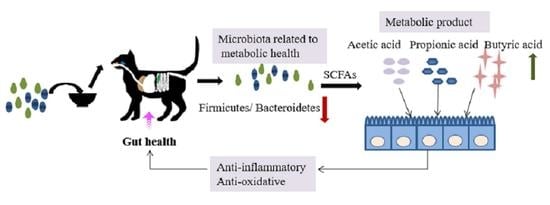
Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Feline Gut Health through the Fecal Microbiota and Its Metabolite SCFAs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Probiotic
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sample Collection and Fecal Microbiota Analysis
2.5. Fermentation Metabolite Analysis
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for Fecal Inflammatory Markers
2.7. Fecal Supernatant Antioxidant Capacity Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Intestinal Flora Structure of Healthy Cats
3.2. Phylum-Level Structural Analysis
3.3. Genus-Level Structural Analysis
3.4. Alpha Diversity Analysis
3.5. Dimension Reduction Analysis
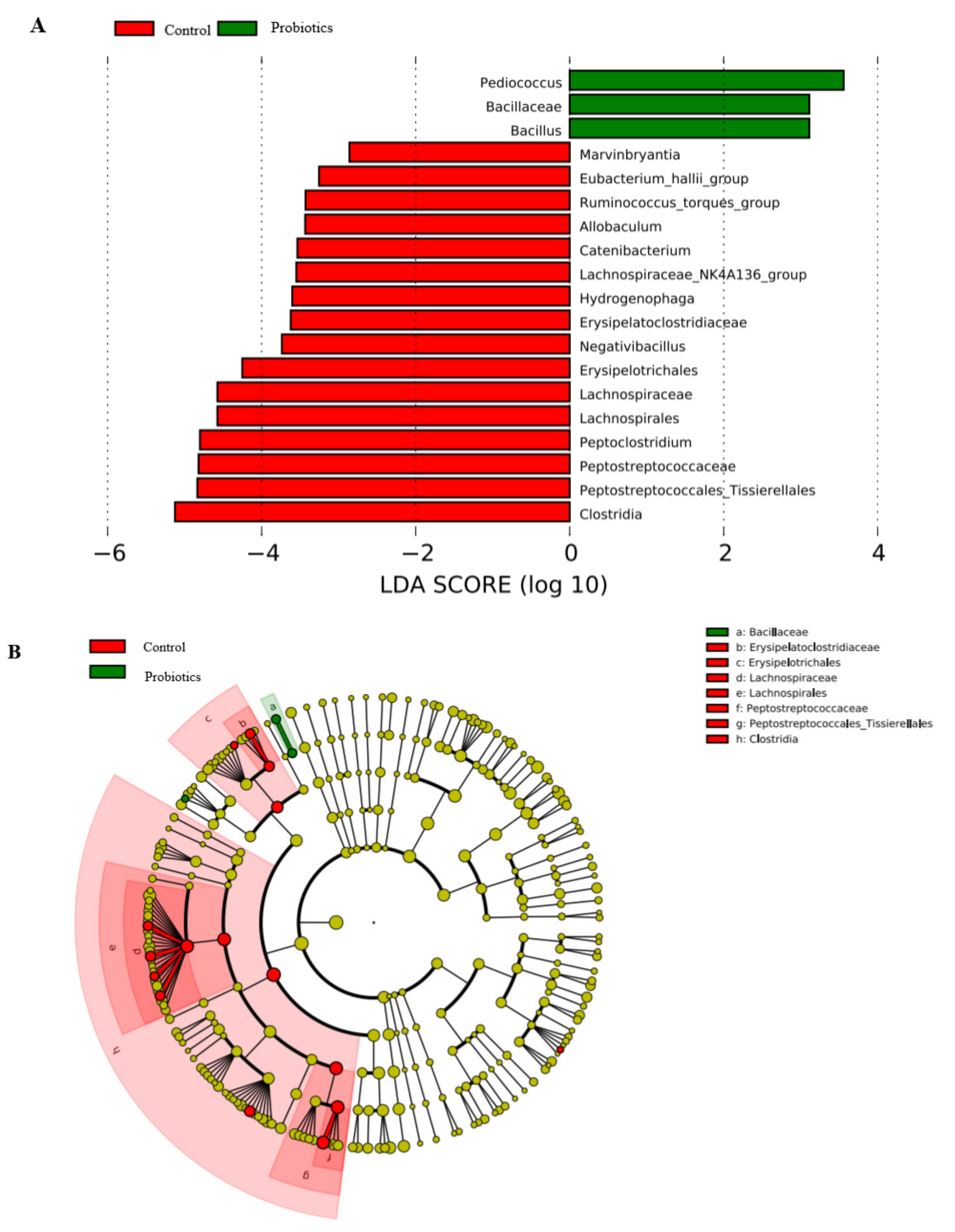
3.6. LEFSe Difference Analysis
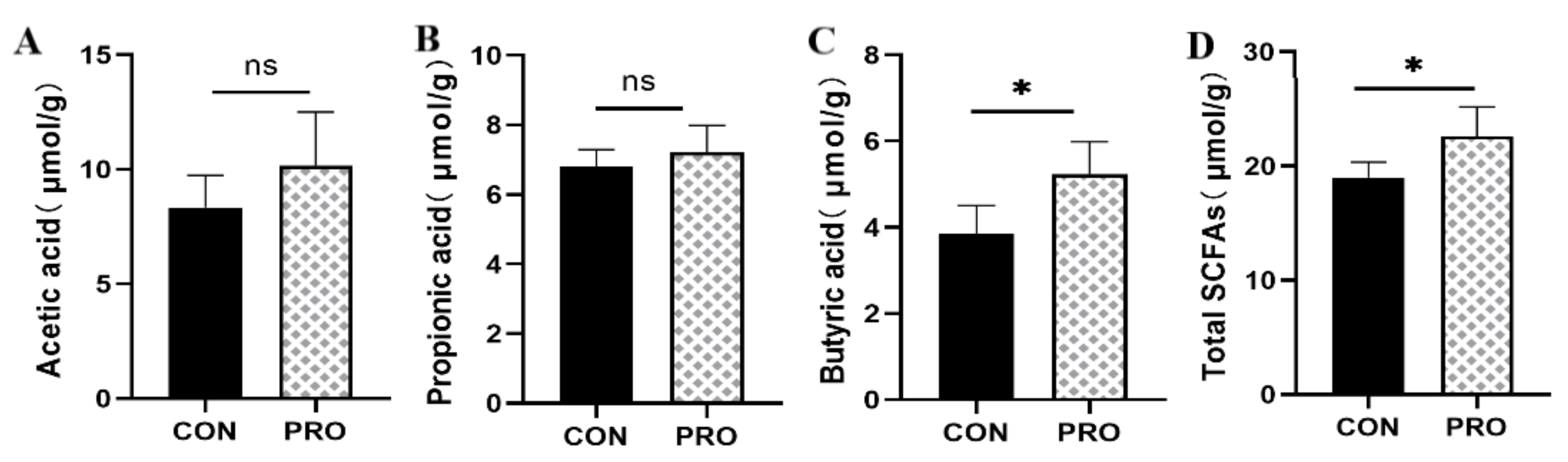
3.7. Microbiota-Derived SCFA Production
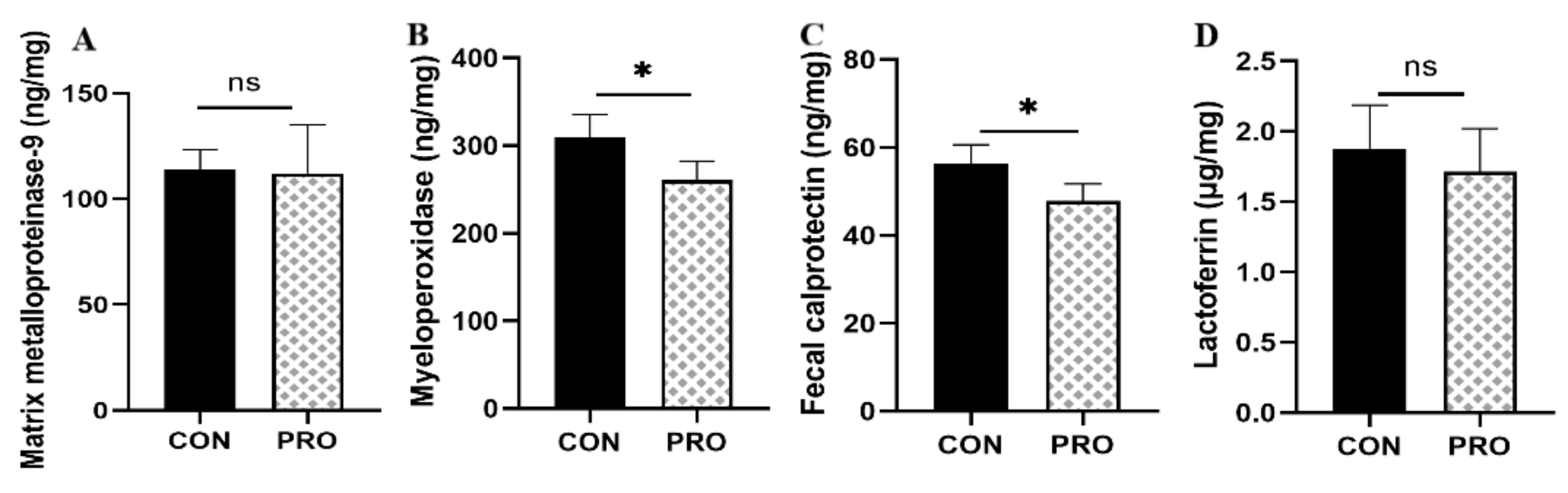
3.8. Fecal-Related Inflammatory Indicators
3.9. Fecal Antioxidant Capacity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, R.J. Absorption and metabolism of microorganisms and host nutrients in the digestive tract. China Feed 2003, 2, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Probiotics in Food: Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2006; p. viii. 50p. [Google Scholar]
- Kligler, B.; Cohrssen, A. Probiotics. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 78, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, A.; Tagliacarne, S.C.; Valsecchi, C.; Boggini, T.; Cattaneo, F.; Licari, A.; Caimmi, S.; Castellazzi, A.M. Probiotics and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 96–113. [Google Scholar]
- Collinson, S.; Deans, A.; Padua-Zamora, A.; Gregorio, G.V.; Li, C.; Dans, L.F.; Allen, S.J. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 12, CD003048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.S.; Hou, P.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, F.R.; Chen, N.; Shu, L.H.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.H.; Han, X.X.; Cai, X.X.; et al. Prevention and treatment of diarrhoea with Saccharomyces boulardii in children with acute lower respiratory tract infections. Benef. Microbes 2013, 4, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zuo, Z.X.; Mao, A.P. Effect of probiotics on inducing remission and maintaining therapy in ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and pouchitis: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2014, 20, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korterink, J.J.; Ockeloen, L.; Benninga, M.A.; Tabbers, M.M.; Hilbink, M.; Deckers-Kocken, J.M. Probiotics for childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2014, 103, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlFaleh, K.; Anabrees, J. Probiotics for prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 9, CD005496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P.; Slizewska, K. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, F.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Basit, A.W.; Dodoo, C.; Chatterjee, R.; Smith, B.; Gaisford, S. A four-strain probiotic exerts positive immunomodulatory effects by enhancing colonic butyrate production in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 555, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.T.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, M.J. Improving effect of a probiotic mixture on memory and learning abilities in d-galactose-treated aging mice. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowiak-Kopec, P.; Slizewska, K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids by Human Intestinal Microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, L.V. Chapter 18—Common Organisms and Probiotics: Saccharomyces boulardii. In The Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology; Floch, M.H., Ringel, Y., Allan Walker, W., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 145–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pais, P.; Almeida, V.; Yilmaz, M.; Teixeira, M.C. Saccharomyces boulardii: What Makes It Tick as Successful Probiotic? J. Fungi 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Li, R.; Luo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Li, R.; Liu, Z. Saccharomyces boulardii alleviates DSS-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation in humanized mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.N.; Hu, S.Y.; Yu, L.Z. Research progress of Pediococcus acidilactici in animal production. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2021, 57, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, W.L.; Chen, G.M.; Qian, M.; Han, J.Z.; Lv, X.C.; Chen, L.J.; Rao, P.F.; Ai, L.Z.; Ni, L. Pediococcus acidilactici FZU106 alleviates high-fat diet-induced lipid metabolism disorder in association with the modulation of intestinal microbiota in hyperlipidemic rats. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Fracassi, F.; Bresciani, F.; Galuppi, R.; Diana, A.; Linta, N.; Bettini, G.; Morini, M.; Pietra, M. Effect of Saccharomyces boulardii in dogs with chronic enteropathies: Double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappin, M.R.; Veir, J.K.; Satyaraj, E.; Czarnecki-Maulden, G. Pilot study to evaluate the effect of oral supplementation of Enterococcus faecium SF68 on cats with latent feline herpesvirus. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, A.; Su, Y. Antagonization of Ghrelin Suppresses Muscle Protein Deposition by Altering Gut Microbiota and Serum Amino Acid Composition in a Pig Model. Biology 2022, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Wan, J.; Su, Y.; Zhu, W. Effects of Early Intervention with Maternal Fecal Microbiota and Antibiotics on the Gut Microbiota and Metabolite Profiles of Piglets. Metabolites 2018, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Mu, C.; Su, Y.; Yu, K.; Zhu, W. Long-term effects of early antibiotic intervention on blood parameters, apparent nutrient digestibility, and fecal microbial fermentation profile in pigs with different dietary protein levels. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E. Fate, activity, and impact of ingested bacteria within the human gut microbiota. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, L.V. Systematic review and meta-analysis of Saccharomyces boulardii in adult patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 2202–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisson, J.F.; Hidalgo, S.; Rozan, P.; Messaoudi, M. Preventive effects of different probiotic formulations on travelers’ diarrhea model in wistar rats: Preventive effects of probiotics on TD. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothoulakis, C. Review article: Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of action of Saccharomyces boulardii. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Wang, J.Z.; Yang, G.L.; Shi, C.W.; Li, N.; Shan, B.L.; Gu, W.; Wang, H. A Strain of Canine Pediococcus Acidilactici and Its Application. China Patent CN109182184B, 20 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.Y.; Sun, H.T.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, C. Effects of Pediococcus acidilactici on Growth Performance and Intestinal Microflora of Weaned Piglets. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2020, 52, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Versalovic, J. Probiotics-host communication: Modulation of signaling pathways in the intestine. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Alexander, C.; Steelman, A.J.; Warzecha, C.M.; de Godoy, M.R.C.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product on fecal characteristics, nutrient digestibility, fecal fermentative end-products, fecal microbial populations, immune function, and diet palatability in adult dogs1. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Otoni, C.C.; Steelman, S.M.; Buyukleblebici, O.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Alteration of the fecal microbiota and serum metabolite profiles in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Lanerie, D.J.; Dowd, S.E.; Paddock, C.G.; Grützner, N.; Steiner, J.M.; Ivanek, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. Effect of a multi-species synbiotic formulation on fecal bacterial microbiota of healthy cats and dogs as evaluated by pyrosequencing. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Jergens, A.; Cerquetella, M.; Berardi, S.; Di Cicco, E.; Bassotti, G.; Pengo, G.; Suchodolski, J.S. Effects of a probiotic (SLAB51™) on clinical and histologic variables and microbiota of cats with chronic constipation/megacolon: A pilot study. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, M.; Franchi, L.; Araya, D.; Díaz-Jiménez, D.; Olivares, M.; Álvarez-Lobos, M.; Golenbock, D.; González, M.J.; López-Kostner, F.; Quera, R.; et al. Escherichia coli isolates from inflammatory bowel diseases patients survive in macrophages and activate NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2014, 304, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlowski, R.; Bernstein, C.N.; Sepehri, S.; Krause, D.O. High prevalence of Escherichia coli belonging to the B2+D phylogenetic group in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2007, 56, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeżewska-Frąckowiak, J.; Seroczyńska, K.; Banaszczyk, J.; Jedrzejczak, G.; Żylicz-Stachula, A.; Skowron, P.M. The promises and risks of probiotic Bacillus species. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeney, D.D.; Zhai, Z.; Bendiks, Z.; Barouei, J.; Martinic, A.; Slupsky, C.; Marco, M.L. Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriocin is associated with intestinal and systemic improvements in diet-induced obese mice and maintains epithelial barrier integrity in vitro. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommineni, S.; Bretl, D.J.; Lam, V.; Chakraborty, R.; Hayward, M.; Simpson, P.; Cao, Y.; Bousounis, P.; Kristich, C.J.; Salzman, N.H. Bacteriocin production augments niche competition by enterococci in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. Nature 2015, 526, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Tian, F.; Yu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Pediococcus acidilactici Strains Improve Constipation Symptoms and Regulate Intestinal Flora in Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 655258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.M.; Olivo, P.M.; Osmari, M.P.; Vasconcellos, R.S.; Ribeiro, L.B.; Bankuti, F.I.; Pozza, M.S.S. Microencapsulation of Probiotic Strains by Lyophilization Is Efficient in Maintaining the Viability of Microorganisms and Modulation of Fecal Microbiota in Cats. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1293481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusi, E.; Rizzi, R.; Polli, M.; Cannas, S.; Giardini, A.; Bruni, N.; Marelli, S.P. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus D2/CSL (CECT 4529) supplementation on healthy cat performance. Vet. Rec. Open 2019, 6, e000368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.S.; Jian, S.J.; Wen, C.Y.; Wen, J.W.; Kuang, T.; Tong, A.; Deng, B.C. Research advances on gut microbiota of cats. China Feed 2022, 13, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Vezza, T.; Utrilla, M.P.; Chueca, N.; Garcia, F.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Galvez, J. Intestinal anti-inflammatory effect of the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii in DSS-induced colitis in mice: Impact on microRNAs expression and gut microbiota composition. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 61, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsilio, S.; Pilla, R.; Sarawichitr, B.; Chow, B.; Hill, S.L.; Ackermann, M.R.; Estep, J.S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Characterization of the fecal microbiome in cats with inflammatory bowel disease or alimentary small cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Pengo, G.; Caldin, M.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Steiner, J.M.; Cohen, N.D.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Comparison of microbiological, histological, and immunomodulatory parameters in response to treatment with either combination therapy with prednisone and metronidazole or probiotic VSL#3 strains in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Camacho, J.; Steiner, J.M. Analysis of bacterial diversity in the canine duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and colon by comparative 16S rRNA gene analysis. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 66, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xiao, C.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Fu, Y. Sodium acetate inhibits Staphylococcus aureus internalization into bovine mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, W.; Rył, A.; Mizerski, A.; Walczakiewicz, K.; Sipak, O.; Laszczyńska, M. Immunomodulatory potential of gut microbiome-derived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczyńska, B.; Wasilewska, A.; Biczysko, M.; Banasiewicz, T.; Drews, M. Short chain fatty acids—Mechanisms of action, potential clinical indications and nutritional indications. Now. Lek. 2011, 80, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Parada Venegas, D.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPont, A.W.; DuPont, H.L. The intestinal microbiota and chronic disorders of the gut. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M. Microbial Inhabitants of Humans: Their Ecology and Role in Health and Disease; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, B.; Ndagijimana, M.; Cruciani, F.; Carnevali, P.; Candela, M.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Brigidi, P. Impact of a synbiotic food on the gut microbial ecology and metabolic profiles. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, K.A.; Hernot, D.C.; Middelbos, I.S.; Francis, C.; Dunsford, B.; Swanson, K.S.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. Low-level fructan supplementation of dogs enhances nutrient digestion and modifies stool metabolite concentrations, but does not alter fecal microbiota populations. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 3244–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubczyk, D.; Leszczyńska, K.; Górska, S. The Effectiveness of Probiotics in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-A Critical Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manceau, H.; Chicha-Cattoir, V.; Puy, H.; Peoc’h, K. Fecal calprotectin in inflammatory bowel diseases: Update and perspectives. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Du, Q.; Shen, J. Targeting Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Mediated Oxidative Stress and Inflammation for Reducing Brain Ischemia Injury: Potential Application of Natural Compounds. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleon-Pennell, K.Y.; Altara, R.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Modesti, A.; Lindsey, M.L. The circular relationship between matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inflammation following myocardial infarction. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhao, D.; Cai, C.; Song, D.; Shen, J.; Xu, A.; Qiao, Y.; Ran, Z.; Zheng, Q. Low-dose penicillin exposure in early life decreases Th17 and the susceptibility to DSS colitis in mice through gut microbiota modification. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Burillo, S.; Pastoriza, S.; Gironés, A.; Avellaneda, A.; Pilar Francino, M.; Rufián-Henares, J.A. Potential probiotic salami with dietary fiber modulates metabolism and gut microbiota in a human intervention study. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meineri, G.; Martello, E.; Atuahene, D.; Miretti, S.; Stefanon, B.; Sandri, M.; Biasato, I.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Ferrocino, I.; Cocolin, L.S. Effects of Saccharomyces boulardii Supplementation on Nutritional Status, Fecal Parameters, Microbiota, and Mycobiota in Breeding Adult Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Mu, J.; Zalan, Z.; Hegyi, F.; Takács, K.; Zhao, X.; Du, M. Protective effect of Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC04 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice is associated with modulation of the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9570–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
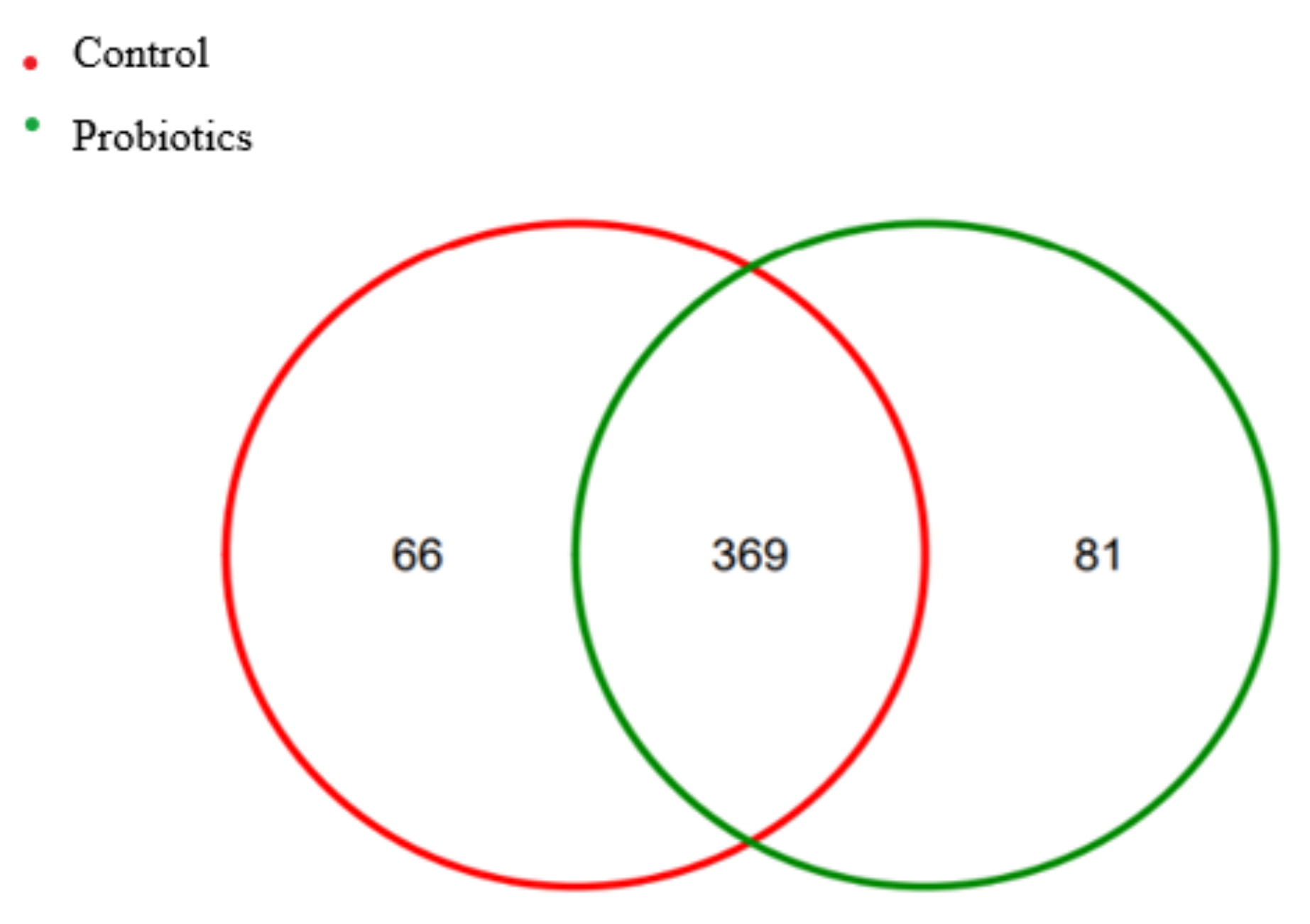

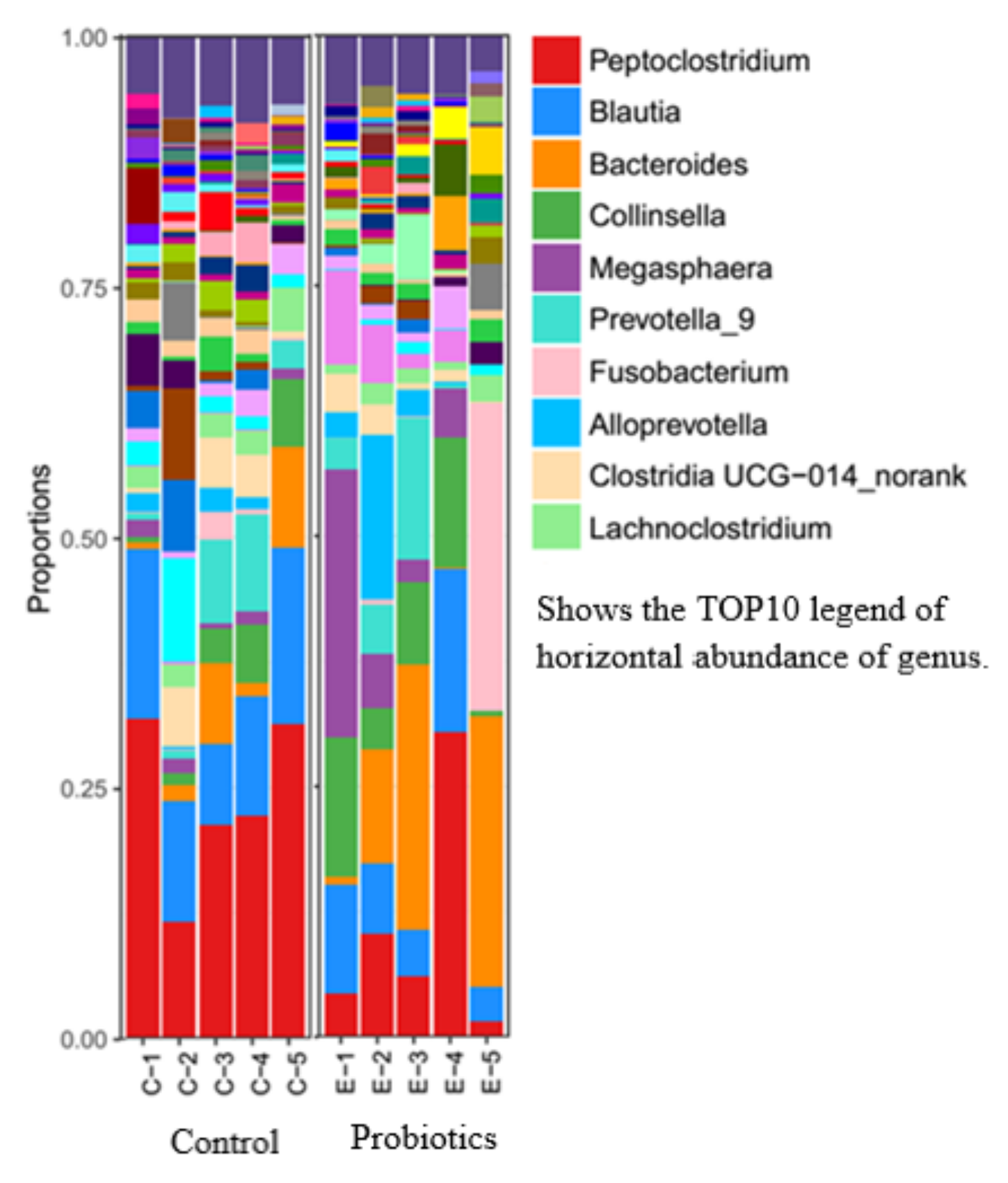
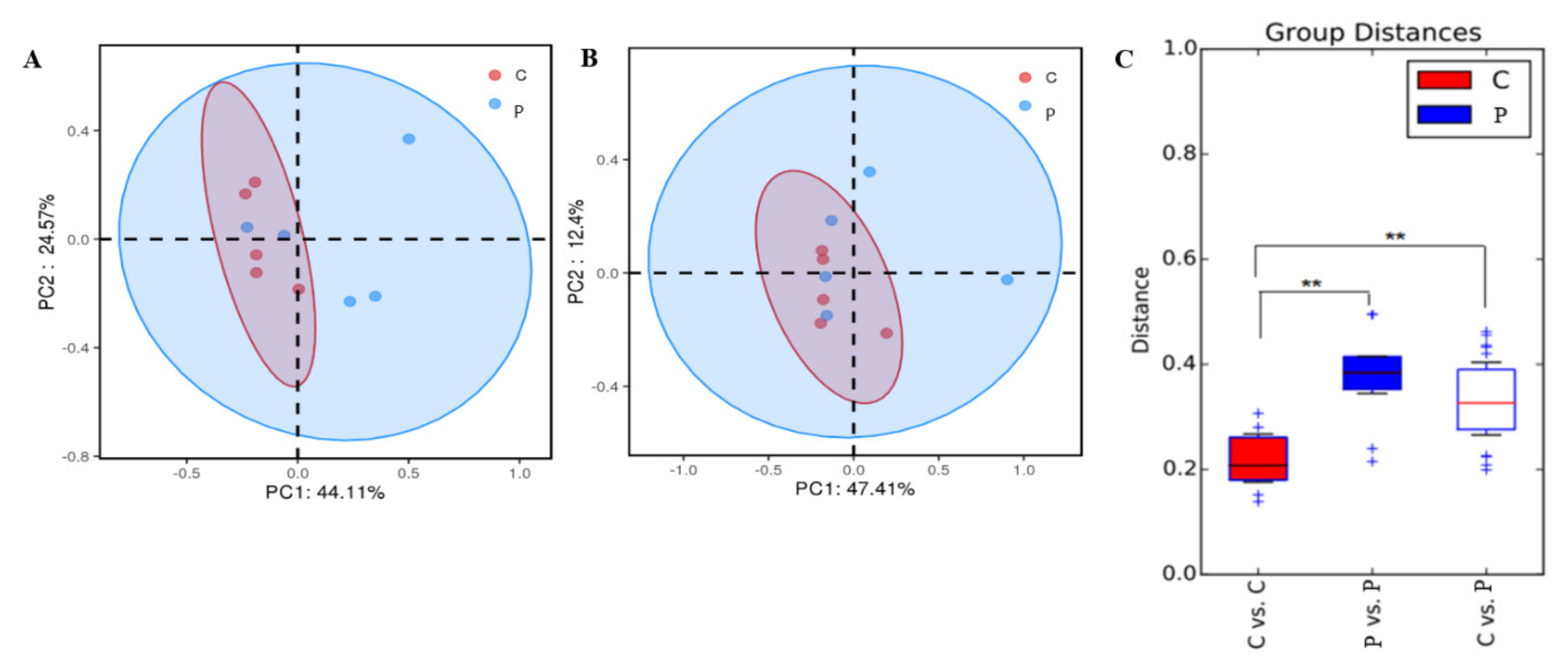

| Phylum | Control | Probiotics |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteroidota | 12.30 ± 8.43 | 25.08 ± 19.68 |
| Firmicutes | 78.07 ± 13.66 | 53.93 ± 22.14 |
| Group | Chao | ACE | Shannon | Simpson | Evenness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 316.68 ± 27.52 | 315.58 ± 29.33 | 3.95 ± 0.25 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.70 ± 0.03 |
| Probiotics | 284.35 ± 71.53 | 283.44 ± 70.47 | 3.55 ± 0.41 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.64 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Ali, I.; Lei, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Feline Gut Health through the Fecal Microbiota and Its Metabolite SCFAs. Metabolites 2023, 13, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020228
Li Y, Ali I, Lei Z, Li Y, Yang M, Yang C, Li L. Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Feline Gut Health through the Fecal Microbiota and Its Metabolite SCFAs. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020228
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yifei, Ilyas Ali, Zhiqi Lei, Yanan Li, Min Yang, Caixia Yang, and Lian Li. 2023. "Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Feline Gut Health through the Fecal Microbiota and Its Metabolite SCFAs" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020228
APA StyleLi, Y., Ali, I., Lei, Z., Li, Y., Yang, M., Yang, C., & Li, L. (2023). Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Feline Gut Health through the Fecal Microbiota and Its Metabolite SCFAs. Metabolites, 13(2), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020228