Abstract
This paper analyses an off-nominal Class E ZVS amplifier, with an R.F. supply choke and the switch on-duty ratio D = 0.5, to identify conditions for its high-frequency and high-efficiency operation. Simple user-friendly analytical expressions for the essential parameters of the amplifier have been derived and subsequently validated by simulation and experimental results. It has been proven that the off-nominal amplifier can be optimized to outperform the nominal Class E amplifier with respect to crucial parameters such as, e.g., power efficiency or the operating frequency in some applications.
1. Introduction
Class E power amplifiers find applications in wireless communication systems as high-efficiency, constant-envelop-signal amplifiers or linearised amplifiers (EER, outphasing method or Doherty configuration) [1,2,3]. The high efficiency of the Class E PA has inspired its use in many other applications, such as: industrial induction heaters, dc/dc converters, plasma generators, wireless power transmission systems (WPT) supplying energy to RFID tags, medical implants and endoscopic capsules, etc. [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Such a wide range of applications often requires Class E amplifiers to be optimized to operate efficiently in the given conditions. A Class E amplifier is typically designed to operate in the nominal or optimum mode of operation with its switch commutating in ZVS and ZVDS (zero-voltage derivative switching) conditions [11,12]. The mode offers high efficiency, but it can be troublesome to adapt its parameters to requirements relating to its application. Matching circuits (LC networks or transformers) often have to be used to obtain the required output power for the specified load resistance and the dc supply voltage [11,13]. This increases the cost and complexity of the amplifier circuit. In addition, it can create new problems, such as circuit mistuning caused by the component instability in a high-Q LC matching network. Moreover, at a high frequency of operation the nominal mode in the Class E amplifier can be impossible to achieve if a transistor switch with a too large output capacitance is used. In the off-nominal (also called sub-optimum [11,14,15,16,17] or variable slope [16]) mode of operation of the Class E amplifier, the transistor switch commutates in ZVS conditions only. Then, there is a greater degree of freedom in designing and optimizing the amplifier parameters [14,18]. In this amplifier, its load resistance and output power can have their values designated independent of each other in a certain range. This helps eliminate the matching circuit [18]. Moreover, the maximum operating frequency of the off-nominal amplifier can be made much higher than the nominal one. The off-nominal Class E amplifier can be also optimized with respect to other parameters, such as power efficiency [19], power loss in the switch or maximum peak voltage/current in the switch, etc.
The off-nominal Class E amplifier with an R.F. supply choke has been analysed in several publications [12,14,15,16,18,19,20,21], with studies concentrating on selected aspects of the amplifier operation. In an earlier study [12], basic analytical relationships for sub-optimum Class E amplifiers were first given. By extending the analysis from this [12], a general expression for the maximum operating frequency for the off-nominal amplifier was obtained in a subsequent study [20]. A more general analysis presented in two different studies [14,15] demonstrated that peak switch voltage and current can be used as designated parameters in the off-nominal amplifier design. An extensive analysis of the amplifier with any off-duty ratio presented in another study [19] was based on numerical solving of the set of complex equations. It was shown that power efficiency in the off-nominal amplifier can be improved if compared to the nominal circuit, but at the expense of the significant reduction of output power. In another study [21], the analysis of the off-nominal Class E amplifier concerned output power/voltage control by frequency or reactance regulation. Power losses in the switch in the off-nominal amplifier were analysed in another work [18], but other aspects of the circuit operation were not considered.
The presented paper is a significant expansion of preliminary research and ideas published in an earlier paper [18]. In this paper, results of the analysis for the off-nominal Class E amplifier with an R.F. supply choke and on-duty ratio D = 0.5 are discussed with respect to practical application issues. Simple analytical design-oriented equations for power losses in the switch and reactive components; peak switch voltage and current; the maximum operating frequency as well as the efficiency of the amplifier have been derived. The analysis has proven that the maximum operating frequency of the off-nominal Class E amplifier can be made even a few times higher than the maximum operating frequency of the nominal/optimum Class E amplifier for both the same output power and dc supply voltage. This means that transistor switches with higher output capacitance can be used at a high operating frequency in the off-nominal amplifier. A method of reducing conduction losses in the transistor switch in the off-nominal amplifier, with designated output power by increasing its dc supply voltage, is also described and its limitations are discussed. A user-friendly design procedure for the off-nominal amplifier with D = 0.5 is proposed and illustrated with two design examples. Design Example I demonstrates the design of the off-nominal amplifier operating at a frequency that is too high for the nominal mode due to high output capacitance of the transistor switch. Design Example II shows how to reduce conduction losses in the switch by increasing the dc supply voltage of the amplifier for the given output power and load resistance. The design procedure used in the examples was validated by a simulation of the 30 W/13.56 MHz amplifier and measurements of 50 W/140 kHz experimental amplifier for Design Example I and Design Example II, respectively.
2. Circuit Analysis
A diagram of the analysed Class E amplifier is shown in Figure 1a. The amplifier is analysed for the following assumptions:
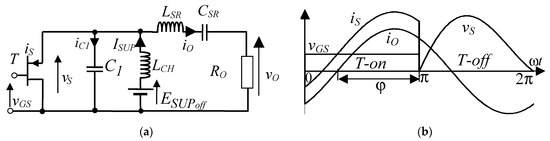
Figure 1.
Class E off-nominal amplifier with D = 0.5 (a) and its waveforms (b) LCH—supply choke; LSR, CSR, R—series resonant circuit components; C1—total parallel capacitance of the switch.
- (1)
- Transistor T is an ideal switch operating at the constant frequency f with zero switching times and normalized on-duty ratio D = 0.5;
- (2)
- All reactive components are linear and lossless, and choke LCH inductance is large enough to neglect its ac component;
- (3)
- The equation iO(ωt) = IO·sin(ωt + φ) is a sinusoidal output current with amplitude IO and phase φ;
- (4)
- At the switch turn-on instant the switch voltage vS(ωt = 2π) = 0 and its derivative is negative dvS(ωt = 2π)/dωt ≤ 0.
By modifying values of the components C1, LSR, CSR and RO, a nominal Class E amplifier can become an off-nominal amplifier. Hence, it significantly simplifies the analytical description of the off-nominal amplifier if its parameters are normalised to respective parameters of the nominal reference amplifier. Then, parameters of the off-nominal amplifier can be found from simple closed-form equations. This approach allows the designer to avoid using troublesome design data tables as proposed in one study [14], or retrieving some necessary parameters from a plot [15]. For both amplifiers it is also assumed that their operating frequencies f are equal and their dc supply voltages are equal ESUPoff = ESUPnom.
From the set of equations derived in one paper [21] for the Class E amplifier with an R.F. supply choke and D = 0.5, the following relations for the off-nominal amplifier are obtained:
where:
- xSRoff—normalised resultant reactance of the LSR–CSR branch at the operating frequency f for the off-nominal amplifier;
- Rnomr—total load resistance of the reference nominal amplifier;
- rO—total normalised load resistance Roff for the off-nominal amplifier;
- pO—normalised dc supply power for the amplifier (pO∈<0;1>, and for {pO = 1, rO = 1}-the amplifier operates in the nominal mode);
- PSUPoff, PSUPnom—dc supply power of the off-nominal and nominal Class E amplifiers, respectively.
As given by one study [11], in the nominal Class E amplifier operating with D = 0.5, its dc supply power PSUPnom and load resistance Rnom is expressed as
By using Equations (2), (4) and (5) and taking into account that ESUPnom = ESUPoff, the Equation (6) is expressed as
From (7), normalized dc supply power pO equals
For the nominal reference amplifier, its total load resistance Rnomr is found from (4) and (6)
Values of the reactive components for the off-nominal Class E amplifier from Figure 1 are obtained from equations for the nominal amplifier [11] and, therefore, for clarity they remain referenced to Rnomr
where QSRnomr—loaded quality factor for the series branch LSR–CSR of the nominal reference amplifier.
Voltage vS and current iS waveforms in the transistor T are derived in the same way as for the nominal circuit [11] but expressed by means of introduced normalised parameters, and they are given as follows:
where φ—phase shift of output current iO.
The waveform of the current iC1 in shunt capacitor C1 is given by:
Peak value VSMAXoff of the switch voltage vS occurs at ωtVSMAX
Peak value ISMAXoff of the switch current iS equals to
Power losses in transistor T are found, under assumption that they are small enough not to affect the waveforms [11,19]. Conduction power losses PCondoff in the switch T for off-nominal operation are obtained by integrating the switch current iS(ωt)
where rDSon—on resistance of the transistor switch T.
Switching losses in transistor T at its turn-off instant are estimated, assuming that the switch current iS falls linearly from its initial value iS(π), charging capacitor C1 during fall time tf << T = 1/f [11,17]
Power losses in the switch in the nominal amplifier are found from (20), (21) as the special case for pO = 1 and PSUPoff = PSUPnom, which agrees with the estimation given in [11]
Turn-on switching losses in the transistor T are neglected as small, assuming that transistor T is turned on when vS ≈ 0 (0 ≤ ωt < π) [11,19].
3. Analysis for Specific Conditions
Based on the presented general analytical description of the off-nominal Class E amplifier, its operation in specified conditions is analysed and relations defining the parameters of the amplifier are derived.
3.1. Equal dc Supply Voltages ESUPoff = ESUPnom
In the analysed conditions, the dc supply voltages of the off-nominal Class E amplifier and the nominal Class E reference amplifier are equal ESUPoff = ESUPnom. Off-nominal operation of the amplifier is obtained for any normalised dc power in the range pO∈<0;1>. From (20), (22) normalised conduction losses in the switch pCondoffE for the off-nominal amplifier are
The plot of conduction losses in the switch pCondoffE vs. dc power pO in Figure 2a shows that designing the off-nominal amplifier to operate with pO < 1 (which also means decreased output power) reduces conduction losses in the switch. The drain efficiency ηDoffE for the off-nominal amplifier for ESUPoff = ESUPnom can be found from (9), (20) and (21) as
where Rnomr is found from (6).
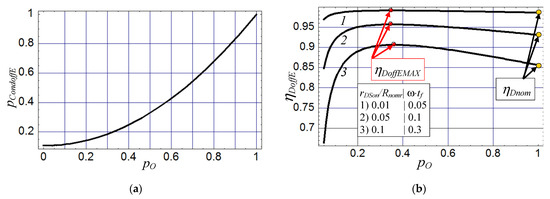
Figure 2.
Normalised conduction losses in the switch pCondoffE (a) and drain efficiency ηDoffE (b) of the off-nominal Class E amplifier vs. normalised dc power supply pO for ESUPoff = ESUPnom (the maximum value of drain efficiency ηDoffE and its value for the nominal operation are marked with red and yellow circles, respectively).
By solving dηDoffE/dpO = 0, one can determine the value of normalised dc power pO(ηDoffEMAX) for the maximum drain efficiency ηDoffEMAX for the given set of normalised switch on-resistance rDSon/Rnom and normalised turn-off time ω·tf as follows
The plots in Figure 2b demonstrate that the drain efficiency ηDoffE increases as pO (along with output power) decreases, starting from its nominal value pO = 1 (PSUPnom = PSUPoff). The maximum drain efficiency ηDoffEMAX occurs at approximately pO(ηDoffEMAX) ≈ 0.35. If conduction losses in the switch T are significant, then the value of ηDoffEMAX can be made higher up to a few percent (6% for curve—3 in Figure 2b) beyond the drain efficiency of the nominal amplifier ηDnom. For small values of pO- > 0, the drain efficiency ηDoffE decreases because load resistance Roff becomes small (rO- > 0 as pO- > 0,see Figure 3a) and then power losses in the switch resistance rDSon become significant if compared to the output power. When designing the amplifier, it is often necessary to take into account power losses in reactive components. Power loss in shunt capacitor C1 can be estimated from (9), (15) and (17) as
where rC1—series resistance of C1.
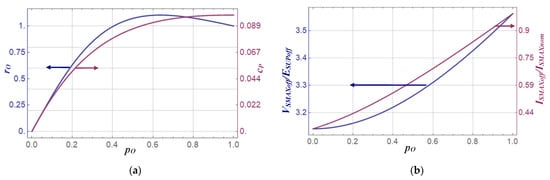
Figure 3.
Normalised load resistance rO and output power capability cp (a), normalised switch peak current ISMAXoff/ISUPnom and normalised peak switch voltage VSMAXoff/ESUPoff (b) vs. normalised dc supply power pO for ESUPoff = ESUPnom.
Loss PLSR in the series inductance LSR and loss PCSR in capacitor CSR are caused by conducted output current iO, and are found from Equations (2), (5) and (9) as
where ηoffE—total efficiency for the off-nominal amplifier (includes switch losses and reactive component losses); rLSR, rCSR—series resistance of inductance LSR and capacitor CSR, respectively.
Power loss in R.F. supply choke LCH results from dc supply current ISUPoff, and using (9) it is equal to
Total efficiency ηoffE for the off-nominal amplifier can be estimated as
From the plot in Figure 3a, it is seen that the off-nominal amplifier can be designed to operate with pO < 1 and load resistance Roff > Rnomr (rO > 1) or Roff ≤ Rnomr (rO ≤ 1). From derivative (2) drO/dpO = 0, the maximum value of Roff is RoffMAX = (1/π + π/4) × Rnomr = 1.1037 × Rnomr for pO = 2/π. To boost the efficiency of the off-nominal amplifier it can be designed to operate with load resistance Roff = Rnomr (rO = 1) but at reduced output power (pO < 1). By solving simple Equation (2) for rO = 1, it is found that then normalised dc power is pO = 4/π2 ≈ 0.4053. The obtained value of pO is consistent with the result (pO = 0.4070 for rO = 1) achieved in one study [19] in a much more laborious way by numerical solving of a set of complex equations. This demonstrates the efficacy of the here proposed analytical description of the amplifier. The plots of the normalised peak switch current ISMAXoff/ISMAXnom and normalised peak switch voltage VSMAXoff/ESUPoff vs. pO are displayed in Figure 3b. From the plots it is seen that the peak switch voltage VSMAXoff and peak switch current ISMAXoff decrease as the output power is reduced, and their values are smaller than those for the nominal amplifier. The normalised slope s of the switch voltage vS(ωt) at the switch turn-on instant (ωt = 2π) can be derived from (14) as s = (1/ESUPoff) × dvs/dωt = π × (pO − 1). Its minimum value s = −π occurs for pO = 0, and maximum s = 0 for pO = 1 (optimum operation). Power-output capability defined as cp = (ISUPoff × ESUPoff)/(ISMAXoff × VSMAXoff) can be found from (14), (15), (18) and (19). The plot of cp versus pO displayed in Figure 3a shows that cp is quite high even when power pO < 0.5 (cp(pO = 0.5) = 0.0865).
This is explained by peak switch current ISMAXoff/ISMAXnom decreasing as pO becomes smaller (Figure 3b). The presented analysis demonstrates that by designing the off-nominal amplifier to operate with reduced dc power (pO < 1) at ESUPoff = ESUPnom, its efficiency can be improved.
3.2. Equal dc Supply Voltages ESUPoff = ESUPnom and Equal dc Supply Power PSUPoff = PSUPnom
Here, it is assumed that dc supply voltages ESUPoff = ESUPnom = const. and dc supply power PSUPoff = PSUPnom = const. for both the off-nominal and the nominal amplifiers are equal, respectively. Thus, normalised conduction losses pCondoffPE in the switch found from (20) and (22) are given by
The drain efficiency ηDoffPE for the off-nominal amplifier for ESUPoff = ESUPnom, PSUPoff = PSUPnom is estimated from (9), (20), (21) as
Since the off-nominal amplifier operates with constant dc supply power PSUPoff = const. its parameters are presented vs. normalised load resistance Roff/Rnom, which from (5), (6) and (7) equals to
In Figure 4a the plot of normalised conduction losses pCondoffPE in the switch vs. load resistance Roff/Rnom shows that conduction losses in the switch increase as load resistance decreases. Similarly, the drain efficiency ηDoffPE is also reduced (Figure 4b) as normalised resistance Roff/Rnom decreases. This results from the assumption that PSUPoff = const., which requires that any decrease of load resistance Roff/Rnom has to be compensated for by the increase of the amplitude IO of the load current iO to fulfil the assumption. Hence, the switch peak current ISMAXoff (Figure 4a) also increases as Roff/Rnom is reduced, leading to higher losses in the switch. The plot of the normalised peak switch voltage VSMAXoff/ESUPoff vs. Roff/Rnom shows that the value of the maximum voltage across the switch decreases as load resistance is diminished. Hence, the switch peak current ISMAXoff (Figure 4a) also increases as Roff/Rnom is reduced, leading to higher losses in the switch. The plot of the normalised peak switch voltage VSMAXoff/ESUPoff vs. Roff/Rnom shows that the value of the maximum voltage across the switch decreases as load resistance is diminished.
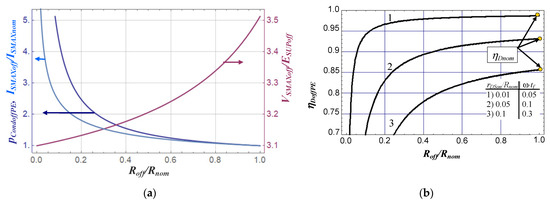
Figure 4.
Normalised conduction losses pCondoffPE, normalised switch peak current ISMAXoff/ISUPnom, normalised peak switch voltage VSMAXoff/ESUPoff (a) and drain efficiency ηDoffPE (b) vs. normalised load resistance Roff/Rnom for ESUPoff = ESUPnom and PSUPoff = PSUPnom= const. (yellow circles in (b) mark the value of drain efficiency ηDoffPE for the nominal operation Roff=Rnom).
This is the effect of the increased value of capacitance C1, which has to be increased to maintain PSUPoff = const. when Roff is reduced (see (9), (12)).
A typical problem occurring while designing a nominal Class E amplifier for designated voltage ESUPnom, dc power PSUPnom and the operating frequency f is that the frequency f exceeds the maximum operating frequency fMAXnom of the nominal amplifier (f > fMAXnom). Above frequency fMAXnom, shunt capacitance C1 is not fully discharged prior to the switch T turn-on, which results in switching losses (non-ZVS) and reduced efficiency. For the nominal Class E amplifier (D = 0.5), the maximum operating frequency is found from (6) and (12) [12] as fMAXnom = PSUPnom/(2π2·C1 × ESUPnom2) ≈ 0.05066 × PSUPnom/(C1 × ESUPnom2). The off-nominal Class E amplifier can operate in ZVS mode at frequencies that are higher than the maximum fMAXnom. The maximum operating frequency fMAXoff for the off-nominal amplifier (D = 0.5) is obtained from (9) and (12) as
For PSUPoff = PSUPnom, ESUPoff = ESUPnom, and an identical value of the switch shunt capacitance C1, the ratio fMAXnom/fMAXoff of the maximum frequencies for off-nominal and nominal operation of the Class E amplifier can be expressed as
By selecting a small enough value of normalised dc power pO < 1 the maximum operating frequency fMAXoff can be increased even several times over the value of maximum frequency fMAXnom of the nominal amplifier for the same values of output power, dc supply voltage and shunt capacitance C1. However, the small value of pO increases losses in the switch (31), decreasing the drain efficiency ηDoffPE (Figure 4b). A relation between the ratio fMAXnom/fMAXoff and the normalised conduction losses pcondoffPE can be found from (31) and (35) for PSUPoff = PSUPnom, ESUPoff = ESUPnom as
Using (36) one can find out how the increase in the frequency fMAXoff affects conduction losses in the switch T (switching losses are neglected for simplicity). From Figure 5a it is seen that, e.g., for fMAXnom/fMAXoff = 0.5 is pcondPE = 1.317, which means that conduction losses PCondoff in the switch increase slower than the rise of the operating frequency fMAXoff (two times). Thus, it is possible to design an efficient off-nominal amplifier to operate at a given PSUPoff, ESUPoff and a high frequency fMAXoff>fMAXnom if power losses in the switch are sufficiently small. This is displayed in Figure 5b by the plots of ηDoffPE vs. fMAXoff/fMAXnom. When designing the off-nominal amplifier to operate above fMAXnom, it is also useful to estimate the required on-resistance rDSon of the switch for the assumed drain efficiency ηDoffPE. A simplified estimation of the normalised on-resistance rDSon/Rnom can be found from (32) by neglecting the usually small switching losses (PSWoff = 0). Then using (35) one arrives at the expression
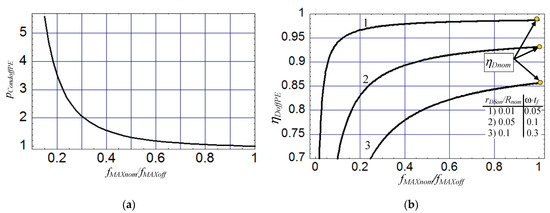
Figure 5.
Normalised conduction losses pCondoffPE in the transistor (a) and drain efficiency ηDoffPE (b) vs. normalised maximum operating frequency fMAXnom/fMAXoff for the off-nominal amplifier for PSUPoff = PSUPnom, ESUPoff = ESUPnom (yellow circles in (b) mark the value of drain efficiencyηDoffPE for the nominal operation).
The equation (37) can be also used for the preliminary assessment of the attainable drain efficiency ηDoffPE for normalised frequency fMAXnom/fMAXoff for a switch T with known rDSon.
3.3. Equal dc Supply Power PSUPoff = PSUPnom and Equal Load Resistance Roff = Rnom
In some applications Class E amplifiers are used as H.F. high-current drivers for low-resistance loads such as loop antennas (with low radiation resistance) or low-impedance power transmitting coils (e.g., RFID or an endoscopic transmitting coil). High currents in the amplifier circuit can result in high losses in its components. The transistor switch is usually most vulnerable because both switching and conduction losses occur in it. Typically, to reduce conduction losses in components a matching circuit is used that transforms low-resistance load to a higher value “seen” by the amplifier. This, however, increases the cost and complicates the amplifier circuit. In the off-nominal amplifier it is possible to reduce conduction losses in the transistor switch by increasing the dc supply voltage ESUPoff. Then, the matching circuit may become unnecessary. To compare switch losses in the nominal and off-nominal Class E amplifiers, let us assume that both amplifiers are loaded with equal load resistance Rnom = Roff, have equal dc power PSUPnom = PSUPoff and dc supply voltage ESUPoff>ESUPnom. From (2), (7), (20) and (21)–(23), normalised conduction losses pCondoffPR and normalised switching losses pSWPR in the transistor T are found as
The plot of normalised conduction losses pCondoffPR vs. normalised dc supply voltage ESUPnom/ESUPoff is presented in Figure 6a. From the plot it can be seen that increasing the dc supply voltage ESUPoff decreases the ratio ESUPnom/ESUPoff and it consequently reduces conduction losses PCondoff in the transistor T if compared to transistor losses PCondnom in the nominal amplifier. There is, however, a limit in reducing conduction losses in the switch T by this method. As the ratio (ESUPnom/ESUPoff) → 0, then the normalised conduction losses pCondoffPR → (π2 + 4)/(π2 + 28) ≈ 0.3663. This is explained by the fact that then ESUPoff → ∞, the dc supply current ISUPoff → 0 and the conduction losses in transistor T result only from conducting output current iO (then PCondoff = IO2 × rDSon/4). The case ESUPoff → ∞ is of no practical use, but if one assumes, e.g.,pCondoffPR = 0.5 (50% decrease of conduction losses in the switch T), then from (38) is ESUPnom/ESUPoff = 0.4594 and from (14) is VSMAXoff/ESUPoff = 3.178. Increasing ESUPoff also causes switching losses pSWPR to rise (39), but usually for tf << T switching losses are much smaller than conduction losses.
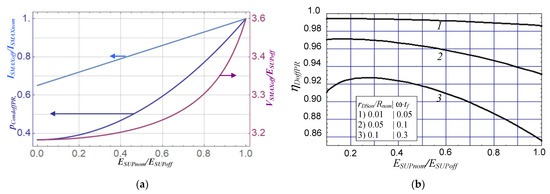
Figure 6.
Normalised conduction losses pCondoffPE, switch peak current ISMAXoff/ISUPnom, peak switch voltage VSMAXoff/VSMAXnom (a) and drain efficiency ηDoffPR (b) vs. normalised dc supply voltage ESUPoff/ESUPnom for PSUPoff = PSUPnom and Roff = Rnom.
From (2) and (25), the drain efficiency ηDoffPR of the off-nominal amplifier for PSUPoff = PSUPnom and Roff = Rnom is expressed as
From (40) by neglecting switching losses one obtains an estimation of the normalized switch on-resistance rDSon/Rnom for the assumed value of drain efficiency ηDoffPR.
The plots in Figure 6a,b demonstrate that increasing dc supply voltage ESUPoff reduces conduction losses pCondoffPR in the switch T, and it can improve drain efficiency ηDoffPR by 5–6%. However, the increase of ESUPoff more than 3–4 times over ESUPnom can lead to drop in the efficiency ηDoffPR because of switching losses in T (curve 3 in Figure 6b). The plots of peak switch current ISMAXoff/ISMAXnom and peak switch voltage VSMAXoff/ESUPoff displayed in Figure 6a show that they tend towards finite values ISMAXoff/ISMAXnom → (4 + π2)0.5/(2 + (4 + π2)0.5) ≈ 0.6505 and VSMAXoff/ESUPoff → π.
4. Design Examples, Simulations and Experimental Verification
4.1. Design Example I
To verify the efficacy of the presented analysis in the H.F. range, a practical example of an off-nominal Class E amplifier (as in Figure 1a) is designed and verified by simulation with LTspice. The simulation is carried out for two types of switches: (a) an ideal bi-directional switch T with zero switching times, on-resistance rDSon = 16 mΩ and (b) a model of eGaN FET transistor EPC2016-Infineon (VDSMAX = 100 V, rDSon = 16 mΩ, estimated equivalent output capacitance of the transistor CT = 340 pF). Calculated and simulated parameters of the amplifier are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Design example I—specification and comparison of results.
The off-nominal amplifier is designed for the following specification: dc supply voltage ESUPoff = 24 V, dc supply power PSUPoff = 30 W (to simplify the design, power losses in reactive components are assumed small and neglected), operating frequency—foff = 13.56 MHz, QSRnomr = 10—loaded quality factor, normalized fall-time of the drain current ωtf = 0.05, drain efficiency ηDoffPE > 0.99. For the given data, the maximum operating frequency fMAXnom of the nominal Class E amplifier is too low (from (34) fMAXnom = fMAXoff (pO = 1) = 7.76 MHz). SincefMAXnom < foff, the nominal Class E amplifier with D = 0.5 cannot be used in this design. It is, therefore, necessary to use the off-nominal amplifier. To design the off-nominal amplifier, the normalised dc power pO has to be chosen. Its maximum value is pOMAX = fMAXnom/foff = 7.76/13.56 = 0.5723, but the preferred value of pO, ensuring high efficiency (Figure 2b), is pO = 0.35. An advantage of using lower pO is also that the shunt capacitance C1 is increased, which reduces its nonlinearity resulting from transistor output capacitance CT (C1 = Cext(linear) + CT). Nonlinear CT is responsible for the increased value of the peak switch voltage VSMAXoff [22,23]. Values of the calculated basic parameters for the example I amplifier are given in Table 2. The calculated drain efficiency is ηDoffPE = 0.996, which is better than its preliminary assumed value of 0.99. This results from the lower rDSon resistance of EPC2016. The maximum allowable value of the switch on-resistance rDsonmax for the assumed ηDoffPE > 0.99 is given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Design example I—calculated values of the basic parameters.
Simulated waveforms for the amplifier with the model of eGaN FET EPC2016 are depicted in Figure 7a. The gate driver of the transistor was a voltage source generating a rectangular waveform (D = 0.5), changing from 0 V to 5 V with the rise/fall times equal to 0.5 ns and its internal resistance RDRV = 1.5 Ω. Higher than calculated values of simulated peak voltage VSMAXoff of the switch and higher output power PO result from the use of finite values of inductance LCH and loaded quality factor QSRnomr. Moreover, in the simulation with the model of eGaN FET EPC2016, the nonlinearity of the transistor output capacitance CT additionally increased the value of the peak drain voltage VSMAXoff. The example I amplifier can operate at even a much higher frequency, but with increased power losses. Assuming drain efficiency ηDoffPE = 0.99, ωtf = 0.05, rDSon = 16 mΩ from (32) is pO = 0.236, which results in foff = fMAXnom/pO = 7.76 MHz/0.236 = 32.88 MHz and power losses PCondoff = 0.165 W, PSWoff = 0.132 W. Thus, the maximum operating frequency of the off-nominal Class E amplifier can be flexibly adjusted to the designer’s needs.
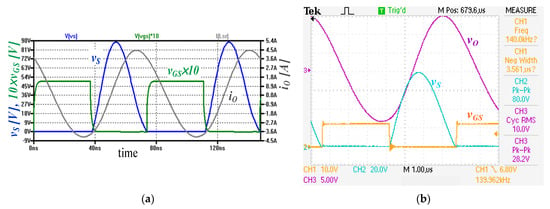
Figure 7.
(a) Waveforms simulated with LTSpice for design example I with the model of EPC2016 transistor; (b) voltage waveforms in the experimental off-nominal Class E amplifier for design example II; vS—drain voltage, vGS—gate voltage, iO—output current; vO—output voltage.
4.2. Design Example II
To verify the method of reducing conduction losses in the switch, an off-nominal Class E amplifier was designed, built and tested. The circuit specifications were as follows: f = 140 kHz, D = 0.5, output resistor RO = 2 Ω, output power PO = 50 W, assumed total efficiency of the amplifier (driving losses excluded) ηoffassum = 0.95, drain efficiency ηDoffPR > 0.99, loaded quality factor QSRnomr = 8, dc supply power PSUPoff = PSUPnom = PO/ηoffassum = 50/0.95 = 52.63 W, total load resistance of the off-nominal amplifier Roff = Rnom = RO/ηoffassum= 2/0.95 = 2.105 Ω, fall time of the switch current tf = 50 ns. If, for the given specifications, a nominal Class E amplifier (pO = 1, rO = 1)is used, then it has to operate with a dc supply voltage ESUPnom = 13.86 V (6), losses: conduction PCondnom = 0.410 W (22) and switching PSWnom = 8.484 mW (23), as well as peak switch voltage VSMAXnom = 49.37 V (14).
To reduce conduction losses in transistor T, a dc supply voltage for the off-nominal amplifier was arbitrarily chosen to be a standard value ESUPoff = 24 V (it can be any value higher than ESUPnom).
By comparing estimated values of conduction losses PCondnom in the nominal amplifier and losses PCondoff in the example II amplifier (Table 3), one can notice an over 42% reduction of conduction losses in the off-nominal amplifier.

Table 3.
Design example II—calculated values of the basic parameters.
The actual values of components used in the experimental amplifier were as follows: LCH= 364.8 μH, LSR = 20.63 μH, CSR = 87.31 nF, C1 = 93.03 nF, RO = 2 Ω (RNP-50s/Nikkom), transistor T-IFRB4228 150 V/12 mΩ. To possibly reduce losses in reactive components, both inductive components were wound with Litz wire 270 × 0.071 (LCH—38 turns, LSR—13 turns)on custom gapped ETD44/22/15 3F3 ferrite cores and, as capacitors,CSR and C1 low-loss MLCC C0G TDK capacitors were used. The measured efficiency of the built circuit (excluding driver loss) was ηmeas = 0.95 = ηoffassum, which agrees well with the calculated value of efficiency ηoffcalc = 0.954 obtained from (30) for rC1 = rCSR = 2 mΩ, rLSR = 0.07 Ω and rLCH = 0.1 Ω.
In Figure 7b, voltage waveforms in the experimental circuit are shown. Higher than predicted peak switch voltage VSMAXoff resulted from: the finite value of the used choke LCH inductance, as well as from distortion of output current iO caused by a finite QSRnomr value. The schematic of the experimental circuit and the photograph of the actual amplifier are shown in Figure 8a,b, respectively.
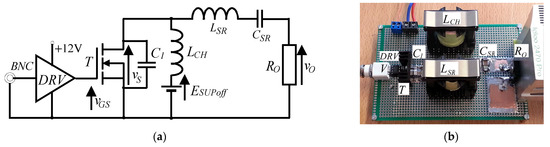
Figure 8.
Schematic of the example II amplifier (a) and the actual circuit (b); DRV—driver TC4422.
5. Conclusions
In the paper, an off-nominal Class E amplifier with an R.F. supply choke and duty ratio D = 0.5 was analysed to assess its potential to operate with high efficiency at a high operating frequency. Simple closed-form analytical expressions have been derived to estimate essential parameters of the amplifier such as: power losses in the transistor switch, its maximum operating frequency, power efficiency, peak voltage across the switch, etc. The derived equations provide an effective, easy and flexible way to optimize the amplifier in respect to its various parameters, largely eliminating the need to use data tables, plots or numerical solvers to extract amplifier parameters.
By means of design examples, simulation and measurements it has been demonstrated that the off-nominal Class E amplifier can operate at a frequency much higher than the nominal Class E amplifier, and that conduction losses in the transistor switch can be effectively reduced by increasing the dc supply voltage of the amplifier. The obtained results can be useful in designing Class E amplifiers for applications in transmitters for wireless communication systems, in wireless power transmission systems supplying energy to RFID tags, sensors or medical instruments such as wireless endoscopic capsules, etc., as well as in resonant dc/dc converters or induction heaters.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Tsai, K.-C.; Gray, P.R. A 1.9-GHz, 1-W CMOS class-E power amplifier for wireless communications. IEEE J. SolidState Circuits 1999, 34, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunihiro, K.; Hori, S.; Kaneko, T. High Efficiency Power Amplifiers for Mobile Base Stations: Recent Trends and Future Prospects for 5G. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2018, 101, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajedin, M.; Elfergani, I.T.E.; Rodrigez, J.; Abd-Alhamed, R.; Barciela, M.F. A servey on RF and microwave Doherty power amplifier for mobile handset applications. MDPI Electron. 2019, 8, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczuk, M.K.; Czarkowski, D. Resonant Power Converters; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 347–378. [Google Scholar]
- De Mulder, E.; Aerts, W.; Preneel, B.; Verbauwhede, I.; Vandenbosch, G. Case study: A Class E power amplifier for ISO-14443A. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits & Systems, Liberec, Czech Republic, 15–17 April 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoecklin, S.; Volk, T.; Yousaf, A.; Reindl, L. A programmable and self-adjusting Class E amplifier for efficient wireless powering of biomedical implants. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrairi, M.K.; Sulaiman, N.B.; Sidek, R.B.; Mutashar, M.S. Unique Micro System Stimulator with High Data Rate and Efficient Power Recovery Circuit. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2016, 92, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Cheng, X.; Li, Q.; Ye, J. Wireless charging system using resonant inductor in Class E power amplifier for electronics and sensors. MDPI Sens. 2020, 20, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Martınez, J.A.; Pena-Eguiluz, R.; Lopez-Callejas, R.; Mercado-Cabrera, A.; Alvarado, R.V.; Barocio, S.R.; de la Piedad-Beneitez, A. Power Supply for Plasma Torches Based on a Class-E Amplifier Configuration. Plasma Process. Polym. 2008, 5, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Castellanos, S.; Xu, S.; Wood, B.; Ren, H.; Ho Tse, Z.T. Applications of Wireless Power Transfer in Medicine: State-of-the-Art Reviews. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basar, R.; Ahmad, M.Y.; Cho, J.; Ibrahim, F. Application of Wireless Power Transmission Systems in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy: An Overview. Sensors 2014, 14, 10929–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suetsugu, T.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Design procedure of class-E amplifier for off-nominal operation at 50% duty ratio. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2006, 53, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsugu, T.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Off-nominal operation of class-E amplifier at any duty ratio. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. IReg. Pap. 2007, 54, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, M.; Annema, A.J.; Nauta, B. Generalized analytical design equations for variable slope Class-E power amplifier. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, Nice, France, 10–13 December 2016; pp. 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, F.H.; Sokal, N.O. Transistor power losses in the Class E tuned power amplifier. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1978, 13, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, F.H. Idealized operation of the Class E tuned power amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1977, 24, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajewski, M. A Class E ZVS amplifier with basic matching circuits. In Proceedings of the 2020 Baltic URSI Symposium (URSI), Warsaw, Poland, 5–8 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediano, A.; Molina, P. Frequency limitation of a high-efficiency class E tuned RF power amplifier due to a shunt capacitance. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (Cat. No.99CH36282), Anaheim, CA, USA, 13–19 June 1999; pp. 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima, T.; Wei, X.; Sekiya, H.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Power conversion efficiency of Class-E power amplifier outside nominal operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 15–18 May 2011; pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajewski, M. Output Voltage Control in the Class E ZVS Inverter by Frequency or Reactance Regulation. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2020, 96, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajewski, M.; Kazubski, W. A resonant Class E amplifier for low resistance load. In Proceedings of the Baltic URSI Symposium (URSI), Warsaw, Poland, 5–8 October 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsugu, T.; Kazimierczuk, M.K. Comparison of Class-E amplifier with nonlinear and linear shunt capacitance. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2023, 50, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediano, A.; Molina-Gaudo, P.; Bernal, C. Design of Class E amplifier with nonlinear and linear shunt capacitances for any duty cycle. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).