Effective Non-Stationary Clutter Suppression Method via Elevation Oblique Subspace Projection for Moving Targets Detection with a Space-Based Surveillance Radar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Signal Model and Clutter Characteristic Analysis
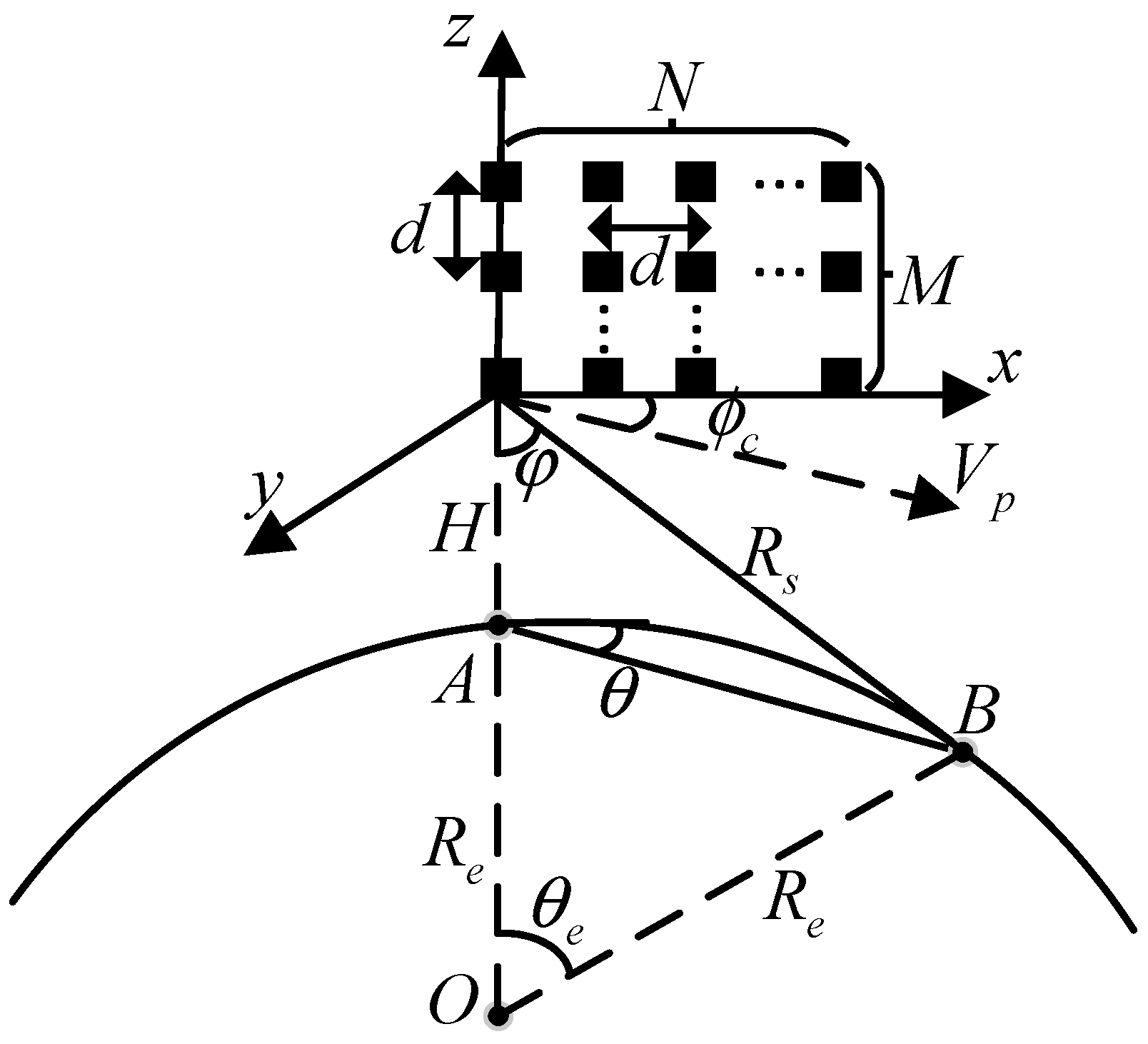
2.1. Signal Model of SBSR
2.2. Analysis of the Range Ambiguity Characteristics for the SBSR
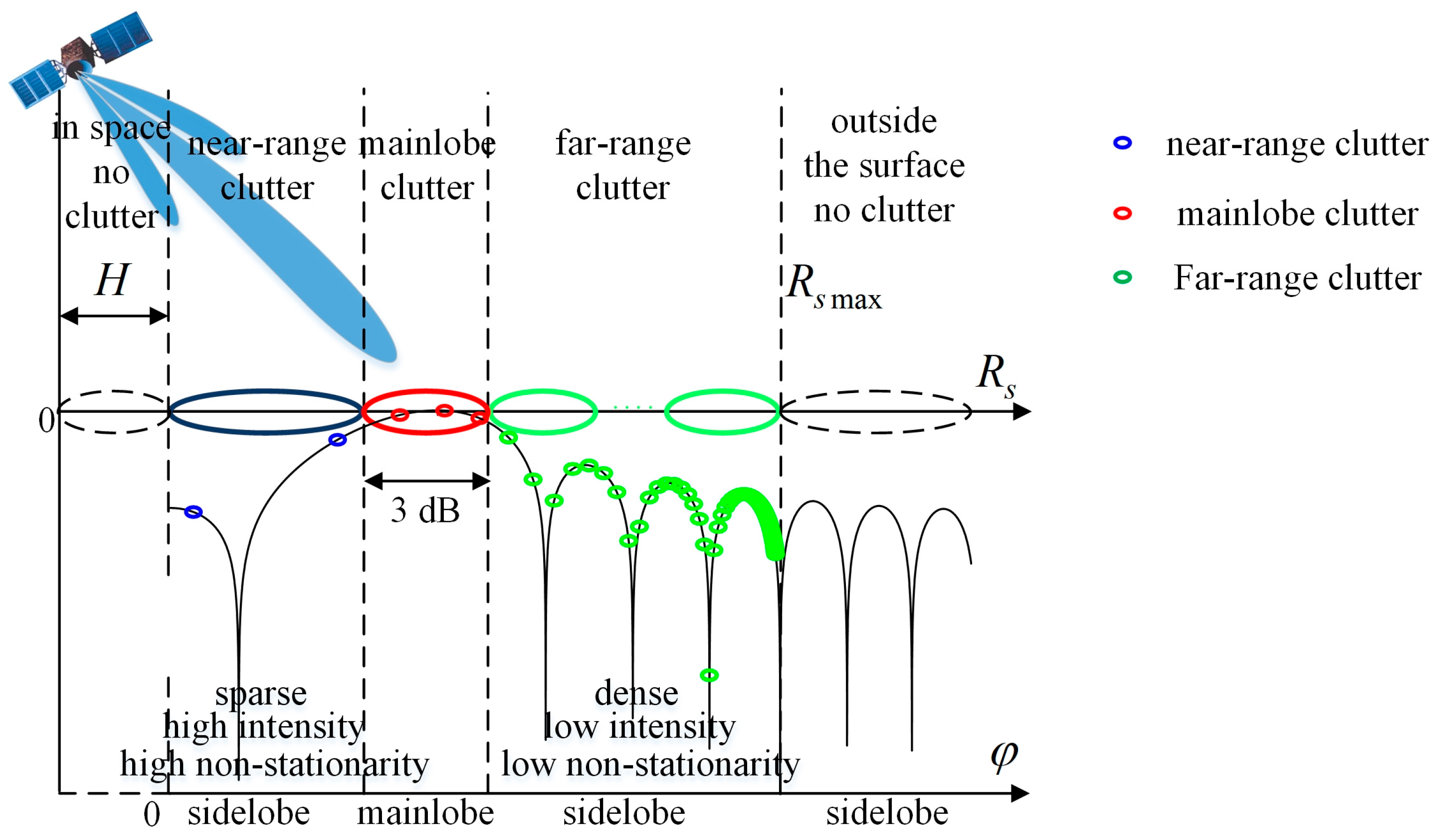
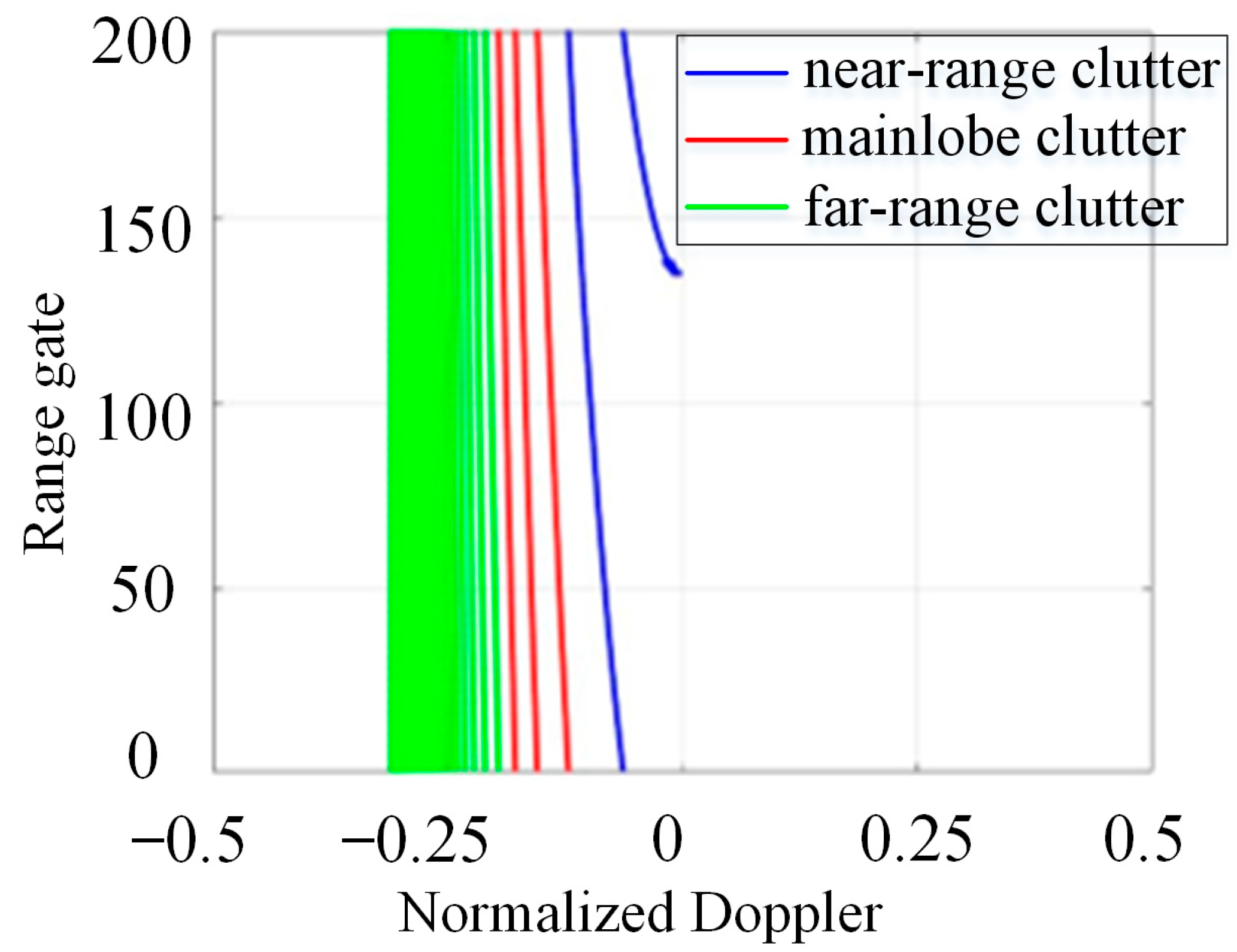
2.3. Analysis of Non-Stationarity for the Clutter of the SBSR
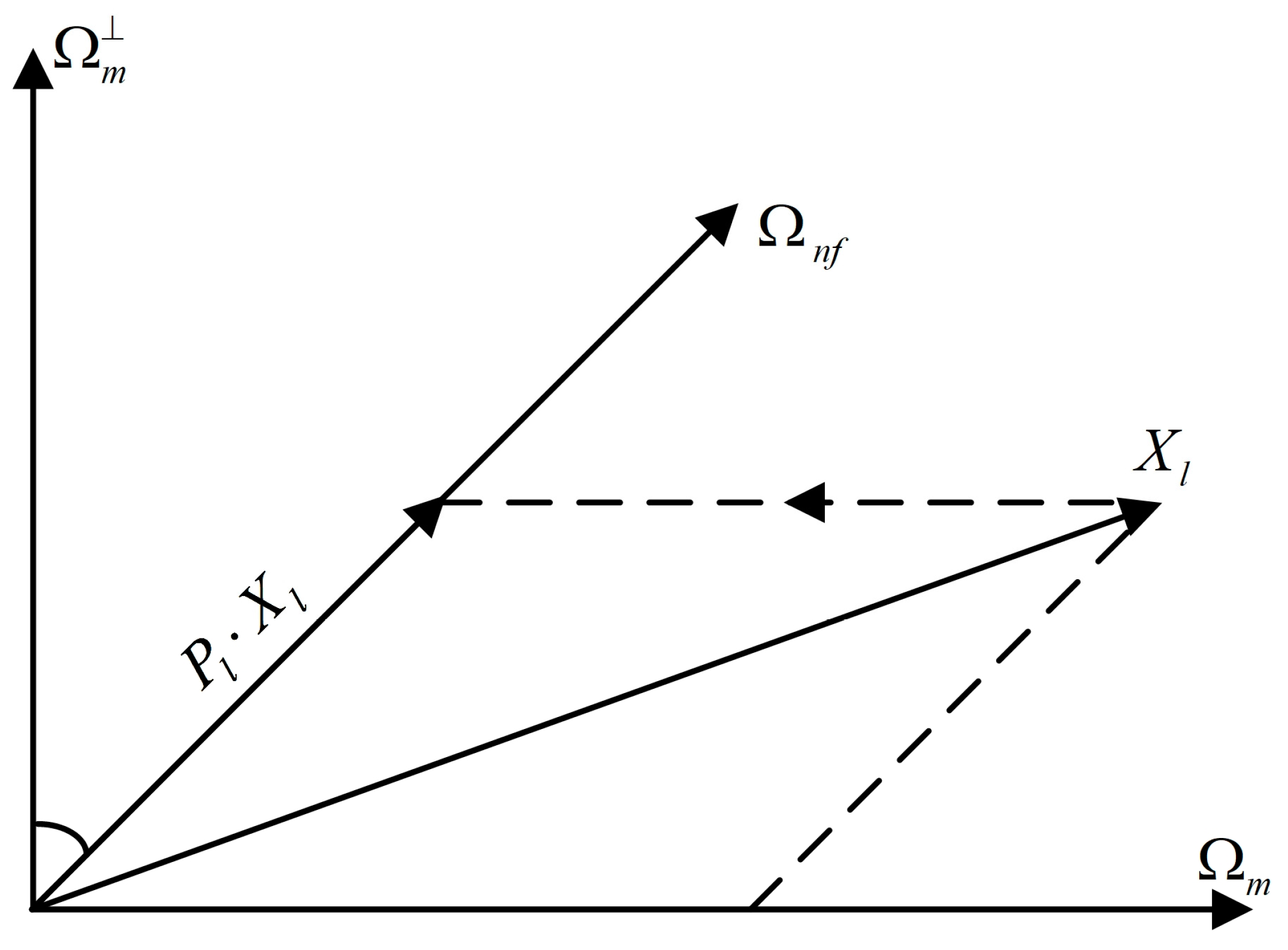
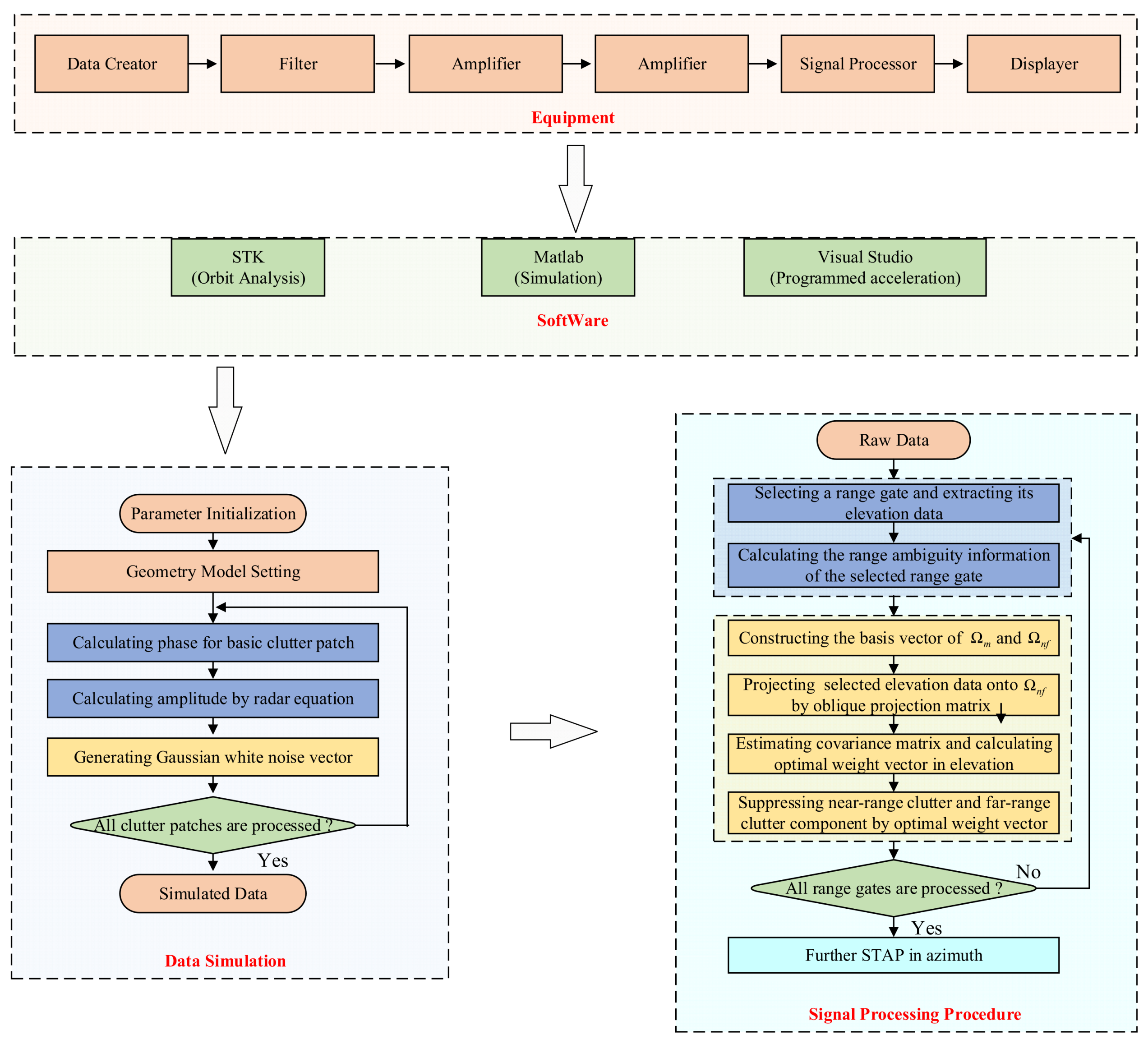
3. The Proposed Method
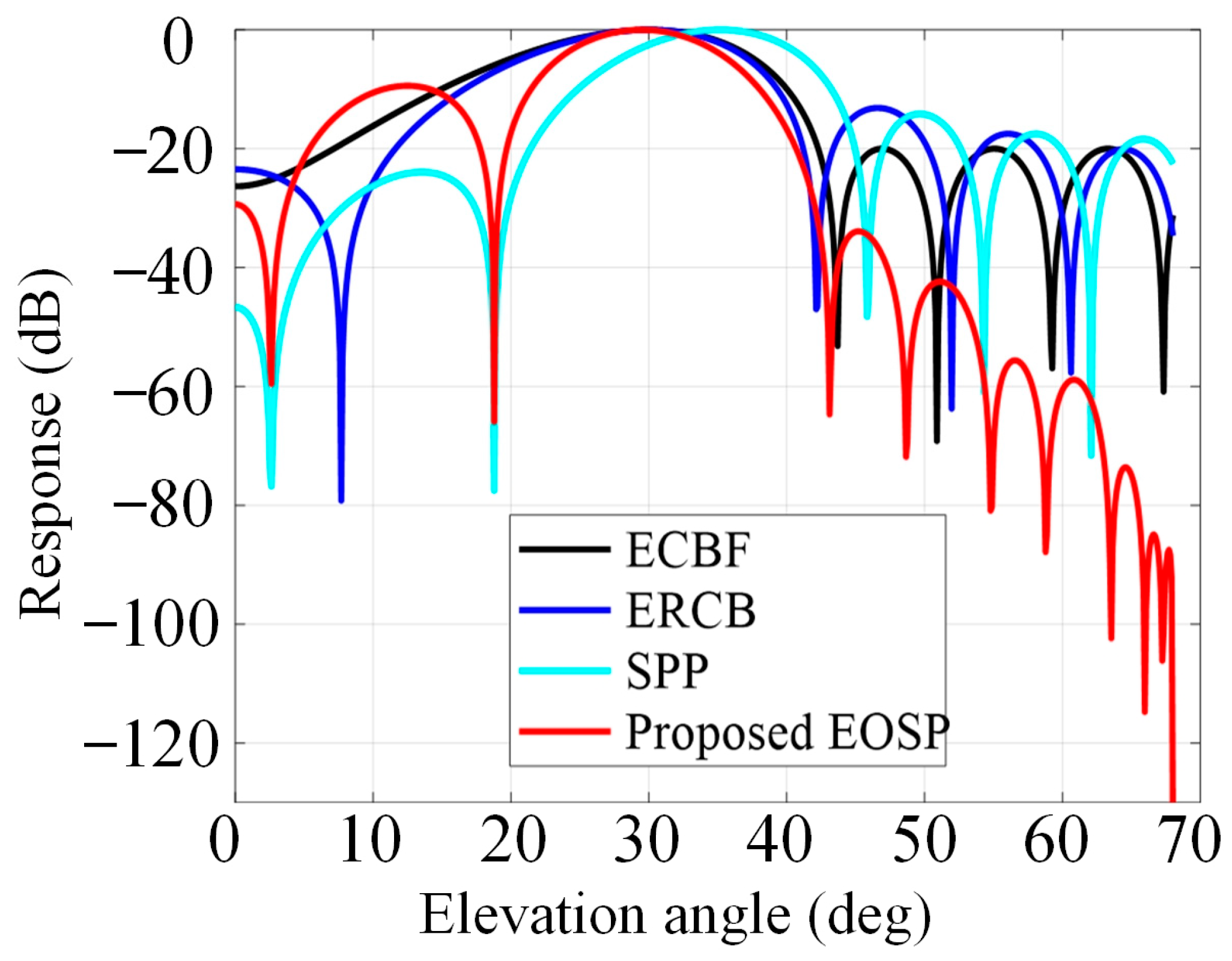
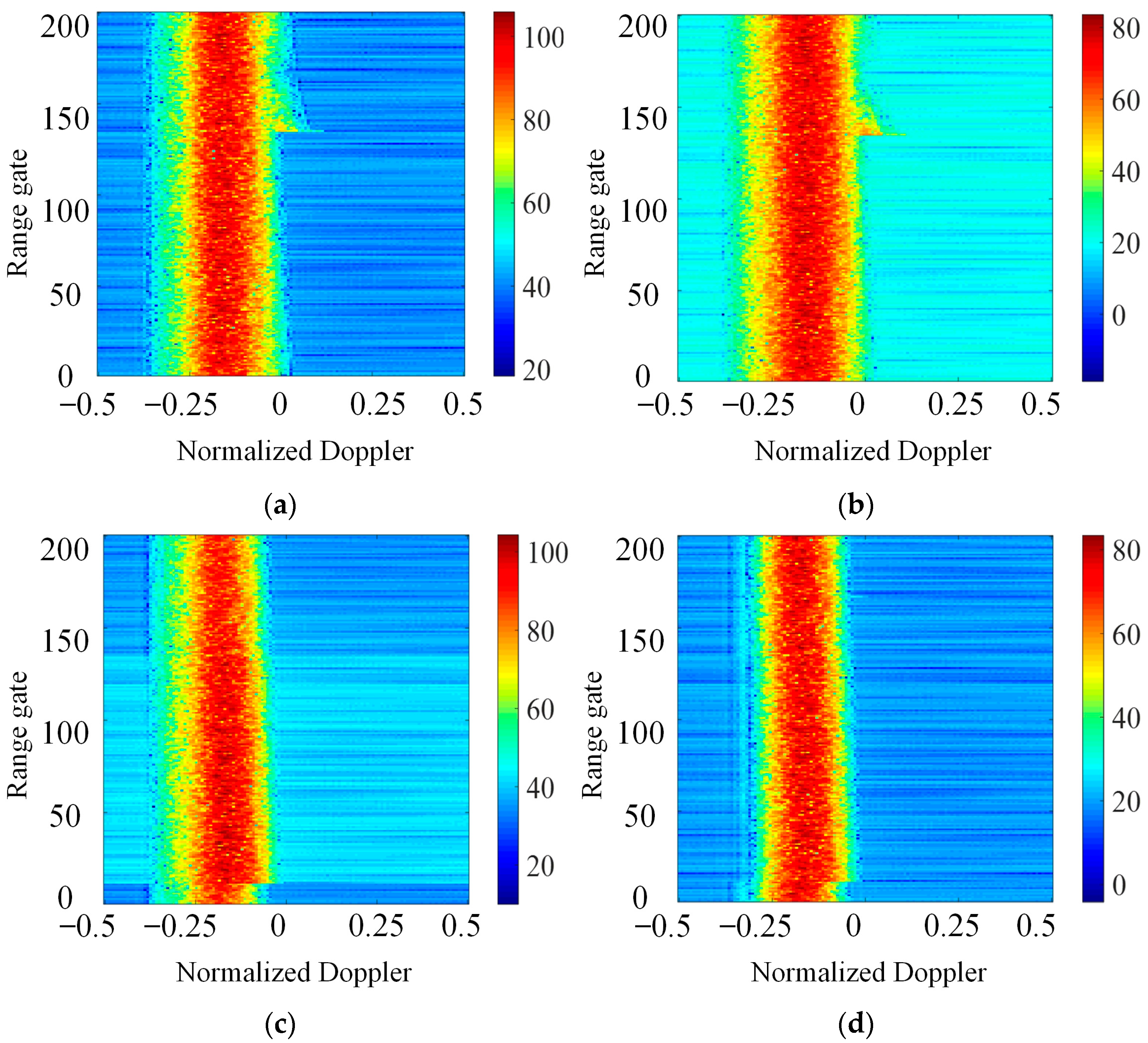
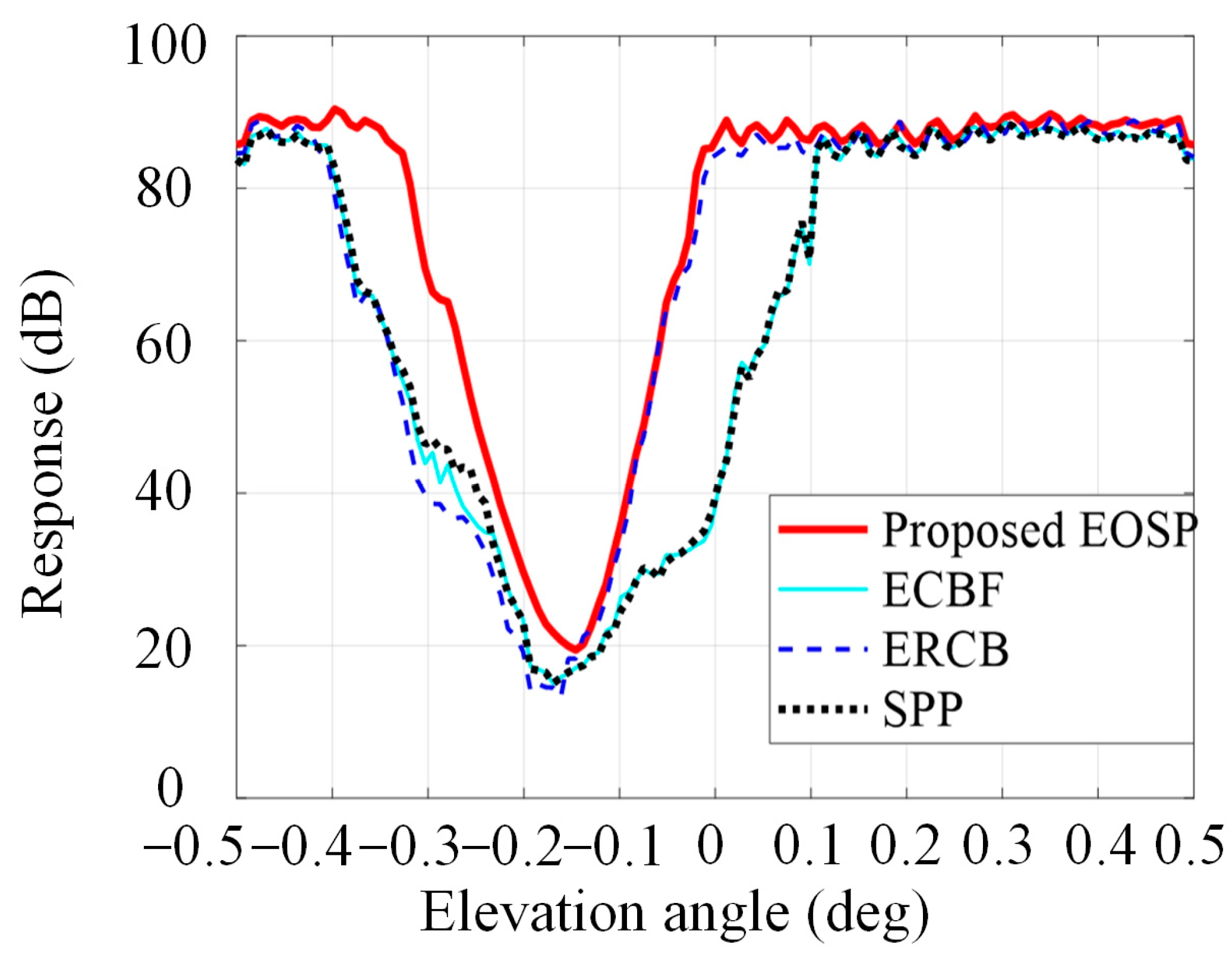
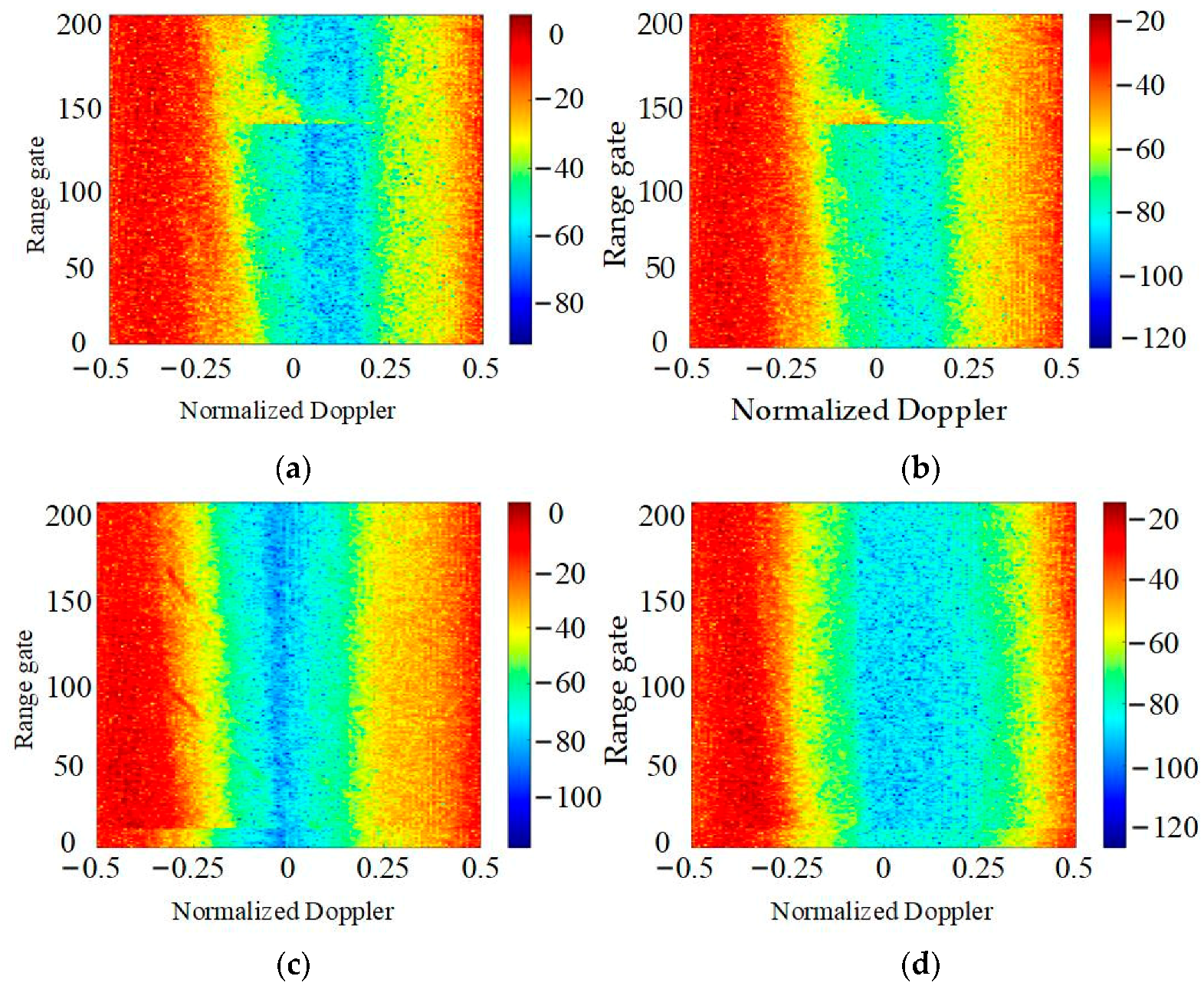
4. Experiment Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Yu, H.; Liang, B.; Yang, D.-G. Real-Time Processing of Spaceborne SAR Data with Nonlinear Trajectory Based on Variable PRF. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Xing, M.; Guo, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. Ground Moving Target Indication for the Geosynchronous-Low Earth Orbit Bistatic Multichannel SAR System. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5072–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sun, G.-C.; Xing, M.; Hu, Y.; Guo, L.; Bao, Z. Clutter Suppression via Subspace Projection for Spaceborne HRWS Multichannel SAR System. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Xing, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Research on Multi-Domain Dimensionality Reduction Joint Adaptive Processing Method for Range Ambiguous Clutter of FDA-Phase-MIMO Space-Based Early Warning Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Xing, M.; Wang, Y. Improved Dimension-Reduced Structures of 3D-STAP on Nonstationary Clutter Suppression for Space-Based Early Warning Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liao, G.; Zhu, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, C. Range-Ambiguous Clutter Suppression for the SAR-GMTI System Based on Extended Azimuth Phase Coding. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8147–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.; Himed, B.; Li, K.Y. Effect of earth’s rotation and range foldover on space-based radar performance. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2006, 42, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, I.S.; Mallett, J.D.; Brennan, L.E. Rapid Convergence Rate in Adaptive Arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1974, AES-10, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xie, W.; Wang, Y. Short-Range Clutter Suppression for Airborne Radar Using Sparse Recovery and Orthogonal Projection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, T.B.; Temple, M.A.; Wicks, M.C. Clutter suppression using elevation interferometry fused with space-time adaptive processing. Electron. Lett. 2001, 37, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, T.; Wu, J.; Bao, Z. Short-Range Clutter Suppression for Airborne Radar by Utilizing Prefiltering in Elevation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Meng, X.; Bao, Z. Clutter Suppression for Airborne Non-Sidelooking Radar Using ERCB-STAP Algorithm. IET Radar Sonar. Nav. 2010, 4, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X. Efficient adaptive approach for airborne radar short-range clutter suppression. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2012, 6, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, W.; Duan, K.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y. Short-range clutter suppression based on subspace projection preprocessing for airborne radar. In Proceedings of the CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 October 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Xu, H.; Yuan, H.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y. Reduced-DOF Three-Dimensional STAP via Subarray Synthesis for Nonsidelooking Planar Array Airborne Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 3311–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, R.T.; Scharf, L.L. Signal processing applications of oblique projection operators. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Matrix Analysis and Applications; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Orbit height | 500 km |
| Carrier frequency | 0.5 GHz |
| Crab angle | 3.77 deg |
| Azimuth angle | 90 deg |
| Elevation angle | 30 deg |
| Number of pulses | 128 |
| Array number in azimuth | 256 |
| Array number in elevation | 16 |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 5000 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, X. Effective Non-Stationary Clutter Suppression Method via Elevation Oblique Subspace Projection for Moving Targets Detection with a Space-Based Surveillance Radar. Electronics 2023, 12, 3110. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143110
Wang X, Ruan Y, Zhang X. Effective Non-Stationary Clutter Suppression Method via Elevation Oblique Subspace Projection for Moving Targets Detection with a Space-Based Surveillance Radar. Electronics. 2023; 12(14):3110. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143110
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaofeng, Yaduan Ruan, and Xinggan Zhang. 2023. "Effective Non-Stationary Clutter Suppression Method via Elevation Oblique Subspace Projection for Moving Targets Detection with a Space-Based Surveillance Radar" Electronics 12, no. 14: 3110. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143110
APA StyleWang, X., Ruan, Y., & Zhang, X. (2023). Effective Non-Stationary Clutter Suppression Method via Elevation Oblique Subspace Projection for Moving Targets Detection with a Space-Based Surveillance Radar. Electronics, 12(14), 3110. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143110





