Abstract
In this paper, we present a fast and accurate numerical approach applied to specific American-style derivatives, namely American power call and put options, whose main feature is that the underlying asset is raised to a power. The study is set in the Black–Scholes framework, and we consider continuously paying dividends assets and arbitrary positive values for the power. It is important to note that although a log-normal process raised to a power is again log-normal, the resulting change in variables may lead to a negative dividend rate, and this case remains largely understudied in the literature. We derive closed-form formulas for the perpetual options’ optimal boundaries and for the fair prices. For finite maturities, we approximate the optimal boundary using some first-hitting properties of the Brownian motion. As a consequence, we obtain the option price quickly and with relatively high accuracy—the error is at the third decimal position. We further provide a comprehensive analysis of the impact of the parameters on the options’ value, and discuss ordinary European and American capped options. Various numerical examples are provided.
Keywords:
American power options; optimal boundaries; perpetual options; finite maturity options; capped options MSC:
35R35; 35Q91; 60G44; 91G20
JEL Classification:
C41; C61; G12; G13
1. Introduction
American-style derivatives, especially American-style options, are some of the most traded instruments in modern financial markets. Their main feature is the holder’s right to early exercise, which makes them useful both for hedging purposes and for additional profits. However, the existing variety of financial risks has motivated investors to seek new opportunities to protect themselves from market uncertainty. Thus, in recent years, in addition to the large number of non-ordinary (exotic) options, many new instruments and financial strategies have emerged, inspiring researchers to explore their properties and invent methods for their evaluation. The following is a non-exhaustive list covering some of the most recent developments in the field: American options under stochastic volatility []; numerical evaluation of options under Heston’s model []; generalized American derivatives leading to one- or two-sided optimal stopping problems [,,]; financial instruments leading to first-exit tasks [,,]; American put options written on zero-coupon bonds []; novel numerical methods for pricing American options [,,,]; a projection and contraction approach for pricing different kinds of American options [,]; critical analysis of Monte Carlo simulations for pricing American options []; vulnerable American options without maturity constraints []; financial derivatives leading to double continuation regions [,]; the hedging task for American options in the presence of transaction costs []; acceleration clauses reducing the option’s life []; American barrier options in light of the first time digitals []; a Monte Carlo simulation approach for pricing American time-capped options [].
We add to this growing literature by investigating and proving new properties of American power options. Unlike ordinary options, the underlying asset of a power option is raised to a power, so that investors may hedge different non-linear financial risks thanks to the non-linear payoff function, see, e.g., []. Their utility can be understood as follows: an ordinary option pays its holder the overprice (call) or the underprice (put); if the investor wants relatively larger compensation when the underlying asset falls deeply in-the-money, then powers greater than one can provide such payoffs—the higher the power, the greater the increase in payment. On the other hand, the option’s writer may prefer to pay proportionally less when the underlying asset is deeply in-the-money, and powers less than one lead to such payoffs—the lower the power, the smaller the increase in payment.
Power options are actually traded financial instruments and have been studied in some detail under different assumptions. For example, European-style power options in the Black–Scholes setting are investigated by [], while stochastic volatility models are examined by [,,], and some power options written on assets driven by Lévy jump processes and under Heston’s assumptions are explored in []. The authors in [] consider European-style power options under uncertain differential equations, whereas [,] apply the Mellin transform method for pricing American power put options. More recently, [] has presented a fast and efficient finite difference method under the non-dividend assumptions, and [,] have examined the power version of both European and American exchange options.
Our study of American power options is based on the hypothesis that the underlying asset is described by a log-normal process, assuming continuously paid dividends. Although the power of a log-normal process is again log-normal, some difficulties arise. In particular, if the original model is driven by the risk-free rate r, volatility , and dividend , then raising it to the nth power leads to a model with parameters , , and . Note that the initial and the new risk-free rates have to be equal due to some risk-neutral considerations, which implies that for some parameter values the dividend rate is negative. Therefore, it is not possible to study power options through a simple change in parameters, which explains why these models remain largely understudied (we refer to [,] for some examples).
Our approach for dealing with dividends is to introduce an additional discount factor, following []. Using this transformation, we obtain the shape of the optimal regions and the corresponding early exercise boundaries. In particular, we prove that if a point is optimal for a call/put option, then all points above/below it are also optimal. This suggests that the state space can be divided into two parts by a single boundary, namely the early exercise or optimal boundary, so that for a call/put option, immediate exercise will be optimal for all points above/below it. Moreover, we show that the boundary is increasing/decreasing with respect to the time to maturity for call/put options. A well-known fact for ordinary call options is that early exercise is never optimal when there are no dividends, i.e., the additional discounting factor is zero. In that case, the optimal boundary is infinitely large, which we show is also true for power call options, but only for powers greater than one and for small enough discount factors (dividends). We prove that this limit is zero when the power is equal to one, and finite when the power is strictly less than one. In addition, we study perpetual options for which there are no maturity constraints and show that the optimal boundary is time-independent, deriving closed-form expressions for it and for the fair option price.
We further consider the problem of approximating the optimal boundary when the time horizon is finite. We first obtain its value when the time to maturity tends to zero, and then derive the value at each subsequent node in a time partition that maximizes the holder’s financial utility. It turns out that three or four points are quite enough for a precise approximation, since the estimated option price is very close to the true one, with error appearing in the third decimal place. For greater accuracy, we may approximate the boundary on a denser grid, in which case the free boundary differential equation that describes the American option pricing task can be viewed as a boundary value problem stated in a known region, to which we apply a modification of the Crank–Nicolson finite difference approach. We provide various numerical experiments to illustrate and validate the obtained theoretical results.
Finally, we discuss the so-called capped call/put options, where exercise cannot take place at a price higher/below than some predetermined level. It turns out that results for capped non-power options carry over to power options, e.g., the optimal boundary for a capped power call/put option is the minimum/maximum of the boundary of the corresponding uncapped option and the cap level.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we define our model and derive the shape of the exercise regions. Perpetual options are examined in Section 3, while the corresponding finite maturity options are considered in Section 4. We present several numerical examples in Section 5. Some evidence for the S&P 500 Index during the 2008 global financial crisis is discussed in Section 6. Supplementary results are collected in Appendices Appendix A–Appendix C.
2. Exercise Regions
Suppose that the underlying asset is modeled by the log-normal process
under the filtered probability space , where is the risk-neutral measure and defines a Brownian motion. The constant r is the risk-free rate, and we denote by the additional discount factor. We assume that , but negative values for r are still possible. We denote by the infinitesimal generator of the process (1) and by the associated differential operator:
Let be the maturity date, and denote by the power to which the underlying asset is raised. The payoff functions are given by
where we view the constant K as a strike. Sometimes, we shall parametrize N with respect to the time to maturity, , and we shall write instead of . This is possible due to the Markovian nature of process (1), which allows us to assume that the initial time is zero. We will denote the option price by or , respectively. The proposition below states that we can think of the additional discount factor as a dividend rate.
Proposition 1.
By an -model, we shall mean a financial market model that consists of an underlying asset paying continuous dividends at rate δ, a risk-free asset with rate of return r, and an option discounted by the factor λ. Under these assumptions, an -model is equivalent to an -one.
Proof.
See Proposition 2.3 in []. □
Remark 1.
Proposition 1 shows that the conditions and lead to both a positive risk-free rate and a non-negative dividend rate for a regular option model (i.e., without discounting).
The price function of an American power option can be written as
where the supremum is taken over , the set of all stopping times with values between t and T. Thus, we can define the associated optimal points as follows:
Definition 1.
A point is optimal for the holder if .
Definition 1 formalizes mathematically the idea that it is optimal for the holder to exercise the option at time t at a spot price x if the amount he will receive, , is greater than the financial outcome of any other strategy (stopping time), . On the other hand, we will say that the point is optimal with respect to the time-to-maturity parametrization when the point is optimal with respect to the original one. A necessary condition for optimality is presented in the following proposition.
Proposition 2.
If a point is optimal, then .
Proof.
Note that the inequality is equivalent to the variational inequality
which holds in the optimal region. □
The shape of the optimal regions is obtained in the following proposition.
Proposition 3.
Suppose that is an optimal point. If we have a call option and , then the point is also optimal. Otherwise, if we have a put option and , then the point is also optimal. Moreover, the optimal boundary of a call option increases with respect to the time to maturity, while the put one decreases.
Proof.
We will consider only the put case, since the call one is symmetric. First, note that if a point (parametrized with respect to the time to maturity) is optimal, then is also optimal, for every . This is true because longer maturities provide richer sets of financial strategies for the option’s holder.
Suppose now that, for some , the point is optimal, but is not. Let be the first hitting moment of x by the asset, starting from y. For an arbitrary stopping time , we shall denote by the strategy . This strategy gives no worse financial outcome than because is an optimal point for all . Also, for every u such that , because for such sample paths , the inequality holds, see Lemma A1. It now follows from Dynkin’s formula that
Hence, immediate exercise is the holder’s best strategy. This completes the proof. □
Given Proposition 3, we conclude that the state space can be divided into two connected parts—all points in the first set are optimal, while in the second set keeping the option is preferable. Moreover, these sets are separated by a time-function, so that for call/put options the optimal one is above/below it. This function is also known as the optimal boundary and we will denote it by , where is the time to maturity.
Next, we obtain the values of the optimal boundary near the expiration as well as in the perpetual case, i.e., and . Later, we will use these values to approximate the whole boundary.
2.1. The Boundary Value at Maturity
First, we discuss the boundary value when . An important role is played by the constant L, defined as
The following two propositions determine the initial boundary value.
Proposition 4
(Call). Consider a call option. If , then . Otherwise, if , then
Proof.
Applying the differential operator defined in (2) to the call payoff above the strike, gives
If , then , so it follows from Proposition 2 that . Suppose now that . Obviously, because the call option pays nothing below the strike. On the other hand, by Proposition 2. Suppose that there is a point belonging to the continuation region near maturity. Using that for all x in this set and the fact that solves the Black–Scholes equation, , we get
The contradiction completes the proof. □
Proposition 5
(Put). Consider a put option. If , then . Otherwise, if , then
Proof.
In this case, the operator becomes
The largest x for which is given namely by (5). The rest of the proof is identical to that of Proposition 4. □
Corollary 1.
The following statements hold.
- For a call option, if , then early exercise is never optimal, which is possible only when . If and , then .
- For a put option, if and , then .
Proof.
The corollary is a consequence of Lemma A2 and Propositions 3, 4 and 5. □
Recall that corresponds to the case of an ordinary American option. Then is equivalent to and leads to the well-known fact that early exercise of a call is never optimal in the absence of discounting (dividends). On the other hand, if (equivalently, ), then if and only if , so we have whenever . Similarly, for put options, we have whenever . See Propositions 3.4 and 3.5 in [] for more details.
2.2. Impact of the Power Value
Next, we investigate the behavior of the initial point of the optimal boundary as a function of the power n. To that end, let us define the constants , , , and by
We have the following dependence on the power value.
Proposition 6.
Define .
- If , then
- (a)
- Call options: for , and for .
- (b)
- Put options: for every n.
- If , then
- (a)
- Call options: for , for , and for .
- (b)
- Put options: for , and for . The limit point is
Proof.
Consider L, defined in (4), as a function of the power n, i.e., . Then L is a quadratic function of n with a positive first coefficient, , and by Lemma A3. Hence, for , and for . Let us define
whose root is just . Then , since
Therefore, . Note that the condition is equivalent to . Combining Propositions 4 and 5 with the second statement of Lemma A2, we establish the behavior of the boundaries. Finally, (7) follows from
□
Remark 2.
Recall that the discount factor λ can be viewed as a dividend rate. For power call options, if , the first statement of Lemma A2 shows that , so early exercise can be optimal. Otherwise, if , then this is true only for sufficiently large values of λ, namely for . If we have an ordinary option, i.e., , then we arrive at the well-known fact that premature exercise can be optimal only for .
2.3. Capped Options
It turns out that the results for ordinary American capped options can be extended to power options. Letting F be the cap level, the payment functions (3) for capped options become
where ∨ and ∧ denote the maximum and minimum, respectively. The main result is contained in the following proposition.
Proposition 7.
Denote the optimal boundary of the capped option by . For put options, ; otherwise, for call options, .
Proof.
We will look only at the put case, since the call one is symmetric. The proof of Proposition 3.1 in [], which considers non-power options, i.e., , is divided into four parts, depending on whether the point satisfies (A) , (B) , (C) , or (D) . We can prove the present statement in the same way in the first three cases. However, the proof of the fourth case, which is identical only when or, equivalently, when and , differs precisely in Equation (3.8) from [], which for power options should be
where denotes the minimum between the first hitting time of F and the maturity date T. Note that we have used Proposition 5 and Dynkin’s formula above, keeping in mind that for , since . □
In the following, we will consider only uncapped options.
2.4. European Options
By Proposition 4, non-negative values of L make it unprofitable to exercise a power call option prematurely, so it turns into a European-styled option. Non-dividend European power options have been studied by [], while we consider the general case below.
Proposition 8.
Proof.
Let be the measure, defined by the Radon–Nikodym derivative
Obviously, the -dynamics is and the -Brownian motion is defined by
Hence, the call price can be derived as
We finish the proof by changing the measure from to and keeping in mind the form of the -Brownian motion in (8). The put option can be evaluated analogously. □
We shall prove a result that has an analogue for ordinary American options, namely that early exercise of an American call is never optimal when there are no dividends (). First, we need the following lemma:
Lemma 1.
The process is a martingale, where L is given by (4).
Proof.
The lemma follows from the fact that . □
Proposition 9.
If , then early exercise is never optimal for an American power call option, making it European-styled.
Proof.
Suppose that the opposite is true, that is, there exists an optimal point for a power call option with . Let be an arbitrary stopping time with values between t and T. Using Lemma 1 and the inequalities and , we obtain
The contradiction completes the proof. □
Remark 3.
Proposition 9 is consistent with the conclusions of Propositions 3 and 4.
3. Perpetual Options
We now consider options without maturity constraints. The first results look at power call options.
Proposition 10
(Call). If , then early exercise of a power call option is never optimal. Moreover, the option price is when , and when . If , then the early exercise boundary is given by
and leads to the price
when . If , then the price is .
Proof.
Suppose that , the initial asset price is a small enough value x, and the option maturates when the underlying asset hits the level ; we will denote this moment by . Note that can be viewed as the first hitting time of the level for a Brownian motion with drift , where and are given in (6). Also, in (6) can be rewritten as
Regarding the price, we have
Obviously, the last term tends to zero. From (A4), we see that the expectation in the second term tends to infinity as . Hence, the second term also tends to zero, since this expectation is multiplied by and , see also Theorem 3.2 in []. Keeping (A8) in mind, we conclude that the price can be written as
and its derivative with respect to c is given by
By Lemma A3, , so the price function (12) achieves its maximum for c given in (9). The formula (10) is obtained by plugging (9) into (12).
The case was discussed in Proposition 9. In addition, Lemma A4 together with Propositions A1 and A6 shows that the second term in (11) is zero also in this case. Hence, the price is again given by (12). Here, however, the derivative (13) is always positive due to Lemma (A3); therefore, the optimal boundary must be , confirming that early exercise of a call is never optimal when .
Suppose that . The option price can be calculated as the limit of (11). By Lemma A3, , so the first term in (11), which is given by (12), tends to infinity. Since the second term is non-negative and the third one is zero, we conclude that .
The only case left to consider is or, equivalently, . In this case, the first term in (11) tends to . Using Proposition A1, we see that the second term becomes
where is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution. By Lemma A4, its arguments tend to , as , because . Therefore, (14) tends to zero. We complete the proof by observing that the third term in (11) is also zero. □
We now turn to put-style options.
Proposition 11
(Put). The early exercise boundary of a put option is
which leads to the price
when . If , then .
Proof.
Assume that the initial asset price is a sufficiently large enough x, and that the option maturates at the first hitting of c, where . The price function is given by
Similar arguments to the ones in the proof of Proposition 10 show that the second and the third term in (17) are zero whether or . In this case, however, we have to use (A3) instead of (A4). The first term can be evaluated using (A9), so that (17) becomes
and its derivative with respect to c is given by
Thus, we can easily check that the price (18) achieves its maximum for the boundary given by (15), which leads to the price (16) when . □
Corollary 2.
The optimal boundary has the following asymptotic behavior as a function of n.
- The call optimal boundary tends to , as .
- The put optimal boundary tends to , as , and to the strike, as .
4. Finite Maturities
In this section, we consider options with finite maturities and try to approximate the entire optimal boundary. When working on a denser grid, the free boundary equation that describes the option price turns into a boundary value problem in a known region, and we present a Crank–Nicolson finite difference approach to solve it.
4.1. Optimal Boundary
Let us divide the time interval into l sub-intervals. Thus, we shall evaluate the optimal boundary at the time grid using exponents of continuous piecewise linear functions, . We denote the values at the grid nodes by . Let x be the initial value of the underlying asset, and the first hitting time of the boundary. For a call option, we exclude the case , where the optimal boundary is infinitely large, and assume that x is small enough. Conversely, for a put option, we assume a large enough value for x. We can view the stopping time as the first hitting time for a Brownian motion of the function,
where
if the hitting happens in the interval . Under these assumptions, the call price function is given by
where
and the put price function is given by
The expectations in (20) can be obtained from Propositions A4 and A5. On the other hand, call pricing leads to an upper hitting problem, so the expectations in (19) can be derived by symmetric arguments, see also [].
We approximate the optimal boundary backwards. Let us first consider a put option. The level corresponds to the level at maturity, so its value can be obtained from Proposition 5. Suppose we know all the values after some moment m, i.e., . Consider the price , defined in (20), as a function of c in the interval . We choose this interval because the optimal boundary decreases with respect to the time to maturity. Let be the value of c for which the function achieves its maximum for a given initial point x. Then our approximation for the optimal boundary at the previous grid node will be the largest x for which and corresponds to the largest initial point at which immediate exercise is optimal.
The optimal boundary for a call option is evaluated in a similar way, with given in Proposition 4. Note that we only need to consider the case . Now, the function is given by (19), so we maximize it in the interval , since the call boundary increases with respect to the time to maturity. Our approximation is the smallest x for which and corresponds to the lowest initial point for which immediate exercise is optimal.
4.2. Pricing as a Boundary Value Problem
Alternatively, we may approximate the optimal boundary at a denser grid and consider option pricing as a boundary value problem (BVP, hereafter) in a known region. For a call option, the region is and leads to the BVP
For a put option, the region is and leads to the BVP
Note that the continuation region is open from above. It is therefore useful to introduce a sufficiently large enough upper bound where the price function is approximately zero.
4.3. Crank–Nicolson Finite Difference Approach
Equations (21) and (22), which describe the options’ valuation problem, are modifications of the heat equation, which is widely studied in mathematics and physics, and there are several classical finite difference methods for solving it. The explicit algorithm is relatively fast, but it is stable only when the ratio between the time step and the square of the state step is below . Furthermore, the accuracy is proportional to the time step and the square of the state one. On the other hand, the implicit algorithm has the same accuracy but is always convergent. The cost of this feature is the relatively larger computational time due to the emergent linear systems that must be solved at each step. Another widely used method is the Crank–Nicolson approach. The error of this method is significantly smaller, since it is also proportional to the square of the time step. Despite the fact that this approach is only A-stable and not L-stable, its speed and accuracy motivate its use. Moreover, this method is specifically constructed for heat-style equations, which explains its wide application in the field. More precise results in terms of stability and accuracy can be derived from the theory of the classical heat equation, , which in our case is obtained from
where
We present a method for solving the above BVP in a closed region based on the Crank–Nicolson finite difference approach. Let us assume that the lower boundary is and the upper boundary is .
- We divide the space uniformly with M time nodes and N state nodes, and . We denote by the solution at the -th node, where i corresponds to time and j to the state variable. The values are the prices at maturity, while are the initial option prices; note that we work backwards.
- We approximate the boundary at points using the algorithm from Section 4.1. For a call option, corresponds to the upper boundary , while . For a put option, and . Note that we choose to be significantly lower than M in order to reduce computational time. We then estimate the entire boundary using a cubic spline interpolation.
- The terminal condition is incorporated by
- Let us denote by and the boundaries’ values at the grid nodes. Let be the largest j such that , and the smallest j such that . Then for call options, and for put options.
- For a call option, the lower and upper boundary conditions are incorporated byFor a put option,
5. Numerical Results
We present several numerical experiments based on the following parameter values: risk-free rate , additional discount factor , volatility , strike , and power n between zero and two. We assume that the initial asset price is for call options, and for put options.
Figure 1a,b compare the optimal boundaries for different powers: , , , and . The results are given with respect to time t, assuming a maturity of . The first figure relates to call options, while the second figure relates to put options, with perpetual values marked by circles. The values of the constant L, defined in (4), are , , , and , respectively. It turns out that L changes its sign at .
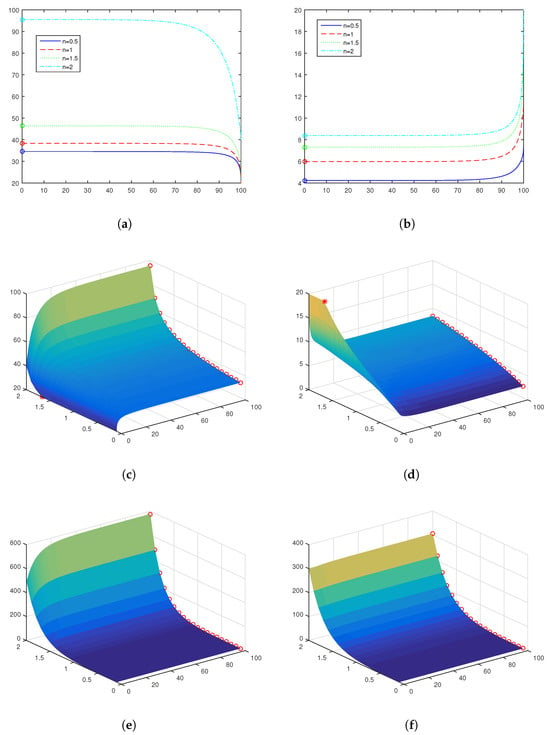
Figure 1.
Optimal boundaries and prices. (a) Call boundaries; (b) put boundaries; (c) call boundary surface; (d) put boundary surface, the red asterisk marks the point at which the initial boundary detaches from the strike; (e) call prices; (f) put prices.
The entire boundary surface can be seen in Figure 1c,d. Note that here we parametrize with respect to the time to maturity. It follows that negative values of L lead to a finite call boundary, which is larger when n increases, and tends to infinity when n tends to the critical value at which L changes its sign, . As shown in Corollary 1 and Proposition 6, the initial boundary detaches from the strike at the point , marked by a red asterisk. Figure 1e,f shows the behavior of the price, with red circles denoting the corresponding perpetual values.
The behavior of the initial and perpetual values of the put boundary is given as a function of the power in Figure 2a. Formula (7) applied to the current parameters implies an initial value of , as , which is marked by a blue point on the graph. We denote with a blue asterisk the level after which the initial boundary coincides with the strike, which occurs at . By Corollary 2, as , the perpetual value becomes , which is plotted by a red circle. The same corollary shows that the limit, as , is the strike.
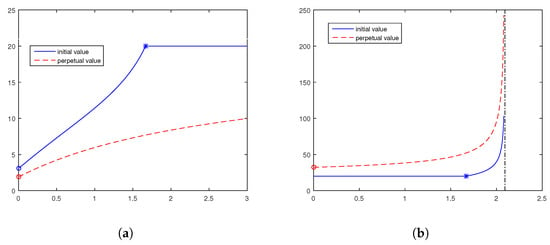
Figure 2.
Optimal boundaries w.r.t the power. (a) Put; (b) call. The levels below which the initial boundary coincides with the strike are marked by blue asterisks.
The behavior of the call boundaries can be seen in Figure 2b. The level below which the initial boundary coincides with the strike is and is marked by a blue asterisk. By Corollary 2, as , the perpetual value becomes . The level at which L changes its sign is and is indicated by the black dash-dotted line. If the power is larger than this value, , then early exercise is never optimal, which means that the boundaries are infinitely large. We can also see that both boundaries tend to infinity, as .
Finally, we compare the speed of our approach with the classical approach by Cox et al. [] based on binomial trees. The computations were performed with the MATLAB 2024a software platform on a 13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-1355U 1.70 GHz computer configuration. Put option prices and time consumption are given in Table 1. The parameters used are , , , , , and . The comparison is made for classical American options (i.e., ), since the binomial tree method is implementable specifically in this case. We execute our algorithm with one, two, three, and four steps. On the other hand, we use binomial trees with time lags of , , , and . We can conclude that our approach is significantly faster with respect to the required accuracy.

Table 1.
American option prices and the computational times.
6. Some Evidence for the S&P 500 Index
We will investigate the behavior of the financial markets in the wake of the 2008 global financial crisis, which began on Sep 15, 2008 with the default of Lehman Brothers. A series of turbulent days followed, which led to outstanding securities falling by nearly ten percent on 29 September, from USD to USD , and the specific reason was the rejection of the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act in the U.S. Congress. For our purpose, we will use the prices of several European-style options on that date as well as on the previous business day, 26 September 2008. These options maturate on 20 December 2008, and the risk-free rate on 26 and 29 September is and , respectively, which are calculated using 13-week Treasury bills. The data set contains 27 call and 31 put options with different strikes for 26 September 2008, and 45 call and 37 put options for 29 September 2008. More precisely, we use the best bid and ask values, and obtain the price by averaging. From these prices, we derive the implied volatilities that characterize the options and apply the approach outlined in this paper to estimate the associated European and American power options. In this way, we can compare the state of the market before and after the shock on 29 September 2008.
The strips for the call and put implied volatilities generated by the ask-bid spread can be seen in Figure 3a,b. The values calculated at the midpoints are given by the solid lines. We can draw several conclusions: first, both ask-bid spreads lead to a relatively narrow strip before the market shock. Also, both the call and put strips have joint points. On the contrary, the ask-bid spreads are very large on 29 September 2008, leading to a very wide strip for the implied volatility. Moreover, the put and call strips are very far apart and do not intersect. Also, the best bid for the deeply out-the-money put option (strike ) is , which is outside the admissible range for put options, . This would result in zero volatility; see the put strip in Figure 3b.
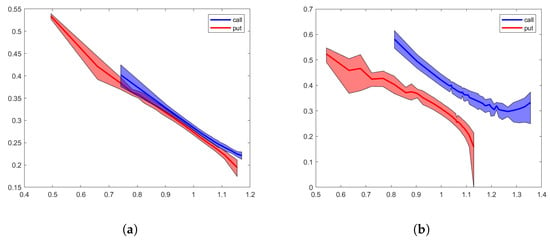
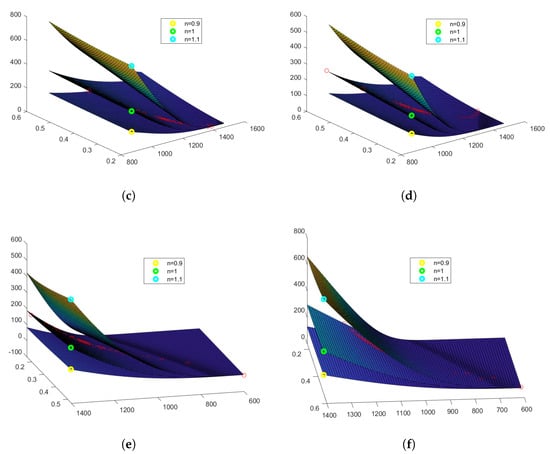
Figure 3.
Implied volatilities, short maturities—20 December 2008: (a) 26 September 2008; (b) 29 September 2008; (c) 26 September, call; (d) 29 September, call; (e) 26 September, put; (f) 29 September, put.
The prices of hypothetical American-style power options on 26 and 29 September 2008 can be seen in Figure 3c,d for the calls, and Figure 3e,f for the puts. Note that the CBOE-listed options written on the S&P 500 Index (SPX) are European-styled only. On the other hand, the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust is a fund that tries to replicate the index, and the options written on it, the so-called SPY options, are American-styled. In this study, we only use statistical data for SPX. The graphs are given with respect to the strike and (implied) volatility. We have plotted three graphs with respect to different powers: , , and , so that the middle graph corresponds to classical American options. Red circles mark the observed real market prices of European options. Note that they are very close to the prices of the corresponding American options because of the short time to maturity and low interest rate. Moreover, American options for and become European options, by Proposition 9.
The prices of some options with strike are given in Table 2. Columns 2 to 4 report the option style (call or put), maturity date, and the observed market price, respectively. The next column contains the implied volatilities that these prices generate. We then give the prices of European and American power options for powers , which are calculated with respect to the implied volatilities. Note that the prices of both European and American call options coincide for or , by Proposition 9. Also, these prices are equal to the observed ones when .

Table 2.
Option prices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization—T.S.Z., H.S. and M.S.; methodology—T.S.Z., H.S. and M.S.; software—H.S., M.S. and T.S.Z.; validation—H.S.; formal analysis—T.S.Z., M.S. and H.S.; investigation—T.S.Z., H.S. and M.S.; resources—T.S.Z. and H.S.; data curation—H.S.; writing—original draft preparation—T.S.Z., H.S. and M.S.; writing—review and editing—H.S.; visualization—H.S.; supervision—T.S.Z. and M.S.; project administration—T.S.Z.; funding acquisition—T.S.Z. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Center of Excellence in Informatics and Information and Communication Technologies established under the Grant No BG05M2OP001-1.001-0003, financed by the Science and Education for Smart Growth Operational Program and co-financed by the European Union through the European Structural and Investment funds.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express sincere gratitude to the anonymous reviewers for the helpful and constructive comments, which substantially improved the quality of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Appendix A. Some Propositions
Lemma A1.
If and for some x, then for all .
Proof.
We can easily check that , where L is given by (4). □
Lemma A2.
Let the constant L be defined as in (4).
- If , then .
- If and , then .
Proof.
Regarding the first statement, if , we can rewrite (4) as to see that ; if , then we can use (4) directly.
The second statement is reached by several easy calculations. □
Lemma A3.
Proof.
Proof.
The first statement follows from
The inequality is equivalent to (A2), which is true when . □
Appendix B. Some Hitting Time Properties
Let be a continuous piecewise linear function, , with respect to the time grid , and . We assume that , i.e., a lower hitting problem. The upper one is analogous, since Brownian motion is symmetric. Let us denote by the first hitting time of the boundary. We first consider linear functions and write .
Proposition A1.
If and , then
If and , then
Proof.
The proof is a consequence of Theorem 3.2 in []. □
Proposition A2.
The probability of is
Proof.
See Equation (3) in [] or Proposition 3.1 in []. □
Proposition A3.
Proof.
See Theorem 3.1 in []. □
We now consider piecewise linear boundaries.
Proposition A4.
Proof.
See Theorem 4.1 in []. □
Corollary A1.
If , then
Proof.
We have to rewrite (A3) for . □
Proposition A5.
Proof.
See Theorem 4.2 in []. □
Proposition A6.
The following statements hold for any constants and .
- If , then .
- If , then .
Proof.
The proof follows from , which is proven in []. □
We also need the following formulas, reported in [], pg. 223, (2.0.1).
Proposition A7.
Let ζ be the first hitting time of the level for a Brownian motion with drift μ. If , then
If , then
Appendix C. Finite Difference Terms
- If , then
- If , then
- If , then
References
- Zhang, Q.; Song, H.; Hao, Y. Semi-implicit FEM for the valuation of American options under the Heston model. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozpınar, S.; Uzunca, M.; Karasözen, B. Reduced-Order modeling for Heston stochastic volatility model. Hacet. J. Math. Stat. 2024, 53, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Koo, H.; Park, K. Optimal finite horizon contract with limited commitment. Math. Financ. Econ. 2022, 16, 267–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T. On some generalized American style derivatives. Comput. Appl. Math. 2024, 43, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T. Quadratic American Strangle Options in Light of Two-Sided Optimal Stopping Problems. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmowski, Z.; Pérez, J.; Yamazaki, K. Double continuation regions for American options under Poisson exercise opportunities. Math. Financ. 2021, 31, 722–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kim, G. Analytic Valuation Formula for American Strangle Option in the Mean-Reversion Environment. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmowski, Z.; Stȩpniak, P. Last-Passage American Cancelable Option in Lévy Models. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2023, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Song, H.; Hao, Y. Primal-dual active set method for evaluating American put options on zero-coupon bonds. Comput. Appl. Math. 2024, 43, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zheng, X. A deep learning method for pricing high-dimensional American-style options via state-space partition. Comput. Appl. Math. 2024, 43, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Primal-dual active set algorithm for valuating American options under regime switching. Numer. Methods Partial. Differ. Equ. 2024, 40, e23104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Song, H.; Yang, J.; Zhou, B. Error analysis of finite difference scheme for American option pricing under regime-switching with jumps. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2024, 437, 115484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Huang, W.; Ma, J. An efficient and provable sequential quadratic programming method for American and swing option pricing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 316, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Projection and contraction method for the valuation of American options under regime switching. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2022, 109, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zuo, P.; Du, H.; Wu, F. Projection and Contraction Method for Pricing American Bond Options. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reesor, R.; Stentoft, L.; Zhu, X. A critical analysis of the Weighted Least Squares Monte Carlo method for pricing American options. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 64, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, Z. Defaultable perpetual American put option in a last passage time model. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2024, 209, 110018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battauz, A.; Donno, M.D.; Sbuelz, A. Real Options and American Derivatives: The Double Continuation Region. Manag. Sci. 2015, 61, 1094–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battauz, A.; Rotondi, F. American options and stochastic interest rates. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2022, 19, 567–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudenège, L.; Molent, A.; Zanette, A. Backward hedging for American options with transaction costs. Decis. Econ. Financ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battauz, A.; Staffolani, S. American options with acceleration clauses. Decis. Econ. Financ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ha, H.; Kong, B. Pricing first-touch digitals with a multi-step double boundary and American barrier options. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 59, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepniak, P.; Palmowski, Z. Pricing time-capped American options using a least squares Monte Carlo method. J. Comput. Financ. 2025, 28, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, R. Power options: Hedging nonlinear risks. J. Risk 2000, 2, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heynen, R.; Kat, H. Pricing and hedging power options. Financ. Eng. Jpn. Mark. 1996, 3, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, A. General valuation principles for arbitrary payoffs and applications to power options under stochastic volatility. Financ. Mark. Portf. Manag. 2003, 17, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Moon, K.S.; Wee, I.S. Valuation of power options under Heston’s stochastic volatility model. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2012, 36, 1796–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macovschi, S.; Quittard-Pinon, F. On the pricing of power and other polynomial options. J. Deriv. 2006, 13, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Sheng, Y. Valuation of power option for uncertain financial market. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 286, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadugba, S.; Nwozo, C. Mellin Transform Method for the Valuation of the American Power Put Option with Non-Dividend and Dividend Yields. J. Math. Financ. 2015, 5, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadugba, S.; Nwozo, C. Perpetual American power put options with non-dividend yield in the domain of Mellin transforms. Palest. J. Math. 2020, 9, 371–385. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.K. A simple numerical method for pricing American power put options. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 139, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenman, L.P.; Clark, S.P. Power exchange options. Financ. Res. Lett. 2005, 2, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Lin, X.; Yu, S. A note on the never-early-exercise region of American power exchange options. Oper. Res. Lett. 2016, 44, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J. Pricing American options under negative rates. J. Comput. Financ. 2014, 25, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiryaev, A.; Kabanov, Y.; Kramkov, D.; Mel’nikov, A. Toward the theory of pricing of options of both European and American types. II. Continuous time. Theory Probab. Its Appl. 1995, 39, 61–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T. Discounted perpetual game call options. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 131, 109503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T. A new approach for pricing discounted American options. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2021, 97, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T. Pricing discounted American capped options. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 156, 111833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T. Some limits for the Laplace transform of the Brownian motion’s first hit to a linear function. Serdica Math. J. 2024, 50, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaevski, T. Laplace transforms for the first hitting time of a Brownian motion. Comptes Rendus l’Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2020, 73, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Ross, S.; Rubinstein, M. Option pricing: A simplified approach. J. Financ. Econ. 1979, 7, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pötzelberger, K. Boundary crossing probability for Brownian motion and general boundaries. J. Appl. Probab. 1997, 34, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R. Values of Mills’ Ratio of Area to Bounding Ordinate and of the Normal Probability Integral for Large Values of the Argument. Ann. Math. Stat. 1941, 12, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodin, A.; Salminen, P. Probability and Its Applications. In Handbook of Brownian Motion—Facts and Formulae; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).