Abstract
A deteriorating nail standard is a growing problem as the global prevalence of diabetes is increasing. Systemic treatment with mineral supplements may not be recommended, mainly due to the high doses required to deliver optimal therapeutic concentrations. In this work, we evaluate nail polish formulations for the local delivery of strengthening elements to the nail plate. Specifically, we assess calcium and silicon release from nail polish base coat formulations containing three different concentrations of White Portland Cement to water, as well as to artificial and human nails. The delivery of calcium and silicon to the dorsal nail plate was determined by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry, scanning electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study showing that such dual elemental delivery to human nails can be achieved from nail polish formulations. Hence, this work may form the basis for new inventions where therapeutic functionalities can be integrated with the mechanical and cosmetic properties of a base coat nail polish. Future permeability studies are required to verify long-term effects on the nail standard, induced by the formulations under study.
1. Introduction
Our current life style has drastically increased the global prevalence of diabetes. In 2017, 8.8% of the global population was diagnosed with this chronic disease and the prevalence is expected to further increase to 9.9% by the year 2045 [1]. While considerable research and drug development efforts are in place to diminish the major risks related to being diagnosed with diabetes, there are still problematic areas where adequate solutions are lacking. Diabetic patients often have a deteriorated nail standard since the breakdown of sugar can affect the quality of the nail plate [2,3]. In fact, the fingernail quality, as manifested through the calcium content, density, porosity, roughness, hardness, protein, and disulphide bond content, has been investigated as a means to monitor tissue damage in type 2 diabetes patients [3].
The macrostructure of the human nail consists of four major parts: the proximal nail fold (PNF), the nail matrix and nail plate, the nail bed, and the hyponychium [4]. The nail matrix underneath the PNF gives origin to the nail plate, which is comprised of a dorsal (top) layer, an intermediate (middle) layer, and a ventral (bottom) layer [4]. At the molecular level, the main protein composing all three layers of the nail plate is α-keratin [4]. In the intermediate layer, which comprises 50% of the thickness of the nail plate, the α-keratin fibers are aligned perpendicularly to the axis of nail growth [4,5]. The α-keratin fibers are crosslinked by disulphide bonds, which further densify the molecular structure and hinder the delivery of active substances to the nail bed. Other components of the nail plate are water (7–25%), lipids (0.1–1.0%), and calcium [5]. The importance of calcium in the keratinized structure of the nail has persistently been investigated [6] and its depletion in the nail plate has been demonstrated in diabetes patients [3]. Additionally, clinical studies have shown that the oral intake of silicon supplements can significantly reduce nail brittleness [7]. Today, people with a deteriorated nail standard can take calcium and silicon supplements to improve nail health, since these elements may play a role in nail strengthening [7,8]. Moreover, bone health has been correlated to nail properties [9]. While oral silicon and calcium have been proven to significantly enhance the bone quality in osteoporosis patients [10], a topical route might be more adequate for the delivery of these elements to the nail plate due to a reduced circulation to the nail matrix in diabetes patients [11], but also due to the high systemic doses that could be required for an optimal therapeutic effect.
Permeation is a well-known mechanism of the transport and delivery of active substances in non-living membranes through diffusion. The human nail is generally considered to be a hydrophilic gel membrane with a relatively low permeability [12], which constitutes a matter of concern in the design of new nail cosmetic lacquers due to the low, but not insignificant, possibility of potentially harmful substances permeating into the epithelium [13]. In spite of this, transungual drug delivery by topical treatment continues to be an attractive method for treating afflictions of the nails, such as onychomycosis and psoriasis [14]. Topical steroids, such as vitamin D and 5-fluorouracil, are the preferred treatment for psoriasis of the nail [5,14]. Topical treatments are usually recommended over systemic treatments due to i) drug–drug interactions, ii) counter indications, and iii) a low drug concentration at the nail bed requiring too high doses of the systemic drug [5,14]. Therefore, determining the permeability of the nail plate and enhancing it have been topics of research conducted by formulation scientists and biophysicists in recent years [15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Active substances, including relatively large molecule antifungals [20,22], and smaller entities, such as plasma-generated NO2 [23], have been successfully delivered through keratinized surfaces by various methods. Smaller molecules are expected to permeate well through the nail plate [5]. Besides, an enhanced permeability is expected in afflicted nails due to the higher porosity, lower density, lower hardness, lower protein, and lower disulphide bond content [3,15].
In this work, we investigate whether calcium and silicon can be delivered locally to the nail by using traditional nail polish as a transungual delivery system, thus avoiding the drawbacks of systemic administration. Specifically, we investigate whether the elements can be released from commercial nail polish formulations while performing a proof-of-concept study examining the delivery of calcium and silicon to the human nail. A successful outcome could thus render nail polish with a dual function as a delivery vehicle for therapeutic ions and as a beauty product.
Presently, nail polish comes in many different forms. The original formulas, however, date back to 3000 BC China and through history, nail polish has been used to show off social class by different color pigments [24]. Today’s nail polish, containing a mix of organic polymers, pigments, and other brand-specific components, is essentially used for the decoration and protection of the nail plate [25]. The idea of locally delivering therapeutic agents to the nail is not new: A number of formulations for antifungal nail treatments have been developed and reviewed [26,27]. To the best of our knowledge, however, there is no nail polish on the market that has been developed for the release of calcium and silicon in order to treat the deteriorated nail quality related to diabetes. Moreover, the release of these ions into artificial and/or human nails has not been previously studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Nail polish: To form the basis for a delivery system that may simultaneously function as a beauty product, we used the commercial base coat nail polish 7 Day Base Coat (item number 1092-164-0000, Depend Cosmetics AB, Halmstad, Sweden) as a carrier of calcium and silicon. Base coats are used to prevent discoloration from pigmented nail polish and to give the nail a smooth surface [28]. They are usually denoted as Step 2 layers (to be applied after a Step 1 cleanser procedure). Since the base coat is applied as the innermost layer in direct contact with the nail, the functional elements do not have to pass a barrier nail polish layer, as would be the case if a pigmented, so-called Step 3 layer, or a top coat (Step 4 layer), was to be utilized as the delivery vehicle. Calcium and silicon source: White Portland Cement (WPC, Aalborg Portland A/S, Aalborg, Denmark), containing calcite (CaCO3), dicalcium silicate (2CaO⋅SiO2), and tricalcium silicate (3CaO⋅SiO2), was used as a source of calcium and silicon. Nails: Artificial (testing substrate) nails (Vitro-nails®, IMC Inc, Bunnell, FL, USA), as well as human nails (donated by one of the authors), were used to analyze the presence of calcium and silicon after the application of nail polish.
2.2. Preparation and Analysis of the White Portland Cement
Sieving: The as-delivered White Portland Cement (WPC) was sieved (Retsch Vibratory Sieve Shaker AS 200 Basic, Retsch GMBH, Haan, Germany) to obtain a particle size < 25 μm to allow for optimal particle dispersion in the base coat. Elemental analysis: The amount of Ca, Si, Cr, Mn, Fe, Cu, Ti, and Ni in the sieved powder was analyzed by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry in an ICP-OES Avio 200 (Perkin Elmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) by using commercial calibration standards (Perkin Elmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) monitored at the emission lines 317.933 nm (Ca), 251.611 nm (Si), 283.563 nm (Cr), 257.610 nm (Mn), 238.204 nm (Fe), 324.752 nm (Cu), 368.519 nm (Ti), and 341.476 nm (Ni). Sample solutions (1 mg/mL) were prepared by dissolving the sieved powder into 2 vol% HNO3 for 24 h at 37 °C. The samples were thereafter filtered (0.45 μm) and diluted with MilliQ water to appropriate testing concentrations. A precision test was automatically done in Syngistix 2.0 for ICP-OES (PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The relative standard deviation (RSD) value was reported, as it is indicative of the short-term precision of several measurements for a strong emission line. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): The morphology of the sieved powder was analyzed on a TM-1000 tabletop SEM (Hitachi Ltd., Chiyoda, Japan), with a solid-state back-scattered electron detector, at an acceleration voltage of 15 keV, an emission current of 195 pA or 52 μA, and a working distance of 7 mm. The samples were prepared by mounting the powder on SEM stubs using a double-sided adhesive carbon tape and removing the excess powder with a compressed air gun. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD): The phase composition of the powder was investigated by XRD with a D5000 (Siemens AG, Munich, Germany) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418Å) using a step size of 0.050°.
2.3. Preparation of Nail Polish Formulations
Modified Nail Polish Formulation: Three nail polish formulations containing WPC were prepared by adding 5.2, 10.0, and 15.0 mg, respectively, of the sieved WPC into 5 mL of nail polish. For simplicity, these nail polish formulations will be called np1, np2, and np3, respectively. The samples were homogenized by shaking with two zirconia beads (5 mm) in each bottle, to ensure a homogeneous particle distribution. SEM: The modified nail polish formulations were used to paint (coat) plastic surfaces, which were left to dry overnight. Upon drying, the samples were examined by SEM to obtain information about the WPC particle distribution in the dry nail polish.
2.4. Calcium and Silicon Release from Nail Polish
Release into MilliQ water: An area of 1.0 × 1.5 cm2 of each sample nail polish was painted on a plastic surface and left to dry overnight. The dry nail polish samples were then carefully weighed and adjusted to ensure that the same amount of nail polish was used. The samples were placed in separate centrifuge tubes filled with 50 mL of MilliQ water. The surface area-to-volume ratio of water was set to 1.5 cm2/mL, according to ISO Standards 10993-12:2002 and 10993-15:2000 [29,30]. The centrifuge tubes were additionally covered with Parafilm to prevent evaporation and stored in an oven at 37 °C. The calcium and silicon contents in the MilliQ water were analyzed by ICP-OES after 4 and 48 h by using commercial calibration standards (Perkin Elmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) monitored at the emission lines 317.933 nm (Ca) and 251.611 nm (Si). Release onto nails: Artificial nails were painted with a ~1.5 mm thick layer of the three different nail polish formulations (np 1–3). A human nail was painted with np3. All nail samples were stored at 37 °C for 120 h. The nail polish was thereafter removed with acetone and the nails were examined by SEM. Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX): The elemental content in artificial and human nails painted with np3 was analyzed using the EDX function in the TM-1000 SEM (Hitachi Ltd., Chiyoda, Japan) using an acquisition time of 120 s, a process time of 4 s, and an acceleration voltage of 15.0 kV.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the White Portland Cement
The elemental analysis performed on the sieved WPC showed that in addition to calcium and silicon, which are inherent to the WPC, the material also contained Cr (14.0 mg/kg), Fe (1962.0 mg/kg), Cu (22.9 mg/kg), Ti (458.0 mg/kg), Mn (131.0 mg/kg), and Ni (48.5 mg/kg). To the best of our knowledge, none of the observed trace elements have been found to be harmful for nails in low doses, while iron, on the other hand, is known to have beneficial effects [31]. Figure 1 shows an X-ray diffractogram and an SEM image (inset) of the sieved WPC. It can be observed that the particle size of the sieved powder is below 25 µm, as intended. As expected [32], the material was composed of calcite (CC), dicalcium silicate (C2S) and tricalcium silicate (C3S).
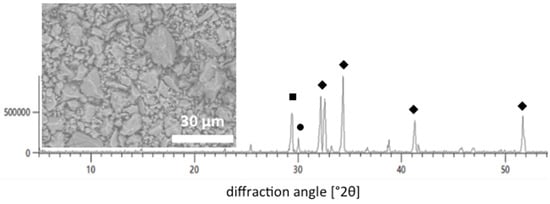
Figure 1.
X-ray diffractogram and SEM (inset) of the material (White Portland Cement) used as a calcium and silicon source in the modification of a base coat nail polish formulation. (■) CC = calcite; (●) C2S = dicalcium silicate; (♦) C3S = tricalcium silicate.
3.2. Analysis of the Modified Nail Polish Formulations
Figure 2a shows photography of the three modified nail polish formulations, along with SEM micrographs (Figure 2b,c) of their dry layers. Figure 2a shows that the nail polish formulations become increasingly opaque with an increasing WPC content, indicating that the particle density in the painted layers should increase correspondingly. Whilst no particles ~25 µm in size are observed in the SEM images, all images in Figure 2 show that the particles are not fully dissolved in the base nail polish formulation. This was expected, since an excess of water would have been needed to allow all particles to fully dissolve.
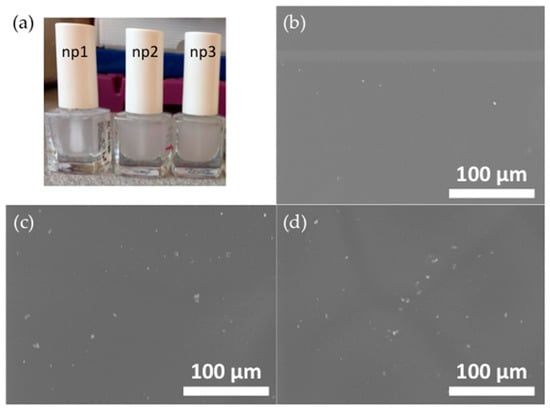
Figure 2.
Photography of (a) the modified nail polish formulations and SEM micrographs of the dry modified nail polish formulations: (b) np1, (c) np2, and (d) np3.
3.3. Calcium and Silicon Release from Nail Polish Formulations
Figure 3 shows the amount of calcium and silicon released into MilliQ water from the three different nail polish formulations, as detected using ICP-OES. The results show that an increasing amount of both calcium and silicon is released with an increasing amount of WPC in the formulations. It can also be observed that the amount released after 48 h is higher than the amount released after 4 h. Whereas the increase in the released amount as a function of time is quite moderate for calcium, the released amount of silicon is 3–4 times higher after 48 h compared to 4 h for np2 and np3. Sample np1 was shown to release a very similar amount of calcium and silicon at both time points. It is noticeable that during the initial release (4 h) from the two samples with the highest WPC content, calcium is dominating, while after a prolonged release (48 h), the amount of silicon released from all samples is similar to or higher than the corresponding amount of calcium (up to 1.6 times higher for np3). The latter is interesting bearing in mind that the Ca/Si ratio of WPC significantly exceeds 1 in both molar and weight units.
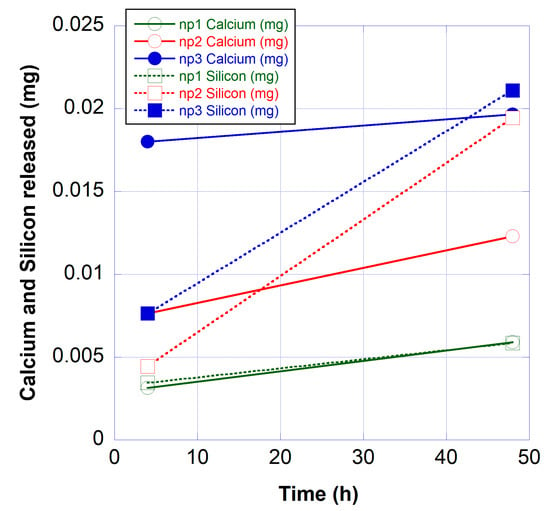
Figure 3.
Total amount of calcium and silicon released from dry nail polish layers into 50 mL of MilliQ water, as obtained from inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) were less than 2% for all data points.
It should be noted that the dry nail polish immersed in MilliQ water contained ~0.2–0.5 mg of WPC, so the released amount of both elements under study is of the order of 1% of the corresponding elemental content in the nail polish layer.
Figure 4 shows SEM micrographs of the artificial nails after having been coated with the three different nail polish formulations for 120 h. An increasing amount of particles can be observed with increasing WPC in the formulations. The EDX analysis also confirmed that the particles observed in the artificial nail that had been exposed to np3 (Figure 4c) indeed contained calcium and silicon; an analysis of an area containing several particles found an elemental content of Al (54.5 wt%), Si (32.3 wt%), Ca (9.1 wt%), and other elements (4.0 wt%). Therefore, it was concluded that calcium and silicon from the nail polish entered the artificial nail.
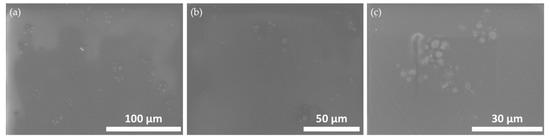
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs of artificial nails after having been coated with (a) np1, (b) np2, and (c) np3 for 120 h.
4. Discussion
To demonstrate that the local delivery of calcium and silicon is possible on human nails, the experiment was repeated on a donated human nail. Figure 5 shows the SEM image of this nail after having been coated with np3 for 120 h.
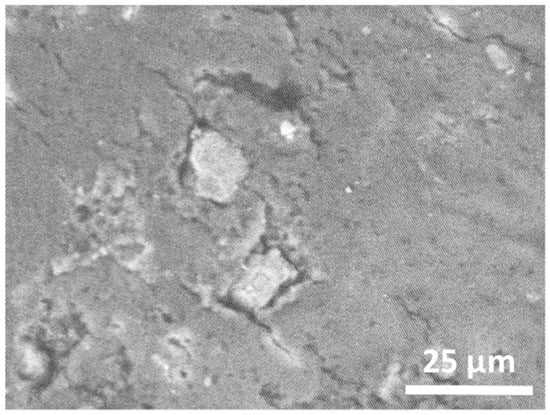

Figure 5.
SEM micrograph of the dorsal part of a human nail after having been coated with np3 for 120 h.
An EDX analysis of an area containing several of the observed particles showed an elemental content of Al (34.5 wt%) due to the substrate used, Si (21.4 wt%), Ca (22.6 wt%), and other elements (22.5 wt%). It should be noted that particles like those observed in Figure 4 and Figure 5 were not detected in SEM images of the artificial nails and pieces of the human nail that had not been covered with the nail polish formulations. From the above analysis, it is difficult to judge whether it is the elements calcium and silicon that are released from the nail polish formulations into the nails, where they, together with elements present in the nail, form the agglomerates observed in the SEM micrographs, or if it is unsolved WPC particles that stick strongly to the nails after the polish has been removed with acetone. In this case, the size of the agglomerates suggests that it might the latter. Regardless of this, Figure 5 indicates that the calcium- and silicon-containing particles are well integrated into the nail structure. The fact that the WPC particles are not fully dissolved in the nail polish formulations, as shown in Figure 2, may open up the opportunity for the delivery of small reservoirs of calcium and silicon that could enable the long-term release of these elements into the nail.
From these WPC particles, calcium and silicon are more likely to be delivered either in their original uncharged mineral form (CaCO3, 2CaO⋅SiO2, and 3CaO⋅SiO2), or in their most common ionic states (Ca2+ and Si4+), whose ionic radii are 1 and 4 Å, respectively [33]. The permeation of uncharged organic substances through the nail plate has been thoroughly evaluated in the literature and has generally been found to be size-dependent and higher than that of the corresponding charged species [34,35]. Even though, to the authors’ knowledge, there are no studies focusing on the transungual permeation of uncharged inorganic minerals, some inorganic salts have been used as permeation enhancers themselves, partly due to their ability to increase nail hydration [36]. This is in accordance with earlier investigations showing that water, as opposed to organic solvents, enhanced the permeability of uncharged organic compounds [37]. For this reason, water-based nail polishes may be better carriers of calcium and silicon since inorganic minerals could act as their own enhancers. On the other hand, the diffusivity of Ca2+ has been studied, and it has also been shown that cations are more easily transported than anions through the negatively-charged keratin [38]; that is, at pH values higher than the isoelectric point of keratin, which is known to be pH(I)~5.0 [5]. However, since the permselectivity of the nail plate also depends on the size (hydrodynamic radii of the solutes in the nail polish) and valence of the ions being transported, that is, smaller ions with lower valences are more easily transported [38], an investigation of the permeability of Ca2+ and Si4+ with respect to all these variables would be necessary to gain further insight into the delivery capabilities of the modified nail polish formulations to the ventral part of the nail plate in vivo.
In an in vivo pilot evaluation of the calcium- and silicon-enriched nail polish formulation, np3 was worn on every second finger of both hands as a base coat underneath commercial pigmented Step 3 and 4 layers for a week. As a negative control, the base coat without WPC was employed underneath the same Step 3 and 4 layers on the remaining fingers. No significant difference in the mechanical properties, such as adhesion and being prone to scratching, could be detected between these two types of layers.
5. Conclusions
This work evaluated base nail polish coating formulations for the local delivery of calcium and silicon to nails. The release from formulations containing three different concentrations of White Portland Cement to water, as well as to artificial and human nails, was analyzed by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry, scanning electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. It was found that the delivery of both elements to the artificial nail and to the dorsal part of a human nail takes place, something that opens up the opportunity for new inventions, where the therapeutic functionalities of calcium and silicon can be integrated with the mechanical and cosmetic properties of a base coat nail polish. To verify the long-term effects on the nail standard, induced by the formulations under study, future permeability analyses are required.
Author Contributions
M.S. and V.E. conceived and designed the experiments; M.S., V.E., and L.B. performed the experiments; M.S., V.E., and A.L. analyzed the data and interpreted data; M.S. wrote the paper; and A.L. corrected the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bristow, I. Non-ulcerative skin pathologies of the diabetic foot. Diabetes-Metab Res. 2008, 24, S84–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihota, P.; Yadav, R.N.; Dhiman, V.; Bhadada, S.K.; Mehandia, V.; Kumar, N. Investigation of diabetic patient’s fingernail quality to monitor type 2 diabetes induced tissue damage. Sci. Rep.-UK 2019, 9, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baswan, S.; Kasting, G.B.; Li, S.K.; Wickett, R.; Adams, B.; Eurich, S.; Schamper, R. Understanding the formidable nail barrier: A review of the nail microstructure, composition and diseases. Mycoses 2017, 60, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, H.N.; Repka, M.A.; Narasimha Murthy, S. Transungual drug delivery: An update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslind, B.; Wroblewski, R.; Afzelius, B.A. Calcium and sulfur location in human nail. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1976, 67, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barel, A.; Calomme, M.; Timchenko, A.; Paepe, K.D.; Demeester, N.; Rogiers, V.; Clarys, P.; Vanden Berghe, D. Effect of oral intake of choline-stabilized orthosilicic acid on skin, nails and hair in women with photodamaged skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2005, 297, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravina, P.; Sayaji, D.; Avinash, M. Calcium and its role in human body. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 4, 659–668. [Google Scholar]
- Saeedi, P.; Shavandi, A.; Meredith-Jones, K. Nail Properties and bone health: A review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugdaohsingh, R. Silicon and bone health. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2007, 11, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Hillson, R. Nails in diabetes. Pract Diabetes 2017, 34, 230–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Miyamoto, M.; Sugibayashi, K.; Morimoto, Y. Drug permeation through the three layers of the human nail plate. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubé, F.; Poupon, A.; Zinck, P.; Müller-Goymann, C.; Reichl, S.; Nardello-Rataj, V. Physicochemical investigations of native nails and synthetic models for a better understanding of surface adhesion of nail lacquers. Eur J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 131, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrín Gómez, E.; Anguiano Igea, S.; Delgado-Charro, M.B.; Gómez Amoza, J.L.; Otero Espinar, F.J. Microstructural alterations in the onychomycotic and psoriatic nail: Relevance in drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueiras-Nieto, L.; Gómez-Amoza, J.L.; Delgado-Charro, M.B.; Otero-Espinar, F.J. Hydration and N-acetyl-l-cysteine alter the microstructure of human nail and bovine hoof: Implications for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2011, 156, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, K.A.; Abdalghafor, H.M.; Lane, M.E. The human nail—Barrier characterisation and permeation enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 435, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palliyil, B.B.; Li, C.; Owaisat, S.; Lebo, D.B. Lateral drug diffusion in human nails. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsai, M.-T.; Tsai, T.-Y.; Shen, S.-C.; Ng, Y.C.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-D.; Yang, C.-H. Evaluation of laser-assisted trans-nail drug delivery with optical coherence tomography. Sensors 2016, 16, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanstone, S.; Cordery, S.F.; Stone, J.M.; Gordeev, S.N.; Guy, R.H. Precise laser poration to control drug delivery into and through human nail. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, D.; Egiziano, E.; Burgalassi, S.; Tampucci, S.; Terreni, E.; Tivegna, S.; Chetoni, P. Influence of a combination of chemical enhancers and iontophoresis on in vitro transungual permeation of nystatin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline-Schoder, A.; Le, Z.; Zderic, V. Ultrasound-enhanced drug delivery for treatment of onychomycosis. J. Ultras Med. 2018, 37, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlahovic, T.; Merchant, T.; Chanda, S.; Zane, L.T.; Coronado, D. In vitro nail penetration of tavaborole topical solution, 5%, through nail polish on ex vivo human fingernails. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2015, 14, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Im, Y.-H.; Xiong, Z.; Elg, D.T.; Graves, D.B. Uptake and diffusion of plasma-generated reactive nitrogen species through keratinized membrane. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 195201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaundri, S.K.; Jain, N.K. History of cosmetics. Asian J. Pharm. 2009, 3, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Andrè, J.; Baran, R. Nail cosmetics: Handle of skin care. In Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; Bare, A.O., Paye, M., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 745–767. [Google Scholar]
- Pati, N.B.; Dey, B.K.; Sudip, D.; Subhas, S. Nail drug delivery system: A review. J. Adv. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2012, 2, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, G.S.; Kumar, P.P.; Murugan, K.B. Nail as a promising drug delivery system for controlled release. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 4, 907–915. [Google Scholar]
- Iorizzo, M.; Piraccini, B.M.; Tosti, A. Nail cosmetics in nail disorders. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2007, 6, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardization, I.O.f. ISO 10993: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. In Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Standardization, I.O.f. ISO 10993: Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. In Part 15: Identification and Quantification of Degradation Products From Metals and Alloys; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Seshadri, D.; De, D. Nails in nutritional deficiencies. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2012, 78, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzman, P.E.; Feng, P.; Bullard, J.W. Phase analysis of Portland cements by combined quantitative X-ray powder diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stan. 2016, 121, 47–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertin, D.; Lippold, B.C. In-vitro permeability of the human nail and of a keratin membrane from bovine hooves: Prediction of the penetration rate of antimycotics through the nail plate and their efficacy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Sumi, M.; Numajiri, S.; Miyamoto, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Sugibayashi, K.; Morimoto, Y. In vitro permeation of several drugs through the human nail plate: Relationship between physicochemical properties and nail permeability of drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 21, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.B.; Sammeta, S.M.; Vaka, S.R.; Narasimha Murthy, S. A study on the effect of inorganic salts in transungual drug delivery of terbinafine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, K.A.; Flynn, G.L.; Marvel, J.R. Physicochemical characterization of the human nail: Solvent effects on the permeation of homologous alcohols. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1985, 37, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baswan, S.M.; Li, S.K.; LaCount, T.D.; Kasting, G.B. Size and charge dependence of ion transport in human nail plate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).