Abstract
Tenoxicam, a selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, has potent analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects and is frequently used for out-of-hospital pain control. Even though other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were incriminated in Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) appearance, the literature is scarce regarding this agent. We report a case of tenoxicam-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis, detailing the multidisciplinary approach in a patient presenting skin detachment of 90% of the total body surface area, with concomitant ocular, oral, nasal, and vaginal mucosae involvement. A skin biopsy confirmed the diagnosis. The immediate cessation of the incriminated drug and rapid initiation of systemic steroids, along with topical therapies, and isolation into a specific environmental condition to limit skin infection were the cornerstones of therapeutic management. The patient was discharged with skin hyperpigmentation area and mild anxiety as long-term sequels. This report emphasized that severe or complicated cases should be transferred to a specialized burn center to reduce mortality risk and long-term morbidity.
1. Introduction
Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are serious mucocutaneous reactions associated especially with drugs such as antibiotics (sulfonamides, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, penicillin, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones), anticonvulsants (lamotrigine, phenobarbital, and carbamazepine), allopurinol, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, acetaminophen, and antiretrovirals [1,2,3,4]. There are recent reports about SJS/TEN development in association with anticancer agents (daunorubicin, alpelisib, fulvestrant, and enzalutamide) [5,6,7,8]; elastomeric pump use for chronic pain management in a patient with late-stage ovarian cancer, probably due to ondansetron [9]; armodafinil and modafinil [10,11]; chlordiazepoxide [12]; pirfenidone [13]; or after sulfadoxine–pyrimethamine overdose [14]. Lesions usually appear 4–28 days after the patient is exposed to the incriminating agent [15].
If there is less than 10% epidermal detachment, the diagnosis is SJS, with a mortality risk of 1–5%. If there is between 10–30% involvement of skin, the diagnosis is SJS-TEN overlap syndrome. The more severe TEN designation is used when epidermal detachment is greater than 30%. TEN has been observed to have a mortality rate of >40% [16,17]. The incidence is 0.4–6 per million people each year [18,19]. Patients with cancers and immunodeficiency, as well as women, are more vulnerable in developing adverse drug reactions [20]. A recent study by Gronich et al. identified additional risk factors including psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, a history of cerebrovascular accident or diabetes mellitus, and previous drug allergies [21]. SJS and TEN are delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions to specific drug administrations; therefore, these reactions are considered medical emergencies that require rapid diagnosis and prompt therapeutic management [15]. Individuals with a genetic predisposition are more susceptible [22]. Some reports showed that there may be a connection between human leukocyte antigens (HLA)-B*12 and (HLA)-B*73:01 and oxicam-induced TEN in European populations [23,24].
Tenoxicam is an NSAIDs in the oxicam group used as a potent analgetic agent [25]. In addition, it has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activity [26]. The most common side effects include gastrointestinal bleeding [27], skin rashes, and central or peripheral nervous system disorders [28,29]. However, rare cases of hepatic injury [30]; alopecia [31]; nephrotoxicity [32], especially in patients with pre-existing renal dysfunction and the elderly [33,34]; hypoglycemia [35]; and agranulocytosis were reported [36]. Nevertheless, there are concerns regarding the safety profile of cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors, especially in patients with cancer or immunosuppression and a history of hypersensitivity [37]. Ward et al. stated that even if the risk of SJS or TEN onset after NSAIDs is extremely low, there are some at-risk categories, like the elderly, women, and patients during the first month after the drug initiation, especially when oxicam derivates are used [38].
A French study targeting the adverse drug reactions associated with NSAID administration showed that the highest risks for significant gastrointestinal, hepatic, renal, or cutaneous adverse events were associated, in order of severity and frequency, with ketoprofen, nimesulide, meloxicam, and tenoxicam compared with the other NSAIDs [39]. There are reports about SJS or TEN appearances after selective cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor use, with valdecoxib, celecoxib, piroxicam, etoricoxib, and rofecoxib being usually incriminated [2,40,41,42]. Mockenhaupt et al. demonstrated that NSAID-induced SJS/TEN has low risk overall, with the oxicam class having a higher risk, especially during treatment initiation [43]. The EuroSCAR study also reported that the use of oxicam-NSAIDs (meloxicam, piroxicam, and tenoxicam) is associated with a high risk of severe cutaneous adverse reaction occurrence within 8 weeks of treatment and that these agents should be avoided as first-line therapies. It also emphasizes the importance of identifying the moment of drug administration for such cases [1].
Over the years, various cases of SJS/TEN have been reported in relation to analgesic drug utilization. Tenoxicam was found to be the causative agent for TEN/SJS in some studies, but there are no singular reported cases about this drug [1,39]. Friedman et al. reported a case of TEN appearance because of celecoxib use for carpal tunnel syndrome treatment. Due to the disease severity, the patient was transferred to a burn center, having a good long-term prognostic [44]. However, Perna et al. reported a fatal case of TEN after celecoxib use for lower back pain in a female patient [45]. Etoricoxib taken for pain-control in a female with osteoarthritis was involved in severe TEN appearance reported by Kameshwari et al., with a good outcome following glucocorticoid therapy as the main treatment [2]. A fatal case after etoricoxib use in a young female patient with a sprained ankle was presented by Roy et al., with rapid deterioration under corticosteroids [46]. Massari et al. reported a case of ketoprofen-induced TEN associated with acute vanishing bile duct syndrome [47], similarly to a case presented by Kim et al., but the causative agent for TEN in this patient was ibuprofen [48]. Ibuprofen was also incriminated in a female case of severe toxic epidermal necrolysis following its use for upper respiratory tract infection symptoms. Treatment with high-dose corticosteroids had good results [49]. Severe drug-induced TEN was also reported in relation to diclofenac sodium, with a favorable outcome following plasmapheresis use [50].
Frey et al. published a population-based case–control observational study showing a causative relationship between cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and SJS/TEN appearance [51]. Another study by La Grande et al. emphasized the need to increase awareness regarding the severe, life-threatening adverse reactions of COX-2 inhibitors [40]. Lastly, a recent surveillance data analysis regarding the adverse reactions reported after NSAID use highlighted some extremely important issues: among NSAID monotherapies with acetaminophen, ibuprofen, aspirin, diclofenac, and celecoxib, ibuprofen had the highest association with SJS, but the lowest fatality rate, with celecoxib having the latest onset time to SJS appearance and diclofenac being associated with the highest risk of death [52].
Considering the large consumption of painkillers, especially anti-inflammatory drugs, with or without medical prescriptions, we consider it important to reiterate the need to control this phenomenon, especially in terms of preventing fatal adverse reactions. Starting by presenting the case of our patient, we continued with an updated review of the main diagnostic and treatment features related to this severe allergic reaction of tenoxicam use.
2. Case Presentation
A 50-year-old Caucasian female, with a history of arterial hypertension and no history of drug allergy, was referred to our hospital five days after a rash eruption on the neck and neckline and oral erosions, which progressively worsened. Ten days before presentation, she received tenoxicam 20 mg/day for lower back pain. After 5 days, she developed the aforementioned symptoms and received 16 mg of methylprednisolone twice a day and 5 mg/day of levocetirizine from her dermatologist and discontinued tenoxicam. However, the condition worsened, and she was admitted into the burn unit of the Emergency Clinical Hospital of Bucharest. She had a polymorphous vesicular and bullous eruption affecting almost 90% of her total body surface area (TBSA) (almost 10% skin detachment) (Figure 1), as well as skin erosion all over her face, hands, thighs, back, and genital region. The patient presented oral, nasal, ocular, and vaginal mucosa lesions, with mild dysphagia, severe asthenia, tachycardia (heart rate > 120 beats per minute), and a tendency for hypotension (blood pressure, 75/46 mmHg), which was fluid-responsive. The complete blood count showed leukocytosis at 11.000/uL, hyperglycemia of 165 mg/dL, hyponatremia of 130 mmol/L, hypokalemia of 3.15 mmol/L, and hypocalcemia of 0.99 mmol/L. All the other bioumoral parameters (baseline biochemistry, coagulation panel, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, lactate, fibrinogen, albumin, total protein, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, bilirubin, cholesterol, creatine kinase, and creatine kinase-MB) were within a normal range. Genetic tests could not be performed during hospitalization. The diagnosis was considered as TEN. A SCORTEN [53] score (Table 1) of 3 points was calculated. Using the algorithm for the assessment of drug causality in epidermal necrolysis (ALDEN) [54], we obtained a score of 6 points, indicating that the suspected drug was very likely the causative agent. Additionally, a Naranjo score [55] of 9 points sustained the implication of the incriminated agent. Nikolsky’s sign (tenderness of the tegument, with dislodgment of the epidermis and extension of the blisters at lateral pressure application) [22] was positive. Upon admission, systemic corticosteroids were initiated with 500 mg of methylprednisolone twice a day for 5 days, followed by tapering, along with 5 mg/day of levocetirizine, 40 mg/day of omeprazole, a replacement of fluid loss to maintain a urinary output of 0.5–1 mL/kg/hour, a correction of electrolyte imbalances, nutritional support, pain control, and general hygiene using chlorhexidine 4%. For the nasal mucosa lesions, the otorhinolaryngologist prescribed topical applications with hydrocortisone butyrate, and they prescribed topical hyaluronic acid for the oral ulcerations. The ophthalmological consultation revealed eyelid and conjunctival lesions, eye pain, and slightly blurred vision, and a topical treatment with a tobramycin/dexamethasone ophthalmic solution, along with periodic flushing with a saline solution, was initiated. The patient was evaluated by the gynecologist, who diagnosed vulvovaginitis based on an erythematous vulva and vaginal mucosa with moderate leukorrhea. A full bacterial screening was performed upon admission, identifying the presence of Staphylococcus epidermis in the ears, conjunctival secretions, and Escherichia coli in vaginal secretion. Considering that the main differential diagnosis for SJS/TEN are mainly infectious diseases, along with the increased risk of infections in face of important rapid skin detachment, the patient was evaluated by an infectious disease specialist. Due to the low SCORTEN score, along with minor leukocytosis and negative procalcitonin, there was no need for antibiotic initiation. On the second day of hospitalization, due to erosive lesions on the oral and nasal mucosa and evolving epidermal detachment (almost 30%), a skin biopsy was performed, confirming the previously established diagnosis of SJS-TEN overlap 48 h after admission to the intensive care unit. The histopathological appearance was suggestive of vesicular dermatosis with transepidermal necrolysis, which was consistent with Stevens–Johnson syndrome (Figure 2). Starting from the 10th day of intensive care, a regression of the lesions was observed, with the appearance of areas of tissue re-epithelialization. Urinary bacteriological examination revealed the presence of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, both of which are sensitive to quinolones, and due to the association of dysuria and leukocytosis, the nephrologist decided to initiate antibiotic therapy with 500 mg/day of levofloxacin for 5 days. Systemic cortisone therapy was tapered from intravenous to oral administration until complete discontinuation. Under this complex management, after three weeks, the skin was fully re-epithelized, with areas of skin hyperpigmentation (Figure 3) and mild anxiety. The patient was able to be discharged with the recommendation to avoid the lifelong use of all selective COX inhibitors agents.
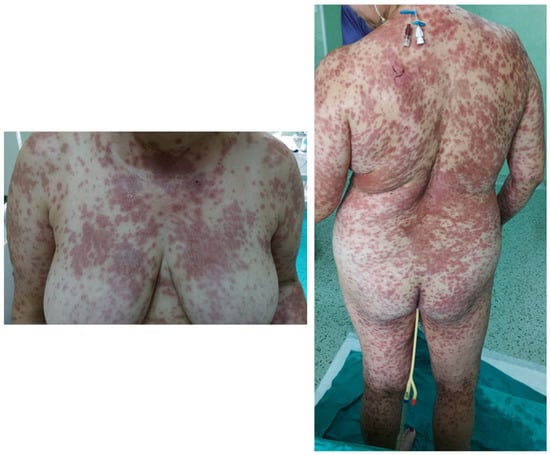
Figure 1.
Polymorphous vesicular and bullous eruption affecting almost 90% of her total body surface area (TBSA) with areas of skin detachment.

Table 1.
The patient’s SCORTEN score.
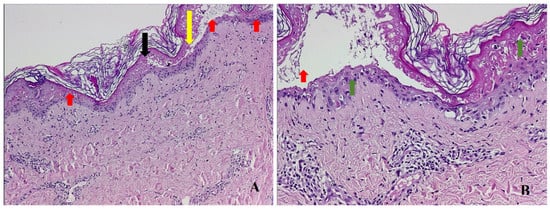
Figure 2.
Skin biopsy—hematoxylin eosin staining showing transepidermal necrosis (black arrow) and dermis–epidermis detachment (yellow arrow), multiple inflammatory cells, and vacuolization at the dermo–epidermal junction (red arrows). (A) (HE, ×50); lymphocytic inflammation at the dermis level and at the dermo–epidermal junction (green arrows). (B) (HE, ×200).
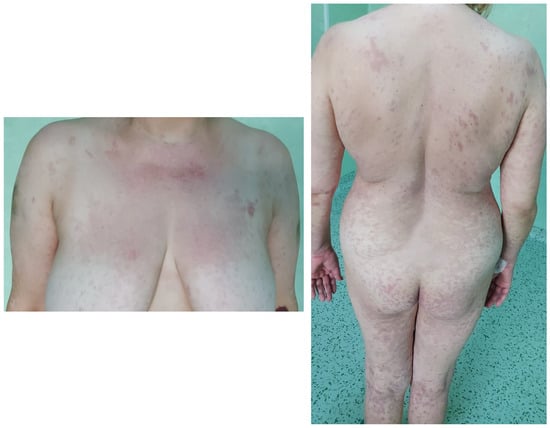
Figure 3.
Resolution of skin lesions with persistent areas of hyperpigmentation.
3. Discussion
3.1. Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
It is well known that there are no established diagnosis criteria for SJS and TEN, even though they are among the few dermatological emergencies. The diagnosis was based on clinical features obtained during a detailed physical examination, along with the existence of a causative drug, and histological confirmation. Usually, the mucocutaneous eruption (diffuse erythema) onset coincides with a febrile episode and malaise (prodrome), followed by macula and larger bulla formation and skin detachment, which are associated with compromising the integrity of at least two mucous membranes (systemic involvement) [1,18,19,22,56,57,58]. Oral erosions and crust formation, keratoconjunctivitis, and the loss of nails or eyebrows are commonly observed. Due to keratinocytes necrosis, the epidermis’s detachment from the dermis appears (keratinocytes lose their shape and their adhesion ability), which is associated with the formation of extremely painful blisters [58,59,60].
3.2. Skin Biopsy and Pathophysiology
A skin biopsy may help identify a differential diagnosis, and it is recommended for severe forms [61]. There are some burn centers taking biopsies in all patients with high clinical suspicion [62,63]. In our case, the biopsy was performed considering the severe form of the syndrome and confirmed the presence of transepidermal necrolysis. The main histopathological feature in SJS/TEN skin lesions is keratinocyte apoptosis leading to epidermal necrosis, followed by dermo–epidermal disjunction [64]. Lymphocyte infiltration at the dermis level is often observed [65]. There are still controversies regarding SJS/TEN pathophysiology, with some studies leaning towards the involvement of immune-mediate reactions, including not only the innate immune system but also the adaptive one [66]. The excessive activation of CD 8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells, along with the enhanced production of granulysin (a proapoptotic protein), has been associated with keratinocyte apoptosis and disease severity [67]. Furthermore, the soluble Fas ligand (sFasL), resulting from keratinocyte or peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), interacts with the Fas receptor on the cell membrane of keratinocytes, promoting their own apoptosis. Serum sFasL has shown potential for the early diagnosis of SJS/TEN [68]. Subsequently, keratinocyte apoptosis is extended by the activated inflammatory cascade, especially via tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and reactive oxygen species [69].
3.3. Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of SJS/TEN includes various infectious diseases, especially bullous pemphigoid, pemphigus vulgaris, and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) [70]. Infections caused by herpes simplex virus and Mycoplasma pneumoniae can lead to oral mucositis and skin involvement but are not associated with skin detachment [16]. Other differential diagnoses include acute generalized bullous pustulosis (AGEP), autoimmune blistering diseases (paraneoplastic pemphigus), and generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE) [56,71]. Lastly, acute graft versus host reaction may be confused with SJS/TEN, but it usually appears within 2 weeks after the cell transplant [56]. By considering the patient’s history, conducting bacteriological screening, and assessing bioumoral markers, we have excluded the main differential diagnoses.
3.4. Prognostic Scores
The SCORTEN score is widely used as a prognostic toll, and it is recommended to be calculated on day 1 and 3 of hospitalization [53]. It consists of seven independent variables as follows: age ≥ 40 years, cancer/malignancy presence, heart rate ≥ 120 beats per minute, body surface area detached ≥ 10% at day 1, serum glucose > 14 mmol/L, serum blood urea nitrogen > 10 mmol/L, and serum bicarbonate < 20 mmol/L. The score varies from 0 to ≥5, with mortality rates increasing with each point above 0 (3.2%, 12.1%, 35.3%, 58.3%, and >90%) [56]. A recent study has shown that this scoring system is accurate in predicting mortality when the value is high, and therefore, new prognosis scores should be used in cases with a low SCORTEN score [72]. In our case, the risk of mortality was 35.3%, but we should take into consideration that a patient with epidermal necrolysis of around 90% of the body surface area is predisposed to many complications. Therefore, a rapid, and multidisciplinary approach is always recommended in severe forms of SIS or TEN, even if the prediction scores are favorable.
The ABCD-10 (age, bicarbonate, cancer, dialysis, 10% body surface area) scale has been recommended for prognosis evaluation as an alternative for SCORTEN score, especially for patients with previous comorbidities. However, reports have shown that the ABCD-10 score could predict in-hospital mortality, especially in patients developing acute kidney injury (AKI). The SCORTEN scale should be used for predicting inpatient mortality for cases with epidermal necrolysis [73,74,75]. Sassolas et al. showed that the ALDEN algorithm, due to its sensitivity, can be used as a reference method for the assessment of drug causality in patients with SJS/TEN [54].
3.5. Treatment Algorithm and Multidisciplinary Approach
The algorithm treatment is not well established [76]. The main principles of treatment in SJS and TEN involve the withdrawal of the causative agent, supportive care, nutritional support, and systemic corticosteroid therapy. However, these treatments should be adapted based on the patient’s clinical status, history of comorbidities, current chronic medication, and the systemic immune and inflammatory response [16,61,77]. Plasmapheresis may be used by removing the causative agent, but the results are controversial [78,79]. Intravenous immunoglobulins show promising results for the treatment of SJS/TEN syndromes, especially in combination with systemic corticosteroids [80,81,82]. There are some reports about the usefulness of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, calcineurin inhibitors, or combination therapies in such cases [83,84,85]. Current recommendations suggest a multi-faceted regimen, with the use of systemic corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulins being under continuous assessment [56]. We opted for a corticosteroid regimen, including systemic and topical applications, to inhibit the inflammatory cells and the associated cytokines [86]. Additionally, we applied topical drug solutions to all affected mucosal areas, resulting in a staged detachment of the epidermis, the progressive resolution of the mucosal ulcerations, and re-epithelization. We have not used the active debridement of the necrotic epidermis. Studies have shown that the detached epidermis acts as a biologic dressing and hastens the process of re-epithelization [34].
As we emphasized before, considering that SJS/TEN are rare diseases, there are still controversies regarding the optimum therapeutic management. An important meta-analysis published by Zimmermann et al. showed that early systemic corticosteroids, used as pulse therapy, have beneficial effects. In addition to these, promising results have also been shown by cyclosporine, especially regarding mortality. The use of intravenous immunoglobulins (Ig) is not supported by this analysis [87]. Hirahara et al. stated that using high doses of corticoids early in the disease leads to inflammation inhibition, decreasing the serum levels of interleukins [88]. Others suggested that these high doses are associated with increased risks of infections and gastrointestinal bleedings [89]. Currently, the UK guidelines do not recommend any specific active interventions except for supportive care in cases of SJS/TEN [77]. The Japanese guidelines state that treatment should start with steroids at 0.2–5 mg/kg/day as a first-line therapy, followed by intravenous Ig and plasmapheresis as last resorts in patients with severe unresponsive forms [81].
In addition to cutaneous lesions, there is frequent multiorgan involvement, especially ophthalmological, genitourinary, cardiovascular, and pulmonary. Hypoxia, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, emphysema, hepatitis, urethritis, glomerulonephritis, skin infection, vaginal synechiae, and sepsis have been reported [4,9,15,90]. In our case, the severe cutaneous reactions were associated with eye, nose, oral, and vaginal involvement, and the infectious component presented late and required multidisciplinary therapeutic management to obtain the best outcome. A study by Lim et al. conducted in a burn unit emphasized the need for specialized intensive care management due to the severity, rapid progression, and unpredictable nature of the syndromes [62]. The current United Kingdom (UK) guidelines prioritizes multidisciplinary supportive care above systemic treatment [77].
Burn units can offer a proper environment in terms of optimum fluid repletion and the prevention of infection, two of the main key aspect of patients with severe form of TEN [83]. The UK guidelines regarding the management of patients with SJS/TEN implies that cases with clinical deterioration, extensive epidermal detachment, local pus or sepsis, or delayed wounds should be referred to a burn center [77].
Due to the systemic involvement, long-term sequels are commonly seen after SJS or TEN. They include skin hyperpigmentation, hair loss, ocular problems (dry eye, chronic conjunctivitis, and foreign body sensation), oral mucosa problems, scarring, anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and the inability to resume daily work [91]. Some patients require transfer to a rehabilitation center before returning home or require a caregiver. All these factors contribute to an impaired quality of life. For patients with conjunctival involvement, long-term complications are dry eye syndrome, photophobia, ectropion, corneal abrasions or ulcers, lid adhesions, and the loss of visual acuity [63,92]. As for patients with vulvovaginal involvement, the main reported complications are synechiae formation and vaginal stenosis, requiring surgery [63,93]. The appearance of hypertrophic scars is extremely rare [94]. Fortunately, in our case, the only long-term complications were skin hyperpigmentation, which we believe will correct in time with proper management and avoidance of sun exposure, and mild anxiety. All the above stresses the importance of the long-term follow-up of these patients in order to promptly treat complications to reduce further morbidity.
4. Conclusions
Allergies to common pain medication are becoming more frequent due to the abuse of painkillers; therefore, actions must be taken to stop this phenomenon and to increase vigilance for adverse reactions. The present case report strengthens the need for a multidisciplinary approach in patients presenting with severe toxic epidermal necrolysis and multiorgan involvement. The immediate cessation of the incriminated drug; the rapid initiation of systemic steroids, along with topical therapies; and isolation into a specific environmental condition are of paramount importance to prevent mortality and to decrease morbidity. Nevertheless, we reiterate that severe or complicated cases should be transferred to a specialized burn center.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.P.N., M.T., I.P. and A.N.; methodology, T.P.N., M.T., I.P. and A.N.; validation, T.P.N., M.T., I.P. and A.N.; investigation, T.P.N. and M.T.; resources, T.P.N. and M.T.; data curation, T.P.N. and M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, T.P.N., M.T., I.P. and A.N.; writing—review and editing, T.P.N., M.T., I.P. and A.N.; visualization, T.P.N., M.T., I.P. and A.N.; supervision, T.P.N. and A.N.; project administration, T.P.N. and A.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Case reports are exempt from ethical approval in our public medical institution.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report and the accompanying images.
Data Availability Statement
Research data are available, upon reasonable request, to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the personnel of the Intensive Care Burn Unit of the Bucharest Emergency Clinical Hospital for taking part in this patient’s medical care.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mockenhaupt, M.; Viboud, C.; Dunant, A.; Naldi, L.; Halevy, S.; Bouwes Bavinck, J.N.; Sidoroff, A.; Schneck, J.; Roujeau, J.C.; Flahault, A. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Assessment of medication risks with emphasis on recently marketed drugs. The EuroSCAR-study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameshwari, J.S.; Devde, R. A case report on toxic epidermal necrolysis with etoricoxib. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halevy, S.; Ghislain, P.D.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Fagot, J.P.; Bouwes Bavinck, J.N.; Sidoroff, A.; Naldi, L.; Dunant, A.; Viboud, C.; Roujeau, J.C.; et al. Allopurinol is the most common cause of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Europe and Israel. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Ochi, F.; Chisaka, T.; Jogamoto, T.; Eguchi, M. Acetaminophen-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome with lethal lung injury: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakya, P.; Sharma Nepal, A. Daunorubicin induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e04475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, C.J.; Desai, A.; Rafferty, W.; Abou Hussein, A.K. Case report: Alpelisib-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 954027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Conde, M.; López-Ibáñez, N.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; Mendonça, F.M.I. Fulvestrant-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2019, 94, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Chai, H.; Yang, M.; Wei, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Caused by Enzalutamide: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 736975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokan, A.; Gavrić Lovrec, V.; Takač, I. A Case of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in Recurrent Late-Stage Ovarian Cancer Patient after Management of Chronic Pain with Elastomeric Pump. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 2928–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holfinger, S.; Roy, A.; Schmidt, M. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome after Armodafinil Use. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, V.; Philippidou, M.; Walsh, S.; Creamer, D. Stevens-Johnson syndrome induced by modafinil. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 43, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaro, T.; Kumar, A.; Pistun, O.; Dixit, D. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Associated with Chlordiazepoxide. J. Pharm. Technol. 2018, 34, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Perosanz-Lobo, D.; Fernández-Nieto, D.; Burgos-Blasco, P.; Aroca-Ruiz, M.; Fernández-Guarino, M. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by pirfenidone. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2021, 87, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogiji, E.D.; Maduba, C.C.; Nnadozie, U.U.; Okorie, G.M.; Ukoh, U.C.; Ezeanosike, E.; Umeokonkwo, C.D. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis overlap following sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine overdose: A case report. PAMJ-Clin. Med. 2022, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, M.; Mainetti, C.; Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli, B.; Harr, T. Current Perspectives on Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 47–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastuji-Garin, S.; Rzany, B.; Stern, R.S.; Shear, N.H.; Naldi, L.; Roujeau, J.C. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch. Dermatol. 1993, 129, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Wolkenstein, P.; Brochard, L.; Ortonne, N.; Maître, B.; Revuz, J.; Bagot, M.; Roujeau, J.C. Open trial of ciclosporin treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.L.; Carson, J.L.; Halpern, A.C.; Schinnar, R.; Snyder, E.S.; Shaw, M.; Tilson, H.H.; Joseph, M.; Dai, W.S.; Chen, D.; et al. A population-based study of Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Incidence and antecedent drug exposures. Arch. Dermatol. 1991, 127, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, N.; Jossi, J.; Bodmer, M.; Bircher, A.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R.; Spoendlin, J. The Epidemiology of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in the UK. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraogi, P.P.; Nayak, C.S.; Pereira, R.R.; Dhurat, R.S. Inadvertent Provocative Oral Ondansetron use Leading to Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in an HIV-infected Patient. Indian J. Dermatol. 2012, 57, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronich, N.; Maman, D.; Stein, N.; Saliba, W. Culprit Medications and Risk Factors Associated with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Population-Based Nested Case-Control Study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.A.; McDonough, P.H.; Lee, B.W. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Part I. Introduction, history, classification, clinical features, systemic manifestations, etiology, and immunopathogenesis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 173.e1–173.e13; quiz 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roujeau, J.C.; Huynh, T.N.; Bracq, C.; Guillaume, J.C.; Revuz, J.; Touraine, R. Genetic susceptibility to toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch. Dermatol. 1987, 123, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonjou, C.; Borot, N.; Sekula, P.; Ledger, N.; Thomas, L.; Halevy, S.; Naldi, L.; Bouwes-Bavinck, J.N.; Sidoroff, A.; de Toma, C.; et al. A European study of HLA-B in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis related to five high-risk drugs. Pharm. Genom. 2008, 18, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, O.G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of tenoxicam. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1994, 26, 16–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.P.; Todd, P.A. Tenoxicam. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 1987, 34, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merry, A.F.; Webster, C.S.; Holland, R.L.; Middleton, N.G.; Schug, S.A.; James, M.; McGrath, K.A. Clinical tolerability of perioperative tenoxicam in 1001 patients—A prospective, controlled, double-blind, multi-centre study. Pain 2004, 111, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vischer, T.L. Efficacy and tolerability of tenoxicam—An overview. Eur. J. Rheumatol. Inflamm. 1987, 9, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, D.; Waterworth, R.F. A study of the safety of tenoxicam in general practice. N. Z. Med. J. 1989, 102, 582–583. [Google Scholar]
- Katsinelos, P.; Katsos, I.; Patsiaoura, K.; Xiarchos, P.; Goulis, I.; Eugenidis, N. Tenoxicam-associated hepatic injury: A case report and review. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 9, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroca García, M.D.; Luna Rodríguez, C.; Gallego Navarro, M.A.; Ortiz de Solar, E. Alopecia secundaria a tenoxicam. Un efecto adverso no descrito? [Alopecia secondary to tenoxicam. An undescribed adverse effect?]. Aten. Primaria 1997, 20, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Heintz, R.C. Tenoxicam and renal function. Drug Saf. 1995, 12, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannenbaum, H.; Davis, P.; Russell, A.S.; Atkinson, M.H.; Maksymowych, W.; Huang, S.H.; Bell, M.; Hawker, G.A.; Juby, A.; Vanner, S.; et al. An evidence-based approach to prescribing NSAIDs in musculoskeletal disease: A Canadian consensus. Canadian NSAID Consensus Participants. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1996, 155, 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.D.; Endre, Z.; Miles, W.; Prankerd, R.; Chilvers, M.; Willgoss, D. Tenoxicam IV for major gynaecological surgery—Effects on renal function. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2000, 28, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Ruíz Ruiz, D.; Ramos Barrantes, I.; Martín Arias, L.H.; Carvajal García-Pando, A. Hipoglucemia secundaria a tenoxicam [Hypoglycemia secondary to tenoxicam]. Rev. Clin. Esp. 1992, 191, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Sevillano, A.; Blázquez Encinar, J.C.; Femenia Pérez, M.; Mora Rufete, M.A. Agranulocitosis inducida por Tenoxicam, con buena respuesta al factor estimulante de colonias (G-CSF) [Tenoxicam-induced agranulocytosis, with good response to colony stimulating factor (G-CSF)]. An. Med. Interna 1993, 10, 519–520. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, P.; Panik, R.; Bhattacharya, A.; Ahirwar, D.; Chandy, A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: An update. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2013, 3, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.E.; Archambault, R.; Mersfelder, T.L. Severe adverse skin reactions to nonsteroidal nti-inflammatory drugs: A review of the literature. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapeyre-Mestre, M.; Grolleau, S.; Montastruc, J.L.; Association Française des Centres Régionaux de Pharmacovigilance (CRPV). Adverse drug reactions associated with the use of NSAIDs: A case/noncase analysis of spontaneous reports from the French pharmacovigilance database 2002–2006. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 27, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Grenade, L.; Lee, L.; Weaver, J.; Bonnel, R.; Karwoski, C.; Governale, L.; Brinker, A. Comparison of reporting of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in association with selective COX-2 inhibitors. Drug Saf. 2005, 28, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layton, D.; Marshall, V.; Boshier, A.; Friedmann, P.; Shakir, S.A. Serious skin reactions and selective COX-2 inhibitors: A case series from prescription-event monitoring in England. Drug Saf. 2006, 29, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Malvestiti, A.A.; Hafner, M.D. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: A review. Rev. Assoc. Méd. Bras. 2016, 62, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mockenhaupt, M.; Kelly, J.P.; Kaufman, D.; Stern, R.S.; SCAR Study Group. The risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: A multinational perspective. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 10, 2234–2240. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, B.; Orlet, H.K.; Still, J.M.; Law, E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis due to administration of celecoxib (Celebrex). South. Med. J. 2002, 95, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, A.G.; Woodruff, C.A.; Markus, R.F.; Hsu, S. Toxic epidermal necrolysis as a complication of treatment with celecoxib. Dermatol. Online J. 2003, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.S.; Mukherjee, S.; Era, N.; Mukherjee, M. Etoricoxib-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis: A fatal case report. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2018, 50, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, M.; Peccerillo, F.; Bonzano, L.; Pavone, P.; Motolese, A.; Froio, E.; Motolese, A. Ketoprofen-induced severe toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with vanishing bile duct syndrome leading to liver transplantation. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Yang, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.H. Ibuprofen associated acute vanishing bile duct syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in an infant. Yonsei Med. J. 2014, 55, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; Zanetto, U.; Kolli, S.; Morjaria, R. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: The red eye and red herrings in casualty. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanabroo, D.; Schmitz-Landgraf, W.; Czarnetzki, B.M. Plasmapheresis in severe drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch. Dermatol. 1985, 121, 1548–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, N.; Bodmer, M.; Bircher, A.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R.; Spoendlin, J. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in Association with Commonly Prescribed Drugs in Outpatient Care Other than Anti-Epileptic Drugs and Antibiotics: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.H.; Yin, X.D.; Zeng, N.; Zhou, Z.X.; Mao, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Li, Z.L. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Following Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs: A Real-World Analysis of Post-marketing Surveillance Data. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 896867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastuji-Garin, S.; Fouchard, N.; Bertocchi, M.; Roujeau, J.C.; Revuz, J.; Wolkenstein, P. SCORTEN: A severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, B.; Haddad, C.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Dunant, A.; Liss, Y.; Bork, K.; Haustein, U.F.; Vieluf, D.; Roujeau, J.C.; Le Louet, H. ALDEN, an algorithm for assessment of drug causality in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Comparison with case-control analysis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 88, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo, C.A.; Busto, U.; Sellers, E.M.; Sandor, P.; Ruiz, I.; Roberts, E.A.; Janecek, E.; Domecq, C.; Greenblatt, D.J. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 30, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodiuk-Gad, R.P.; Chung, W.H.; Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Shear, N.H. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An Update. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 16, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, E.; Papaliodis, D.N.; Papaliodis, G.N.; Daoud, Y.J.; Ahmed, A.R.; Foster, C.S. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: A review of the literature. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005, 94, 419–436; quiz 436–438, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujeau, J.C.; Stern, R.S. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.P. A contemporary snippet on clinical presentation and management of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Scars Burn. Heal. 2022, 8, 20595131221122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marija, S.; Ivana, B.; Nina, R.; Dragan, N.; Zlatko, B.; Branislav, J.; Jelena, P.; Dusica, S. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a child with lupus-associated pancreatitis. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richer, V.; Bouffard, D.; Bélisle, A.; Duranceau, L.; Perreault, I.; Provost, N. Acute blistering diseases on the burn ward: Beyond Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Burns 2013, 39, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, V.M.; Do, A.; Berger, T.G.; Nguyen, A.H.; DeWeese, J.; Malone, J.D.; Jordan, K.; Hom, F.; Tuffanelli, L.; Fillari, P.; et al. A decade of burn unit experience with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Clinical pathological diagnosis and risk factor awareness. Burns 2016, 42, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, J.; Hopman, W.; Gomez, M.; Cartotto, R. Late outcomes in adult survivors of toxic epidermal necrolysis after treatment in a burn center. J. Burn. Care Rehabil. 2005, 26, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Chung, W.H.; Huang, H.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Hung, S.I. Direct interaction between HLA-B and carbamazepine activates T cells in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1562–1569.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartotto, R. Burn Center Care of Patients with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, W.J. Pharmacological interaction of drugs with antigen-specific immune receptors: The p-i concept. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 2, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, R.; Shimizu, T.; Shibaki, A.; Nakamura, H.; Watanabe, H.; Shimizu, H. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome are induced by soluble Fas ligand. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, A.; Jackson, C.; Harun, N.; Cooper, A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Review of pathogenesis and management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Wang, T.J.; Lin, M.H.; Chen, T.J. A Review of the Systemic Treatment of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.S.; Sabharwal, N.; Patti, R.; Kupfer, Y. Allopurinol-Induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harr, T.; French, L.E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strużyna, J.; Surowiecka, A.; Korzeniowski, T.; Korulczyk, P.; Drozd, L.; Stachura, A.; Torres, K.; Krajewski, A. Accuracy of SCORTEN in predicting mortality in toxic epidermal necrolysis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noe, M.H.; Rosenbach, M.; Hubbard, R.A.; Mostaghimi, A.; Cardones, A.R.; Chen, J.K.; Cotliar, J.; Davis, M.D.P.; Dominguez, A.; Fox, L.P.; et al. Development and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for In-Hospital Mortality among Patients with Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis-ABCD-10. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Navarro, I.; Briz-Redón, Á.; Botella-Casas, G.; Sahuquillo-Torralba, A.; Calle-Andrino, A.; de Unamuno-Bustos, B.; Piqueras-García, J.; Roca Ginés, J.; Magdaleno Tapial, J.; Alegre de Miquel, V.; et al. Accuracy of SCORTEN and ABCD-10 to predict mortality and the influence of renal function in Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duplisea, M.J.; Roberson, M.L.; Chrisco, L.; Strassle, P.D.; Williams, F.N.; Ziemer, C.M. Performance of ABCD-10 and SCORTEN mortality prediction models in a cohort of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.L. The management of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2012, 53, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creamer, D.; Walsh, S.A.; Dziewulski, P.; Exton, L.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Dart, J.K.; Setterfield, J.; Bunker, C.B.; Ardern-Jones, M.R.; Watson, K.M.; et al. UK guidelines for the management of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis in adults 2016. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 1194–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, Y.M.; Hirahara, K.; Mizukawa, Y.; Kano, Y.; Shiohara, T. Efficacy of plasmapheresis for the treatment of severe toxic epidermal necrolysis: Is cytokine expression analysis useful in predicting its therapeutic efficacy? J. Dermatol. 2011, 38, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczeklik, W.; Nowak, I.; Seczynska, B.; Sega, A.; Krolikowski, W.; Musial, J. Beneficial therapeutic effect of plasmapheresis after unsuccessful treatment with corticosteroids in two patients with severe toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2010, 14, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, R.; Huang, S.; Are, A.; Motaparthi, K. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Review of Diagnosis and Management. Medicina 2021, 57, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, M.; Kano, Y.; Fujita, H.; Kambara, T.; Matsukur, S.; Katayama, I.; Azukizawa, H.; Miyachi, Y.; Endo, Y.; Asada, H.; et al. Efficacy of additional i.v. immunoglobulin to steroid therapy in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, C.H.; Gillenwater, T.J.; Nagengast, E.; McCullough, M.C.; Peng, D.H.; Garner, W.L. Combination therapy: Etanercept and intravenous immunoglobulin for the acute treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Burns 2019, 45, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Fook-Chong, S.; Koh, H.Y.; Thirumoorthy, T.; Pang, S.M. Cyclosporine treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: Retrospective analysis of a cohort treated in a specialized referral center. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balai, M.; Meena, M.; Mittal, A.; Gupta, L.K.; Khare, A.K.; Mehta, S. Cyclosporine in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Experience from a Tertiary Care Centre of South Rajasthan. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 12, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolum, J.A.; Bailey, A.M.; Baum, R.A.; Metts, E.L. A Review of the Management of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. Adv. Emerg. Nurs. J. 2019, 41, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mockenhaupt, M. The current understanding of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 803–813; quiz 814–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Sekula, P.; Venhoff, M.; Motschall, E.; Knaus, J.; Schumacher, M.; Mockenhaupt, M. Systemic Immunomodulating Therapies for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahara, K.; Kano, Y.; Sato, Y.; Horie, C.; Okazaki, A.; Ishida, T.; Aoyama, Y.; Shiohara, T. Methylprednisolone pulse therapy for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: Clinical evaluation and analysis of biomarkers. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halebian, P.H.; Corder, V.J.; Madden, M.R.; Finklestein, J.L.; Shires, G.T. Improved burn center survival of patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis managed without corticosteroids. Ann. Surg. 1986, 204, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantaphakul, H.; Sanon, T.; Klaewsongkram, J. Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.; Chansky, P.B.; Bashyam, A.R.; Boettler, M.A.; Challa, N.; Dominguez, A.; Estupinan, B.; Gupta, R.; Hennessy, K.; Huckell, S.N.; et al. Long-term Physical and Psychological Outcomes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNiro, K.L.; Honari, S.; Hippe, D.S.; Dai, A.; Pham, T.N.; Caceres, M.; Mandell, S.P.; Duong, P.Q.; McMullen, K.A.; Gibran, N.S. Physical and Psychological Recovery Following Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Patient Survey. J. Burn. Care Res. 2021, 42, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneux, E.; Wolkenstein, P.; Haddad, B.; Roujeau, J.C.; Revuz, J.; Paniel, B.J. Vulvovaginal involvement in toxic epidermal necrolysis: A retrospective study of 40 cases. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 91, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, R.L.; Schulz, J.T.; Ryan, C.M.; Schnitzer, J.J.; Lawlor, D.; Driscoll, D.N.; Donelan, M.B.; Tompkins, R.G. Long-term consequences of toxic epidermal necrolysis in children. Pediatrics 2002, 109, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).