Abstract
This systematic scoping review was conducted to determine the extent of existing research on professionals’ attitudes toward school attendance problems (SAPs), including school refusal (SR), truancy (TR), school withdrawal (SW), and school exclusion (SE), in basic education. Five databases (ERIC, Academic Search Ultimate, Scopus, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) were systematically searched for relevant literature. Forty-five studies met the inclusion criteria that were set prior to the search and were eligible for inclusion. The results of this systematic scoping review reveal that there has been a continuous increase in studies addressing professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs since 2000, with the greatest number of studies published after 2019 and in Europe. Most studies were descriptive, cross-sectional, and used a qualitative approach and the most common informants were school-based professionals (i.e., teachers, school administrators, and other school staff). The included studies used a variety of concepts referring to SAPs and types of SAPs, underlining the present challenges in terminology and definitions that characterize the research field. The results of this review contribute to identifying gaps in knowledge and offer guidelines for future research as a prerequisite to enhance the contemporary comprehension of SAPs in research and in practice.
1. Introduction
Professionals working within a variety of disciplines are frequently involved in addressing and intervening in school attendance problems (SAPs). SAPs typically develop in students during basic education [1,2] and are recognized as a collection of different types of absence (e.g., skipping class, tardiness, early departure, or complete absence) and/or general difficulties attending school caused by various individual or contextual factors [3]. There is an increasing concern regarding SAPs in numerous countries. Determining the frequency of SAPs is challenging due to the many existing terms and concepts in use. While numbers vary across studies and contexts, estimates indicate a prevalence rate ranging from 0.4 to 28% [4,5,6,7,8,9].
SAPs can be categorized into four types: school refusal (SR), truancy (TR), school withdrawal (SW), and school exclusion (SE) [10]. Both SR and TR refer to difficulties attending school or absences from school that are student-initiated but are distinguished because SR is typically associated with internalizing symptoms [10,11,12] while TR is generally associated with externalizing behavior [10,13]. In contrast to SR, TR is also commonly concealed from parents or caregivers [10,13]. The third type, SW, is generally characterized as absenteeism initiated by parents or caregivers [10] while SE was only recently suggested to be regarded as a type of SAP that stems from school-based decisions [10]. School absenteeism and SAPs are generally considered problematic when the student (1) is missing at least 25% of school time for at least 2 weeks, (2) has severe difficulty attending school for at least 2 weeks, or (3) has an absence of at least 10 days of school during a 15-week period, with absence defined at 25% or more of the school day [5].
The multifaceted nature of SAPs demands an interdisciplinary approach, frequently including the involvement of professionals from different disciplinary fields in addition to the student, their parents, and school personnel [14,15,16]. Thus, professionals must be aware of the various reasons for SAPs as the way SAPs are perceived by those who address them is likely to affect how students are met, understood, and supported [17,18]. Positive attitudes have been described as significant for supporting the capacity of professionals to intervene in SAPs [19] while professionals’ negative attitudes carry the potential to exacerbate students’ SAPs [18]. However, it is known that addressing SAPs may be a frustrating experience for professionals [16] and findings from previous studies suggest that professionals may have difficulties identifying deficiencies in their practices that contribute to SAPs. For example, a UK study examining the views of students, parents, and professionals on factors contributing to SAPs found that students and parents emphasized school factors to a larger extent than professionals, who focused more on factors within the family [20]. Similarly, recent studies have found that school-based professionals still more often explain SAPs as associated with factors that are external to the school context [21,22,23].
Researchers have stated that to fully understand SAPs, there is a need for more knowledge about professionals’ attitudes and experiences with SAPs [17,24]. However, SAPs have been examined across diverse disciplines, with scholars employing various concepts and definitions to reference the phenomenon [25]. Consequently, the existing literature on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs is currently fragmented and difficult to reach. Hence, the need for a systematic overview arises to provide insight into the empirical research on the topic and to reveal areas where knowledge is lacking as a necessary step toward enhancing research on the topic. This systematic scoping review therefore aims to determine the geographic, methodological, and conceptual characteristics of existing research on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs. The results of this study will contribute to enhancing the understanding of existing research on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs through ensuring accessibility of knowledge, identifying knowledge gaps, and laying the groundwork for future research.
2. Research Questions
The aim of this systematic scoping review is to identify and systematically describe existing research on the attitudes of different professionals toward SAPs in basic education. More specifically, the following research questions are raised:
- How many studies focus on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs in basic education and what are their characteristics in terms of publication type, publication year, continent, and country?
- Which methodological approaches characterize the research conducted on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs and what types of professions have been studied?
- Which types of SAPs are examined in each study and at what school levels have the studies been undertaken?
3. Materials and Methods
To address these research questions, we conducted a systematic scoping review. A systematic scoping review aims to identify the types of available evidence and analyze gaps of knowledge on a particular topic [26,27,28]. This approach is valuable for comprehensively mapping existing literature. Our systematic scoping review aligns with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines [27,29,30], ensuring a rigorous and transparent methodology. The PRISMA-ScR Checklist is presented in Supplementary Materials. A scoping review protocol to guide the execution of the review was developed and uploaded to Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/cvfqa/, accessed on 23 December 2022) in December 2022, prior to the database search.
3.1. Inclusion Criteria
The formulation of specific inclusion criteria aligns with the overarching research questions, serving as a thorough strategy to comprehensively identify all relevant studies within the research literature. These inclusion criteria are detailed below:
Population: the scope of this review centers on professionals and practitioners actively engaged in addressing SAPs in basic education through their respective occupations;
Concept: the focus extends to publications that report on the attitudes of professionals toward SAPs in basic education. Moreover, this encompasses related terminologies, such as perceptions, views, perspectives, beliefs, or understanding;
Context: the examination is limited to studies focused on children and adolescents encountering challenges with school attendance. This pertains to categories of SAPs, such as school refusal (SR), truancy (TR), school withdrawal (SW), school exclusion (SE), or equivalent terms. The context of interest is limited to the sphere of basic education, encompassing primary/elementary and upper primary/intermediate/lower secondary/middle school settings (aged 6–16);
Types of Studies: the review selectively includes empirical research, which captures research reports, journal articles, and doctoral theses;
Publication Language: the analysis is limited to sources presented in full-text format in the English language.
In line with these criteria, any sources that failed to meet one or more of these conditions were meticulously excluded from consideration. An additional criterion required the accessibility of sources in full text to the authors. This accessibility was facilitated either through online availability or through access to relevant libraries. This selection process aligns with the requirements for a comprehensive and systematic review [26,27].
3.2. Search Strategy
The identification of literature focusing on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs in basic education was based on a systematic search of relevant databases (ERIC, Academic Search Ultimate, Scopus, PsycINFO, and Web of Science).
The search string was aligned with the population, concept, and context (PCC) framework [27] and was further developed with the input of a research librarian and a group of researchers experienced in conducting systematic reviews. On 4 January 2023, the final search using the modified search string was conducted in the five databases (Table 1). Limiters to the English language and peer-reviewed documents were applied to the search of all databases.

Table 1.
Search string applied in the database search.
3.3. Screening Proces
The screening process aimed to exclude studies that did not meet the defined inclusion criteria for mapping. EPPI-Reviewer Web 4 software was used for screening, coding, and reporting. This software ensures that the assessment of the relevant literature is systematic, structured, and transparent [31]. Both title and abstract screening and full-text screening were performed by two colleagues, independently, and then compared in EPPI-Reviewer to reach a joint decision in the event of disagreement related to the exclusion of studies. Figure 1 illustrates the identification, screening, and inclusion of studies.
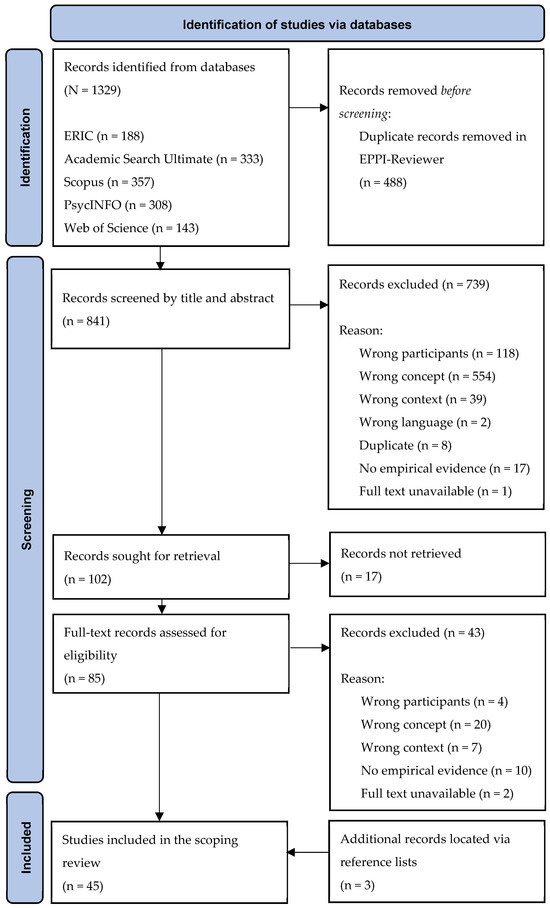
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow chart for item selection and inclusion.
3.4. Data Extraction
Data extraction from the 45 included studies was conducted using EPPI-Reviewer Web 4 software. The data extraction form was initially pilot-tested individually by two of the reviewers on a small sample of the studies (n = 7) and revised accordingly prior to data extraction.
The final form of data items included (1) study characteristics (e.g., publication year, type of publication, continent, country, study purpose), (2) methodological characteristics (i.e., research method, study design, data collection approach), (3) sample characteristics (i.e., number of participants, types of professions included), and (4) study context (i.e., school level, type of SAP (i.e., SR, TR, SW, SE), authors’ conceptualization of the type of SAP examined).
4. Results
Forty-two documents were identified through the database search and met the inclusion criteria. The reference lists of all included studies were searched for additional sources, resulting in the further inclusion of three studies. A total of 45 documents were included in the review. As several codes in the data extraction form (i.e., (2) methodological characteristics, (3) sample characteristics, and (4) study context) permitted multiple coding, the total number of codes applied was in some cases larger than 45. Table 2 provides an overview of the main data extracted from each included study.

Table 2.
Overview of the included studies.
4.1. Characteristics of the Studies
Publication type: The largest number of included studies were journal articles (thirty-nine studies, 86.6%) while the remaining studies were doctoral theses (five studies, 11.1%) and one study was a research report (one study, 2.2%).
Study purpose: Nearly all studies were nonexperimental and descriptive (forty-two studies), a few aimed to explore relationships (four studies), and only one study was experimental (multiple coding, n = 47).
Year: Figure 2 provides an overview of the number of studies published on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs in the period from 1975 to 2023.
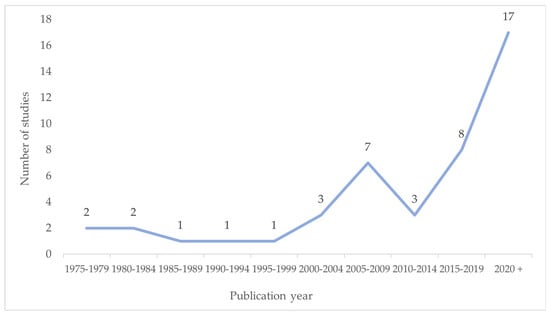
Figure 2.
Number of studies published on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs in the period from 1975 to 2023 (single coding, n = 45).
The search and the included sources show that the majority of studies addressing professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs were published after 2005 (77.7%, 35 studies). A total of 55.5% of the studies were published after 2015 (25 studies) and 37.7% were published after 2020 (17 studies). A total of 4.4% of the studies were published between 1975 and 1979 (two studies) or between 1980 and 1984 (two studies). A total of 2.2% of the studies were published within each year spanning from 1985 to 1989 (one study), 1990 to 1994 (one study), and 1995 to 1999 (one study) and 6.6% of the studies were published between 2000 and 2004 (three studies). There was an increase in studies on the topic between 2005 and 2009 (15.5%, seven studies) and a decrease between 2010 and 2014 (6.6%, three studies). A total of 17.7% of the studies (eight studies) were published from 2015 to 2019 and there was a substantial increase from 2020 to 2023.
Continent: The included studies were distributed across five different continents: Asia (three studies, 6.6%), Africa (two studies, 4.4%), North America (eleven studies, 24.4%), Europe (twenty-eight studies, 62.2%), and Oceania (one study, 2.2%).
Country: The studies were undertaken in 14 different countries. Most studies were conducted in the UK (17 studies, 37.7%) or the USA (11 studies, 24.4%). Figure 3 shows an overview of studies conducted in the different countries.
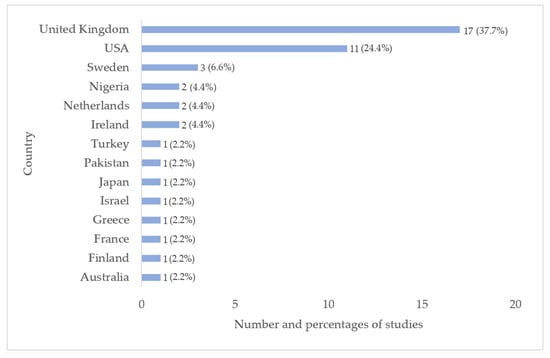
Figure 3.
Number and percentages of studies conducted in the different countries (single coding, n = 45).
4.2. Methodological Approaches
Research methods: Most of the included studies were qualitative (twenty-three studies, 51.1%) and the remaining studies were either quantitative (nine studies, 20%) or mixed methods (thirteen studies, 28.8%).
Study designs: The included studies used different study designs (four studies combined two designs). A cross-sectional design was most frequent (twenty-one studies), followed by case study (fourteen studies), descriptive study (five studies), comparative study (five studies), cohort study (one study), block randomized study (one study), concept mapping (one study), and ethnographic study (one study) designs (multiple coding, n = 49).
Data collection methods: To collect the data, the included studies used different methodological approaches. Fifteen of the studies used a multimethod data collection approach (eleven studies used two methods, two studies used three methods, and two studies used four methods). The most frequent data collection methods were 1:1 interviews (twenty-two studies) and questionnaires (twenty-one studies, of which three were open-ended and eighteen were closed). Other data collection methods used were focus group interviews (twelve studies), records of student attendance data (six studies), group discussions (three studies), concept mapping (one study), and documents (one study) (multiple coding, n = 66).
4.3. Sample Characteristics
Types of professions: A variety of professionals were subjects of the included studies. Since there was a difference in occupation titles and descriptions across countries, professionals were categorized during data extraction into seven groups of professionals: (1) teachers, (2) other school staff (e.g., school counselors, special educators, teaching assistants), (3) school administrators (e.g., principals, head teachers, school leaders), (4) education service staff (e.g., education welfare officers, school attendance officers), (5) social service staff (e.g., family counselors), (6) healthcare professionals (e.g., doctors, nurses, physiotherapists), and (7) psychologists. The categorization of profession types is shown in Figure 4.
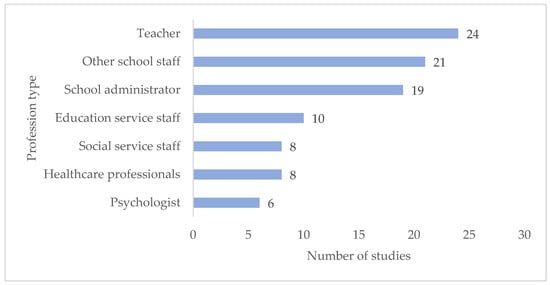
Figure 4.
Types of professionals included in the samples of the studies (multiple coding, n = 96).
The type of professional that was most asked about their attitudes toward SAPs was teachers (twenty-four studies), followed by other school staff (twenty-one studies) and school administrators (nineteen studies). Education service staff were asked in ten of the studies, social service staff in eight of the studies, healthcare professionals in eight of the studies, and psychologists in six of the studies.
Almost half of the studies included only one type of professional (twenty-one studies) in their sample while eleven studies included two profession types. The remaining studies included three (four studies), four (five studies), five (three studies), or six (one study) types of professions in their sample. In addition, a small proportion of these studies included the perspectives of students (nine studies) or parents (eight studies), of which four studies involved the perspectives of students, parents, and professionals at once [20,32,33,34].
4.4. Concepts
Concepts: A total of nineteen concepts were used to refer to school absenteeism or SAPs. The most frequently used concept was “truancy” (nineteen studies), followed by “school refusal” (seven studies), “school absenteeism” (seven studies), “school phobia” (five studies), and “school attendance problems” (three studies). Additionally, “School refusal behavior”, “school attendance issues”, “school non-attendance”, and “problematic school absenteeism” were each used in two studies while “unacceptable absence”, “tardiness”, “parentally condoned absences”, “children with home responsibilities”, “dropout”, “sickness absence”, “school withdrawal”, “emotionally based school non-attendance”, “school attendance difficulties”, and “chronic school absenteeism” were each used in one study. Figure 5 shows how professionals’ attitudes related to the different concepts have been studied over the years.
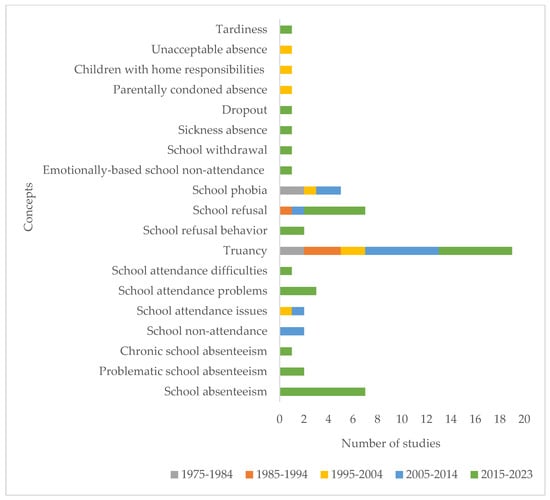
Figure 5.
Concepts explored by publication year range (multiple coding, n = 59).
Some of the concepts were more frequently used in recent studies (e.g., school refusal, school attendance problems, and school absenteeism) while others were a bit more prevalent in less recent studies (e.g., school phobia). Some concepts (e.g., truancy) have been steadily employed throughout the years.
Types of SAPs: The 19 concepts that were used in the included studies were further categorized under one of the contemporary approaches to conceptualizing SAPs and categorizing types of SAPs as SR, TR, SW, and SE, in line with the conceptualizations of Heyne et. al. [10] and Kearney et. al. [3]. The categorization of concepts is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Categorization of concepts used in the included studies.
4.5. School Level
The scoping review included research undertaken in basic education, meaning primary or secondary school. Several studies (n = 16) addressed SAPs at more than one school level (nine studies were undertaken at two school levels, four studies were undertaken at three school levels, and three studies were undertaken at four school levels). A slightly larger proportion of research was conducted in secondary school (34 studies) than in primary school (23 studies). Some studies were conducted in high school (ten studies) or preschool (two studies) in addition to primary or secondary school (Figure 6).
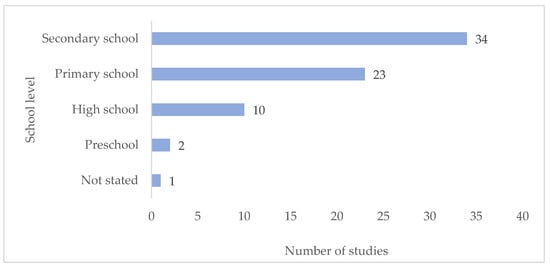
Figure 6.
Number of studies undertaken for the different school levels (multiple coding, n= 70).
5. Discussion
This systematic scoping review aimed to identify the extent of existing research on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs and to provide an overview of the characteristics and methodological approaches of the studies, types of professions studied, and use of concepts related to SAPs. After a systematic search of relevant peer-reviewed documents in five databases and a search of reference lists, a total of 45 studies met the inclusion criteria.
5.1. Characteristics of the Studies
The results of this systematic scoping review show that there has been a steady increase in empirical studies conducted on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs since 2000, with the majority of eligible studies being journal articles. Most studies were published after 2005 and more than half of all included studies were published after 2015. The continuous increase in empirical research on the topic reflects the growing focus on SAPs over the last decade due to SAPs being addressed from the perspectives of an increasing number of different disciplines [25]. Although difficulties attending school are not a new phenomenon, they have received more research attention in recent years and have been referred to as a vexing problem encountered by professionals within different disciplinary fields [74]. However, the most significant increase in published studies took place between 2020 and 2023, which could be related to the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic. During the COVID-19 lockdown, many children and adolescents experienced an increase in symptoms of depression and anxiety [75,76]. Related to school absences, a US study found that many parents planned to keep their children home at the reopening of schools after the COVID-19 lockdown [77]; a UK study showed that COVID-related absences increased after the reopening of schools in late 2020 [78]. There is also some evidence that absences from school continued to increase after the pandemic [79]. Moreover, much of the recent research on SAPs has switched from focusing solely on theories that attribute SAPs to individual reasons (e.g., clinical perspectives) to emphasizing theorization of contextual or ecological factors that may contribute to the development or maintenance of SAPs (e.g., [80,81,82,83]). Acknowledgment of the role of contextual and school factors in SAP development and maintenance has perhaps contributed to a growing interest among researchers to assess school personnel’s and other professionals’ attitudes or perceptions toward SAPs, which could explain the present increase in research on the topic.
The forty-five studies included in this scoping review were undertaken in fourteen different countries across five different continents. The distribution of studies across countries on different continents underscores the recognition of SAPs as a worldwide issue [24,84]. In contrast, most studies eligible in this scoping review were undertaken in Europe and North America, which are also the two continents where lower secondary school completion rates are highest (98%) [85]. This distribution of studies is consistent with the fact that the vast majority of research on school attendance and absenteeism generally comes from these areas and that there is a critical need for research in areas with lower school completion rates [86]. In the current review, only two studies were undertaken in such areas: one in Pakistan (Southern Asia, 75% completion rate) and one in Nigeria (sub-Saharan Africa, 38% completion rate) [84]. The highest proportion of studies on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs was undertaken in Europe and in the UK. School absenteeism is a significant focus in UK policy and the UK is one of few countries offering yearly national statistics on school attendance at all school levels [87], which may have contributed to an increased research focus.
5.2. Methodological Characteristics
Most of the included studies on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs were qualitative and descriptive, offering contextual and in-depth insight into the topic. Research on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs seems to be a relatively new field given that most of the studies on the topic were published within the last few years. The predominance of qualitative studies may be explained by the fact that the exploration of new phenomena often uses such approaches. However, there was a significant presence of mixed method and quantitative studies, with some studies including larger samples to allow for comparison and generalization to similar contexts. Nevertheless, nearly all included studies were nonexperimental, and cross-sectional and case study designs were most prevalent. Cross-sectional and case study designs are suitable for establishing the prevalence of professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs; however, they provide only a snapshot of attitudes at a specific time with a limited possibility of drawing causal inferences. Hence, there seems to be a need for experimental studies aiming to investigate how professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs are formed and how they might impact students with SAPs, which has previously been referred to as an area where future research is needed [17]. To address this gap, researchers should aim to incorporate standardized measures of professionals’ attitudes before and after the implementation of targeted interventions to reduce SAPs as a means to detect changes in attitudes resulting from participation in specific interventions. Studies should also aim to investigate whether changes in professionals’ attitudes, resulting from participation in an intervention, influence student outcomes (e.g., attendance) by comparing them with the outcomes of a control group.
The use of various data collection methods and combinations of methods provides insight into the topic from several methodological perspectives. The most frequent data collection methods were 1:1 interviews and questionnaires. However, nearly all questionnaires were customized for the specific studies and aimed to measure a variety of constructs related to professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs, thus limiting comparability between studies.
5.3. Types of Professions
The study samples covered a variety of professionals who were categorized into seven groups during data extraction. School personnel were significantly overrepresented in the samples, with the most investigated group of professionals being teachers, other school staff, and school administrators. School-based professionals are often among the first to recognize changes in attendance and play a crucial role in identifying SAPs and intervening at an early stage, which is a prerequisite for preventing SAPs from developing into more serious problems [88,89,90]. Thus, the attitudes and perceptions of school-based professionals toward SAPs are important for ensuring that students showing signs of SAPs are identified and sufficiently supported. Moreover, due to the complex nature of SAPs, an interdisciplinary approach is strongly emphasized in the literature [14,88]. Interventions for SAPs should involve the student, their caretakers, school-based professionals, and professionals from other disciplinary fields, depending on the severity and nature of the SAP and the needs of the student and/or the family [14,15,16]. The multifaceted nature of SAPs and their relation to various individual, family, and contextual factors, therefore, often necessitate expertise in certain domains. Hence, several study samples included psychologists and professionals working within educational, social, and healthcare services, covering a variety of occupations that were frequently involved in addressing SAPs. However, nearly half of the studies included only one profession type in their sample and only a small proportion of the studies included the perspectives of students or parents while fewer involved the perspectives of students, parents, and professionals at once. As known from previous research, stakeholders may have differing attitudes regarding SAPs. While students and parents often attribute SAPs to school-related factors, professionals more often point to factors related to individual or parental influences [20,21,22,23]. Hence, researchers have expressed the need for studies incorporating the voices of different professionals, parents, and students to enhance the comprehension of SAPs and develop more effective strategies to combat them [24].
5.4. Types of SAPs
The varying use of concepts referring to SAPs in the studies mirrors the history of definitional issues that have characterized the research on SAPs in general [3,10]. The examination of SAPs from the perspectives of a range of different disciplines (e.g., education, medicine, policy, psychology, social works, economics, criminal justice) has led to a fractured body of literature that is characterized by redundancy in the use of terminology [86].
In the scoping review, several of the concepts referring to SAPs, SR, and SW were used in only one or two studies each. Most studies used concepts referring to SAPs, followed by concepts referring to SR. Only three studies referred to the contemporary understanding of TR, two studies referred to SW, and no studies referred to SE. However, SE was only recently suggested to be regarded as a type of SAP [10]. Consequently, there seems to be a lack of studies examining professionals’ attitudes toward SE.
Some of the concepts referring to SAPs were highly similar, such as SAPs, “school attendance difficulties”, and “school attendance issues”. SAPs are broadly and generally conceptualized as difficulties attending school or the presence of different types of absenteeism, including complete absence, skipping class, early departure, and tardiness [3]. The fourth type, “tardiness”, was examined in one of the included studies referring to “an individual risk for future problematic behavior leading to absenteeism...” [71], which indicates emerging SAPs [10]. The establishment of SAPs is often seen in conjunction with Kearney’s [15] cutoff criteria for when absenteeism or difficulties attending school are considered problematic. Some of the included studies used the concepts of “problematic school absenteeism”, “chronic school absenteeism”, and “unacceptable absence”. On the one hand, these concepts are even more general than SAPs, as they generally do not include or distinguish between types of absenteeism. On the other hand, they can be said to have a narrower focus than SAPs because they primarily emphasize a cutoff for when the amount of absence is to be considered “problematic”, “chronic”, or “unacceptable”. Nevertheless, these criteria vary greatly across studies and across national and local organizations [91].
The broader concepts of “school absenteeism” and “school non-attendance” were used in several studies. Carroll [92] argues that using general terminology is advantageous because such terms do not imply that the issue lies within the child or with the parents. On the other hand, Heyne et. al. [10] suggest that using general terminology rather than differentiating between types of absenteeism may undermine relevant information, which has implications for conducting research, as well as practical implications for the assessment and planning of interventions. From the perspective of policy, school systems across various countries commonly distinguish between absenteeism as either authorized/legitimate/excused or unauthorized/illegitimate/unexcused [15]. Authorized absenteeism usually involves illness but may also include reasons such as family emergencies, family vacations or subjective, diffuse, or minor somatic symptoms or health complaints [3,93]. One of the studies eligible in this scoping review used the concept of “sickness absence” [58], referring to authorized absenteeism due to sickness. However, the usage of this concept was not limited to authorized absenteeism due to physical illness but also included social, psychological, and lifestyle causes [94]. Such causes are also commonly seen in association with unauthorized absenteeism [6,82,95]. Distinguishing between authorized and unauthorized absenteeism has thus been noted as potentially detrimental, as absenteeism that is technically authorized could be masked by unreliable explanations for absenteeism by parents [2] or the authorization could conceal serious health, family, or other problems related to SAPs [96,97].
The concept of “dropout” was used in one study undertaken in primary, secondary, and high school [67]. However, this concept mainly refers to the lack of completion of high school and is generally not used in the context of compulsory basic education [98].
The most prevalent concept was TR, which was also the concept that was most steadily used in the included studies from 1975 until recently as it is one of the oldest terms used to refer to SAPs [3]. However, TR lacks a uniform definition [99,100] and has historically been defined both narrowly and broadly [101]. As is apparent from the results of the current review (Table 3), both conceptualizations are currently found in the literature [10]. At present, TR is often narrowly defined and, thus, considered a type of SAP recognized as absence from school or the proper school location without the permission of school authorities, alongside the attempt to conceal the absence from the parents [10]. Defined broadly, TR is more generally considered unauthorized absence from school [99,101] and has been used interchangeably with concepts such as “chronic school absenteeism” [99]. In terms of research focusing on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs, most studies seem to adopt the broader definition of TR. Unexpectedly, only three studies utilized a narrow definition of TR [32,39,60]. Employing broader definitions of TR might contribute to undermining the various factors contributing to different types of SAPs.
In contemporary approaches to differentiating between SAPs, TR is typically distinguished from SR, in that SR often occurs in conjunction with internalizing symptoms and emotional distress and is usually not concealed from the parents [10,11]. However, the concept of “school refusal behavior” (SRB) is sometimes used as an umbrella term for student-initiated absences and for SR and TR [102,103]. The term SRB was employed in two of the studies included in the scoping review. In one study, it served as an umbrella term for SR and TR [34]; meanwhile, it was used interchangeably with SR in the other study [49].
SR was the second most prevalent concept used in the included studies. However, several studies used “school phobia”, a term that has previously been used interchangeably with SR [10]. School phobia was one of the first terms referring to SR [104] but has received less attention than SR in more recent years as it has been described as more focused on the reason behind the behavior rather than the actual behavior [90]. Moreover, the terms “emotionally based school non-attendance” [40] and SW [49] were employed in one study each to refer to SR; the former was used on the grounds that terms such as SR and school phobia are “overly locating the ‘problem’ within the school setting, or as perpetuating negative stereotypes about the affected pupils” [40]. The latter term, SW, was used interchangeably with SR but is generally distinguished from SR, as it refers to parent-initiated absence as opposed to student-initiated absence [10]. The term SW was, however, introduced early as absenteeism from school due to parents’ needs or their inability to accept social responsibilities and obligations related to school attendance [105,106]. A nuanced understanding of SW acknowledges that reasons for SW are more varied [10]. In the scoping review, only two studies referred to the contemporary understanding of SW with the terms “children with home responsibilities” [46] and “parentally condoned absences” [20]. The former term was used to refer to one specific type of SW where the student is kept home to take care of chores or other responsibilities within the family [46] while the latter term was used to refer generally to parents keeping students away from school [20], which is similar to the conceptualization of SW that is currently found in the literature [10]. Overall, the included studies’ various usages of concepts and definitions underscore the already widely acknowledged need to establish a consistent terminology to refer to SAPs and SAP types.
5.5. School Level
Professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs were examined in both primary and secondary school contexts. A larger proportion of the included studies were undertaken in secondary school than in primary school. Generally, SAPs have most frequently been discussed as an issue concerning secondary school students [1]; however, it is widely acknowledged that many students start to have school absences in the earlier school years [2,107]. Lack of school attendance during primary and secondary education has been linked to a range of negative consequences, including continued absenteeism and weaker academic, social, and behavioral outcomes in later school years and in young adulthood [108,109,110,111,112]. These consequences underscore the importance of professionals’ engagement in prevention and early interventions [112], which are likely influenced by their attitudes and way of perceiving SAPs.
6. Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, although an extensive systematic search procedure was conducted, it cannot be assured that all studies on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs that would have met the inclusion criteria for the current scoping review were located, which also applies to studies that were published after the final search (4 January 2023) was conducted. This may be due to the combination of the search string, searched databases, and the priori-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria of this review. Second, the scope of the review was limited to the inclusion of empirical research encompassing research reports, journal articles, or doctoral theses written in full text in English. Hence, studies in other languages, gray literature, textbooks, and unpublished studies that could have contributed relevant knowledge were excluded.
7. Implications
The results of the current study contribute to identifying gaps in knowledge that have implications for future research.
Although an increasing number of studies on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs is being conducted, the vast majority of studies included in this review were qualitative and descriptive in purpose. Moreover, the quantitative and mixed method studies were mainly nonexperimental and employed custom questionnaires to measure professionals’ attitudes, which serves to fragment the literature and limit the potential for comparison between studies. Thus, the quantitative literature lacks an existing standardized tool aiming to measure professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs. Future studies should aim to investigate how professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs are formed and their potential repercussions on students, which may be facilitated through the application of experimental designs.
The included studies examined the attitudes of a range of different professionals involved in addressing SAPs. Some studies included different types of professionals in their samples, while some studies additionally included the perspectives of parents or students. However, few studies incorporated the views of various stakeholders at once. Future studies should, thus, aim to simultaneously incorporate the perspectives of students, parents, and different professionals, acknowledging the potential for differing attitudes among stakeholders.
Conceptual redundancy is an acknowledged challenge in the SAP literature and it was notably present in the current review. The lack of compliance in terminology creates confusion among researchers, practitioners, and stakeholders, which has implications for both research and practice. For researchers, it is difficult to obtain a grasp of existing knowledge when various concepts are employed across studies. For practice, it is very likely that how different concepts are defined and categorized affects how students with SAPs are perceived by professionals and, eventually, how they are supported. Although attempts and proposals to sort out and unify the terminology have been made [3,10,99], inconsistent use of terminology is still very much present in the literature.
This systematic scoping review is the first to comprehensively map the characteristics of the existing research on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs. To enhance the understanding of professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs, future studies should aim to systematically synthesize the evidence on the topic, thereby providing a comprehensive overview of prevalent attitudes within the field. The highlighted findings of each study included in the current systematic scoping review are presented in Supplementary Materials.
8. Conclusions
Overall, the majority of the studies included were journal articles (86.6%), had a descriptive study purpose (89.3%), used a qualitative approach (51.1%), were cross-sectional (42.8%), and were undertaken in Europe (62.2%) and the UK (37.7%). The studies were characterized by a diverse use of data collection methods and professionals within various disciplines were included in the study samples. Most studies examined the attitudes of school-based professionals, nearly half of the studies examined the attitudes of only one profession type, and few studies included the perspectives of parents or students. The results of this study reveal that there has been a steady increase in research on this topic since 2000 and a substantial increase since 2020. However, the literature on professionals’ attitudes toward SAPs is fragmented and there is a need for compliance in terms of the terminology, definitions, and standardization of measurement tools.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/educsci14010066/s1. Aim and highlighted findings of the included studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.E.H. and T.H.; methodology, M.I.F. and S.E.H.; software, M.I.F.; validation, S.E.H., M.I.F., and T.H.; formal analysis, S.E.H. and M.I.F.; investigation, S.E.H., M.I.F., and T.H.; resources, S.E.H., M.I.F., and T.H.; data curation, M.I.F. and S.E.H.; writing—original draft preparation. S.E.H.; writing—review and editing, S.E.H., M.I.F. and T.H.; visualization, S.E.H. and M.I.F.; supervision, M.I.F. and T.H.; project administration, S.E.H., M.I.F., and T.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sugrue, E.P.; Zuel, T.; LaLiberte, T. The ecological context of chronic school absenteeism in the elementary grades. Child. Sch. 2016, 38, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. Managing School Attendance: Successful Intervention Strategies for Reducing Truancy; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, C.A.; Gonzálvez, C.; Graczyk, P.A.; Fornander, M.J. Reconciling contemporary approaches to school attendance and school absenteeism: Toward promotion and nimble response, global policy review and implementation, and future adaptability (Part 1). Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knollmann, M.; Knoll, S.; Reissner, V.; Metzelaars, J.; Hebebrand, J. School avoidance from the point of view of child and adolescent psychiatry: Symptomatology, development, course, and treatment. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, C.A. School absenteeism and school refusal behavior in youth: A contemporary review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2008, 28, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, H.L.; Costello, J.E.; Angold, A. School refusal and psychiatric disorders: A community study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2003, 42, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fremont, W.P. School Refusal in Children and Adolescents. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 68, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar]
- de Aldaz, E.G.; Vivas, E.M.P.; Gelfand, D.M.; Feldman, L.M. Estimating the prevalence of school refusal and school-related fears: A Venezuelan sample. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1984, 172, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.A. School Refusal Behavior in Youth: A Functional Approach to Assessment and Treatment; American Psychological Association: Washington DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyne, D.; Gren-Landell, M.; Melvin, G.; Gentle-Genitty, C. Differentiation between school attendance problems: Why and how? Cogn. Behav. Pract. 2019, 26, 8–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, I.; Nichols, K.; Pritchard, C. School phobia: Its classification and relationship to dependency. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 1969, 10, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, N.J.; Bernstein, G.A. School refusal in children and adolescents: A review of the past 10 years. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2001, 40, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havik, T.; Ingul, J.M. How to Understand School Refusal. Front. Educ. 2021, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingul, J.M.; Havik, T.; Heyne, D. Emerging school refusal: A school-based framework for identifying early signs and risk factors. Cogn. Behav. Pract. 2019, 1, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.A. An interdisciplinary model of school absenteeism in youth to inform professional practice and public policy. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2008, 20, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.A.; Bensaheb, A. School absenteeism and school refusal behavior: A review and suggestions for school-based health professionals. J. Sch. Health 2006, 76, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.G.; Place, M. Practitioner review: School refusal: Developments in conceptualisation and treatment since 2000. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens Armstrong, A.M.; McCormack Brown, K.R.; Brindley, R.; Coreil, J.; McDermott, R.J. Frequent fliers, school phobias, and the sick student: School health personnel’s perceptions of students who refuse school. J. Sch. Health 2011, 81, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, B. What it takes to keep children in school: A research review. Educ. Rev. 2015, 67, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, H.; Wilson, V.; Davidson, J.; Kirk, S. Absence from School: A Study of Its Causes and Effects in Seven LEAs; Queen’s Printers: Nottingham, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Havik, T.; Bru, E.; Ertesvåg, S.K. Parental perspectives of the role of school factors in school refusal. Emot. Behav. Difficulties 2014, 19, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren-Landell, M.; Allvin, C.E.; Bradley, M.; Andersson, M.; Andersson, G. Teachers’ views on risk factors for problematic school absenteeism in Swedish primary school students. Educ. Psychol. Pract. 2015, 31, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havik, T.; Ingul, J.M. Remote Education/Homescooling During the COVID-19 Pandemic, School Attendance Problems, and School Return—Teachers’ Experiences and Reflections. Front. Educ. 2022, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyne, D.; Gentle-Genitty, C.; Gren-Landell, M.; Melvin, G.; Chu, B.; Gallé-Tessonneau, M.; Askeland, K.G.; Gonzàlvez, C.; Havik, T.; Ingul, J.M.; et al. Improving school attendance by enhancing communication among stakeholders: Establishment of the International Network for School Attendance (INSA). Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 29, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, C.A.; Dupont, R.; Fensken, M.; Gonzálvez, C. School attendance problems and absenteeism as early warning signals: Review and implications for health-based protocols and school-based practices. Front. Educ. 2023, 8, 1253595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.D.J.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; McArthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, D.; Thomas, J.; Oliver, S. An Introduction to Systematic Reviews, 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–352. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; McKenzie, J.E. Introduction to PRISMA 2020 and implications for research synthesis methodologists. Res. Synth. Methods 2022, 13, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Graziosi, S.; Brunton, J.; Ghouze, Z.; O’Driscoll, P.; Bond, M. EPPI-Reviewer: Advanced Software for Systematic Reviews, Maps and Evidence Synthesis; EPPI-Centre, Social Science Research Institute, University College London: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Adana, B.S. A comparison of teachers’ and pupils’ views on truancy in Nigerian secondary schools. Niger. J. Guid. Couns. 1987, 3, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Akaneme, I.N.; Nwosu, E.N.; Sunday, E.G.; Uloh-Bethels, A.C.; Nwosu, P.O.; Robinson, A.; Ekwealor, F.N. Parents’ and teachers’ perceived strategies for reducing truancy among secondary school students: Implication for students’ behaviour modification. Soc. Sci. 2016, 11, 3426–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, T. School Psychologists’ Knowledge of School Refusal Behavior in Children and Adolescents. Ph.D. Thesis, Alliant International University, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bentz, W.K.; Davis, A. Perceptions of Emotional Disorders among Children as Viewed by Leaders, Teachers, and the General Public. Am. J. Public Health 1975, 65, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blackmon, B.J.; Cain, D.S. Case manager perspectives on the effectiveness of an elementary school truancy intervention. Sch. Soc. Work. J. 2015, 40, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bone, R.R. Truancy during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Its Contributive Factors and Effects. Ph.D. Thesis, Trevecca Nazarene University, Nashville, TN, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, P.J.; Dodge, K.A.; Gifford, E.J.; Schulting, A.B. A New Program to Prevent Primary School Absenteeism: Results of a Pilot Study in Five Schools. Grantee Submiss. 2017, 82, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.; Mellors, M. Teachers’ Perceptions of School Refusers and Truants. Educ. Rev. 1990, 42, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, S.; Bond, C.; Knox, L. Emotionally Based School Non-Attendance: Two Successful Returns to School Following Lockdown. Educ. Psychol. Pract. 2022, 38, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.; Harvey, K.; Waite, P. School staffs’ experiences of supporting children with school attendance difficulties in primary school: A qualitative study. Emot. Behav. Diffic. 2022, 27, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devenney, R.; O’Toole, C. ‘What kind of education system are we offering’: The views of education professionals on school refusal. Int. J. Educ. Psychol. 2021, 10, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devenney, R. Exploring Perspectives of School Refusal in Second-Level Education in Ireland. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Ireland Maynooth, Maynooth, Ireland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Finning, K.; Harvey, K.; Moore, D.; Ford, T.; Davis, B.; Waite, P. Secondary school educational practitioners’ experiences of school attendance problems and interventions to address them: A qualitative study. Emot. Behav. Diffic. 2018, 23, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finning, K.; Waite, P.; Harvey, K.; Moore, D.; Davis, B.; Ford, T. Secondary school practitioners’ beliefs about risk factors for school attendance problems: A qualitative study. Emot. Behav. Diffic. 2020, 25, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, N.J. Professional Models of School Absence Associated with Home Responsibilities. Br. J. Sociol. Educ. 1995, 16, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, G.F. The Relationships of the Department of Education- Honolulu Police Department Truancy Program on Average Daily Attendance and the Attitudes of Secondary School Truants, Nontruants, Teachers and Administrators Toward Truancy on Oahu. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogsteder, M.H.H.; Douma, L.N.; Eskens, C.G.A.; Berendsen, R.L.; Vanneste, Y.T.M.; Schaafsma, F.G. Professionals’ and students’ perceived needs for an online supportive application for reducing school absence and stimulating reintegration: Concept mapping study. JMIR Form. Res. 2021, 5, e24659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Înoue, S. Interview-Based Qualitative Descriptive Study on Risk Factors of School Withdrawal among Elementary School Children. Children 2022, 9, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljakovic, M.; Kelly, A. Working with school-refusing young people in Tower Hamlets, London. Clin. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassiter-Dennis, J. Using Student Engagement and Reengagement to Reduce Chronic School Absenteeism. Ph.D. Thesis, Walden University, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.; Benoit, J.P.; Moro, M.R.; Benoit, L. School Refusal or Truancy? A qualitative study of misconceptions among school personnel about absenteeism of children from immigrant families. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, B.; Lester, K.J.; Michelson, D. ‘She didn’t know how to go back’: School attendance problems in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic—A multiple stakeholder qualitative study with parents and professionals. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 2022, 93, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melander, K.; Kortteisto, T.; Hermanson, E.; Kaltiala, R.; Mäki-Kokkila, K.; Kaila, M.; Kosola, S. The perceptions of different professionals on school absenteeism and the role of school health care: A focus group study conducted in Finland. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.N.; Jome, L.M. School psychologists and the assessment of childhood internalizing disorders: Perceived knowledge, role preferences and training needs. Sch. Psychol. Int. 2008, 29, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.N.; Jome, L.M. School psychologists and the secret illness: Perceived knowledge, role preferences, and training needs regarding the prevention and treatment of internalizing disorders. Sch. Psychol. Int. 2010, 31, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.; Howell, A.; Lynch, D.; Dungan, J. Approaches to Improving School Attendance: Insights from Australian Principals. Leadersh. Policy Sch. 2021, 20, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijl, E.K.; Vanneste, Y.T.M.; Feron, F.J.M.; Mathijssen, J.J.P.; de Rijk, A.E. Stakeholder perspectives on primary school pupils and sickness absence—Exploring opportunities and challenges. Educ. Rev. 2021, 75, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulou, M.; Norwich, B. Teachers perceptions of students with emotional and behavioural difficulties: Severity and prevalence. Eur. J. Spec. Needs Educ. 2000, 15, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.; Butler, A.J. Teachers’ perceptions of school phobic and truant behaviour and the influence of the youth tutor. J. Adolesc. 1978, 1, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. The views of head teachers and teachers on attendance issues in primary schools. Res. Educ. 2004, 72, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. The views of education social workers on the management of truancy and other forms of non-attendance. Res. Educ. 2006, 75, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. An evaluation of the views of secondary staff towards school attendance issues. Oxf. Rev. Educ. 2006, 32, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. Managing school attendance: The professional perspective. Teach. Dev. 2007, 11, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. The views of learning mentors on the management of school attendance. Mentor. Tutoring 2007, 15, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K. The Causes of Non-Attendance: An Empirical Study. Educ. Rev. 2008, 60, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, S.; Arseven, Z.; Kılıç, A. Causes of Student Absenteeism and School Dropouts. Int. J. Instr. 2016, 9, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, Z.; Ishaq, M.; Farooq, N.; Imran, M. Teacher’s Perception about Various Factors Contributing to Truant Behavior among Secondary School Students. Dialogue 2019, 14, 230. [Google Scholar]
- Shaked, H. Israeli Principals’ Considerations Regarding the Actions They Take to Prevent Student Absenteeism. Leadersh. Policy Sch. 2022, 21, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, A.-S.M.; Cedersund, E. School staff’s reflections on truant students: A positioning analysis. Pastor. Care Educ. 2013, 31, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warne, M.; Svensson, Å.; Tirén, L.; Wall, E. On time: A qualitative study of Swedish students’, parents’ and teachers’ views on school attendance, with a focus on tardiness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, V.; Malcolm, H.; Edward, S.; Davidson, J. ‘Bunking off’: The impact of truancy on pupils and teachers. Br. Educ. Res. J. 2008, 34, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziesemer, C. Student and staff perceptions of truancy and court referrals. Soc. Work. Educ. 1984, 6, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.A.; Graczyk, P.A. Multi-tiered systems of support for school attendance and its problems: An unlearning perspective for areas of high chronic absenteeism. Front. Educ. 2022, 7, 1020150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignardi, G.; Dalmaijer, E.S.; Anwyl-Irvine, A.L.; Smith, T.A.; Siugzdaite, R.; Uh, S.; Astle, D.E. Longitudinal increases in childhood depression symptoms during the COVID-19 lockdown. Arch. Dis. Child. 2021, 106, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawes, M.T.; Szenczy, A.K.; Klein, D.N.; Hajcak, G.; Nelson, B.D. Increases in depression and anxiety symptoms in adolescents and young adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 3222–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroshus, E.; Hawrilenko, M.; Tandon, P.S.; Christakis, D.A. Plans of US parents regarding school attendance for their children in the fall of 2020: A national survey. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southall, E.; Holmes, A.; Hill, E.M.; Atkins, B.D.; Leng, T.; Thompson, R.N.; Dyson, L.; Keeling, M.J.; Tildesley, M.J. An analysis of school absences in England during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmas, R. The role of the GP in maximising school attendance. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2023, 73, 414–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, A.L.; Clark, J.S. Student absenteeism and ecological agency. Improv. Sch. 2022, 25, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, K.; Tougas, A.-M.; Robert, V.; Boulanger, C. School Refusal in Youth: A Systematic Review of Ecological Factors. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2022, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havik, T.; Bru, E.; Ertesvåg, S.K. School factors associated with school refusal- and truancy- related reasons for school non-attendance. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 2015, 18, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knage, F.S. Beyond the school refusal/truancy binary: Engaging with the complexities of extended school non-attendance. Int. Stud. Sociol. Educ. 2021, 32, 1013–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren-Landell, M. School Attendance Problems: A Research Update and Where to Go; Jerringfonden: 2021. Available online: https://jerringfonden.se/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/202101-Jerringfonden-Antologi-A5-sammanslagen.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2024).
- UNESCO. Combining Data on Out-of-School Children, Completion and Learning to Offer a More Comprehensive View on SDG 4; UNESCO Institute for Statistics: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, C.A.; Benoit, L.; Gonzálvez, C.; Keppens, G. School attendance and school absenteeism: A primer for the past, present, and theory of change for the future. Front. Educ. 2022, 7, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Kingdom Department for Education. Pupil Absence in Schools in England. Autumn Term 2022/23. 2023. Available online: https://explore-education-statistics.service.gov.uk/find-statistics/pupil-absence-in-schools-in-england (accessed on 6 January 2024).
- Kearney, C.A.; Graczyk, P.A. A multidimensional, multi-tiered system of supports model to promote school attendance and address school absenteeism. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2020, 23, 316–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, C.A.; Bates, M. Addressing school refusal behavior: Suggestions for frontline professionals. Child. Sch. 2005, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambirajah, M.S.; Grandison, K.J.; De-Hayes, L. Understanding School Refusal: A Handbook for Professionals in Education, Health and Social Care; Jessica Kingsley Publishers: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, M.A.; Attisha, E.; Lerner, M.; De Pinto, C.D.; Beers, N.S.; Gibson, E.J.; Gorski, P.; Kjolhede, C.; O’leary, S.C.; Schumacher, H.; et al. The Link between School Attendance and Good Health. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20183648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, H.C.M. The effect of pupil absenteeism on literacy and numeracy in the primary school. Sch. Psychol. Int. 2010, 31, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havik, T.; Bru, E.; Ertesvåg, S.K. Assessing reasons for school non-attendance. Scand. J. Educ. Res. 2015, 59, 316–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanneste, Y.; Mathijssen, J.J.; van de Goor, I.L.A.M.; Rots-de Vries, C.; Feron, F.J. Extensive medical absenteeism among secondary school students: An observational study on their health condition from a biopsychosocial perspective. Open J. Prev. Med. 2015, 05, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzálvez, C.; Díaz-Herrero, Á.; Vicent, M.; Sanmartín, R.; Pérez-Sánchez, A.M.; García-Fernández, J.M. School refusal behavior: Latent class analysis approach and its relationship with psychopathological symptoms. Curr. Psychol. 2020, 41, 2078–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.A. Managing School Absenteeism at Multiple Tiers: An Evidence-Based and Practical Guide for Professionals; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tonge, B.J.; Silverman, W.K. Reflections on the field of school attendance problems: For the times they are a-changing? Cogn. Behav. Pract. 2019, 26, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witte, K.; Cabus, S.; Thyssen, G.; Groot, W.; van Den Brink, H.M. A critical review of the literature on school dropout. Educ. Res. Rev. 2013, 10, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentle-Genitty, C.; Karikari, I.; Chen, H.; Wilka, E.; Kim, J. Truancy: A look at definitions in the USA and other territories. Educ. Stud. 2015, 41, 62–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppens, G.; Spruyt, B. Towards a typology of occasional truancy: An operationalisation study of occasional truancy in secondary education in Flanders. Res. Pap. Educ. 2017, 32, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, I. School refusal and truancy. Arch. Dis. Child. 1997, 76, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.A.; Silverman, W.K. A preliminary analysis of a functional model of assessment and treatment for school refusal behavior. Behav. Modif. 1990, 14, 340–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, C.A.; Silverman, W.K. The evolution and reconciliation of taxonomic strategies for school refusal behavior. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 1996, 3, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.M.; Falstein, E.I.; Szurek, S.A.; Svendsen, M. School phobia. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 1941, 11, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, I.; Butler, A.; Hullin, R.; Smith, R.; Tyrer, S. Features of children taken to juvenile court for failure to attend school. Psychol. Med. 1978, 8, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.H.; Nursten, J.P. School refusal: A comprehensive view of school phobia and other failures of school attendance. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 1962, 32, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottfried, M.A. Chronic absenteeism in the classroom context: Effects on achievement. Urban Educ. 2019, 54, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Pianta, R.C. School absenteeism in the first decade of education and outcomes in adolescence. J. Sch. Psychol. 2019, 76, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocque, M.; Jennings, W.G.; Piquero, A.R.; Ozkan, T.; Farrington, D.P. The importance of school attendance: Findings from the Cambridge study in delinquent development on the life-course effects of truancy. Crime Delinq. 2017, 63, 592–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakh, M.; Coughenour, C.; Assoumou, B.O.; Vanderstelt, M. The Relationship between School Absenteeism and Substance Use: An Integrative Literature Review. Subst. Use Misuse 2020, 55, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppens, G. School absenteeism and academic achievement: Does the timing of the absence matter? Learn. Instr. 2023, 86, 101769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Hofkens, T.L.; Pianta, R.C. Absenteeism in the First Decade of Education Forecasts Civic Engagement and Educational and Socioeconomic Prospects in Young Adulthood. J. Youth Adolesc. 2020, 49, 1835–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).