Abstract
In backend VLSI design, congestion and timing are critical factors. However, due to the high complexity of semiconductor design and the specialization required at each design stage, frontend and backend designs are often conducted independently. This can lead to difficulties in achieving overall optimization of the design. This paper addresses this issue not by solving it comprehensively but by focusing specifically on the communication methods between internal modules of the chip. We analyze cell placement and routing congestion and explore methods to optimize communication efficiency by considering timing issues in advance. Specifically, the study compares and analyzes the efficiency of different methods for selecting target modules by the primary module under various conditions. Focusing on the commonly used Chip Select (CS) and Identification (ID) methods, we examine how each method’s complexity and performance are affected by the number and type of target modules controlled and propose design approaches to optimize module-to-module communication. This paper offers recommendations on module selection methods based on design conditions and provides practical guidelines for designers to enhance communication efficiency effectively.
1. Introduction
Figure 1 illustrates the general flow of semiconductor design. Semiconductor design is divided into Front-end design and Back-end design to maximize expertise at each design stage and manage the complexity of the design. Front-end design handles the logical design, while Back-end design involves the physical placement and routing. However, if the Front-end design is not adequately reflected in the Back-end design due to this separation, the performance of the final chip may not be optimized [1,2]. Back-end design is the process of implementing the logical operations designed in the Front-end as physical elements [3]. Understanding how the Front-end design translates into physical elements in the Back-end design can lead to more efficient design processes. Nevertheless, due to the specialized nature of each design stage and the high complexity of semiconductor design, predicting the outcomes of Front-end design on the Back-end can be challenging.
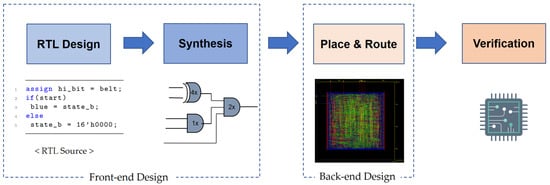
Figure 1.
Overview of the semiconductor design flow.
This paper aims to address this issue by comparing and analyzing two control methods considered in Front-end design: using registers and using wires. Registers are variables used to store data and maintain the current value until a new value is assigned, making them primarily used in procedural assignments. In contrast, wires refer to physical connections and are mainly used to connect outputs in continuous assignments. Although registers and wires serve different purposes, they share a commonality in that they can both initiate communication using Chip Select wires or stored ID values when selecting and controlling modules in the design. In other words, both methods can achieve the same functionality.
Figure 2a illustrates an example of Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) communication, while Figure 2b shows an example of communication using ID values. In Back-end design, registers are included in standard cells in the form of flip-flops and are physical elements of a fixed size. Wires, on the other hand, are elements that connect cells to each other or macros to cells, and their length and shape can vary depending on the Place and Route (P&R) process. For instance, when a single primary controls four target modules, using IDs allows two registers to be assigned unique ID values such as ‘00’, ‘01’, ‘10’, and ‘11’, with communication conducted such that only target modules with the corresponding ID respond. Conversely, in the wire-based approach, physical connection wires are directly linked to each target module, and signals are sent to select specific target modules. The wire connections can become complex if they need to bypass other cells or macro blocks, resulting in variations in wire length and shape depending on the design environment. While the wire-based approach may be advantageous when the number of target modules is small, it becomes increasingly complex as the number of target modules grows, with a corresponding increase in routing congestion. Routing congestion is closely related to performance, one of the key metrics in semiconductor design alongside power and area (PPA) [4,5,6,7,8].
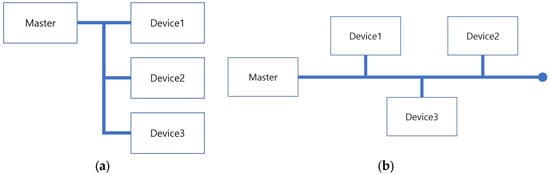
Figure 2.
Examples of bidirectional communication methods: (a) SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) communication method; (b) Communication method using ID (Identification).
This paper aims to predict the routing congestion of Back-end design from Front-end design and analyze how Front-end design impacts Back-end design to optimize design performance. The paper is organized as follows: first, a review of existing research trends related to placement and routing is presented, explaining the impact of Front-end design on Back-end design. Next, the results of the Back-end design following Front-end design are provided, and an analysis is conducted on which Front-end design elements influence Back-end design performance. Finally, conclusions are drawn based on the experimental environment and results.
2. Evaluation Metrics—Routing Congestion and Performance
This section addresses how to evaluate the impact of Front-end design on Back-end design. When optimizing semiconductor design for performance, minimizing routing congestion, as mentioned in Section 1, is crucial, and it is advantageous to minimize the Worst Negative Slack () value.
We first explain routing congestion, then discuss , and finally explore the relationship between routing congestion, , and performance.
Placement and Routing (P&R) is a critical phase in semiconductor design, involving the efficient placement of components and the optimization of their interconnections [3]. This stage significantly impacts the design’s performance, power consumption, and area (PPA) [4]. Optimal placement and routing minimize signal delays, maximize power efficiency, and are key factors in determining overall design quality [9,10,11].
Numerous studies have been conducted to optimize Back-end design. For instance, research on path optimization through maze routing [12], optimization problem-solving using pruning rules [13], studies on minimizing standard cell movement [14], standard cell placement considering obstacles and minimizing deviation [15], hierarchical bin-based approaches [16], placement acceleration using multi-dimensional trees [17], detailed placement and routing improvements based on cell density [18], and placement density-aware routing studies [19] have all contributed to this field. Recently, there has been active research on placement and routing algorithms combined with artificial intelligence [20,21,22]. Additionally, studies on the interaction between placement and routing are also referenced in this paper [12,14,15,16,17,23].
Key factors affecting routing congestion include the number of control lines, cell placement density, and routing constraints (e.g., crossings, merges). To reduce congestion, it is essential to optimize placement density to decrease the congestion of routing paths, use space efficiently, and minimize unnecessary crossings. Optimizing the placement of control lines to reduce routing conflicts and satisfying routing constraints are also important. This involves minimizing path delays and finding efficient routes [24]. Consequently, establishing optimal paths is crucial for addressing timing issues.
Deriving a clear formula for the relationship between the increase in control lines and routing congestion is challenging. Depending on the situation, linear or exponential models may apply. However, the main factors affecting routing congestion can be summarized as the number of control lines to be routed, cell placement density, and routing constraints.
Figure 3a illustrates the shortest path (in blue) connecting Macro 2 to Standard Cell 4. This path encounters Standard Cell 5, necessitating a detour. Additionally, the segment (in red) connecting Macro 2 to Standard Cell 6 is already congested with numerous wires, resulting in a shortage of routing resources. In such cases, as shown in Figure 3b, the routing must be rerouted to avoid congestion, leading to an increase in the overall wire length. The definition of (Worst Negative Slack) is given by Equation (1).
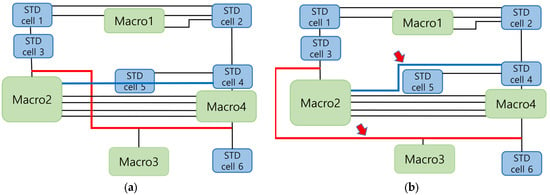
Figure 3.
Example of a routing path: (a) Routing path before modification; (b) Routing path after modification. The red and blue lines in (a) indicate original routing paths that were congested and required rerouting. In (b), the corresponding red and blue lines show the alternate paths taken after rerouting, each matched to their original color. The red arrows indicate the direction of signal flow along the rerouted paths.
Setup violations occur when the arrival time of a path, including both cell delay and net delay, does not meet the required timing constraints. This is more likely to happen when a detour path is chosen instead of the shortest path. Consequently, timing issues are closely related to routing congestion, and it is essential to establish optimal paths in Front-end design.
Several studies have used metrics such as routing congestion [24,25,26,27,28], [29], clock tree synthesis results [30], and coupling effects [31] to evaluate placement and routing. These metrics demonstrate that routing congestion plays a significant role in design performance.
3. Impact and Scope of Front-End Design Elements on Back-End Design
This section analyzes the impact and scope of how wires and registers affect the Back-end design based on Front-end design approaches. To achieve this, we compare the design methods using Chip Select (CS) control lines with those using register-based ID control. To ensure that both design methods serve the same function, we incorporate a block in the ID control method’s internal module to verify ID values and include a process for generating the CS signal.
Figure 4 illustrates the design with an added block for verifying ID values. To compare the results of the two design methods, the evaluation criteria mentioned in Section 2 were set in terms of congestion and values. Additionally, conditions such as the number of required gates, chip size, and growth rates with increasing target modules were included in the analysis.

Figure 4.
Code for selecting target modules assigned with ID values.
Figure 5a shows the case where a primary controls two target modules. When using CS control lines, additional CS1 and CS2 control lines, marked in red, are added, and the red dashed box indicates the area that the CS control lines must avoid. In the case of using register control with assigned ID values, a register is added to each target module, and congestion is calculated based on the placement of the existing target logic and the registers.
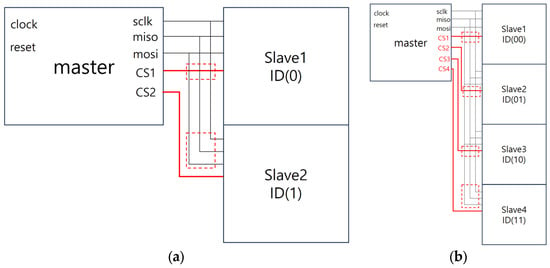
Figure 5.
Example of routing paths with an increasing number of target modules: (a) When controlling 2 target modules; (b) When controlling 4 target modules. The dotted red boxes highlight congested areas where routing paths overlap and must be avoided, increasing routing complexity.
Figure 5b illustrates the scenario where the primary controls four target modules. With four CS control lines, more areas need to be avoided compared to Figure 5a, making the routing paths more congested. In contrast, with register control using assigned ID values, the congestion affecting the external routing is relatively lower due to the placement of registers and target module logic within each target. When controlling eight target modules, the area that needs to be avoided in Figure 5b doubles.
The number of target modules was selected as powers of 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256 to reflect the natural scaling pattern of ID-based control, which utilizes binary register-based addressing. This choice aligns with the inherent architecture of ID decoding, where control logic expands in powers of two. Using this sequence ensures that both ID-based and CS-based control methods are evaluated under consistent and comparable conditions, thereby enabling a fair and structurally grounded performance comparison.
Figure 6 illustrates the process for calculating routing congestion, starting from the FloorPlan stage, which includes setting the chip size, and progressing through the placement stage, where the layout of macro modules and standard cells is carried out.
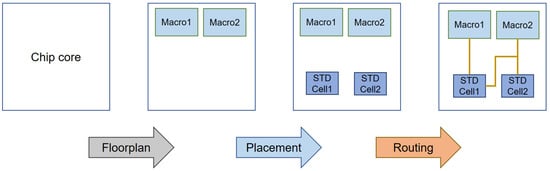
Figure 6.
Placement and routing stages.
Figure 7a represents the pre-stage for placement and routing, corresponding to the FloorPlan stage shown in Figure 6. In Figure 7a, the row is the basic unit for placing standard cells, and the site determines the size of the standard cells, with rows being multiples of sites.
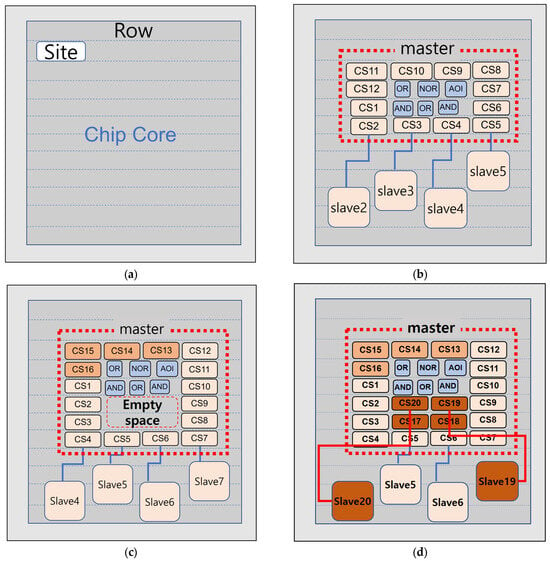
Figure 7.
Placement of the CS control register by module size: (a) Description of rows and sites for cell placement; (b) Placement result of the primary module; (c) Creation of empty space as the CS control register is placed at the edge with the addition of 4 CS control lines; (d) Placement of the CS control register inside the module, rather than at the edge, with the addition of more CS control lines.
Figure 7b illustrates the standard cell placement process for primary module design. When using CS control lines, CS control registers are generated, and placement of these registers at the edges of the module is advantageous for routing. Conversely, if the registers are placed inside the module, they must avoid existing standard cells or blocks in front of the control registers, increasing congestion.
Figure 7c shows the scenario when the number of CS control lines increases from 12 to 16. When CS control registers are placed at the edges, standard cells within the primary module create empty spaces due to the control lines. An increase in the number of CS control lines results in further expansion of these empty spaces.
Figure 7d depicts the situation when CS control registers are placed inside the module. In this case, the control registers must be arranged to avoid existing standard cells, which significantly increases routing congestion. As the number of control registers increases, routing congestion tends to grow non-linearly.
This suggests that the ratio between the primary module size and the control register area is closely related to routing congestion. Once the peripheral area of the primary module reaches saturation, additional registers must be placed internally, leading to further routing complexity, as illustrated in Figure 7d.
For instance, when controlling 16 secondary modules using the Chip Select (CS) method, a total of 16 CS control flip-flops are required. If these control registers can be placed along the periphery of the primary module, it is advantageous to scale the overall module size accordingly to reduce routing congestion. However, if the primary module is too small to accommodate these registers externally, internal placement becomes necessary, exacerbating congestion.
In consideration of these structural characteristics, Section 3.1 and Section 3.2 of this paper provide a detailed analysis of the relationship between CS control register placement and routing congestion.
Section 3.1 examines how the increase in the number of target modules affects the placement structure of control registers and routing congestion, assuming a fixed primary module size.
Section 3.2, on the other hand, investigates the minimum primary module size required to ensure peripheral placement of CS control registers, given a fixed number of secondary modules. This analysis provides structural insight into the trade-offs between control logic placement and routing efficiency.
3.1. Area Impact of Increasing CS Registers in a Fixed Primary Module
The ID-based control method maintains a constant primary module size regardless of the number of target modules. As a result, it does not effectively reflect structural changes or physical layout complexity. In contrast, the Chip Select (CS) control method requires a dedicated control register (1-bit flip-flop, hereafter FF) for each target module. As the number of target modules increases, the number of control FFs increases accordingly, directly impacting the primary module’s area and routing structure.
Table 1 shows how the gate composition of the primary module changes as the number of controlled modules increases. “Total Gates” indicates the overall gate count, “FF Count” refers to the number of control FFs, and “Other Logic Gates” includes all logic gates excluding FFs. The “Area-Normalized FF Count” assumes each FF occupies an area six times that of a standard logic gate. The “FF Area Ratio” shows the percentage of the primary module’s area occupied by FFs.

Table 1.
Gate Composition and Area-Equivalent Flip-Flop Analysis for CS Controlled Primary Module.
As shown in the table, the total gate count increases with the number of target modules, primarily due to the growth in FF count. The contribution from other logic gates remains relatively small, indicating that most of the area expansion in the primary module is driven by the control FFs.
Figure 8 illustrates a configuration where FFs are placed around the periphery of the primary module. The blue region represents the internal logic area. To ensure peripheral placement of FFs, the internal logic of the primary module must occupy a sufficiently large area. However, if the control logic is small, peripheral FF placement becomes impractical, and some FFs are placed inside the module. This can increase routing congestion, as shown in Figure 7d.
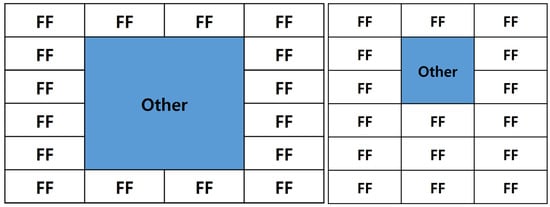
Figure 8.
Example of peripheral control FF placement with central logic block.
It should be noted that internal placement of FFs does not always lead to severe routing congestion. However, if control FFs overlap with critical routing paths—particularly in space-constrained modules with limited routing freedom—local routing conflicts may occur, negatively affecting global routing optimization. This effect tends to worsen nonlinearly once design complexity exceeds a certain threshold. Thus, the placement location of control FFs can be considered a significant factor influencing overall physical design quality.
3.2. Minimum Module Size to Avoid Internal Congestion
While Section 3.1 analyzes the impact of increasing the number of target modules under a fixed primary module size, this section takes the opposite approach. Here, we examine the minimum size requirement for the primary module that allows all control flip-flops (FFs) in the CS-based design to be placed along the periphery, assuming the number of target modules is fixed.
For example, controlling 16 secondary modules requires 16 control FFs. Assuming each FF has a physical size of 11.2 μm (W) × 4 μm (H), ideally, four FFs must be placed along each side of the primary module, which implies a minimum side length of 44.8 μm. In practice, however, cell spacing, routing clearance, and placement constraints must also be taken into account, requiring a larger area than this ideal value.
This relationship can be described by the following equation:
This formula provides a way to estimate the minimum primary logic area required to place control FFs along the boundary based on the number of controlled modules. It helps quantify the physical constraint imposed by CS-based control structures.
For example, when controlling 16 secondary modules, the “C” layout in Figure 9 offers an efficient structure that allows control flip-flops (FFs) to be placed along the periphery while maximizing the usable internal logic area (highlighted in blue). Assuming each FF occupies 11.2 μm (W) × 4 μm (H) and each basic NAND gate occupies 2 μm × 4 μm, the blue area in the C layout results in an approximate usable space of (11.2 × 4 × 3) × (4 × 3) = 1612.8 μm2, which is sufficient to accommodate roughly 60 basic logic gates.
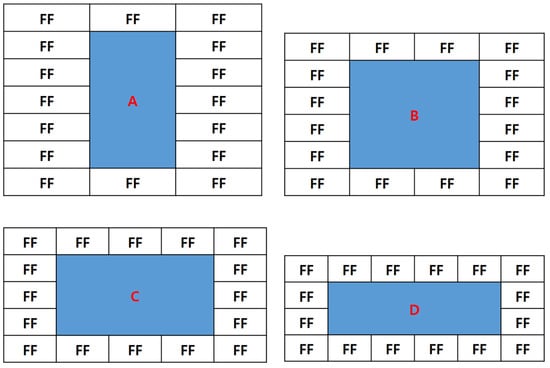
Figure 9.
Primary module area configurations with peripheral control FF placement. A–D indicate feasible layout forms for accommodating peripheral FFs.
Using the same assumption, for the case of eight target modules, the minimum required logic area within the primary module should be large enough to fit at least ten logic gates in order to ensure that all control FFs can be placed at the periphery.
According to the data in Table 1, the primary logic area is sufficient for up to eight target modules. However, starting from 16 modules, the logic area becomes insufficient to maintain full peripheral FF placement. As the number of controlled modules increases to 32, 64, 128, and 256, the internal logic region becomes relatively smaller while the number of control FFs continues to increase. This inevitably forces some FFs to be placed inside the module.
This situation suggests that as the number of controlled modules increases, the routing congestion may grow non-linearly due to limited space and increased overlap between control registers and routing paths.
4. Experimental Setup and Data Analysis
4.1. Experimental Setup and Methodology
To evaluate the routing congestion and timing impact of two control methodologies Chip Select (CS)-based control lines and ID-based control registers, a series of synthesis and place and route (P&R) experiments were conducted.
- RTL Simulation Tool: Cadence Xcelium;
- Synthesis Tool: Cadence Genus;
- Place and Routing Tool: Cadence Innovus;
- Library/LEF and Other Process Files Provided by the Foundry (90 nm standard cell process);
- Standard Cell Sizes
- o
- D-flip-flop (1-bit): 11.2 μm (W) × 4 μm (H);
- o
- 2-input NAND Gate: 2 μm (W) × 4 μm (H).
Each design variant was synthesized and placed using consistent floor planning and utilization settings. The number of target modules varied from 4 to 256, and all evaluations were based on post-P&R results. Key performance metrics included total gate count, physical layout area, routing congestion, and Worst Negative Slack ().
4.2. Routing Congestion and Gate Count Analysis
Figure 10 illustrates routing congestion captured from Innovus. Figure 10a presents a congestion map, while Figure 10b quantifies the congestion in selected regions. For instance, “H: 6/5” in the light blue zone indicates that 6 routing paths are required horizontally, but only 5 are available, necessitating detours for one wire.
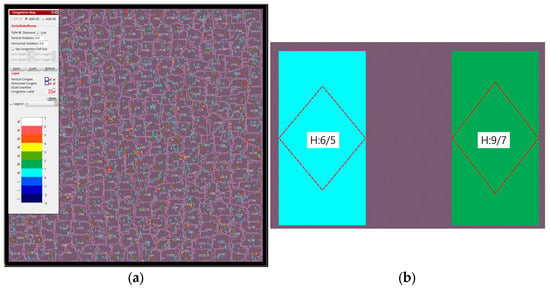
Figure 10.
Routing congestion map: (a) Routing congestion; (b) Quantification of routing congestion.
Table 2 presents the synthesis and P&R results for the CS control line design, showing how area, wirelength, and routing congestion vary with the number of target modules.

Table 2.
Synthesis and P&R Results with CS Control Line Design.
Table 3 summarizes the corresponding results for the ID-based control register design, including metrics such as logic gate count, routing area, and congestion trends.

Table 3.
Synthesis and P&R Results with ID Control Register Design.
Figure 11 presents a graphical comparison of total power consumption between the REG and CS control methods as the number of target modules increases. The trend confirms that power scales linearly, with the REG design consistently consuming more power due to its internal logic.
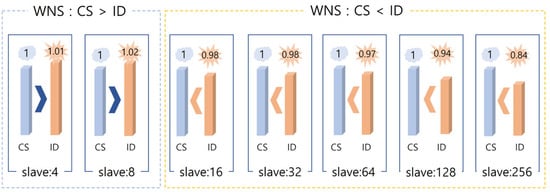
Figure 11.
Comparison of Worst Negative Slack () between the ID-based control register (REG) design and the chip-select (CS) control line design, showing the impact of increasing the number of target modules on timing degradation.
4.3. Evaluation Under Fixed Area Constraints
Table 4 shows the ID-based design performance under fixed physical area conditions. Even though the logic gate count increases with more target modules, routing congestion remains nearly constant. This indicates that the ID-based design can maintain acceptable routability even under constrained layout dimensions. Although the core utilization increases significantly in this setting, routing congestion does not increase noticeably. Figure 12 shows the corresponding area comparison between the ID-based and CS-based designs.

Table 4.
P&R Results of ID Control Method under Fixed Area Conditions.
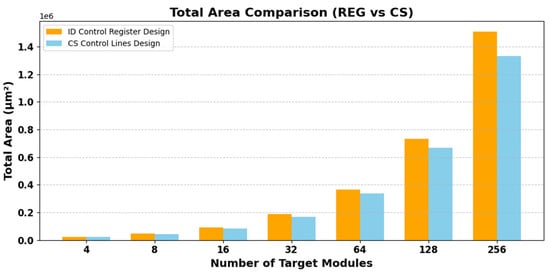
Figure 12.
Total area comparison between the ID-based control register (REG) design and the chip-select (CS) control line design as the number of target modules increases. The results are based on post placement area measurements obtained from place and route (P&R).
4.4. Power Consumption Comparison
Table 5 provides a breakdown of power consumption in the ID-based control design, including leakage, internal, and switching power components. As the number of target modules increases, all power components scale proportionally. Power consumption in the ID-based design increases proportionally with the number of target modules, while remaining within acceptable levels for all cases. This trend is visualized in Figure 13, which compares the total power consumption of the ID-based and CS-based designs across all configurations.

Table 5.
Power Consumption with ID Control Register Design.
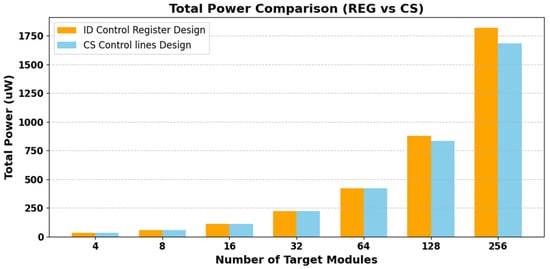
Figure 13.
Total power comparison between the ID-based control register (REG) design and the chip-select (CS) control line design, evaluated across varying numbers of target modules. Power includes leakage, internal, and switching components.
5. Results
This study conducted a comparative analysis of two control schemes Chip Select (CS) and Identification (ID)-based control registers that perform the same functional role from the perspective of physical design metrics such as layout area, routing congestion, gate complexity, and power consumption. The goal was to provide design guidelines for selecting the appropriate control scheme in primary–secondary architectures for SoC (System-on-Chip) and inter-module communication systems.
The experiment was conducted under a fixed primary module size using a 90 nm CMOS process. The flip-flop size was set to 11.2 × 4 μm and the NAND gate size to 2 × 4 μm. Under these conditions, when the number of controlled modules was 16 or fewer, the CS method showed superior results in area, power, and logic complexity due to its ability to place control registers around the periphery of the primary module.
However, when the number of controlled modules increased to 32 or more, the physical constraint of the primary caused control logic to penetrate into the core, making the ID method more advantageous in terms of routing stability and scalability. Although the ID method incurred approximately 10% additional area due to its decoding logic, it maintained manageable routing congestion even in high-density layouts. In terms of power, ID-based control exhibited a linear increase in consumption with the number of modules, but the results remained within acceptable limits for practical system sizes.
Importantly, the findings of this study suggest that the selection of control architecture should be based not only on the number of controlled modules but also on the available area of the primary module. Even for the same number of targets, the CS method may be favorable if the primary has sufficient physical area, while the ID method may be more suitable when space is limited. Therefore, both the scale of the control system and the physical size of the primary module should be considered jointly in the selection process.
In conclusion, the efficiency of a control scheme is significantly influenced not only by the number of modules it controls but also by the physical constraints of the primary module. Under the design conditions explored in this study, the CS method is more suitable for small-scale systems with 16 or fewer targets, while the ID method offers a more scalable and robust alternative for larger systems with 32 or more modules. These results can serve as practical design guidelines for control architecture selection in real-world semiconductor systems, depending on system constraints and physical design considerations.
It is important to note that this study focused on a simplified communication structure consisting of a single primary and multiple secondary modules under a fixed workload and process condition (90 nm). Therefore, results may not be directly generalizable to complex SoC architectures that include dynamic traffic patterns, hierarchical communication structures, or advanced P&R optimizations using AI/ML techniques.
While this study was conducted under a uniform and fixed communication workload to ensure structural comparison between control methods, we acknowledge that real-world systems often involve dynamic and complex traffic patterns, such as burst transmissions or contention scenarios. These can significantly affect the performance and scalability of the control architecture. As a limitation, this aspect is not addressed in the current work. In future research, we plan to explore the impact of diverse traffic models through realistic simulation environments to better evaluate control scheme robustness under practical SoC workloads.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Hassoun, S.; Sasao, T. Logic Synthesis and Verification, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, A.M.; Chopde, A. Physical Design: Methodologies and Developments. arXiv 2024, arXiv:240904726. [Google Scholar]
- Golshan, K. Physical Design Essentials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Maity, S.; Jana, S.K. Design of a Power-Performance-Area (PPA) Optimized MOS Current Mode Logic Pre-scaler. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 42, 5783–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Zhang, Y. Thermal-driven multilevel routing for 3-D ICs. In Proceedings of the 2005 Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Shanghai, China, 18–21 January 2005; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Sapatnekar, S.S. A timing-constrained algorithm for simultaneous global routing of multiple nets. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design ICCAD-2000 IEEE/ACM Digest of Technical Papers (Cat No 00CH37140), San Jose, CA, USA, 5–9 November 2000; pp. 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Hu, J.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, M.; Shen, Z.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, K. Machine learning for electronic design automation: A survey. ACM Trans. Des. Autom. Electron. Syst. 2021, 26, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q. A survey on machine learning-based routing for VLSI physical design. Integration 2022, 86, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillis, J.; Cheng, C.-K.; Lin, T.-T. Optimal wire sizing and buffer insertion for low power and a generalized delay model. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1996, 31, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohoon, J.; Kairo, J.; Lienig, J. Evolutionary algorithms for the physical design of VLSI circuits. In Advances in Evolutionary Computing: Theory and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 683–711. [Google Scholar]
- Tabrizi, A.F.; Darav, N.K.; Rakai, L.; Kennings, A.; Swartz, W.; Behjat, L. A detailed routing-aware detailed placement technique. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Montpellier, France, 8–10 July 2015; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, V.M.; Kumar, M.P.; Maheshwari, S.N. An O (|V| 3) algorithm for finding maximum flows in networks. Inf. Process. Lett. 1978, 7, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achterberg, T.; Koch, T.; Martin, A. Branching rules revisited. Oper. Res. Lett. 2005, 33, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, P.; Schlichtmann, U.; Johannes, F.M. Abacus: Fast legalization of standard cell circuits with minimal movement. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Physical Design, Portland, OR, USA, 13–16 April 2008; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, S.; Ho, T.-Y. OAL: An obstacle-aware legalization in standard cell placement with displacement minimization. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International SOC Conference (SOCC), Belfast, UK, 9–11 September 2009; pp. 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Wu, T.-Y.; Chiang, P.-Y. A hierarchical bin-based legalizer for standard-cell designs with minimal disturbance. In Proceedings of the 2010 15th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Taipei, Taiwan, 18–21 January 2010; pp. 568–573. [Google Scholar]
- Netto, R.; Livramento, V.; Guth, C.; Dos Santos, L.C.; Guntzel, J.L. Speeding up incremental legalization with fast queries to multidimensional trees. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 11–13 July 2016; pp. 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, X.; Gao, J.-R.; Viswanathan, N.; Liu, W.-H.; Li, Z.; Alpert, C.J.; Pan, D.Z. MrDP: Multiple-row detailed placement of heterogeneous-sized cells for advanced nodes. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2017, 37, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Q. An effective iterative density aware detailed placement algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 1–5 June 2014. pp. 1444–1447.
- Amuru, D.; Zahra, A.; Vudumula, H.V.; Cherupally, P.K.; Gurram, S.R.; Ahmad, A.; Abbas, Z. AI/ML algorithms and applications in VLSI design and technology. Integration 2023, 93, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Godil, S.; Khailany, B.; Kirby, R.; Liao, H.; Nath, S.; Raiman, J.; Roy, R. Optimizing vlsi implementation with reinforcement learning-iccad special session paper. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), Munich, Germany, 1–4 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.-T.; Chandna, A.; Guan, D.; Ho, A.; Kim, M.; Li, Y.; Ren, H. Novel Transformer Model Based Clustering Method for Standard Cell Design Automation. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Symposium on Physical Design, Taipei Taiwan, 12–15 March 2024; pp. 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, J.L. Algorithms to Improve Area Density Utilization, Routability and Timing During Detailed Placement and Legalization of VLSI Circuits. 2019. Available online: https://lume.ufrgs.br/handle/10183/197078 (accessed on 4 May 2025).
- Cheng, W.-K.; Guo, Y.-Y.; Wu, C.-S. Evaluation of routability-driven macro placement with machine-learning technique. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Symposium on Next Generation Electronics (ISNE), Taipei, Taiwan, 7–9 May 2018. pp. 1–3.
- Liu, S.; Sun, Q.; Liao, P.; Lin, Y.; Yu, B. Global placement with deep learning-enabled explicit routability optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; pp. 1821–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.-K.; Wu, C.-S. Machine Learning Techniques for Building and Evaluation of Routability-driven Macro Placement. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Taiwan (ICCE-TW), Yilan, Taiwan, 20–22 May 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Kuang, J.; Zhao, G.; Huang, D.J.-H.; Young, E.F. PROS: A plug-in for routability optimization applied in the state-of-the-art commercial EDA tool using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, Virtual, 2–5 November 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Shen, G.; Li, D.; Hao, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, G.; Heng, P.A. LHNN: Lattice hypergraph neural network for VLSI congestion prediction. In Proceedings of the 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 July 2022; pp. 1297–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Tabrizi, A.F.; Darav, N.K.; Xu, S.; Rakai, L.; Bustany, I.; Kennings, A.; Behjat, L. A machine learning framework to identify detailed routing short violations from a placed netlist. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–29 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Lee, J.; Agnesina, A.; Samadi, K.; Lim, S.K. GAN-CTS: A generative adversarial framework for clock tree prediction and optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Westminster, CO, USA, 4–7 November 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Hong, X.; Jing, T.; Zhang, L.; Gu, J. A coupling and crosstalk-considered timing-driven global routing algorithm for high-performance circuit design. Integration 2006, 39, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).