Highlights
- Inspired by adiabatic quantum mechanics, this work considers a generalization of the obtained principal bundle by allowing the fibers to consist of disjoint unions of group orbits. Such a bundle is referred to as a semi-principal bundle.
- These semi-principal bundles support equivariant parallel transport in a similar way to principal bundles. The main difference is that parallel transport may now end up in a different group orbit, meaning that group translations can no longer describe the situation.
- The group description can be restored by picking a reference point in each orbit. Such points together are referred to as a basis or frame. This enables the passage to a (principal) frame bundle in close analogy with vector bundles.
- This work contributes to the more general question on the mathematics behind gauge theories, in particular those having an exchange symmetry.
Abstract
We study fiber bundles where the fibers are not a group G but a free G-space with disjoint orbits. The fibers are then not torsors but disjoint unions of these; hence, we like to call them semi-torsors. Bundles of semi-torsors naturally generalize principal bundles, and we call these semi-principal bundles. These bundles admit parallel transport in the same way that principal bundles do. The main difference is that lifts may end up in another group orbit, meaning that the change cannot be described by group translations alone. The study of such effects is facilitated by defining the notion of a basis of a G-set, in analogy with a basis of a vector space. The basis elements serve as reference points for the orbits so that parallel transport amounts to reordering the basis elements and scaling them with the appropriate group elements. These two symmetries of the bases are described by a wreath product group. The notion of basis also leads to a frame bundle, which is principal and so allows for a conventional treatment. In fact, the frame bundle functor is found to be a retraction from the semi-principal bundles to the principal bundles. The theory presented provides a mathematical framework for a unified description of geometric phases and exceptional points in adiabatic quantum mechanics.
MSC:
55R10; 57M60
1. Introduction
Fiber bundles are mathematical objects generalizing the idea of a product space. This versatile definition now has a prominent role in many theories in both mathematics and physics. The basic principle is that the total space locally looks like a product of a small piece of the base and some fixed space, called the fiber. However, imposing a particular structure on the fiber reveals the existence of various specifications of fiber bundles, each with its distinctive properties. A well-known example is the vector bundle, where the fiber is a vector space.
Another famous class of bundles is formed by the principal bundles. However, here, one must be careful when specifying the fiber. Given a topological or Lie group G, a principal G-bundle has a fiber given by the underlying space of G, endowed with some additional structure. The important observation here is that this is not the group structure; hence, the fiber should not be identified with the original group G. Instead, the fiber has the structure of a G-space; a space endowed with a continuous, or even smooth, G-action. The fiber of a principal bundle is thus a G-torsor, i.e., a free and transitive G-space. A significant difference between G as a group and G as a torsor is the existence of a canonical base point. This is of the utmost importance in gauge theory; the freedom in fixing a gauge only exists in the absence of such a canonical choice. For more on the relevance of principal bundles in gauge theory, see [1].
Given that principal bundles are thus fiber bundles based on torsors, and that torsors are specific group spaces, clearly there exist more general classes of bundles with similar properties. That is, principal bundles form a specific subclass of the group-space bundles. This paper explores a controlled extension of this subclass. It turns out that allowing not just torsors but general group spaces as a fiber opens up many possibilities. In fact, the fibers could easily have a bundle structure of their own. We thus extend to the class where the fibers are free group spaces that are a disjoint union of torsors. As such, we call these particular spaces ‘semi-torsors’, and the bundles they form, we call ‘semi-principal bundles’.
These semi-principal bundles support a theory of parallel transport, which is also where we find our original motivation for this study. This relates to the field of adiabatic quantum mechanics. Namely, if one adiabatically varies non-Hermitian quantum Hamiltonians, then the evolution of the eigenstates is described by the parallel transport on a semi-principal bundle; see [2]. A particular phenomenon in this field is that quantum states may be exchanged; the Hamiltonian is restored to its original value, yet the quantum states do not, and they return with different energies. The mathematics is straightforward. For a finite-dimensional Hamiltonian operator H, the set of all eigenstates of H is a -space under the standard scaling action. Each eigenray is a -torsor; thus, if H has distinct eigenvalues, all its eigenvectors together form a -semi-torsor. Varying H then leads to a semi-principal bundle. The parallel transport on this bundle may return one to another state, that is, one ends up in another group orbit. This exemplifies the main difference between holonomy on principal and semi-principal bundles; for principal bundles, lifts always end in the same group orbit, and so any holonomy can be represented by a group element, while for semi-principal bundles, this need not be. The question of how to deal with this leads us to the notion of a basis for a group set.
The set-up of the paper is as follows. As it is important to know the main differences between a bundle of groups and a bundle of group spaces, we study these in more detail in Section 2. This leads us to the notions of semi-torsor and semi-principal bundle, which we define and investigate in Section 3. In particular, we demonstrate how these support the connection 1-forms and parallel transport. As just indicated, our main issue here will be that horizontal paths need not return to their original group orbit. This brings us to an equivalent of vector-space bases for group sets in Section 4. We investigate the symmetry group of these bases, which is a wreath product and can be represented by generalized permutation matrices. This will allow us to explicitly describe the holonomy in a way that is also relevant to the adiabatic quantum mechanics. We finish by considering the frame bundle of a semi-principal bundle in Section 5, where this solution using bases/frames is present in the geometry itself. In Section 6, we will summarize the main results.
2. Group Bundles versus Group-Space Bundles
Let us compare group and group-space bundles, starting with considering fiber bundles in general and then specifying this to groups and group spaces. By definition, the key property of any fiber bundle is its local triviality. It is this property that allows one to endow the fiber with additional structure, which then lifts to a structure on the entire bundle. Let us take the fiber in a category whose objects are topological spaces with additional structure and whose morphisms are continuous maps preserving this additional structure. A fiber bundle with fiber in consists of the data , where F is an object of called the model fiber, B and M are topological spaces, and is a continuous surjection. This tuple is subject to the defining property that every point has a neighborhood U and a homeomorphism such that the following hold:
- ;
- is an isomorphism in , for all .
Hence, B, or more precisely each fiber , should be equipped with the structure as given by , in such a way that a continuous structure on B is obtained. In the following, we will take to the category of topological groups, and the category of group spaces, as well as subcategories of these. The case of manifolds is then a natural adaptation. Morphisms of fiber bundles follow the same general structure. A morphism from is a pair of continuous maps and such that and, for all , , viewed in local trivializations, is a map in . In the following, we will only consider the case where is an identity, so we only specify and simply write .
2.1. Group Bundles
We start with taking to be the category of topological groups, which will result in the subclass of group bundles. We will first state the definition of a group bundle that we will use in this paper.
Definition 1.
Let G be a topological group. A group bundle with model fiber Gis a fiber bundle such that the following hold:
- Each fiber of B has a group law. More precisely, writing for the fiberwise product bundle over M, there is a bundle mapsuch that is a group for all . Moreover, the corresponding inverse map should be continuous.
- Each point has a neighborhood U and a homeomorphism such that , and for each the map is an isomorphism of groups.
A map of group bundles is a bundle map such that is a morphism of groups for all . The group bundles and these maps together form the category of group bundles.
This definition is in line with, for example, [3] (p. 330) and [4] (Definition 2.8). Here, we explicitly require that the group multiplications of the fibers fit together in a continuous bundle map. In addition, we also demand local triviality of the projection. Observe that vector bundles are a special case of group bundles; a vector bundle is a group bundle with a commutative model group and compatible scalar multiplication. It follows that all non-trivial vector bundles provide non-trivial group bundles, proving that not all group bundles are trivial.
We now wish to illustrate general group bundles by going over some basic results and examples. First, observe that transition functions take values in the group . This clearly distinguishes group bundles from principal bundles, as the latter’s transition functions take values in G, which is in general not isomorphic to .
Lemma 1.
The transition functions of a group bundle with model G take values in the automorphism group of G.
Proof.
Let us consider local trivializations , such that the overlap is non-empty. For , the maps are isomorphisms of groups. Hence, the transition map is identity on the U component, hence restricting to any yields an automorphism of G. □
Another property of group bundles is the existence of a global section. Given the fiberwise group law axiom, each fiber , with , is a group; hence, in particular, it has a unit . This gives rise to the map , , which is a section of ; hence, we call it the unit section of the group bundle. In the case of vector bundles, this section is known as the zero section and provides an embedding of the base space M in B. For general group bundles, there is the following statement.
Proposition 1.
Given a group bundle , the unit section is an embedding. Moreover, if G is discrete, then B can be topologically partitioned into the image of , which is homeomorphic to M, and the complement of this image.
Proof.
Clearly, is injective. Locally on , looks like the embedding , , which shows that is an embedding. If G is discrete, then is closed and open in . Hence, the image of is locally disjoint from other parts of B, and hence, it is globally so, as is global. □
Again, we emphasize a significant difference between group bundles and principal bundles. It is well known that a principal bundle admitting a global section must be trivial. Here, we see that group bundles always admit a global section, but this does not imply the triviality of the bundle. Indeed, any non-trivial vector bundle provides a counterexample, but we will now go over some other examples. We will take M to be the circle . In this case, we may view a group bundle B with model group G as a quotient of the trivial group bundle by gluing and by an automorphism of G.
Example 1
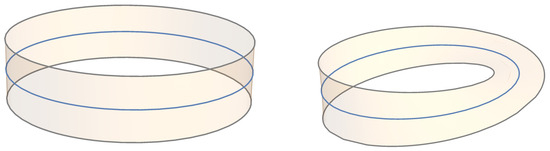
(-bundles over the circle). Let us view as the additive group of remainders modulo 3, whose elements are , , and . The group consists of two elements, namely, and . Naturally, gluing via will yield the trivial bundle over , i.e., the bundle B is isomorphic to the group bundle . The unit section traces out the subspace , which is indeed well separated from its complement and homeomorphic to the base .
Gluing along means that and are exchanged upon returning, hence returning to themselves after a second round. We may thus picture them to traverse the boundary of a Möbius band. The element , which follows the unit section, will again trace out a circle. Hence, the total space of this bundle consists of a circle and the boundary of a Möbius band, and thus is homeomorphic to two disjoint circles. It thus cannot be homeomorphic to the trivial bundle, as this consists of three disjoint circles. Compare the illustrations of the bundles in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Representatives of the two non-isomorphic classes of -bundles over the circle; see Example 1. The shaded cylinder and Möbius band are visual aids. In both cases, the unit section traces out the middle circle, whereas the other group elements follow the boundary.
Observe that this example treats the most elementary non-trivial group bundle. Indeed, the circle requires at least one automorphism to be specified, and the smallest group possessing non-trivial automorphisms is . Naturally, if G is trivial, then is trivial, as the fiber has only one point. In case , the bundle will also be trivial; one can use Lemma 1 to conclude that all transition functions are trivial, or alternatively use Proposition 1 to remark that B consists of two disjoint copies of M and hence is trivial.
The argument in Example 1 holds for any group G with . Indeed, the identity map in yields the trivial bundle , while the non-identity map yields a non-trivial bundle. For instance, picking yields infinitely many copies of the boundaries in Figure 1. That is, either each is glued to n and one obtains rings on the infinite cylinder, or each n is glued to and one obtains rings on the infinite Möbius band.The choice reproduces the familiar picture of a cylinder whose edge circles are glued to obtain a torus, i.e., a Klein bottle. As is naturally a subgroup of , the case can again be viewed as lines on a surface, where the surface is now given by a -bundle. Pictorially, one places four equidistant points on a circle, which become straight lines on a cylinder, and by gluing the edge circles of this cylinder, one finds all lines coming back to themselves on the torus, i.e., two lines coming back and two lines exchanging on the Klein bottle.
A final remark is that the (isomorphism class of) a group bundle over the circle may be the same for different automorphisms of G. For one, if the automorphisms can be connected by a path, then the resulting bundles are isomorphic. As an example, if , then , and the class of the obtained bundle only depends on the part. In addition, conjugate automorphisms of G also yield isomorphic bundles. This, we illustrate in Example 2.
Example 2
(-bundles over the circle). Let us consider , where , and similarly for the cyclic permutations of these equations. The elements a, b and c thus satisfy identical relations, and indeed the automorphisms are given by permuting a, b and c amongst themselves. Hence, is isomorphic to .
Although this group has six elements, there are fewer isomorphism classes. Let us go over all permutations in . Naturally, the identity permutation will yield the trivial group bundle . All the transpositions will yield another class, as do the three cycles.
Take for instance. This means that we glue the four intervals in such that the intervals of a and b form a single circle, whereas the intervals of 1 and c will each form a separate circle. For and , one will obtain essentially the same picture, revealing that the obtained bundles are isomorphic. For and , a similar argument holds; now the intervals of a, b, and c are connected to a single circle, and the only difference between the two gluings is the order in which the pieces of the circle are traversed.
We thus see that the obtained bundle class is the same for automorphisms in the same conjugacy class of . Moreover, each conjugacy class yields another class of group bundles; the obtained spaces are homeomorphic to 4, 3, and 2 circles, respectively.
2.2. Group-Space Bundles
Let us shift our attention to group sets instead of groups. This brings us closer to principal bundles, as these are a special class of group-space bundles. Indeed, the axioms on the fiber of a principal bundle are similar to the axioms of a group set. We will investigate these objects in more detail here and later on in the paper, and so we wish to review some basic statements on group sets.
Definition 2.
Let G be a group with unit e. A G-set is a tuple where F is a set and A is a left action of G on F, i.e., a map
such that and one has and . For convenience, we will simply refer to the G-set as F, which we understand as a set endowed with a left action A by G. In case G is a topological group, F is a topological space, and the action map A is continuous, F is called a G-space. Similarly, if G is a Lie group, F is a manifold, and the action map A is smooth, then F is a G-manifold.
A function between a G-set F and a -set is called ξ-equivariant, where is a homomorphism, if
In particular, a G-map is a function between two G-sets that is -equivariant, i.e., . In case F and are G-spaces or G-manifolds, the map α is also required to be continuous, i.e., smooth. Moreover, the category formed by G-sets and G-maps is called the category of G-sets. Similarly, one has the category of G-spaces and G-manifolds.
A G-set is called free/transitive if the action is free/transitive, which is equivalent to the map
being respectively injective/surjective. Denoting the action quotient map as , the image of the above map, i.e., all pairs of elements in the same orbit, can be written as
If F is both free and transitive, then F is called a principal homogeneous space for G, or G-torsor.
The fibers of a principal G-bundle are thus G-torsors. Of course, a particular G-torsor is the underlying space of G where the action is given by left translation. Clearly, any G-torsor F is isomorphic to this G-torsor; any orbit map establishes an isomorphism of G-torsors. A straightforward generalization of principal bundles is thus group-space bundles, which can be defined as follows.
Definition 3.
Let G be a topological group and F a G-space. A G-space bundle with model F is a fiber bundle such that the following hold:
- Each fiber of B is a G-space. That is, there is a bundle mapsuch that is a G-space for all .
- Each point has a neighborhood U and a homeomorphism such that , and for each , the map is an isomorphism of G-spaces.
Let B be a G-space bundle and be a -space bundle. A map of group-space bundles is a bundle map such that is ξ-equivariant for all , i.e., for all and , where is a homomorphism.
This defines the category of group-space bundles. From it, one obtains special subcategories by restricting the model group space to a prescribed class. The principal bundles are readily recognized as the restriction of group-space bundles to the case where the model fiber is a torsor. The group-space bundles are more general in the following sense.
Lemma 2.
The principal bundles are a full subcategory of the group-space bundles.
Proof.
As a G-torsor is a G-space, any principal bundle is a group-space bundle. In addition, any map of principal bundles is a map of group-space bundles. This proves the subcategory claim. It is full, as any group-space bundle map between principal bundles is an equivariant bundle map, hence a map of principal bundles. □
A significant difference between principal bundles and general group-space bundles is the way in which the structure group can describe changes in the fiber. This is relevant already for the transition functions but also when one considers holonomy. The nature of the transition functions can be found in the standard way, as performed for group bundles previously, and results in the following.
Lemma 3.
The transition functions of a group-space bundle with model fiber F take values in the automorphism group , i.e., the group of invertible group space maps .
Let us first relate this back to principal G-bundles, in which case F may be taken as the G-torsor G. The left-equivariant invertible maps are exactly the right translations; hence, . In other words, the group G faithfully describes all relevant changes in the fiber F. This need not be so for general group spaces F. Intuitively speaking, if F is not free, then G has redundant elements, and if F is not transitive, then G is too small. A more formal description of is given in Appendix A.
Another significant difference is the internal structure of the fiber F. By this, we mean that F itself can have an interesting topology. Let us consider the quotient map . Remarkably, if q is locally trivial, the tuple is itself a group-space bundle. This bundle need not be trivial; in fact, one can take F to be (the total space of) any non-trivial principal G-bundle. This means that non-trivial topology can appear not only on the global level but also already on the fiber level.
3. Semi-Torsors and Semi-Principal Bundles
3.1. Basic Properties
We are now in the position to introduce our main objects of study. As just seen, allowing general group spaces to be the model fiber of the bundle means that even fibers themselves can have non-trivial topology. We will thus restrict ourselves to a certain class of group spaces, for which the fibers have both a clear automorphism group and the quotient map is trivial. The first condition brings us to free group spaces. The second condition is fulfilled in the standard torsor case with a single orbit, but multiple orbits are still possible as long as these form a partition of the group space in open and closed subsets. That is, we arrive at G-spaces F such that F is free and is discrete. It readily follows that F must be isomorphic to as G-spaces, which reveals the trivial topology. As all such G-spaces are of the form , i.e., a disjoint union of ‘standard’ torsors, we propose to call them semi-torsors. We will start phrasing the results for manifolds, and leave the topological equivalents as implicit.
Definition 4.
Let G be a Lie group and F a G-manifold. Then, F is a semi-torsor if F is free and is discrete.
Clearly, every torsor is a semi-torsor—they form the case where consists of a single point. As principal bundles correspond to torsors, the bundles corresponding to the semi-torsors will form a generalization of the principal bundles. We call these bundles semi-principal bundles, as they locally look like a sum of principal bundles. We define these in the following definition. A schematic overview of how these bundles relate to group spaces and other classes of bundles can be found in Figure 2.
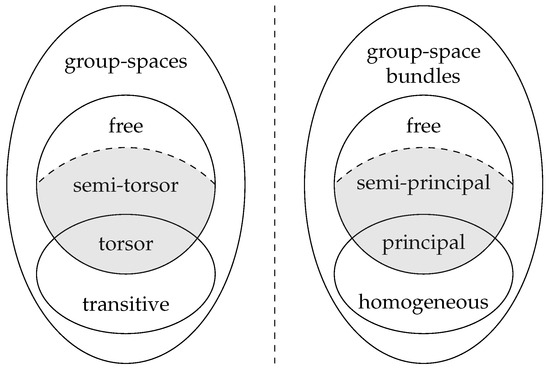
Figure 2.
Correspondence between classes of group spaces and the classes of group-space bundles having these as fibers. This paper focuses on the gray parts, i.e., the semi-torsors and semi-principal bundles, which extend the torsors and principal bundles.
Definition 5.
Given a Lie group G, a semi-principal G-bundle is a group-space bundle , where the model fiber F is a G-semi-torsor. That is, B is endowed with a fiber-preserving G-action, local trivializations of B are G-equivariant, and the model fiber F is a free G-manifold such that is discrete.
Unlike principal bundles, the projection map of a semi-principal bundle need not coincide with the action quotient , where is endowed with the unique smooth manifold structure such that Q becomes a surjective submersion. Indeed, when taking the action quotient, the fiber F is reduced to , which need not consist of a single point. Nevertheless, this new fiber is a discrete space, and as proven below, forms a covering of M. As Q will still define a principal bundle, the following result says that any semi-principal G-bundle is a principal G-bundle on top of a covering space.
Proposition 2.
Let be a semi-principal G-bundle with model fiber F, set . The map defines a principal G-bundle. Moreover, the quotient space is itself an X-bundle over M, i.e., a regular -fold covering. This bundle is defined by the reduced map given by the relation , i.e.,
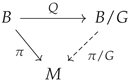 is a commutative diagram of semi-principal bundles.
is a commutative diagram of semi-principal bundles.

Proof.
As is G-invariant, it is constant on the fibers of Q. As Q is a smooth submersion, the map is a well-defined smooth map [5] (Thm 4.30). To see the local forms of Q and , let us use a G-equivariant local trivialization of . One can reduce to orbits, and as , this results in the commutative diagram
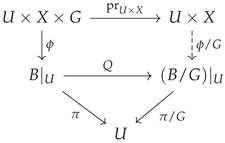 where all solid arrows are smooth.
where all solid arrows are smooth.

Let us consider the induced map . It is smooth, as is a smooth map that is constant on the fibers of the smooth submersion . In fact, is a diffeomorphism. Being the quotient of a bijection, it is bijective. Its inverse is smooth as well; is a smooth map that is constant on the fibers of the smooth submersion Q. Hence, is a local trivialization of provided that . The latter can be deduced from
where may be chosen arbitrarily because of G-equivariance. Hence, is an X-bundle over M, and as X is discrete, this is a covering.
We then turn our attention to . Using the same maps as above, one can find a local trivialization for Q, namely, , . As is G-equivariant, so is this diffeomorphism, and as it satisfies
it is a local trivialization of Q. This implies Q is a principal G-bundle. □
This result clearly reveals two special cases of semi-principal bundles. Naturally, one case is where the bundle is actually principal, which means that and Q coincide. The other special case is that and coincide, which happens if and only if G is trivial. Here, the definition of the semi-principal bundle reduces to that of a fiber bundle with discrete fiber, i.e., a regular covering space.
An example of a generic semi-principal bundle can be found in Example 3 below. Here, we consider the trivial principal -bundle over the circle , i.e., the torus, but we wind it around multiple times to obtain a coil-like object. The resulting projection is no longer a principal bundle, but it does remain semi-principal. We will repeatedly build upon this example throughout the paper.
Example 3
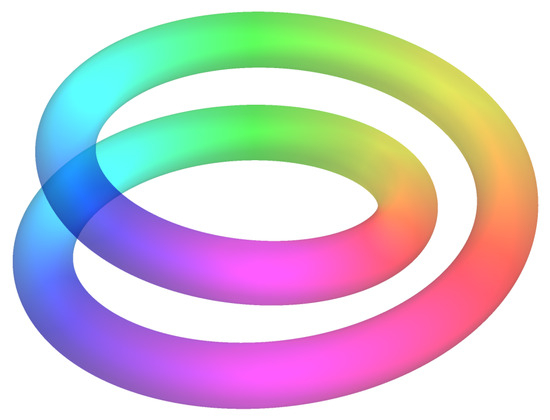
(Winding torus). Let us consider the torus , endowed with the standard -action on its second factor. The projection on the first factor then realizes the torus as a trivial principal -bundle over the circle. However, we can also view as a semi-principal bundle over in the following way.
Consider the map , with as an integer, given by winding the circle k times around, i.e., for z on the unit circle in . Then, winds the torus k times around the circle. The picture to have in mind is illustrated in Figure 3 for the case . Clearly, defines a semi-principal -bundle with model fiber , i.e., k disjoint circles. For , so that , the bundle is non-trivial as can be deduced using topology. Namely, the trivial semi-principal -bundle over with model fiber is given by the projection on the first factor, so that in particular the total space consists of k disjoint tori. As the total space of is always a single torus, it follows that is non-trivial for .

Figure 3.
Illustration of the bundle in Example 3. This space is topologically a torus, but the projection indicates that it winds twice around its base circle. Points with the same color are projected to the same point in .
We now move to the observation that semi-principal bundles admit parallel transport in almost exactly the same way as principal bundles do. We will first prepare ourselves for this theory by studying connections that are compatible with the group action, leading to a generalization of the Maurer–Cartan form on semi-torsors. After this, we will show how such connection forms define parallel transport on semi-principal bundles.
3.2. Group Compatible Connections and a Generalization of the Maurer–Cartan Form
Parallel transport is conveniently described using connection 1-form, so let us start by considering the appropriate 1-forms for semi-torsors and semi-principal bundles. One way of writing the axioms for a 1-form to be a principal connection is by assuming two relations involving the G-action on the manifold. In other words, these axioms do not need to know more than a G-manifold structure. Let us write the action map as , where acting with g is denoted as . One can also consider a specific point , and restrict A to . The differential , where again denotes the Lie algebra of G, is known as the infinitesimal action at f. We now have the notation to state the following definition, using only the two standard axioms of a principal connection.
Definition 6.
Let G be a Lie group with algebra and let F be a (left) G-manifold. A -valued 1-form ω on F is called a G-connection 1-form, or just G-connection, if
- for all ,
- for all .
As this definition only concerns the G-manifold structure, it readily applies to semi-principal and principal bundles. For these cases, one also evades the following technical issue. Namely, a G-connection need not exist for an arbitrary G-manifold. The left-inverse axiom of implicitly states that will be a right-inverse; hence, must be injective for all . In other words, the action has to be free on a local level. Again, we will not treat the general theory but consider the case of semi-principal bundles. We remark that we choose the name G-connection to avoid confusion. As Proposition 2 indicates, a G-manifold can be a principal bundle for one bundle projection and a semi-principal bundle for another. The axioms of a G-connection 1-form do not make reference to such differences; hence, we wish to avoid terminology suggesting such reference.
The case of a G-connection on a G-semi-torsor F turns out to be special. In this case, F admits exactly one G-connection. The key observation is that if the infinitesimal action is invertible, then the G-connection is fixed.
Proposition 3.
Any G-semi-torsor F has a natural G-connection ω given by
Moreover, this is the only G-connection on F.
Proof.
As the action is free, is injective for all . As is discrete, ; hence, is a linear isomorphism. Hence, the condition uniquely specifies . To verify that is a G-connection, it remains to check the equivariance. This reads, with Y a tangent vector in ,
where we use the relation . □
This 1-form can be considered an extension of (a left-action version of) the usual canonical 1-form on G, also known as the Maurer–Cartan form [6]. A crucial difference is that the above form does not need any identification of (a part of) F with G. Moreover, in case F is G viewed as a (left) G-torsor, one does obtain the usual formula. Indeed, then and one finds
which is indeed the Maurer–Cartan form in the case of a left-action.
Another perspective on this connection involves the map
which by choice of image is always surjective. For a free action, this map is also injective, and an inverse function exists. It is even a diffeomorphism; the dimensions of the source and target space coincide, and the differential has full rank. Let us write the smooth inverse as
where is the smooth map sending to the unique element such that . That is, the division map allows one to track the group element relating points in F. Its derivative will thus yield an infinitesimal generator, which yields again the unique G-connection on F in the following way.
Proposition 4.
The canonical G-connection on a G-semi-torsor F can alternatively be written as
where is a curve in F.
Proof.
As , and always lie in the same orbit; hence, the stated division is well defined. It suffices to check the G-connection axioms; in fact, the left-inverse property alone is already sufficient according to Proposition 3. Taking and , this verification reads
The equivariance can also be verified using the identity :
□
The semi-torsor assumption cannot be omitted; the points and should be in the same orbit for any path , and hence the dimensions of F and G should be equal. Of course, here we still assume the action to be free; otherwise, the division would be ill defined. Hence, F can only consist of separated copies of the standard G-torsor, meaning F is a G-semi-torsor.
Again, this notation reduces to (the left-action version of) the Maurer–Cartan form in case F is the G-torsor G. This time, the key relation is , so for a curve such that it holds that
Nevertheless, the division map does not need to employ a right translation, making it more general.
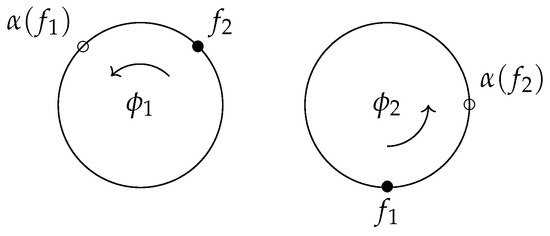
Example 4
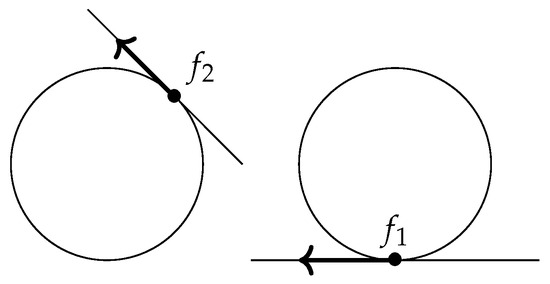
(Connection on disjoint circles). Let us illustrate the connection for the -set . Pick a point . The infinitesimal action basically identifies the tangent line at f with . Hence, there is a canonical way to associate any tangent vector to a number, which gives the 1-form ω. This association is illustrated in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
At each point f in F, the infinitesimal action identifies (here, the tangent line) with the Lie algebra (here ). A tangent vector thus canonically corresponds to a unique algebra element.
3.3. Parallel Transport on Semi-Principal Bundles
The next step is to demonstrate that a G-connection on a semi-principal G-bundle induces a G-equivariant parallel transport. In other words, we wish to show that this property of principal bundles extends to all semi-principal bundles. One can prove this in various ways. One way is to use the observation that a semi-principal bundle locally looks like the projection , which locally looks like the principal projection , hence allowing for a similar argument to principal bundle theory. Alternatively, one can use the result on principal bundles and extend it using the decomposition from Proposition 2. Let us employ the latter method in the following proof.
Proposition 5.
A semi-principal G-bundle with a G-connection admits G-equivariant parallel transport.
That is, let be a semi-principal G-bundle and ω a G-connection on B. Given any piecewise smooth curve and an initial point above , there is a unique horizontal lift through b, specified by and . Moreover, the lift of γ starting from is . In particular, the parallel transport map given by is well defined and G-equivariant.
Proof.
By Proposition 2, the semi-principal bundle decomposes as a principal G-bundle and a covering . Lifting the curve from M to a curve in with initial point then follows from covering theory. Now, is a G-connection, hence a principal connection concerning the principal G-bundle . As b lies above , one can lift to a unique in B such that . Hence, any curve in M lifts to a unique curve in B given an initial condition and the 1-form . If the starting point is , then only the lifting from to B changes. However, as is a principal bundle, the lift becomes as claimed. □
We have thus demonstrated that the parallel transport maps are well defined and G-equivariant, but there is a crucial difference with respect to parallel transport on principal bundles. Namely, on semi-principal bundles, need not return a point to the same group orbit. Principal bundles guarantee this by having a single group orbit as fiber, but for semi-principal bundles, this is not so. The group action is thus not sufficient to express the map with. This brings us to the main difference between the parallel transport on principal and more general semi-principal bundles: although both have well-defined and equivariant parallel transport, the holonomy on semi-principal bundles need not be expressible with a group element. An illustration of this in provided in Example 5. This phenomenon provides the main motivation for the study of bases in the coming sections.
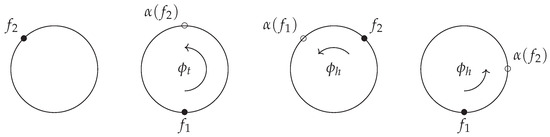
Example 5.
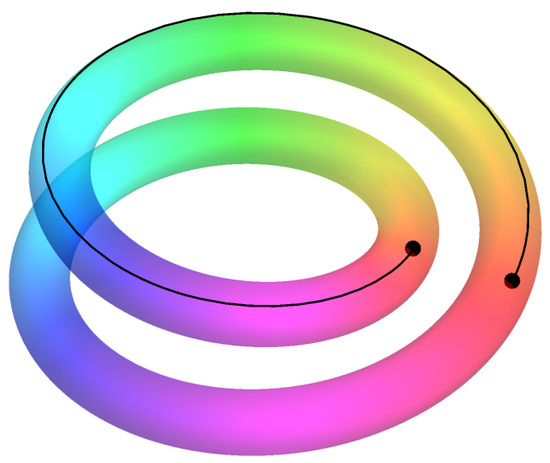
We have already seen the torus as a -bundle by acting on the second factor. Decomposing the torus like this, a -connection on is obtained by declaring that a path is horizontal if it has a constant second factor. This -connection is then compatible with all of the projections .
When the bundle is semi-principal, in particular, for , the parallel transport will contain the following. Let γ be a path in the base that makes a single turn. As seen in Figure 5, its lift Γ will end up in the original fiber but in a different circle/orbit as before. Consequently, the points and cannot be related by an element of . This picture is also close to the physical setting of adiabatic quantum mechanics, where states with a -phase freedom can be exchanged upon traversing a loop, i.e., . The parallel transport cannot be described by a phase factor alone.

Figure 5.
Example of parallel transport on the double torus. The path is well defined, and translating the initial point yields the translated lift as usual. However, as the final point lies in another orbit within the fiber, this holonomy cannot be expressed with an element of .
4. Bases of a Group Set
In this section, we will introduce and study the notion of the basis, also called frame, of a group set. This will include the study of the space formed by all the frames of a group set and its symmetry group, which will be a wreath product. We can then demonstrate how maps of semi-torsors can be expressed in matrix form using such a basis. To finish, we inspect how going from a semi-torsor to its torsor of frames defines a functor.
4.1. Basis of a Group Set
Similar to the notion of basis of a vector space, one can define the basis of a G-set F. Intuitively speaking, such a basis should be a tuple of elements of F, where X is the indexing set such that any point in F can be ‘reached’ using these points in a unique way, and that a G-map from F to any other G-set is specified once the images of the are known. We will use that a tuple is equivalent to a function by the relation , and we will often use the formalism throughout this paper for convenience. We will use tilde notation to indicate tuples throughout this paper.
Let us first discuss how this ‘reaching of points’ can be phrased in a formal way, staying in close analogy to vector spaces. In linear algebra, if V is a real vector space, then given a tuple of vectors in V, there is the associated map from coefficients to the vector space as
As this map is already linear, it is an isomorphism of vector spaces if and only if it is bijective. This question is usually subdivided in the properties of linear independence and spanning set. That is, the tuple is linearly independent if and only if is injective, and similarly, the tuple is a spanning set if and only if is surjective. If V admits a finite basis, then all bases of V have the same number of vectors, and the dimension of V is defined to be this finite number. If not, then V is called infinite dimensional.
This argument can be copied almost completely once we agree on a specific G-map induced by a tuple of G-set elements. A G-set will in general not supply us with an addition +, but there is some sort of scaling given by the group action: . It is now straightforward to extend this map to tuples; we define this map below and also extend the definition of a basis to G-sets. Here, we agree on the canonical G-set structure on given by the action .
Definition 7.
Let X be an index set, and consider the set of functions , or equivalently the set of ordered tuples with for all . Given such a tuple, we define its associated map to be the G-map
A tuple is called a basis of F if the associated map is an isomorphism of G-sets. The subset of consisting of all bases of F we denote as .
Let us first illustrate this definition in some simple cases, prior to delving into further properties. To start, in case F is a finite set—canonically a G-set for G the trivial group —one finds that the bases of F are just the set consisting of all tuples that list all elements of F exactly once. This illustrates a factorial dependence on the number of orbits, which is a general fact. It also motivates our use of the factorial symbol ! in some future constructions. We then provide a simple example with non-trivial G.
Lemma 4.
For F a finite set, viewed as a group set under the trivial group,
Proof.
For G, the trivial group, the map reduces to . If F has n elements, pick . The map is an isomorphism if and only if it is bijective, meaning its associated tuple should yield any given point of F exactly once. □
Example 6
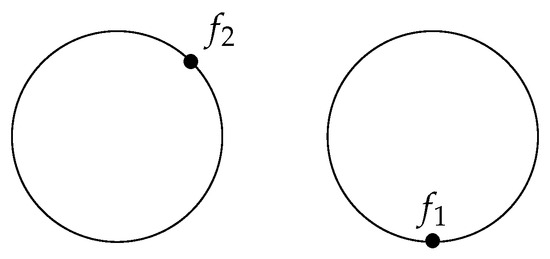
(Frames of two circles). Let us consider a simple case. Let us take , and two disjoint circles. Physically, this can represent two distinct eigenstates, which are determined only up to the usual phase factor. We draw the circles in the plane, and use the convention that G rotates positively, i.e., counterclockwise. Given any point , the group action will take us to any point on the same circle, but the other circle is out of reach. We thus need two points and , one for each circle, in order to reach any point in F using the group action, e.g., those in Figure 6. This we can write in the above style by having , where indeed
is an isomorphism of -sets, even of -manifolds.

Figure 6.
In case of the -set , a frame consists of a pair of points , one for each circle/orbit. The circles neither carry preferred points nor any order amongst themselves; these only come after choosing a frame.
In Figure 6, we label the circle on the right as circle 1, and the circle on the left as circle 2—neither circle has an intrinsic label, and any label is an external choice. Notice that the number of possible labels grows factorially in the number of circles.
Before discussing the existence of these bases, let us first consider the following. Namely, the scaling of vector spaces may differ in a crucial way from the group action used here. If one wants to preserve some idea of linear independence, it is important that implies for generic f. However, this need not hold for a general group action; it holds only for free actions. Hence, one may expect that the idea of a basis only matches intuition when F is free. This is indeed sufficient; the map is an isomorphism if and only if it is bijective, so we need both injectivity and surjectivity. The map is surjective if and only if every orbit contains at least one of the , and if F is free, then is injective if and only if the lie in different orbits. This indeed mimics the properties of linear independence and spanning set. In fact, having a basis and being free is equivalent as stated in the following lemma. We also prove the intuitive statement that all bases of a given G-set have the same cardinality; this ‘dimension’ is now the number of orbits , which can be infinite.
Lemma 5.
A G-set F has a basis if and only if F is free. Moreover, for a free G-set F, the index set X is unique up to bijection, in particular, .
Proof.
If F has a basis, then as G-sets. As the latter is free, so is F. Conversely, assume F is free. Then, every orbit in F is bijective to G. We only need to specify base points for each orbit; these base points will form the basis. That is, for each orbit , pick a point in this orbit and denote it by . This defines a section s of the quotient map . To check that s is a basis of F, we consider its induced map given by . This has an explicit inverse
where is the group element such that . This element is well defined; it exists, as f and lie in the same orbit, and it is unique, as F is free. Hence, s is a basis of F with index set .
Assuming F is free, pick two bases and with index sets and , respectively. Then, is a G-isomorphism. Hence, the orbit sets are bijective, which yields . Hence, all index sets of the G-set F are bijective. We just saw that is always an index set; hence, any other index set X must be bijective to . □
Given this result, we will restrict ourselves to free F from now on. Also, we take but sometimes still write X for clarity. In addition, one may observe that in the previous proof, one does need s to be a section; an orbit may be sent to a point in another orbit as long as all orbits are visited exactly once. We like to emphasize this freedom at certain places by not using the quotient notation.
We remark that has an interesting interpretation concerning the model of a G-set. Given a finite-dimensional real vector space V, one often identifies it with for some m using a linear isomorphism. In this way, the vector spaces , , provide models for real (finite-dimensional) vector spaces. One may then ask what the model space is in case of G-sets, and the above indicates that this is . This is valid for free G-sets, as any free F is isomorphic to , hence being of the correct form. The bases are then the labels of such isomorphisms .
We finish this inspection of individual bases with the following statements on G-maps in relation to bases. Again, we emphasize the similarity with the theory of vector spaces.
Lemma 6.
Let be G-sets and a G-map. Then, we have the following:
- 1.
- For any , one has ;
- 2.
- If F is free, the map α is fully determined by its values on a basis;
- 3.
- If both F and are free, then α is an isomorphism if and only if α sends a basis to a basis.
Proof.
For the first, observe , which indeed yields . For the second, assume is another G-map that coincides with on a basis of F. Pick any ; it is related to the basis via for some and . Using this decomposition, one finds
and as f is arbitrary, . The third then follows as well; given that is a G-isomorphism, then is a G-isomorphism if and only if is, i.e., if and only if is a basis of . □
4.2. The Space of Bases of a Group Set
We will now shift our scope and study the properties of the bases of F as a whole, i.e., we study . This we do using a kind of basis criterion in terms of the quotient map q. Basically, we pose the question when a candidate basis , i.e., any element in for a chosen index set X bijective to , lies in .
The basic observation is that the invertibility of , as it is equivariant, can be deduced by just knowing how the elements are distributed over the orbits of F, i.e., by knowing the map . More explicitly, fits in the commutative diagram
 which indicates that is reduced to orbits. This yields the following criterion for a candidate tuple to be a basis.
which indicates that is reduced to orbits. This yields the following criterion for a candidate tuple to be a basis.
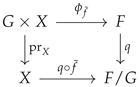
Lemma 7.
Let F be a free G-set. Then, is a basis if and only if is bijective.
Proof.
First, observe that is injective if and only if reaches every orbit at most once. In other words, every fiber of q contains at most one element of the basis . This is equivalent to being injective. Dually, the map is surjective if and only if every orbit is reached at least once. In other words, every fiber of q contains at least one element of the basis . This is equivalent to being surjective. □
Hence, the question of whether a particular lies in can be answered by inspecting whether is bijective. We are thus inclined to look at the map , which we formally write as
In other words, this map is the X-fold product of q. We may thus write Lemma 7 as the following pre-image statement.
Corollary 1.
Let F be a free G-set, set , and denote by the group of bijections of X. The set inside is the pre-image of under .
We remark that the set is a special subset of ; the latter has a natural monoid multiplication given by composition, and is the set of units of this monoid.
We will now start to take topology into account; we assume G is a topological group and F is a G-space. The set thus inherits the quotient topology such that q is continuous. For any set X, inherits the product topology, and the map is continuous. In this setting, Corollary 1 can be used to deduce some topological properties of . This requires us to consider the topology of X, which should be homeomorphic to the topology of given the bijectivity from Lemma 5. We will restrict ourselves to discrete X, i.e., F should be a semi-torsor; this preserves the index set intuition and guarantees that the previous results on G-sets are still valid. Pictorially, this means that the orbits inside F form a partition of F into open and closed subsets. Under this assumption, the following holds.
Corollary 2.
If F is a G-semi-torsor, then is open and closed in .
Proof.
As X is discrete, so is (with the product topology). Hence, is an open and closed subset of . As is continuous, the claim follows from Corollary 1. □
In case G is a Lie group and F is a G-manifold, this corollary implies that is an open and closed submanifold of . We assume G to be finite-dimensional in this paper, but as we allow for infinite X, the manifold can be infinite dimensional.
We remark that the similar version of Corollary 2 for vector spaces need not hold. For V, a real vector space of finite dimension n, this statement would be that the set inside is open and closed. However, is only an open subset of . This can be proven by observing that inside is similar to inside the space of all real matrices. Now is the pre-image and so open. It is not closed; there are sequences of invertible matrices that converge to a non-invertible matrix. This argument does not hold in the case of G-spaces if we assume that the orbits are disjoint. Given a sequence of bases, look at the induced sequence of orbit-representatives in X. As X is discrete, a sequence in X converges if and only if it becomes constant. That is, if the original sequence converges, then the basis elements settle in particular orbits, which must be different. As the orbits are disjoint, also the limit of the has basis elements in different orbits. That is, the limit of the bases is itself a basis.
Let us consider the frame of the -set given by disjoint circles as needed for the winding torus. It is clear that the set of frames is homeomorphic with a product of the group times the permutation group of the orbit space X. This is generally true as we will prove in the following section.
Example 7.
We defined in Example 3 the bundle with model fiber . This model fiber can also be viewed as , i.e., we pick an arbitrary ordering of the circles for our convenience. A frame of is then a tuple , with and such that is a permutation of . Concerning its topological properties, we see that varying the yields a k-dimensional torus . Furthermore, one obtains such a torus for any permutation of , i.e., the tori can be indexed by the permutation group . This means that is homeomorphic to , i.e., many tori of dimension k.
4.3. Wreath Product Action
In preparing the claim that the frame bundles with model fiber of the form are principal bundles, it is natural to show that is a torsor. Intuitively speaking, this will describe how one can construct a new basis from a given one. This reasoning is similar to arguing that can turn any basis of a real n-dimensional vector space V into another, which is captured by its action on the set of bases . An important property of this action is that the precise vector space V need not be known; the existing basis vectors are just mixed in such a way that a new basis is obtained. This observation is crucial in defining the frame bundle of a vector bundle, and in some sense we will show a G-space equivalent here.
Let us start with the action on tuples of G-set elements, i.e., the action on the set of functions . A first symmetry is that any element of the tuple may be scaled independently from the others. This is given explicitly by the action
where is the function defined by pointwise multiplication; . Of course, this is the natural -set structure on inherited from F.
Another symmetry of is to change labels, or in the tuple view, to rearrange positions. More algebraically; as is a function space, it has a natural action by given by pre-composing with the inverse permutation:
These actions of and on can be merged into a single action by a specific group, namely, the wreath product of G and X. There are multiple constructions known under the term wreath product [7], but we shall use it as follows. We only need the information that G is a group and X is a set. The key construction is the canonical (left) action of on given by , i.e., again shuffling the tuple according to . As the map is an automorphism of the group , the action defines a map . That is, the action specifies a semi-direct product with multiplication given as
This group is known as a wreath product and written as . This notation allows for groups other than to act on X, but as we will only use , we simply denote this group by . Let us at this point give an explicit example before moving to further properties.
Example 8
(Wreath product action on frames of two disjoint circles). We again consider and . Again, does not carry any special points, whereas does have one in its neutral element. To emphasize this in the picture, we visualize elements of as points on a circle, but elements of we visualize as rotation arrows. The action first relabels the basis elements, and then acts with the groups elements; see Figure 7 for an example.

Figure 7.
Illustration of how the wreath product acts on a tuple of points; here, in the case of F, the -set . First, the labels are exchanged according to the permutation, and then the group elements act according to this new labeling.
Let us briefly review some basic properties on this wreath product. For , i.e., the unit group of a field , and , the wreath product is faithfully represented by generalized permutation matrices. These are the matrices in having only a single non-zero entry in each row and column. An explicit representation is , where is a standard permutation matrix. If G is a topological/Lie group, then is as well via the semi-direct product realization. The connected subgroup of is that of . Hence, in case G is a Lie group with algebra , the algebra of is , which we view as the space of functions . It follows that , so for infinite X and non-discrete G, one formally obtains an infinite-dimensional object. However, because locally looks like separate copies of G and we assume G to be finite dimensional, we do not dwell on this.
Having introduced the wreath product, we may now define how it acts on . We simply combine the previous actions on by stating that a pair acts by first acting with and then acting by . When thinking of the wreath product in terms of generalized permutation matrices, this action resembles matrix–vector multiplication by viewing as a column vector.
Proposition 6.
The map
defines a -action on . Moreover, is an invariant subset, even a -torsor.
Proof.
Let us check that the proposed map indeed defines a -action. Clearly, the identity element of fixes any , and for the homomorphism property, one checks
So, indeed ; hence, the above map defines a -action.
To check the restriction to , we check the criterion of Lemma 7. If , then is invertible and hence
is invertible. Hence, , implying that the action restricts to . Concerning the last claim, pick two frames and . Then, and are invertible; hence, one obtains a permutation . It follows that and have the same underlying permutation, as . Hence, for each , the elements and lie in the same G-orbit, and as F is free, they are related by a unique group element . This means that and are related by a unique element of . Hence, any two frames can be related by a unique element of , i.e., the action is free and transitive. □
We wish to make a technical remark on the choice of the group. Observe that the symmetry group of the basis can also be argued to be . Indeed, given any two bases and , the map is an element of , even the unique element which brings to . It follows that this action on is also free and transitive. Hence, one could pick either or as the symmetry group of F. However, there is a subtle yet significant difference between the two.
Let us illustrate this difference in the more familiar setting of a real vector space V of dimension n. Clearly, has a natural action by ; a matrix acts on a basis as
where repeated indices are summed over. However, one may argue that the symmetry group of is , as this is the automorphism group of V. The action of on a basis is
This is again free and transitive, similar to the -action. Of course, is isomorphic to . However, let us try to use these actions to define new actions but now on , where is another real vector space of dimension n. We see that the -action can be copied verbatim; A acting on a basis of is simply . This is not so for the -action; takes elements of V and not of . Even in the case , this subtle issue arises. In this notation, under the -action, every vector in the new basis depends on all the old ones, whereas under the -action, every new vector depends only on the previous one. In particular, if one perturbs only one of the basis vectors, then this may change all vectors under the -action but only one under the -action. As a final remark, note that vector bundles describe a smooth family of vector spaces. When defining the frame bundle of a vector bundle, it is this crucial that a global -action can be defined, despite the fact that every fiber involves another vector space.
For G-sets, we find a similar argument; instead of using , we will use . This will be important when we discuss bundles involving G-spaces later on. A more detailed exploration of and how it is isomorphic to the wreath product is given in Appendix A.
4.4. Representing Equivariant Maps Using Matrices
Having seen the relevant group for G-bases, namely, the wreath product, we can continue with how to use G-bases for representing equivariant maps. The analogy with vector spaces is again a good lead. There, if is a basis of the given vector space, one can express the linear map A using a matrix by calculating and and relating these back to and . The matrix is then the array of all the coefficients, which are unique but depend on the choice of basis. To list the procedure explicitly,
For semi-torsors, we have essentially the same equation. If is a basis of the given semi-torsor, one can express the G-equivariant map using a matrix by calculating and and listing how these relate to and . Let us first give an example, and then state the general argument.
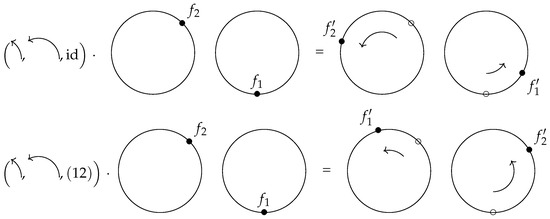
Example 9.
Let us take a situation like the parallel transport map on the double torus. That is, we consider the -semi-torsor , and there is an equivariant map α. We pick a basis of , and calculate and , leading to a situation as in Figure 8. In this case, we find

Figure 8.
Using a frame to describe an equivariant map, such as parallel transport. One expresses and using the basis and so finds the (matrix) coefficients.
The zeros here just mean that those entries are not needed. This matrix representing α is a generalized permutation matrix; it can be decomposed as
that is, as the product of a diagonal and a permutation matrix. The diagonal matrix lists all the needed group translations, while the permutation matrix describes how the orbits are exchanged. The exact elements again depend on the chosen frame .
This extraction of the matrix works for arbitrary bases of a semi-torsor, even in the case when relates semi-torsors with a different amount of orbits. To describe this, let be a basis of F, and a basis of . The main point is that will always be in the orbit of a unique , and these elements will then differ by a unique element , i.e., . Defining the matrix A, with elements in G, by
then generalizes the previous recipe. At this point, A is just an array of elements in G. In a special case, namely, when G is commutative, one recovers the property that matrix multiplication corresponds to the composition of maps.
Lemma 8.
Let and be G-equivariant maps of G-semi-torsors, and let be a frame of F and a frame of . Pick a basis of so that α and β are represented by matrices A and B with respect to the appropriate bases. If G is commutative, then the matrix representing equals the matrix product .
Proof.
Say . The matrix has at position the element as
If G is commutative, this equals . Going over all i, we find the n non-trivial coefficients for , and these coincide with those obtained from the multiplication . □
For a self-map , changing the basis causes the matrix A to change by conjugation. That is, if is changed to , then A is conjugated by the generalized permutation matrix representing . A logical question is then what properties of A are invariant under the choice of basis. Similar to linear algebra, this can be performed by investigating the invariant subspaces of —please remember that contains the actual information, of which A gives some non-unique representation. This leads to equivalents of the Jordan normal form and eigenvalues for these matrices as we describe in the following.
Proposition 7.
Let F be a G-semi-torsor and an automorphism. Then, we have the following:
- , for some index set I, decomposes F into minimal α-invariant subspaces, i.e., for all i.
- If G is commutative and a particular consists of orbits, then equals translation by an element of G.
- By picking the appropriate basis of F, the matrix A can be written in block diagonal form. A block represents a restriction , with size given by the number of orbits k, and one may choose one of the following normal forms for it. The first of these is, with the identity,and a second form is, given any such that ,
Proof.
Clearly, the index set I is obtained by taking the original orbit space X and identifying orbits that are mapped into one another by . We focus on a particular minimal subspace . If consists of k orbits, then by minimality, preserves the orbits in . Picking , we find for some . To inspect how this depends on f, let us write another element in the orbit as with . If G is commutative, one finds both
and as F is free, this yields , and applying yields . That is, is constant on the orbit through f. It is even constant on the invariant subspace ; as equivariance yields , we see that in the next orbit is scaled by the same group element. It follows that is constant on the subspace , and we write this group element as . The first normal form is obtained by picking a basis as follows. One picks any , and then inductively sets . It then follows that all group elements are the identity, except when dealing with , which gives and so proves the first normal form. The second normal form is obtained by the rule . We only need to check that this yields , which follows from
□
Example 10.
In the situation of the previous example, is already a minimal invariant subspace, as both orbits are mapped to one another. For the characteristic group element, we consider , as there are two orbits, and we see that . The invariant group element is thus , and is thus given by the sum of the angles, which is the ‘return angle’.
The normal forms offer us two standard ways to distribute this total angle over the steps. The first is to perform the entire angle in one step, and the second is to distribute it evenly over the steps. This is illustrated in Figure 9 below. In the picture, α lays the right circle over the left one with a rotation of degrees, and the left circle over the right one with degrees. The return angle is thus 180 degrees. The first option picks a frame where the entire angle occurs when evaluating . The second option picks a frame where this angle is distributed evenly over and . We can choose any of the roots of the 180 degree rotation, so either or degrees each time. The matrices are thus

Figure 9.
Bases for the two normal forms. Left: first normal form with the entire angle in the last step. As , the rotation there vanishes. Right: second normal form, with the angle evenly distributed over the steps.
In Figure 9, we chose the + option in the second normal form.
4.5. Functorial Property
The previous material indicates that a G-semi-torsor F can be mapped to the -torsor . Such a statement hints at a functorial property, which brings us to the question which equivariant maps will induce a map on frames in the canonical way . As we assume that and are free, this can be answered by looking at orbits only. We first show that induces a unique map on the quotients, and that the invertibility of this map is equivalent to the posed question.
Lemma 9.
Let be -semi-torsors with orbits spaces for . Let be a ξ-equivariant map. Then, α descends to a unique map on orbits . That is, there is a unique arrow such that the following diagram commutes:
Moreover, an equivariant map lifts to a map if and only if is a bijection, i.e., if α is a bijection on orbit level. In this case, and after identifying and with X for simplicity, is equivariant with respect to the group map .
Proof.
By equivariance, maps a -orbit in inside a single -orbit in . That is, the map is -invariant. Hence, exists as a function. More generally, as the are discrete, this map is also continuous. Let us thus consider the induced maps on the bases. The statement is trivial in case and are not bijective; then, bases of and have unequal cardinality, but also cannot be a bijection. Hence, we treat the case . In this case, there is a well-defined function given by . To check that is a basis of whenever is a basis of , we use the criterion in Lemma 7. This concerns the invertibility of
From this equation, it follows that for to be invertible whenever is, it is both necessary and sufficient that is a bijection. Concerning equivariance, note that is -equivariant. Moreover, is also -equivariant as
That is, is equivariant with respect to both and , which implies that is equivariant with respect to the map given by . As the actions are restricted to the frames, the restriction of to the frames is again equivariant with respect to . □
The requirement in this result is not automatic; there exist equivariant maps of semi-torsors that are not a bijection on orbit level. A simple example is mapping to G via identity maps. Hence, taking the frame space can only form a functor from semi-torsors to torsors if the maps between semi-torsors are restricted to those where is a bijection. Let us thus define the following categories.
Definition 8.
Define STor to be the category whose objects are semi-torsors and whose maps are equivariant morphisms α so that is a bijection. Given a Lie group G, write for the restriction of STor to G-semi-torsors and -equivariant morphisms.
By restricting the category of group spaces to torsors, one obtains the category Tor of torsors, and also the category by requiring the group to be G and morphisms to be -equivariant. It is clear that Tor is a full subcategory of STor. Taking the frame space then defines a retraction in the following sense.
Theorem 1.
The assignment
defines a covariant functor . Moreover, this functor is (essentially) constant on Tor.
Proof.
Observe that the source is a well-defined category; any identity map trivially satisfies the condition of Lemma 9, and the composition of maps preserves this condition; if and are composable maps which satisfy that and are bijections, then as , also does. By Proposition 6 and Lemma 9, the assignment is well defined on objects, i.e., maps. Given the explicit form of in Lemma 9, it follows that and . Hence, the assignment is a functor. As is a -torsor and is equivariant, this functor takes the image in the category of torsors. If F is already a torsor, then X consists of a single point, and the condition of Lemma 7 is vacuous, so . Hence, the functor is (essentially) constant on the torsors. □
If one fixes the structure group G, then one can say more. The image of consists of torsors whose structure groups are of the form . Given a particular torsor in this image, up to isomorphism, the original semi-torsor can be recovered by taking a quotient. The idea is that a semi-torsor F can be recovered from by considering all elements that appear in any particular position in the tuples. This position we may choose ourselves, e.g., we only consider the first position. This is equivalent to quotienting by the subgroup of all group elements that do not touch position x. This yields a method applicable to any -torsor, and we obtain an equivalence of categories. In order to show this, it is convenient to first treat the following lemma. This shows that the model -torsor, being the space viewed as a torsor, indeed reduces to , which we expect, as is isomorphic to (as torsors). The action we will use can be obtained by viewing elements of as generalized permutation matrices, and as a column vector consisting of all zeros, except for h at place x.
Lemma 10.
There is an action of on defined by
The stabilizer of is the subgroup . Moreover, the induced map , where the quotient is endowed with the G-action on slot x, is an isomorphism in .
Proof.
To check the action property, observe that
Furthermore, lies in the stabilizer of if and only if and . That is, the place indexed by x is not touched. Hence, the stabilizer is canonically identified with . Viewing as a G-space as indicated, the orbit map is G-equivariant, and so the quotient yields an isomorphism of G-semi-torsors. □
An equivalence of categories can now be obtained as follows. To avoid confusion concerning the class of all discrete topological spaces, we restrict to the finite case.
Proposition 8.
For a fixed Lie group G, the frame functor induces an equivalence of categories
where the superscript indicates the restriction to finite index sets.
Proof.
Let us show that this restricted functor is both fully faithful and essentially surjective. Given a -torsor T so that T is isomorphic to the space viewed as torsor, by Lemma 10 one has , and hence the functor is essentially surjective. To show it is fully faithful, let be two G-semi-torsors with equal index set . Let be any map of -torsors. Pick any frame . Using its image frame , define the map , which does not depend on our choice of . Clearly, is the unique morphism satisfying . Hence, the functor is also fully faithful, and the equivalence follows. □
5. The Frame Bundle of a Semi-Principal Bundle
In this final section, we introduce the frame bundle of a semi-principal bundle, which again closely resembles the frame bundle of a vector bundle. We have already seen semi-principal parallel transport, and demonstrated how frames can be used to study this. With the frame bundle, frames become an inherent part of the bundle structure itself. As the frame bundle is principal, it thus allows for a conventional way to study parallel transport straightaway. We will first define the frame bundle, then demonstrate its functorial nature, and finish with the passage of a connection on a semi-principal bundle to a connection on the frame bundle.
5.1. The Frame Bundle of a Semi-Principal Bundle
We thus start by defining the frame bundle of a semi-principal G-bundle with model fiber F. Let us stay close to the argument we had for , which consist of two steps. First, we showed that has a natural -action on it, to then view as a special subspace. We have the same steps here. To start, instead of , we first inspect the -action on the X-fold fiberwise product bundle of B.
Proposition 9.
Given a semi-principal G-bundle with index set X, then the fiberwise product bundle is canonically a -space bundle.
Proof.
It is convenient to realize as a pull-back of the X-fold direct product bundle
As B is a G-space, clearly is a -space by a similar argument to that we used for in Proposition 6. Likewise, is a -space, and is equivariant for the canonical group map . Moreover, admits -equivariant local trivializations. Indeed, let be a local G-equivariant trivialization of B. This induces the map
which is a local trivialization of . It is -equivariant; the -equivariance is by construction, and the -equivariance is immediate, cf. the verification in the proof of Lemma 9.
Let us move to . Obviously, tuples in may contain elements from different fibers of B, and we obtain the fiberwise product by demanding that they come from a single fiber. This can be expressed geometrically using the constant/diagonal map sending to the constant function . This realizes the fiberwise product bundle as a pull-back, whose corresponding diagram is
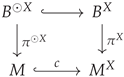 so that both bundles have model fiber . In this way, the topology and manifold structure of are clear, and is smooth. Moreover, as the image of c is -invariant, it follows that inherits a -action from that leaves invariant. A local trivialization of B induces the local trivialization of given by
which is -equivariant. □
so that both bundles have model fiber . In this way, the topology and manifold structure of are clear, and is smooth. Moreover, as the image of c is -invariant, it follows that inherits a -action from that leaves invariant. A local trivialization of B induces the local trivialization of given by
which is -equivariant. □
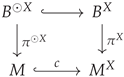
We can now view the frame bundle of B as the subspace of where the elements define bases as performed formally in the following definition. Given the previous result, it is only a minor step to prove the bundle property of , which we perform directly afterwards.
Definition 9.
Given a semi-principal G-bundle , its frame bundle is defined as the bundle
Theorem 2.
If is a semi-principal G-bundle, then its frame bundle is an open subbundle of , and forms a principal bundle
Proof.
Given Proposition 9, it suffices to verify that is locally an open subbundle of . Let be a trivializing open of B, consider the induced local trivialization . As is open and closed in by Corollary 2, the map restricts to a -equivariant isomorphism from onto its image. This image is , as for each the map establishes an isomorphism of G-spaces. Hence, is an open subbundle of with model fiber . As is a -torsor by Proposition 6, the bundle is principal. □
We place the following comment concerning the notation . This notation makes explicit reference to the G-manifold B but implicitly uses the bundle map as well. As seen in Example 11 below, different projection maps may lead to different frame bundles, yet the total space of these projection maps is the same G-manifold. We thus write with the understanding that B is short for the entire bundle structure.
Example 11
(Frame bundle of winding torus). Let us again consider the semi-principal bundles . The total space is the same for all these bundles, but the frame bundles are different for every k. We already know that the model fiber is , and that . These have a different dimension for every k, from which it clearly follows that the frame bundle will be different for each k.
The following question we did not yet answer here: if one wishes to have a well-defined permutation action on the bundle, is it really necessary to leave B behind and move to instead? In other words, does such an action not already exist on B itself? The need for this change is proven in Appendix B, where we find that one can only stay on B if B is trivial. That is, the local labeling with index set X will in general not suffice in order to define a global permutation action. The solution that provides for this problem is to use the positions in the frame tuples instead—these positions are defined globally.
5.2. Functoriality of Taking the Frame Bundle
We move on to the functorial nature of the association . In Theorem 1, we proved the functorial nature in the case of semi-torsors, and here we show its extension to semi-principal bundles. Clearly, the objects of the source category are the semi-principal bundles. However, the admissible maps will not be all equivariant bundle maps; inspecting a single fiber brings us back to Lemma 9, which indicates that a map should be a bijection on orbits. This condition readily lifts to the level of bundles, and is a sufficient condition to obtain an induced map on the frame bundles as proven below.
Lemma 11.
Let be an equivariant bundle map of semi-principal bundles over M, where the map on groups is , and . Then, α descends to a fiberwise map on orbits . That is, in the following diagram, the lower arrow exists and is a bundle map.
Moreover, α induces a map of bundles
if and only if is a bundle isomorphism. In this case, is equivariant with respect to the map , so in particular, is a map of principal bundles.
Proof.
As is equivariant, exists as a function, which is fiber-preserving, as the action is so. To prove it is smooth, one can look locally over a trivializing open or use that is a surjective submersion. Hence, is a well-defined bundle map. As is a bundle map, so is its product . The restriction of is also a bundle map, as is an open subbundle of by Theorem 2. This restriction takes the image in if and only if the map maps bases to bases. By Lemma 9, this is if and only if is a bijection for all m. However, as is a bundle map, this is equivalent to being an isomorphism. The equivariance of readily follows; a similar derivation as in Lemma 9 applies. Hence, restricts to the map if and only if is a bundle isomorphism, in which case is a map of principal bundles. □
This result tells us that the frame functor is not applicable to the full subcategory of group-manifold bundles obtained by restricting the fibers to semi-torsors but retaining all possible maps of group-manifold bundles. To obtain a genuine frame functor, we must restrict the maps to those which satisfy that is a bundle isomorphism. Similar to the semi-torsor case in Theorem 1, this will yield a subcategory; is always an isomorphism, and a composition of admissible maps is again admissible as . Because of its interest in the frame bundle construction, we wish to list this category in a definition.
Definition 10.
The category of semi-principal bundles over a base M, denoted by , is defined to have as objects the semi-principal bundles over M and as morphisms all equivariant bundles maps α such that is an isomorphism. Given a Lie group G, write for the restriction of to semi-principal G-bundles and -equivariant maps.
Clearly, as we deliberately discard some maps by the orbit condition, is a subcategory but not a full subcategory of the group-manifold bundles over M. On the other hand, the principal bundles and their morphisms are still contained in the semi-principal bundles. Let us write for the category of principal bundles, and for the restriction to principal G-bundles and -equivariant maps with G as a Lie group. We then find that can be seen as a specific extension of .
Lemma 12.
The category is a full subcategory of . That is, all principal bundles are semi-principal and whenever P and are principal bundles over M.
Proof.
All principal bundles are semi-principal bundles, as any torsor is a semi-torsor. Pick a principal G-bundle P and a principal -bundle over M, and consider an equivariant bundle map . As and and preserves fibers, one has up to an isomorphism. That is, the condition that is an isomorphism is automatically satisfied. As this is the only axiom that distinguishes between morphisms in and , it follows that . □
Back to the frame bundles, one may observe that taking the frame bundle maps to its full subcategory . This association is functorial, and can be interpreted as a kind of retract. The formal statement is the following theorem, which is the bundle equivalent of Theorem 1.
Theorem 3.
The assignment
defines a covariant functor . Moreover, this functor is (essentially) constant on .
Proof.
By Theorem 2, this functor is well defined on the objects, and by Lemma 11, it is also well defined concerning morphisms. It is easily seen that identity maps and compositions are preserved; hence, the map is a (covariant) functor. Also, if B is a principal bundle, i.e., X is a point, then the basis condition is vacuous and . □
Example 12.
An remarkable application of this result is obtained for the quotient map . Indeed, this is a morphism in , where we view as an semi-principal bundle with a trivial structure group. The corresponding bundle map diagram is
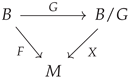 with model fibers indicated. Applying the functor results in the bundle map diagram
with model fibers indicated. Applying the functor results in the bundle map diagram
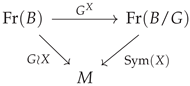 where each arrow is a principal bundle with the indicated structure group.
where each arrow is a principal bundle with the indicated structure group.


As with the semi-torsors, also the frame bundle functor induces an equivalence of categories if one fixes the structure group G.
Proposition 10.
For a fixed Lie group G and base manifold M, the frame bundle functor induces an equivalence of categories
where the superscript indicates the restriction to finite index sets.
Proof.
This follows Proposition 8 on semi-torsors; quotienting by for each n individually yields again an inverse functor as can be verified using local triviality. □
We finish this exploration of the category with the following results on its morphisms.
Lemma 13.
Let be a morphism in , equivariant with respect to a group map . Then, α can be expressed locally as
where is a trivializing open of both and .
Proof.
For , let be local trivializations of , where is non-empty. As is an isomorphism, it follows that ; hence, we call them both X. Restricting the to U and identifying , one has the map . This is a bundle map; hence, the follows. It is also equivariant; hence, a -orbit is mapped inside the -orbit . The induced map on orbits is a bijection by assumption; hence, by identifying with X differently if needed, one may assume for all , which proves the part. The middle map thus remains. Here, note that equivariance reads such that is fixed by the points . This defines a smooth function , which can be translated to be constant by absorbing it in the -part of (which does not interfere with the choice for X earlier). However, then, , meaning equals the proposed map. □
Corollary 3.
The map α is injective/surjective if and only if ξ is. Moreover, in case it is surjective, α defines a principal -bundle.
Proof.
Let us use the map again. As and only differ by identity maps, is injective/surjective if and only if is. Hence, is injective/surjective if and only if is. Finally, as is a closed normal subgroup of , if is surjective, there is the principal bundle . Hence, locally looks like , where V is a trivializing open in . Hence, can be restricted to the map , which is clearly -invariant. As any point in has a neighborhood of the latter form, it follows that defines a principal -bundle whenever it is surjective. □
This latter result is the remarkable observation that maps of semi-principal bundles may themselves be principal bundles. We observe that the quotient map provides an example.
5.3. Connection on the Frame Bundle
Let us finish with the connection that the frame bundle inherits from the semi-principal bundle. That is, we need to check how a G-connection on B carries over to a -connection on . The procedure is straightforward, as is a submanifold of . Namely, the latter has a canonically induced connection by stating that a curve
in is horizontal if and only if the curves in B are horizontal for all . Equivalently, in the 1-form formalism, the bundle is naturally endowed with the -connection 1-form defined by
We note that this formally leads to infinite dimensional groups and algebras in case X is infinite, but as seen in the curve picture, the connection is nevertheless well defined. A connection on is obtained by restriction of to , i.e., one takes the pull-back of along the inclusion . This induced 1-form is indeed a -connection. A proof of this requires knowledge of the adjoint representation of ; hence, we inspect this first.
Lemma 14.
The adjoint representation is given by the rules
Proof.
As , it suffices to compute the two listed maps. The relevant conjugation maps are
The first one recalls that the Ad of is X copies of the Ad of G. The second immediately shows that derivatives follow the same permutation as the tuple. □
Proposition 11.
Let B be a semi-principal G-bundle with G-connection ω. The 1-form
is a -connection on . In particular, is a principal connection.
Proof.
To start, indeed takes values in the algebra , which is the algebra of . The condition that is a left-inverse for the infinitesimal action on is satisfied, as it is the case per copy, i.e., for each independently. To check the equivariance of , let us consider the - and -actions separately. The -action can again be inspected per , and reduces to the equivariance of . Concerning the permutations, fix . Then, . Hence, is a -connection. □
This statement is a hint that the frame bundle functor extends to bundles with connection, which indeed holds according to the upcoming theorem. The intuition is that the connection information on B and is in essence the same; the latter consists of copies of the first (compare the equivalence in Proposition 10). However, the connection has the convenient property that its holonomy can be written more explicitly, namely, using elements of .
Theorem 4.
Let be a semi-principal -bundle with -connection for . Let be a ξ-equivariant morphism compatible with the connections, i.e., . Then, is compatible with the frame bundle connections and . That is, the frame bundle functor extends to semi-principal bundles with connection.
Proof.
The compatibility of can be verified entrywise. Writing , , for the inclusions, and using ,
and so the claim on the frame bundle functor follows. □
We finish with the remark that a morphism of semi-principal bundles can be used to transfer a connection from one bundle to another. A trivial example is the quotient map ; any connection on B is reduced to the lifting of a curve through a covering map. We observe that this statement will place one in the context of the previous theorem.
Proposition 12.
Let be semi-principal -bundles for with equal index set X. Let be a ξ-equivariant morphism. Then, any -connection on induces a unique -connection on , satisfying
Proof.
As semi-principal bundles locally look like principal bundles, similarly, for the maps between them, one can use the same argument as for principal bundles, e.g., [8] (Proposition II.6.1). □
6. Discussion
In this paper, we started by exploring fiber bundles, where the model fiber is a group or a group space. We found these to be significantly different. In addition, we found that principal bundles form a special class of group-space bundles, namely those whose fiber is a torsor.
We then shifted our attention to an intermediate class of group spaces and group-space bundles. Within the group spaces, we considered those whose fiber is free and has a discrete quotient, and called these semi-torsors. The corresponding group-space bundles, we called group-space bundles. We demonstrated how the notion of principal connection can be generalized to that of G-connection, with which semi-principal bundles have a well-defined parallel transport. This we performed after showing how semi-torsors have a natural 1-form compatible with the G-manifold structure, which generalizes the Maurer–Cartan form. This parallel transport led us to an important question, namely, how to study maps of semi-torsors, in particular, those which mix different orbits.
We found a solution by introducing the notion of a basis of a G-set F, in analogy with the basis of a vector space. The basis elements serve as reference points for the different orbits. An equivariant map like parallel transport can then be described by reordering the elements and applying the appropriate group translations. These changes are simultaneously described using the wreath product , being the symmetry group of the space of bases of F. The wreath product can be represented by the generalized permutation matrix, which can thus be used to express equivariant maps. We finished with the functorial nature of the association , which also prepared us for the final part.
Indeed, in the last part, we saw how a semi-principal bundle has a frame bundle, and how this association is likewise functorial. The frame bundle is a principal -bundle and naturally inherits a connection from the original semi-principal bundle. As it is principal, the frame bundle allows one to describe parallel transport in the conventional way.
As stated in the introduction, our main motivation to study semi-torsors and semi-principal bundles comes from the field of adiabatic quantum mechanics. For the exact way in which these structures arise there, we refer to [2]. In short, one obtains a semi-torsor rather than a torsor, as eigenrays can be well separated for an individual Hamiltonian, yet can be connected by variation of the Hamiltonian. More geometrically, locally eigenrays are distinct objects, yet globally, they are part of the one and the same structure. This topological property allows for interchanges of eigenstates by adiabatic evolution. The frame bundle functor then recasts this theory into the more familiar setting of principal bundles.
In addition to this, we observe a resemblance of the frame bundle theory with the model in [9,10]. This studies the fractional quantum Hall effect, in particular, electrons that are in a bilayer phase. A -symmetry appears for both layers separately, and in addition, there is a -symmetry describing an exchange. The total group that appears is then , i.e., in the notation of this paper, and the gauge fields and their transformations follow the properties of found here. In [10], also the case is touched upon, and in both cases, a new parameter space is constructed with which one can reduce the theory to the standard symmetry group . The bundles presented in this paper shed additional light on this process, in that it can be interpreted as moving from to , where the new parameter space is then an n-fold cover of the original space M.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, E.J.P.; Writing—original draft, E.J.P.; Writing—review & editing, E.J.P. and H.W.; Supervision, H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Daniël Boer for the fruitful discussions, and the anonymous referees whose careful remarks helped to improve the quality the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Automorphism Group of a Group Set
In this appendix, we show that the wreath product and the automorphism group of the model free G-set are isomorphic. We first show that fits in a special short exact sequence (SES), cf. the semi-direct product structure of the wreath product. Afterwards, we treat an explicit isomorphism, which can be derived using an argument similar to that of dual spaces.
In both parts, we will use the following notation. Observe that any two bases are related by a unique element specified by the equality
of maps . This yields , which is a composite of G-isomorphisms; hence, lies indeed in . This notation is compatible with the more general division in the main text; the division here corresponds to viewing as an -torsor.
Appendix A.1. Short Exact Sequence Using Quotient Map
To start, let us examine the group for F a free G-set. A first observation is that an element of must induce a bijection on the orbit space . That is, the following holds.
Lemma A1.
For any map , there is a unique map such that the diagram
 commutes. This association defines a map of groups
which admits sections.
commutes. This association defines a map of groups
which admits sections.
Proof.
The map is well defined, as is G-invariant and so constant on the fibers of q. If also , then by combining two of the above squares, one can deduce , i.e., is a homomorphism. As , it follows that all images of are invertible; hence, has an image in . To show that admits sections, let us argue using a section of q. Then, for each , one has a map
This map is basis dependent but nevertheless invertible and G-equivariant, hence an element of . If one only varies the permutation , one obtains a map of groups
To check that this is a section of , observe that as is a section of q. A computation then shows
□
As admits sections, it must be surjective; hence, let us consider its kernel. This is readily seen to be the subgroup
i.e., the group of orbit-preserving automorphisms. In other words, it is the group of deck transformations of q, hence the notation . One thus arrives at the following SES, which can be considered a corollary of the previous lemma. The used notation highlights that this sequence is obtained by considering the automorphisms of the objects in “”.
Corollary A1.
Let F be a free G-set. The group fits in the short exact sequence
which is right-split.
This result need not hold for a general G-set F. In that case, is still a homomorphism with kernel , but it need not be surjective, let alone admit sections. That is, only the part
is exact. This sequence need not extend to the right, as the image of need not be normal in . Any may only shuffle orbits of the same shape; hence, a counterexample is any F where at least two orbits differ but also two orbits are isomorphic. This does not happen in case F is free, in which case the sequence closes to a SES. There are other assumptions one can place on F, but we will not study these in this paper.
Appendix A.2. Automorphism Group of the Quotient Map
We now wish to rewrite in a more explicit form. The elements of this group act on the fibers of q, which are isomorphic to G; hence, they can be specified using an element of G for each orbit. To describe this, we use a division operation on F, which is not to be confused with the previous division (on ). That is, for we denote by the unique group element satisfying
Here, we view F as a G-semi-torsor by viewing a set as a discrete space; hence, also, this division is in line with the main text. However, we wish to state the following familiar rules for this division .
Lemma A2.
Assume F is a free G-set, let . The following rules hold:
- Inverse: .
- Cancellation: for any in the same orbit as and , one has .
- Scaling: for any , one has . In particular, for , one has .
- Invariance: if , then .
Observe that the division is ‘covariant’ with respect to in its right slot, whereas in its left slot, it is ‘contravariant’. By this, we mean that for and , one has
such that the order is preserved, whereas for the other slot, it is reversed as
We can now specify an isomorphism . Let us use again a section of q; in this way, each lies in the orbit x, so no shuffling of orbits will happen in what follows. The idea is that each translates the orbit by a group element, which can be found as
One thus has the map
which is a homomorphism, as the division on F is covariant in its right slot. As one can reconstruct from given , this map is invertible, hence an isomorphism. We thus find the following result.
Lemma A3.
If F is a free G-set, then .
We wish to place some remarks here. First, this isomorphism depends on the chosen section ; picking another section of q, one has for some elements and finds
This means that, if one restricts to bases which are sections, the identification is unique up to the inner automorphism of . In particular, the identification is canonical if and only if G is commutative. A second remark is that instead of being the element mapping to , it is actually the inverse of this. An intuitive answer as to why this is can be found in the pairing argument we discuss below.
Combining Lemma A3 with the SES in Corollary A1 shows that the group is isomorphic to the semi-direct product , which is the wreath product . We now wish to discuss this more explicitly in the following.
Appendix A.3. Wreath Product as Model Automorphism Group of Semi-Torsor
Let us specify an explicit isomorphism . Here, we also allow G to be a topological group or a Lie group, and require automorphisms to respect this additional data. To do this, we assume that X as the orbit space is again discrete such that is a model G-semi-torsor. An explicit map is given by
such that a pair is mapped to
Lemma A4.
The map is an isomorphism.
Proof.
Let us check that this map is well defined. First, we note that the returned functions are indeed (left) G-equivariant; acts by right-translation and does not touch the G-slot. These maps are also bijective and continuous, or even smooth; hence, they lie in . A quick check shows that I is a homomorphism; hence, it remains to show that I is invertible.
Take . First, note that returns the underlying unique permutation of , so only the -element remains to be found. For this purpose, observe that is the identity on the X factor. Hence, one may define uniquely by the requirement
or in function form
Note that both sides contain left-equivariant maps. The map is the inverse of I. As we will see now, it is a homomorphism as well. The combination clearly has , and the similar rule for the -element follows from
such that equals . The latter is exactly the G-component in the multiplication of the wreath product. Hence, I is an isomorphism of groups. □
The form of I can actually be deduced by an argument similar to that of dual spaces. In particular, this argument explains why enters via an inverse (in fact also has an inverse with respect to previous equations). A motivating argument is as follows. Fix some , let be a basis with basis index set X. Then, there is a unique pair such that
so the pair can be seen as the coordinates of f. Let us change the basis by acting with on . Then, f is given as
so in the new basis, the point f has coordinates . Hence, the inverse on the group element can be found by looking for the map on coordinates induced by the change of basis.
We discuss this in terms of a pairing map. This map is canonical; it takes coordinates and a basis and returns the element that this pair describes, i.e., . More formally, for the G-set F, this is the map defined as
The key observation is the following invariance argument.
Lemma A5.
Any induces a unique map via the invariance condition
This assignment defines a homomorphism .
Proof.
We recall that the are G-isomorphisms for any basis . The invariance condition reads
Hence, , provided the latter is independent of . This can verified by a direct check but also by the following argument. Let us use the map and observe that it commutes with the -action, as it lies in . Moreover, cf Lemma 6. Hence, in the basis , one obtains
Hence, is a well-defined map. As the ’s are G-isomorphisms, so is ; hence, it lies in . The homomorphism claim readily follows from the invariance condition and uniqueness of the counteracting map. □
Given the description , one can explicitly compute the induced homomorphism. We then quickly recognize the map I as
and analogously
We remark that a similar argument can be phrased for vector spaces. In particular, one may consider the map
Note that this explicitly pairs coordinates and bases to describe a certain element. In this case, acts on , and the induced map is given by the contragredient map .
Appendix B. Permutation Action on Semi-Principal Bundle
In this appendix, we show that a semi-principal bundle B with index set X will in general not support a faithful -action. For simplicity, we will consider the reduced bundle , or taking another perspective, we assume G is the trivial group. For the ease of the example, we take X to be finite. Hence, for some natural number n, and B is a regular covering space.
Some motivation to consider this is to check if an faithful -action can be defined already on B. If that is the case, one may wonder if the step to may be avoided. Concerning the individual fibers, there is no problem; choose a bijection to and transfer the action of on via conjugation. However, it is this choice of bijection that might not be possible on a global scale; it is not guaranteed that all the local choices glue together to form a global -action.
Let us check if such a bijection is needed. The case is trivial. The case is also not a problem; one simply declares that the permutation exchanges the only two objects in each fiber, which certainly forms a global action. However, in case , one does not obtain a well-defined action in general. Informally, this is because now one really needs to know the labels of the fiber elements. Indeed, to specify the action of, for example, when there are 3 objects, it is necessary to know which of the objects is labeled by 3. Hence, specifying the action of is equivalent to specifying which of the objects is labeled by 3. This observation leads us to the following result.
Lemma A6.
Let A be a set with n elements, where . A faithful -action on A, or in other words an isomorphism , induces a unique equivariant bijection .
Proof.
Pick , consider the subgroup of permutations of that leave i fixed, i.e., the stabilizer of i in . Then, there is at least one element that is fixed by ; otherwise, would contain a permutation affecting all elements of , including i, which is a contradiction. This element is unique for , as then contains permutations moving every element of except i. Hence, there is a well-defined map , . This map is equivariant; pick and , then for any , one has . Hence, , or . As is arbitrary, is fixed by ; hence, , showing equivariance. It remains to show that is a bijection. It suffices to show that all are distinct. This follows from the observation that at least n distinct objects are needed to have a faithful -action. As one can explicitly find the bijection in the above way, it is unique. □
We may use this result per fiber in the bundle theory. In essence, the global -action is equivalent to specifying a global labeling, which in turn provides a trivialization of the bundle.
Proposition A1.
Let be an -bundle, where . There is an faithful fiber-preserving -action on B if and only if B is trivial.
Proof.
The ‘if’ statement is clear. For the ‘only if’, define fiberwise; for , is mapped to the pair , where is the index obtained by applying Lemma A6 on the -space . Hence, is a bijection, as it is so at each fiber. Using the local triviality of B and continuity of the -action, it follows that is locally constant; hence, is a homeomorphism. That is, B is trivial. □
Ironically, this means that one may work with an -action on B only if no permutation will appear in parallel transport. The reason why a frame does not have this problem is clear; in that case, not a locally defined label but instead the globally defined location in the ordered tuple matters.
References
- Hamilton, M.J. Mathematical Gauge Theory; Universitext; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, E.J.; Boer, D.; Waalkens, H. A Unified View on Geometric Phases and Exceptional Points in Adiabatic Quantum Mechanics. SIGMA 2022, 18, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, A. Algebraic Topology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie, K. Classification of principal bundles and Lie groupoids with prescribed gauge group bundle. J. Pure Appl. Algebra 1989, 58, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M. Introduction to Smooth Manifolds; Graduate Texts in Mathematics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartan, É. Sur la structure des groupes infinis de transformation. Ann. Sci. Lecole Norm. Super. 1904, 21, 153–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M. Group Theory I; Grundlehren der Mathematischen Wissenschaften; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; Volume 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Nomizu, K. Foundations of Differential Geometry; Interscience Publishers: Geneva, Switzerland, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Barkeshli, M.; Wen, X.G. U(1) × U(1) ⋊ Z2 Chern-Simons theory and Z4 parafermion fractional quantum Hall states. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 045323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkeshli, M.; Jian, C.M.; Qi, X.L. Twist defects and projective non-Abelian braiding statistics. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 045130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).