Multifunctional Effects of N-Carbamylglutamate on Skin-Related Cells: Antioxidant, Anti-Aging, Anti-Melanogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Analysis of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Reduction Activity
2.5. Measurement of Melanin Content
2.6. Determination of Cellular Tyrosinase Activity
2.7. Type 1 Procollagen Synthesis
2.8. Inhibitory Activity of MMP-1 and MMP-3
2.9. Measurement Nitric Oxide (NO) Inhibitory Activity
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
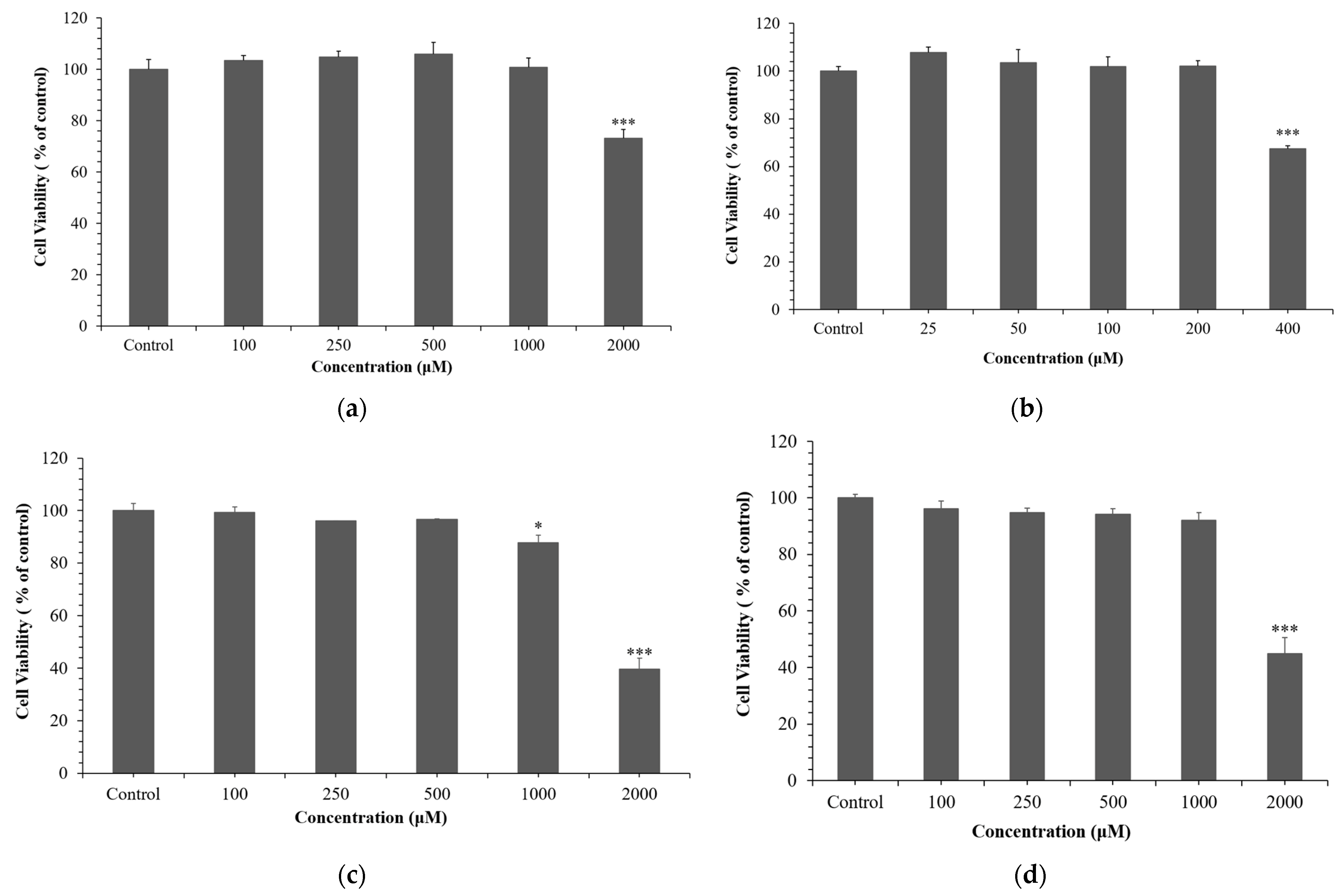
3.1. Effect of NCG on Cell Viability
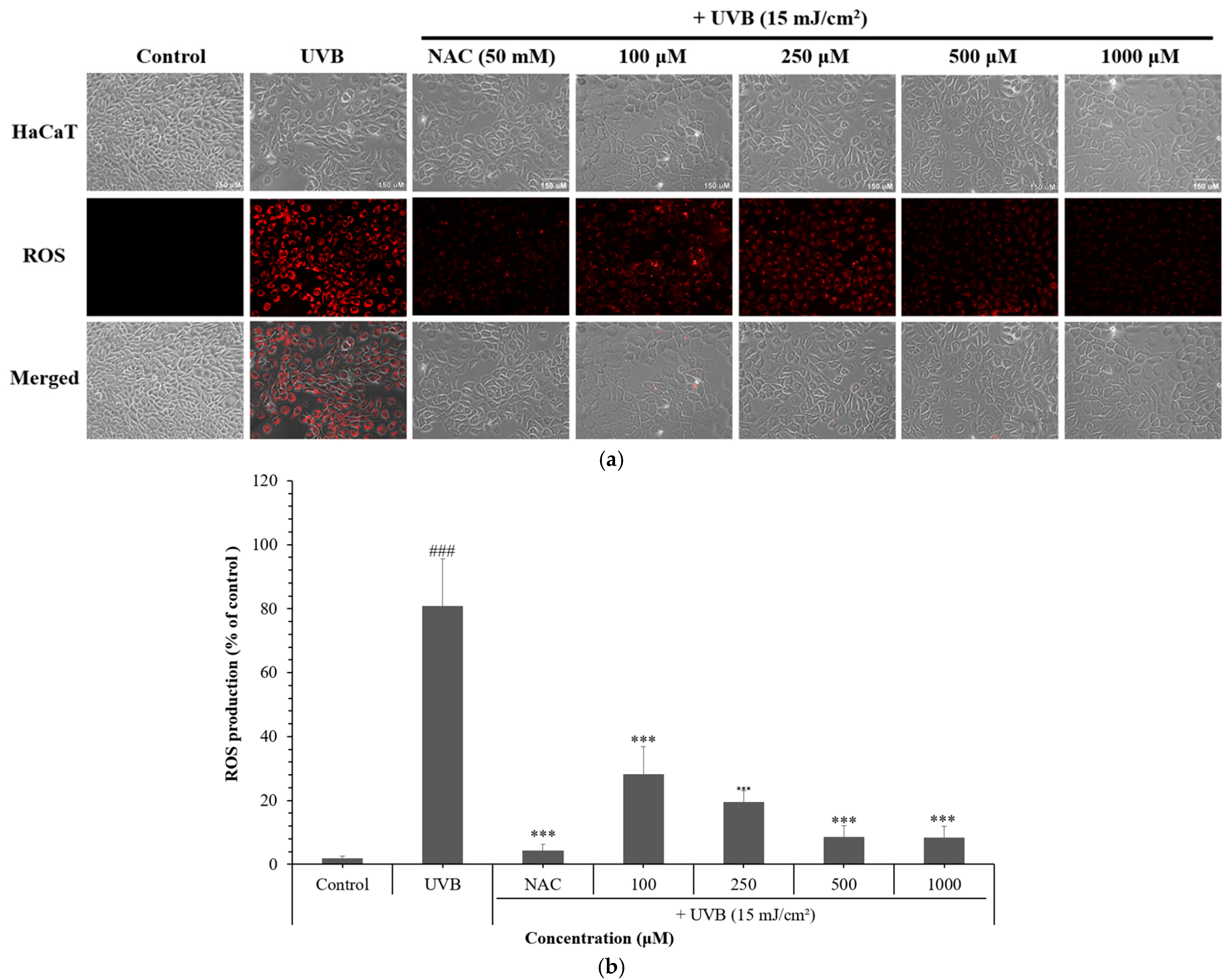
3.2. Effects of NCG on Intracellular and Mitochondrial ROS Levels
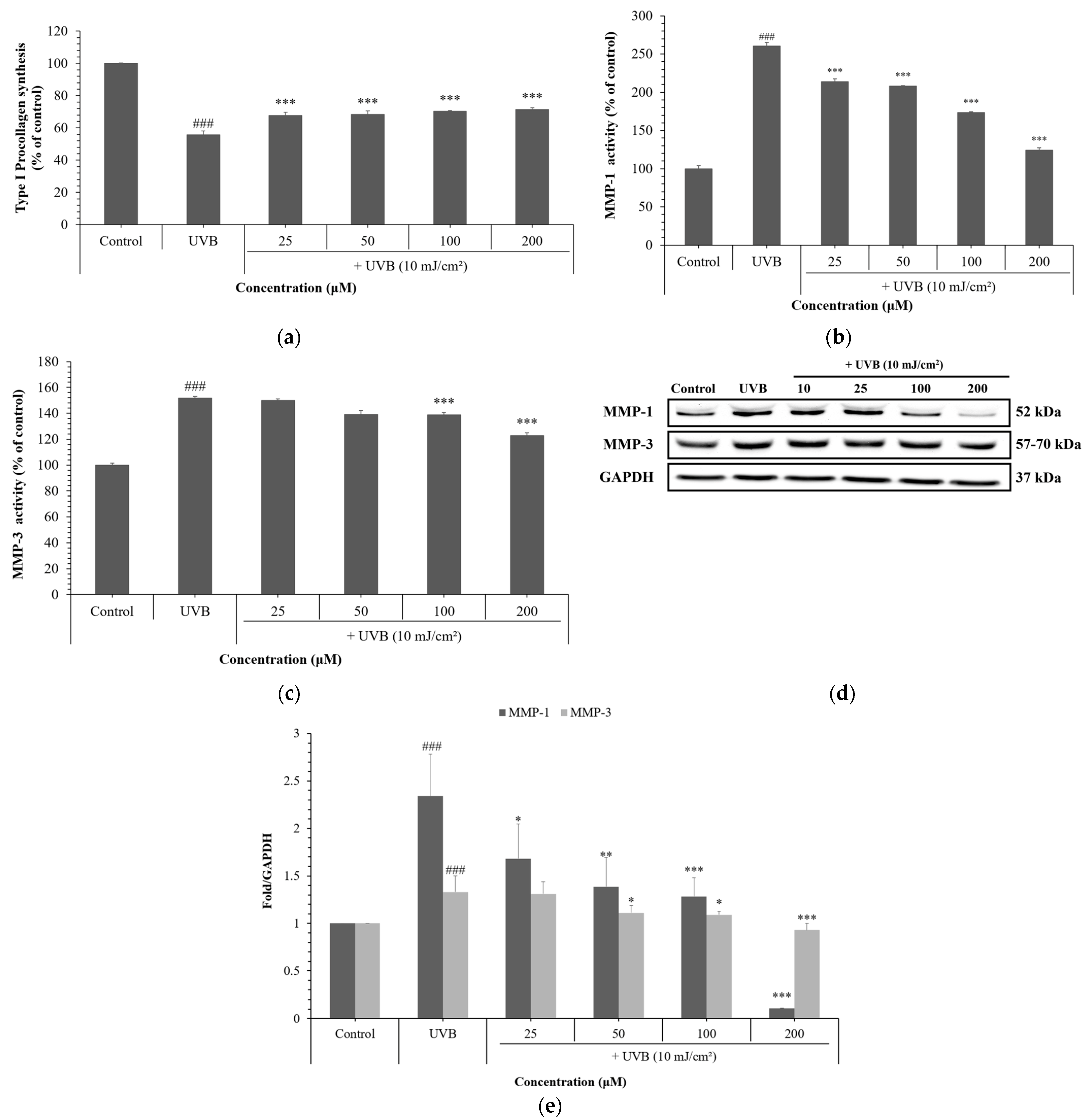
3.3. Effects of NCG on UVB-Induced Skin Aging in HDFs
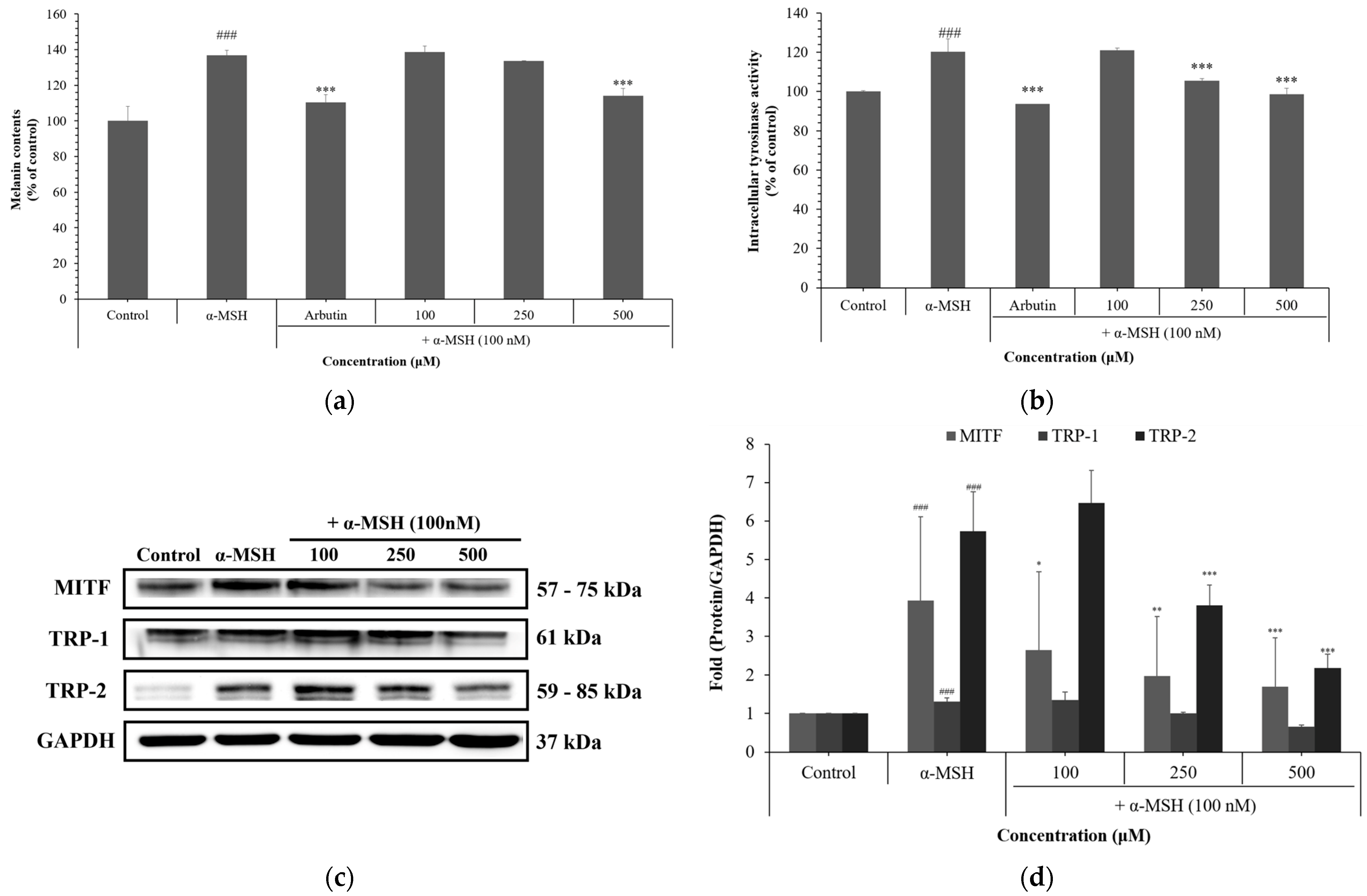
3.4. Effects of NCG on Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells
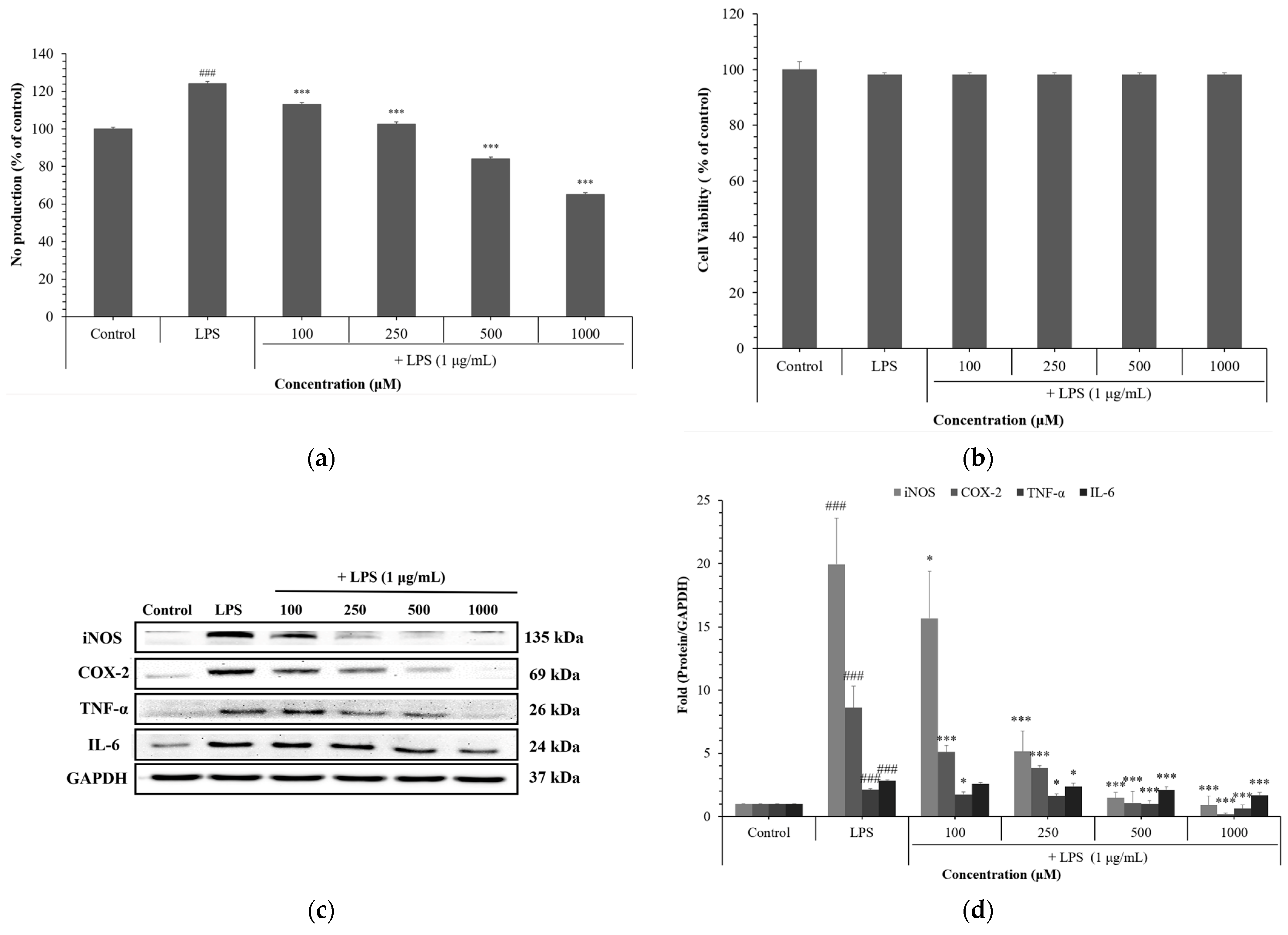
3.5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of NCG
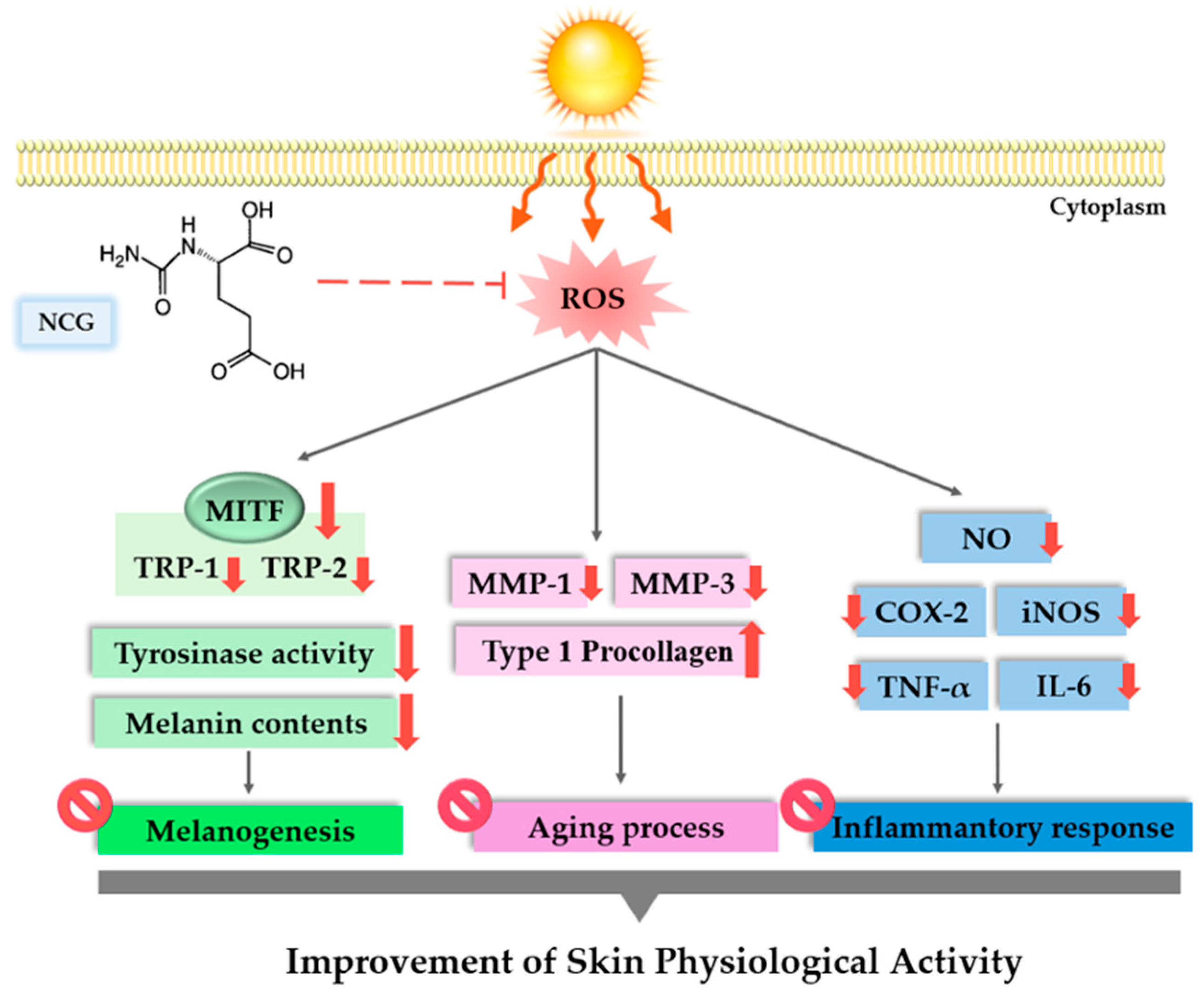
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Rho, N.K.; Park, K.Y. Skin aging from mechanisms to interventions: Focusing on dermal aging. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1195272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. Biochemical, structural and physical changes in aging human skin, and their relationship. Biogerontology 2022, 23, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Jiratchayamaethasakul, C.; Lee, S.H. Protocatechuic aldehyde attenuates UVA-induced photoaging in human dermal fibroblast cells by suppressing MAPKs/AP-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, S.M.; Bulfone-Paus, S.; Griffiths, C.E.; Watson, R.E. Inflammaging and the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, E. Inflammation and Aging: The Skin Inflammasome in the Context of Longevity Science. J. Cell. Immunol. 2025, 7, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Photoaging: UV radiation-induced inflammation and immunosuppression accelerate the aging process in the skin. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Rai, V.; Agrawal, D.K. Regulation of collagen I and collagen III in tissue injury and regeneration. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, A.T.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, D. MLK3 regulates inflammatory response via activation of AP-1 pathway in HEK293 and RAW264. 7 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, A.; Golovanov, A.P. Lipopolysaccharide structure and the phenomenon of low endotoxin recovery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 180, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yang, T.; Yu, D.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, S. Current insights and future perspectives of ultraviolet radiation (UV) exposure: Friends and foes to the skin and beyond the skin. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.R.; Mitrani, R.; Werth, V.P. Effect of TNFα blockade on UVB-induced inflammatory cell migration and collagen loss in mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 213, 112072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavinato, M.; Jansen-Dürr, P. Molecular mechanisms of UVB-induced senescence of dermal fibroblasts and its relevance for photoaging of the human skin. Exp. Gerontol. 2017, 94, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.W.; Hung, Y.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Fang, J.Y.; Yang, P.M.; Chen, M.H.; Pan, T.L. Comparison of the biological impact of UVA and UVB upon the skin with functional proteomics and immunohistochemistry. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybnikář, M.; Malaník, M.; Šmejkal, K.; Švajdlenka, E.; Shpet, P.; Babica, P.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Ondřej, J.; Treml, J. Dibenzocyclooctadiene Lignans from Schisandra chinensis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa-Mineoka, R.; Ueta, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Nishigaki, H.; Katoh, N. Roles of interferon regulatory factor 3 in skin inflammation: Possible involvement of regulatory mechanisms. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.; Chen, X.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Jia, R.; Zou, Y.; Li, L.; Yin, Z.; He, C.; Liang, X.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced inflammation through suppressing the signaling cascades of TLR4-NF-κB/MAPKs/IRF3. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazid, A.B.; Jang, Y.A.; Jeong, S.A.; Lim, B.O. Cypress tree (Chamaecyparis obtusa) Bark extract inhibits melanogenesis through repressing CREB and MITF signalling pathways in α-MSH-stimulated B16F10 cells. Food Agric. Immunol. 2022, 33, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.Y.; Sun, S.O.; Ko, J.Y.; Oh, Y.S.; Cho, S.S.; Park, D.H.; Park, K.M. New synthesized Galloyl-RGD inhibits Melanogenesis by regulating the CREB and ERK signaling pathway in B16F10 melanoma cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.Y.; Woo, I.K.; Cha, Y.J.; Lee, N.K.; Jang, H.J.; Paik, H.D. Anti-melanogenic and Antioxidant Activities of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains in Skin Cells via the CREB/MITF and Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakoeswa, F.R.S.; Maharani, F.; Satria, Y.A.A.; Awanis, G.S.; Febrianty, A.F. Topical anti-aging agents: State-of-the-art review. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 55, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, M.; Colombo, F. Skin anti-aging effect of oral vitamin a supplementation in combination with topical retinoic acid treatment in comparison with topical treatment alone: A randomized, prospective, Assessor-blinded, parallel trial. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mew, N.A.; Payan, I.; Daikhin, Y.; Nissim, I.; Nissim, I.; Tuchman, M.; Yudkoff, M. Effects of a single dose of N-carbamylglutamate on the rate of ureagenesis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2009, 98, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shao, D.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shen, Y.; Shan, Z.; Haibing, T.; Shi, S. Effects of dietary N-carbamylglutamate supplementation on growth performance, tissue development and blood parameters of yellow-feather broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Mao, P.; Xiong, X.; Ma, Z.; Xie, Z.; Gao, M.; Wu, Q.; Ma, W. Effect of N-Carbamylglutamate Supplementation on Growth Performance, Jejunal Morphology, Amino Acid Transporters, and Antioxidant Ability of Weaned Pigs. Animals 2023, 13, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, L.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Shi, X. Protective effects of quercetin on UVB irradiation-induced cytotoxicity through ROS clearance in keratinocyte cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.H.; Xu, S.P. Juglanin administration protects skin against UVB-induced injury by reducing Nrf2-dependent ROS generation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavinda, M.H.D.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, G.Y. Anti-melanogenic properties of FBCC–EP850 derived from Carex pumila Thunb. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2024, 14, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai-Kastoori, L.; Schutz-Geschwender, A.R.; Harford, J.A. A systematic approach to quantitative Western blot analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 593, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krutmann, J.; Schikowski, T.; Morita, A.; Berneburg, M. Environmentally-induced (extrinsic) skin aging: Exposomal factors and underlying mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naharro-Rodriguez, J.; Bacci, S.; Hernandez-Bule, M.L.; Perez-Gonzalez, A.; Fernandez-Guarino, M. Decoding Skin Aging: A Review of Mechanisms, Markers, and Modern Therapies. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Gao, X.; Xie, W. Research progress in skin aging and immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Yi, L.; Tong, X.; Kang, L.; Pei, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ding, Y.; et al. Roles of inflammation factors in melanogenesis. Mol. Med. Rep. Mol. 2020, 21, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawabteh, A.M.; Jibreen, A.; Karaman, D.; Thawabteh, A.; Karaman, R. Skin pigmentation types, causes and treatment—A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuelli, M.; Sartini, D.; Molinelli, E.; Campagna, R.; Pozzi, V.; Salvolini, E.; Simonetti, O.; Campanati, A.; Offidani, A. The double-edged sword of oxidative stress in skin damage and melanoma: From physiopathology to therapeutical approaches. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.R.; Ansary, T.M.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Diversified stimuli-induced inflammatory pathways cause skin pigmentation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, L.; Scala, E.; Caiazzo, G.; Lembo, S.; Marino, R.; Megna, M.; Patri, A.; Di Caprio, R.; Balato, A. Possible role of BMP-4 in the hyper-pigmentation of psoriatic plaques after anti-TNF-α treatment. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 4120–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, E.; Karaman-Jurukovska, N.; Mammone, T.; Idowu, O.C. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in dark skin: Molecular mechanism and skincare implications. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 2555–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocheva, G.; Slominski, R.M.; Janjetovic, Z.; Kim, T.K.; Böhm, M.; Steinbrink, K.; Reiter, R.J.; Kleszczyński, K.; Slominski, A.T. Protective role of melatonin and its metabolites in skin aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, D.; Mohammed, M.T. Oxidative stress: Implications on skin diseases. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 4150–4157. [Google Scholar]
- Papaccio, F.; Caputo, S.; Bellei, B. Focus on the contribution of oxidative stress in skin aging. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparavigna, A. Role of the extracellular matrix in skin aging and dedicated treatment-state of the art. Plast. Aesthetic Res. 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Dan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xiang, L. Implications of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7881717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansary, T.M.; Hossain, M.R.; Kamiya, K.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Inflammatory molecules associated with ultraviolet radiation-mediated skin aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.C.; Hu, H.C.; Yu, S.Y.; Tsai, Y.H.; Korinek, M.; Wu, Y.C.; Chang, F.R.; Chen, Y.J. Development on potential skin anti-aging agents of Cosmos caudatus Kunth via inhibition of collagenase, MMP-1 and MMP-3 activities. Phytomedicine 2023, 110, 154643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Qiu, X.; Ouyang, J.; Dai, J.; Min, S. Matrix metalloproteinase 3: A promoting and destabilizing factor in the pathogenesis of disease and cell differentiation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 663978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, E.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, B.S.; Park, S.M.; Hyun, C.G. Anti-melanogenic effects of hydroxyectoine via mitf inhibition by jnk, p38, and akt pathways in b16f10 melanoma cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19858523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.W.; Ha, J.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, S.N. Anti-melanogenesis effect of dehydroglyasperin C through the downregulation of MITF via the reduction of intracellular cAMP and acceleration of ERK activation in B16F1 melanoma cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Fisher, D.E. MITF and UV responses in skin: From pigmentation to addiction. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2019, 32, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, G.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, X.; Leng, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, J. Embelia Laeta aqueous extract suppresses acute inflammation via decreasing COX-2/iNOS expression and inhibiting NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J.; Lee, N.; Choi, S.E.; Jeon, J.Y.; Han, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.J. Amphiregulin Induces iNOS and COX-2 Expression through NF-κB and MAPK Signaling in Hepatic Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 2364121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Cao, W.; Liu, G.; Fang, T.; Wu, X.; Jia, G.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.; et al. Arginine, N-carbamylglutamate, and glutamine exert protective effects against oxidative stress in rat intestine. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Xiao, L.; Cao, W.; Fang, T.; Jia, G.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, J. Changes in the metabolome of rats after exposure to arginine and N-carbamylglutamate in combination with diquat, a compound that causes oxidative stress, assessed by 1 H NMR spectroscopy. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, F.F.; Jiang, L.Y.; Wang, D.M.; Zhao, F.Q.; Liu, J.X. Supplementation with N-carbamoylglutamate during the transition period improves the function of neutrophils and reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 5786–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target Protein | Catalog No. | Host Species | Dilution Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | E12-057 | Mouse | 1:5000 |
| TRP-1 | ab178676 | Rabbit | 1:10,000 |
| TRP-2 | ab2211144 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| MITF | #12590 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| MMP-1 | sc-58377 | Mouse | 1:400 |
| MMP-3 | AF513 | Goat | 1:5000 |
| TNF-α | #12744 | Mouse | 1:200 |
| COX-2 | #35-8200 | Mouse | 1:500 |
| IL-6 | #P620 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
| iNOS | #PA1-036 | Rabbit | 1:1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.R.; Song, N.R.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Byun, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jung, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, K.M. Multifunctional Effects of N-Carbamylglutamate on Skin-Related Cells: Antioxidant, Anti-Aging, Anti-Melanogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060250
Choi SR, Song NR, Shin SY, Kim KM, Byun JH, Kim SJ, Jung DH, Kim SJ, Park KM. Multifunctional Effects of N-Carbamylglutamate on Skin-Related Cells: Antioxidant, Anti-Aging, Anti-Melanogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(6):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060250
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Sa Rang, Nu Ri Song, Seo Yeon Shin, Ki Min Kim, Jae Hee Byun, Seon Ju Kim, Dai Hyun Jung, Su Jung Kim, and Kyung Mok Park. 2025. "Multifunctional Effects of N-Carbamylglutamate on Skin-Related Cells: Antioxidant, Anti-Aging, Anti-Melanogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities" Cosmetics 12, no. 6: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060250
APA StyleChoi, S. R., Song, N. R., Shin, S. Y., Kim, K. M., Byun, J. H., Kim, S. J., Jung, D. H., Kim, S. J., & Park, K. M. (2025). Multifunctional Effects of N-Carbamylglutamate on Skin-Related Cells: Antioxidant, Anti-Aging, Anti-Melanogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Cosmetics, 12(6), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060250







