Abstract
Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced the effectiveness of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. This study focuses on the development and evaluation of a domain-specific AI chatbot designed to support international student admissions by leveraging LLM-based RAG pipelines. We implement and compare multiple pipeline configurations, combining retrieval methods (e.g., Dense, MMR, Hybrid), chunking strategies (e.g., Semantic, Recursive), and both open-source and commercial LLMs. Dual evaluation datasets of LLM-generated and human-tagged QA sets are used to measure answer relevancy, faithfulness, context precision, and recall, alongside heuristic NLP metrics. Furthermore, latency analysis across different RAG stages is conducted to assess deployment feasibility in real-world educational environments. Results show that well-optimized open-source RAG pipelines can offer comparable performance to GPT-4o while maintaining scalability and cost-efficiency. These findings suggest that the proposed chatbot system can provide a practical and technically sound solution for international student services in resource-constrained academic institutions.
1. Introduction
In modern universities, students often face difficulties in understanding the rules and procedures related to course registration and graduate admissions. The information is typically scattered across multiple documents and platforms, making it challenging to locate and comprehend. This problem is especially critical for international students unfamiliar with the academic system and language barriers. Furthermore, administrative staff are burdened with answering repetitive questions, leading to inefficiencies in student support services. Automating this process through an AI-powered chatbot can enhance the accessibility of information, improve support efficiency, and reduce staff workload [1].
Several prior studies have attempted to address this issue through rule-based systems and fixed FAQ-style bots [2,3,4]. While these systems can respond to predefined queries, they often fail to handle variations in question phrasing and cannot adapt to new or unseen questions. Recent developments in large language models (LLMs) have introduced more flexible capabilities for question answering. However, many existing studies apply LLMs without proper retrieval mechanisms or evaluation strategies, which leads to unreliable or hallucinated answers [5,6].
To overcome these challenges, the field has increasingly adopted Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approaches. RAG combines LLMs with retrieval modules that fetch relevant context from external knowledge sources before generating a response [5]. State-of-the-art (SOTA) RAG papers often propose new modules or modify the existing RAG structure, such as a new retriever, a new fusion technique, a reranker, or a generation method [7,8,9,10,11,12]. These existing RAG-related studies have proven effective in general benchmarks or broad domains, but there is a relative lack of practicality verification and application cases in actual specific domains (education domain, college admission support) [13,14,15,16,17,18]. In particular, there are many technical factors to consider in domain-specific Q&A, such as the diversity of user questions, original text–question linkage, and real-time processing (latency). However, existing studies are biased toward benchmarks/automatic evaluations and lack precise evaluations using actual user interests (actual questions) or human-tagged datasets [19,20,21,22,23,24].
Based on recent advances in RAG technology, this study applies the RAG system to the college admission Q&A domain and performs multi-faceted performance evaluations and latency measurements using LLM-generated and human-tagged QA sets for various model/pipeline combinations. Through this, we aim to verify whether the open source LLM-based system can be a practical alternative to actual services.
This study has three contributions:
- Domain-specific RAG application and evaluation: By applying RAG technology to the real and new (under-explored) domain of graduate school admissions, we developed a chatbot that solves the problem of fragmented information access in the graduate school admissions process. While many RAG papers are focused on “Benchmarks” and lack real service scenario-based evaluations, this study builds a college admissions Q&A specialized dataset to verify the feasibility of practical use through real-world performance comparison and evaluation.
- Evaluation refinement: We systematically experiment with various RAG pipelines with various RAG sub-technologies (commercial LLM/open-source LLM, Splitter, Retriever combinations, etc.) and precisely compare their performances. Unlike previous studies [25] that relied only on qualitative feedback, this study introduced a dual evaluation method that uses both LLM generation and human-tagged answer sets. For two sets of answers, the system is evaluated using the performance metrics of the RAG pipeline (answer relevance, fidelity, context recall, and context accuracy) and heuristic natural language processing metrics (ROUGE, BLEU, METEOR, and SemScore). The results provide insights into real-world environments by comparing the evaluation results for two sets of answers, as well as which search and generation combination generates the highest quality answers.
- Deploy ability analysis from a real-use perspective: This system utilizes both proprietary and open-source models to balance performance and latency. We experimentally evaluate the system using a combination of different search engines and chunking strategies and show that the open-source model can match or surpass the performance of commercial LLMs such as GPT-4o when properly optimized. To examine the efficiency of the system, we measure the response time of each RAG stage at the pipeline level and compare and analyze it on a dataset-by-dataset basis. Then, we compare and evaluate the accuracy based on RAG answer quality and the system efficiency based on latency. We address that although the open source LLM optimization can replace the commercial model in terms of answer quality, there is a trade-off with the efficiency for each open-source specialized model. This provides useful information for practical choices for public institutions with limited budget and computing resources, including national universities and international student support centers. Finally, by suggesting the applicability and limitations in real-world settings and improvement strategies for future research, this study provides a scalable and adaptable solution for educational institutions seeking to improve digital support services for international applicants.
2. Materials and Methods
The overall architecture of the chatbot system is based on a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline implemented in Python using LangChain and FAISS. The system combines document retrieval and large language model (LLM) generation to deliver accurate and context-aware responses (Figure 1).
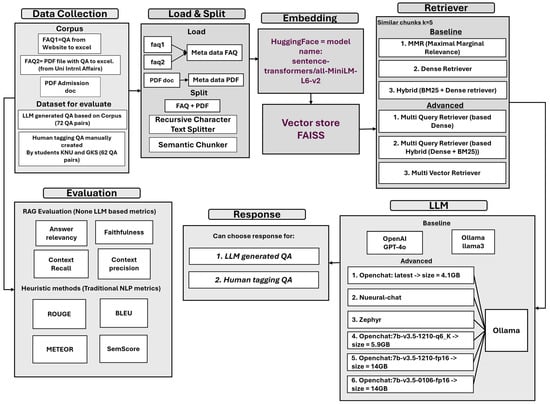
Figure 1.
System architecture of the chatbot.
Institutional documents were first split into manageable textual segments using two methods: Recursive Character Split and Semantic Chunking. Both Semantic Chunking and Recursive Character Split were applied across all datasets (PDF and FAQs). Each chunking method was tested using the same retrieval settings in order to compare their impact on system performance. This experimental design allowed for a systematic evaluation of how each chunking method interacts with various retrieval strategies.
Text segments were then embedded using the all-MiniLM-L6-v2 model from the SentenceTransformers library, producing 384-dimensional dense vector representations. These vectors were stored in a FAISS index configured to use cosine similarity with a top-k setting of 5 for retrieval. At inference time, multiple retrieval strategies were explored, including Dense Retrieval, Maximal Marginal Relevance (MMR), Hybrid Retrieval (BM25 + Dense), MultiQueryRetriever, and MultiVectorRetriever. The system supports both commercial and open-source LLMs. GPT-4o was accessed through the OpenAI API, while open-source models such as OpenChat and LLaMA3 were deployed locally via the Ollama platform. All processing was performed on a local machine equipped with GPU acceleration when available. The design enables modular experimentation with different retrieval and generation components for systematic evaluation.
The main development and execution environments are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Development environment.
- i.
- Dataset collection
This study uses three primary data sources provided by Kongju National University: (1) a PDF-based graduate admission guide (29 pages), (2) a set of 38 FAQs extracted from the university website (FAQ1), and (3) 11 additional admission-related FAQs obtained from the university’s International Affairs Office (FAQ2). These documents contain information about application procedures, eligibility, deadlines, language requirements, and scholarships. Due to institutional policies, these internal documents are not publicly available, but they can be shared upon request for academic purposes.
- ii.
- Load and splitting
After collecting the documents, they were loaded into the system. Each text is labeled with metadata to show its source. FAQ1 and FAQ2 are labeled as “meta data FAQ”, and the PDF is labeled as “meta data PDF”. Then, the texts are split into small parts called chunks, which makes it easier to search for relevant information later. Two chunking methods were used. RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter splits the text based on characters and text structure. Semantic Chunker splits the text based on meaning, trying to keep the logic of each chunk clear and complete.
- iii.
- Embedding and vector store
Each text chunk is converted into a numerical vector. The conversion is performed using a HuggingFace model “sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2” from the Sentence Transformers library [26] which turns the text into a list of numbers (a vector) that captures its meaning. This embedding captures the semantic content of the chunk in a format suitable for dense vector search. The resulting embeddings were stored in a FAISS-based vector store for efficient retrieval.
- vi.
- Retriever
To retrieve the most relevant chunks in response to a query, a variety of retrieval strategies were implemented. Standard retrievers include MMR (Maximal Marginal Relevance), a classical algorithm that promotes diversity while maintaining relevance [27], Dense Retriever, based on vector similarity, commonly adopted in dense passage retrieval (DPR) frameworks [28] and Hybrid Retriever, combining sparse retrieval (BM25) and dense embeddings, as utilized in the BEIR benchmark [29].
There are also advanced retriever methods which are MultiQuery Retriever (Dense), MultiQuery Retriever (Hybrid), which expand the query using LLM-generated paraphrases. And MultiVector Retriever, which embeds queries into multiple sub-vectors to capture richer semantics [30]. In all cases, the top-k = 5 most relevant chunks were retrieved for downstream processing.
- v.
- Language model (LLM)
After the most relevant chunks are found, they are combined with the user’s question and sent to LLM, which generates the final answer. The system supports both commercial and open-source models. One of them is the GPT-4o from OpenAI [31] which is a powerful paid model. And the second one is Ollama [32]. It is a platform that supports free models such as llama3 [33], OpenChat [34], Zephyr [35] and Neural-chat [36], all of which are publicly available on HuggingFace.
These models differ in size and capabilities (from 4 GB to 14 GB), which allows testing different options and comparing results. The LLM does its best to generate an accurate, helpful, and logically connected answer based on the retrieved context.
- vi.
- Dual Reference QA Datasets
The primary users of this chatbot are prospective students seeking admissions-related information. To evaluate the performance of the RAG system under controlled conditions, we constructed two separate answer datasets: one generated by a large language model (LLM-generated QA) and one manually annotated (Human-tagged QA). For each user question, both datasets were used as reference answers in separate evaluations. This dual-dataset setup enabled a systematic comparison of how different model configurations performed across consistent input queries.
The human-tagged QA dataset consists of 62 manually constructed question–answer (QA) pairs, developed in collaboration with international students at Kongju National University and current Global Korea Scholarship (GKS) scholars. The questions were designed to reflect authentic information needs based on the students’ firsthand experiences and common challenges encountered during the admission process. Each answer was manually written and verified by a research team member, using official documents provided by the university as reference materials, including the Graduate Admissions Guidebook, FAQs, and other relevant institutional resources.
To ensure a structured and balanced evaluation, all 62 QA pairs in the human-tagged dataset, along with the 72 pairs in the LLM-generated dataset, were manually categorized into eleven thematic groups based on topic: language requirements, application deadlines, required documents, application process, scholarships, financial matters, tuition fees, dormitory and application fees, result notifications, contact and support, and other (miscellaneous questions not falling into the above categories). This thematic classification was used to verify topic coverage balance across datasets and ensure consistency during evaluation.
- vii.
- Evaluation
RAGAS [37] metrics such as Answer Relevancy, Faithfulness, Context Recall, Context Precision are specifically designed for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Unlike traditional metrics that rely on a direct match with a reference answer, RAGAS evaluates how well the generated answer aligns with the retrieved context, ensuring the response is grounded and faithful to the source. Classic NLP metrics such as ROUGE [38], BLEU [39], METEOR [40], and BERTScore (SemScore) [41] are added to enable comparison with existing works in text generation and machine translation.
As a baseline, we computed the mean performance for each metric across all QA pairs under each experimental condition. To further assess result variability and reliability, we additionally calculated the standard deviation (SD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for each metric. These statistical measures help interpret whether observed performance differences between configurations are statistically meaningful or potentially due to random variation.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Highlighting RAGAS Metrics
Although both RAGAS and traditional NLP-based metrics were used to evaluate answer quality, the main analysis focuses on RAGAS metrics—faithfulness, answer relevancy, context recall, and context precision. This is because RAGAS is specifically designed for RAG systems, evaluating not just lexical overlaps but the alignment between the generated answer and retrieved context. It provides deeper insight into the internal components of the RAG pipeline, such as retrieval effectiveness and factual grounding, which traditional metrics cannot capture.
While NLP-based metrics are included for comparison (Table 2 and Table 3), they often penalize semantically correct answers that differ in phrasing from the reference. In several experiments, high RAGAS scores coincided with low BLEU or ROUGE, highlighting the limitations of surface-level metrics in this context. Therefore, this study prioritizes RAGAS metrics to more accurately reflect the quality and faithfulness of RAG-generated answers across both LLM-generated and human-tagged QA datasets.

Table 2.
Evaluation of LLM-generated QA dataset: Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.

Table 3.
Evaluation of human-tagged QA dataset: Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.
A strong correlation was observed between the evaluation outcomes of LLM-generated and human-tagged QA datasets across most metrics. In particular, the same top-performing configurations such as Algo-3 (GPT-4o with Hybrid retrieval) and Algo-5 (LLaMA3 with Dense retrieval) consistently ranked highest on both datasets. For instance, Algo-5 yielded high scores on answer relevancy, context recall, and BLEU metrics in both settings (e.g., BLEU: 0.1529 on LLM-generated vs. 0.0352 on human-tagged; answer relevancy: 0.8013 vs. 0.7606), indicating stable effectiveness across evaluation modalities.
Moreover, the relative rankings of pipeline variants such as Algo-1 to Algo-12 showed similar trends between Table 2 and Table 3. Low-performing configurations, such as Algo-6 and Algo-12, performed poorly in both datasets validating that the evaluation protocol is consistent and that the chosen metrics reliably reflect quality differences. This cross-dataset alignment suggests that model-based QA generation and human-authored QA yield comparable insights when assessing pipeline effectiveness.
3.1.1. Comparison Performance and LLMs with LLM-Generated QA Dataset
The results (Table 2) demonstrate that the combination of Semantic Chunking and Dense Retriever consistently yields (Algo-5) the best performance across key RAG metrics—Answer Relevancy—0.8013, Faithfulness—0.8646, Context Recall—0.7153 and Context precision—0.5593. This configuration outperformed Recursive Character Split and all other retrieval strategies, including MMR and Hybrid (BM25 + Dense). While the Hybrid method showed moderate results, especially Algo-6, MMR delivered the lowest scores overall. These findings highlight the importance of semantically meaningful text segmentation and dense vector retrieval in enhancing RAG-based QA quality. OpenAI GPT-4o model consistently outperformed Ollama (LLaMA3) (Algo-5 in Table 2) across all evaluation metrics, including RAGAS and traditional NLP metrics. The best results were achieved using GPT-4o combined with Semantic Chunking and Dense Retriever (Algo-5). The average score of RAGAS metrics was 0.735125. Although Ollama also benefited from the same configuration, its scores remained lower overall (Algo-11). The average score of RAGAS metrics was 0.676175. This confirms that model architecture plays a pivotal role in RAG pipeline performance, with proprietary models currently holding a measurable advantage.
3.1.2. Comparison Performance and LLMs with Human-Tagged QA Dataset
In the human-tagged QA evaluation, the combination of Semantic Chunking and Dense Retriever once again led to the highest scores (Algo-5 in Table 3) in key RAGAS metrics: Answer Relevancy was 0.7606, Faith-fulness—0.8538, Context Recall—0.6306 and Context Precision—0.6549. Compared to other methods, the Dense Retriever consistently delivered strong performance, while Hybrid retrieval showed slightly weaker results in faithfulness (0.0621). The MMR retriever demonstrated the lowest effectiveness across nearly all metrics, confirming its limitations in handling complex, human-written queries. OpenAI GPT-4o model outperformed Ollama (LLaMA3) in all RAGAS and traditional NLP metrics (Algo-5 in Table 3). The best performance was achieved with Semantic Chunking and Dense Retriever in GPT-4o model. The average score of RAGAS metrics was 0.724975 (Algo-5). But when it comes to Ollama-based models, the highest performance of open-source LLaMA3 was observed for Algo-8 (Table 3) reached an average score of 0.6761, which employed Recursive Text Splitter and a Dense Retriever. The results from Table 2 and Table 3 highlight that system performance in RAG-based QA is strongly influenced by three factors: the choice of LLM, the chunking method, and the retrieval strategy. A comparative analysis of the three retrieval strategies: MMR, Dense, and Hybrid (BM25+Dense) reveals that the Dense Retriever consistently outperformed the other methods across all settings. This shows that it can effectively select and prioritize relevant text passages during both LLM-generated QA and human-tagged QA. And Notably, GPT-4o maintained its superiority even in the more challenging human-tagged setting, offering better faithfulness, relevance, and consistency.
Additionally, the LLM-generated QA dataset outperformed the human-tagged dataset across most evaluation metrics. To understand this discrepancy, a manual error analysis was conducted. The analysis revealed that the LLM-generated set is more aligned with model training data and has fewer ambiguous phrasings, leading to higher scores. In contrast, the human-tagged questions often included varied linguistic styles and implicit assumptions, making them more difficult for the system to handle accurately.
3.2. Challenges of Human-Curated QA in Retrieval-Augmented Pipelines
To ensure a structured and fair comparison, all questions from both the LLM-generated and human-tagged QA datasets were manually classified into 11 thematic categories, such as language requirements, application deadlines, required documents, scholarships, and others. For each category, representative question pairs with similar semantics were selected from both datasets and used for manual error analysis, focusing on metrics like faithfulness and answer relevancy. Despite matching by category, the LLM-generated dataset consistently showed higher performance across several groups, indicating that its answers were often more closely aligned with the expected information than those from the human-tagged dataset.
The superior performance of the LLM-generated QA dataset can be largely attributed to the alignment between the source documents and the LLM’s question generation process. Since the model formulated questions directly based on the input dataset, the questions were well-structured. In contrast, the human-made QA dataset reflected students’ real-world concerns, which were often broader or more general in nature and not always directly addressed in the source materials. As a result, retrieved contexts were sometimes incomplete or imprecise, introducing noise into the pipeline and causing a decline in metric scores.
The difference in evaluation results between the LLM-generated QA dataset and the human-tagged QA dataset can be explained by differences in how each dataset is constructed and how the evaluation criteria apply to them. The QA pairs automatically generated by LLMs tend to show strong consistency in language use and sentence structure. They also maintain a highly uniform answer format. In contrast, the human-tagged dataset reflects more diverse vocabulary, sentence construction, and summarization styles, even when expressing the same meaning, leading to more variation and subjectivity.
Specifically, the LLM-generated QA dataset benefits from its structured generation process, where both the question and the answer are created with direct reference to the source document. This results in a strong connection between the QA pair and the original content, along with consistent grammar and formatting. These characteristics often lead to higher scores in both RAG evaluation metrics and traditional NLP metrics.
On the other hand, the human-tagged dataset reflects the real concerns of students and includes questions that are often broader or not directly tied to the original source material. As a result, the retrieval pipeline struggles to find accurate matching contexts, leading to incomplete or mismatched outputs. This increases noise and lowers scores across multiple evaluation metrics. Additionally, due to the diversity in language and subjective answer formatting, even semantically correct answers may receive lower numeric scores.
In summary, consistency in answer selection, structured sentence formation, and strong linkages between questions and source documents are key factors that influence evaluation outcomes. These elements are closely tied to the dataset type and must be considered when interpreting evaluation results. Therefore, future work involving LLM-generated QA data or real human-tagged datasets should take these differences into account and make efforts to improve the accuracy and consistency of the evaluation process to ensure more reliable results.
3.3. Measuring Latency of GPT-4o and LLAMA3
To assess real-world applicability, latency experiments were conducted under the system configuration shown in Table 4. Latency was measured at three RAG stages: embedding, retrieval, and generation. The total latency represents the sum of these components, with results averaging over each algorithm.

Table 4.
Environment details for latency measurements.
Table 5 and Table 6 shows latency comparisons for GPT-4o (Algo-1 to 6) and LLaMA3 (Algo-7 to 12), evaluated on both LLM-generated and human-tagged QA datasets. Across both datasets, LLaMA3 consistently demonstrated a lower total latency than GPT-4o. The fastest LLaMA3-based configuration (Algo-7) achieved a response time of 1.5809 s, nearly twice as fast as the fastest GPT-4o setup (Algo-1 at 3.0338 s). This confirms that while GPT-4o may offer better accuracy, LLaMA3 provides superior response speed.

Table 5.
Latency analysis of RAG pipeline variants (LLM-generated QA): Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.

Table 6.
Latency analysis of RAG pipeline variants (human-tagged QA): Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.
3.4. Improving the Performance of Ollama Models
While GPT-4o delivered consistently high-quality answers, its reliance on a paid API makes it less suitable for continuous deployment in public institutions or budget-limited environments. One of the main goals of this study was to narrow the performance gap between free open-source models provided by Ollama and the commercial GPT-4o model from OpenAI. To achieve this, the system incorporated advanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques. Several experiments were conducted using different Ollama models and retrieval methods to explore whether the quality of responses could be significantly improved despite the smaller model size and initially lower performance when compared to GPT-4o.
An Ollama model LLAMA3 was executed locally on a personal workstation equipped with:
- -
- GPU: NVIDIA Quadro RTX 4000 (8 GB VRAM)
- -
- CPU: Intel Core i9-10900X @ 3.70 GHz
- -
- RAM: 16 GB
- -
- OS: Windows 11 Pro
- -
- Framework: Ollama (local deployment, version 0.6.8), LangChain (version 0.3.25), FAISS (version 1.9.0.post1)
The second model, OpenChat, was deployed on a higher-spec workstation equipped with more memory and a more powerful GPU. This configuration was necessary due to OpenChat’s higher model complexity and greater computational requirements compared to LLaMA 3. It was executed locally on a personal workstation equipped with:
- -
- GPU: Intel (R) UHD Graphics 770 (32 GB VRAM)
- -
- CPU: 13th Gen Intel (R) Core (TM) i7-13700
- -
- RAM: 64 GB
- -
- OS: Windows 11 Pro
- -
- Framework: Ollama (local deployment, version 0.6.8), LangChain (version 0.3.25), FAISS (version 1.9.0.post1)
In contrast, the GPT-4o model was accessed via the OpenAI API, which runs on proprietary cloud infrastructure managed by OpenAI. It was not executed locally but served as a benchmark for performance, latency, and quality comparisons with the local models.
Although Ollama models are freely available and lighter in size, our experiments demonstrated that it is possible to achieve strong performance by combining these models. Specifically, OpenChat with well-designed prompts and advanced retrieval strategies. We tested various Ollama models such as OpenChat-7b-v3.5-0106-fp16, Zephyr-7b-beta, and Neural-Chat-7b-v3.1v (Table 7 and Table 8). Among them, OpenChat delivered the best results, largely because it was trained on a wide range of dialog data and outperforms ChatGPT (https://chatgpt.com, accessed in 10 March 2025) on multiple benchmarks. OpenChat-7b-v3.5-0106-fp16 is provided as a free, open-source model with a compact size of 14 GB. Its lightweight design allows easy local deployment on limited GPU (NVIDIA RTX 3090/4090 or higher) without incurring API usage fees. This makes it a highly practical choice for public institutions with constrained budgets and computing resources, including national universities and international student support centers.

Table 7.
Evaluation Results of RAG Pipelines (Human-tagged QA): Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.

Table 8.
Evaluation results of RAG pipelines (LLM-Generated QA): Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.
However, when used in isolation for factual QA tasks, the model demonstrates clear limitations. Without access to up-to-date external knowledge, it tends to hallucinate and may struggle to provide logically detailed explanations. These shortcomings arise because, in standalone operation, OpenChat relies solely on its pre-trained, general-purpose language capabilities rather than on retrieved domain content.
To overcome these issues, the current study integrates OpenChat into a RAG framework. A document-based embedding retrieval strategy is first applied to fetch the most relevant passages from a curated knowledge base. Then, domain-optimized prompt engineering guides the model to ground its responses in these retrieved documents. By combining retrieval and tailored prompts, OpenChat functions as the generation engine within a RAG system, providing more accurate answers.
To improve the performance of the free and open-source model LLaMA3, explored several advanced methods. These included testing different Ollama-compatible models such as OpenChat, zephyr, neural-chat and some kind of OpenChat versions and applying more advanced retrieval methods and splitting strategies. The focus was placed on MultiQuery Retrieval and hybrid retrievers (Dense + BM25) combined with Recursive text splitting. As shown in Table 2 and Table 3, the GPT-4o model initially demonstrated higher average scores across all key RAGAS evaluation metrics, including answer relevancy, faithfulness, context recall, and context precision, in both LLM-generated QA and human-tagged QA datasets. Specifically, the best-performing configuration of GPT-4o (Algo-5) achieved an average score of 0.7351 in the LLM-generated QA task and 0.7249 in the human-tagged QA task.
Only two algorithms were subjected to additional testing in Table 8 because they provide the highest average RAGAS scores in the initial evaluation (Table 7) on the human-tagged QA dataset. First, all eleven configurations (algo13-algo23) from Table 7 were evaluated and analyzed. Then the top two were selected: openchat:7b-v3.5-q6_K with MultiQuery (dense) retrieval and openchat:7b-v3.5-0106-fp16 with MultiQuery hybrid (dense + BM25) and both using Recursive splitting on the LLM-generated QA dataset. By focusing on these best-performing methods, repetition of all eleven (algo13-algo23) human-tagged QA experiments was avoided, resulting in two runs for LLM-generated QA (the original twelve plus the two additional tests).
The effectiveness of these enhancements is presented in Table 7 and Table 8. In Table 7 (Human-tagged QA), Algo-23 used the model openchat:7b-v3.5-0106-fp16 with Recursive splitting and a MultiQuery Hybrid Retriever (BM25 + Dense). This configuration achieved an improved average score of 0.7377, surpassing GPT-4o’s best result (0.7249). Similarly, in Table 8 (LLM-generated QA), the same model setup reached an average of 0.7408, which also exceeds the GPT-4o baseline of 0.7351.
In addition, we experimented with enhanced retrieval methods, including MultiQuery Retriever and MultiVector Retriever. The MultiQuery Retriever improves performance by generating several semantically diverse paraphrases of the original user query using a language model, which increases the chances of retrieving relevant context. The MultiVector Retriever allows a single document to be represented using multiple vector embeddings, each reflecting a different aspect of the content, for example, the full text, the title, a summary, or extracted keywords.
These results clearly demonstrate that by combining advanced retrieval strategies and optimized text splitting with open-source models, it is possible to achieve competitive and even superior performance compared to proprietary models like GPT-4o. This finding highlights the potential of free LLMs when paired with carefully designed RAG pipelines. This is particularly meaningful for national universities or public institutions where budget constraints often make the use of paid APIs impractical.
But while advanced methods and the use of high-performing open-source models such as openchat:7b-v3.5-0106-fp16 led to improved evaluation metrics (as shown in Table 7 and Table 8), this improvement came at the cost of increased latency. As shown in Table 5, Table 6, Table 9 and Table 10 (with Advanced metrics), both retrieval time and generation time increased significantly when switching from baseline algorithms (Algo-1 to Algo-12) to advanced ones (algo-13 and further). For example, in the LLM-generated QA dataset, retrieval time increased 6 times from 0.0053 s (algo-11 Table 5) to 6.1295 s (algo-14 Table 9), and generation time increased 7.97 times from 1.221 s (algo-8 Table 5) to 9.1957 s (algo-14 Table 9). A similar trend was observed in the human-tagged dataset, where retrieval time increased 6 times from 0.0034 s (algo-11 Table 6) to 6.1369 s (algo-23 Table 10), and generation time increased 9.8 times from 1.3706 s (algo-6 Table 6) to 11.25 s (algo-23 Table 10).

Table 9.
Latency analysis of selected RAG pipelines (LLM-Generated QA): Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.

Table 10.
Latency analysis of selected RAG pipelines (Human-tagged QA): Each row labeled “Algo-x” represents a distinct test condition, defined by a unique combination of LLM, text split method, and retrieval strategy.
The primary reason for this latency increase is the size and computational complexity of the openchat:7b-v3.5-0106-fp16 model, which occupies approximately 14 GB of memory. Due to its large size, the model requires more time to process queries and generate responses. This results in slower retrieval and generation phases, especially on machines with limited memory or processing power. In some cases, system slowdowns were observed during execution, further contributing to longer response times. Despite this, the performance gains in answer quality metrics justify the trade-off in latency for tasks. However, optimization strategies may be needed to balance accuracy and speed effectively.
While high-performing configurations such as OpenChat:7b with hybrid retrieval and recursive chunking delivered superior accuracy across most evaluation metrics, this came at a significant latency cost, often exceeding acceptable limits for real-time applications. The large model size (14 GB) combined with complex retrieval pipelines resulted in response times that may not meet the responsiveness expectations for end-users. In practical terms, the tradeoff between latency and quality should be considered based on the nature of the user interaction. For real-time chatbot scenarios, such as general inquiries or FAQ-style interfaces, where users expect answers within 3–5 s, lightweight configurations using GPT-4o or LLaMA3 with simpler retrieval strategies (e.g., MMR or BM25) are more appropriate. These pipelines provide sufficiently high accuracy while maintaining low latency and better scalability.
In contrast, for moderately latency-tolerant or non-real-time scenarios such as step-by-step admissions guidance, document preparation, or internal information lookup by university staff, it is more acceptable to tolerate longer response times in exchange for improved answer quality and contextual precision. In such cases, using slower but more accurate pipelines (e.g., OpenChat with hybrid search) can be justified, especially when information fidelity and contextual completeness are critical. These observations suggest that model and pipeline selection should be use-case aware, balancing the tradeoff between accuracy and latency according to the operational context and user expectations.
4. Conclusions and Future Works
This study proposed and evaluated a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system for answering questions related to university admissions. The results demonstrated that while GPT-4o initially achieved higher performance across several RAGAS metrics, the open-source LLaMA3 and OpenChat models were able to match and even surpass these results when combined with advanced techniques such as MultiQuery Retrieval and hybrid retrievers. In particular, the model openchat:7b-v3.5-0106-fp16 with Recursive splitting and hybrid retrieval achieved the highest average scores on both LLM-generated and human-tagged QA datasets, outperforming GPT-4o in key evaluation categories such as answer relevancy, faithfulness, context recall and context precision. These findings highlight that open-source solutions, when properly optimized, can serve as strong alternatives to commercial LLMs.
Despite the promising results, several limitations regarding the generalizability of this study should be acknowledged. First, the proposed RAG system and experimental settings were tailored to a specific domain of international student admissions using a well-structured document set provided by a single university. As such, performance metrics derived from this setting may not fully extend to broader or more diverse domains, particularly those lacking clear source documents or consistent terminology. Second, although our evaluation includes both LLM-generated and human-annotated QA sets, the number of questions was relatively limited, and responses were constructed by a single annotator. These factors may restrict the representativeness of the benchmark and the robustness of conclusions. Third, the study focused on a fixed set of large language models (GPT-4o, LLaMA3, OpenChat) and pipeline configurations, which may become outdated as newer models and architectures emerge. Consequently, further validation is required to confirm the stability and transferability of the findings under different model scales, document types, and user intents. Future work will involve extending the system to more varied use cases and testing with dynamically evolving content to assess its adaptability and long-term reliability.
Although the proposed system achieved strong performance in answer quality, this came at the cost of increased latency, particularly due to the large size of advanced models (e.g., 14 GB for OpenChat), which impacted retrieval and generation times. Since latency is a critical factor for real-time applications, future work should aim to improve system efficiency without compromising accuracy. Reducing response time to under 3–5 s is often considered important for real-time user interactions in chatbot systems, based on industry best practices. To achieve this, future research could explore lightweight model distillation or quantization, efficient GPU memory management and parallelization strategies, improved catching or pre-fetching for retrieval, and optimized retriever reranking to avoid unnecessary document loading. Addressing these areas would enhance the system’s readiness for real-time environments by combining high-quality output with faster and more reliable performance.
The current RAG system utilizes a fixed linear pipeline, lacking adaptive mechanisms such as query rewriting, dynamic retrieval selection, and real-time output correction, which limits its flexibility and accuracy. To address these limitations, future work will explore extending the system into an Agentic RAG architecture [42,43] using the modular LangGraph framework [44]. In this design, each query will be classified by type (e.g., factual lookup, summarization, complex reasoning) and dynamically routed to specialized RAG agents with tailored retrieval and prompt settings. A lightweight rewriting agent will refine ambiguous queries before retrieval, while dedicated “Corrective RAG” and “Self-RAG” agents will monitor the generation output for faithfulness and relevance. If confidence thresholds are not met, the system will automatically initiate corrective actions such as re-retrieval or prompt refinement. This dynamic branching structure enhances factual accuracy, contextual relevance, and robustness under diverse query conditions. Implementation will follow recent studies on modular, feedback-driven generation systems, aiming to empirically validate improvements in both response quality and reliability.
To better align the system with real user needs, a real-time feedback interface will be integrated into the chatbot front end, allowing users to rate each response based on clarity, usefulness, and accuracy using a Likert scale, with an optional field for detailed comments. All feedback, including timestamps, will be securely stored in a central database to facilitate continuous monitoring of user satisfaction and identification of recurring issues. This user feedback will guide iterative system development, with low-rated responses informing model fine-tuning, retrieval adjustments, and prompt refinement for frequently misunderstood topics. Additionally, testing various prompt styles and retrieval strategies will help determine the most effective configurations prior to full deployment. By incorporating this human-in-the-loop framework, the RAG system will be able to evolve continuously, leading to sustained improvements in both objective performance metrics and perceived service quality.
Author Contributions
M.K.Z.k.: Data curation, Writing—Original draft preparation, Visualization, Investigation, Software; Y.S.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Validation, Supervision, Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
“This research was supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science, ICT), Republic of Korea, under the National Program for Excellent in SW, supervised by the IITP (Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation) in 2025” (2024-0-00073).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the DATA-UX LAB at Kongju National University for feedback during development and the GKS scholarship program for providing academic support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BLEU | Bilingual Evaluation Understudy |
| BM25 | Best Matching 25 |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| DB | Data Base |
| FAQ | Frequently Asked Questions |
| FAISS | Facebook AI Similarity Search |
| GPT | Generative Pretrained-trained Transformer |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| LLAMA | Large Language Model Meta AI |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| MMR | Maximal Marginal Relevance |
| METEOR | Metric for Evaluation of Translation with Explicit Ordering |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
| OS | Operating System |
| RAG | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
| RAGAS | Retrieval-Augmented Generation Assessment Score |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| ROUGE | Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation |
References
- Adeshola, I.; Adepoju, A.P. The opportunities and challenges of ChatGPT in education. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2024, 32, 6159–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyton, K.; Unnikrishnan, S.; Mulligan, B. A review of university chatbots for student support: FAQs and beyond. Discover Education 2025, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Chatbot: Design, Architecture, and Applications. Bachelor’s Thesis (Senior Capstone Thesis), University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 3 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nobre, G.X.; Moraes, G.; Franco, W.; Moreira, L.O. A Chatbot Approach to Automating FAQ Responses in an Undergraduate Course Domain. TCC. Thesis, Federal University of Ceará, Fortaleza, Brazil, 2019; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Yu, W.; Ma, W.; Zhong, W.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Peng, W.; Feng, X.; Qin, B.; et al. A Survey on Hallucination in Large Language Models: Principles, Taxonomy, Challenges, and Open Questions. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2024, 1, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, X.; Nie, J.-Y.; Wen, J.-R. HaluEval: A Large-Scale Hallucination Evaluation Benchmark for Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; Bouamor, H., Pino, J., Bali, K., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Singapore, 2023; pp. 6449–6464. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, Y. RAG and RAU: A Survey on Retrieval-Augmented Language Models in Natural Language Processing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.19543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, S.; Hossain, E.; Keith, J.; Tripathi, H.; Ghiasi, F.; Amiri Golilarz, N.; Amirlatifi, A.; Mittal, S.; Rahimi, S. From Questions to Insightful Answers: Building an Informed Chatbot for University Resources. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.08120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swacha, J.; Gracel, M. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Chatbots for Education: A Survey of Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Superbi, J.; Pereira, H.; Santos, E.; Lattari, L.; Castro, B. Enhancing Large Language Model Performance on ENEM Math Questions Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation. In Proceedings of the Brazilian e-Science Workshop, Brasília-DF, Brazil, 14 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, G.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, A. Improving Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Medicine with Iterative Follow-up Questions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2310.19988. [Google Scholar]
- Radeva, I.; Doychev, A.; Georgiev, I.; Tontchev, N. CRP-RAG: A Retrieval-Augmented Generation Framework for Supporting Complex Logical Reasoning and Knowledge Planning. Electronics 2024, 14, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, J. Web Application for Retrieval-Augmented Generation: Implementation and Testing. Electronics 2023, 13, 1361. [Google Scholar]
- Amugongo, L.M.; Mascheroni, P.; Brooks, S.G.; Doering, S.; Seidel, J. Retrieval Augmented Generation for Large Language Models in Healthcare: A Systematic Review. PLoS Digit. Health 2025, 4, e0000877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Using the Retrieval-Augmented Generation to Improve the Question-Answering System in Human Health Risk Assessment. Electronics 2024, 14, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsain, A.; El Housni, H. Large Language Model-powered Chatbots for Internationalizing Student Support in Higher Education. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.14702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, G.X.; Moraes, G.; Franco, W.; Moreira, L.O. A Chatbot Approach to Automating FAQ Responses in an Educational Setting. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education (ITiCSE ‘19), Aberdeen, UK, 15–17 July 2019; p. 590. [Google Scholar]
- Silkhi, H.; Bakkas, B.; Housni, K. Comparative Analysis of Rule-Based Chatbot Development Tools for Education Orientation: A RAD Approach. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Networking, Intelligent Systems and Security (NISS 2024), Meknes, Morocco, 18–19 April 2024; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, P.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.Y.; Min, B.; Castelli, V. RAG-QA Arena: Evaluating Domain Robustness for Long-form Retrieval-Augmented Question Answering. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.13998. [Google Scholar]
- Saad-Falcon, J.; Khattab, O.; Potts, C.; Zaharia, M. ARES: An Automated Evaluation Framework for Retrieval-Augmented Generation Systems. B. In Proceedings of the 2024 NAACL-HLT (Long Papers), Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; Duh, K., Gomez, H., Bethard, S., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Mexico City, Mexico, 2024; pp. 338–354. [Google Scholar]
- Es, S.; James, J.; Espinosa Anke, L.; Schockaert, S. RAGAs: Automated Evaluation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation. B. In Proceedings of the 18th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, St. Julians, Malta, 17–22 March 2024; Aletras, N., De Clercq, O., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: St. Julians, Malta, 2024; pp. 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ru, D.; Qiu, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, T.; Shi, P.; Chang, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, S.; Li, H.; et al. RAGChecker: A Fine-grained Framework for Diagnosing Retrieval-Augmented Generation. In NeurIPS 2024 Datasets & Benchmarks Track; Association for Computational Linguistics: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Pascale, A.; Carnerero-Cano, J.; Tchrakian, T.; Marinescu, R.; Daly, E.; Padhi, I.; Sattigeri, P. Human-annotated contradictory instances. WikiContradict: A Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs on Real-World Contradictory Knowledge. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 37 (NeurIPS 2024) 2024, 37, 109701–109747. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalloo, E.; Jafari, A.; Zhang, X.; Thakur, N.; Lin, J. HAGRID: A Human-LLM Collaborative Dataset for Generative Information-Seeking with Attribution. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.16883. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.; Quan, T. URAG: Implementing a Unified Hybrid RAG for Precise Answers in University Admission Chatbots—A Case Study at HCMUT. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1012. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, N.; Gurevych, I. Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, J.; Goldstein, J. The Use of MMR, Diversity-Based Reranking for Reordering Documents and Producing Summaries. In Proceedings of the 21st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Melbourne, Australia, 24–28 August 1998; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 335–336. [Google Scholar]
- Karpukhin, V.; Oguz, B.; Min, S.; Lewis, P.; Wu, L.; Edunov, S.; Chen, D.; Yih, W.T. Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.04906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Reimers, N.; Daxenberger, J.; Gurevych, I. BEIR: A Heterogeneous Benchmark for Zero-shot Evaluation of Information Retrieval Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, M.; Xiong, C.; Srinivasan, K.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J. Multi-Vector Retriever: Learning Diverse Representations for Efficient and Effective Dense Retrieval. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14625. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. GPT-4o Technical Report. Available online: https://openai.com/index/gpt-4o/ (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Gruber, J.B.; Weber, M. Rollama: An R package for using generative large language models through Ollama. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.07654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattafiori, A.; Dubey, A.; Jauhri, A.; Pandey, A.; Kadian, A.; Aidahle, A.; Letman, A.; Mathur, A.; Schelten, A.; Vaughan, A.; et al. The Llama 3 Herd of Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.21783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenChat. Available online: https://huggingface.co/openchat/openchat_3.5 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Zephyr. Available online: https://huggingface.co/HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Neural Chat. Available online: https://huggingface.co/Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- RAGAS. Retrieval-Augmented Generation Evaluation. Available online: https://github.com/explodinggradients/ragas (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Lin, C.-Y. ROUGE: A Package for Automatic Evaluation of Summaries. In Text Summarization Branches Out, Proceedings of the ACL-04 Workshop, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; Association for Computational Linguistics: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.-J. BLEU: A Method for Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Lavie, A.; Agarwal, A. METEOR: An Automatic Metric for MT Evaluation with High Levels of Correlation with Human Judgments. In Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, Prague, Czech Republic, 23 June 2007; pp. 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Kishore, V.; Wu, F.; Weinberger, K.; Artzi, Y. BERTScore: Evaluating Text Generation with BERT. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09675. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Dong, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.; Hase, P.; Kandpal, N.; Reid, M.; Wang, X.; Klein, D.; et al. Agentic RAG: Orchestrating Modular Agents with Language Graphs. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.12947. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.-Q.; Gu, J.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Ling, Z.-H. Corrective RAG: Feedback-Driven Retrieval-Augmented Generation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.11751. [Google Scholar]
- LangGraph. Available online: https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/ (accessed on 28 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).