Abstract
This paper presents a 1024-bit self-adaptive memory address decoder based on Dual Mode Logic (DML) design style to allow working in two modes of operation (i.e., dynamic for high-performance and static for energy-saving). The main novelty of this work relies on the design of a controlling mechanism that mixes both of these modes of operation to simultaneously benefit from their inherent advantages. When performance is the primary target, the mixed operating mode is enabled, and the self-adjustment mechanism identifies at run time the logic gates that have to work in the energy-efficient mode (i.e., static mode), while those belonging to the critical path operate in the faster dynamic mode. Moreover, our address decoder can run in the fully static mode for the lowest energy consumption when speed is not a primary concern. A 65 nm CMOS technology was exploited to simulate and compare our solution with other logically equivalent dynamic and static designs. Operated in the mixed mode, the proposed circuit exhibits negligible speed reduction (8.7%) in comparison with a dynamic logic based design while presenting significantly reduced energy consumption (28%). On the contrary, further energy is saved (29%) with respect to conventional logic styles when our design runs in its energy efficient mode.
1. Introduction
The increased use of portable devices along with the upswing of the Internet of Things (IoT) has changed the circuit design paradigm into having a more energy efficient focus to preserve limited battery lifetimes, without significantly compromising the performance [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. For several decades [10], the static CMOS logic family has imposed itself as the design standard for digital systems. CMOS static gates implement logic functions exploiting two complementary networks: the pull-up network (PUN) and the pull-down network (PDN) composed by PMOS and NMOS transistors, respectively. There main limitations on the speed performance of CMOS static logic gates, especially for high fan-in gates, are the large input capacitance and the contention between the PUN and the PDN during the gate switching [10,11,12]. In order to counteract these drawbacks, dynamic domino logic can be used for the design of high-speed data paths [13,14,15,16,17,18], at the expense of higher energy and increased sensibility to process variations [19,20,21,22,23].
The Dual Mode Logic (DML) family has been proposed as an alternative for digital design with the ability to combine the speed of a dynamic logic style with the energy efficiency and robustness of static CMOS logic [24,25,26]. This property is maximized if a mixed mode (i.e., using static and dynamic at the same time) is enabled within the same design [25,27], where each attribute, performance, or energy efficiency is chosen according to the system requirements.
In this paper, the design of a 1024-bit self-adaptive address decoder (SAAD) based on the DML design methodology under the 65 nm TSMC technology is presented. The SAAD allows mixed mode running to achieve both high speed and energy efficiency. Even though previous work has already presented a DML Address Decoder (AD) [28], the novelty of this work revolves around the implementation of a controller to enable mixed mode operation [25,29] as well as the use of a non-conventional AD architecture based on [30]. An AD benchmark circuit was chosen since it is frequently used in register files, SRAM, DRAM, and other types of memories, therefore it’s delay is a significant component of a memory global latency [28,31,32]. For comparison purposes, different ADs were also designed based on static CMOS, DML, and dynamic domino structures.
The most significant results of this work can be summarized as follows. In the mixed mode, the proposed SAAD reduces average energy consumption of about 28% with respect to its fully-dynamic DML counterpart with a penalty of only 8.7% in terms of running frequency. In addition, it is also about 90% faster than its fully-static DML AD counterpart. When speed is not mandatory, our design (operated in static DML mode) exhibits energy consumption similar to that of the DML fully-static design. This leads proposed SAAD to be less energy hungry of about 28% as compared to the standard CMOS implementation. All the above advantages are combined with an area occupation comparable to that of the CMOS-based solution. Moreover, the proposed circuit turns out to be robust to temperature and process variations.
2. Dual Mode Logic Overview
DML allows a digital circuit to operate in dynamic or static mode [33], according to the system requirements. This is achieved by adding at least one additional clocked transistor to the static CMOS core [24,28], thus obtaining 4 different types of DML gates, as shown in Figure 1. Adding a pMOS transistor to the pull-up network (PUN) defines a Type-A DML gate, while adding a nMOS to the pull-down network (PDN) gives rise to a Type-B DML gate. Similar to conventional dynamic families, a second additional transistor can be included to define a footed Type-A or a headed Type-B cell. To achieve maximum benefit, the DML design methodology usually connects these Type-A and Type-B gates in a chain one after the other, effectively alternating the type of each cell [34].
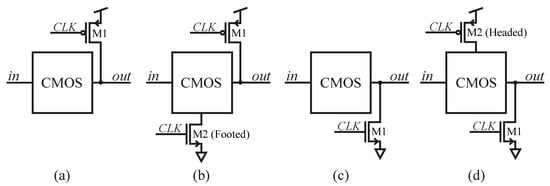
Figure 1.
Basic DML gate topologies: (a) Type-A logic gate, (b) Type-A footed logic gate, (c) Type-B logic gate, and (d) Type-B Headed logic gate.
As occurs for standard dynamic logic, the clock toggling allows for two separate phases: pre-charge (or pre-discharge) and evaluation. In the pre-charge phase, the output is charged/discharged to VDD/GND for a Type-A/Type-B logic gate [21,26,34]. In the evaluation stage, the output is asserted according to the gate inputs. If a DML gate has to be switched to the static mode, the CLK signal must be maintained at a high/low level for Type-A/Type-B gates. This turns off the clocked transistors resulting in a CMOS-like structure [28] with a minimal parasitic capacitance added to the output of each single gate [20].
The gate topology choice and size of transistors are crucial for optimal running of a DML design [34]. In the dynamic mode, given that a fast evaluation is sought after, the optimal DML topology is that with pre-charge (pre-discharge) transistor placed in parallel to the network with the larger number of stacked transistors [34]. Moreover, transistors in the evaluation networks need to be sized for optimal speed, whereas devices belonging to the complementary network can be downsized to decrease input gate capacitance and intrinsic delay of the gate, thus further favoring the dynamic operation. Note that the DML gates, being based on static CMOS topologies, inherently provide better robustness than conventional dynamic gates while operating in the dynamic mode (due to the inherent keeper represented by the minimum sized network) [21,27]. When the DML static mode is enabled, the above-mentioned sizing approach leads to reduced performance. This, however, comes with a substantial energy saving.
It is worth noting that the DML operation modes can be tuned at low level of design granularity according to the system requirements, designer considerations, or automatically by an input-driven control (as in this work) [22,25,27,28,29,35]. This means that DML static and dynamic operations can be enabled at the same time in different portions of the circuit. In this way, the potentials of the DML style are fully exploited to achieve unique energy–delay trade-offs. This is shown in Figure 2, which reports simulation data for a 20-stage NOR2-NAND2 DML chain. Simulations to evaluate energy and delay were performed for supply voltages ranging from 0.4 to 1.2 V. For the DML design, static, dynamic, and mixed (i.e., static and dynamic modes enabled at the same time) working modes were considered. At a given supply voltage, the static DML mode allows lower energy, while the dynamic DML mode leads to the faster implementation. When the two modes are “mixed” within the same architecture, both DML static and dynamic benefits (i.e., improved speed and energy) coexist at the same time.
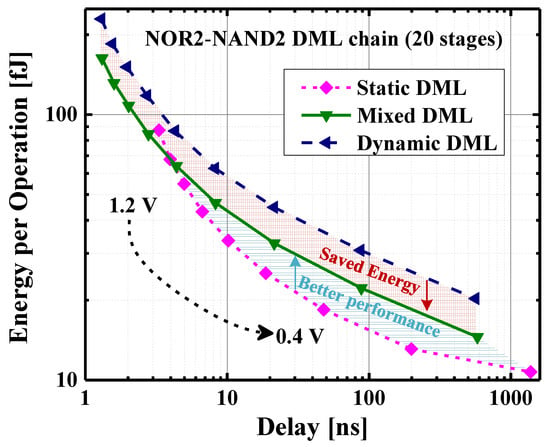
Figure 2.
Energy-delay trade-offs of DML modes. Simulation data considers a 20-stage NAND2-NOR2 DML chain.
DML’s main attribute for this work is its high flexibility for energy and delay optimizations when on-the-fly operating in the mixed mode, as will be introduced in the following section.
3. Address Decoder Design
The proposed SAAD allows a better energy-delay trade-off as compared to conventional static and dynamic CMOS designs, at the expense of negligible increased circuit complexity. This is achieved thanks to strategically distributed controllers (for both type A and type B DML gates), which allow the circuit to operate in mixed DML mode on the base of the actual circuit’s workload.
3.1. Address Decoder Architecture
Figure 3 shows the architecture implemented based on [30], where an AD of any size is built by exploiting low fan-in gates. A traditional static CMOS-based AD can be converted into this non-conventional design with different NOR/NAND stages using De Morgan’s laws, thus avoiding the use of complex logic gates that present higher energy consumption and delay (due to the increase in the number of transistors) such as high fan-in AND gates [30]. The logic path of the design begins and ends with NOR gates since the AD has an even number of inputs and a logic “1” output must be asserted. Only the first stage receives two inputs since it contains a block composed by four NOR gates and two inverters. Meanwhile, each block in the stage is composed by gates of the same type without individual inverters. These stages are formed by two equal blocks: one receives the direct input signal, while the other one receives the complemented input signal from the single stage inverter.
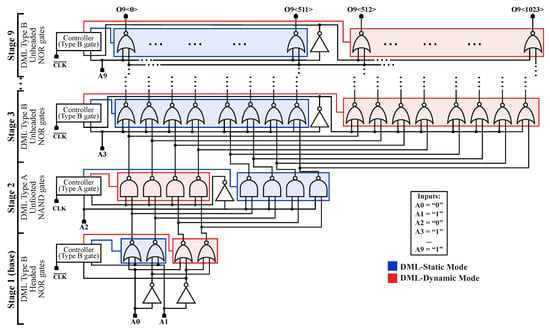
Figure 3.
The 1024-bit Self-Adaptive DML Address Decoder (SAAD).
Note that the AD can be seen as a NOR-NAND chain, thus making it particularly suitable for an efficient alternating Type-A/Type-B DML implementation. It is worth mentioning that Type-B headed gates are used on the first stage on the DML AD to correctly interface with standard CMOS logic [28].
3.2. Decision Logic
Two different controllers were designed: one for DML Type-A stages (see Figure 4a) and another one for DML Type-B stages (see Figure 4b). Each DML stage use its own controller, which consists of two sub-circuits (referred as “D1” and “D2” in Figure 4), each one responsible for the running of half of the gates of the stage. D1 is fed by the stage input A and delivers its output ( or ) to the pre-charge transistor of the DML gates that are to receive the non-negated form of the input. Meanwhile, D2 receives the negated input and connects its output ( or ) to the pre-discharge transistor of the DML gates that are to receive this input. The interplay of D1 and D2 allows half of each stage to be operated in dynamic mode while achieving a static work on the other half. Figure 5 shows an example of input and output waveforms illustrating the behavior of the controlling mechanism.
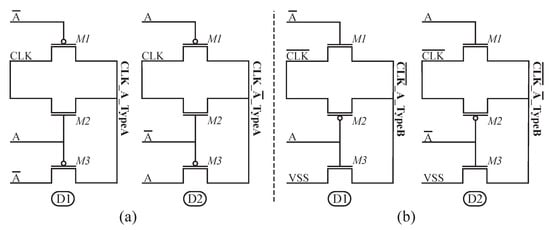
Figure 4.
Controller schematics using Pass Transistor Logic: (a) Controller for Type-A stages. (b) Controller for Type-B stages.
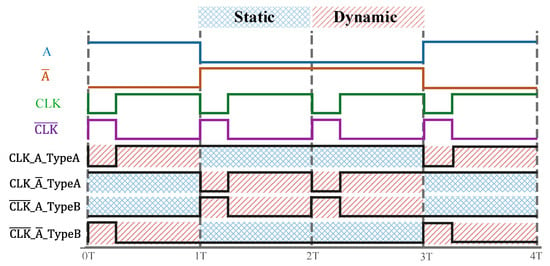
Figure 5.
Input and output waveforms of the controllers used in the Type-A and Type-B stages.
Each controller, formed by three transistors M1–M3, is designed with Pass Transistor Logic (PTL) [35]. Transistors M1 and M3 allow the switch between dynamic and static mode by making the enable signal either A or . The controllers also have a transmission gate (M1 and M2), and it is enabled to operate in the dynamic mode, thus passing a full swing signal, whether it is a logic “0” or “1”. Note that the energy consumed by the controllers is minimum owing to the reduced number of transistors (i.e., small area overhead). Only the input signals (A, , , and ) were used as control signals and as transistor supply voltages.
The decision logic uses the inputs of each stage to speed up the half of each respective stage where the asserted output’s path is located. In a Type-A (NAND-gate) stage, the gates of the direct input receiving block (which constitutes half of the stage) will operate in dynamic mode if the input A of the stage is a logic “1” (thus implying a 50% chance that the output is 0); meanwhile, the gates of the negated input receiving block will operate in static mode. The behavior is inverted if the input A is a logic “0”. On the other hand, in a Type-B (NOR-gate) stage, the gates of the direct input receiving block will operate in dynamic mode if A is a logic “0” (which implies a 50% chance that the output will be 1) while the block that receives the negated input will operate in static mode. The behavior is inverted in this case as well. This convention is summarized in Table 1 and can be visualized in Figure 3 for a particular combination of inputs.

Table 1.
Modes of operation for blocks as a function of block topology and input vectors.
4. Results
The proposed SAAD was designed using a full-custom approach, and evaluated in Synopsis Custom Compiler tool by exploiting a commercial 65 nm TSMC technology. For the sake of comparison, in addition to the proposed SAAD circuit, three additional ADs were designed using the CMOS, DML, and dynamic design methodologies. Figure 6 shows the energy-frequency characteristics for VDD ranging from 0.4 V to 1.2 V. The dynamic ADs like dynamic DML, and domino, are grouped in Figure 6a, while the static ones such as CMOS-based, static self-adaptive DML, and static DML, are presented in Figure 6b. When running in the high speed mode, the self-adaptive DML based AD (i.e., SAAD), which operates in dynamic and static modes simultaneously (i.e., mixed mode), was included in both static and dynamic design styles. When comparing the proposed SAAD circuit against the dynamic styles (refer to Figure 6a) for the 0.4 V–1.2 V voltage range, we can observe that our design is, on average, about 22% and 9% slower than the domino and fully-dynamic DML based ADs, respectively. Nevertheless, since the adopted controlling mechanism allows a large portion of the circuit to operate in static DML mode, our circuit reduces its average energy consumption of about 14% and 28% with respect to its domino and fully-dynamic DML counterparts. Moreover, when referring to designs based on static styles (refer to Figure 6b), the SAAD operated in mixed-mode is also about 15% and 91% faster than the conventional static CMOS and the fully-static DML designs, respectively. When energy is the primary constraint, the proposed SAAD design operating in static mode (i.e., static self-adaptive DML based AD) as well as the fully-static DML circuit are the best solutions. These two result in less energy hungry of about 29% as compared to the static CMOS implementation.
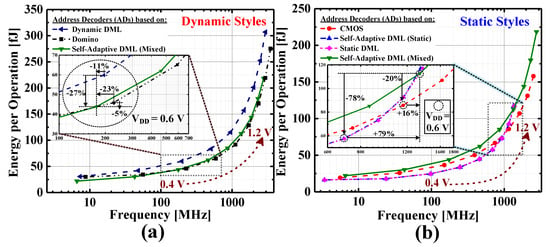
Figure 6.
Energy—frequency characteristics for VDD ranging from 0.4 to 1.2 V in steps of 0.1 V. The dynamic families are grouped on (a), while the static families are presented on (b).
A temperature sweep from −25 °C to 125 °C was considered to evaluate frequency and energy per operation at VDD = 0.5 V. Obtained results are shown in Figure 7. When operating in the mixed mode, the proposed circuit has a similar behavior in terms of frequency as the fully-dynamic DML AD. The proposed SAAD tracks the behavior of the static DML AD very well when operating in the static DML mode. Due to the adopted sizing methodology [20], the fully-static DML circuit as well as the proposed self-adaptive DML design operating in the static mode result to be more susceptible in terms of energy per operation as temperature increases. Nevertheless, these circuits ensure lower energy per operation for temperatures below 100 °C.
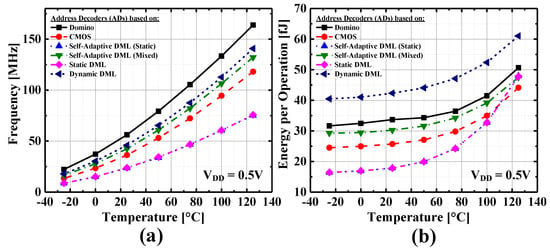
Figure 7.
Address Decoder temperature variation analysis from −25 °C to 125 °C at 0.5 V for: (a) Frequency. (b) Energy.
In order to evaluate the process sensitivity of the compared designs, we considered the following process corners: Typical–Typical (TT), Slow–Slow (SS), Slow–Fast (SF), Fast–Slow (FS), and Fast–Fast (FF). Obtained simulation results in terms of frequency and energy consumption evaluated for VDD = 0.4 V and 1.0 V are reported in Figure 8 and Figure 9, respectively. As expected, the dynamic domino-based design excels in terms of speed in all the process corners, while also being the most energy consuming implementation. On the contrary, the DML-based designs achieve the lowest energy consumption when working in static DML mode while resulting the slower implementations. Overall, the proposed SAAD offers the best energy-delay trade-off when working in the mixed DML mode, and this result is confirmed in all the process corners.
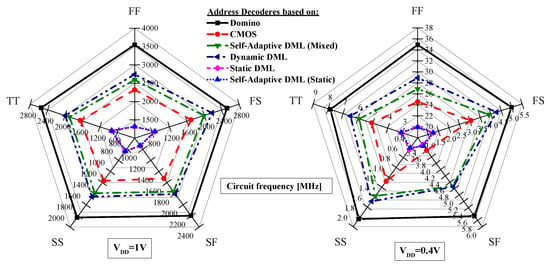
Figure 8.
Address decoder process corner analysis at 1.0 V and 0.4 V.
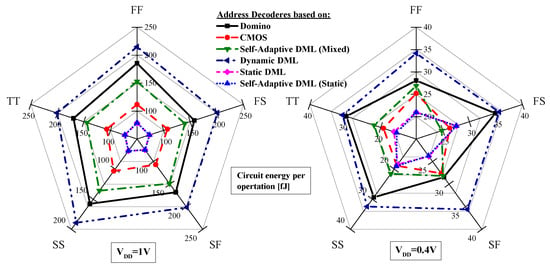
Figure 9.
Address decoder process corner analysis at 1.0 V and 0.4 V.
In Table 2, the silicon area occupation of the proposed SAAD is shown in comparison to its competitors. As compared to the standard uncontrolled DML implementation, only 84 additional transistors are required, leading to an increase in terms of occupied area of less than 6%. However, thanks to the adopted sizing criterion in the evaluation networks of logic gates along with minimum size transistors for complementary networks [25,26], the area occupation of the proposed design is comparable (∼3% more) to that of the standard CMOS design.

Table 2.
Area Comparison.
5. Conclusions
In this work, we have presented a novel DML-based Self-Adaptive Address Decoder (SAAD), which allows a simultaneous operation in dynamic and static modes within a single circuit. The proposed circuit considers an unconventional address decoder (AD) architecture, as well as a design of a control mechanism, which combines the two modes of operation of DML. To evaluate its high-performance and energy-savings, the proposed design has been benchmarked with logically equivalent implementations. The comparative analysis has been carried out through circuit simulations, while exploiting a commercial 65 nm TSMC technology. Obtained results show that, when comparing to equivalent static and dynamic implementations, the proposed SAAD offers the best energy-delay trade-off when working in the mixed DML mode while assuring the lowest energy consumption when speed is not mandatory. This confirms the proposed DML-based Self-Adaptive AD to be an energy-efficient and high-performance noteworthy alternative for portable and IoT devices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.V., C.M., A.M., S.B., M.R., E.G., L.M.P., L.T. and R.T.; formal analysis, K.V., C.M., A.M., S.B., M.R., E.G., L.M.P., L.T. and R.T.; investigation, K.V., C.M., A.M., S.B., M.R., E.G., L.M.P., L.T. and R.T.; writing—review and editing, K.V., C.M., A.M., S.B., M.R., E.G., L.M.P., L.T. and R.T.; supervision, R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DML | Dual Mode Logic |
| SAAD | Self-Adaptive Address Decoder |
| AD | Address Decoder |
| TSMC | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company |
| PUN | Pull-Up Network |
| PDN | Pull-Down Network |
| PTL | Pass Transistor Logic |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
References
- Alioto, M. Enabling the Internet of Things: From Integrated Circuits to Integrated Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrakasan, A.P.; Daly, D.C.; Finchelstein, D.F.; Kwong, J.; Ramadass, Y.K.; Sinangil, M.E.; Sze, V.; Verma, N. Technologies for ultradynamic voltage scaling. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanuzza, M.; Margala, M.; Corsonello, P. Cost-effective low-power processor-in-memory-based reconfigurable datapath for multimedia applications. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–10 August 2005; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinefelter, A.; Roberts, N.E.; Shakhsheer, Y.; Gonzalez, P.; Shrivastava, A.; Roy, A.; Craig, K.; Faisal, M.; Boley, J.; Oh, S.; et al. 21.3 A 6.45 μW self-powered IoT SoC with integrated energy-harvesting power management and ULP asymmetric radios. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taco, R.; Levi, I.; Lanuzza, M.; Fish, A. Low voltage logic circuits exploiting gate level dynamic body biasing in 28 nm UTBB FD-SOI. Solid State Electron. 2016, 117, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.; Savanth, A.; Howard, D.; Gaddh, R.; Prabhat, P.; Flynn, D. 8.1 An 80 nW retention 11.7 pJ/cycle active subthreshold ARM Cortex-M0+ subsystem in 65 nm CMOS for WSN applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, B.H.; Chandrakasan, A.P. Ultra-dynamic voltage scaling (UDVS) using sub-threshold operation and local voltage dithering. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2005, 41, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsonello, P.; Frustaci, F.; Lanuzza, M.; Perri, S. Over/undershooting effects in accurate buffer delay model for sub-threshold domain. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Chong, K.S.; Chang, J.S.; Gwee, B.H. An Ultra-Low Power Asynchronous-Logic In-Situ Self-Adaptive VDD System for Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2012, 48, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaey, J.M.; Chandrakasan, A.P.; Nikolić, B. Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, H.; Arekapudi, S.; Busta, E.; Fischer, T.; Golden, M.; Horiuchi, A.; Meneghini, T.; Naffziger, S.; Vinh, J. Design of the two-core x86-64 AMD “Bulldozer” module in 32 nm SOI CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 47, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frustaci, F.; Lanuzza, M.; Zicari, P.; Perri, S.; Corsonello, P. Designing high-speed adders in power-constrained environments. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2009, 56, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklobdzija, V.G.; Montoye, R.K. Design-performance trade-offs in CMOS-domino logic. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1986, 21, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursun, V.; Friedman, E.G. Domino logic with variable threshold voltage keeper. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2003, 11, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frustaci, F.; Lanuzza, M.; Zicari, P.; Perri, S.; Corsonello, P. Low-power split-path data-driven dynamic logic. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2009, 3, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, C.J.; Bayoumi, M.A. Single-phase SP-domino: A limited-switching dynamic circuit technique for low-power wide fan-in logic gates. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2008, 55, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, R.J.H.; Elliott, D.G. Clock-logic domino circuits for high-speed and energy-efficient microprocessor pipelines. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2007, 54, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Kursun, V. Leakage power characteristics of dynamic circuits in nanometer CMOS technologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2006, 53, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioto, M.; Palumbo, G.; Pennisi, M. Understanding the effect of process variations on the delay of static and domino logic. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2009, 18, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, I.; Kaizerman, A.; Fish, A. Low voltage dual mode logic: Model analysis and parameter extraction. Microelectron. J. 2013, 44, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaizerman, A.; Fisher, S.; Fish, A. Subthreshold Dual Mode Logic. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2013, 21, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzhaninov, V.; Levi, I.; Fish, A. Design Flow and Characterization Methodology for Dual Mode Logic. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanuzza, M.; De Rose, R.; Frustaci, F.; Perri, S.; Corsonello, P. Comparative analysis of yield optimized pulsed flip-flops. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, A.; Kaizerman, A.; Fisher, S.; Levi, I. Device and Method for Dual-Mode Logic. U.S. Patent 8,901,965,B2, 21 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Taco, R.; Levi, I.; Lanuzza, M.; Fish, A. An 88-fJ/40-MHz [0.4 V]–0.61-pJ/1-GHz [0.9 V] Dual-Mode Logic 8 × 8 bit Multiplier Accumulator with a Self-Adjustment Mechanism in 28-nm FD-SOI. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2019, 54, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavit, N.; Stanger, I.; Taco, R.; Lanuzza, M.; Fish, A. A 0.8-V, 1.54-pJ/940-MHz Dual-Mode Logic-Based 16×16-b Booth Multiplier in 16-nm FinFET. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett. 2020, 3, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, I.; Fish, A. Dual Mode Logic—Design for Energy Efficiency and High Performance. IEEE Access 2013, 1, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavits, L.; Taco, R.; Shavit, N.; Stanger, I.; Fish, A. Dual Mode Logic Address Decoder. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seville, Spain, 10–21 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanger, I.; Shavit, N.; Taco, R.; Lanuzza, M.; Fish, A. Silicon Evaluation of Multimode Dual Mode Logic for PVT-Aware Datapaths. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, I.; Zachara, L.; Kos, A. Designing Method of Compact n-to-2n Decoders. Int. J. Electron. Telecommun. 2013, 59, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, Y.; Bdiri, S.; Derbel, F. An ultra-low power wake up receiver with flip flops based address decoder. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 12th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD15), Mahdia, Tunisia, 16–19 March 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benini, L.; De Micheli, G.; Macii, E.; Sciuto, D.; Silvano, C. Asymptotic zero-transition activity encoding for address busses in low-power microprocessor-based systems. In Proceedings of the Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, Urbana-Champaign, IL, USA, 13–15 March 1997; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, I.; Fish, A. Dual Mode Logic: A New Paradigm for Digital IC Design; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, I.; Belenky, A.; Fish, A. Logical Effort for CMOS-Based Dual Mode Logic Gates. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2014, 22, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, I.; Bass, O.; Kaizerman, A.; Belenky, A.; Fish, A. High Speed Dual Mode Logic Carry Look Ahead Adder. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seoul, Korea, 20–23 May 2012; pp. 3037–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).