Abstract
Sialic acid, typically positioned at the terminal ends of glycoprotein or glycolipid chains via glycosyltransferase activity, is indispensable for intercellular recognition and signal transduction. Aberrant sialylation has been implicated in disrupted cell communication and oncogenic signaling, contributing to carcinogenesis. Consequently, targeting sialic acid metabolism has emerged as a promising strategy for cancer diagnosis and therapy. This review first delineates the physiological biosynthesis of sialic acid and molecular mechanisms underlying its pathological dysregulation. We then examine the sialic acid–Siglec axis as an immune checkpoint in cancer immunotherapy, highlighting its functional convergence and divergence from the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. Furthermore, we elucidate how aberrant sialylation drives malignant transformation. Finally, we synthesize current therapeutic strategies targeting the sialic acid–Siglec axis, with particular emphasis on implementing nanomaterial-based platforms in clinical translation. These advances may yield novel diagnostic tools and therapeutic targets for glycobiology-guided precision medicine.
1. Introduction
Cancer is a disease characterized by aberrant cellular proliferation, with its tumorigenesis and progression representing a multistep, complex process involving diverse molecular and cellular events. Post-translational modifications (PTMs)—covalent alterations of amino acid side chains in translated proteins—play a crucial role in regulating protein activity, localization, stability, and interaction networks [1]. Common PTMs include phosphorylation, acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, SUMOylation, glycosylation, etc.
Glycosylation is a ubiquitous and highly diverse PTM in eukaryotic cells, characterized by the covalent attachment of glycans to proteins or lipids [2,3]. This process occurs primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus, where glycosyltransferases and glycosidases sequentially assemble, modify, and trim carbohydrate structures. Mammalian glycans incorporate the following key monosaccharides: glucose (Glc), galactose (Gal), N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), mannose (Man), fucose (Fuc), xylose (Xyl), glucuronic acid (GlcA), iduronic acid (IdoA) and sialic acid (predominantly N-acetylneuraminic acid, Neu5Ac) [4].
Glycosylation is classified into distinct types, which mainly include N-linked glycosylation (Asn residues), O-linked glycosylation (Ser/Thr residues), glycolipids (glycan-linked lipids), etc. [5]. The fidelity of distinct glycosylation types is critically dependent on multiple regulatory factors including substrate availability, precise enzyme localization, stringent transcriptional control, and compartmentalized organelle-specific trafficking. Aberrant glycosylation profoundly influences critical cellular processes including proliferation, immune evasion, and metastatic potential [4]. Characteristic pathological alterations encompass: (1) disrupted N-/O-linked glycosylation pathways, (2) impaired glycolipid/glycoprotein metabolism, and (3) dysregulated sialylation—particularly the tumor-associated overexpression of sialyl Lewis antigens (SLea, SLex) [6]. As the terminal residue of most vertebrate glycans, sialic acid (catalyzed by glycosyltransferases) mediates cell–cell recognition and signaling [7,8]. Malignant progression is marked by two hallmark sialylation-related phenomena: First, hypersialylation drives immune escape through multiple mechanisms—either by suppressing NK cell and macrophage effector functions [9,10,11] or by concealing tumor-associated antigens (e.g., STn expression in early carcinogenesis) [12,13]. Second, pathological sialylation contributes to systemic dysfunction including: (i) compromised serum glycoprotein activity (affecting coagulation and immune responses) [14], (ii) neurodevelopmental impairments via altered neurotransmitter receptor glycosylation [15], and (iii) sustained inflammatory and autoimmune conditions [16]. These disease-associated modifications establish sialylation signatures as clinically valuable biomarkers for malignancies, infectious processes, and inflammatory disorders.
In summary, the importance of abnormal sialylation is reflected in its profound effects on cell recognition, signaling, protein function, molecular transport, immune regulation, and pathophysiological processes. Understanding and studying abnormal sialylation can not only help to reveal the mechanism of the disease but also explore new targets for diagnosis and treatment. Targeting sialic acid for cancer diagnosis and treatment is a promising research direction. Although sialylation has been shown to be a therapeutic target for cancer treatment, its associated immunosuppression often results in poor treatment outcomes. Therefore, we start from the synthesis pathway of sialic acid again, aiming to understand the normal synthesis pathway of sialic acid in cells and the specific mechanism of abnormal changes. This article describes the significance of sialic acid–Siglec as a checkpoint for cancer immunotherapy. Next, we combined with recent advances to provide a more comprehensive picture of how changes in sialylation lead to the development of cancer cells. Finally, we summarize the therapeutic approaches targeting sialic acid and specifically describe the role of novel nanomaterials in the clinical treatment of sialic acid. We aim to provide new diagnostic options or therapeutic targets for glycan-mediated therapeutic interventions.
2. The Normal Synthetic Pathway of Sialic Acid
Sialic acids constitute a family of nine-carbon α-keto acid sugars (C1–C9) derived from neuraminic acid, with structural diversity arising from natural modifications at specific carbon positions, predominantly including N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), and 2-keto-3-deoxynonulosonic acid (KDN) in mammalian systems [17] (Figure 1). These negatively charged sugars typically occupy terminal positions on glycoconjugates, where their biosynthesis initiates through a four-step cytoplasmic pathway: (1) UDP-GlcNAc is converted to ManNAc-6-P by the bifunctional GNE enzyme (mutations in which cause sialuria and inclusion body myopathy); (2) Neu5Ac-9-P is synthesized by NANS through condensation of ManNAc-6-P with phosphoenolpyruvate; (3) NANP-mediated dephosphorylation yields free Neu5Ac; and (4) CMAS catalyzes CMP-Neu5Ac formation in the nucleus for subsequent Golgi transport via SLC35A1 [18,19] (Figure 2). Humans uniquely lack functional CMAH, restricting endogenous production to Neu5Ac while enabling dietary incorporation of Neu5Gc from red meat and dairy sources [20,21] with pathological consequences including oncogenic effects evidenced by elevated Neu5Gc in malignancies correlating with dietary intake and promotion of hepatocellular carcinogenesis in CMAH-deficient models [22]. The Golgi apparatus facilitates diverse sialic acid modifications (O-acetylation, O-methylation, O-sulfation) and linkage variations (α2-3, α2-6, α2-8, or alternating α2-8/α2-6) through over 20 sialyltransferase subtypes, including polysialic acid (PolySia) formation via α2-8 linkages [18]. Degradation occurs through four spatially distinct neuraminidases (NEU1-lysosomal, NEU2-cytosolic, NEU3-plasma membrane, NEU4-mitochondrial) that cleave sialic acids into ManNAc and pyruvate for recycling or excretion, with dysregulation contributing to pathological states ranging from carcinogenesis (through immune evasion mediated by hypersialylation) to infectious susceptibility (via viral exploitation of sialic acid variants for cellular entry) [23]. These complex biosynthetic, modificative, and catabolic pathways underscore the critical role of sialic acid biology in health and disease.
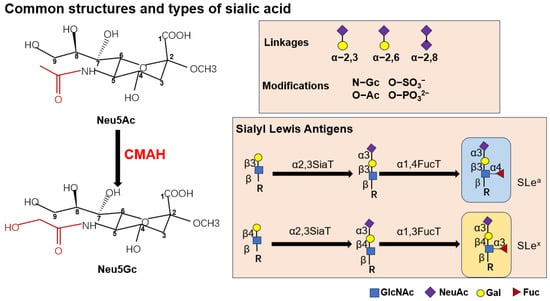
Figure 1.
Common structures and types of sialic acid. Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc are similarly structured, and they possess different groups at the C-5 position, which are expressed in red. Neu5Ac is converted to Neu5Gc with the participation of CMAH enzyme. The common linkage of sialic acid includes α-2,3-, α-2,6- and α-2,8-linked. SLea and SLex are common forms of sialic acid associated with tumors, which are synthesized in response to different substrate-specific sialyltransferases.
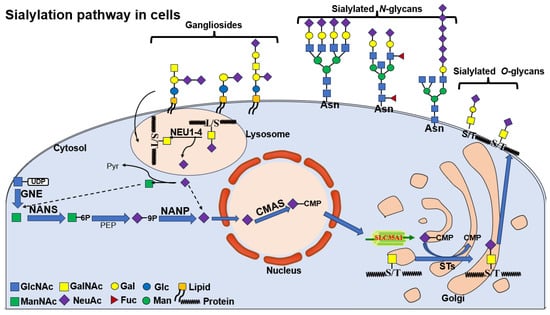
Figure 2.
Sialylation pathway in cells. The nucleotide glycan UDP-GlcNAc, the product of hexosamine pathway, is converted into ManNAc by UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase (whose encoding gene is GNE in humans). ManNAc is metabolic precursor for the synthesis of sialic acid and produces Neu5Ac in the cytosol, which then enters the nucleus to produce CMP-Neu5Ac. CMP-Neu5Acs are transported into Golgi where they are used by sialyltransferase to produce glycoproteins or glycolipids, respectively. Finally, sialic acids are recycled by neuraminidases, regenerating sialic acid monomers that can be re-used. The figure shows three types of sialylated glycans, which involve sialylated N-glycans, sialylated O-glycans and gangliosides.
3. Abnormal Sialic Acid Synthesis
Abnormal sialic acid synthesis, characterized by (1) enhanced glycan substrate availability, (2) upregulated sialyltransferase expression, and (3) diminished sialidase activity, serves as a hallmark of cellular malignant transformation. This triad of abnormalities drives premature termination of glycosylation pathways and consequent hypersialylation, manifesting as elevated sialylated glycans on tumor cell surfaces. The dynamic balance of sialylation is precisely regulated by two counteracting enzyme systems, which are sialyltransferases that catalyze sialic acid addition and sialidases (neuraminidases) that mediate its removal from glycoconjugates. The stoichiometry of these opposing enzymatic activities ultimately determines cellular sialic acid content, with tumorigenesis frequently exhibiting a characteristic shift toward net sialylation through both increased synthetic capacity (sialyltransferase overexpression) and impaired degradation (sialidase suppression).
3.1. The Impact of Sialyltransferases in Cancer Progression and Therapy
Different sialyltransferase families are associated with distinct cancer types (Table 1). Altered sialyltransferase activity significantly influences cancer cell behavior through multiple mechanisms. A key example is ST6GalNAcI, whose upregulation drives synthesis of the STn antigen by transferring α2,6-linked sialic acid to O-GalNAc residues [24]. This enzyme exhibits unique biological significance as the sole sialyltransferase capable of STn biosynthesis in human cells. Elevated ST6GalNAcI expression in breast and prostate cancer models directly induces STn expression and promotes metastatic progression through epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) activation [25,26]. The oncogenic effects of ST6GalNAcI extend across multiple cancer types through diverse molecular mechanisms. For example, it activates STAT5b to upregulate IGF-1 expression in gastric cancer, suggesting therapeutic potential for metastatic disease [27]. In ovarian cancer stem cells, its silencing attenuates malignant properties including proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumorigenicity [28]. When combined with atezolizumab, ST6GalNAcI may serve as a highly sensitive diagnostic biomarker for lung cancer detection [29].
The ST3Gal sialyltransferase family similarly contributes to cancer progression in ovarian cancer [30,31]. Another critical enzyme, ST6GAL1, demonstrates widespread oncogenic activity through its overexpression in multiple malignancies including prostate cancer, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, osteosarcoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and glioblastoma [32,33,34,35,36]. ST6GAL1 additionally promotes therapy resistance by suppressing apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma stem cells, rectal cancer, and pancreatic cancer models [37,38,39], highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target across diverse cancer types.

Table 1.
Human Sialyltransferases.
Table 1.
Human Sialyltransferases.
| Sialyltransferase Family | Sialyltransferase | Preferred Acceptor Saccharide | Glycan Specificity | Type of Cancer | Regulation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST3Gal | ST3Gal-I | Galβ1,3GalNAc | O-glycan | BLCA, LIHC, BRCA | Uplation | [40,41,42] |
| ST3Gal-II | Galβ1,3GalNAc | O-glycan | OV | Uplation | [43] | |
| ST3Gal-III | Galβ1,3(4)GlcNAc | O-glycan, N-glycan | PAAD | Uplation | [44] | |
| ST3Gal-IV | Galβ1,4(3)GlcNAc | N-glycan, O-glycan | PAAD | Uplation | [44] | |
| ST3Gal-V | Galβ1,4Glc-ceramide | Glycolipid | BLCA | Downlation | [45] | |
| ST3Gal-VI | Galβ1,4GlcNAc | N-glycan, Glycolipid | COAD, BLCA, STAD, LUAD, MMLIHC | Downlation | [46,47,48,49,50] | |
| Uplation | [51] | |||||
| ST6Gal | ST6Gal-I | Galβ1,4GlcNAc | N-glycan | COAD, READ, OV, PRAD, LIHC, NSCLC | Uplation | [38,52,53,54,55] |
| ST6Gal-II | Galβ1,4GlcNAc | N-glycan | THCA | Uplation | [56] | |
| ST6GalNAc | ST6GalNAc-I | GalβNAcα1,O-Ser/Thr Galβ1,3GalNAcα1, O-Ser/Thr | O-glycan | LIHC, OV, COAD, BRCA, PRAD, ESCA | Uplation | [25,28,57,58,59] |
| Downlation | [60] | |||||
| ST6GalNAc-II | Galβ1,3GalNAcα1, O-Ser/Thr | O-glycans | COAD, READ, BRCA | Uplation | [61] | |
| Downlation | [62] | |||||
| ST6GalNAc-III | Siaα2,3Galβ1,3GalNAc | O-glycans | NSCLC | Downlation | [54] | |
| ST6GalNAc-IV | Siaα2,3Galβ1,3GalNAc | O-glycans | THCA, LIHC | Uplation | [63,64] | |
| ST6GalNAc-V | GM1b | Glycolipid | PRAD | Downlation | [65] | |
| ST6GalNAc-VI | All α-series gangliosides | Glycolipid | BLCA | Downlation | [66] | |
| ST8Sia | ST8Sia-I | Siaα2,3Galβ1,4Glc-ceramide | Glycolipid | BRCA | Uplation | [67] |
| ST8Sia-II | Siaα2,3Galβ1,4GlcNAc | N-glycan on NCAMa | SCLC | Uplation | [68] | |
| ST8Sia-III | Siaα2,3Galβ1,4GlcNAc | N-glycan on NCAMa | --- | --- | --- | |
| ST8Sia-IV | (Siaα2,8)nSiaα2,3Galβ1-R | N-glycan on NCAM | --- | --- | --- | |
| ST8Sia-V | GM1b, GT1b, GD1a, GD3 | Glycolipid | --- | --- | --- | |
| ST8Sia-VI | Siaα2,3(6)Gal | Sialic acid on O-glycan | NBL | Uplation | [69] |
3.2. Abnormal Sialidase Activity in Disease
The four human sialidases (NEU1–NEU4) exhibit distinct substrate specificities, leading to diverse roles in pathological conditions. Among them, NEU1 is implicated in multiple diseases, including lysosomal storage disorders, infections, cancers, and neurodegenerative disorders, due to its regulation of critical signaling pathways, making it a potential therapeutic target for cancer and immune-related diseases [70]. In ovarian cancer, NEU1 is highly expressed, and its knockdown via siRNA suppresses tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis by disrupting lysosomal and oxidative phosphorylation pathways [71]. Additionally, NEU1 has emerged as a potential target in melanoma, autism spectrum disorders, and respiratory diseases [72,73,74]. NEU2 modulates cancer stemness, as demonstrated by its desialylation-mediated inhibition of Sonic Hedgehog signaling, reducing stem-like properties in pancreatic cancer spheroid cells [75]. NEU3 overexpression enhances tumor aggressiveness in bladder cancer [76] and confers resistance to apoptosis in colon cancer [77]. Conversely, NEU4 is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, where its tumor-suppressive function involves CD44 desialylation to inhibit cell migration [78]. These findings highlight the critical and varied roles of sialidases in disease progression, positioning them as promising targets for therapeutic intervention.
4. Significance of Targeting the Sialic Acid–Siglec Axis
The sialic acid-binding lectin family comprises three major groups: selectins (P-, L-, and E-selectin), Factor H, and sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins (Siglecs). Selectins, belonging to the C-type lectin family, mediate cellular interactions through recognition of SLex structures, playing critical roles in leukemia cell trafficking and cancer metastasis. Factor H serves as a key regulatory protein in the alternative complement pathway, modulating immune responses. The Siglec family, consisting of over 14 type I transmembrane lectins expressed on nearly all immune cell types, specifically recognizes diverse sialoglycan structures and regulates immune cell signaling [79]. These sialic acid-binding proteins collectively form the “Sialic–Siglec axis,” which has emerged as a promising therapeutic target due to its involvement in immune modulation, cancer progression, and inflammatory processes. The differential expression patterns and glycan-binding specificities of these lectins offer opportunities for developing selective interventions in malignancies, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases.
4.1. Siglec Family Classification and Function
The Siglec family comprises sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins that serve as transmembrane receptors primarily expressed on immune cells, mediating cell–cell interactions through recognition of sialylated glycoproteins and glycolipids. These receptors play crucial roles in immune regulation by modulating adhesion, cell signaling, and endocytosis processes [80,81,82]. The human Siglec family includes 14 members divided into two evolutionary groups: (1) conserved Siglecs (Siglec-1/CD169, -2/CD22, -4/MAG, and -15) sharing 25–30% sequence identity and (2) rapidly evolving CD33-related Siglecs (Siglec-3/-5/-6/-7/-8/-9/-10/-11/-14/-16) with 50–99% sequence identity that have diversified through gene duplication and exon shuffling [83,84].
Structurally, Siglecs feature an N-terminal V-set immunoglobulin domain for sialic acid binding, variable C2-set Ig domains, and intracellular signaling motifs [85]. Functionally, they can be categorized as the following 3 types: (1) inhibitory Siglecs (9 members) containing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) that recruit SHP-1/SHP-2 phosphatases to suppress immune responses; (2) activating Siglecs (Siglec-14/15/16) with transmembrane charges that associate with DAP10/12 adaptors to trigger SYK-mediated activation through MAPK and AKT pathways; (3) non-signaling Siglecs (Siglec-1/-4) lacking intracellular domains (Figure 3).
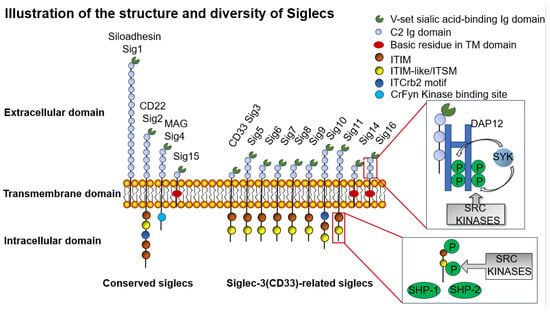
Figure 3.
Illustration of the structure and diversity of Siglecs. There are two main groups of Siglecs: those that are highly conserved, as shown on the left, and a more diverse group of CD33-related Siglecs, as shown on the right. All Siglecs have an extracellular V-type Ig domain and at least one C2-type Ig domain. Many Siglecs also contain at least one cytoplasmic ITIM domain, involved in immunosuppressive signaling. The 3 Siglecs (Siglecs14/15/16) have a positive charge in their transmembrane domains, mediating association with DAP12 to activate immune responses. This causes recruitment and activation of SYK, leading to phosphorylation of protein kinases of downstream targets resulting in cell activation, while the remaining 9 Siglecs carry ITIM motifs, whose domains are phosphorylated by Src family kinases, which subsequently lead to the recruitment of SH2 domains containing phosphatases SHP-1 and/or SHP-2, which dephosphorylate downstream components of the immunostimulatory pathway, thereby inhibiting the immune response.
Siglec–sialoglycan interactions occur in both cis (same cell) and trans (adjacent cell) configurations, with cis-binding predominating due to high local sialic acid concentrations on immune cells [86]. These interactions establish self-recognition through sialic acid-based molecular patterns (SAMPs) that maintain immune homeostasis [87], contrasting with pathogen-triggered immune activation. Dysregulation of this system contributes to pathological conditions, including cancer, which develop through tumor cell hypersialylation, autoimmune disorders such as IgA nephropathy, and inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease [88]. The dual roles of Siglecs in immune regulation and disease pathogenesis highlight their potential as therapeutic targets for immune modulation and cancer treatment.
4.2. Generation of Immunosuppressive Microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment (TME) represents a complex ecosystem where immune cell dysfunction promotes malignant tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis [89]. Siglecs, expressed on various immune cell subsets, serve as important phenotypic markers whose dysregulated expression in TME contributes to tumor development [90,91] (Table 2). These receptors facilitate tumor immune escape through interactions with tumor-associated sialoglycans, creating broad immunosuppressive effects across multiple immune cell populations.

Table 2.
Preclinical evidence of Siglec-mediated immune modulation in the tumor microenvironment.
Myeloid cells, the predominant immune population in solid tumors, play central roles in establishing immunosuppressive TME [103] and exhibit remarkable plasticity—macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes and granulocytes dynamically adapt to TME signals, promoting tumor proliferation, angiogenesis and immune suppression [104,105]. Sialic acid has emerged as a critical regulator of myeloid cell polarization toward pro-tumor phenotypes, making it an attractive target for cancer immunotherapy [10,92].
The Siglec–sialic acid axis serves as a fundamental regulatory mechanism in TME, with Siglec-7/-9/-10/-15 showing particularly strong expression on tumor-associated myeloid cells, NK cells and T cell subsets [93,95,106,107]. This molecular interaction profoundly influences immune function by modulating monocyte differentiation, macrophage polarization, DC activation, neutrophil effector functions, and NK/T cell anti-tumor activity. Current evidence demonstrates Siglec-mediated immunosuppression occurs through multiple mechanisms: myeloid cell reprogramming via sialic acid–Siglec interactions promotes alternative macrophage activation and DC dysfunction; lymphocyte inhibition through Siglec engagement dampens NK and T cell cytotoxic responses; and certain Siglecs function as novel immune checkpoints in TME. These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of disrupting the sialic acid–Siglec axis to reverse immunosuppression and restore anti-tumor immunity, offering new opportunities for cancer immunotherapy development. The ability of Siglecs to regulate multiple immune cell populations within TME positions them as promising targets for combination therapies aiming to overcome current limitations in cancer treatment (Figure 4).
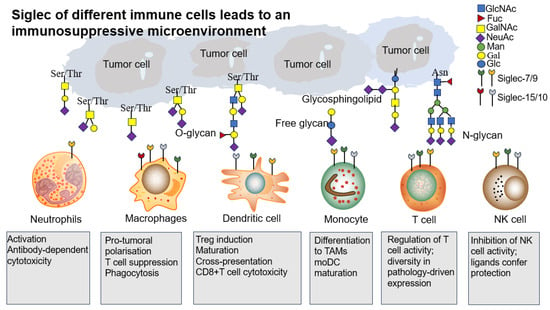
Figure 4.
Siglec of different immune cells leads to an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Schematic of the Siglec–sialic acid axis shaping myeloid cell and lymphocyte cell function. Siglec-7/9/10/15 expression and their sialic acid ligand in the TME.
4.2.1. Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs)
TAMs primarily originate from peripheral blood monocytes that undergo M2-polarized differentiation under the influence of tumor-derived signals and microenvironmental cues. During this process, macrophages develop tissue-specific Siglec expression patterns. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, upregulated ST3GAL1 and ST3GAL4 sialyltransferases promote monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation through Siglec-mediated signaling pathways [95]. Siglec-9 plays a particularly critical role in this differentiation process, and its engagement further suppresses anti-tumor T cell responses, contributing to immune evasion [108]. Additionally, Muc1-associated sialoglycan truncation drives macrophages toward a TAM-like phenotype characterized by elevated programmed death protein 1 (PD-L1) expression, effectively creating an immunosuppressive checkpoint [93]. These mechanisms collectively demonstrate how sialic acid–Siglec interactions shape TAM polarization and function within the tumor microenvironment, ultimately facilitating immune escape and tumor progression. The dual role of specific Siglecs in both macrophage differentiation and subsequent T cell suppression highlights their potential as therapeutic targets for reprogramming the immunosuppressive TME.
4.2.2. Neutrophils
Neutrophils, while essential for innate immunity and pathogen clearance, adopt immunosuppressive functions in cancer and chronic inflammation through sialic acid–Siglec interactions. Tumor-associated neutrophils express multiple Siglecs (Siglec-5, -7, -9, and -10) that engage with hypersialylated tumor cells, leading to functional inhibition [109]. The Sialic–Siglec-9 axis in particular suppresses antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against tumors, representing a key immune evasion mechanism. Recent studies reveal that Siglec-F+ splenic neutrophils induce systemic immunosuppression post-infection [110], while Siglec signaling broadly restrains neutrophil effector functions—including degranulation, chemotaxis, reactive oxygen species production, and cytokine release—through inhibitory phosphorylation cascades. Beyond intrinsic suppression, Siglec-activated neutrophils secrete TGF-β and IL-10 to dampen NK cell cytotoxicity and macrophage activation, creating a feedforward immunosuppressive network within the TME. Therapeutic disruption of these pathways (e.g., via Siglec-9 blockade) enhances neutrophil-mediated tumor killing in preclinical models, highlighting this axis as a promising immunomodulatory target.
4.2.3. Dendritic Cells (DCs)
As professional antigen-presenting cells, DCs play a pivotal role in initiating tumor-specific T cell responses and represent crucial targets for immunotherapy [111,112]. Emerging evidence demonstrates that Siglec receptors significantly modulate DC function through multiple mechanisms: (1) Siglec-G impairs cross-presentation capacity in murine DCs by disrupting MHC class I-peptide complex formation [96]; (2) Siglec-E engagement by sialoglycans regulates DC activation thresholds [97]; and (3) tumor-associated DCs from cancer patients exhibit elevated expression of inhibitory Siglecs (-7, -9, and -10) that contribute to immune suppression [95]. Therapeutic targeting of Siglec–DC interactions shows promising immunomodulatory effects: Siglec-7 blockade enhances T cell priming and DC activation in vitro by disrupting glycan-mediated immunosuppressive signaling [113], while the tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib promotes DC migration by reducing Siglec-9/-3 phosphorylation, potentially augmenting chemoimmunotherapy efficacy [114]. These findings highlight the critical balance between Siglec-mediated inhibition and DC activation, suggesting that selective disruption of specific Siglec pathways (particularly Siglec-7/-9) could enhance DC-based antitumor immunity. Further elucidation of Siglec–DC interactions across different cancer types may yield novel combinatorial immunotherapy approaches tailored to overcome microenvironmental immunosuppression.
4.2.4. Natural Killer Cells (NK Cells)
NK cells are specialized lymphocytes that belong to the innate immune system. They do not rely on specific antigen presentation but are able to directly recognize and kill infected cells or tumor cells. NK cells kill target cells directly by releasing cytotoxic molecules. In addition, they are able to secrete various cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), to regulate the immune response. NK cells recognize target cells by activating and inhibiting receptors on their surface. Activating receptors recognize and bind to stress or mutant molecules on the surface of target cells, while inhibiting receptors bind to MHC-I molecules on the surface of normal cells, preventing NK cells from attacking normal cells. Human NK cells mainly express Siglec-7 and -9 [86], which engage with tumor-associated sialoglycans to suppress NK cell function through multiple mechanisms: (1) Siglec-9 binding to MUC16 on ovarian cancer cells inhibits anti-tumor responses [115]; (2) immune synapse formation induces Siglec-7 ligand accumulation and sustained inhibitory signaling through delayed glycoconjugate endocytosis [100]; and (3) in multiple myeloma, Siglec-7 engagement facilitates tumor escape from NK cell surveillance [9]. These interactions demonstrate how tumor cells exploit the Siglec checkpoint axis to evade NK-mediated immunity. Therapeutic strategies targeting Siglec-7/9 (e.g., antibody blockade or glycan remodeling) may therefore enhance NK cell anti-tumor activity, particularly in Siglec ligand-high malignancies like ovarian cancer and multiple myeloma. The differential expression of Siglec receptors across NK cell subsets (e.g., CD56bright vs. CD56dim) further suggests opportunities for precision immunotherapies tailored to specific tumor microenvironments.
4.2.5. Lymphocyte
The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment extends beyond myeloid cells to include lymphocytes, with both B and T cells exhibiting Siglec-mediated regulation of anti-tumor immunity. B lymphocytes predominantly express CD22 (Siglec-2), a conserved receptor that modulates B cell activation thresholds through ST6GAL1-catalyzed sialylation, maintaining immune tolerance [16,116]. Clinically, the anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody SM03 has shown efficacy in Phase III trials by disrupting CD22-SHP1-mediated NF-κB suppression, restoring B cell responsiveness in malignancies [117], while CD22-targeted CAR-T therapy demonstrates potent activity against B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia [118]. T lymphocytes primarily express Siglec-7 and -9, which engage tumor-associated sialoglycans to inhibit activation and proliferation—particularly in glioblastoma, where Siglec-9 functions as a macrophage-associated immune checkpoint that limits T cell responses to immunotherapy [119].
The broader Siglec–ligand network facilitates immune evasion through multiple tumor-specific mechanisms: (1) CD24-Siglec-10 interactions inhibit phagocytosis in ovarian/breast cancers [120]; (2) SELPLG engages Siglec-7 to promote myeloma immune escape [9]; (3) MUC1/MUC16 O-glycans bind Siglec-9 on monocytes/macrophages in breast cancer [115,121]; and (4) GD3 ganglioside suppresses NK cytotoxicity via Siglec-7 in melanoma [122]. These findings position Siglecs as multifunctional immune checkpoints that tumors exploit through varied glycoconjugate interactions. Therapeutic targeting of specific Siglec–ligand axes (e.g., CD24-Siglec-10 or GD3-Siglec-7) may overcome microenvironmental immunosuppression, with emerging strategies including Siglec-blocking antibodies, glycan remodeling enzymes, and combination approaches with existing immunotherapies. The cell-type-specific expression patterns of Siglecs across lymphocyte subsets further enable precision targeting to restore anti-tumor immunity while minimizing systemic autoimmunity risks.
4.3. Feasibility of Early Malignant Tumor Detection Using Sialic Acid and Siglecs
The sialic acid–Siglec axis represents a promising frontier for both early cancer detection and immunotherapy, particularly for tumors resistant to conventional immune checkpoint blockade. As innate immune checkpoints, Siglec receptors and their sialoglycan ligands play critical roles in tumor immune evasion by regulating phagocytosis and immune surveillance [123]. While current immunotherapies targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 have shown remarkable success in certain cancers [124,125], their efficacy remains limited by immunosuppressive tumor microenvironments and the “cold tumor” phenotype characterized by poor T cell infiltration [126,127]. This therapeutic gap has spurred interest in Siglec-targeted approaches, leveraging their unique expression patterns and mechanisms of immune regulation. Clinically, Siglec-2 (CD22) has emerged as a validated target in B-cell malignancies, with antibody-drug conjugates and bispecific CD19/Siglec-2 CAR-T therapies demonstrating efficacy in relapsed B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia [128]. Meanwhile, Siglec-15 has garnered attention as a potential alternative to PD-L1 blockade, with the NC318 antibody currently in Phase I/II trials for PD-1/PD-L1-resistant cancers [129,130]. Beyond direct tumor targeting, Siglec blockade (e.g., anti-Siglec-7/-9/-10) can restore NK/T cell cytotoxicity [109,113,120], while interventions against tumor-associated sialoglycans (e.g., CD24-Siglec-10, GD3-Siglec-7) may enhance phagocytosis and NK activity [120,122]. For early detection, aberrant sialylation patterns and Siglec overexpression in premalignant lesions offer potential as diagnostic biomarkers through liquid biopsies or molecular imaging. However, challenges remain, including tumor heterogeneity in Siglec expression, risks of autoimmune toxicity from systemic blockade, and the need for rational combination strategies with existing therapies [131]. The dual utility of the sialic acid–Siglec axis, as both a detection marker and therapeutic target, positions it as a transformative platform in oncology, particularly for immunologically “cold” tumors refractory to current immunotherapies. Ongoing clinical evaluation of Siglec-directed agents and deeper mechanistic understanding of Siglec biology in the tumor microenvironment will be crucial for realizing this potential and expanding treatment options for cancer patients.
5. The Impact of Sialylation on Cancer Development
Hypersialylation, a hallmark of cancer, drives tumor aggressiveness by promoting immune evasion, altering cell adhesion, enhancing metastasis, and conferring resistance to chemo/radiotherapy [132]. This aberrant glycosylation modulates multiple oncogenic pathways across various cancers (pancreatic, colon, breast, ovarian, melanoma, and lung): (1) excessive sialylation of death receptors (FasR, TNFR1) inhibits apoptosis [133,134,135]; (2) sialylated growth factor receptors (e.g., FGFR1) aberrantly activate ERK/FAK signaling, fueling proliferation, angiogenesis, and invasion [133]; and (3) tumor-associated sialylselectin ligands (SLea, SLex, CD44) facilitate hematogenous metastasis by mediating circulating tumor cell adhesion to vascular endothelium [136], which is a mechanism exemplified by SLex-high breast cancers exhibiting preferential metastatic tropism [137].
Clinically, sialic acid-rich glycoconjugates serve as established biomarkers (CA19-9/SLex in pancreatic cancer; CA125/MUC16 in ovarian cancer; CA15-3/MUC1 in breast cancer) [138], while specific sialyltransferases show prognostic potential. ST6GAL1 correlates with advanced stage, chemoresistance, and metastatic recurrence [139], with therapeutic targeting of ST6Gal-1-high triple-negative breast cancer stem cells demonstrating improved efficacy through glycan engineering approaches [140]. Similarly, ST8SiaII marks metastatic neuroblastoma [141], and GM3 synthase (ST3GAL3) depletion suppresses castration-resistant prostate cancer by reducing cancer stemness and EMT markers [142]. These findings position sialylation enzymes and their products as both diagnostic indicators and therapeutic vulnerabilities across malignancies, with emerging strategies focusing on sialyltransferase inhibition, glycan remodeling, and sialoglycan-targeted immunotherapy to disrupt pro-tumorigenic sialic acid signaling.
6. Methods of Targeting Siglec–Sialylation Therapy
The Siglec–sialic acid interaction represents a promising immunotherapeutic target, with multiple intervention strategies under investigation to disrupt this immunosuppressive axis and enhance anti-tumor immunity.
6.1. Antibody Therapy
As Siglecs are surface receptors expressed on most immune cells, antibody-based therapies represent a strategic approach to exert cytotoxic effects by targeting immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. These include antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), anti-Siglec bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs), and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies (Figure 5).
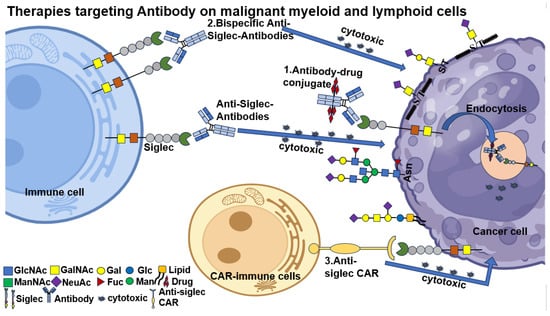
Figure 5.
Therapies targeting antibodies on malignant myeloid and lymphoid cells. Targeting antibody therapies include monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, chimeric antigen T cell (CAR-T) therapy and antibody-drug conjugate. CAR T-cell therapies have been developed that target Siglecs displayed on the surface of cancer cells, leading to cytotoxicity in those cells. Cytotoxic granules are depicted as black dots. Illustrated ADCs are composed of an anti-Siglec conjugated to a cytotoxic small-molecule payload. The antibody portion of the drug targets Siglecs, which are displayed on the surface of cancer cells, leading to internalization of the antibody and the drug and subsequent release of the cytotoxic payload within the cancer cell.
6.1.1. Monoclonal Antibody (mAb)
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) utilizing anti-Siglec mAbs demonstrate dual mechanisms of action: target specificity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. These mAbs specifically bind Siglecs on immune cells, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immune responses and attenuating immunosuppression within the TME. Furthermore, they disrupt interactions between tumor-associated sialoglycans and Siglecs, preventing immune evasion. Preclinical studies validate the therapeutic potential of Siglec-targeting mAbs. For instance, Siglec-15, highly expressed on TAMs, represents a promising ICI target due to its role in cancer immune evasion. The anti-Siglec-15 mAb NC318 has demonstrated therapeutic efficacy in preclinical models and is currently undergoing phase I/II clinical evaluation [129]. Additionally, the anti-CD22 mAb SM03 mitigates CD22/SHP1-mediated suppression of NF-κB signaling, restoring B-cell responsiveness in malignancies [117].
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) constitute an emerging class of potent therapeutics comprising mAbs linked to cytotoxic payloads. These agents selectively deliver potent cytotoxins to tumor cells while sparing normal tissues, thereby overcoming key limitations of conventional chemotherapy and providing an improved therapeutic index [143]. ADCs exhibit significant activity against refractory cancers, with several agents receiving clinical approval [144]. FDA-approved ADCs for solid tumors include those targeting HER2, TROP-2, and Nectin-4 [145,146,147]. Siglecs undergo ligand- or antibody-induced endocytosis followed by recycling to the cell surface, rendering them optimal ADC targets [148,149,150]. Several Siglec-targeting ADCs are in development, with some already implemented clinically. For example, gemtuzumab ozogamicin (anti-CD33 ADC) is used for CD33+ acute myeloid leukemia, while inotuzumab ozogamicin (anti-CD22 ADC) is for relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia [151].
6.1.2. Bispecific Antibody (BsAbs)
BsAbs can recognize and bind to two different antigens or epitopes, redirect immune cells to tumor cells, deliver drugs to tumors, and block two biological pathways important to tumors for cancer treatment [152,153,154]. Fc domain-containing BsAbs engage Fcγ receptors on immune effector cells (e.g., NK cells, monocytes, macrophages), inducing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. However, complement binding may trigger complement-dependent cytotoxicity, potentially causing nonspecific immune activation during treatment [155]. Among T-cell-engaging BsAbs, bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) represent a clinically validated subclass. BiTEs comprise two single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) from anti-tumor-associated antigen and anti-CD3 mAbs, connected via short linkers [156]. These scFvs—containing immunoglobulin heavy and light chain variable domains—exhibit 100- to 10,000-fold greater tumor cell killing potency than conventional BsAbs or IgG mAbs [157]. AMG330, a CD33/CD3-targeting BiTE, demonstrates significant tumor growth inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia xenograft models [158]. Similarly, CD19/CD22 [159] and CD20/CD22 [160] BsAbs show enhanced efficacy over monospecific targeting. Additionally, Siglec6-targeted T-cell-recruiting BsAbs effectively eliminate chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells while sparing Siglec6−-healthy B cells [123].
6.1.3. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Therapeutic Approaches
CAR-T therapy involves genetic modification of patient-derived T cells to express synthetic receptors that recognize specific tumor antigens [161]. These CARs enable precise targeting of cancer cells, enhancing T cell-mediated tumor killing. Following ex vivo expansion, CAR-T cells are reinfused into patients, minimizing host immune rejection. Despite challenges including cytokine release syndrome and limited solid tumor efficacy, CAR-T therapy has achieved remarkable success in hematologic malignancies such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and specific lymphomas [162]. CAR-T cells persist as memory phenotypes, enabling rapid and durable responses superior to conventional therapies [163,164]. FDA-approved CAR-T products target refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and ALL [165].
CAR-T cells targeting Siglec-2 (CD22) and Siglec-3 (CD33) receptors show clinical efficacy against leukemia and lymphoma, respectively [166,167,168]. CD22-directed CAR-T therapy effectively inhibits ALL progression [118]. Recent studies indicate Siglec-6-targeted CAR-T cells induce remission in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) without requiring allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [169]. Bispecific CD19/CD22 CAR-T therapy overcomes antigen escape in relapsed/refractory B-ALL, demonstrating durable responses in Phase I trials [170,171]. Additionally, CD33-targeted CAR-NK cells reduce leukemia burden and prevent bone marrow engraftment in AML xenografts, suggesting a novel AML treatment paradigm [172]. A recent Phase I dose-escalation study confirmed durable clinical activity of CD22 CAR-T (CAR22) in patients progressing after CD19 CAR-T therapy, validating CD22 as a salvage target for CAR-T-resistant lymphomas [173]. These advances underscore the significant clinical potential of CAR-T approaches.
6.2. Siglec Inhibitor
In recent years, significant efforts have been directed toward developing Siglec blockers as cancer immunotherapies. These agents function by disrupting inhibitory interactions between immune cell Siglecs and their ligands expressed on cancer cells, thereby blocking the immunosuppressive effects of inhibitory Siglecs while simultaneously promoting immune activation. Recent studies demonstrate that inhibiting GD2 binding to macrophage Siglec-7 enhances anti-tumor immunity, further increasing phagocytosis and amplifying the efficacy of CD47 blockade [174].
6.3. Sialylation Inhibitor
Altering the synthesis and expression of sialoglycan groups while reducing sialoglycan density in tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment represents an alternative approach to block immunosuppressive effects. This includes utilizing sialic acid mimics to inhibit sialic acid biosynthesis and developing sialic acid biosynthesis inhibitors. Sialidase treatment may also influence cancer progression by modifying signaling in tumor cells and immune cells (Figure 6).
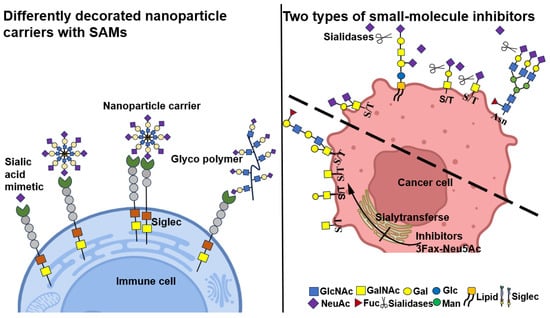
Figure 6.
Differently decorated nanoparticle carriers with SAMs and two types of small-molecule inhibitors. Carbon groups (C-) in the sialic acid backbone that could be substituted to design high-affinity SAMs. The nanoparticle carriers decorated with sialic acid mimetics for high-affinity binding to Siglecs and Membrane-targeting salivary glycopolymers can bind to Siglec on immune cells with high specificity. Immunosuppression of siglec–sialic acid interactions is prevented by the application of small-molecule inhibitors targeting sialidase and sialyltransferase, which reduce or hinder sialic acid synthesis and prevent siglec–sialic acid interactions.
6.3.1. Sialtransferase Inhibitors
Enzymatic reduction in sialoglycan density in tumors has been tested and is currently under investigation in human clinical trials. An αHER2 antibody–sialidase conjugate efficiently and selectively removes diverse sialoglycans from breast cancer cells. In syngeneic murine breast cancer models, desialylation enhanced immune cell infiltration and activation while extending survival time [175]. This intervention repolarized TAMs, bolstering anti-tumor immunity and inhibiting tumor progression. Another study chemically fused recombinant sialidase with trastuzumab, a human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-specific antibody. This antibody–sialidase conjugate mediated HER2-dependent desialylation, reducing natural killer (NK) cell binding to inhibitory Siglec receptors and enhancing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) in tumor cells [176].
6.3.2. Sialic Acid Mimics (SAMs)
SAMs are synthetic molecules structurally mimicking sialoglycoproteins that function as high-affinity Siglec ligands. SAMs can either block tumor cell-expressed Siglecs or competitively inhibit natural Siglec binding, thereby disrupting Siglec–ligand interactions to modulate Siglec signaling and immune responses in disease contexts [177]. Another promising strategy involves intratumoral injection of SAMs to locally block sialic acid expression. This approach increased tumor-infiltrating NK cells and CD8+ T cells while reducing regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, ultimately enhancing CD8+ T cell-mediated cytotoxicity and suppressing tumor growth [178].
The fluorinated sialic acid analog Ac53FaxNeu5Ac disrupts sialic acid expression in tumor cells [179]. By inhibiting sialyltransferases (STs), impairing sialic acid–glycan binding, and modulating cellular sialic acid content, studies demonstrate that Ac53FaxNeu5Ac-mediated sialic acid blockade in dendritic cells enhances CD8+ T cell proliferation induced by mouse bone marrow-derived DCs [180].
Additionally, SAMs show potential in drug delivery applications. Nanoparticles incorporating CD22-targeting SAMs have been designed to deliver cytotoxic agents (e.g., doxorubicin) to CD22-expressing malignant B cells [181]. Sialic acid-conjugated liposomes enable neutrophil/monocyte-mediated tumor homing of epirubicin for targeted therapy [182]. Furthermore, Bull et al. demonstrated that encapsulation in tumor-targeting nanoparticles prevents metastasis in murine lung cancer models while circumventing systemic toxicity associated with global sialylation inhibition [183].
6.3.3. Development of Novel Sialylation Materials
High-affinity binding is essential for receptor aggregation and subsequent Siglec signaling when competing with natural ligands. A promising alternative involves polyvalent displays of SAMs achieved by either conjugating SAMs to nanoparticles or polymers or modifying living cell glycocalyx via bioorthogonal synthesis [132,184]. SAM-modified nanoparticles, including liposomes, gold nanoparticles, and dendrimer/PLGA-based systems, have been utilized for targeted delivery to Siglec-expressing cells [185] or to modulate Siglec signaling through glycan-decorated surfaces [186,187]. Cells bearing these mucin-mimetic glycopolymers exhibit significantly enhanced Siglec-7 binding and protection from Siglec-7+ NK cell-mediated killing. Subsequent investigations revealed concurrent phosphorylation of Siglec-7, SHP-1 recruitment, and suppression of NK cell cytotoxic activity. These findings suggest that soluble or membrane-incorporated glycopolymers may function as SAM carriers capable of engaging immune cell Siglecs and triggering immunosuppressive signaling. Further studies are warranted to validate their biological potential in in vivo cancer models.
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
This review summarizes specific alterations in glycosylation, particularly sialylation in cancer. Sialic acid is ubiquitously expressed across all cell types, with abnormally elevated levels serving as a hallmark of malignant transformation. Aberrant sialylation disrupts cell–cell interactions and signaling pathways, driving immune dysfunction that impairs natural killer cell and macrophage activity. These alterations facilitate immune evasion and promote chronic inflammation.
Recent research underscores the critical regulatory role of Siglec receptors in immune cell function. The Siglec–sialoglycan axis represents a promising immune checkpoint target for cancer immunotherapy, modulable through either Siglec receptor blockade or sialoglycan cleavage via sialidases.
Targeting sialoglycans and immune cell Siglec receptors has emerged as a novel strategy for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Antibody-based and glycan-directed approaches have established Siglecs as attractive therapeutic targets for hematological malignancies including lymphoma and leukemia. We further synthesize recent advances in sialic acid inhibitors, providing systematic guidance for future clinical translation and development of next-generation therapeutics. Several inhibitors targeting specific Siglecs (notably Siglec-15) are currently undergoing clinical evaluation. However, comprehensive understanding of Siglec inhibitors’ efficacy profiles, potential side effects, and combinatorial potential with standard therapies remains to be fully elucidated.
As research progresses, sialic acid-targeted therapies hold significant promise for transforming cancer treatment. Therefore, rigorous investigation of sialylation mechanisms using advanced methodologies and contemporary detection technologies is increasingly imperative.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. (Yuecheng Zhang), W.L. and L.S. conceived and wrote the article; Z.G., Y.Z. (Yuhan Zhang) and S.A. reviewed and edited the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22264023); Health Research Project of Shaanxi Province (2022E019); Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2024JC-YBQN-0150); and PhD start-up fund of Yan’an University (YDBK2022-15).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Medical Experimental Research Centre of Yan’an University for assistance with the platform and instrumentation. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China as well as other projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hei, H. Advances in post-translational modifications of proteins and cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1229397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, J. Protein glycosylation. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R229–R231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjoldager, K.T.; Narimatsu, Y.; Joshi, H.J.; Clausen, H. Global view of human protein glycosylation pathways and functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 21, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, S.R.; Ju, T.; Cummings, R.D. Protein glycosylation in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2015, 10, 473–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reily, C.; Stewart, T.J.; Renfrow, M.B.; Novak, J. Glycosylation in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannagi, R.; Yin, J.; Miyazaki, K.; Izawa, M. Current relevance of incomplete synthesis and neo-synthesis for cancer-associated alteration of carbohydrate determinants—Hakomori’s concepts revisited. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008, 1780, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A.; Gagneux, P. Multifarious roles of sialic acids in immunity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1253, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, G.; Weigle, B.; Crocker, P.R. Siglec and anti-Siglec therapies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 62, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.; Sarkar, S.; Natoni, A.; Stark, J.C.; Riley, N.M.; Bertozzi, C.R.; Carlsten, M.; O’Dwyer, M.E. Targeting hypersialylation in multiple myeloma represents a novel approach to enhance NK cell-mediated tumor responses. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3352–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczak, M.A.; Rodrigues Mantuano, N.; Kirchhammer, N.; Sanin, D.E.; Jacob, F.; Coelho, R.; Everest-Dass, A.V.; Wang, J.; Trefny, M.P.; Monaco, G.; et al. Targeting cancer glycosylation repolarizes tumor-associated macrophages allowing effective immune checkpoint blockade. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Tao, J. Sialylated immunoglobulin G: A promising diagnostic and therapeutic strategy for autoimmune diseases. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5430–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, N.T.; Bennett, E.P.; Gomes, J.; Magalhaes, A.; Gomes, C.; David, L.; Dar, I.; Jeanneau, C.; DeFrees, S.; Krustrup, D.; et al. ST6GalNAc-I controls expression of sialyl-Tn antigen in gastrointestinal tissues. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2011, 3, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, S.; Adriaenssens, E.; Ottenberg, K.; Furlan, A.; Courtand, G.; Vercoutter-Edouart, A.S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Delannoy, P.; Le Bourhis, X. ST6GalNAc I expression in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells greatly modifies their O-glycosylation pattern and enhances their tumourigenicity. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, C.; Sasmal, A.; Varki, A. From “Serum Sickness” to “Xenosialitis”: Past, Present, and Future Significance of the Non-human Sialic Acid Neu5Gc. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Karnebeek, C.D.; Bonafé, L.; Wen, X.Y.; Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Balzano, S.; Royer-Bertrand, B.; Ashikov, A.; Garavelli, L.; Mammi, I.; Turolla, L.; et al. NANS-mediated synthesis of sialic acid is required for brain and skeletal development. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macauley, M.S.; Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C. Siglec-mediated regulation of immune cell function in disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, E.A.; Moons, S.J.; Timmermans, S.; de Jong, H.; Boltje, T.J.; Büll, C. Sialic acid O-acetylation: From biosynthesis to roles in health and disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.L.; Chen, X.; Schnaar, R.L.; Varki, A. Sialic Acids and Other Nonulosonic Acids. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Darvill, A.G., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 185–204. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, A.P.; Sun, L.; Schulz, M.A.; Tian, W.; Ashikov, A.; van Scherpenzeel, M.; Hermans, E.; Clausen, H.; Yang, Z.; Lefeber, D.J. Activity of N-acylneuraminate-9-phosphatase (NANP) is not essential for de novo sialic acid biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangvoranuntakul, P.; Gagneux, P.; Diaz, S.; Bardor, M.; Varki, N.; Varki, A.; Muchmore, E. Human uptake and incorporation of an immunogenic nonhuman dietary sialic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12045–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeld, A.K.; Pearce, O.M.; Diaz, S.L.; Pham, T.; Varki, A. Metabolism of vertebrate amino sugars with N-glycolyl groups: Elucidating the intracellular fate of the non-human sialic acid N-glycolylneuraminic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 28865–28881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samraj, A.N.; Pearce, O.M.; Läubli, H.; Crittenden, A.N.; Bergfeld, A.K.; Banda, K.; Gregg, C.J.; Bingman, A.E.; Secrest, P.; Diaz, S.L.; et al. A red meat-derived glycan promotes inflammation and cancer progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruit, C.M.; Nemanichvili, N.; Okamatsu, M.; Takematsu, H.; Boons, G.J.; de Vries, R.P. N-Glycolylneuraminic Acid in Animal Models for Human Influenza A Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewell, R.; Bäckström, M.; Dalziel, M.; Gschmeissner, S.; Karlsson, H.; Noll, T.; Gätgens, J.; Clausen, H.; Hansson, G.C.; Burchell, J.; et al. The ST6GalNAc-I sialyltransferase localizes throughout the Golgi and is responsible for the synthesis of the tumor-associated sialyl-Tn O-glycan in human breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 3586–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Cao, H.; Lei, C.; Liu, J. ST6GALNAC1 promotes the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells via the EMT pathway. Genes Genom. 2023, 45, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkley, J.; Oltean, S.; Vodák, D.; Wilson, B.T.; Livermore, K.E.; Zhou, Y.; Star, E.; Floros, V.I.; Johannessen, B.; Knight, B.; et al. The androgen receptor controls expression of the cancer-associated sTn antigen and cell adhesion through induction of ST6GalNAc1 in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34358–34374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, F.; Sato, Y.; Hirakawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Ono, M.; Osuga, T.; Okagawa, Y.; Uemura, N.; Arihara, Y.; Murase, K.; et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing of ST6GalNAc I suppresses the metastatic potential in gastric cancer cells. Gastric Cancer 2016, 19, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Cao, Y.X.; Zhou, X.; Wei, B.; Zhan, L.; Sun, S.Y. Stimulative role of ST6GALNAC1 in proliferation, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer stem cells via the Akt signaling pathway. Cancer Cell. Int. 2019, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabiad, M.A.; Harb, O.A.; Abozaid, M.; Embaby, A.; Mandour, D.; Hemeda, R.; Shalaby, A.M. The Diagnostic and Prognostic Roles of Combined Expression of Novel Biomarkers in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Immunohistochemical Study. Iran. J. Pathol. 2021, 16, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, Z.; Majdaeen, M.; Agbele, A.T.; Abedi-Firouzjah, R. Functions of Sialyltransferases in gynecological malignancies: A systematic review. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 254, 155159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev. Cell. 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, E.; Archer Goode, E.; Garnham, R.; Hodgson, K.; Orozco-Moreno, M.; Turner, H.; Livermore, K.; Putri Nangkana, K.; Frame, F.M.; Bermudez, A.; et al. ST6GAL1-mediated aberrant sialylation promotes prostate cancer progression. J. Pathol. 2023, 261, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalerao, N.; Chakraborty, A.; Marciel, M.P.; Hwang, J.; Britain, C.M.; Silva, A.D.; Eltoum, I.E.; Jones, R.B.; Alexander, K.L.; Smythies, L.E.; et al. ST6GAL1 sialyltransferase promotes acinar to ductal metaplasia and pancreatic cancer progression. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e161563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Ren, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S. Knockdown of ST6Gal-I inhibits the growth and invasion of osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 72, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Lu, J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yan, X.; Cui, Y.; Xiao, X.; Fang, M.; Yang, F.; Sawaki, H.; et al. ST6GAL1 inhibits metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via modulating sialylation of MCAM on cell surface. Oncogene 2023, 42, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gc, S.; Tuy, K.; Rickenbacker, L.; Jones, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Miller, C.R.; Beierle, E.A.; Hanumanthu, V.S.; Tran, A.N.; Mobley, J.A.; et al. α2,6 Sialylation mediated by ST6GAL1 promotes glioblastoma growth. JCI Insight 2022, 7, 158799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithson, M.; Irwin, R.; Williams, G.; Alexander, K.L.; Smythies, L.E.; Nearing, M.; McLeod, M.C.; Al Diffalha, S.; Bellis, S.L.; Hardiman, K.M. Sialyltransferase ST6GAL-1 mediates resistance to chemoradiation in rectal cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hao, Y.; Qian, F.; Tang, B.; Yu, P. The glycosyltransferase ST6Gal-I is enriched in cancer stem-like cells in colorectal carcinoma and contributes to their chemo-resistance. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Dorsett, K.A.; Trummell, H.Q.; Yang, E.S.; Oliver, P.G.; Bonner, J.A.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by abrogating gemcitabine-mediated DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videira, P.A.; Correia, M.; Malagolini, N.; Crespo, H.J.; Ligeiro, D.; Calais, F.M.; Trindade, H.; Dall′Olio, F. ST3Gal.I sialyltransferase relevance in bladder cancer tissues and cell lines. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shi, X.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Song, Q.J.; Yang, X.B.; Hu, W.D.; Mei, G.L.; Chen, X.; Mao, Q.S.; Chen, Z. Overexpression of ST3Gal-I promotes migration and invasion of HCCLM3 in vitro and poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picco, G.; Julien, S.; Brockhausen, I.; Beatson, R.; Antonopoulos, A.; Haslam, S.; Mandel, U.; Dell, A.; Pinder, S.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; et al. Over-expression of ST3Gal-I promotes mammary tumorigenesis. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.C.; Sung, P.L.; Hsieh, S.L.; Chou, Y.T.; Lee, O.K.; Wu, C.W.; Wang, P.H. α2,3-sialyltransferase type I regulates migration and peritoneal dissemination of ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29013–29027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Garay, M.; Arteta, B.; Llop, E.; Cobler, L.; Pagès, L.; Ortiz, R.; Ferri, M.J.; de Bolós, C.; Figueras, J.; de Llorens, R.; et al. α2,3-Sialyltransferase ST3Gal IV promotes migration and metastasis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells and tends to be highly expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma tissues. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2013, 45, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Liu, J.H.; Ni, Z.; Ding, G.F.; Wang, Q.Z. Downregulation of ST3GAL5 is associated with muscle invasion, high grade and a poor prognosis in patients with bladder cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shan, Y.; Ma, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, L. LncRNA ST3Gal6-AS1/ST3Gal6 axis mediates colorectal cancer progression by regulating α-2,3 sialylation via PI3K/Akt signaling. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalangood, S.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Zeng, Q.; Yan, Y.; Shen, B.; Yan, J.; Huang, R. Identification of glycogene-type and validation of ST3GAL6 as a biomarker predicts clinical outcome and cancer cell invasion in urinary bladder cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10078–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Fang, L.; et al. The novel role of circular RNA ST3GAL6 on blocking gastric cancer malignant behaviours through autophagy regulated by the FOXP2/MET/mTOR axis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavey, S.V.; Manier, S.; Natoni, A.; Sacco, A.; Moschetta, M.; Reagan, M.R.; Murillo, L.S.; Sahin, I.; Wu, P.; Mishima, Y.; et al. The sialyltransferase ST3GAL6 influences homing and survival in multiple myeloma. Blood 2014, 124, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Long, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, J.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Miao, X.; Huang, R.; Yan, J. Comprehensive landscape of the ST3GAL family reveals the significance of ST3GAL6-AS1/ST3GAL6 axis on EGFR signaling in lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 931132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, X.; Liang, L.; Pan, X.; Lv, H.; Zhao, Y. Sialyltransferase ST3GAL6 mediates the effect of microRNA-26a on cell growth, migration, and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma through the protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, D.R.; Shaikh, F.M.; Lucas, J.A.t.; Lucas, J.A., 3rd; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I expression in ovarian cancer cells promotes an invasive phenotype by altering integrin glycosylation and function. J. Ovarian Res. 2008, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Fan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, D.; Wang, S. ST6Gal-I overexpression facilitates prostate cancer progression via the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65374–65388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, Y.; Lei, T.; Wu, Q.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S. Modification of α2,6-sialylation mediates the invasiveness and tumorigenicity of non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo via Notch1/Hes1/MMPs pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Meng, F.; Huang, T.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, G.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. α2,6-Sialylation promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells migration and invasion via enhancement of nSmase2-mediated exosomal miRNA sorting. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 79, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y. Resveratrol Inhibits the Tumorigenesis of Follicular Thyroid Cancer via ST6GAL2-Regulated Activation of the Hippo Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 16, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Q.; Pawan; Wang, S. Silencing of ST6GalNAc I suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocarcinoma cells through PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12213–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvorjak, M.; Ahmed, Y.; Miller, M.L.; Sriram, R.; Coronnello, C.; Hashash, J.G.; Hartman, D.J.; Telmer, C.A.; Miskov-Zivanov, N.; Finn, O.J.; et al. Cross-talk between Colon Cells and Macrophages Increases ST6GALNAC1 and MUC1-sTn Expression in Ulcerative Colitis and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkley, J.; Livermore, K.; Rajan, P.; Elliott, D.J. RNA splicing and splicing regulator changes in prostate cancer pathology. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaya, T.; Sawada, G.; Amano, S.; Kume, K.; Ito, C.; Endo, F.; Konosu, M.; Shioi, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Takahara, T.; et al. Downregulation of ST6GALNAC1 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Luo, S.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, L.; Shan, Y.; Zhou, H. miR-182 and miR-135b Mediate the Tumorigenesis and Invasiveness of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Targeting ST6GALNAC2 and PI3K/AKT Pathway. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3447–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, C.M.; Reginato, M.J. Sticking to sugars at the metastatic site: Sialyltransferase ST6GalNAc2 acts as a breast cancer metastasis suppressor. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miao, X.; Jia, L.; Zhou, H.; Song, X.; Zhou, M.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Feng, X.; Zhao, Y. miR-4299 mediates the invasive properties and tumorigenicity of human follicular thyroid carcinoma by targeting ST6GALNAC4. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Li, J.; Liang, R.B.; Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, G. Identification and Experimental Validation of the Prognostic Significance and Immunological Correlation of Glycosylation-Related Signature and ST6GALNAC4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell Carcinoma 2023, 10, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Luo, L.; Gao, W.; Bu, C.; Huang, J. miR-182 modulates cell proliferation and invasion in prostate cancer via targeting ST6GALNAC5. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e9695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, S.; He, H.; Ai, K.; Xu, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X. CircRNA-ST6GALNAC6 increases the sensitivity of bladder cancer cells to erastin-induced ferroptosis by regulating the HSPB1/P38 axis. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenackers, A.; Vanbeselaere, J.; Cazet, A.; Bobowski, M.; Rombouts, Y.; Colomb, F.; Le Bourhis, X.; Guérardel, Y.; Delannoy, P. Accumulation of unusual gangliosides G(Q3) and G(P3) in breast cancer cells expressing the G(D3) synthase. Molecules 2012, 17, 9559–9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H. Effects of the regulation of polysialyltransferase ST8SiaII on the invasiveness and metastasis of small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.K.; An, H.K.; Ko, M.J.; Kim, K.S.; Mun, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, C.H.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, Y.C. Upregulation of Human ST8Sia VI (α2,8-Sialyltransferase) Gene Expression by Physcion in SK-N-BE(2)-C Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 2, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelik, A.; Illes, K.; Mazhab-Jafari, M.T.; Nagar, B. Structure of the immunoregulatory sialidase NEU1. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf8169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.R.; Zhang, L.P.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Li, W.J.; Fang, S.Y.; Shen, L.; Gao, Y.L. Effects of sialidase NEU1 siRNA on proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion in human ovarian cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 411, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Gao, L.; Cheng, H.B.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, J. Sialidase NEU1 May Serve as a Potential Biomarker of Proliferation, Migration and Prognosis in Melanoma. World J. Oncol. 2022, 13, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gu, Y.; He, W.; Kuo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; He, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y. Correlation Between Sialidase NEU1 mRNA Expression Changes in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 870374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Li, D.; Wang, A.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, B.; Li, N.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S. The role of sialidase Neu1 in respiratory diseases. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.; Mondal, S.; Butti, R.; Prasanna Gunasekaran, V.; Chatterjee, U.; Halder, A.; Kundu, G.C.; Mandal, C. Desialylation of Sonic-Hedgehog by Neu2 Inhibits Its Association with Patched1 Reducing Stemness-Like Properties in Pancreatic Cancer Sphere-forming Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuta, T.; Ito, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Sugawara, S.; Hosono, M.; Sato, M.; Miyagi, T. Sialidase NEU3 Contributes to the Invasiveness of Bladder Cancer. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakugawa, Y.; Wada, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamanami, H.; Ouchi, K.; Sato, I.; Miyagi, T. Up-regulation of plasma membrane-associated ganglioside sialidase (Neu3) in human colon cancer and its involvement in apoptosis suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10718–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dou, P.; Akhtar, M.L.; Liu, F.; Hu, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiao, S.; et al. NEU4 inhibits motility of HCC cells by cleaving sialic acids on CD44. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5427–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockhausen, I.; Wandall, H.H.; Hagen, K.G.T.; Stanley, P. O-GalNAc Glycans. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Darvill, A.G., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Crocker, P.R.; Varki, A. Siglecs, sialic acids and innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, P.R. Siglecs: Sialic-acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins in cell-cell interactions and signalling. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2002, 12, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, P.R. Siglecs in innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angata, T.; Margulies, E.H.; Green, E.D.; Varki, A. Large-scale sequencing of the CD33-related Siglec gene cluster in five mammalian species reveals rapid evolution by multiple mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13251–13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.S. Non-canonical roles of Siglecs: Beyond sialic acid-binding and immune cell modulation. Mol. Aspects Med. 2023, 90, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Wan, T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, X. Cloning and characterization of Siglec-10, a novel sialic acid binding member of the Ig superfamily, from human dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28106–28112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C.; Varki, A. Siglecs and their roles in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bärenwaldt, A.; Läubli, H. The sialoglycan-Siglec glyco-immune checkpoint-a target for improving innate and adaptive anti-cancer immunity. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gil, A.; Li, T.A.; Kim, J.; Schnaar, R.L. Human sialoglycan ligands for immune inhibitory Siglecs. Mol. Aspects Med. 2023, 90, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlino, M.S.; Larkin, J.; Long, G.V. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet 2021, 398, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczak, M.A.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Trefny, M.P.; Thommen, D.S.; Boligan, K.F.; von Gunten, S.; Tzankov, A.; Tietze, L.; Lardinois, D.; Heinzelmann-Schwarz, V.; et al. Self-associated molecular patterns mediate cancer immune evasion by engaging Siglecs on T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4912–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wall, S.; Santegoets, K.C.M.; van Houtum, E.J.H.; Büll, C.; Adema, G.J. Sialoglycans and Siglecs Can Shape the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läubli, H.; Pearce, O.M.; Schwarz, F.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Deng, L.; Stanczak, M.A.; Deng, L.; Verhagen, A.; Secrest, P.; Lusk, C.; et al. Engagement of myelomonocytic Siglecs by tumor-associated ligands modulates the innate immune response to cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14211–14216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatson, R.; Tajadura-Ortega, V.; Achkova, D.; Picco, G.; Tsourouktsoglou, T.D.; Klausing, S.; Hillier, M.; Maher, J.; Noll, T.; Crocker, P.R.; et al. The mucin MUC1 modulates the tumor immunological microenvironment through engagement of the lectin Siglec-9. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarlucea-Benitez, I.; Weitzenfeld, P.; Smith, P.; Ravetch, J.V. Siglecs-7/9 function as inhibitory immune checkpoints in vivo and can be targeted to enhance therapeutic antitumor immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107424118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Boelaars, K.; Brown, K.; Eveline Li, R.J.; Kruijssen, L.; Bruijns, S.C.M.; van Ee, T.; Schetters, S.T.T.; Crommentuijn, M.H.W.; van der Horst, J.C.; et al. Sialic acids in pancreatic cancer cells drive tumour-associated macrophage differentiation via the Siglec receptors Siglec-7 and Siglec-9. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Cao, X. The lectin Siglec-G inhibits dendritic cell cross-presentation by impairing MHC class I-peptide complex formation. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdicchio, M.; Ilarregui, J.M.; Verstege, M.I.; Cornelissen, L.A.; Schetters, S.T.; Engels, S.; Ambrosini, M.; Kalay, H.; Veninga, H.; den Haan, J.M.; et al. Sialic acid-modified antigens impose tolerance via inhibition of T-cell proliferation and de novo induction of regulatory T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Manni, M.; Bärenwaldt, A.; Wieboldt, R.; Kirchhammer, N.; Ivanek, R.; Stanczak, M.; Zippelius, A.; König, D.; Rodrigues Manutano, N.; et al. Siglec Receptors Modulate Dendritic Cell Activation and Antigen Presentation to T Cells in Cancer. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 828916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuchkovska, A.; Glanville, D.G.; Scurti, G.M.; Nishimura, M.I.; White, P.; Ulijasz, A.T.; Iwashima, M. Siglec-5 is an inhibitory immune checkpoint molecule for human T cells. Immunology 2022, 166, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Yu, C.; Rodrigues, E.; Shi, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, P.; Chapla, D.G.; Gao, T.; Zhuang, R.; Moremen, K.W.; et al. Modulation of Siglec-7 Signaling Via In Situ-Created High-Affinity cis-Ligands. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, J.E.; Canham, S.M.; Bertozzi, C.R. Glycocalyx engineering reveals a Siglec-based mechanism for NK cell immunoevasion. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandus, C.; Boligan, K.F.; Chijioke, O.; Liu, H.; Dahlhaus, M.; Démoulins, T.; Schneider, C.; Wehrli, M.; Hunger, R.E.; Baerlocher, G.M.; et al. Interactions between Siglec-7/9 receptors and ligands influence NK cell-dependent tumor immunosurveillance. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Ruffell, B. Macrophages as regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; Xing, B.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, H.; Du, P.; et al. A pan-cancer single-cell transcriptional atlas of tumor infiltrating myeloid cells. Cell 2021, 184, 792–809.e723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, K.; Patel, A.A.; Kong, W.T.; Piot, C.; Halitzki, E.; Dunsmore, G.; Khalilnezhad, S.; Irac, S.E.; Dubuisson, A.; Chevrier, M.; et al. Cross-tissue single-cell landscape of human monocytes and macrophages in health and disease. Immunity 2021, 54, 1883–1900.e1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varchetta, S.; Brunetta, E.; Roberto, A.; Mikulak, J.; Hudspeth, K.L.; Mondelli, M.U.; Mavilio, D. Engagement of Siglec-7 receptor induces a pro-inflammatory response selectively in monocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandala-Sanchez, E.; Zhang, Y.; Reinwald, S.; Dromey, J.A.; Lee, B.H.; Qian, J.; Böhmer, R.M.; Harrison, L.C. T cell regulation mediated by interaction of soluble CD52 with the inhibitory receptor Siglec-10. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatson, R.; Graham, R.; Grundland Freile, F.; Cozzetto, D.; Kannambath, S.; Pfeifer, E.; Woodman, N.; Owen, J.; Nuamah, R.; Mandel, U.; et al. Cancer-associated hypersialylated MUC1 drives the differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages with a pathogenic phenotype. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, M.; Chan, C.; Jansen, J.H.M.; Bräutigam, M.; Kölling, M.A.; Gehlert, C.L.; Baumann, N.; Mester, S.; Foss, S.; Andersen, J.T.; et al. Disruption of the sialic acid/Siglec-9 axis improves antibody-mediated neutrophil cytotoxicity towards tumor cells. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1178817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Luo, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Xie, P.; Zhou, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Z.; et al. Siglec-F(+) neutrophils in the spleen induce immunosuppression following acute infection. Theranostics 2024, 14, 2589–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wculek, S.K.; Cueto, F.J.; Mujal, A.M.; Melero, I.; Krummel, M.F.; Sancho, D. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broz, M.L.; Binnewies, M.; Boldajipour, B.; Nelson, A.E.; Pollack, J.L.; Erle, D.J.; Barczak, A.; Rosenblum, M.D.; Daud, A.; Barber, D.L.; et al. Dissecting the tumor myeloid compartment reveals rare activating antigen-presenting cells critical for T cell immunity. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, N.; Daly, J.; Drummond-Guy, O.; Krishnamoorthy, V.; Stark, J.C.; Riley, N.M.; Williams, K.C.; Bertozzi, C.R.; Wisnovsky, S. The glycoimmune checkpoint receptor Siglec-7 interacts with T-cell ligands and regulates T-cell activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerreter, T.; Köchel, C.; Jesper, D.; Eichelbrönner, I.; Putz, E.; Einsele, H.; Seggewiss-Bernhardt, R. Dasatinib enhances migration of monocyte-derived dendritic cells by reducing phosphorylation of inhibitory immune receptors Siglec-9 and Siglec-3. Exp. Hematol. 2014, 42, e771–e773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belisle, J.A.; Horibata, S.; Jennifer, G.A.; Petrie, S.; Kapur, A.; André, S.; Gabius, H.J.; Rancourt, C.; Connor, J.; Paulson, J.C.; et al. Identification of Siglec-9 as the receptor for MUC16 on human NK cells, B cells, and monocytes. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, S.J.; Linder, A.T.; Brandl, C.; Nitschke, L. B Cell Siglecs-News on Signaling and Its Interplay with Ligand Binding. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.L.; Li, Z.; Ma, F.; Wang, D.; Song, N.; Chong, C.H.; Luk, K.K.; Leung, S.O. SM03, an Anti-CD22 Antibody, Converts Cis-to-Trans Ligand Binding of CD22 against α2,6-Linked Sialic Acid Glycans and Immunomodulates Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Deng, B.; Yin, Z.; Lin, Y.; An, L.; Liu, D.; Pan, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, T.; et al. Combination of CD19 and CD22 CAR-T cell therapy in relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia after allogeneic transplantation. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; He, J.; Huang, C.; Liao, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Siglec-9 acts as an immune-checkpoint molecule on macrophages in glioblastoma, restricting T-cell priming and immunotherapy response. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 1273–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkal, A.A.; Brewer, R.E.; Markovic, M.; Kowarsky, M.; Barkal, S.A.; Zaro, B.W.; Krishnan, V.; Hatakeyama, J.; Dorigo, O.; Barkal, L.J.; et al. CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 572, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanida, S.; Akita, K.; Ishida, A.; Mori, Y.; Toda, M.; Inoue, M.; Ohta, M.; Yashiro, M.; Sawada, T.; Hirakawa, K.; et al. Binding of the sialic acid-binding lectin, Siglec-9, to the membrane mucin, MUC1, induces recruitment of β-catenin and subsequent cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31842–31852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, T.; Teranishi, T.; Alphey, M.S.; Crocker, P.R.; Hashimoto, Y. A small region of the natural killer cell receptor, Siglec-7, is responsible for its preferred binding to alpha 2,8-disialyl and branched alpha 2,6-sialyl residues. A comparison with Siglec-9. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6324–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, F.; Guo, R.; Bian, Z.; Song, Y. Targeting macrophages in hematological malignancies: Recent advances and future directions. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Siddiqui, B.A.; Anandhan, S.; Yadav, S.S.; Subudhi, S.K.; Gao, J.; Goswami, S.; Allison, J.P. The Next Decade of Immune Checkpoint Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 838–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korman, A.J.; Garrett-Thomson, S.C.; Lonberg, N. The foundations of immune checkpoint blockade and the ipilimumab approval decennial. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Jasinski-Bergner, S.; Lazaridou, M.F.; Subbarayan, K.; Massa, C.; Tretbar, S.; Mueller, A.; Handke, D.; Biehl, K.; Bukur, J.; et al. Tumor-induced escape mechanisms and their association with resistance to checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garris, C.S.; Arlauckas, S.P.; Kohler, R.H.; Trefny, M.P.; Garren, S.; Piot, C.; Engblom, C.; Pfirschke, C.; Siwicki, M.; Gungabeesoon, J.; et al. Successful Anti-PD-1 Cancer Immunotherapy Requires T Cell-Dendritic Cell Crosstalk Involving the Cytokines IFN-γ and IL-12. Immunity 2022, 55, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, J.Y.; Patel, S.; Muffly, L.; Hossain, N.M.; Oak, J.; Baird, J.H.; Frank, M.J.; Shiraz, P.; Sahaf, B.; Craig, J.; et al. CAR T cells with dual targeting of CD19 and CD22 in adult patients with recurrent or refractory B cell malignancies: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, L.N.; Flies, D.B.; Nie, X.; Toki, M.; Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Zarr, M.; Zhou, X.; et al. Siglec-15 as an immune suppressor and potential target for normalization cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, S.; Song, D.; Yuan, J.; Mullin, B.H.; Xu, J. Molecular structure, expression, and the emerging role of Siglec-15 in skeletal biology and cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murciano-Goroff, Y.R.; Warner, A.B.; Wolchok, J.D. The future of cancer immunotherapy: Microenvironment-targeting combinations. Cell. Res. 2020, 30, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büll, C.; Stoel, M.A.; den Brok, M.H.; Adema, G.J. Sialic acids sweeten a tumor’s life. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3199–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobie, C.; Skropeta, D. Insights into the role of sialylation in cancer progression and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdbrooks, A.T.; Britain, C.M.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated cancer cell survival via sialylation of the TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) death receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaraz, R.T.; Tian, Y.; Bhattarcharya, R.; Tan, E.; Chen, S.H.; Dallas, M.R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Konstantopoulos, K.; et al. Metabolic flux increases glycoprotein sialylation: Implications for cell adhesion and cancer metastasis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M112.017558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.G.; Balmaña, M.; Macedo, J.A.; Poças, J.; Fernandes, Â.; de-Freitas-Junior, J.C.M.; Pinho, S.S.; Gomes, J.; Magalhães, A.; Gomes, C.; et al. Glycosylation in cancer: Selected roles in tumour progression, immune modulation and metastasis. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 333, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A.; Drake, R.R. Glycosylation and its implications in breast cancer. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2019, 16, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, P.M.; Cho, W.; Li, B.; Prakobphol, A.; Johansen, E.; Anderson, N.L.; Regnier, F.E.; Gibson, B.W.; Fisher, S.J. Sweetening the pot: Adding glycosylation to the biomarker discovery equation. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichert, B.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Galatenko, V.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L. Prognostic role of the sialyltransferase ST6GAL1 in ovarian cancer. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Li, M.; Yao, X.; Yang, H.; Luo, Z.; Luo, P.; Su, M. Nanointegrative Glycoengineering-Activated Necroptosis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells Enables Self-Amplifiable Immunotherapy for Systemic Tumor Rejection. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, e2303337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, I.Y.; Vickers, A.; Cheung, N.K. Sialyltransferase STX (ST8SiaII): A novel molecular marker of metastatic neuroblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.M.; Mohapatra, B.C.; Luan, H.; Mushtaq, I.; Chakraborty, S.; Kumar, S.; Wu, W.; Nolan, B.; Dutta, S.; Storck, M.D.; et al. GD2 and its biosynthetic enzyme GD3 synthase promote tumorigenesis in prostate cancer by regulating cancer stem cell behavior. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khongorzul, P.; Ling, C.J.; Khan, F.U.; Ihsan, A.U.; Zhang, J. Antibody-Drug Conjugates: A Comprehensive Review. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Goetsch, L.; Dumontet, C.; Corvaïa, N. Strategies and challenges for the next generation of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Miles, D.; Gianni, L.; Krop, I.E.; Welslau, M.; Baselga, J.; Pegram, M.; Oh, D.Y.; Diéras, V.; Guardino, E.; et al. Trastuzumab emtansine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardia, A.; Mayer, I.A.; Vahdat, L.T.; Tolaney, S.M.; Isakoff, S.J.; Diamond, J.R.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Moroose, R.L.; Santin, A.D.; Abramson, V.G.; et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan-hziy in Refractory Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Balar, A.V.; McGregor, B.A.; Heath, E.I.; Yu, E.Y.; Galsky, M.D.; Hahn, N.M.; Gartner, E.M.; Pinelli, J.M.; et al. Pivotal Trial of Enfortumab Vedotin in Urothelial Carcinoma After Platinum and Anti-Programmed Death 1/Programmed Death Ligand 1 Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2592–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.A.; Carroll, D.J.; Cao, Y.; Salicru, A.N.; Bochner, B.S. Leveraging Siglec-8 endocytic mechanisms to kill human eosinophils and malignant mast cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1774–1785.e1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delputte, P.L.; Van Gorp, H.; Favoreel, H.W.; Hoebeke, I.; Delrue, I.; Dewerchin, H.; Verdonck, F.; Verhasselt, B.; Cox, E.; Nauwynck, H.J. Porcine sialoadhesin (CD169/Siglec-1) is an endocytic receptor that allows targeted delivery of toxins and antigens to macrophages. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, D.; Press, O.W. Constitutive endocytosis and degradation of CD22 by human B cells. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 4466–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Stelljes, M.; Martinelli, G.; Liedtke, M.; Stock, W.; Gökbuget, N.; O’Brien, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, T.; et al. Inotuzumab Ozogamicin versus Standard Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, F.; Cao, J.; Lu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H. Anticancer bispecific antibody R&D advances: A study focusing on research trend worldwide and in China. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, M.; Ren, F.; Meng, X.; Yu, J. The landscape of bispecific T cell engager in cancer treatment. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurs, F.V.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Vries, E.G.E.; de Groot, D.J.A. A review of bispecific antibodies and antibody constructs in oncology and clinical challenges. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 201, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Ravetch, J.V. Functional diversification of IgGs through Fc glycosylation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3492–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löffler, A.; Kufer, P.; Lutterbüse, R.; Zettl, F.; Daniel, P.T.; Schwenkenbecher, J.M.; Riethmüller, G.; Dörken, B.; Bargou, R.C. A recombinant bispecific single-chain antibody, CD19 x CD3, induces rapid and high lymphoma-directed cytotoxicity by unstimulated T lymphocytes. Blood 2000, 95, 2098–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, E.; Hofmeister, R.; Kufer, P.; Schlereth, B.; Baeuerle, P.A. BiTEs: Bispecific antibody constructs with unique anti-tumor activity. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, M.; Feulner, J.; Schaffer, S.; Kischel, R.; Kufer, P.; Schneider, K.; Henn, A.; Rattel, B.; Friedrich, M.; Baeuerle, P.A.; et al. T lymphocytes can be effectively recruited for ex vivo and in vivo lysis of AML blasts by a novel CD33/CD3-bispecific BiTE antibody construct. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachanova, V.; Frankel, A.E.; Cao, Q.; Lewis, D.; Grzywacz, B.; Verneris, M.R.; Ustun, C.; Lazaryan, A.; McClune, B.; Warlick, E.D.; et al. Phase I study of a bispecific ligand-directed toxin targeting CD22 and CD19 (DT2219) for refractory B-cell malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.A.; Chang, C.H.; Goldenberg, D.M. Anti-CD22/CD20 Bispecific antibody with enhanced trogocytosis for treatment of Lupus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.I.; Sheppard, N.C.; Riley, J.L. Genetic engineering of T cells for immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 427–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogalekar, M.P.; Rajendran, R.L.; Khan, F.; Dmello, C.; Gangadaran, P.; Ahn, B.C. CAR T-Cell-Based gene therapy for cancers: New perspectives, challenges, and clinical developments. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 925985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochenderfer, J.N.; Dudley, M.E.; Carpenter, R.O.; Kassim, S.H.; Rose, J.J.; Telford, W.G.; Hakim, F.T.; Halverson, D.C.; Fowler, D.H.; Hardy, N.M.; et al. Donor-derived CD19-targeted T cells cause regression of malignancy persisting after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2013, 122, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalos, M.; Levine, B.L.; Porter, D.L.; Katz, S.; Grupp, S.A.; Bagg, A.; June, C.H. T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 95ra73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyiadzis, M.M.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; Brentjens, R.J.; Kochenderfer, J.N.; Neelapu, S.S.; Maus, M.V.; Porter, D.L.; Maloney, D.G.; Grupp, S.A.; Mackall, C.L.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T therapies for the treatment of hematologic malignancies: Clinical perspective and significance. J. Immuno. Ther. Cancer 2018, 6, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Niu, Q.; Deng, B.; Liu, S.; Wu, T.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. CD22 CAR T-cell therapy in refractory or relapsed B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2854–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; An, N.; Wang, Y.; Xing, H.; Tian, Z.; Tang, K.; Liao, X.; et al. CD33-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells with Different Co-Stimulators Showed Potent Anti-Leukemia Efficacy and Different Phenotype. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddie, C.; Lekakis, L.J.; Marzolini, M.A.V.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Peddareddigari, V.G.R.; Khokhar, N.; Chen, R.; Basilico, S.; et al. Dual targeting of CD19 and CD22 with bicistronic CAR-T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2023, 141, 2470–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetani, H.; Navarro-Bailón, A.; Maucher, M.; Frenz, S.; Verbruggen, C.; Yeguas, A.; Vidriales, M.B.; González, M.; Rial Saborido, J.; Kraus, S.; et al. Siglec-6 is a novel target for CAR T-cell therapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 1830–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, C.; Burkhardt, B.; Chan, J.K.C.; Leoncini, L.; Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Ogwang, M.D.; Orem, J.; Rochford, R.; Roschewski, M.; Siebert, R. Burkitt lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Wu, Z.; Jia, H.; Tong, C.; Guo, Y.; Ti, D.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Correction to: Bispecific CAR-T cells targeting both CD19 and CD22 for therapy of adults with relapsed or refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albinger, N.; Pfeifer, R.; Nitsche, M.; Mertlitz, S.; Campe, J.; Stein, K.; Kreyenberg, H.; Schubert, R.; Quadflieg, M.; Schneider, D.; et al. Primary CD33-targeting CAR-NK cells for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.L.; Dreger, P. CD22 CAR T-cell therapy: New hope for patients with large B-cell lymphoma. Lancet 2024, 404, 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theruvath, J.; Menard, M.; Smith, B.A.H.; Linde, M.H.; Coles, G.L.; Dalton, G.N.; Wu, W.; Kiru, L.; Delaidelli, A.; Sotillo, E.; et al. Anti-GD2 synergizes with CD47 blockade to mediate tumor eradication. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.A.; Stanczak, M.A.; Mantuano, N.R.; Xiao, H.; Pijnenborg, J.F.A.; Malaker, S.A.; Miller, C.L.; Weidenbacher, P.A.; Tanzo, J.T.; Ahn, G.; et al. Targeted glycan degradation potentiates the anticancer immune response in vivo. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Woods, E.C.; Vukojicic, P.; Bertozzi, C.R. Precision glycocalyx editing as a strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10304–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, A.; Wöhner, M.; Prescher, H.; Brossmer, R.; Nitschke, L. Targeting of CD22-positive B-cell lymphoma cells by synthetic divalent sialic acid analogues. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 2792–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büll, C.; Boltje, T.J.; Balneger, N.; Weischer, S.M.; Wassink, M.; van Gemst, J.J.; Bloemendal, V.R.; Boon, L.; van der Vlag, J.; Heise, T.; et al. Sialic Acid Blockade Suppresses Tumor Growth by Enhancing T-cell-Mediated Tumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3574–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillahan, C.D.; Antonopoulos, A.; Lefort, C.T.; Sonon, R.; Azadi, P.; Ley, K.; Dell, A.; Haslam, S.M.; Paulson, J.C. Global metabolic inhibitors of sialyl- and fucosyltransferases remodel the glycome. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balneger, N.; Cornelissen, L.A.M.; Wassink, M.; Moons, S.J.; Boltje, T.J.; Bar-Ephraim, Y.E.; Das, K.K.; Søndergaard, J.N.; Büll, C.; Adema, G.J. Sialic acid blockade in dendritic cells enhances CD8(+) T cell responses by facilitating high-avidity interactions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Completo, G.C.; Sigal, D.S.; Crocker, P.R.; Saven, A.; Paulson, J.C. In vivo targeting of B-cell lymphoma with glycan ligands of CD22. Blood 2010, 115, 4778–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Sui, D.; Liu, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Luo, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y.; Song, Y. Sialic acid conjugate-modified liposomes enable tumor homing of epirubicin via neutrophil/monocyte infiltration for tumor therapy. Acta Biomater. 2021, 134, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büll, C.; Boltje, T.J.; van Dinther, E.A.; Peters, T.; de Graaf, A.M.; Leusen, J.H.; Kreutz, M.; Figdor, C.G.; den Brok, M.H.; Adema, G.J. Targeted delivery of a sialic acid-blocking glycomimetic to cancer cells inhibits metastatic spread. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angata, T.; Nycholat, C.M.; Macauley, M.S. Therapeutic Targeting of Siglecs using Antibody- and Glycan-Based Approaches. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.C.; Sigal, D.S.; Saven, A.; Paulson, J.C. Targeting B lymphoma with nanoparticles bearing glycan ligands of CD22. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nycholat, C.M.; Duan, S.; Knuplez, E.; Worth, C.; Elich, M.; Yao, A.; O’Sullivan, J.; McBride, R.; Wei, Y.; Fernandes, S.M.; et al. A Sulfonamide Sialoside Analogue for Targeting Siglec-8 and -F on Immune Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14032–14037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macauley, M.S.; Pfrengle, F.; Rademacher, C.; Nycholat, C.M.; Gale, A.J.; von Drygalski, A.; Paulson, J.C. Antigenic liposomes displaying CD22 ligands induce antigen-specific B cell apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).