Optimizing Stereotactic Intracranial Neoplasm Treatment: A Systematic Review of PET Integration with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
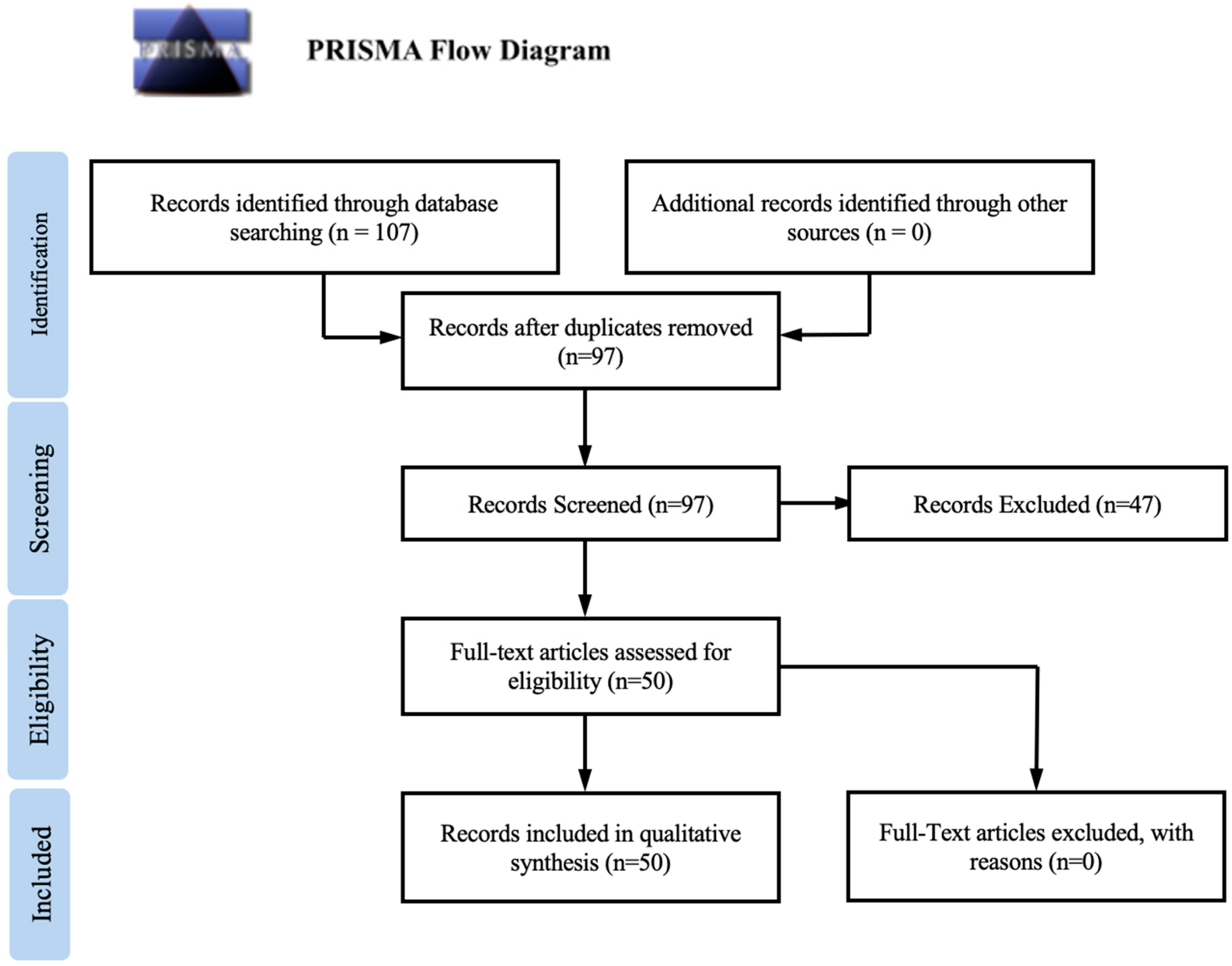
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Data Analysis
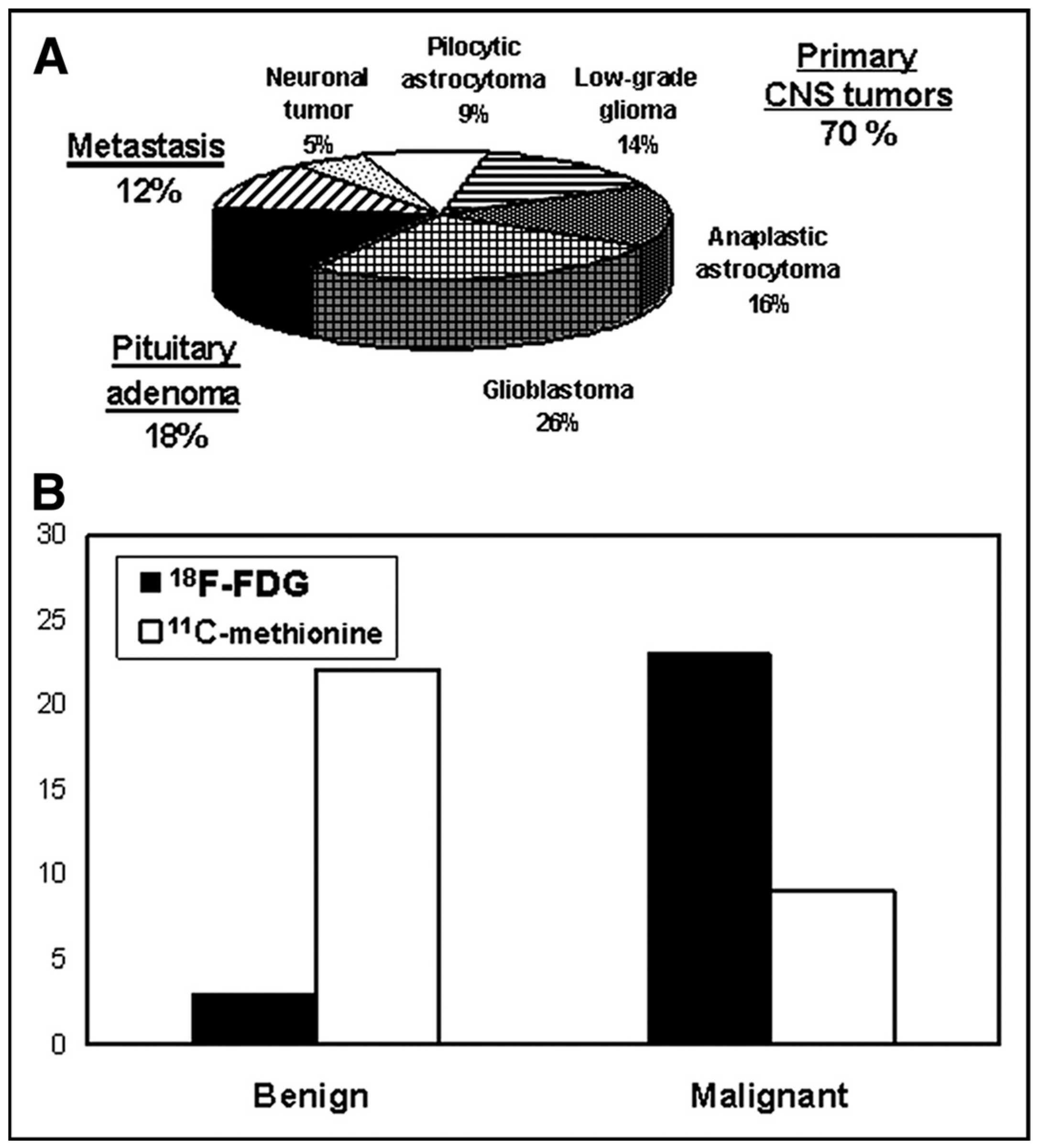
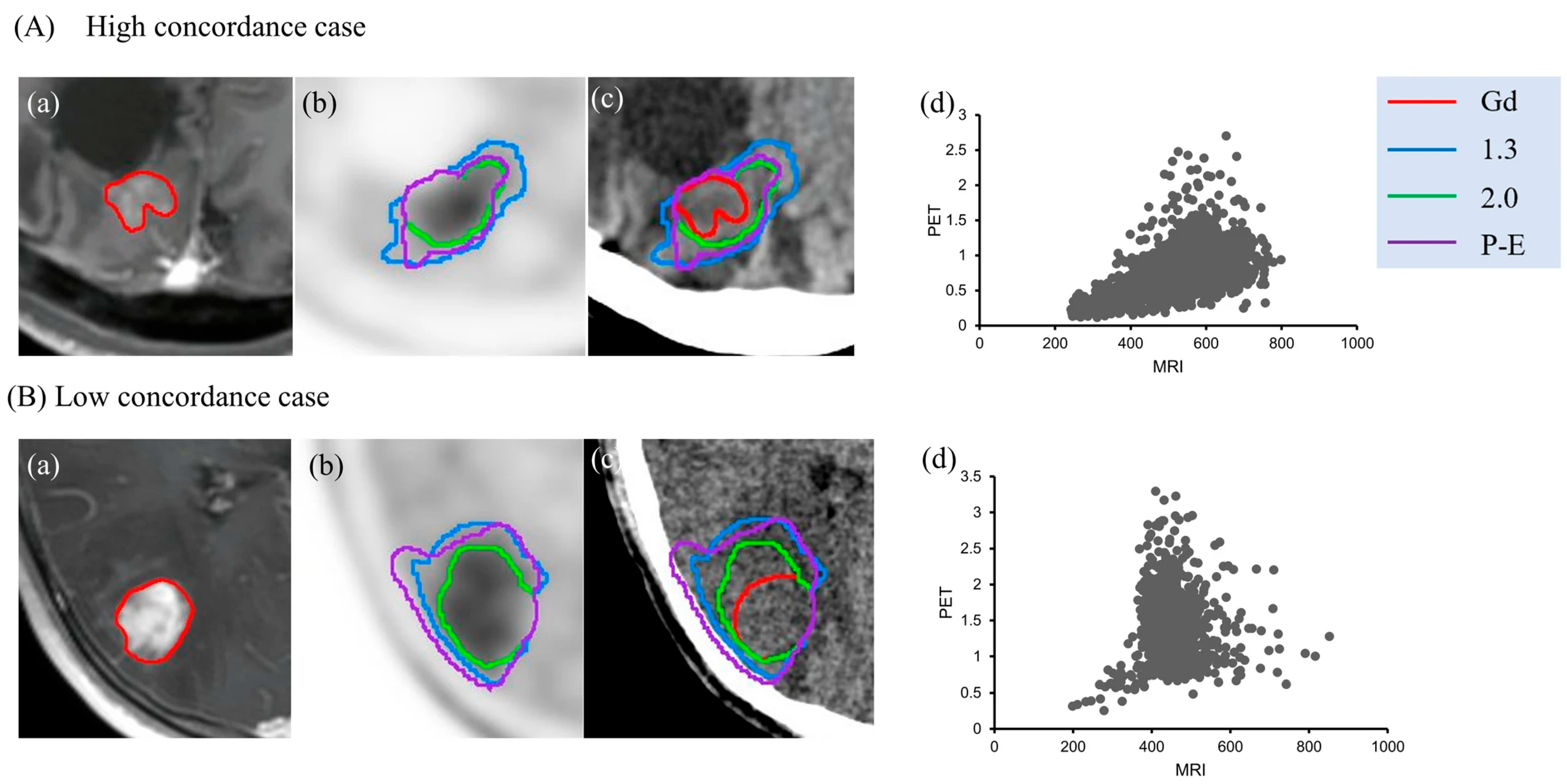
3. Results
3.1. Planning of Radiosurgery
3.2. Radiotracers
3.3. Differentiating Between Lesion Recurrence and Radiation Necrosis
3.4. Combination Imaging
3.5. Microscopic Infiltrations
4. Discussion
4.1. Planning of Radiosurgery
4.2. Radiotracers
4.3. Differentiating Between Lesion Recurrence and Radiation Necrosis
4.4. Combination Imaging
4.5. Microscopic Infiltrations
4.6. Prognosis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [11C]acetate | 1-11C-acetate |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| BTV | Biological Tumor Volume |
| CA-IX | Carbonic Anhydrase IX |
| CE-MRI | Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC | [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-1-NaI3-octreotide |
| [68Ga]Ga-DOTATATE | [68Ga]Ga-DOTA,Tyr3]-octreotate |
| [68Ga]Ga-DOTATOC | [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-D-Phe-Tyr3-octreotide |
| [18F]FAZA | [18F]fluoroazomycin arabinoside |
| [18F]FET | [18F]fluoro-ethyl-tyrosine |
| [18F]FDG | [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose |
| [18F]FDOPA | [18F]FDOPA-6-[18F]fluoro-l-dopa |
| [18F]FRP-170 FPIA | [18F]fluoro-methyl-2-nitroimidazole [18F]fluoropivalate |
| GKRS | Gamma Knife Radiosurgery |
| GLUT-1 | Glucose Transporter 1 |
| GTV | Gross Tumor Volume |
| HIF-1alpha | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-alpha |
| LAT1 | L-type amino acid transporter 1 |
| LAT2 | L-type amino acid transporter 2 |
| [11C]MET | [11C]methionine |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MRS | Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy |
| MTV | Metabolic Tumor Volume |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RCTs | Randomized Controlled Trials |
| SABR | Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy |
| SRS | Stereotactic Radiosurgery |
| SSTR | Somatostatin Receptor |
| SSTR-2 | Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 |
| SUV | Standardized Uptake Value |
| T/N | Tumor Tissue to Normal Tissue Ratio |
References
- Desai, R.; Rich, K.M. Therapeutic Role of Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Neuro-Oncology. Mo. Med. 2020, 117, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jones, T. The role of positron emission tomography within the spectrum of medical imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1996, 23, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.; Townsend, D. History and future technical innovation in positron emission tomography. J. Med. Imaging 2017, 4, 011013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, A.; Bailo, M.; Cicone, F.; Carideo, L.; Quartuccio, N.; Mortini, P.; Falini, A.; Cascini, G.L.; Minniti, G. Advanced Imaging Techniques for Radiotherapy Planning of Gliomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Leiva-Salinas, C.; Muttikkal, T.J.E.; Flors, L.; Puig, J.; Wintermark, M.; Patrie, J.T.; Rehm, P.K.; Sheehan, J.P.; Schiff, D. FDG PET/MRI Coregistration Helps Predict Response to Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Patients with Brain Metastases. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levivier, M.; Wikier, D.; Goldman, S.; David, P.; Metens, T.; Massager, N.; Gerosa, M.; Devriendt, D.; Desmedt, F.; Simon, S.; et al. Integration of the metabolic data of positron emission tomography in the dosimetry planning of radiosurgery with the gamma knife: Early experience with brain tumors. Technical note. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93 (Suppl. 3), 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travers, S.; Joshi, K.; Miller, D.C.; Singh, A.; Nada, A.; Biedermann, G.; Cousins, J.P.; Litofsky, N.S. Reliability of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography in Differentiating Metastatic Brain Tumor Recurrence from Radiation Necrosis. World Neurosurg. 2021, 151, e1059–e1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, G.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Martin, H.; Barsoum, P.; Dodoo, E. Adaptive hypofractionated gamma knife radiosurgery for a large brainstem metastasis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2016, 7 (Suppl. 4), S130–S138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yomo, S.; Oda, K.; Oguchi, K. Single- versus 2-session Gamma Knife surgery for symptomatic midsize brain metastases: A propensity score-matched analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, M.; Mohsenian Sisakht, A.; Kazemi Gazik, F.; Shahrokhi, P.; Rastegar, K.; Karamzade-Ziarati, N. PET-guided gamma knife radiosurgery in brain tumors: A brief review. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2021, 9, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levivier, M.; Massager, N.; Wikler, D.; Lorenzoni, J.; Ruiz, S.; Devriendt, D.; David, P.; Desmedt, F.; Simon, S.; Van Houtte, P.; et al. Use of stereotactic PET images in dosimetry planning of radiosurgery for brain tumors: Clinical experience and proposed classification. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pirotte, B.; Acerbi, F.; Lubansu, A.; Goldman, S.; Brotchi, J.; Levivier, M. PET imaging in the surgical management of pediatric brain tumors. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2007, 23, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonova, G.; Kozubikova, P.; Liscak, R.; Novotny, J., Jr. Leksell Gamma Knife treatment for pilocytic astrocytomas: Long-term results. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 18, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St George, E.J.; Plowman, P.N. The role of the Gamma Knife and PET in neuro-oncology. CME Cancer Med. 2002, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Galldiks, N.; Law, I.; Pope, W.B.; Arbizu, J.; Langen, K.J. The use of amino acid PET and conventional MRI for monitoring of brain tumor therapy. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 13, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yano, H.; Shinoda, J.; Iwama, T. Clinical Utility of Positron Emission Tomography in Patients with Malignant Glioma. Neurol. Med.-Chir. 2017, 57, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Domeki, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Yokoyama, H.; Ogata, H.; Okamoto, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Sasaki, K.; Tsuchioka, T.; et al. Treatment strategy for brain metastases from esophageal cancer. Tumori J. 2020, 106, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, P.; Kocher, M.; Ceccon, G.; Bauer, E.K.; Stoffels, G.; Viswanathan, S.; Ruge, M.I.; Neumaier, B.; Shah, N.J.; Fink, G.R.; et al. Combined FET PET/MRI radiomics differentiates radiation injury from recurrent brain metastasis. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 20, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momose, T.; Nariai, T.; Kawabe, T.; Inaji, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Maehara, T.; Oda, K.; Ishii, K.; Ishiwata, K.; et al. Clinical benefit of 11C methionine PET imaging as a planning modality for radiosurgery of previously irradiated recurrent brain metastases. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 39, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomura, N.; Kokubun, M.; Saginoya, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Kikuchi, Y. Differentiation between Treatment-Induced Necrosis and Recurrent Tumors in Patients with Metastatic Brain Tumors: Comparison among 11C-Methionine-PET, FDG-PET, MR Permeability Imaging, and MRI-ADC-Preliminary Results. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Belohlávek, O.; Simonová, G.; Kantorová, I.; Novotný, J., Jr.; Liscák, R. Brain metastases after stereotactic radiosurgery using the Leksell gamma knife: Can FDG PET help to differentiate radionecrosis from tumour progression? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol Imaging 2003, 30, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levivier, M.; Wikler, D., Jr.; Massager, N.; David, P.; Devriendt, D.; Lorenzoni, J.; Pirotte, B.; Desmedt, F.; Simon, S., Jr.; Goldman, S.; et al. The integration of metabolic imaging in stereotactic procedures including radiosurgery: A review. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97 (Suppl. 5), 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umana, G.E.; Ferini, G.; Harikar, M.M.; Venkataram, T.; Costanzo, R.; Scalia, G.; Palmisciano, P.; Brunasso, L.; Paolini, F.; Sciortino, A.; et al. Detection of “Incidentalomas” on Brain and Body 68Ga-DOTATOC-PET Scans: A Retrospective Study and Case Illustration. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 5867–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.N.; Van Simaeys, G.; Devriendt, D.; Sadeghi, N.; Dewitte, O.; Massager, N.; David, P.; Levivier, M.; Goldman, S. Three-dimensional Gaussian model to define brain metastasis limits on 11C-methionine PET. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 89, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, F.; Inserra, F.; Scalia, G.; Ippolito, M.; Cosentino, S.; Crea, A.; Sabini, M.G.; Valastro, L.; Patti, I.V.; Mele, S.; et al. 68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT Follow Up after Single or Hypofractionated Gamma Knife ICON Radiosurgery for Meningioma Patients. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, R.S.; Chang, C.P.; Guo, W.Y.; Pan, D.H.; Ho, D.M.; Chang, C.W.; Yang, B.H.; Wu, L.C.; Yeh, S.H. 1-11C-acetate versus 18F-FDG PET in detection of meningioma and monitoring the effect of gamma-knife radiosurgery. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibahara, I.; Kumabe, T.; Kanamori, M.; Saito, R.; Sonoda, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Iwata, R.; Higano, S.; Takanami, K.; Takai, Y.; et al. Imaging of hypoxic lesions in patients with gliomas by using positron emission tomography with 1-(2-[18F] fluoro-1-[hydroxymethyl]ethoxy)methyl-2-nitroimidazole, a new 18F-labeled 2-nitroimidazole analog. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroth, M.D.; Prasath, J.; Willuweit, A.; Stoffels, G.; Sellhaus, B.; van Osterhout, A.; Geisler, S.; Shah, N.J.; Eble, M.J.; Coenen, H.H.; et al. Uptake of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine in reactive astrocytosis in the vicinity of cerebral gliomas. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapelli, P.; Callea, M.; Fallanca, F.; Castellano, A.; Bailo, M.; Scifo, P.; Bettinardi, V.; Conte, G.M.; Monterisi, C.; Rancoita, P.M.V.; et al. 18F-FAZA PET/CT in pretreatment assessment of hypoxic status in high-grade glioma: Correlation with hypoxia immunohistochemical biomarkers. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2021, 42, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, H.; Tashiro, Y.; Fujio, S.; Goto, M.; Arita, K. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma within a cavernous hemangioma of the cavernous sinus. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2011, 28, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, K.; Christ, E.R.; Mindermann, T.; Wieser, H.G. Transient MR changes and symptomatic epilepsy following gamma knife treatment of a residual GH-secreting pituitary adenoma in the cavernous sinus. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 903–908, discussion 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Jung, T.Y.; Jung, S.; Kim, I.Y.; Moon, K.S.; Kwon, S.Y.; Jang, W.Y. Quantitative Feasibility Evaluation of 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography Images in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: Phantom-Based Study and Clinical Application. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2019, 62, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kits, A.; Martin, H.; Sanchez-Crespo, A.; Delgado, A.F. Diagnostic accuracy of 11C-methionine PET in detecting neuropathologically confirmed recurrent brain tumor after radiation therapy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippitz, B.E.; Kraepelien, T.; Hautanen, K.; Ritzling, M.; Rähn, T.; Ulfarsson, E.; Boethius, J. Gamma knife radiosurgery for patients with multiple cerebral metastases. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2004, 91, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.Y.; Kim, I.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Jung, S.; Moon, K.S.; Jang, W.Y.; Kang, S.R.; Cho, S.G.; et al. Optimization of diagnostic performance for differentiation of recurrence from radiation necrosis in patients with metastatic brain tumors using tumor volume-corrected 11C-methionine uptake. EJNMMI Res. 2017, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alongi, P.; Iaccarino, L.; Losa, M.; Del Vecchio, A.; Gerevini, S.; Plebani, V.; Di Muzio, N.; Mortini, P.; Gianolli, L.; Perani, D. PET Evaluation of Late Cerebral Effect in Advanced Radiation Therapy Techniques for Cranial Base Tumors. Curr. Radiopharm. 2018, 11, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szeifert, G.T.; Massager, N.; Brotchi, J.; Levivier, M. Morphological redifferentiation in a malignant astrocytic tumor after gamma knife radiosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97 (Suppl. 5), 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzynski, S.R.; Janicki, T.J.; Burzynski, G.S.; Marszalek, A. Long-term survival (>13 years) in a child with recurrent diffuse pontine gliosarcoma: A case report. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 36, e433–e439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tamura, K.; Aoyagi, M.; Wakimoto, H.; Ando, N.; Nariai, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Ohno, K. Accumulation of CD133-positive glioma cells after high-dose irradiation by Gamma Knife surgery plus external beam radiation. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, N.D.; Adams, C.; Davis, G.L.; Starke, R.M.; Buro, J.; Nasr, N.; McRae, D.; Cernica, G.; Caputy, A.; Hong, R.; et al. Effectiveness of Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography as a Guide for Palliative Radiation Therapy for Spinal Metastases. World Neurosurg. 2018, 115, e67–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.Y.; Jung, S.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Jang, W.Y.; Moon, K.S.; Lim, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Kang, S.R.; Min, J.J.; et al. The Application of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Deformed 11C-Methionine-Positron Emission Tomography Images in Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2019, 97, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenstein, A.; Haug, A.R.; Miller, C.; Hintschich, C. Ga-68-DOTA-TATE PET/CT for discrimination of tumors of the optic pathway. Orbit 2015, 34, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefano, A.; Vitabile, S.; Russo, G.; Ippolito, M.; Marletta, F.; D’arrigo, C.; D’urso, D.; Gambino, O.; Pirrone, R.; Ardizzone, E.; et al. A fully automatic method for biological target volume segmentation of brain metastases. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2016, 26, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundo, L.; Stefano, A.; Militello, C.; Russo, G.; Sabini, M.G.; D’Arrigo, C.; Marletta, F.; Ippolito, M.; Mauri, G.; Vitabile, S.; et al. A fully automatic approach for multimodal PET and MR image segmentation in gamma knife treatment planning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 144, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrens, M.; Malamitsi, J.; Karaiskos, P.; Valotassiou, V.; Laspas, F.; Andreou, J.; Stergiou, C.; Prassopoulos, V. Although Non-diagnostic Between Necrosis and Recurrence, FDG PET/CT Assists Management of Brain Tumours After Radiosurgery. In Vivo 2016, 30, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Maruyama, K.; Igaki, H.; Tago, M.; Saito, N. The value of image co ration during stereotactic radiosurgery. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 151, 465–471, discussion 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayenga, H.N.; Bishop, A.J.; Wardak, Z.; Sen, C.; Mickey, B. Intraspinal Dissemination and Local Recurrence of an Intracranial Hemangiopericytoma. World Neurosurg. 2019, 123, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marafi, F.; Sadeq, A.; Esmail, A.; Usmani, S. Case of Adult Metastatic Medulloblastoma Demonstrated on 18F-DOPA PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, e318–e320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levivier, M.; Massager, N.; Wikler, D.; Goldman, S. Modern multimodal neuroimaging for radiosurgery: The example of PET scan integration. In Gamma Knife Radiosurgery; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2004; Volume 91, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Register, S.; Clarke, J.W.; Chaudhury, A.R.; Lo, S.S. Pathologic complete response of a solitary melanoma brain metastasis after local ablative radiation therapy: Case report. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Greco, M.C.; Milazzotto, R.; Liardo, R.L.E.; Acquavia, G.; La Rocca, M.; Altieri, R.; Certo, F.; Barbagallo, G.M.; Basile, A.; Foti, P.V.; et al. Relapsing High-Grade Glioma from Peritumoral Zone: Critical Review of Radiotherapy Treatment Options. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, R.; Pesaresi, A.; Bianconi, A.; Zotta, M.; Deandreis, D.; Morana, G.; Zeppa, P.; Melcarne, A.; Garbossa, D.; Cofano, F. A Systematic Review of Amino Acid PET Imaging in Adult-Type High-Grade Glioma Surgery: A Neurosurgeon’s Perspective. Cancers 2022, 15, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.; Inglese, M.; Grech-Sollars, M.; Aravind, P.; Dubash, S.; Barwick, T.D.; O’nEill, K.; Wang, J.; Saleem, A.; O’cAllaghan, J.; et al. Feasibility of [18F]fluoropivalate hybrid PET/MRI for imaging lower and higher grade glioma: A prospective first-in-patient pilot study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 50, 3982–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Zwart, P.L.; van Dijken, B.R.J.; Holtman, G.A.; Stormezand, G.N.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Jan van Laar, P.; van der Hoorn, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of PET Tracers for the Differentiation of Tumor Progression from Treatment-Related Changes in High-Grade Glioma: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 13, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, E.; Assadi, M.; Nasiri, M.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. Targets for Molecular Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs): An Overview and Update. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niitsu, H.; Fukumitsu, N.; Tanaka, K.; Mizumoto, M.; Nakai, K.; Matsuda, M.; Ishikawa, E.; Hatano, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Kamizawa, S.; et al. Methyl-11C-L-methionine positron emission tomography for radiotherapy planning for recurrent malignant glioma. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2024, 38, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Article | Demographics/Subject Information | Utility of PET (Yes/No) | Utility of PET-MRI (Yes/No) | Radiotracers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levivier (2002) [22] | Review of experience with 150 stereotactic biopsies, 43 neuronavigation procedures, and 34 cases treated with GKS | Yes | Yes | FDG, [11C]MET |
| Levivier (2000) [6] | Validation of technique for fiducial marker imaging, importation, and handling of PET data with GammaPlan planning software | Yes | Yes | FDG, MET |
| Simonova (2016) [13] | 25 patients with pilocytic astrocytomas that underwent GKS | Not Applicable (N/A) | N/A | N/A |
| Domeki (2020) [17] | 8 patients treated for esophageal cancer that developed brain metastases | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Sinclair (2016) [8] | Case study | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Yomo (2019) [9] | 219 patients with 252 symptomatic midsize brain metastases | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Castellano (2021) [4] | Review of the current literature | Yes | Yes | FDG, MET, FET, F-DOPA |
| Umana (2022) [23] | 61 patients (18 patients with 25 brain lesions, 43 patients with 85 body lesions) | Yes | No | (68)Ga-DOTATOC |
| Galldiks (2016) [15] | Review of the current literature | Yes | No | FET, MET, F-DOPA |
| Tang (2008) [24] | 3D Gaussian model with 25 brain metastases as experimental data | Yes | Yes | MET |
| Azar (2021) [10] | Review of the current literature | Yes | Yes | FDG, MET |
| Momose (2014) [19] | 88 patients that underwent GK-SRS | Yes | Yes | MET |
| Barone (2021) [25] | 20 patients with pre-operative PET/CT | Yes | No | (68)Ga-DOTATOC |
| Liu (2010) [26] | 22 meningioma patients | Yes | No | 1-(11)C-acetate, (18)F-FDG |
| Shibahara (2010) [27] | 8 patients with FRP-170 injections and PET imaging | Yes | Yes | FRP-170, FDG |
| Piroth (2013) [28] | 33 Fisher CDF rats with F98-glioma cell implants | Yes | No | (18)F-FET |
| Mapelli (2021) [29] | 20 patients with brain MRI suggestive of high-grade glioma | Yes | No | 18F-FAZA |
| Hirano (2011) [30] | Case report | Yes | No | FDG |
| Schindler (2006) [31] | Case report | Yes | No | FDG |
| Travers (2021) [7] | 242 patients with previous whole-brain radiation therapy or sterotactic radiosurgery | No | No | (18)F-FDG |
| Leiva-Salinas (2019) [5] | 85 patients with brain metastases from non-CNS neoplasms treated with GKS | Yes | Yes | FDG |
| Lim (2019) [32] | Imaging from 14 metastatic brain tumors | No | Yes | MET |
| Belohlávek (2003) [21] | 25 patients with 57 metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery | Yes | No | FDG |
| Tomura (2017) [20] | 15 GKS patients with metastatic brain tumors | Yes | No | MET, FDG |
| Kits (2018) [33] | 30 patients with irradiated intracranial tumors | Yes | No | MET |
| Lippitz (2004) [34] | 215 GKS patients | Yes | No | FDG |
| Jung (2017) [35] | 48 patients with 77 metastatic brain lesions | Yes | No | MET |
| Alongi (2018) [36] | 6 patients with possible late brain effects following radiation therapy | Yes | No | 18F-FDG |
| Szeifert (2002) [37] | Case report | Yes | No | MET |
| Burzynski (2014) [38] | Case report | Yes | No | Not specified |
| Tamura (2010) [39] | 32 GKS/EBRT patients with malignant gliomas | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Almeida (2018) [40] | 72 patients with spinal metastases treated with stereotactic ablative radiation therapy | Yes | No | FDG |
| Lohmann (2018) [18] | 52 patients with new or progressive contrast-enhancing brain lesions on MRI following radiotherapy | Yes | Yes | FET |
| Jung (2019) [41] | 12 newly developed metastatic brain tumors | Yes | Yes | MET |
| Klingenstein (2015) [42] | 13 patients with ambiguous, symptomatic lesions of the optic pathway | Yes | No | Ga-68-DOTA-TATE |
| Stefano (2016) [43] | Algorithm for BTV delination | No | No | N/A |
| Levivier (2004) [11] | 57 GKS patients with stereotactic PET on the same day as stereotactic MRI or CT | Yes | Yes | FDG, MET |
| Rundo (2017) [44] | 19 brain metastatic tumors analyzed by a novel automatic PET/MRI segmentation method for GKS patients | Yes | Yes | MET |
| Torrens (2016) [45] | 27 PET/CT studies co-registered with MRI performed on 16 patients | Yes | Yes | FDG |
| Koga (2009) [46] | Co-registration from 180 radiosurgery sessions | Yes | Yes | FDG |
| Hayenga (2019) [47] | Case report | No | No | FDG |
| Marafi (2022) [48] | Case report | Yes | No | (18)F-DOPA |
| Pirotte (2007) [12] | 400 consecutive pediatric brain tumors | Yes | No | FDG, MET |
| Levivier (2004) [49] | 80 LGK patients treated with combination MR/CT and PET guidance | Yes | Yes | Not specified |
| Register (2010) [50] | Case report | Yes | No | FDG |
| Lo Greco (2022) [51] | Review of the current literature | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| De Marco (2022) [52] | Systematic Review | Yes | Yes | MET, FET, 18F-DOPA, FDG |
| Islam (2023) [53] | Ten adult glioma patients imaged with FPIA PET/MRI protocols | Yes | Yes | FPIA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subtirelu, R.C.; Teichner, E.M.; Writer, M.; Bryan, K.; Patil, S.; Khan, T.; Herpin, L.; Patel, R.N.; Christner, E.; Parikh, C.; et al. Optimizing Stereotactic Intracranial Neoplasm Treatment: A Systematic Review of PET Integration with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Diseases 2025, 13, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070215
Subtirelu RC, Teichner EM, Writer M, Bryan K, Patil S, Khan T, Herpin L, Patel RN, Christner E, Parikh C, et al. Optimizing Stereotactic Intracranial Neoplasm Treatment: A Systematic Review of PET Integration with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Diseases. 2025; 13(7):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070215
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubtirelu, Robert C., Eric M. Teichner, Milo Writer, Kevin Bryan, Shiv Patil, Talha Khan, Lancelot Herpin, Raj N. Patel, Emily Christner, Chitra Parikh, and et al. 2025. "Optimizing Stereotactic Intracranial Neoplasm Treatment: A Systematic Review of PET Integration with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery" Diseases 13, no. 7: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070215
APA StyleSubtirelu, R. C., Teichner, E. M., Writer, M., Bryan, K., Patil, S., Khan, T., Herpin, L., Patel, R. N., Christner, E., Parikh, C., Werner, T., Alavi, A., & Revheim, M.-E. (2025). Optimizing Stereotactic Intracranial Neoplasm Treatment: A Systematic Review of PET Integration with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. Diseases, 13(7), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13070215







