Abstract
We developed evaluation indicators for sports facilities for people with disabilities and adopted the universal design to conduct Delphi surveys on sports facilities and sports experts. First, the range of universal design element reflection and the method of deriving the evaluation indicators were established through a literature review. Second, 21 experts conducted the first Delphi survey to select the important features of the seven principles of universal design and describe the necessary sub-factors to consider when designing sports facilities. The described elements were divided into 15 categories, and 49 sub-factors were extracted. Third, based on the evaluation of the indicators’ content, acceptance was investigated, and the survey data were analyzed through indicators of reliability and validity of the sub-factors and categories. Fourth, we discussed whether to accept the standard value on the basis of the evaluation index through an expert meeting. Subsequently, the final evaluation index was obtained. The developed evaluation index should be applied by the operators and users of public sports facilities, and validation work is needed. Guidelines for applying the universal design to various sports facilities for people with disabilities should be developed. The financing of sports facilities applying the universal design and related policies should be discussed.
1. Introduction
Currently, in Korea, aging-related problems are increasing owing to the rapid increase in the elderly population along with the economic development and advances in medical technology [1]. Specifically, the number of older people with disabilities caused by aging is steadily increasing owing to adverse environmental factors and industrial accidents [2]. This has become a social problem, and practical alternatives for the normal life of older adults and all people with disabilities are greatly required. Therefore, the government, academics, and social groups are actively investigating and attempting to meet the requirements of the elderly and disabled population, e.g., by improving the living environment of people who are underprivileged and their movement and access to facilities and information, eliminating inconveniences and obstacles.
So far, these social efforts have mainly considered specific disadvantaged groups, such as older adults and all categories of people with disabilities. “Barrier-free” is a social movement and policy implemented to remove physical and psychological barriers that hinder people who are socially disadvantaged, such as those with disabilities. Currently, people with and without disabilities live together. Therefore, as barrier-free gives priority to those with disabilities, in reality, it has caused problems by consciously alienating them, further emphasizing their disability [3]. Consequently, designing and providing separate environments and products that support the status and needs of specific users has become valuable. However, considering potential users such as the elderly and all categories of people with disabilities, a universal design (UD)—which provides designed environments and products that can be used safely and conveniently by all, so that people with and without disabilities can live together [4]—has become necessary.
The UD was developed from the concept of a barrier-free living environment [5]. It is a design that does not separate people with and without disabilities and creates an accessible environment reflecting the users’ needs and consequently suitable for all [6]. The users participate, provide opinions, and reach an agreement with experts in each field [7]. The UD has already been defined and utilized, considering the environmental characteristics of different countries, in particular the United States and Europe [8]. The UD Center of North Carolina State University in the USA performed a project titled “Studies to Further the Development of UD” (no. H133A40006). During the project activities, seven UD principles (equitable use, flexibility in use, simple and intuitive use, perceptible information, tolerance for error, low physical effort, and size and space for approach and use) were developed with a focus on the built environment, products, and communication [9]. The seven UD principles guide the design process, are used to systematically evaluate proposed designs, and help designers and consumers characterize more useful design solutions [10,11].
In the United Kingdom, guidelines for sports facilities with an inclusive design, a concept similar to the UD, were presented at the national level [12]. In addition, Japan had 114 UD sports facilities as of 2014. Many European countries encourage the use of sports facilities, regardless of whether people have disabilities [13].
In contrast, in Korea, convenience facilities for people with disabilities are well established owing to legal regulations. However, sports facilities not satisfying the legal standards are not suitable for people with disabilities. A recent study investigated the demand by users and operators of public sports facilities of UD sports facilities for people with disabilities. It found that non-disabled users were favorable to the construction of UD sports facilities and the use of related programs. In addition, to become a sports facility that can be used fairly by people with and without disabilities, it is necessary to expand the scope of the legislation related to the installation of convenience facilities for people with disabilities in sports facilities [14]. Recognizing the importance of sports facilities that can be used by anyone without discrimination, the government announced plans to increase the number of sports centers to 150 by 2025 [15].
In accordance with this trend, in Korea, the environment and facilities have been evaluated through the “life environment certification system without obstacles”. However, appropriate evaluations have been difficult, owing to the burden of costs and procedures; therefore, integrated and emotional evaluations of the environment and facilities are not applied [16]. Considering the number of future public sports facilities, the development of evaluation indicators to objectively evaluate various sports-related facilities is required. Consequently, institutional directions, such as strengthening user services, convenience, and safety support, have been suggested.
Concerning research on sports facilities that apply the UD, studies have been published on the development of a user perception measurement tool [17] and the creation of a learning environment [18], reporting examples of facilities that can be understood from users’ viewpoints. Some studies only dealt with methods [19,20], and only a limited range of topics have been covered. The UD for a living environment where various users coexist has been frequently applied in the public environment and facility fields by local governments. Furthermore, it has had a great influence on related academic research fields. However, studies on sports facilities for people with disabilities that consider the UD are required. Specifically, research on this topic is necessary because no indicators have been developed to objectively evaluate sports facilities to which the UD is applied.
Therefore, we established the scope of UD elements and a method of deriving evaluation indicators through a literature review, extracted the factors to be considered for UD-applied sports facilities through two Delphi surveys, and determined the elements of the evaluation indicators through expert meetings.
2. Materials and Methods
This mixed-methods study utilized qualitative (expert interviews and content analysis) and quantitative (frequency analyses) instruments.
2.1. Participants (Panel Experts)
The participants had worked in a specialized field for more than 10 years and had an analytical perspective on the research topic and expertise with abundant field experience; thus, they could provide insight into the overall context and process. The panel consisted of 21 people from four fields: seven architects, seven experts on people with disabilities, four experts on older adults, and three UD experts. Table 1 shows the personal characteristics of the panel experts. The selection of the study participants was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by the Gachon University Institutional Review Committee (no. 1044396-202007-HR-125-01).

Table 1.
Personal characteristics of the expert panel.
2.2. Instruments and Procedure
2.2.1. Procedure
A standard feasibility study was derived over four steps. First, the range of UD element reflection and the method of deriving the evaluation indicators were established through a literature review. Second, 21 experts conducted the first Delphi survey to select the features applied preferentially to the seven UD principles and described the sub-factors to be considered when designing sports facilities. The described elements were divided into 15 categories, and 50 sub-factors were extracted. Third, based on the evaluation indicators content classified through the first Delphi survey, acceptance was investigated through a five-point Likert scale, and the survey data were analyzed through indicators of reliability and validity of the sub-factors and categories. Fourth, we discussed whether to accept the standard value as a result of the evaluation index through an expert meeting. Subsequently, the final evaluation index was completed. The detailed study procedure is shown in Figure 1.
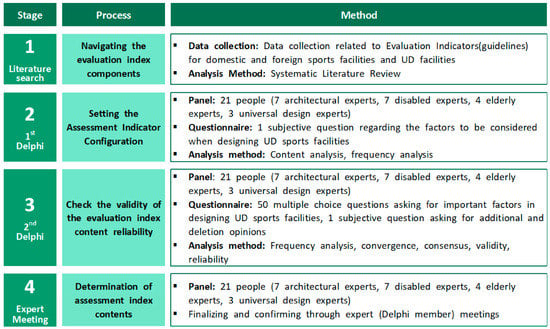
Figure 1.
Research procedure.
2.2.2. Systematic Literature Review
The scope of UD element reflection and the method of deriving evaluation indicators were established through a systematic literature review. According to the process of literature search suggested by Petticrew and Roberts [21] and Fatorić and Seekamp [22]—“create keywords”, “conduct search”, “collect publications”, and “select publications”—the literature search was conducted in the order of “analyze publications” and “report and discuss”.
The keywords were “UD facilities” and “sports facilities”, and the Korean literature was searched using the “Research Information Sharing Service” provided by the Korea Education and Research Information Service. The international literature was also searched using “Google Scholar”. The publication period of the literature was set from 2011 to 2022, and bibliographic information was included, on the basis of the following steps. First, duplicate data were sorted, and selection and exclusion criteria were applied based on the article titles. Second, selection and exclusion criteria were applied based on the abstracts. When it was difficult to select a document only based on the abstract, the full text was searched and confirmed. Only data from studies or reports from public institutions were considered. Through this process, 80 domestic studies and 237 international studies were primarily searched. Third, the studies for the final analysis were selected through the title and abstract. The subjects of the selected literature were “UD facilities”, and the subjects of interest were “evaluation” and “guidelines”. The context of the literature was the evaluation criterion for UD facilities.
The studies in the second round were classified into 24 domestic and 64 international studies, and the researchers reviewed the suitability of the literature for the final analysis. We selected 14 studies: 9 related to UD facilities in Korea [16,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30], 3 related to Korea’s inclusive design sports facilities [31,32,33], and 2 concerning overseas facilities based on UD and inclusive design [12,34]. The research team carefully read the collected literature and examined the content judged to be relevant to this study.
2.2.3. Delphi Technique
- First Delphi survey
The first Delphi survey allowed the panel to freely describe their answers to a subjective question that enquired about the factors to be considered when designing a sports facility for people with disabilities considering the UD. In addition, the factors to be applied first to the seven UD principles were selected.
- Second Delphi survey
The second Delphi survey was a multiple-choice questionnaire regarding the 50 sub-factors of the 13 criteria obtained when considering the UD for physical education facilities through the first Delphi. In addition, for the 50 sub-factors, elements to be added or deleted were indicated. Mean, standard deviation, convergence, agreement, content validity, and reliability were analyzed.
2.2.4. Expert Interviews
Criteria for interpreting the convergence, mean, standard deviation, agreement, content validity, and reliability values obtained through the Delphi surveys were established. Whether to converge, modify, or delete each sub-factor was discussed (Table 2).

Table 2.
Evaluation indicators for determining the sub-factors.
2.2.5. Data Analysis
The collected data were analyzed using mean, standard deviation, median, minimum, maximum, interquartile range, concordance, convergence, and content validity using SPSS for Windows version 12.0 and Excel. The data were analyzed by criterion, through intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs). The benchmark mean and standard deviation were set to <3.50 and 1.0, respectively [35]. The degree of agreement and convergence level were set at 0.75 or higher and 0.50 or higher, respectively [36]. The content validity standard was set to 0.37 or higher, since the number of Delphi panelists was 21. The ICC suggested relatively stable values when the number of samples was small [37]. In general, the reliability index of the ICC was judged to be very high, relatively high, moderately high, and reasonable if it was 0.80 or more, 0.60 or more, 0.40 or more, and 0.20 or more, respectively [38].
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search Results
Nine studies related to UD facilities in Korea [16,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30], three studies related to Korea’s inclusive-design sports facilities [31,32,33], two studies concerning overseas UD and inclusive design [12,34], and the elements of the evaluation indicators, such as background and necessity, goals, scope, and principles of the introduction of UD facilities, were reviewed. The literature review results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Literature search results.
3.2. Delphi Survey Results
3.2.1. First Delphi Survey
Through the first Delphi survey, the elements to consider for the evaluation index for sports facilities for people with disabilities considering a UD were set. Thirteen criteria (gymnasium, accessibility, gym finishing material, stairs, elevator, corridor, lobby, entrance, reception desk, toilet, shower changing room, ancillary facilities, and common facilities finishing material) and 50 sub-factors were derived. The criteria were primarily classified into “living space” and “common space.” The living room space was defined as “factors of movement,” and the common space was defined as “movement and passage” and “incidental service.” The detailed results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Criteria and sub-factors of the first Delphi survey.
3.2.2. Second Delphi Survey
The second Delphi survey confirmed the criteria and sub-factors of the evaluation indicators by examining the composition of the evaluation index for physical education facilities for people with disabilities, considering the UD derived from the first Delphi survey, using a five-point Likert scale.
The mean values and standard deviation values of the indicators were confirmed. When the five-point Likert scale was used in most previous studies, items with an average value of <3.50 and a standard deviation >1.00 were removed. The values of the mean and standard deviation were converged for all sub-factors. Second, the degree of convergence and the agreement were analyzed to refine the sub-factors. For the third-order item refinement, the content validity was less than the standard values for only one sub-factor item (no. 9). In the reliability verification, the index of the ICC was confirmed. The value of the ICC result was reliable, as for all items, it was 0.20 or higher. Table 5 provides the details showing the suitability of the evaluation index according to the Delphi survey.

Table 5.
Criteria and sub-factors of the Delphi evaluation index.
3.3. Results of the Expert Meeting
An expert meeting was held to confirm the contents of the evaluation index for sports facilities for people with disabilities considering the UD. The sub-factors of the guard line were evaluated according to the convergence criteria set by the panel.
One sub-factor fell short of the standard and was deleted. Therefore, as shown in Table 5, an evaluation index based on 13 criteria and 49 sub-factors for sports facilities for people with disabilities considering the UD was finally confirmed.
4. Discussion
This study developed an evaluation index for sports facilities for people with disabilities considering the UD. Opinions on what factors should be considered when evaluating sports facilities based on the seven UD principles were collected and analyzed through an expert panel via the Delphi method.
The results revealed 3 median criterion factors and 13 lower criterion factors to consider for an evaluation index for sports facilities to which the UD is applied. Specifically, important reference elements are first, a living space for exercise that can be accessed safely and easily; second, a common space for the purpose of movement and passage that can safely provide convenience of movement; and, third, a common space for the purpose of promoting incidental services and social functions.
Space classification according to the general building law includes living space for a certain purpose and common space for temporary use [39]. According to these classification criteria, this study classified three median criteria—factors of movement, movement and passage, and incidental service—and further derived 13 sub-criteria.
First, the main reference factor living space is a space used for the original purpose of exercise owing to the nature of the gym, and the lower reference factors were classified into gymnasium and accessibility. Sports and leisure facilities should be designed to support and encourage the participation of people with mobility and disabilities in physical and social activities [40]. In particular, in the case of school sports facilities, the effectiveness of physical education should be increased through a redesign based on the UD, so that young students can access and use them more easily [41]. To emphasize the social value of sports and leisure programs that can strengthen social solidarity [42], the local residents’ use of public sports facilities should be promoted.
Owing to the nature of the living room space for exercise, sports facilities should be planned considering the users’ body types, physical strength, audience viewership, spatial diversification, safety, and convenience. Older adults’ health status and exercise ability should be considered. In addition, older adults’ vision requires consideration. The deterioration of older adults’ color discrimination ability hinders their ability to accurately perceive space, shape, and distance [43]. Thus, the wall colors, elevator locations, and format of information boards are important.
In contrast, difficulty in access to facilities is an environmental barrier to participation in sports [44]. A study reviewed physical activity restrictions perceived by children with disabilities and reported that inappropriate facilities and access limitations were barriers. Simultaneously, the accessibility of facilities should be improved to promote participation [45]. In particular, according to the UD principle “Size and Space for Access and Use,” non-disabled people and wheelchair users should have a comfortable access to any place. Furthermore, accessibility to facilities should be considered to make access easier for women wearing skirts or for small users [46]. In addition, the facility design to increase accessibility, such as those designs reported to have a significant effect on physical activity behavior [47], can have a positive influence on the use of public sports facilities as well as on the health of participating individuals.
Second, public spaces were classified into five reference sub-factors under movement and passage: stairs, lifts, corridors, lobby, and entrance doors. It is possible to reduce unnecessary movement and reduce the effort required, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of exercise for those who visit gyms.
Lobbies and corridors often contain slippery marble and granite finishes. Hence, it is necessary to use materials so to improve users’ stability. In particular, it was reported that it was necessary to consider the width of facilities and the presence of safety handles [48]. To prevent stair accidents, anti-slip materials must be considered.
Safety-related objects, such as handles to grip to avoid falls, should be easy to operate regardless of users’ age, knowledge, or ability. They should not cause unnecessary burdens on the user. Furthermore, their use should be simple and intuitive [49]. In addition, the lobby should be easy to use for everyone. Hence, the access distance from other spaces should be short, and all locations should be clearly marked [50].
Ultimately, for all users, including wheelchair users, people using crutches, and older adults with reduced mobility, the presence of non-skid floors and the installation of identifiable signs, pathways, and handrails will help prevent falls. Gyms need to be designed so they can be used by people of all ages and sexes, rather than by excessively considering their interior design. In particular, since stairs, passages, lobbies, and elevators are common spaces for movement, it is important to choose a design that can minimize the occurrence of minor safety problems and provide convenience.
Third, common space was classified into five sub-factors: reception desk, toilet, shower and changing room, ancillary facilities, and closing of public facilities under ancillary services. Ancillary facilities are additional facilities that satisfy various needs by providing convenient further services to the users in addition to the essential exercise service of public sports facilities. From this viewpoint, ancillary facilities within a public gym can be used as a space to promote social activities. In particular, interaction between users can promote social cohesion [20]. A study [51] reported that shower and convenience facilities should be expanded in sports facilities for people with disabilities. In addition, the necessity of ancillary service facilities in public spaces was also mentioned.
The reason the space for ancillary services in public sports facilities is increasing is that these supplementary service facilities are gradually expanding to meet the needs of users. In contrast, it is generally difficult to safely use existing outdoor playground facilities, as they do not provide countermeasure against physical danger. This was shown to be true also for older adults who cannot move for a relatively long time since these facilities do not offer any rest space [52].
Public sports facilities applying the UD principles will be suitable for all people. They will allow fair use and flexibility of use, provide recognizable information and simple and intuitive space, demand a low physical effort, and offer a suitable space, ensuring increasing accessibility and use [20].
This study has some limitations. The scope of the research was limited, and the research method lacked objectivity. Since the opinions of 13 experts were analyzed using the Delphi research method, it is difficult to generalize the results. Therefore, it is necessary to validate the evaluation index. However, the main strength of this study is the application of the seven UD principles and a proposal of how they can be used to promote social integration and equity.
5. Conclusions
This study was conducted to develop sub-factors and define criteria for an evaluation index of sports facilities for people with disabilities considering the UD, through an expert panel via the Delphi method. The criteria for the evaluation index developed through a literature review and Delphi surveys were, first, “factors of movement” and “living space”, which consisted of “gymnasium”, “accessibility”, and “gym finishing material”. Furthermore, “common space movement and passage” consisted of “stairs”. “elevator”, “corridor”, “lobby”, and “entrance”. “Incidental services of common space” consisted of “reception desk”, “toilet”, “shower changing room”, “ancillary facilities”, and “common facilities’ finishing material”. Hence, 49 sub-factors were derived.
The recommendations of this study are as follows. First, the developed evaluation index should be applied by the operators and users of public sports facilities used by both people with disabilities and those who are unemployed, and validation work should be conducted. Second, as a follow-up, guidelines for applying the UD to various sports facilities for people with disabilities should be developed. Third, it is necessary to discuss financial-related matters concerning the installation of facility equipment. Lastly, awareness education programs on whether UD sports facilities should be built and used by everyone without inconvenience should be developed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.Y., S.-W.J. and A.O.; methodology, A.O.; software, S.-W.J.; validation, E.Y., S.-W.J. and A.O.; formal analysis, S.-W.J.; investigation, A.O.; resources, S.-W.J.; data curation, S.-W.J.; writing—original draft preparation, A.O.; writing—review and editing, E.Y.; visualization, A.O.; supervision, E.Y.; project administration, A.O.; funding acquisition, E.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research project was supported by the Sports Promotion Fund of Seoul Olympic Sports Promotion Foundation from Ministry of Culture, Sports, and Tourism of the Republic of Korea (R&D/1375026989).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Gachon University (no. 1044396-202007-HR-125-01).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent was obtained from the participants to publish this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hwang, M.J. Welfare of the aged and community care in an aging society. J. Public Soc. 2020, 10, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Democratic Party of Korea. Half of the Disabled People Aged 65 or Older. Customized Policies Are Urgently Needed. 21 October 2020. Available online: https://www.fnnews.com/news/202010210944037277 (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Orkwis, R. Curriculum Access and Universal Design for Learning; ERIC Clearinghouse on Disabilities and Gifted Education: Arlington, TX, USA, 1999; ERIC/OSEP Digest Number E586. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.Y. Universal Design in Apartment Bathroom; Korean Studies Information Co., Ltd.: Paju, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Satoshi, K. From barrier-free to universal design: An international perspective. Assist. Technol. 2010, 10, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibrock, C. Beautiful Universal Design: A Visual Guide; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Steinfeld, E.; Maisel, J.L. Universal Design: Creating Inclusive Environments; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Preiser, W.; Smith, K.H. Universal Design Handbook, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- NC State University, The Center for Universal Design. The Principles of Universal Design. 1997. Available online: https://projects.ncsu.edu/ncsu/design/cud/about_ud/udprinciplestext.htm (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Story, M.F. Principles of Universal Design. Universal Design Handbook. 2001. Available online: https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/40536722/0071629238Universal-with-cover-page-v2.pdf?Expires=1664821993&Signature=LGu3yTWya7pTQPP4yu9OwAHqrrBqpm2QDK46sbt7DiBMVTTngcqGa8esI0vhMergR3n1Lcn2UjJbhdwjIWv2941NiL8DP79KHNv8c0Yj7Ld2RITmHlSLROwe-R8BhoDh0zi~kAiTrTDG5y93r2H6Zx0Q26VL961H3gm-OYhWyqQH9ZDIMifKJsc7v7vM0b4FDVKbU~BtgRRYgcLeMEyxJ0MFvZ44WAZzJDXsEEUo339n9m6KYy4mZ6do04DXyEQ2s7AZeTf6Ljt6hWQDuoC0LrjpMVKjHO6qinTdjCBW0r33UBHEabJO9peqkdcudSAwiEx8NcuSHY2prtjudKGYkQ__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA#page=58 (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Mueller, M. Universal Service: Competition, Interconnection, and Monopoly in the Making of the American Telephone System; American Enterprise Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Disability Sport NI. Disability Sport NI has Produced a Series of Design & Management Guidelines 1–4. 2016. Available online: https://www.dsni.co.uk/sports-facility-access/design-management-guidelines (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism. Pyeongchang Paralympics’ Impression, Promoting Sports for the Disabled. 14 August 2018. Available online: https://www.mcst.go.kr/kor/s_notice/press/pressView.jsp?pSeq=16824&pMenuCD=0302000000&pCurrentPage=28&pTypeDept=23&pSearchType=01&pSearchWord= (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Yi, E.S.; Oh, A. Analysis of demands on the application of universal design for sports facilities for the disabled. Korean J. Adapt. Phys. Act. 2021, 29, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism. Contest for 25 Bandabi Sports Centers in 2021. 25 June 2020. Available online: https://www.mcst.go.kr/kor/s_notice/press/pressView.jsp?pSeq=18103&pMenuCD=0302000000&pCurrentPage=98&pTypeDept=&pSearchType=01&pSearchWord= (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Han, C.H. Development of evaluation indicators for the space environmental universal design of Seoul welfare facilities. J. Commun. Des. 2015, 53, 20–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.H.; Chang, K. Developing a measure of user-perceived universal design for sport facilities. S. Afr. J. Res. Sport Phys. Educ. Recreat. 2018, 40, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock-Shangraw, R. Creating inclusive youth sport environments with the universal design for learning. J. Phys. Educ. Rec. Danc. 2013, 84, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangaard, S.; Ryhl, C. Vandhalla—A sport centre and a successful example of first-generation universal design. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2016, 229, 243–245. [Google Scholar]
- Nurdiani, N.; Katarina, W.; Grestio, I. The universal design approach on sport center in Jakarta to create livable public facilities. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 426, 101006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fatorić, S.; Seekamp, E. Are cultural heritage and resources threatened by climate change? A systematic literature review. Clim. Chang. 2017, 142, 227–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyeonggi Provincial Government Gyeonggi-do Public Design Guidelines. 2010. Available online: https://memory.library.kr/items/show/50320 (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Gyeongsangnam-do Office. Universal Design Guidelines for South Gyeongsang Province. 2020. Available online: https://www.cng.go.kr/country/00003681.web?gcode=1003&idx=520127&amode=view& (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Park, C.H.; Seong, K.C. Analysis of priority recognition between space consumers and producers on the public space to apply universal design. Des. Converg. Study 2020, 19, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoul City Hall, Guidelines for the Integration of Universal Design in Seoul. 2017. Available online: https://news.seoul.go.kr/culture/archives/80023 (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Seong K-C. A study on application of universal design in school building. J. Korea Inst. Healthc. Archit. 2018, 24, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Seong, G.C.; Chae, C.G. Research a study on the concept of architectural planning in consideration of people with disabilities. J. Korea Inst. Healthc. Archit. 2003, 9, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yeunsook, L.; Changhoun, A.; Dongjoo, L. Aging-friendly outdoor exercise environmental design guideline with universal design. KIEAE J. 2012, 12, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Tourism Organization. Establishing Guidelines for barrier-Free Tourism Facilities and Services. 2015. Available online: https://datalab.visitkorea.or.kr/site/portal/ex/bbs/View.do?cbIdx=1129&bcIdx=13289&cateCont=tlt02&searchKey=&searchKey2=&tgtTypeCd (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- PyeongChang Organizing Committee for the 2018 Olympic & Paralympic Games; POCOG Accessibility Manual: Seoul, Korea, 2022.
- Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism. Press Release: Pyeongchang Paralympics’ Impressions and Revitalization of Sports for the Disabled. Attachment Data 1. Measures to Promote Sports for the Disabled for Distribution. 14 August 2018. Available online: https://www.mcst.go.kr/kor/s_notice/press/pressView.jsp?pSeq=16824&pMenuCD=0302000000&pCurrentPage=28&pTypeDept=23&pSearchType=01&pSearchWord= (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Seong, K.C.; Chai, C.G.; Kang, T.S. A study on the areal analysis of the sports center for the disabled user. J. Korea Inst. Healthc. Archit. 2008, 14, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tokyo Metropolitan Sports Center for Persons with Disabilities. Facility Information. Available online: https://tsad-portal.com/mscd/facility/information (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Kim, B.W. Delphi Analysis Method; Kim’s Information Strategy Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2015; ISBN 9791170120940. [Google Scholar]
- Lawshe, C.H. A quantitative approach to content validity. Pers. Psychol. 1975, 28, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonett, D.G. Sample size requirements for estimating intraclass correlations with desired precision. State Med. 2002, 21, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, D.Y.; Seong, K.Y. The Detail of Architecture Plan; Seowoobooks: Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roberta, C.; Masashi, K.; Olga, P.L. User-environment interaction: The usability model for universal design assessment. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2021, 4, 55–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ackah-Jnr, F.R.; Danso, J.B. Examining the physical environment of Ghanaian inclusive schools: How accessible, suitable and appropriate is such environment for inclusive education? Int. J. Incl. Educ. 2019, 23, 188–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, R.D. Bowling alone: America’s declining social capital. J. Democr. 1995, 6, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmedi, D.; Becker, S.; Heyl, V.; Wahl, H.W.; Himmelsbach, I. Behavioral consequences of age-related low vision. Vis. Impair. Res. 2002, 4, 15–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaarsma, E.A.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Geertzen, J.H.B.; Dekker, R. Barriers to and facilitators of sports participation for people with physical disabilities: A systematic review. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport 2014, 24, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, N.; Synnot, A.J.; Barr, M. Perceived barriers and facilitators to physical activity for children with disability: A systematic review. Br. J. Sport Med. 2012, 46, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.J. User-Centered Universal Design Method and Case Study; Idambooks: Paju, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, L.J.; Dunsiger, S.I.; Marcus, B.H. Validation of walk score for estimating access to walkable amenities. Br. J. Sport Med. 2011, 45, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhou, H.; Tian, L.; Hwang, Y.S. Study on universal design evaluation applied to indoor public spaces in public libraries. Korean Inst. Inter. Des. J. 2021, 23, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, Y.S. A study on the evaluation of universal design features in complex cultural space in urban regeneration projects. Korean Inst. Intert Des. J. 2021, 30, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kang, A.L. The assessment of common space elderly care facilities applying the universal design principle: Focused on the city elderly care facilities in Seoul·Gyeionggi area. J. Korean Soc. Des. Cult. 2012, 18, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Roh, H. Analysis of improvement factors and relative importance about Korean sports training center for the disabled. Korea J. Adapt Phys. Act. 2016, 24, 67–82. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Kweon, Y. A study on the need for senior playground based on evaluation of universal design index. J Korea Inst. Spat Des. 2021, 16, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).