Abstract
Lane detection plays a fundamental role in autonomous driving systems, yet it remains challenging under complex real-world conditions such as low illumination, occlusion, and degraded lane markings. In this paper, we propose a novel lane detection framework, Informative Feature Pyramid Network (Info-FPNet), designed to improve multi-scale feature representation and alignment for robust lane detection. Specifically, the proposed architecture integrates two key modules: an informative feature pyramid (IFP) module and a cross-layer refinement (CLR) module. The IFP module selectively aggregates spatially and semantically informative features across different scales using pixel shuffle upsampling, feature alignment, and semantic encoding mechanisms, thereby preserving fine-grained details and minimizing aliasing effects. The CLR module applies region-wise attention and anchor regression to refine coarse lane proposals, enabling better localization of curved or occluded lanes. Experimental results on two public benchmarks, CULane and TuSimple, demonstrate that the proposed Info-FPNet outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in terms of F1 score and is robust under challenging conditions such as nighttime, strong reflections, and occlusions. Furthermore, the proposed method maintains real-time inference speed and low computational overhead, validating its effectiveness and practicality in real-world applications.
1. Introduction
Lane detection plays a pivotal role in autonomous driving systems, providing the foundation for accurate vehicle control and navigation [1,2]. By identifying the boundaries of the lane, the system can make decisions regarding steering, speed control, and collision avoidance. However, lane detection in real-world environments remains a significant challenge due to the complex driving scenarios characterized by one or more of the following conditions: (1) poor visibility due to low lighting (e.g., nighttime with or without streetlights); (2) strong light interference (e.g., sunlight reflection on road surfaces); (3) partial or complete occlusion of lane markings due to vehicles, shadows, or obstacles; and (4) degraded lane appearance caused by worn paint, road damage, or sensor noise [3]. Early works in lane detection explored traditional methods for lane line extraction, relying on handcrafted features and simple geometric models [4,5]. Despite advancements, many of these methods struggle to generalize across diverse driving environments, especially in the presence of dynamic factors like traffic and unpredictable weather.
Recent research in lane detection has shifted toward deep learning approaches, which have shown promising results in improving robustness and accuracy [6]. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely used in detecting lane boundaries in various scenarios [7,8]. These methods, while effective, often face challenges when dealing with complex road geometries, such as sharp curves, intersections, or unmarked lanes. To address these, several novel architectures have emerged, including the use of dilated convolutions [9] and attention mechanisms [10,11]. A comprehensive review further discusses how these methods have evolved, outlining their strengths and limitations [12]. While these methods show significant improvement in lane detection under controlled conditions, their performance often deteriorates in more challenging scenarios due to the failure to capture multi-scale and multi-modal information effectively.
Information fusion, which involves integrating features from multiple sources or scales, holds considerable potential in enhancing lane detection accuracy. By combining low-level features (such as edges) with high-level semantic information (such as road context), lane detection models can better handle the variability in road conditions and occlusions. Recently, Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) have become a cornerstone for multi-scale feature fusion in lane detection [13,14,15,16] and demonstrated the benefits of multi-scale information fusion in improving the robustness of lane detection systems. However, the fusion approaches based on FPNs suffer from three key limitations:
- Channel Information Loss. Fixed lateral connections in conventional FPNs often discard critical channel-wise details, degrading feature representation [17].
- Feature Misalignment. Misaligned feature maps from different pyramid levels introduce noise, pa ticularly for curved or discontinuous lanes [17,18].
- Computational Overhead. Complex fusion modules, such as those in attention-based networks, incur prohibitive computational costs, hindering real-time deployment [11,19].
These shortcomings highlight the need for lightweight yet adaptive fusion mechanisms tailored to lane detection.
To address these gaps, this paper proposes a unified framework called the Informative Feature Pyramid Network (Info-FPNet), which combines two key modules: the informative feature pyramid (IFP) module for selective multi-scale fusion, and the cross-layer refinement (CLR) module for progressive feature enhancement through inter-layer guidance. The IFP emphasizes semantically rich and spatially discriminative information, while the CLR iteratively refines lane-relevant features by aligning hierarchical representations across different depths. Together, the Info-FPNet can capture both fine-grained local features and high-level semantic cues, enabling more accurate and reliable lane detection even in complex scenarios such as low illumination, occlusions, or worn-out markings. Our method addresses the limitations of current approaches by improving feature extraction, handling occlusions more effectively, and enhancing performance in complex road conditions. The proposed approach is evaluated across various benchmarks and real-world datasets, showing significant improvements over existing techniques in terms of accuracy and robustness.
The main contributions of this article are summarized as follows:
- An effective and lightweight lane detection framework (Info-FPNet) is proposed, which is designed to address the challenges of lane detection in complex driving environments. The proposed architecture improves upon conventional FPN-based methods by enhancing multi-scale feature representation and alignment.
- An informative feature pyramid (IFP) module is designed, which combines pixel shuffle upsampling, feature alignment, and semantic encoding to selectively aggregate spatial and semantic information. This reduces aliasing effects and preserves detailed lane structures across scales.
- A cross-layer refinement (CLR) module is introduced that utilizes region-wise attention and anchor-based regression to refine coarse lane proposals. This enhances the localization accuracy of curved and occluded lanes while maintaining computational efficiency.
- Comprehensive experiments conducted on CULane and TuSimple benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both accuracy and robustness. Notably, Info-FPNet outperforms existing methods under challenging conditions such as night-time, strong reflections, and occlusions, while maintaining real-time inference speed.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Lane Detection
Early lane detection methods primarily relied on handcrafted features and geometric assumptions. Techniques, such as Hough Transform, edge detection, and polynomial fitting, were commonly used to extract lane markings from road images [20,21]. While these methods achieved reasonable performance in structured environments, their robustness significantly degraded in complex scenarios involving shadows, occlusions, worn-out lane markings, or varying illumination. Moreover, these approaches generally lacked the ability to model global context and temporal consistency, which are crucial in real-world autonomous driving. Their static assumptions and sensitivity to noise limited their adaptability and scalability in diverse environments.
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Lane Detection
With the advent of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), data-driven approaches have become the dominant paradigm in lane detection. Early works like SCNN (Spatial CNN) [22] introduced spatial message propagation mechanisms to capture long-range dependencies among lane pixels. Subsequently, ENet-SAD [23] integrated self-attention distillation to enhance feature representation while maintaining real-time efficiency. Ultra Fast Lane Detection (UFLD) [24] further improved computational speed by reformulating lane detection as a row-wise classification problem.
In recent advances, LaneATT [25] proposed anchor-based lane representation and transformer-style attention modules for lane-object matching. CondLaneNet [26] extended this line of work with dynamic conditional convolutions that allow the model to adapt to diverse lane topologies and road geometries. Other approaches such as UFLD [27] and LaneFormer [28] have attempted to balance inference speed and accuracy by employing lightweight backbones and compact lane encoders. Despite these improvements, detecting lanes under extreme visual conditions, such as nighttime driving or occlusion, remains a challenge for purely data-driven CNN models.
2.3. Information Fusion-Based Lane Detection
Information fusion has emerged as a promising strategy to improve the robustness of lane detection under environmental variability. Multi-modal fusion methods that combine LiDAR, semantic maps, or temporal sequences have shown notable success [29,30,31] but often require high-cost sensors and are difficult to deploy in real-time systems. To reduce hardware dependency, many recent efforts have focused on single-image fusion strategies that enhance spatial and semantic consistency across different feature hierarchies.
Notably, Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) have been widely adopted to enable multi-scale feature integration. FPNs improve detection by combining high-resolution spatial features from early layers with semantically rich features from deeper layers. Attention-based mechanisms [32] and semantic-aware fusion modules [33] have also been introduced to enhance selective aggregation of lane-relevant features.
However, standard FPNs typically aggregate features indiscriminately across scales, which can lead to aliasing effects, feature redundancy, and misalignment. Recent studies such as IFPNet [34] and BiFPN [35] attempt to address these issues via weighted fusion and learnable feature selection. Nevertheless, challenges remain in ensuring effective alignment and relevance during fusion, particularly under adverse conditions such as illumination changes or occlusion. Moreover, existing fusion methods often overlook feature correlation across layers, leading to suboptimal performance in complex road scenes.
3. Methodology
The overall architecture of the proposed framework for lane detection is illustrated in Figure 1. It primarily consists of two components: informative feature pyramid (IFP) module and cross-layer refinement (CLR) module.
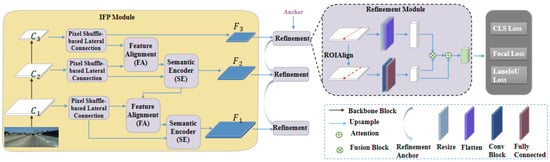
Figure 1.
Architecture of the proposed framework for lane detection. It consists of IFP and CLR modules. The feature maps () are acquired using ResNet [36], subsequently fed into the IFP module. After pixel shuffle-based lateral connecting, feature aligning, and semantic encoding, the fusion feature maps () with more contextual information are obtained. Finally, the feature maps () are fed into the CLR module to refine the lane lines.
3.1. Motivation
In recent years, Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) have been widely adopted in lane detection due to their ability to aggregate multi-scale feature information, enabling the detection of thin and sparse lane markings across varying spatial resolutions. By fusing low-level spatial features with high-level semantic features, FPNs enhance robustness to scale variations and partial occlusions. However, traditional FPNs typically perform uniform or heuristic feature fusion without adequately assessing the informativeness of each feature map. As a result, irrelevant or noisy features from certain levels may dilute discriminative signals, leading to suboptimal performance in complex driving environments—such as cluttered urban roads, occlusions, or adverse weather conditions. This limitation motivates us to design an Informative Feature Pyramid Network (Info-FPNet), which adaptively emphasizes structurally and semantically relevant features across the pyramid hierarchy. By explicitly selecting and enhancing informative features, our method aims to significantly improve lane detection robustness and precision in diverse real-world scenarios.
To further enhance representation capability, we integrate the informative feature pyramid (IFP) module with a cross-layer refinement (CLR) module. The IFP module selectively aggregates salient multi-scale features, while the CLR module refines these fused representations by enabling semantic guidance from deep layers and structural feedback from shallow layers. This bi-directional refinement mechanism helps to preserve fine-grained lane boundaries and enhance contextual understanding, particularly beneficial for challenging scenarios involving dashed lines, occluded lanes, or complex topologies. The synergy between IFP and CLR allows the network to not only focus on what features to use, but also on how to progressively refine them—leading to a more accurate and resilient lane detection pipeline.
3.2. Network Architecture
We design a two-stage framework for lane detection that leverages multi-scale feature extraction and refinement. In this study, the traditional feature extraction networks, the ResNet [36], was employed to extract feature maps at several scales for all experiments due to its favorable trade-off between performance and computational efficiency. This makes it well-suited for real-time applications and allows for fair comparison with many state-of-the-art lane detection models that adopt similar backbones. These feature maps are fused via an informative feature pyramid (IFP) module that preserves rich channel information and spatial detail. The fused pyramid is then processed by a cross-layer refinement (CLR) module. Initial lane proposals (anchors) are generated and refined using features aligned by RoIAlign. This pipeline ensures that high-level semantic context and low-level geometry are both exploited. In practice, the network outputs a set of lane curves represented by a sequence of points for each detected lane. Anchor-based regression (as in LaneATT [25]) is used to predict the exact lane positions from the proposals.
3.2.1. Informative Feature Pyramid (IFP) Module
The IFP module fuses multi-resolution features while overcoming the shortcomings of standard FPNs. It consists of three key components: (1) pixel shuffle (PS), (2) feature alignment (FA), and (3) semantic encoder (SE).
(1) Pixel Shuffle (PS).
In Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) [16], the most straightforward approach of upsampling relies on the interpolation method, which, however, often results in the loss of channel-wise information. To overcome this limitation, in reference to [17], instead of the usual lateral convolutions and bilinear upsampling, we use pixel shuffle to upsample feature maps.
The pixel shuffle, originally designed for image and video super-resolution tasks, rearranges feature map channels to increase spatial resolution without discarding information [37]. Pixel shuffle (sub-pixel convolution) rearranges a tensor of shape into one of shape [37]. Equivalently, if , then it upsamples spatial dimensions by a factor r while preserving all channel information. Info-FPN [17] shows that this PSM (pixel shuffle-based lateral connection) “completely preserves channel information” in the pyramid.
Compared to interpolation-based methods, pixel shuffle enhances spatial resolution by restructuring the depth (channel) dimension into a width and height, thereby preserving the encoded semantic features. Although this transformation reduces the number of channels, it maintains the total information content by distributing it across spatial locations. In our network, we apply a pixel shuffle layer (with factor for example) to each lower-resolution feature map before fusion, thereby avoiding channel bottlenecks and retaining fine-grained detail. The pixel shuffle-based feature transformation is defined as
where denotes the input feature map at feature level i, represents 2× upsampling via pixel shuffle, and denotes a convolution operation with kernel size . Since the backbone network (ResNet) in our architecture uses a stride of 2 for down-sampling, applying 2× upsampling is well-suited for aligning and fusing adjacent feature levels in the pyramid. In the convolution operation, specifically, a 1 × 1 convolution is first applied to align the feature dimensions, followed by a 2 × 2 or 4 × 4 convolution to unify the spatial scale and refine the features. The use of a stride-2 backbone network makes the 2× upsampling appropriate for aligning adjacent feature levels in the pyramid.
By incorporating the pixel shuffle mechanism, our model effectively increases the feature map resolution while avoiding channel degradation commonly caused by interpolation. This design helps preserve fine-grained spatial detail and enhances the model’s ability to understand complex scene structures.
(2) Feature Alignment (FA).
Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) typically enable multi-scale prediction by fusing features from different levels. However, due to semantic and positional misalignment across spatial locations, directly summing features from different levels may lead to feature confusion and degraded representation quality [38]. To address these issues, we introduce a feature alignment (FA) mechanism to mitigate semantic gaps and spatial misalignment in the feature fusion process.
The FA consists of two core components: template matching and offset learning. Template matching is a technique that uses prior patterns to compute similarity for localization or classification. In our case, we perform template matching without explicit priors by generating both the template set and the source features via convolutional layers. The overall template matching procedure is illustrated in Figure 2. Specifically, we first extract candidate patterns (templates) and then learn the similarity distribution between the upsampled features and each template using a convolution. A softmax operation is applied to normalize the response map, producing the probability distribution over different templates. The upsampled feature is then matched with each template according to the learned probability weights, ensuring high correlation between the fused feature and the most relevant patterns. This mechanism effectively reduces feature confusion caused by mismatched semantics during fusion.
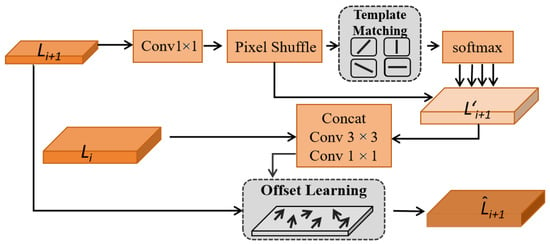
Figure 2.
Architecture of feature alignment (FA) module, which consists of template matching and offset learning to align multi-scale features across levels.
The purpose of introducing FA is to improve the alignment accuracy of multi-scale features so that representations at different levels can be better spatially and semantically integrated. This contributes to enhanced overall feature expressiveness.
The process of template matching is defined by the following equations:
where C is the number of output channels, is the upsampled low-resolution feature map, and y represents the combination of the upsampled feature and the template pattern. denotes the upsampled feature map, is the matching pattern, and ⊗ indicates channel-wise multiplication.
In conventional fusion, feature summation is performed without considering spatial misalignment. To address this issue, we employ an offset learning strategy to adaptively align the spatial locations of features and before fusion. Specifically, the upsampled features and their corresponding templates are concatenated and passed through a sub-network consisting of a convolution followed by a convolution to learn the displacement fields. The offset learning is formulated as
where is the ReLU activation function and denotes batch normalization. The learned offset is used to align each spatial location in the low-resolution feature map to the corresponding location in the high-resolution feature map. After template matching and offset learning, using the alignment function [39], can be aligned with . The aligned feature of can be calculated as follows:
where is the alignment function using a spatial transformer [39].
(3) Semantic Encoder (SE).
Directly adding two signals of different frequencies can result in aliasing artifacts. In the context of Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs), feature fusion is typically performed by combining low-level features with upsampled high-level features, followed by additional convolutional layers to suppress aliasing. However, in classical signal processing, anti-aliasing filters are used to remove aliasing before sampling [40]. In contrast, applying convolutions after fusion introduces redundant computation, while the features remain misaligned before fusion. As a result, fusing inconsistent feature distributions may still lead to aliasing.
To effectively address this issue, we propose a technical semantic encoder (SE) that performs frequency-domain normalization of the fused features before fusion takes place. The SE aims to reduce the impact of aliasing by aligning the statistical distribution of features at different levels. It is designed with a shared-weight mechanism and a lightweight residual structure to learn consistent semantic representations efficiently.
As illustrated in Figure 3, for each pair of low-level and upsampled features to be fused, we apply two SE blocks (with shared weights) to normalize their distributions prior to fusion. Each SE block consists of a residual path that includes one convolution and two convolutions, followed by a nonlinear activation function. This structure enhances semantic consistency between the inputs and enables unified representation learning.
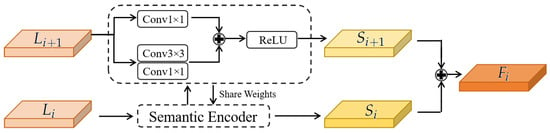
Figure 3.
Architecture of the semantic encoder (SE) module. It captures and aligns contextual features from adjacent scales via weight-sharing convolutional blocks to enhance semantic consistency.
This design significantly reduces aliasing effects and improves the quality of multi-scale feature fusion. By standardizing the frequency-domain distribution of the input features, the SE module maintains alignment between bottom and top features, thereby enhancing the accuracy of lane detection. The mathematical formulation of the semantic encoder (SE) is given by
where denotes the output of the SE. The channel number and spatial size of are consistent with the input , i.e., . After obtaining the SE-encoded features , multi-level features are fused and then passed into the subsequent cross-layer refinement module. The fusion strategy is described as
Here, ⊕ represents element-wise addition. The resulting feature map maintains the same size as the original FPN feature map, which helps preserve the model’s scale and facilitates embedding into the subsequent baseline architecture, ensuring dimensional compatibility during refinement.
In our design, SE learns channel-wise weights and biases that suppress checkerboard artifacts and reinforce meaningful patterns. By smoothing high-frequency noise prior to fusion, SE produces cleaner merged maps. In summary, each pyramid level is processed by SE to yield refined features, which are then combined, and this yields the final output that is rich in semantic content and free of aliasing artifacts.
3.2.2. Cross-Layer Refinement (CLR) Module
The cross-layer refinement (CLR) module takes the fused multi-scale feature map and produces the final lane detections. In reference to CLRNet [16], a line-anchor approach is adopted: a lane line can be represented as a sequence of points along the y-axis, with the fixed pixel intervals for sampling the x-axis. Each anchor X is represented by a sequence of N points . These anchors are subsequently refined using a cross-layer refinement block. The refinement process uses the fused feature maps and anchors as input and applies ROIAlign [41] to extract more precise local features.
Due to the varying spatial dimensions of the feature maps, it is necessary to resize and flatten the anchors to align with the feature maps. We sample evenly-spaced points along the anchor and use bilinear interpolation to obtain the corresponding feature vectors. This yields a pooled feature tensor for the anchor. After ROIAlign, a combination of convolution and fully connected operations is used to align the dimensions and shape with the feature maps. To gather the global context information, the attention matrix M is computed between the lane prior feature and the global feature map as follows:
where C is the number of feature channels, and is a normalization function such as softmax. The attention-weighted aggregated feature matrix T is then computed by
Finally, the refined anchor representation is obtained by adding T back to .
Through RoIAlign and anchor regression, CLR progressively improves the coarse lane proposals using multi-scale context. In summary, the cross-layer refinement module refines lanes by (1) pooling multi-scale fused features with RoIAlign for each anchor, and (2) applying an anchor-based regression head to predict fine offsets. This two-stage strategy, coarse localization followed by detailed refinement, leverages high-level semantics and low-level geometry simultaneously, yielding accurate lane detection with high precision and real-time efficiency.
In this CLR module, a lightweight attention mechanism is employed. Unlike traditional self-attention modules, which suffer from quadratic time and space complexity, our approach mitigates this issue by utilizing channel-wise attention. This design choice not only preserves high accuracy but also ensures that the model remains efficient, capable of real-time lane detection with minimal computational cost.
3.2.3. Lane IoU Loss (LaneIoU)
To analyze the baseline LIoULoss, it is important to note that the original LIoU does not dynamically adapt to the true positions of inclined or curved lanes. It treats lanes in both curved and straight regions with the same static spatial extension, which can cause misalignment, especially at turns. To address this limitation, Honda et al. [14] proposed LaneIoU, which dynamically adjusts the target region based on the geometric orientation of the lane.
In this study, we adopted the LaneIoU concept to further optimize the LIoULoss used in our framework. The key difference between LaneIoU and the original LIoULoss lies in the dynamic extension strategy. Instead of using a fixed number of pixels defined by the dataset to extend the lane line, LaneIoU calculates the adaptive extension region based on the local orientation angle of the lane, as shown in the following equation:
Here, and represent the horizontal and vertical distances between adjacent points on the ground truth lane, and denotes the adaptive extension distance for each point.
In our training process, we employed a hybrid loss function composed of three components: a classification loss and two regression losses—one corresponds to the regression loss for the starting position, orientation, and length, and another . The proposed by Zheng et al. [16] is further improved in this work by incorporating the orientation of the lane lines during regression. The overall loss function is defined as follows:
where , , and are hyperparameters that balance the contributions of each loss term. During training, the model produces detection results from each layer through the cost function, which are then fed into the loss function to optimize the network. During testing, only the detection results from the final layer are output.
4. Experiment and Analysis
In this section, we describe our experiments, which were conducted on a publicly available and challenging dataset of lane detection to validate the proposed Info-FPNet.
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. CULane Dataset
The CULane dataset is a well-known and widely used benchmark for lane detection, originally introduced in the SCNN framework [22]. It consists of a total of 133,235 frames extracted from over 55 h of driving videos. The dataset encompasses nine challenging scenarios, namely normal, crowded, dazzle light, shadow, no line, arrow, curve, crossroad, and night. Among the total samples, 88,800 images are used for training, 9675 for validation, and 34,680 for testing. The test set covers the nine aforementioned categories. All images are resized to 1640 × 590 pixels. A predicted point is considered correct if it lies within 30 pixels of the corresponding annotated point [42]. A predicted lane is counted as a true positive (TP) if more than 50% of its predicted points match the ground truth. The proportion of each category in this challenging test set is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Proportion of each challenging scenario category on the CULane test set.
4.1.2. TuSimple Dataset
The TuSimple dataset is a widely adopted benchmark for evaluating lane detection algorithms, comprising 6408 high-resolution images (1280 × 720 pixels) collected from U.S. highway scenarios under diverse traffic and weather conditions. The dataset is split into 3268 images for training, 358 for validation, and 2782 for testing. Each image captures structured road environments, typically with multiple visible lane markings, making it particularly suitable for assessing lane detection performance in relatively standardized settings.
Following the evaluation protocol proposed in the CondLane method [26], ground truth lanes are represented as 20-pixel-wide lines. A predicted lane point is considered correct if it falls within the 20-pixel bandwidth of the annotated ground truth. A lane prediction is defined as a true positive (TP) if at least 85% of its predicted points are correctly matched to ground truth annotations. This criterion emphasizes both spatial precision and lane completeness, providing a reliable basis for assessing the robustness and accuracy of lane detection models.
4.1.3. Evaluation Metrics
To compare the performance of our method with state-of-the-art competitors on the TuSimple and CULane datasets, we adopt two widely used evaluation metrics in lane detection: accuracy and F1 score. Accuracy is the official evaluation metric for both the TuSimple and CULane benchmarks, as outlined in the respective studies. Following the approach in [22], we used the F1 score in our experiments, which is the harmonic mean of precision and recall. The F1 score is widely regarded as a reliable metric for evaluating model performance, as it balances both the precision of positive predictions and the model’s ability to recall all relevant instances. These metrics are computed as follows:
In the context of lane detection, precision (P) and recall (R) are two fundamental metrics used to evaluate the performance of detection models. Precision (P) measures the proportion of correctly predicted lane points among all points predicted as lane markings. Recall (R) measures the proportion of ground truth lane points that are successfully detected by the model. The F1 score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall to provide a more comprehensive evaluation, making it particularly suitable in scenarios where class label distributions are imbalanced. The F1 score is calculated as follows:
where P and R denote the precision and recall, respectively. P and R are calculated as follows:
where , , and denote the number of true positive, false positive, and false negatives, respectively.
Accuracy is defined as the ratio of correctly predicted instances to the total number of samples in the dataset. The lane detection accuracy is then calculated using the following formula:
This metric jointly evaluates both the precision and recall aspects of lane prediction, reflecting the model’s capability to correctly detect and localize lane markings.
4.2. Implementation Details
All experiments were conducted using PyTorch 1.8 with CUDA 11.2 on an Ubuntu 20.04 system equipped with an NVIDIA RTX 3080 GPU. All input images were uniformly resized to 320 × 800 pixels for both training and inference to ensure computational efficiency and consistency across datasets.
To improve the model’s generalization under diverse environmental conditions, especially under varying illumination, we employed a series of data augmentation techniques inspired by Zheng et al. [16]. These augmentations include random affine transformations such as translation, rotation (within ±10 degrees), and scaling (with random factors ranging from 0.8 to 1.2), as well as random horizontal flipping and random brightness perturbations within the range of . Such augmentations significantly enhance the model’s robustness, particularly in low-light conditions like nighttime driving scenes, by simulating a variety of real-world appearances.
The model utilizes 72 anchors to represent candidate lane positions across the image width. Vertical sampling is applied for lane representation and loss calculation, and it is dataset-specific. For the CULane dataset, training was conducted over 30 epochs with a batch size of 24. Vertical coordinates were sampled from 589 to 230 pixels at 20-pixel intervals. The loss weights were set as follows: classification loss , lane IoU loss , and coordinate regression loss .
For the TuSimple dataset, training was performed over 70 epochs with a batch size of 40. Vertical sampling was conducted from 710 to 150 pixels at 10-pixel intervals. The corresponding loss weights were , , and . These weights were empirically determined to balance learning stability and convergence speed. To avoid gradient explosion during training with the composite loss function, normalization techniques and appropriate weighting strategies were applied.
During optimization, we employed the AdamW optimizer with gradient clipping, normalized loss weighting, and an initial learning rate of [43]. The learning rate was decayed using a cosine annealing schedule with a decay factor of 0.9 [44].
4.3. Ablation Study
To comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness of each proposed component—informative feature pyramid (IFP), cross-layer refinement (CLR), and LaneIoU loss mechanisms—we conducted detailed ablation experiments. The results are summarized in Table 2, demonstrating the incremental and complementary contributions of each module toward enhancing lane detection performance.

Table 2.
Ablation analysis was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the IFP module, CLR module, and LaneIoU. The bold number is the best result. The symbol ✓ indicates that the corresponding module is enabled in the configuration.
First, starting from a baseline model that uses only the standard feature pyramid (FP), we observe a baseline F1 score of 78.27%. When the CLR module is incorporated, the performance increases significantly to 79.73%, highlighting its effectiveness in improving cross-layer feature alignment and semantic fusion. Further adding LaneIoU loss to this configuration yields a modest gain, raising the F1 score to 79.88%, indicating the value of geometrically aware optimization for handling lane curvature and variability.
Replacing the conventional FP with our proposed IFP module alone results in a score of 79.56%, suggesting that IFP is more effective at extracting informative multi-scale representations. When IFP is combined with CLR, the score improves further to 79.84%, reinforcing the complementary nature of cross-layer refinement in enhancing IFP-generated features. Finally, the full integration of IFP + CLR + LaneIoU achieves the highest F1 score of 80.31%, confirming the synergistic benefit of combining all three modules.
In summary, the ablation results clearly validate the individual contributions and collective synergy of the IFP, CLR, and LaneIoU components. By enhancing hierarchical feature representation, improving cross-layer information flow, and optimizing the loss function for geometric consistency, the proposed Info-FPNet framework achieves superior accuracy and robustness, particularly under complex and challenging driving scenarios.
4.4. Experimental Comparison with State-of-the-Arts Methods
4.4.1. Performance on CULane Dataset
As presented in Table 3, our method achieves superior performance across most challenging scenarios on the CULane dataset using ResNet-34 as the backbone. Notably, our approach obtains the highest F1 scores in several key categories, including Normal (94.04%), Shadow (82.56%), Arrow (90.94%), and Curve (75.83%), which are considered among the difficult conditions for lane detection. The substantial improvement in the Shadow category particularly highlights the effectiveness of the proposed Informative Feature Pyramid Network (Info-FPNet) in enhancing feature alignment and robustness under low illumination and partial occlusion. In addition, our approach also achieves competitive results in other challenging categories, ranking second in Dazzle Light (75.14%), No Line (54.69%), and Night (75.43%), further validating the generalization capability of our method under extreme visibility degradation and weak structural cues.

Table 3.
Comparative experimental results in challenging scenarios on CULane dataset. The best results are highlighted in bold. The second-best results are underlined. “-” indicates that results are not available.
Further comparison in Table 4 shows that our method achieves the second-best overall F1 score of 80.31%, closely approaching the best-performing GSENet (80.58%) while outperforming all other baseline methods, including strong competitors such as P-FPN (79.94%), CLRNet (79.73%), and CondLane (78.74%). Although methods such as LaneATT achieve a higher inference speed (171 FPS), they suffer from a significantly lower accuracy (F1 score: 76.68%). In contrast, our approach strikes a favorable balance between accuracy and efficiency, delivering near state-of-the-art performance with a competitive inference speed of 98 FPS. This makes our method well-suited for real-time deployment in practical lane detection applications, where both precision and responsiveness are essential.

Table 4.
Comparative experimental results of adopting different backbones on the CULane dataset. The best results are highlighted in bold. The second-best results are underlined. “-” indicates that results are not available.
These results confirm the effectiveness of our proposed Info-FPNet approach, which enhances feature representation across scales, and the complementary cross-layer refinement mechanism, which further boosts the model’s ability to capture fine-grained lane details in complex driving environments.
4.4.2. Performance on TuSimple Dataset
To comprehensively evaluate the performance and generalization capability of the proposed method, we conducted experiments on the TuSimple dataset, a widely used benchmark for lane detection that focuses on highway scenarios with clear lane markings. The results are reported using two standard metrics: F1 score and Accuracy, as defined in the TuSimple evaluation protocol.
Table 5 presents a comparative analysis of our proposed Info-FPNet method against existing state-of-the-art lane detection approaches, including SCNN [22], RESA [42], LaneATT [25], LSTR [51], CondLaneNet [26], CLRNet [16], P-FPN [15], GSENet [48], TBISA [49], and MHFS-Former [50], under identical experimental settings with different backbone networks (ResNet-18/34/101). Our method consistently achieves superior performance across all three backbone configurations. Specifically, when using ResNet18, our method achieves an F1 score of 98.07% and the highest accuracy of 96.96%, outperforming all other competitors, including P-FPN (F1 score 98.01%, accuracy 96.91%) and GSENet (F1 score 97.98%, accuracy 96.82%). With ResNet34 as the backbone, our method achieves an accuracy of 96.94% and an F1 score of 97.94%, matching the best-performing baseline GSENet. This result highlights the robustness of our approach in preserving lane-level prediction consistency, even under challenging scenarios. Moreover, when using the deeper ResNet101 backbone, our method continues to deliver strong performance with an F1 score of 97.76% and an accuracy of 96.91%, maintaining competitive results against state-of-the-art methods.

Table 5.
Comparative experimental results of adopting different backbones on the Tusimple dataset. The best results are highlighted in bold. The second-best results are underlined. “-” indicates that results are not available.
These results clearly indicate that the proposed method effectively captures lane structures and maintains high prediction precision even under various backbone settings. The consistent improvement across both F1 score and accuracy demonstrates the effectiveness of our information-guided fusion and alignment mechanisms and highlights the general applicability of our framework for real-world lane detection tasks.
4.5. Efficiency Analysis
We conducted an analysis of the model’s computational efficiency by comparing the parameter count with and without the CLR module. The CLR module increases the parameter count by 1.3 M, leading to a total of 12.1 M parameters. To further assess the computational efficiency of the proposed method, the standard evaluation metric of Giga Floating-Point Operations Per second (GFLOPs) was adopted in the experiments. The results are summarized in Table 6. As shown, the model with CLR achieves 21.9 GFLOPs on average, maintaining competitive performance compared to other state-of-the-art lane detection models, such as LaneAF (GFLOPs: 22.2), RESA (GFLOPs: 41.0), LaneATT (GFLOPs: 18.0), and CondLane (GFLOPs: 19.6), etc. These results confirm that the proposed framework maintains a strong balance between detection accuracy and computational cost, making it suitable for real-time applications in autonomous driving scenarios. Despite the increase in parameters, the model remains lightweight and efficient, allowing for fast inference while maintaining high detection accuracy.

Table 6.
Comparative experimental results of computational efficiency on CULane dataset. The best results are highlighted in bold. The second-best results are underlined.
4.6. Qualitative Results Analysis
To evaluate the performance of our method, we present qualitative comparisons of different methods under five representative challenging scenarios in the CULane dataset, including nighttime with streetlights, nighttime without streetlights, strong light reflection, occlusion, and degraded lane markings. The visualization comparison results of our approach against four representative methods: RESA [42], LaneATT [25], CondLane [26], and CLRNet [16] are illustrated in Figure 4. It can be seen that the proposed method consistently outperforms the methods under these adverse conditions.

Figure 4.
Visualization comparison results of different methods under extremely challenging environmental conditions. The blue lines represent the predicted lane markings.
In the first row, corresponding to nighttime scenes with streetlights, the RESA method shows unstable and fragmented lane predictions, often missing sections of lane lines. LaneATT, CondLane, and CLRNet perform relatively well, detecting continuous lane lines, while our method achieves the most stable and uniform results across the entire lane structure.
In the second row, which presents a more challenging case of nighttime without streetlights, all baseline methods (RESA, LaneATT, CondLane, and CLRNet) struggle to identify the rightmost lane line due to poor illumination and weak contrast. In contrast, our method successfully detects and localizes the full set of lane lines, including the faint rightmost one, demonstrating superior robustness under extremely low-light conditions.
In the third row, depicting scenarios with strong light reflection, RESA continues to suffer from severe detection distortion, and LaneATT fails to capture the leftmost lane line. Although CondLane and CLRNet offer slightly improved performance, their results are still incomplete. Our model maintains accurate and full-lane predictions, clearly showing its ability to overcome light-induced artifacts and preserve detection integrity.
In the fourth row, showing occlusion caused by vehicles and person, RESA and LaneATT fail to capture the rightmost occlusion lane line. CondLane and CLRNet perform better, but the accuracy of occluded line detection is not high. Our model demonstrates strong continuity in detection, accurately inferring occluded portions of the lanes based on contextual information.
In the fifth row, which involves degraded or faded lane markings, all baseline methods exhibit varying degrees of failure, either missing lines entirely or providing fragmented outputs. Our method outperforms them by preserving the lane structure even when the visual cues are weak or partially missing, highlighting its superior semantic understanding and robustness.
These qualitative comparisons clearly demonstrate the advantages of our proposed method in handling diverse and complex real-world driving scenarios. By effectively addressing various sources of visual degradation, our model ensures reliable lane detection performance under conditions where traditional and prior deep-learning methods tend to fail.
To further validate the effectiveness of the proposed cross-layer refinement (CLR) module, we conducted a heatmap-based visualization experiment to compare lane localization results with and without the CLR module. As shown in Figure 5, the original input image is presented alongside two corresponding heatmaps: one generated by the complete model incorporating CLR, and the other produced by the model without CLR. For both heatmaps, the four lanes with the highest confidence scores are selected as the output of lane detection. The point density of all predicted lane points from predefined anchors falling on these four lanes is aggregated and visualized as a heatmap, where regions in red correspond to areas with high point density. The heatmap with CLR demonstrates significantly sharper, more continuous, and denser activations along the lane regions, indicating improved spatial localization and enhanced semantic focus. In contrast, the model without CLR yields more diffuse and fragmented responses, reflecting weaker feature alignment and reduced localization accuracy. These visual comparisons further corroborate the CLR module’s contribution to refining feature representations and boosting detection robustness under complex visual conditions.

Figure 5.
Visualization comparison of lane detection with and without CLR module. From left to right: the input image, prediction with CLR module, and prediction without CLR module. It shows the lane point density of all lane points predicted by predefined anchors that fall on the four lanes with the highest confidence scores. Regions in red correspond to areas with high point density.
5. Conclusions
In this work, a robust and efficient lane detection framework, Info-FPNet, is proposed to address the limitations of existing FPN-based methods in complex driving environments. The proposed framework integrates two key components: the informative feature pyramid (IFP) module and the cross-layer refinement (CLR) module. The IFP module selectively aggregates spatially and semantically informative features across multiple scales, thereby enhancing multi-scale feature representation. Meanwhile, the CLR module refines coarse lane predictions by leveraging region-wise attention and anchor-based regression to facilitate accurate localization. Extensive experiments on the CULane and TuSimple datasets demonstrate that our method achieves good performance while maintaining real-time inference speed, highlighting its balance between accuracy and efficiency. The model also exhibits strong robustness in challenging visual conditions such as nighttime, strong light reflection, and occlusion, etc.
In summary, the proposed Info-FPNet delivers a strong balance of accuracy, efficiency, and robustness, outperforming prior methods in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations. Despite these strengths, the current approach still faces limitations. Its performance under cross-domain conditions, such as unseen road topologies or weather variations, remains to be thoroughly validated. The current anchor-based design, although effective, may limit flexibility. Anchor-based methods typically rely on pre-defined anchor points aligned vertically or horizontally in image space. However, such designs struggle to accurately model curved lanes or sharply turning trajectories, especially when the ground truth deviates significantly from the anchor priors. This leads to a mismatch in localization, and potentially missed detections in non-linear lane regions.
Future work will focus on exploring domain generalization techniques to improve adaptability and robustness. We also plan to investigate anchor-free or graph-based lane representations to overcome structural rigidity and better model topological lane relationships. Furthermore, while current datasets use fixed input resolutions, exploring the inference stability of the proposed method under varying image sizes will be a promising direction for future work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Project of Air-Ground Cooperative Intelligent Application R&D Center (Grant 602331001PQ), Shenzhen Polytechnic University Project (Grant 6022310032K, 6023310032K), Opening Foundation of State Key Laboa tory of Cognitive Intelligence, iFLYTEK (Grant COGOS-2023HE07), and Educational Commission of Guangdong Province (Grant 2023ZDZX1082).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Stiller, C.; Urtasun, R. Vision meets robotics: The kitti dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Formosa, N.; Hossain, M.; Quddus, M. Advancements in lane marking detection: An extensive evaluation of current methods and future research direction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Liu, J.L. End-to-end deep learning of lane detection and path prediction for real-time autonomous driving. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, D. Lane detection techniques: A review. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 112, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bar Hillel, A.; Lerner, R.; Levi, D.; Raz, G. Recent progress in road and lane detection: A survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, P. A review of lane detection methods based on deep learning. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 111, 107623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kim, K. Simultaneous traffic sign detection and boundary estimation using convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Jiang, H.; Dai, Q.; Yue, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q. Robust lane detection from continuous driving scenes using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 69, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Murthy, L.; Mukherjee, I.; Biswas, P. A hybrid lane detection model for wild road conditions. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddiralla, V.; Subramanian, S. Effective lane detection on complex roads with convolutional attention mechanism in autonomous vehicles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, W. Lane-GAN: A robust lane detection network for driver assistance system in high speed and complex road conditions. Micromachines 2022, 13, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Quan, S.; Dai, Z.; Yan, W. Lane Detection for Autonomous Driving: Comprehensive Reviews, Current Challenges, and Future Predictions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 5710–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, H.; Uchida, Y. Clrernet: Improving confidence of lane detection with laneiou. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 1176–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, J.; Lian, G.; Wu, J.; Ge, S.; Yang, J. Proportional feature pyramid network based on weight fusion for lane detection. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Cai, D.; He, X. CLRNet: Cross Layer Refinement Network for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, R.; Zhang, L.; Xue, Y. Info-FPN: An informative feature pyramid network for object detection in remote sensing images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 214, 119132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; He, L.; Han, B.; Li, J.; Gao, X. ProFPN: Progressive feature pyramid network with soft proposal assignment for object detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 299, 112078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Fu, X.; Dong, J.; Qin, R.; Chang, J.; Lang, P. SAR ship detection based on end-to-end morphological feature pyramid network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2022, 15, 4599–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminuddin, N.S.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Ali, N.M.; Radzi, S.A.; Saad, W.H.M.; Darsono, A.M. A new approach to highway lane detection by using Hough transform technique. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2017, 16, 244–260. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, M. Real time detection of lane markers in urban streets. In Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 4–6 June 2008; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Spatial as deep: Spatial cnn for traffic scene understanding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning lightweight lane detection cnns by self attention distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1013–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, X. Ultra fast deep lane detection with hybrid anchor driven ordinal classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 46, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixao, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Keep your Eyes on the Lane: Real-time Attention-guided Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Tan, P. Condlanenet: A top-to-down lane detection framework based on conditional convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3773–3782. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Ultra fast structure-aware deep lane detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 276–291. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Deng, X.; Cai, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Xu, C.; Liang, X. Laneformer: Object-aware Row-Column Transformers for Lane Detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 799–807. [Google Scholar]
- Neven, D.; De Brabandere, B.; Georgoulis, S.; Proesmans, M.; Van Gool, L. Towards end-to-end lane detection: An instance segmentation approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, China, 26–30 June 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, A.; Chitta, K.; Geiger, A. Multi-modal fusion transformer for end-to-end autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 7077–7087. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Shi, B.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Li, Y. Multi-modal sensor fusion for auto driving perception: A survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.02703. [Google Scholar]
- Kotseruba, I.; Tsotsos, J.K. Attention for vision-based assistive and automated driving: A review of algorithms and datasets. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 19907–19928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.; Che, S.; Zhou, S.; Guo, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. LHFFNet: A hybrid feature fusion method for lane detection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Han, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, C. IFPNet: Integrated feature pyramid network with fusion factor for lane detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 1888–1897. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J. Detect Lane Line Based on Bi-directional Feature Pyramid Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning and Intelligent Systems Engineering (MLISE), Guangzhou, China, 5–7 August 2022; pp. 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, T.S.; Shi, H. Alignseg: Feature-aligned segmentation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, A.; Fennessy, P. Digital Imaging for Photographers; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, T.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Shi, J. Foveabox: Beyound anchor-based object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7389–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cai, D. Resa: Recurrent feature-shift aggregator for lane detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3547–3554. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualsaud, H.; Liu, S.; Lu, D.B.; Situ, K.; Rangesh, A.; Trivedi, M.M. Laneaf: Robust multi-lane detection with affinity fields. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7477–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, W. Focus on local: Detecting lane marker from bottom up via key point. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14122–14130. [Google Scholar]
- Morley, M.; Atkinson, R.; Savić, D.; Walters, G. GAnet: Genetic algorithm platform for pipe network optimisation. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2001, 32, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Chen, Z.; He, C.; Guan, D.; Cai, C.; Zhou, T.; Wei, J.; Tian, W.; Xie, Z. Gsenet: Global semantic enhancement network for lane detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 15108–15116. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Luo, Z.; Zha, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y. End-to-End Lane Detection: A Two-Branch Instance Segmentation Approach. Electronics 2025, 14, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Zhang, T. MHFS-FORMER: Multiple-Scale Hybrid Features Transformer for Lane Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, T.; Xiong, Z. End-to-end lane shape prediction with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3694–3702. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).