’s κ = 0.87).
Inclusion criteria required participants to meet the following: (a) ability of providing informed consent and comply with study procedures, which required basic literacy skills (corresponding to approximately 5 years of formal education) and fluency in Italian; (b) clinical diagnosis of SCZ according to DSM-5 criteria; (c) age between 18 and 65 years; (d) current treatment with either LAI or second-generation oral antipsychotic for at least three months prior to enrollment; (e) stable clinical condition at baseline, defined as absence of acute psychotic symptoms requiring hospitalization in the past 30 days. Exclusion criteria were: (a) intellectual disability or clinically significant cognitive impairment; (b) major medical or neurological conditions; (c) central nervous system infections; and (d) pregnant or breast-feeding women. Informed consent was obtained from all participants and their legal tutors before joining the study. The study adhered to the Principles of Human Rights as adopted by the 18th World Medical Association (WMA) General Assembly, Helsinki, Finland, June 1964 and amended by the 64th WMA General Assembly, Fortaleza, Brazil, October 2013; it obtained approval from the ethical committee of the Gemelli Foundation, ID 2014 Prot. N. 13864/18 of 21/02/2018.
2.2. Study Design
This was a naturalistic, longitudinal, observational cohort study conducted over a 24-month period with a 12-month follow-up for all patients.
Prior to baseline assessment, patients were non-randomly assigned to two groups. In one group (LAI group), patients were treated with paliperidone palmitate (n = 10) or aripiprazole monohydrate (n = 15). Patients in the oral AP group were treated with one of the following: olanzapine (n = 5), risperidone (n = 8), aripiprazole (n = 8), lurasidone (n = 4), clozapine (n = 7), and brexpiprazole (n = 3). Treatment allocation was based on the clinicians’ individualized judgment, without standardized protocols, and reflected routine clinical decision-making. This approach resulted in two groups that were comparable in key demographic and clinical characteristics, including symptom severity and chlorpromazine-equivalent dosage.
Assessments were conducted at baseline, after 6 months from initiating drug treatment, and after 12 months. At the baseline assessment, clinicians collected demographic and clinical variables on an appropriate socioepidemiological sheet. Demographic variables included age, gender, years of education, marital status, body mass index (BMI), and living status. Clinical variables included current psychopharmacological treatment, antipsychotic dosage standardized to chlorpromazine equivalents, lifetime suicidal ideation or behavior, and SCZ symptom severity. The evaluation of lifetime suicidal ideation was evaluated through the Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) Lifetime version [50]. Psychopathological severity was assessed using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) [51].
Follow-up assessments were conducted at 6 and 12 months and included the following clinical outcomes: suicidal ideation or behavior, relapses, psychiatric hospitalizations, treatment discontinuation (drop-out), and BMI. Suicidal ideation or behavior was assessed using item 1 of the C-SSRS Since Last Visit version, which screens for the presence of any suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Relapse was defined as a ≥12-point increase in the PANSS total score, in line with evidence-based criteria proposed by Siafis and colleagues [52]. Drop-out was evaluated over a 1-year period from each patient’s initial visit and was defined as the occurrence of one or more of the following: (1) discontinuation of treatment for ≥5 weeks despite the psychiatrist’s prescription to maintain it; (2) failure to attend a scheduled psychiatric follow-up within one month of the appointed date; (3) a change in the antipsychotic agent prescribed; or (4) clinician’s decision. These different scenarios were grouped under a single “drop-out” category as they all represent indicators of treatment non-persistence, regardless of the underlying cause. Conversely, admission to a psychiatric ward was considered as indicative of treatment continuity.
At the 12-month follow-up, patients’ subjective attitude toward antipsychotic treatment was assessed using the 10-item Drug Attitude Inventory (DAI-10) [53]. This evaluation was conducted to explore patients’ personal perspectives on their ongoing pharmacological regimen and their overall engagement with treatment.
2.3. Assessment Tools
C-SSRS [50], PANSS [51], and DAI-10 [53] were used to assess suicidal ideation, severity of psychopathology, and subjective attitude toward antipsychotic treatment, respectively.
The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) [50] is a semi-structured clinical interview used to evaluate suicidal ideation and behavior. It includes multiple versions tailored to different time frames, including the “Lifetime” and the “Since Last Visit” versions, which were both used in this study. Total scores range from 1 (whish to be dead) to 5 (suicidal ideation with a plan and intent). Specifically, the C-SSRS begins by asking two questions that assess a participant’s desire to be dead (e.g., “I wish I was dead”) and nonspecific active suicidal thoughts (e.g., “I’ve thought about killing myself”). If the responses to both questions are negative or the answer to Question 1 is yes and Question 2 is no, the participant is considered not to have active suicidal ideation. A binary categorical variable was created based on the reported severity: nonsuicidal ideation (score of 0–1 points) and suicidal ideation (score of 2–5 points) [54]. The scale has been translated in various languages confirming its original good psychometric properties, including high inter-rater reliability (κ > 0.80) and predictive validity for suicidal behavior [55].
The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) [51] is a clinician-administered instrument used to assess symptom severity in patients with SCZ. The scale comprises 30 items grouped into three subscales: Positive symptoms (7 items), Negative symptoms (7 items), and General Psychopathology (16 items). Each item is scored on a 7-point scale, ranging from 1 (absent) to 7 (extreme). Total scores range from 30 to 210, with higher scores indicating more severe psychopathology. The tool has demonstrated adequate internal consistency, external convergent and divergent validity and reliability in foreign language translations [56]; its validated Italian version that we used has demonstrated a 5-factor-structure, with good internal consistency (Cronbach’s α ranging from 0.73 to 0.83 across subscales) and strong inter-rater reliability (ICC > 0.80) [57].
The Drug Attitude Inventory (DAI-10) [53] is a self-report questionnaire used to evaluate the patient’s subjective experience and attitude toward antipsychotic medication. The instrument consists of 10 true/false items that capture beliefs, preferences, and perceived benefits or adverse effects associated with treatment. Positive total scores suggest a favorable attitude toward medication adherence, while negative scores may indicate poor insight or reluctance to continue pharmacotherapy. Its 10-item version has shown similar psychometric properties to the 30-item version, from which it was developed, showing good homogeneity and test–retest reliability [58]. The Italian version used in this study has shown acceptable internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.84) [59].
2.4. Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were computed for all variables. Between-group comparisons (patients treated with LAI vs. those receiving second-generation oral antipsychotics) were conducted using Pearson’s chi-square test (χ2) for categorical variables and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA-1way) for continuous variables. When the assumption of homogeneity of variances was violated, Welch’s ANOVA was applied. For continuous variables we first tested their normality with the Shapiro–Wilk test [60] and then proceeded with parametric tests. For correlations we used Pearson’s r coefficient. No a priori power analysis was conducted, as the sample derived from naturalistic recruitment.
Categorical outcomes assessed at 6 and 12 months (i.e., suicidal ideation, relapse, psychiatric hospitalization, and treatment discontinuation) were analyzed using chi-square tests of independence. Continuous outcomes, including total scores on the DAI-10, PANSS subscales, and BMI, were compared between groups using ANOVA-1way or Welch’s ANOVA, as appropriate. Drop-outs were treated as a clinical outcome rather than missing data; therefore, no imputation was performed, and all patients were retained in the analyses accordingly.
All analyses were performed using the JASP statistical software (version 0.19.3, JASP Team, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) [61] and R (version 4.1.0, R Core Team) [62]. A two-tailed p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
The demographic and clinical characteristics of the sample are present in Table 1. The final sample included 60 patients divided into two groups, 25 receiving LAI and 35 receiving SGA APs. The two groups did not significantly differ in terms of age (p = 0.075), age at onset (p = 0.514), gender distribution (p = 0.965), years of education (p = 0.085), marital status (p = 0.706), and living status (p = 0.182). Baseline BMI (p = 0.080), smoking habits (p = 0.239), substance use (p = 0.426), chlorpromazine equivalents (p = 0.177), lifetime suicidal ideation (p = 0.064), PANSS-General (p = 0.479), -Positive (p = 0.064), and -Negative (p = 0.054) scale scores were also comparable.

Table 1.
Baseline sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of the sample.
3.2. Between-Group Comparisons of Clinical Outcomes
At 6 months, the between-group comparison of the relapse rate did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.080). At 12 months, the relapse rate was significantly lower in the LAI group (n = 2; 8.0%) compared to the Oral AP group (n = 11; 31.4%) (χ2 = 4.72, p = 0.030). Hospitalization rates at 6 months did not differ between groups (p = 0.133), while at 12 months, they were significantly reduced in the LAI group (n = 1; 4.0%) compared to the Oral AP group (n = 9; 25.7%) (χ2 = 4.95, p = 0.026). The prevalence of suicidal ideation or behavior during follow-up was significantly lower in the LAI group both at 6 months (n = 0 vs. n = 5; 0.0% vs. 14.3%; p = 0.048) and at 12 months (n = 2 vs. n = 13; 8.0% vs. 37.1%; p = 0.010). Drop-out rates were significantly lower in the LAI group at 6 months (n = 0; 0.0%) compared to the Oral AP group (n = 7; 20.0%) (p = 0.017), and at 12 months (n = 2 vs. n = 13; 8.0% vs. 37.1%; χ2 = 6.61, p = 0.010). DAI-10 scores were significantly higher in the LAI group than in the Oral AP group (F = 8.76; p = 0.005) at 12 months. Finally, at 12 months, the LAI group showed significantly lower BMI compared to the Oral AP group (F = 5.89; p = 0.019).
The results of the between-group comparisons at the 1-year follow-up are summarized in Table 2 and visually represented in Figure 1.

Table 2.
Between-group comparisons of clinical outcomes at 1-year follow-up.
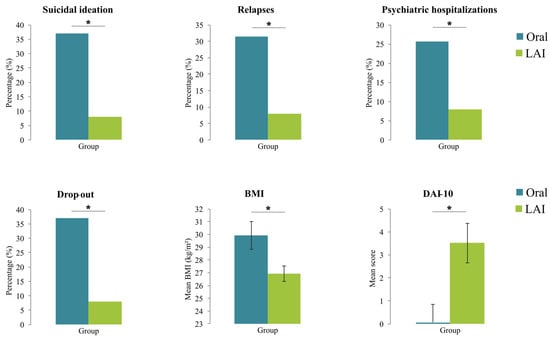
Figure 1.
Between-group comparisons of clinical outcomes at the 1-year follow-up. Bar plots illustrate comparisons between Oral AP (gray-blue) and LAI groups (light green) across six clinical outcomes, i.e., suicidal ideation, relapse, psychiatric hospitalization, drop-out, BMI, and DAI-10. Values represent percentages or means. * indicates p < 0.05. Abbreviations: BMI, Body Mass Index; DAI-10, Drug Attitude Inventory-10 items; LAI, long-acting injectables antipsychotics; Oral, Oral Antipsychotics group.
4. Discussion
This naturalistic longitudinal cohort study compared the clinical outcomes of patients with SCZ treated with LAIs versus SGA oral APs over a 12-month period. The results of this study can be summarized as follows: at the 1-year follow-up, patients treated with LAIs were found to have significantly lower rates of relapse, hospitalization, and suicidal ideation, as well as reduced treatment discontinuation (a proxy of treatment compliance), a more favorable attitude toward pharmacotherapy (a proxy of treatment adherence), and a smaller increase in BMI compared to those receiving oral APs.
The current data suggest that LAI APs may be associated with greater therapeutic advantages than oral antipsychotic drugs in decreasing relapse rates and hospitalizations due to mental conditions over a long-term follow-up. The findings align with a significant corpus of observational and retrospective data endorsing the efficacy of LAIs in sustaining clinical stability and diminishing the risk of relapses and hospitalization in patients with schizophrenia [63,64,65,66,67,68,69]. Given their favorable impact on treatment adherence and relapse prevention, several authors have proposed the use of LAIs in the early phases of schizophrenia, arguing that early and sustained pharmacological intervention may lead to significantly improved long-term outcomes [15,70,71]. However, the literature remains divided on this topic. A meta-analysis by Kishimoto et al. [63], which included 21 RCTs, reported no significant superiority of LAIs over oral APs in relapse prevention, whether assessed at the longest follow-up point or at specific time intervals. In contrast, a later and larger meta-analysis by the same group [15], incorporating RCTs, observational studies, and mirror designs, found LAIs to be associated with a reduced risk of both relapse and hospitalization. The results of more recent experiments are more controversial. A cluster-randomized trial by Kane et al. [29] indicated no difference in overall hospitalization rates, despite a considerably prolonged duration to first hospitalization in patients administered LAIs. Conversely, research concentrating on early-phase schizophrenia has produced inconclusive findings, in that some studies have not shown distinct benefits of LAIs compared to oral formulations in decreasing relapse or hospitalization rates [24,25]. These differences are presumably due, at least in part, to methodological differences. Studies not demonstrating benefit were mostly RCTs, which, due to their methodological rigor, can lack external validity owing to the use of tightly defined patient groups and rigorously regulated procedures that may not accurately represent the intricacies of standard clinical practice, as is the case of our real-world study. In contrast, naturalistic studies include broader and more representative samples, with treatment delivered under real-world conditions. These differences count when meta-analyzing pooled data. Nonetheless, the absence of randomization in our study may have introduced some degree of confounding. Although groups were matched on key baseline variables, unmeasured factors might have influenced treatment allocation and outcomes. We acknowledge this as an inherent limitation of naturalistic designs, but also one that mirrors the complexity of real-world clinical decision-making and supports the relevance of observational data in complementing evidence from RCTs.
Our study also found that individuals receiving LAIs were less likely to report suicidal ideation at the long-term follow-up in comparison to those taking oral formulations. This is in line with previous extensive observational cohort studies and meta-analyses of RCTs, indicating that the administration of LAIs is correlated with reduced mortality compared to the use of oral antipsychotic medications [14,69,72,73]. Patients treated with LAIs had substantially reduced risks of suicide attempts, all-cause mortality, and natural-cause mortality, according to a large population-based cohort study that followed nearly 5000 individuals newly diagnosed with schizophrenia over a 16-year period [73] and in a pooled-data meta-analysis [45]. Although the high rate of mortality associated with schizophrenia is well established, little is known about what contributes to it. Several elements have been suggested as potential causes, including environmental factors, treatment non-adherence, insufficient medical comorbidity management, careless lifestyle, and the recurrence of psychotic episodes [74]. LAIs might contribute to mitigating these risk factors by promoting greater treatment continuity, reducing symptom relapse, and stabilizing illness trajectories [69,75,76]. The potential anti-suicidal effect of LAIs may therefore be mediated indirectly through improved adherence, reduced illness instability, and better control of affective and psychotic symptoms, domains closely linked to suicide risk in patients with schizophrenia, but also relevant across a variety of other psychiatric disorders [77,78,79]. However, lower rates of suicidal ideation in the LAI group may also be influenced by other unmeasured factors. For instance, variations in psychosocial support (e.g., familial engagement, availability of community resources, or involvement in psychosocial therapies) may have played a role in mitigating suicide risk. Likewise, the frequency of clinical follow-up, and the extent of residual symptom intensity, especially concerning emotional symptoms and hopelessness, may have influenced the observed outcomes. Subsequent research should incorporate these variables to thoroughly investigate the causes behind suicidal thoughts in this demographic.
In addition to clinical outcomes, our findings revealed a significantly more positive subjective attitude toward antipsychotic treatment, assessed through the DAI-10, among patients receiving LAIs compared to those on oral formulations. A favorable attitude toward medication is a known predictor of adherence and long-term treatment engagement, reflecting greater treatment satisfaction, insight, and perceived efficacy [80,81]. Moreover, patients in the LAI group exhibited a substantially lower rate of treatment discontinuation over the 12-month period, reinforcing the hypothesis that LAIs may be associated with improvements in objective dimensions of adherence via subjective perception [65,82,83]. Despite this evidence, the prescription of LAIs remains limited in routine clinical practice since many psychiatrists remain cautious toward their use [84]. Three main factors have been identified as contributors to this reluctance: limited availability of second-generation LAI options, patients’ rejection of LAIs, and their fear of relapses due to the switch [85]. Additional barriers include limited flexibility about dosage, low control of potential adverse effects, healthcare system constraints (e.g., reimbursement or accessibility), and the absence of strong guideline recommendations for their early use in first episodes of schizophrenia [86,87,88]. Our results challenge some of these assumptions by showing that, in a naturalistic setting, LAIs may support improved pharmacological adherence in objective terms but may also positively influence patients’ subjective experience of treatment, a widely recognized critical determinant of long-term therapeutic success [89]. Additionally, access to LAIs and clinical attitudes toward their use are also shaped by national healthcare systems. In some countries, limited reimbursement policies or administrative barriers may restrict availability, particularly in outpatient or community settings [90]. These systemic and regulatory factors should be considered when interpreting the underutilization of LAIs in clinical practice.
Beyond symptom control and relapse prevention, antipsychotic treatment in SCZ also carries significant implications for physical health, particularly regarding metabolic risk. Patients with schizophrenia face disproportionately high rates of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that includes obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes, which contribute substantially to excess morbidity and mortality in this population [91,92]. In this context, our findings revealed a significantly lower BMI at 12-month follow-up in the group treated with LAI antipsychotics compared with those receiving oral formulations. Although previous studies have reported inconsistent differences in the overall metabolic risk profile between LAIs and oral antipsychotics [93,94], some metabolic parameters (e.g., total and low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, triglycerides, prolactin levels, waist circumference, and QTc interval) have been shown to be more favorable in patients receiving LAIs [95]. Importantly, the risk of metabolic side effects appears to be more closely related to the specific antipsychotic agent rather than the route or timing of administration. Agents such as clozapine, olanzapine, paliperidone, and quetiapine, whether oral or LAI, are consistently associated with greater risk of weight gain and metabolic disturbance [96,97,98,99,100]. Other studies are in line with our findings, suggesting that LAIs may be associated with less pronounced weight gain compared to oral antipsychotics, particularly when examining specific compounds. Evidence indicates that patients treated with oral aripiprazole tend to gain more weight, and at a faster rate, than those receiving its LAI equivalent [101,102]. More recent data from naturalistic studies with extended follow-up further support these results, highlighting a slower and less severe trajectory of weight gain in patients receiving LAI treatment [103]. The lower BMI observed in our LAI group may reflect not only differences in pharmacokinetic stability and medication exposure but also the indirect benefits of improved adherence and reduced relapse, since antipsychotic-induced weight gain is associated with increased nonadherence, discontinuations, dose escalations, polypharmacy, or emergency interventions, factors frequently associated with non-adherence to treatments [104,105]. This suggests that minimizing dose escalations and maintaining consistent treatment regimens, as facilitated by LAIs, could mitigate the metabolic side effects associated with antipsychotics medications.
LAIs are traditionally reserved for chronic, multiple-episode patients with poor compliance/adherence to treatment. Well, this is no longer sustainable. There is a need to deepen our understanding of neurodevelopmental trajectories in early-phase schizophrenia, particularly regarding treatment response and long-term outcomes, by investigating neurobiological underpinnings through neurophysiological markers [106,107]. Our sample was not composed of patients with chronic SCZ, but comprised first-episode patients as well. Young people with first-episode SCZ were shown to benefit from LAI AP treatment [87,108,109,110]. Hence, there is no reason for which they should be denied effective treatment timely and with no delay, since withholding treatment from a young patient with SCZ could worsen his/her long-term outcomes [111,112] in a period of brain maturation [113].
Limitations
Some limitations must be acknowledged. First, the relatively small sample size (N = 60) limits the statistical power and generalizability of the findings. Second, the absence of randomization introduces a potential risk of selection bias, as treatment allocation was based on clinical judgment rather than random assignment; however, it also allowed for the formation of two groups that were homogeneous in key clinical and demographic characteristics at baseline. Third, while BMI was used as a proxy for metabolic side effects, we acknowledge that it does not fully capture the broader metabolic impact of antipsychotic treatment. Relevant parameters such as fasting glucose, lipid levels, or prolactin were not systematically collected, limiting the depth of our assessment. Similarly, suicidality at follow-up was assessed using item 1 of the C-SSRS (since last visit), which may not fully capture the complexity of suicidal risk. Fourth, the oral antipsychotic group included multiple molecules (e.g., clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, lurasidone, aripiprazole, brexpiprazole), and we did not perform molecule-specific comparisons (e.g., oral vs. LAI aripiprazole), but it should be underlined that just one study did this [46]. This pharmacological heterogeneity could have introduced confounding effects, although we attempted to minimize this by standardizing doses using chlorpromazine equivalents. The ideal oral vs. LAI comparison would have limited the comparison of each LAI to its oral counterpart, but again, we could only compare aripiprazole monohydrate (n = 15) to oral aripiprazole (n = 8) and this would have needed non-parametric statistics that would be less powerful. Furthermore, current trends in aripiprazole LAI administration involve the now-approved two-injection start [114], which has shown pharmacokinetic advantages in patients with psychoses [115], but few of the 15 patients on aripiprazole LAI received the two-injection start, which needs no oral supplementation. Last, even if baseline characteristics were comparable between groups, unmeasured confounding factors, including outpatient care setting, may have influenced clinical outcomes and should be considered when interpreting the results. Despite these limitations, the strengths of this study include its naturalistic design, which enhances real-world applicability, the 12-month follow-up, and the use of validated assessment tools (C-SSRS, PANSS, DAI-10) that ensures reliable assessments of both symptom severity and patient-reported outcomes. Furthermore, we adhered to The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement (Supplementary Table S1), which is a useful instrument for conducting and reporting adequate cohort studies [116].
5. Conclusions
This naturalistic longitudinal study provides further support for the clinical effectiveness of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia. Importantly, our results suggest that long-acting injectable antipsychotics may be associated with indirect benefits for both psychiatric and physical health outcomes, possibly mediated by improved treatment adherence and greater symptom stability. Despite this, long-acting injectable antipsychotics remain underutilized, particularly in early-phases of schizophrenia, due to persistent clinical hesitancy and structural barriers. Our findings raise questions about this cautious approach and support consideration of a shift toward more proactive, personalized use of long-acting injectable antipsychotics, especially in patients with early signs of non-adherence or heightened risk of relapse and suicidality, common characteristics in patients diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/healthcare13141709/s1, Supplementary Table S1. STROBE Statement CheckList for Bardi et al., Healthcare.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.B., L.M., A.S. and G.S. (Gabriele Sani); methodology, F.B., L.M., G.D.K., D.J., G.S. (Gabriele Sani), and A.S.; software, F.B., L.M., G.D.K., and A.S.; validation, F.B., L.M., G.D.K., D.J., G.S. (Gabriele Sani) and A.S.; formal analysis, F.B., L.M., G.B. and A.B.; investigation, F.B., L.M., G.D.K. and D.J.; resources, G.S.; data curation, G.B., A.B. and G.S. (Greta Sfratta); writing—original draft preparation, F.B., L.M., G.D.K., and G.S. (Greta Sfratta); writing—review and editing, F.B., L.M., G.D.K., D.J., G.S. (Gabriele Sani) and A.S.; visualization, F.B., L.M., D.J., G.S. (Gabriele Sani) and A.S.; supervision, A.S. and G.S. (Gabriele Sani); project administration, G.S. (Gabriele Sani). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved on 21 February 2018 by the Ethical Committee of the Gemelli Foundation (approval no. ID 2014 Prot. N. 13864/18).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent for treatment was obtained from all participating patients or from their legal tutors if incapacitated or of minor age. Patients were informed and accepted that the study they were participating in would have been published.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank participants and their families and acknowledge the help of Pattuglia, librarian of the Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, Rome, for providing us with important bibliographic material. The authors also wish to thank the members of the Gemelli RePsy Study Group, composed of the following contributors: Marianna Mazza, Mario Pinto, Tommaso Callovini, Marco Di Nicola, Maria Pepe, Ilaria Marcelli, Sara Rossi, Antonio Restaino, Maria Benedetta Anesini, Guglielmo Donofrio, Anna Quintano, Alessia Fischetti, Stella Margoni, Michela Bellezza, Eugenio Stella, Gianmarco Stella, Marco Massetti, Luca Chisari, Flavia Grisoni, Sara Barbonetti, Francesca Bardi, Romina Caso, Giuseppe Mandracchia, Lodovico Balzoni, Senad Hasaj, Marco Lanzetta, Oksana Di Giacomi, Camilla Scialpi, Elena Lucia Valle, Pietro Del Prete, Davide Tripaldella, Antonio Sottile, Emanuela De Chiara, Claudia Calderoni, Alessandro Michele Giannico, Giulio Carriero, Daniele Segatori, Miriam Milintenda, Andrea Brugnami, Laura Monti, Francesca Focà, Raffaella Franza, Arianna Crupi, Elisa Marconi, Giovanni Camardese, Leonardo Monacelli, Antonio Maria D’Onofrio, Mariateresa Acanfora, Gianluca Boggio, Luca Di Benedetto, Silvia Montanari, Gianna Autullo, Lucio Rinaldi, Elettra Specogna, Elisabetta Benini, Federico Tonioni, Luca Onori, Luca Lo Giudice, Andrea Zanzarri, and Roberto Brugnoli.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AP(s) | Antipsychotic(s) |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| C-SSRS | Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale |
| DAI-10 | 10-item Drug Attitude Inventory |
| FDA | US Food and Drug Administration |
| FGA(s) | First-Generation Antipsychotic agent(s) |
| LAI | Long-Acting Injectable |
| QoL | Quality of Life |
| PANSS | Positive And Negative Syndrome Scale |
| SCZ | Schizophrenia |
| SGA(s) | Second-Generation Antipsychotic agent(s) |
References
- Harrison, P.J. The neuropathology of schizophrenia. A critical review of the data and their interpretation. Brain 1999, 122 Pt 4, 593–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, R.S.; Sommer, I.E.; Murray, R.M.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Weinberger, D.R.; Cannon, T.D.; O’Donovan, M.; Correll, C.U.; Kane, J.M.; van Os, J.; et al. Schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jääskeläinen, E.; Juola, P.; Hirvonen, N.; McGrath, J.J.; Saha, S.; Isohanni, M.; Veijola, J.; Miettunen, J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of recovery in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2013, 39, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.; Woerner, M.G.; Alvir, J.M.; Bilder, R.; Goldman, R.; Geisler, S.; Koreen, A.; Sheitman, B.; Chakos, M.; Mayerhoff, D.; et al. Predictors of relapse following response from a first episode of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1999, 56, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, M.; Watt, D.; Falloon, I.; Smeeton, N. The natural history of schizophrenia: A five-year follow-up study of outcome and prediction in a representative sample of schizophrenics. Psychol. Med. Monogr. 1989, 15, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, C.U.; Rubio, J.M.; Kane, J.M. What is the risk-benefit ratio of long-term antipsychotic treatment in people with schizophrenia? World Psychiatry 2018, 17, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedegaard, H.; Curtin, S.C.; Warner, M. Increase in Suicide Mortality in the United States, 1999–2018; NCHS Data Brief; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020; p. 362.
- Heilä, H.; Haukka, J.; Suvisaari, J.; Lönnqvist, J. Mortality among patients with schizophrenia and reduced psychiatric hospital care. Psychol. Med. 2005, 35, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Barnes, T.R.; Kissling, W.; Engel, R.R.; Correll, C.; Kane, J.M. Relapse prevention in schizophrenia with new-generation antipsychotics: A systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider-Thoma, J.; Efthimiou, O.; Huhn, M.; Krause, M.; Reichelt, L.; Röder, H.; Davis, J.M.; Salanti, G.; Leucht, S. Second-generation antipsychotic drugs and short-term mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomised controlled trials. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018, 5, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Arbter, D.; Engel, R.R.; Kissling, W.; Davis, J.M. How effective are second-generation antipsychotic drugs? A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipale, H.; Tanskanen, A.; Mehtälä, J.; Vattulainen, P.; Correll, C.U.; Tiihonen, J. 20-year follow-up study of physical morbidity and mortality in relationship to antipsychotic treatment in a nationwide cohort of 62,250 patients with schizophrenia (FIN20). World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Tardy, M.; Komossa, K.; Heres, S.; Kissling, W.; Salanti, G.; Davis, J.M. Antipsychotic drugs versus placebo for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiihonen, J.; Haukka, J.; Taylor, M.; Haddad, P.M.; Patel, M.X.; Korhonen, P. A nationwide cohort study of oral and depot antipsychotics after first hospitalization for schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, T.; Hagi, K.; Kurokawa, S.; Kane, J.M.; Correll, C.U. Long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics for the maintenance treatment of schizophrenia: A systematic review and comparative meta-analysis of randomised, cohort, and pre-post studies. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, J.; van Rooijen, G.; Doedens, P.; Numminen, E.; van Tricht, M.; de Haan, L. Antipsychotic medication and long-term mortality risk in patients with schizophrenia; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 2217–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torniainen, M.; Mittendorfer-Rutz, E.; Tanskanen, A.; Björkenstam, C.; Suvisaari, J.; Alexanderson, K.; Tiihonen, J. Antipsychotic treatment and mortality in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2015, 41, 656–663, Erratum in Schizophr. Bull. 2016, 42, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiihonen, J.; Tanskanen, A.; Taipale, H. 20-Year Nationwide Follow-Up Study on Discontinuation of Antipsychotic Treatment in First-Episode Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.M.; Kishimoto, T.; Correll, C.U. Non-adherence to medication in patients with psychotic disorders: Epidemiology, contributing factors and management strategies. World Psychiatry 2013, 12, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heres, S. Long-acting injectable antipsychotics: An underutilized treatment option. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 1263–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, R.S.; Fleischhacker, W.W.; Boter, H.; Davidson, M.; Vergouwe, Y.; Keet, I.P.; Gheorghe, M.D.; Rybakowski, J.K.; Galderisi, S.; Libiger, J.; et al. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in first-episode schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder: An open randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, A.; Aadamsoo, K.; Altamura, A.C.; Franco, M.; Gorwood, P.; Neznanov, N.G.; Schronen, J.; Ucok, A.; Zink, M.; Janik, A.; et al. Paliperidone palmitate versus oral antipsychotics in recently diagnosed schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 169, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subotnik, K.L.; Casaus, L.R.; Ventura, J.; Luo, J.S.; Hellemann, G.S.; Gretchen-Doorly, D.; Marder, S.; Nuechterlein, K.H. Long-Acting Injectable Risperidone for Relapse Prevention and Control of Breakthrough Symptoms After a Recent First Episode of Schizophrenia. A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malla, A.; Chue, P.; Jordan, G.; Stip, E.; Koczerginski, D.; Milliken, H.; Joseph, A.; Williams, R.; Adams, B.; Manchanda, R.; et al. An Exploratory, Open-Label, Randomized Trial Comparing Risperidone Long-Acting Injectable with Oral Antipsychotic Medication in the Treatment of Early Psychosis. Clin. Schizophr. Relat. Psychoses 2016, 9, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medrano, S.; Abdel-Baki, A.; Stip, E.; Potvin, S. Three-Year Naturalistic Study On Early Use Of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics In First Episode Psychosis. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 2018, 48, 25–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winter-van Rossum, I.; Weiser, M.; Galderisi, S.; Leucht, S.; Bitter, I.; Glenthøj, B.; Hasan, A.; Luykx, J.; Kupchik, M.; Psota, G.; et al. Efficacy of oral versus long-acting antipsychotic treatment in patients with early-phase schizophrenia in Europe and Israel: A large-scale, open-label, randomised trial (EULAST). Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 197–208, Erratum in Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Kim, D.D.; Procyshyn, R.M.; Fredrikson, D.H.; Cázares, D.; Honer, W.G.; Barr, A.M. Efficacy of long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotic drugs in early psychosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2022, 16, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, L.; Kim, D.D.; Procyshyn, R.M.; Cázares, D.; Honer, W.G.; Barr, A.M. Long-acting injectable antipsychotics for early psychosis: A comprehensive systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.M.; Schooler, N.R.; Marcy, P.; Correll, C.U.; Achtyes, E.D.; Gibbons, R.D.; Robinson, D.G. Effect of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics vs. Usual Care on Time to First Hospitalization in Early-Phase Schizophrenia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 1217–1224, Erratum in JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzalidis, G.D.; Rapinesi, C.; Chetoni, C.; De Filippis, S. Aripiprazole IM depot as an option for the treatment of bipolar disorder. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 22, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, T.S.; Goa, K.L. Long-acting risperidone: A review of its use in schizophrenia. CNS Drugs 2004, 18, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.H.; Svensson, M.; Shao, H.; Vouri, S.M.; Park, H. Cost-effectiveness analysis of monthly, 3-monthly, and 6-monthly long-acting injectable and oral paliperidone in adults with schizophrenia. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2023, 29, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebaluck, J.; Downes, M.A.; Brown, J.; Harris, K.; Isoardi, K.Z.; Chan, B.S. Case series profile of olanzapine post-injection delirium/sedation syndrome. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 89, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenmayer, J.-P. Long-acting injectable antipsychotics: Focus on olanzapine pamoate. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2010, 6, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detke, H.C.; Weiden, P.J.; Llorca, P.M.; Choukour, M.; Watson, S.B.; Brunner, E.; Ascher-Svanum, H. Comparison of olanzapine long-acting injection and oral olanzapine: A 2-year, randomized, open-label study in outpatients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 34, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, B.M. FDA Investigates Deaths Related to Use of Olanzapine Pamoate. JAMA 2013, 310, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapinesi, C.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Mazzarini, L.; Brugnoli, R.; Ferracuti, S.; De Filippis, S.; Cuomo, I.; Giordano, G.; Del Casale, A.; Angeletti, G.; et al. Long-Acting Injectable (LAI) Aripiprazole Formulations in the Treatment of Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review. Clin. Drug Investig. 2019, 39, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faden, J.; Ramirez, C.; Martinez, V.; Citrome, L. An overview of the currently available and emerging long-acting formulations of risperidone for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2024, 24, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.M.; Harary, E.; Eshet, R.; Tohami, O.; Weiser, M.; Leucht, S.; Merenlender-Wagner, A.; Sharon, N.; Davis, G.L., III; Suett, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of TV-46000, a long-acting, subcutaneous, injectable formulation of risperidone, for schizophrenia: A randomised clinical trial in the USA and Bulgaria. Lancet Psychiatry 2023, 10, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poloni, N.; Ielmini, M.; Caselli, I.; Lucca, G.; Gasparini, A.; Lorenzoli, G.; Callegari, C. Oral Antipsychotic Versus Long-Acting Injections Antipsychotic in Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder: A Mirror Analysis in a Real-World Clinical Setting. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 2019, 49, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Sidana, A.; Malhotra, N.; Tyagi, S. Oral versus long-acting injectable antipsychotic in first episode schizophrenia: A 12 weeks interventional study. Indian J. Psychiatry 2023, 65, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Schneider-Thoma, J.; Siafis, S.; Qin, M.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Davis, J.M.; Priller, J.; Leucht, S. Efficacy, acceptability and side-effects of oral versus long-acting- injectables antipsychotics: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024, 83, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Schneider-Thoma, J.; Siafis, S.; Burschinski, A.; Dong, S.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Davis, J.M.; Priller, J.; Leucht, S. Long-Acting Injectable Second-Generation Antipsychotics vs Placebo and Their Oral Formulations in Acute Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized-Controlled-Trials. Schizophr. Bull. 2024, 50, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-C.; Choi, M.Y.; Choi, J.; Park, E.; Tchoe, H.J.; Suh, J.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Won, S.H.; Chung, Y.-C.; Bae, K.-Y.; et al. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Long-acting Injectable and Oral Second-generation Antipsychotics for the Treatment of Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2018, 16, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aymerich, C.; Salazar de Pablo, G.; Pacho, M.; Pérez-Rodríguez, V.; Bilbao, A.; Andrés, L.; Pedruzo, B.; Castillo-Sintes, I.; Aranguren, N.; Fusar-Poli, P.; et al. All-cause mortality risk in long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics in schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2025, 30, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Li, A.-N.; Sun, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, K.; Xu, X.; et al. Efficacy and safety of aripiprazole once-monthly versus oral aripiprazole in Chinese patients with acute schizophrenia: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority study. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 2022, 239, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; (DSM-5); American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 87–122. [Google Scholar]
- First, M.B.; Williams, J.B.W.; Karg, R.S.; Spitzer, R.L. User’s Guide for the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Disorders, Research Version (SCID-5-RV); American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- First, M.B.; Williams, J.B.W.; Benjamin, L.S.; Spitzer, R.L. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Personality Disorders SCID-5-PD; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Posner, K.; Brown, G.K.; Stanley, B.; Brent, D.A.; Yershova, K.V.; Oquendo, M.A.; Currier, G.W.; Melvin, G.A.; Greenhill, L.; Shen, S.; et al. The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale: Initial validity and internal consistency findings from three multisite studies with adolescents and adults. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The Positive And Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siafis, S.; Brandt, L.; McCutcheon, R.A.; Gutwinski, S.; Schneider-Thoma, J.; Bighelli, I.; Kane, J.M.; Arango, C.; Kahn, R.S.; Fleischhacker, W.W.; et al. Relapse in clinically stable adult patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder: Evidence-based criteria derived by equipercentile linking and diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2024, 11, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, T.P.; Awad, A.G.; Eastwood, R. A self-report scale predictive of drug compliance in schizophrenics: Reliability and discriminative validity. Psychol. Med. 1983, 13, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gipson, P.Y.; Agarwala, P.; Opperman, K.J.; Horwitz, A.; King, C.A. Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2015, 31, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austria-Corrales, F.; Jiménez-Tapia, A.; Astudillo-García, C.I.; Arenas-Landgrave, P.; Xochihua-Tlecuitl, T.; Cruz-Cruz, C.; Rivera-Rivera, L.; Gómez-García, J.A.; Palacios-Hernández, B.; Pérez-Amezcua, B.; et al. The Columbia-suicide severity rating scale: Validity and psychometric properties of an online Spanish-language version in a Mexican population sample. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1157581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lançon, C.; Reine, G.; Llorca, P.M.; Auquier, P. Validity and reliability of the French-language version of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1999, 100, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugnoli, R.; Tarsitani, L.; Mandarelli, G.; Fini, C.; Pancheri, P. Schizofrenia: Il problema delle dimensioni psicopatologiche [Schizophrenia: The issue of psychopathological dimensions]. Giorn. Ital. Psicopatol. 2008, 14, 36–50. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, R.E.; Lindström, E.; Nielsen, J.; Levander, S. DAI-10 is as good as DAI-30 in schizophrenia. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 22, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Arduini, L.; De Cataldo, S.; Stratta, P. Gli aspetti soggettivi del trattamento con farmaci antipsicotici: Studio di validazione della versione italiana della Drug Attitude Inventory (DAI) [Subjective response to neuroleptic medication: A validation study of the Italian version of the Drug Attitude Inventory (DAI)]. Epidemiol. Psichiatr. Soc. 2001, 10, 107–114. (In Italian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JASP Team. JASP (Version 0.19.3) [Computer Software]; JASP Team: Amsterdam, NL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Kishimoto, T.; Robenzadeh, A.; Leucht, C.; Leucht, S.; Watanabe, K.; Mimura, M.; Borenstein, M.; Kane, J.M.; Correll, C.U. Long-acting injectable vs oral antipsychotics for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 192–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.M.; Kishimoto, T.; Correll, C.U. Assessing the comparative effectiveness of long-acting injectable vs. oral antipsychotic medications in the prevention of relapse provides a case study in comparative effectiveness research in psychiatry. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66 (Suppl. S8), S37–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Marcus, S.C.; Zummo, J.; Pettit, A.R.; Stoddard, J.; Doshi, J.A. Antipsychotic Adherence and Rehospitalization in Schizophrenia Patients Receiving Oral Versus Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics Following Hospital Discharge. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2015, 21, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, C.U.; Citrome, L.; Haddad, P.M.; Lauriello, J.; Olfson, M.; Calloway, S.M.; Kane, J.M. The Use of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia: Evaluating the Evidence. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77 (Suppl. S3), 21984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moccia, L.; Bardi, F.; Anesini, M.B.; Barbonetti, S.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Rossi, S.; Caso, R.; Grisoni, F.; Mandracchia, G.; Margoni, S.; et al. Pharmacological Interventions for Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review of Randomised Control Trials. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Fleischhacker, W.W. The Use of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia. Curr. Treat. Options Psychiatry 2017, 4, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiihonen, J.; Mittendorfer-Rutz, E.; Majak, M.; Mehtälä, J.; Hoti, F.; Jedenius, E.; Enkusson, D.; Leval, A.; Sermon, J.; Tanskanen, A.; et al. Real-World Effectiveness of Antipsychotic Treatments in a Nationwide Cohort of 29 823 Patients With Schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, S.M. Long-acting injectable antipsychotics: Shall the last be first? CNS Spectr. 2014, 19, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, R.; Chiliza, B.; Asmal, L.; Mashile, M.; Fusar-Poli, P. Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in Early Psychosis: A Literature Review. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2013, 7, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipale, H.; Mittendorfer-Rutz, E.; Alexanderson, K.; Majak, M.; Mehtälä, J.; Hoti, F.; Jedenius, E.; Enkusson, D.; Leval, A.; Sermon, J.; et al. Antipsychotics and mortality in a nationwide cohort of 29,823 patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 197, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Fang, S.C.; Shao, Y.J. Comparison of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics With Oral Antipsychotics and Suicide and All-Cause Mortality in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Schizophrenia. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e218810, Erratum in JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2210829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.S. The environment and susceptibility to schizophrenia. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 23–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.-C.; Liao, D.-L.; Huang, C.-Y.; Hsu, C.-C.; Cheng, S.-L.; Shao, Y.-J. The effectiveness of long-acting injectable antipsychotics versus oral antipsychotics in the maintenance treatment of outpatients with chronic schizophrenia. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 35, e2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompili, M.; Orsolini, L.; Lamis, D.A.; Goldsmith, D.R.; Nardella, A.; Falcone, G.; Corigliano, V.; Luciano, M.; Fiorillo, A. Suicide Prevention in Schizophrenia: Do Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics (LAIs) have a Role? CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pompili, M.; Amador, X.F.; Girardi, P.; Harkavy-Friedman, J.; Harrow, M.; Kaplan, K.; Krausz, M.; Lester, D.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Modestin, J.; et al. Suicide risk in schizophrenia: Learning from the past to change the future. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nicola, M.; Pepe, M.; Montanari, S.; Spera, M.C.; Panaccione, I.; Simonetti, A.; Sani, G. Vortioxetine improves physical and cognitive symptoms in patients with post-COVID-19 major depressive episodes. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023, 70, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, A.; Bardi, F.; Margoni, S.; Grisoni, F.; Mandracchia, G.; Mazza, M.; Moccia, L.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Janiri, D.; Tosato, M.; et al. Affective temperament modulates the relationship between physical and psychiatric symptoms during long-COVID: Results from the Gemelli against COVID-19 post-acute care service. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 383, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, R.; Chapman, S.C.E.; Parham, R.; Freemantle, N.; Forbes, A.; Cooper, V. Understanding Patients’ Adherence-Related Beliefs About Medicines Prescribed for Long-Term Conditions: A Meta-Analytic Review of the Necessity-Concerns Framework. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Abdellati, K.; De Picker, L.; Morrens, M. Antipsychotic Treatment Failure: A Systematic Review on Risk Factors and Interventions for Treatment Adherence in Psychosis. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 531763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Thompson-Leduc, P.; Ghelerter, I.; Nguyen, H.; Lafeuille, M.H.; Benson, C.; Mavros, P.; Lefebvre, P. Real-World Evidence of the Clinical and Economic Impact of Long-Acting Injectable Versus Oral Antipsychotics Among Patients with Schizophrenia in the United States: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. CNS Drugs 2021, 35, 469–481, Erratum in CNS Drugs 2021, 35, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titus-Lay, E.N.; Ansara, E.D.; Isaacs, A.N.; Ott, C.A. Evaluation of Adherence and Persistence with Oral Versus Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in Patients with Early Psychosis. Ment. Health Clin. 2018, 8, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, M.; Rossler, W. Attitudes Towards Long-Acting Depot Antipsychotics: A Survey of Patients, Relatives and Psychiatrists. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 175, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heres, S.; Reichhart, T.; Hamann, J.; Mendel, R.; Leucht, S.; Kissling, W. Psychiatrists’ Attitude to Antipsychotic Depot Treatment in Patients with First-Episode Schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatry 2011, 26, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parellada, E.; Bioque, M. Barriers to the Use of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in the Management of Schizophrenia. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Lee, S.-H.; Yang, Y.K.; Park, J.-I.; Chung, Y.-C. Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics for First-Episode Schizophrenia: The Pros and Cons. Schizophr. Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 560836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorca, P.M.; Abbar, M.; Courtet, P.; Guillaume, S.; Lancrenon, S.; Samalin, L. Guidelines for the Use and Management of Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics in Serious Mental Illness. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, C.; Lennox, L.; Bell, D. A systematic review of evidence on the links between patient experience and clinical safety and effectiveness. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e001570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.W.; Fulchino, L.; Rogers, J.; Mogun, H.; Polinski, J.; Henderson, D.C.; Schneeweiss, S.; Fischer, M.A. Impact of drug-reimbursement policies on prescribing: A case-study of a newly marketed long-acting injectable antipsychotic among relapsed schizophrenia patients. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2018, 27, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventriglio, A.; Gentile, A.; Stella, E.; Bellomo, A. Metabolic Issues in Patients Affected by Schizophrenia: Clinical Characteristics and Medical Management. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouinard, V.-A.; Pingali, S.M.; Chouinard, G.; Henderson, D.C.; Mallya, S.G.; Cypess, A.M.; Cohen, B.M.; Öngür, D. Factors Associated with Overweight and Obesity in Schizophrenia, Schizoaffective and Bipolar Disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 237, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, S. Safety concerns associated with second-generation antipsychotic long-acting injection treatment. A systematic update. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 36, 20170004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Martinez, V.; Romero-Rubio, D.; Abad-Perez, M.J.; Descalzo-Cabades, M.A.; Alonso-Gutierrez, S.; Salazar-Fraile, J.; Montagud, V.; Facila, L. Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Risk in People Treated with Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventriglio, A.; Baldessarini, R.J.; Vitrani, G.; Bonfitto, I.; Cecere, A.C.; Rinaldi, A.; Petito, A.; Bellomo, A. Metabolic Syndrome in Psychotic Disorder Patients Treated with Oral and Long-Acting Injected Antipsychotics. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayabandara, M.; Hanwella, R.; Ratnatunga, S.; Seneviratne, S.; Suraweera, C.; de Silva, V.A. Antipsychotic-Associated Weight Gain: Management Strategies and Impact on Treatment Adherence. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hert, M.; Dekker, J.M.; Wood, D.; Kahl, K.G.; Holt, R.I.G.; Möller, H.-J. Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes in People with Severe Mental Illness: Position Statement from the European Psychiatric Association (EPA), Supported by the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Psychiatry 2009, 24, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musil, R.; Obermeier, M.; Russ, P.; Hamerle, M. Weight Gain and Antipsychotics: A Drug Safety Review. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2015, 14, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillinger, T.; McCutcheon, R.A.; Vano, L.; Mizuno, Y.; Arumuham, A.; Hindley, G.; Beck, K.; Natesan, S.; Efthimiou, O.; Cipriani, A.; et al. Comparative Effects of 18 Antipsychotics on Metabolic Function in Patients with Schizophrenia, Predictors of Metabolic Dysregulation, and Association with Psychopathology: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, M.; Fransen, A.; Janssen, J.; van Os, J.; Drukker, M. Almost All Antipsychotics Result in Weight Gain: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigooka, J.; Nakamura, J.; Fujii, Y.; Iwata, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Iyo, M.; Uchimura, N.; Nishimura, R.; Shimizu, N.; ALPHA Study Group. Efficacy and Safety of Aripiprazole Once-Monthly in Asian Patients with Schizophrenia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Non-Inferiority Study versus Oral Aripiprazole. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 161, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischhacker, W.W.; Sanchez, R.; Perry, P.P.; Jin, N.; Peters-Strickland, T.; Johnson, B.R.; Baker, R.A.; Eramo, A.; McQuade, R.D.; Carson, W.H.; et al. Aripiprazole Once-Monthly for Treatment of Schizophrenia: Double-Blind, Randomised, Non-Inferiority Study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2014, 205, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shymko, G.; Dobson, L.; Acacio, M.C.; Grace, T.; Tadier, S.; Waters, F. Weight Changes in People with Early Psychosis Treated with Oral or Long-Acting Injectable Aripiprazole. Schizophr. Res. 2023, 251, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, R.; Smith, E.C.C.; Navagnanavel, J.; Au, E.; Maksyutynska, K.; Papoulias, M.; Singh, R.; Panganiban, K.J.; Humber, B.; Mohr, G.H.; et al. The Impact of Weight Gain on Antipsychotic Nonadherence or Discontinuation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2025, 151, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Kwan, A.T.H.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Teopiz, K.M.; Mansur, R.B. Psychotropic Drug-Related Weight Gain and Its Treatment. Am. J. Psychiatry 2024, 181, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, A.; Lijffijt, M.; Kahlon, R.S.; Gandy, K.; Arvind, R.P.; Amin, P.; Arciniegas, D.B.; Swann, A.C.; Soares, J.C.; Saxena, K. Early and late cortical reactivity to passively viewed emotional faces in pediatric bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 253, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, A.; Bernardi, E.; Kurian, S.; Restaino, A.; Calderoni, C.; De Chiara, E.; Bardi, F.; Sani, G.; Soares, J.C.; Saxena, K. Understanding Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Through the Investigation of Clinical, Neuroanatomic, Neurophysiological and Neurocognitive Dimensions: A Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odsbu, I.; Hamina, A.; Hjellvik, V.; Handal, M.; Haram, M.; Tesli, M.; Tanskanen, A.; Taipale, H. Initiation of Antipsychotics During the First Year After First-Episode Psychosis: A Population-Based Study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2025, 151, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, G.L.; Dawson, G.; Zummo, J. Clinical benefits and impact of early use of long-acting injectable antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2016, 10, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugnoli, R.; Rapinesi, C.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Marcellusi, A.; Mennini, F.S.; De Filippis, S.; Carrus, D.; Ballerini, A.; Francomano, A.; Ducci, G.; et al. Model of Management (Mo.Ma) for the patient with schizophrenia: Crisis control, maintenance, relapse prevention, and recovery with long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs). Riv. Psichiatr. 2016, 51, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, R.J.; Henter, I.D. The effects of early and sustained intervention on the long-term morbidity of schizophrenia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1998, 32, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Goff, D.C.; Falkai, P.; Fleischhacker, W.W.; Girgis, R.R.; Kahn, R.M.; Uchida, H.; Zhao, J.; Lieberman, J.A. The Long-Term Effects of Antipsychotic Medication on Clinical Course in Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 840–849, Erratum in Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango, C.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Correll, C.U.; Díaz-Caneja, C.M.; Figueira, M.L.; Fleischhacker, W.W.; Marcotulli, D.; Parellada, M.; Vitiello, B. The transition from adolescence to adulthood in patients with schizophrenia: Challenges, opportunities and recommendations. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 59, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, J.F.; Achtyes, E.D.; Correll, C.U.; Sajatovic, M.; Saklad, S.R. Optimizing treatment with aripiprazole monohydrate: Pharmacokinetic advantages of long-acting injectable formulations, a Consensus Panel Report. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2025, 86, plunlai2424ah1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovini, G.; Lombardozzi, G.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; Lionetto, L.; Russo, F.; Sabatino, A.; Serra, E.; Castorina, S.; Civita, G.; Frezza, S.; et al. Optimising aripiprazole long-acting injectable: A comparative study of one- and two-injection start regimens in schizophrenia with and without substance use disorders and relationship to early serum levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).