Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
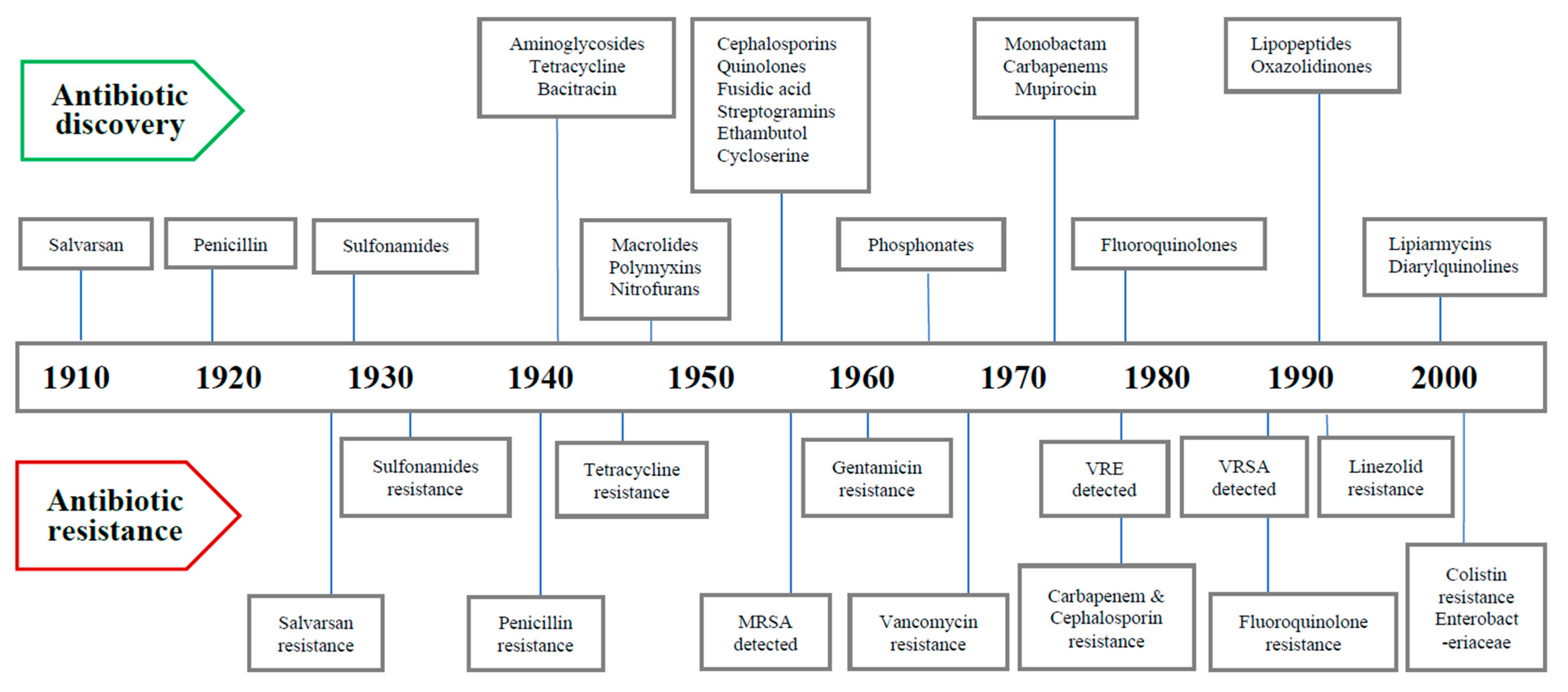
2. Timeline of Major Antibiotics Discoveries and Antibiotic Resistance
3. Superbugs
4. Basis of Antibiotic Resistance
5. Sources and Routes of Transmission of AMR
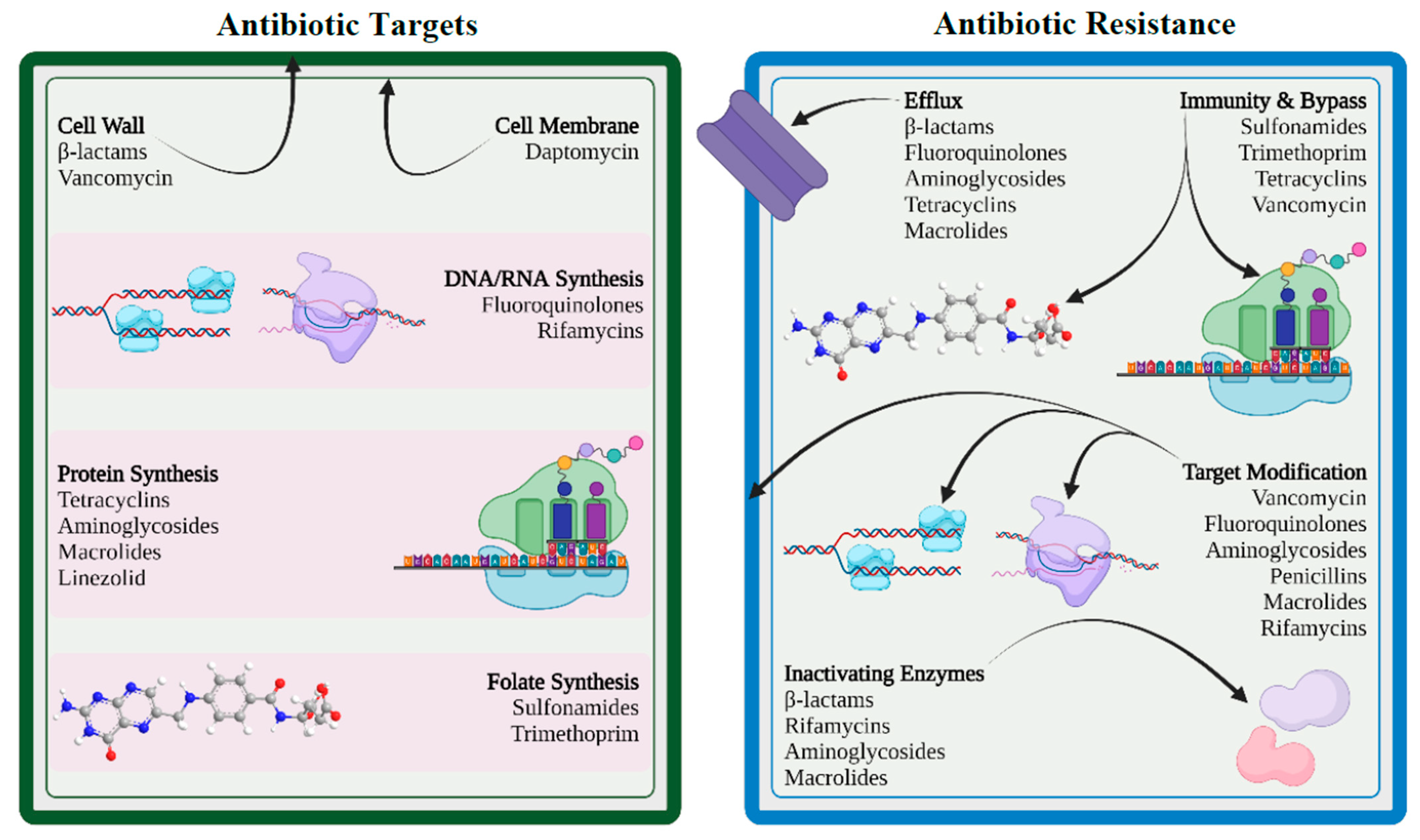
6. Mechanisms of Drug Resistance
6.1. Limiting Drug Uptake
6.2. Modification of Targets for Drug
6.3. Inactivation of Drug
6.4. Efflux of Drug
7. Drivers to AMR
7.1. Misuse and Overuse of Antibiotics
7.2. Increase in Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
7.3. Inappropriate Prescribing Patterns
7.4. Paucity in Futuristic Antibiotics
7.5. Agricultural Use of Antibiotics
7.6. Easy Travel Routes
7.7. Knowledge Gap
8. Clinical Implications of AMR
- Successful treatment of microbial infections including bacterial, fungal, and viral infections is hindered by antimicrobial resistance.
- Emergence and dissemination of new resistant mechanisms threaten the scope of treatment for many common illnesses such as urinary tract infections, upper respiratory tract infections, typhoid, and flu, resulting in treatment failure, permanent disability, or even death.
- The success of cancer chemotherapy, transplantation surgery, and even minor dental procedures will be seriously jeopardized by virtue of AMR unless novel drugs are available.
- AMR infections impose mandatory prolonged treatment with higher healthcare costs and may require expensive alternate drugs.
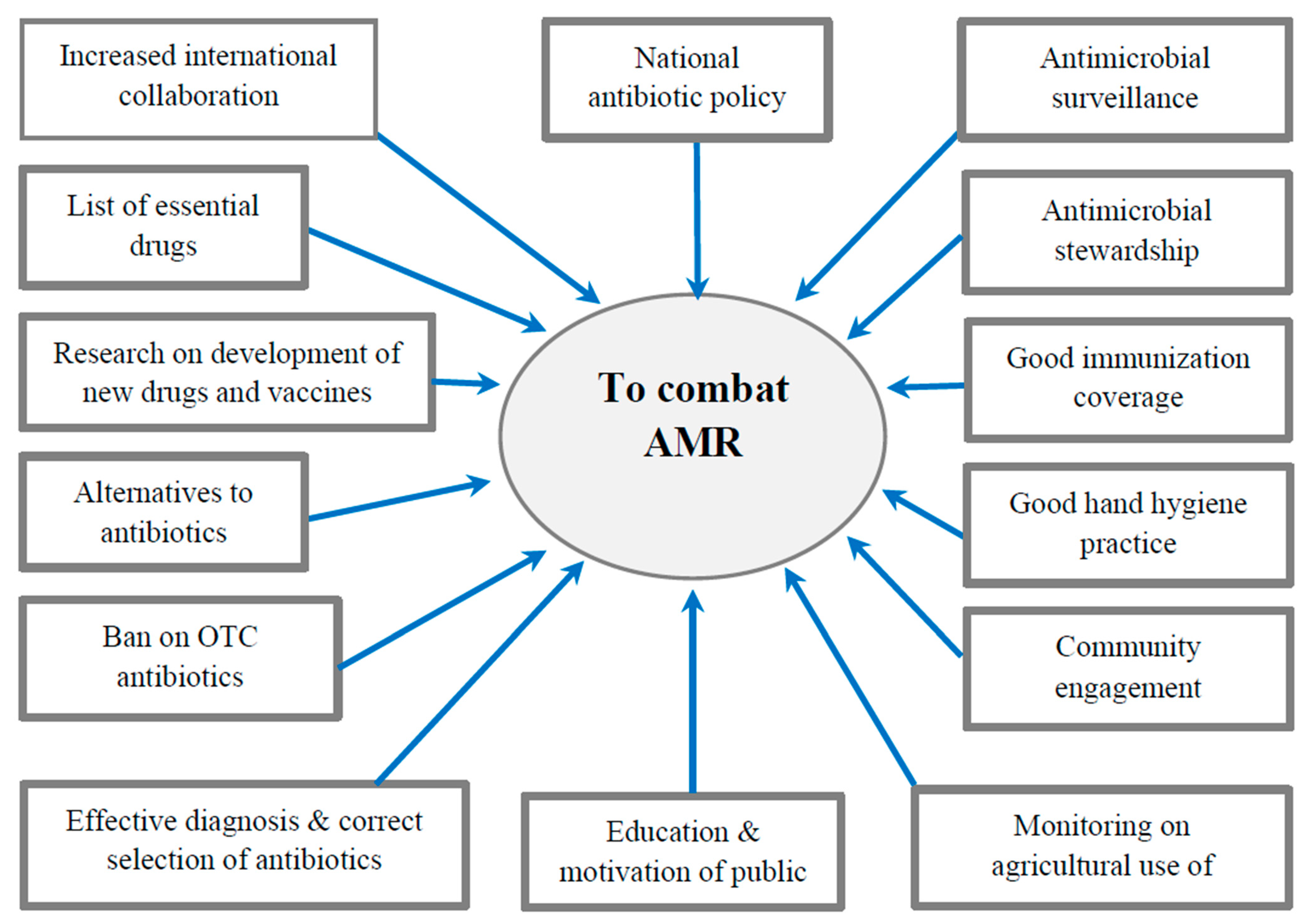
9. How to Combat AMR
9.1. International Measures
- Establishing and strengthening collaboration among international agencies, governments, nongovernmental organizations, and professional groups.
- Establishing surveillance networks for antimicrobial use and AMR globally.
- Building laboratory capacity for the detection and reporting of pathogens with AMR that have global health impacts.
- Establishing and strengthening international tracking systems for quick identification and mitigation of emerging pathogens.
- International monitoring to control counterfeit antimicrobials across the globe.
- Investing in research, new drug discovery, and vaccines.
9.2. National Strategies
- Implementing an “Antibiotic policy” for judicious use in healthcare and agricultural settings.
- Strengthening of national surveillance, monitoring, and evaluation efforts by integration of public health and veterinary sectors.
- Developing innovative point-of-care diagnostic tests for pathogen identification and resistance monitoring.
- Investing in basic and applied research on new antibiotics and vaccines.
- Building capacity and strengthening international collaboration to combat AMR.
- Adopting antimicrobial stewardship in healthcare settings with essential drug list.
9.3. Rational Use of Antibiotics
9.4. Ban on Over-the-Counter (OTC) Antibiotics
9.5. Infection Prevention and Control (IPC)
- Formation of “infection prevention and control committee”.
- Practices of good hand hygiene.
- Proper diagnosis and successful treatment of infection.
- Responsible use of antimicrobial agents.
- Continuous surveillance and monitoring of antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance.
- Establishing quality antimicrobials supply chain.
- Good microbiological laboratory practices.
9.6. Antimicrobial Stewardship Program (ASP)
9.7. Use of Antibiotics in Animals
9.8. Development of New Drugs and Vaccines
9.9. Introduction of Checkpoints
9.10. Community Engagement
9.11. Alternatives to Antibiotics
9.11.1. Phage Therapy
9.11.2. Antivirulence Drugs
9.11.3. Bacteriocins
9.12. One Health
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Williams-Nguyen, J.; Sallach, J.B.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Boxall, A.B.; Durso, L.M.; McLain, J.E.; Singer, R.S.; Snow, D.D.; Zilles, J.L. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance in Agroecosystems: State of the Science. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. How Antimicrobial Resistance Happens. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about/how-resistance-happens.html (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Tenover, F.C. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, S3–S10; discussion S62–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Shi, Q.S.; Huang, X.M.; Xie, X.B. The Three Bacterial Lines of Defense against Antimicrobial Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21711–21733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khameneh, B.; Diab, R.; Ghazvini, K.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S. Breakthroughs in bacterial resistance mechanisms and the potential ways to combat them. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 95, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.F.; Woods, R.J. Antibiotic resistance management. Evol. Med. Public Health 2014, 2014, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A. Antimicrobial resistance, trade, food safety and security. One Health 2018, 5, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samreen; Ahmad, I.; Malak, H.A.; Abulreesh, H.H. Environmental antimicrobial resistance and its drivers: A potential threat to public health. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 27, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARC. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations (The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, London, 2016, United Kingdom). Rev. Antimicrob. Resist. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- WHO. Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB). Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/documents/tuberculosis/multidrug-resistant-tuberculosis-mdr-tb.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Ghimpețeanu, O.M.; Pogurschi, E.N.; Popa, D.C.; Dragomir, N.; Drăgotoiu, T.; Mihai, O.D.; Petcu, C.D. Antibiotic Use in Livestock and Residues in Food-A Public Health Threat: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founou, R.C.; Founou, L.L.; Essack, S.Y. Clinical and economic impact of antibiotic resistance in developing countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.I.; Truman, A.W.; Wilkinson, B. Antibiotics: Past, present and future. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iskandar, K.; Murugaiyan, J.; Hammoudi Halat, D.; Hage, S.E.; Chibabhai, V.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Roques, C.; Molinier, L.; Salameh, P.; Van Dongen, M. Antibiotic Discovery and Resistance: The Chase and the Race. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, A.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Iyer, A.; Mayandi, V.; Leng Goh, E.T.; Lloyd, D.G.; Chalasani, M.L.S.; Verma, N.K.; Prior, S.H.; Beuerman, R.W.; et al. Design and Syntheses of Highly Potent Teixobactin Analogues against Staphylococcus aureus, Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE) in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.B.; Hussain, M.A.; Nye, R.; Mehta, V.; Mamun, K.T.; Hossain, N. A Review on Antibiotic Resistance: Alarm Bells are Ringing. Cureus 2017, 9, e1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suay-García, B.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Present and Future of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Infections. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Prevalence and antibiotic susceptibility pattern of methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus in tertiary care hospitals. Biotechnol. J. Int. 2014, 4, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmanik, A.; Das, S.; Kar, B.; Bose, A.; Dwivedi, G.R.; Pandey, M.M. Current Treatment Strategies Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: A Review. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, N.; Islam, N.F.; Sonowal, S.; Prasad, R.; Sarma, H. Environmental antibiotics and resistance genes as emerging contaminants: Methods of detection and bioremediation. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Perspectives towards antibiotic resistance: From molecules to population. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. General principles of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Drug Discov. Today. Technol. 2014, 11, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, G.; Wright, G.D. Intrinsic antibiotic resistance: Mechanisms, origins, challenges and solutions. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2013, 303, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Hancock, R.E. Adaptive and mutational resistance: Role of porins and efflux pumps in drug resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizi, K.S.; Ghazvini, K.; Noghondar, M.K. Adaptive antibiotic resistance: Overview and perspectives. J. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2018, 6, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godijk, N.G.; Bootsma, M.C.J.; Bonten, M.J.M. Transmission routes of antibiotic resistant bacteria: A systematic review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzemiński, P.; Markiewicz, Z.; Popowska, M. Entry Routes of Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment. In Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes: Environmental Occurrence and Treatment Technologies; Hashmi, M.Z., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- da Costa, P.M.; Loureiro, L.; Matos, A.J. Transfer of multidrug-resistant bacteria between intermingled ecological niches: The interface between humans, animals and the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancey, S.T.; Zähner, D.; Stephens, D.S. Acquired inducible antimicrobial resistance in Gram-positive bacteria. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 959–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, U.; Lee, C.R. Distinct Roles of Outer Membrane Porins in Antibiotic Resistance and Membrane Integrity in Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghai, I.; Ghai, S. Understanding antibiotic resistance via outer membrane permeability. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutt, Y.; Dhiman, R.; Singh, T.; Vibhuti, A.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, R.P.; Raj, V.S.; Chang, C.M.; Priyadarshini, A. The Association between Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance with Possible Ingenious Bio-Remedial Approaches. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, H.; Van Dijck, P.; Coenye, T. Molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial tolerance and resistance in bacterial and fungal biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, R.E.; Dittmore, A.; McPherson, S.A.; Turnbough, C.L., Jr.; Neuman, K.C.; Osheroff, N. Activities of gyrase and topoisomerase IV on positively supercoiled DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 9611–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Sarkar, A. Review on Multiple Facets of Drug Resistance: A Rising Challenge in the 21st Century. J. Xenobiotics 2021, 11, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendlandt, S.; Shen, J.; Kadlec, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.J.; Feßler, A.T.; Wu, C.; Schwarz, S. Multidrug resistance genes in staphylococci from animals that confer resistance to critically and highly important antimicrobial agents in human medicine. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Reviews. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H.; Pagès, J.M. Broad-specificity efflux pumps and their role in multidrug resistance of Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 340–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.; Richmond, G.E.; Piddock, L.J. Multidrug efflux pumps in Gram-negative bacteria and their role in antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushaheen, M.A.; Muzaheed; Fatani, A.J.; Alosaimi, M.; Mansy, W.; George, M.; Acharya, S.; Rathod, S.; Divakar, D.D.; Jhugroo, C.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Dis. A-Mon. DM 2020, 66, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaw, P.S.; Höpner, J.; Mikolajczyk, R. The knowledge, attitude and practice of health practitioners towards antibiotic prescribing and resistance in developing countries-A systematic review. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 43, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, A.; Sifri, Z.; Cennimo, D.; Horng, H. Global Contributors to Antibiotic Resistance. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2019, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Antibiotic Use in the United States, 2022 Update: Progress and Opportunities. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/stewardship-report/current.html (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Michael, C.A.; Dominey-Howes, D.; Labbate, M. The antimicrobial resistance crisis: Causes, consequences, and management. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulia, M.; Kern, M.; Schwei, R.J.; Shah, M.N.; Sampene, E.; Crnich, C.J. Comparing appropriateness of antibiotics for nursing home residents by setting of prescription initiation: A cross-sectional analysis. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolhouse, M.; Waugh, C.; Perry, M.R.; Nair, H. Global disease burden due to antibiotic resistance-state of the evidence. J. Glob. Health 2016, 6, 010306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance: A Global Threat. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/solutions-initiative/stories/ar-global-threat.html (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- DiMasi, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. J. Health Econ. 2016, 47, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Q.; Wang, W.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Lipsitch, M.; Hanage, W.P. Antibiotics in agriculture and the risk to human health: How worried should we be? Evol. Appl. 2015, 8, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Animal production. Available online: https://www.fao.org/antimicrobial-resistance/key-sectors/animal-production/en/ (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Castro-Sánchez, E.; Moore, L.S.; Husson, F.; Holmes, A.H. What are the factors driving antimicrobial resistance? Perspectives from a public event in London, England. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, I.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Pires, J.; Craig, J.; Laxminarayan, R. Global geographic trends in antimicrobial resistance: The role of international travel. J. Travel Med. 2019, 26, taz036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcilla, M.S.; van Hattem, J.M.; Haverkate, M.R.; Bootsma, M.C.J.; van Genderen, P.J.J.; Goorhuis, A.; Grobusch, M.P.; Lashof, A.M.O.; Molhoek, N.; Schultsz, C.; et al. Import and spread of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae by international travellers (COMBAT study): A prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubbin, K.D.; Anholt, R.M.; de Jong, E.; Ida, J.A.; Nóbrega, D.B.; Kastelic, J.P.; Conly, J.M.; Götte, M.; McAllister, T.A.; Orsel, K.; et al. Knowledge Gaps in the Understanding of Antimicrobial Resistance in Canada. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 726484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.R.; Sun, J.; Jump, R.L. A Survey and Analysis of the American Public's Perceptions and Knowledge About Antibiotic Resistance. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Antibiotic resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Lin, T.Z.; Jayasvasti, I.; Tiraphat, S.; Pengpid, S.; Jayasvasti, M.; Borriharn, P. The Predictors Influencing the Rational Use of Antibiotics Among Public Sector: A Community-Based Survey in Thailand. Drug Healthc. Patient Saf. 2022, 14, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Control, A. Global Governance to Tackle Antimicrobial Resistance: The Way Forward. Available online: http://resistancecontrol.info/2019-3/armed-conflicts-and-antimicrobial-resistance-a-deadly-convergence/ (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Majumder, M.A.A.; Rahman, S.; Cohall, D.; Bharatha, A.; Singh, K.; Haque, M.; Gittens-St Hilaire, M. Antimicrobial Stewardship: Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance and Protecting Global Public Health. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 4713–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Action Plan on Antibiotic Resistance. Available online: https://www.emro.who.int/health-topics/drug-resistance/global-action-plan.html (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- WHO. Assessing Non-Prescription and Inappropriate Use of Antibiotics Report on Survey. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/312306/9789289054089-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- WHO. Infection Prevention and Control. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/integrated-health-services/infection-prevention-control (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- CDC. Implementation of Antibiotic Stewardship Core Elements at Small and Critical Access Hospitals. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/core-elements/small-critical.html (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Pinto Ferreira, J.; Battaglia, D.; Dorado García, A.; Tempelman, K.; Bullon, C.; Motriuc, N.; Caudell, M.; Cahill, S.; Song, J.; LeJeune, J. Achieving Antimicrobial Stewardship on the Global Scale: Challenges and Opportunities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidara-Kane, A.; Angulo, F.J.; Conly, J.M.; Minato, Y.; Silbergeld, E.K.; McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines on use of medically important antimicrobials in food-producing animals. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.; Cooke, P.; Ahorlu, C.; Arjyal, A.; Baral, S.; Carter, L.; Dasgupta, R.; Fieroze, F.; Fonseca-Braga, M.; Huque, R.; et al. Community engagement: The key to tackling Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) across a One Health context? Glob. Public Health 2022, 17, 2647–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, L.; Sleiman, A.; Abdel-Massih, R.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols and Alkaloids in Middle Eastern Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, M.Y.; Lahiry, A.; Ferdous, R.; Hasan, M.K.; Kader, M.A.; Alam, A.K.; Saud, Z.A.; Sadik, M.G. Stephania japonica Ameliorates Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice through Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase and Oxidative Stress. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 2022, 8305271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyzun, T.; Mahmud, A.A.; Ahammed, M.S.; Manik, M.I.N.; Hasan, M.K.; Islam, K.M.M.; Lopa, S.S.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Biswas, K.; Afrin, M.R.; et al. Polyphenolics with Strong Antioxidant Activity from Acacia nilotica Ameliorate Some Biochemical Signs of Arsenic-Induced Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Zaman, S.; Biswas, K.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Hasan, M.K.; Alam, A.; Tanaka, T.; Sadik, G. Evaluation of cholinesterase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of Wedelia chinensis and isolation of apigenin as an active compound. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Akbar, M.; Khan, M.A.; Sunita, K.; Parveen, S.; Pawar, J.S.; Massey, S.; Agarwal, N.R.; Husain, S.A. Plant metabolite diosmin as the therapeutic agent in human diseases. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2022, 3, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, J.S.; Mustafa, S.; Ghosh, I. Chrysin and Capsaicin induces premature senescence and apoptosis via mitochondrial dysfunction and p53 elevation in Cervical cancer cells. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3838–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundo, N.K.; Manik, M.I.N.; Biswas, K.; Khatun, R.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Alam, A.; Tanaka, T.; Sadik, G. Identification of Polyphenolics from Loranthus globosus as Potential Inhibitors of Cholinesterase and Oxidative Stress for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment. BioMed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9154406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaning Danquah, C.; Minkah, P.A.B.; Osei Duah Junior, I.; Amankwah, K.B.; Somuah, S.O. Antimicrobial Compounds from Microorganisms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brives, C.; Pourraz, J. Phage therapy as a potential solution in the fight against AMR: Obstacles and possible futures. Palgrave Commun. 2020, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, S.W.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; Otto, M. Different drugs for bad bugs: Antivirulence strategies in the age of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Reviews. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. One Health Initiative. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/one-health-initiative (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- CDC. One Health Basics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/basics/index.html (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- Van Camp, P.J.; Haslam, D.B.; Porollo, A. Prediction of Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria from Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Clift, C.; Schulze, K.; Sagan, A.; Nahrgang, S.; Ait Ouakrim, D.; Mossialos, E. European Observatory Policy Briefs. In Averting the AMR Crisis: What Are the Avenues for Policy Action for Countries in Europe? European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies © World Health Organization 2019 (acting as the host organization for, and secretariat of, the European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11131946
Salam MA, Al-Amin MY, Salam MT, Pawar JS, Akhter N, Rabaan AA, Alqumber MAA. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare. 2023; 11(13):1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11131946
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalam, Md. Abdus, Md. Yusuf Al-Amin, Moushumi Tabassoom Salam, Jogendra Singh Pawar, Naseem Akhter, Ali A. Rabaan, and Mohammed A. A. Alqumber. 2023. "Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health" Healthcare 11, no. 13: 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11131946
APA StyleSalam, M. A., Al-Amin, M. Y., Salam, M. T., Pawar, J. S., Akhter, N., Rabaan, A. A., & Alqumber, M. A. A. (2023). Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare, 11(13), 1946. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11131946







