Simple Summary
Although milk is a significant nutrient source for humans, it can be associated with various bacterial infections. Acinetobacter species can be found in milk due to residual water in milking machines, milk pipelines or coolers, the inadequate cleaning of dairy equipment, tainted udders and teats, the improper transport and storage of milk and the inadequate cleaning of dairy equipment, causing diseases. Most members of the genus Acinetobacter are opportunistic commensals with limited virulence and are clinically insignificant. However, Acinetobacter infections have recently increased in severity due to the frequent use of mechanical breathing devices, venous catheters and antibiotics, and they pose significant public health concerns. Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) is an opportunistic pathogen that causes various nosocomial infections. Studies using animal models and clinical data demonstrated that A. baumannii is a highly virulent species. It is a significant pathogen, especially due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains and their association with many nosocomial infections and community-acquired infections.
Abstract
Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) is an opportunistic pathogen associated with nosocomial infections. In this study, 100 raw milk samples were collected from Qena, Egypt, and subjected to conventional and molecular assays to determine the presence of A. baumannii and investigate their antimicrobial resistance and biofilm formation. Our findings revealed that, among the 100 samples, Acinetobacter spp. were found in 13 samples based on CHROM agar results. We further characterized them using rpoB and 16S-23SrRNA sequencing and gyrB multiplex PCR analysis and confirmed that 9 out of the 13 Acinetobacter spp. isolates were A. baumannii and 4 were other species. The A. baumannii isolates were resistant to β-lactam drugs, including cefotaxime (44%), ampicillin-sulbactam and levofloxacin (33.3% for each), imipenem, meropenem and aztreonam (22.2% for each). We observed different antimicrobial resistance patterns, with a multi-antibiotic resistant (MAR) index ranging from 0.2 to 0.3. According to the PCR results, blaOXA-51 and blaOXA-23 genes were amplified in 100% and 55.5% of the A. baumannii isolates, respectively, while the blaOXA-58 gene was not amplified. Furthermore, the metallo-β-lactamases (MBL) genes blaIMP and blaNDM were found in 11.1% and 22.2% of isolates, respectively, while blaVIM was not amplified. Additionally, eight A. baumannii isolates (88.8%) produced black-colored colonies on Congo red agar, demonstrating their biofilm production capacity. These results showed that, besides other foodborne pathogens, raw milk should also be examined for A. baumannii, which could be a public health concern.
1. Introduction
Milk is a significant nutrient source for humans, but drinking unsafe milk might cause various bacterial infections [1,2], including those by Acinetobacter. These foodborne pathogens might potentially cause human diseases (Malta et al., 2020). The most common sources of Acinetobacter in milk include residual water in milking machines, milk pipelines or coolers, the inadequate cleaning of dairy equipment, tainted udders and teats, the improper transport and storage of milk and the inadequate cleaning of dairy equipment [3].
Acinetobacter species are gram-negative, non-fermenting, aerobic, non-motile, catalase-positive, indole-negative and oxidase-negative bacteria [4,5]. The ideal temperature range for most strains for converting nitrates into nitrites is 33–35 °C [6,7]. They can resist dryness [8] and disinfectants such as phenols and chlorhexidine [9].
Some Acinetobacter spp. can survive temperatures up to 75 °C [7], and this is taken into consideration because, although ultra-heat treatments are effective in eliminating many microbes, there is still much public debate regarding the potential benefits of the high popularity of raw milk consumption. [10]. In addition, some countries, including Egypt and the United States, still prefer to consume locally manufactured dairy products made from raw milk, such as kareish and traditional artisan raw cheddar cheese [11,12].
Although most Acinetobacter members are opportunistic commensals with limited virulence and negligible clinical importance, infections caused by Acinetobacter spp. have increased in severity with the continuous use of mechanical breathing devices and venous catheters and, particularly, the increased use of antibiotics [13].
Acinetobacter can adapt to challenging environmental conditions and potentially develop resistance against several antibiotic classes, making it a significant public health concern. In particular, A. baumannii is associated with most Acinetobacter infections, followed by A. calcoaceticus and A.lwoffii. Other species include A. haemolyticus, A. johnsonii, A. junii, A. nosocomialis, A. pittii, A. schindleri and A. ursingi. Studies using animal models and clinical data demonstrated that A. baumannii is the most virulent species [14]. Although it is ubiquitous, the frequency of the occurrence of the pathogenic species from this genus in food sources and drinking water is not known yet [15].
A. baumannii is a significant pathogen due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains and their association with nosocomial infections and community-acquired infections. The Infectious Diseases Society of America has considered A. baumannii an ESKAPE pathogen, a category which includes Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, A. baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter spp. Escape pathogens are mainly responsible for nosocomial infections worldwide and can resist different antibiotics [16].
Recently, due to the fast acquisition of several antibiotic-resistance genes, particularly for β-lactam antibiotics, MDR A. baumannii has been associated with high morbidity and mortality in children and has challenged conventional therapeutics (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems and monobactams) [17].
Carbapenems are effective against bacterial pathogens that are resistant to extended-spectrum β-lactamases, such as MDR A. baumannii (ESBL) [18]. However, with the increased use of carbapenems, new carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamases have emerged, increasing the chance of treatment failure. Class B metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), such as IMP (imipenemase), VIM (Verona integrin-encoded MβL) and NDM (New Delhi MβL), class C AmpC cephalosporinases, class D carbapenemases/oxacillinases and OXA types have been observed in A. baumannii, including OXA-23-like, OXA-24-like, OXA-51-like and OXA-58-like. [19,20].
Acinetobacter spp. are biofilm producers that can acquire and transfer resistance genes, enhancing their antibiotic resistance ability [21]. Studies have shown that clinical isolates can produce biofilms more efficiently than environmental isolates and that there is a substantial correlation between biofilm production and multiple-drug resistance [22,23,24].
Therefore, in this study, we identified A. baumannii in milk samples and investigated their ability to form biofilms and antimicrobial susceptibility to different families of antibiotics. We also detected OXA and MBL genes responsible for carbapenem resistance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Sampling
We collected 100 raw milk samples from different markets in the Qena provinces between December 2020 and April 2021. The samples were collected in a sterile snap cap milk collection vial, placed in ice-cooled containers and processed within 24 h of collection.
2.2. Isolation of Acinetobacter spp.
Each milk sample (10 µL) was streaked on the chromogenic culture media Acinetobacter (CHROMTM agar Acinetobacter Media Pioneer, Paris, France) and incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. The suspected red Acinetobacter colonies were further subcultured on MacConkey agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) and then on Tryptic soy agar (Lab, Neogen Company, Rochdale, UK) at 37 °C for 24–48 h for purification [2]. The suspected isolates were used for staining and other biochemical assays, including catalase, oxidase, citrate, nitrate reduction, arginine hydrolysis, glucose fermentation, hemolysis, the reaction on the triple sugar iron and the motility test, according to Constantiniu et al. [25].
2.3. Genotypic Identification of A. baumannii
Acinetobacter spp. were identified based on Gurung et al. [2]. Briefly, the rpoB gene of Acinetobacter was amplified and sequenced using two primer sets, as previously described by La Scola et al. [26]. The 16S-23S rRNA gene intergenic spacer regions of the positive rpoB isolates were amplified and sequenced (Supplementary Table S1) to identify the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus–A. baumannii complex, as described previously [27]. Finally, A. baumannii was differentiated from the A. Calcoaceticus–A. baumannii complex by the DNA gyrase subunitB (gyrB)-based Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction method, as described by Higgins et al. [28]. The sequences of primers are described in Supplementary Table S1.
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Acinetobacter’s antimicrobial susceptibility test was conducted using the agar disc diffusion method based on the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines [29]. Mueller–Hinton agar was used (Oxoid, CM0337, Basingstoke, UK). The antibiotics examined included amikacin (30 g/disc), gentamicin (10 g/disc), ampicillin-sulbactam (10 g/disc), piperacillin (100 g/disc), cefotaxime (30 g/disc), cefepime (30 g/disc), imipenem (10 g/disc), meropenem (10 g/disc) and ciprofloxacin (5 μg/disc). The zone diameter breakpoints (mm) were interpreted according to CLSI [26] and the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) [30]. The Multi-Antibiotic Resistant (MAR) index is calculated based on the number of antibiotics that an isolate is resistant to (a) divided by the total number of antibiotics utilized in the study (b) [31], using the equation shown below:
MAR Index = a/b
2.5. Screening of Metallo-β-lactamases Production Using the Disk Method
Indicator strain: E. coli (ATCC 29522) was obtained from the Faculty of Agriculture at Ain Shams University in Giza, Egypt.
A suspension of a tested A. baumannii isolate was made by suspending a full 10 μL inoculation loop of a freshly cultured A. baumannii isolate, taken from a blood agar plate in 400 μL of water. Consequently, the test disc, which contained 10 g of meropenem, was dipped in the suspension and incubated at 35 °C for two hours. The disc was taken out of the suspension using an inoculation loop and put on a Mueller–Hinton agar plate, which was cultured with susceptible E. coli (ATCC 29522) that was prepared as a suspension of 0.5 a McFarland at OD595 and was then incubated at 35 °C. The susceptibility disk’s meropenem was rendered inactive, allowing the E. coli to grow unhindered; this means that the isolates were able to produce carbapenemases. A clear inhibitory zone was produced after 24 h with discs that were incubated in phosphate puffer saline (PBS) as a negative control devoid of carbapenemases [32].
2.6. Detection of Metallo-β-lactamasesgenes
Multiplex PCR was performed to investigate the presence of carbapenemases, including OXA-type, blaOXA-51-like, blaOXA-23-like and blaOXA-58-like, based on a previous study [33]. Amplification was carried out using a final volume of 25 µL, consisting of 1X PCR buffer (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), 1U Taq polymerase (Roche, Meylan, France), 2 mMMgCl2, 200 mM of Deoxynucleo-tide triphosphate (dNTP) (Biotools, Madrid, Spain), 0.2 mM of each primer (Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ, USA) and 1 µL of template DNA. The PCR was carried out using a thermal cycler (Hamburg, Germany) under the following conditions: 94 °C for 5 min, followed by 30 cycles at 94 °C for 30 s, 53 °C for 40 s and 72 °C for 50s, then final extension at 72 °C for 6 min. The PCR products were separated by electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gels (Synacron) and visualized under a UV gel documentation system after staining with ethidium bromide.
According to Kazi et al. [34] the genes blaIMP, blaVIM and blaNDM were amplified using uniplex PCR. The amplification was conducted using a final volume of 25 μL containing: 12.5 μL of PCR Mastermix (Emerald Amp GT), 1 μL for each primer (Table 1), 1.5 μL of the DNA template and 9 μL of PCR-grade water using a thermal cycler (MJ Research, Inc. Watertown). The optimal cycling conditions were 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 29 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s and 72 °C for 30 s, with a final extension of 72 °C for 5 min. The bands were detected on 2% agarose gel electrophoresis.

Table 1.
Accession numbers of Acinetobacter spp. for sequenced rpoB and 16S-23S ribosomal RNA intergenic genes.
2.7. PCR Positive Control
Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates (ATCC 27853) were used as a positive control and were obtained from the Animal Health Research Institute, Dokkki, Egypt.
2.8. Qualitative and Quantatine Methods for the Detction of Biofilm Formation
2.8.1. Congo Red Agar
According to Freeman et al. [35], we prepared Congo red agar using 15 g/L nutrient agar (Oxoid, Thermo ScientificTM, Waltham, MA, USA, CM0003B), 37 g/L sucrose (Oxoid) and 0.8 g/L Congo Red (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). It was stored for up to 48 h and used to measure biofilm production. Biofilm-producing colonies appear as black colonies and can also stain the medium due to exopolysaccharide synthesis [36,37].
2.8.2. Microtiter Plate Technique
This technique was performed according Stepanović et al. [38] Briefly, a brain–heart infusion broth (BHI) (Oxoid, Waltham, CA, USA) was inoculated with A. baumannii strains and was left to grow for 24 h at 37 °C. OD was adjusted to an OD600 of 1 ± 0.05, and then the bacteria were diluted 1:100 with sterile BHI with 1% glucose (Oxoid) before being put in a 96-well polystyrene microplate containing 200 µL of BHI medium and then being incubated overnight at 37 °C. The negative control wells only used the medium. The P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 reference strain was the positive control for biofilm formation. After incubation, the media and the majority of the bacteria were quickly removed from the plates after incubation. A total of 200 µL of PBS 1× was introduced into the wells using a pipette, and after that, the plate was tilted to remove the liquid for pipette-based washing. Washing was repeated two more times. Using crystal violet staining (0.5%), which involves pouring 150 µL of dye into each well and letting them sit at room temperature for 5 min, biofilm formation was assessed. The extra dye was washed out using a pipette. After the plates had air-dried, the leftover dye was dissolved with 200 µL of glacial acetic acid (33% v/v) in each well. Using the ELISA auto-reader (Thermo Fisher MultiskanTM FC), staining was measured at OD620. The criteria for categorized biofilm formation were as follows: biofilm was not formed if OD ≤ ODc (negative), it was weak if ODc < OD < 2 × ODc and it was moderate if 2 × ODc < OD < 4 × ODc. A biofilm was considered strong at 4 × ODc < OD.
3. Results
3.1. Results of the Isolation and Identification of A. baumannii
In this study, out of 100 milk samples collected, 13 were suspected to be contaminated with Acinetobacter spp. based on the CHROM agar observations. Microscopic and biochemical examination showed the presence of gram-negative cocci that were catalase-positive and negative for oxidase and nitrate reduction tests. Moreover, negative results for hemolysis and motility. The isolates showed alkaline reaction in triple sugar iron (K/K) and variable results with citrate, arginine hydrolysis and the glucose fermentation test were demonstrated (Supplementary Table S2).
Furthermore, we used molecular identification to identify different Acinetobacter species by amplifying and sequencing genes, including rpoB, 16S-23SrRNA, and gyrB. The results showed that certain rpoB genes were amplified in the suspected 13 isolates. Finally, these isolates were classified as A. baumannii (nine isolates), A.pitti (two isolates), A. rudis (one isolate) and A. oryzae (one isolate) (Table 1). We observed 99% similarity in the rpoB gene sequences from all strains using pairwise comparison. Further, the intergenic spacer region of the 16S-23SrDNA was sequenced to identify the A. calcoaceticus–A. baumannii complex, and the results showed that, of the 13 Acinetobacter isolates, 11 belonged to the A. calcoaceticus–A. baumannii complex, 9 were A. baumannii and 2 were A. pitti (Table 1).
Multiplex PCR was performed using three primers for the gyrB gene for both A. baumannii and genomic sp. 13TU, and in 11 isolates, a 294-base-pair (bp) amplicon (sp4F to sp4R) was observed, whereas 9 A. baumannii isolates produced the second amplicon of 490 bp (sp2F to sp4R) (Figure 1).
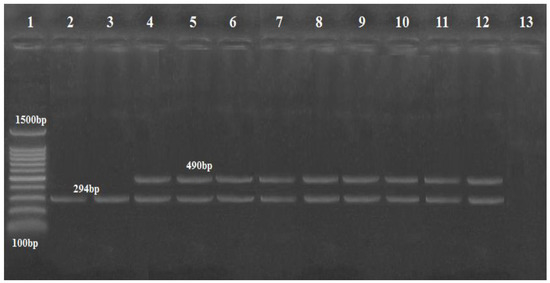
Figure 1.
Agarose gel image showing Acinetobacter isolates differentiated by multiplex PCR using gyr B-primers. Lane: DNA Marker (100 bp ladder Gold Bio Company, Cat.D001, US) lanes (4–12) were A. baumannii at 490 bp; lanes (2 and 3) were Acinetobacter genomic sp. 13TU (394 bp); lane 13: negative control with no DNA template.
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile and MBL Production of A. baumannii Isolates
The antimicrobial susceptibility of A. baumannii (n = 9) was tested against 12 antibiotics (Table 2). However, A. baumannii isolates showed sensitivity to some antibiotics such as amikacin (100%) and ciprofloxacin (88.8%); some isolates exhibited resistance against cefotaxim (44.4% for each), Ampicillin-sulbactam, levofloxacin (33.3% for each), imipenem, meropenem, piperacillin and aztreonam (22.2% for each).

Table 2.
Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of A. baumannii isolates.
Some A. baumannii isolates showed five distinct antimicrobial resistance patterns: 1. levofloxacin, ampicillin-sulbactam, imipenem and aztreonam with MAR (0.33); 2. ciprofloxacin, piperacillin, cefotaxime and meropenem with MAR (0.33); 3. ampicillin-sulbactam, cefotaxime and cefepime with MAR (0.22); 4. levofloxacin, tetracycline, gentamycin and cefotaxime with MAR (0.33); 5. piperacillin, cefotaxime, cefepime and meropenem with MAR (0.33) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Antimicrobial resistance patterns of A. baumannii isolates.
Even though the data clearly indicated some resistance of A. baumannii isolates to β-lactam antibiotics, including penicillin, cephalosporin and carbapenem, we focused on carbapenem resistance because 44.4% (4\9) of isolates showed resistance for imipenem and meropenem. The phenotypic results of the MBL test confirmed the production of carbapenemase in these four out of nine isolates (Figure 2).
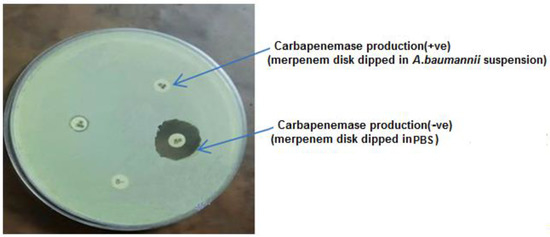
Figure 2.
Ability of A. baumannii for Carbapenemase production.
3.3. PCR Results of the Carbapenem Resistance Genes
The PCR results showed that blaOXA-51 and blaOXA-23 genes were amplified in nine (100%) and five (55.5%) of the A. baumannii isolates, respectively, while the blaOXA-58 gene was not amplified in any isolate (Figure 3). Additionally, the MBL genes, blaIMP, and blaNDM, were found in one (11.1%), and two (22.2%) isolates, respectively (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5), while blaVIM was not amplified in any of them.
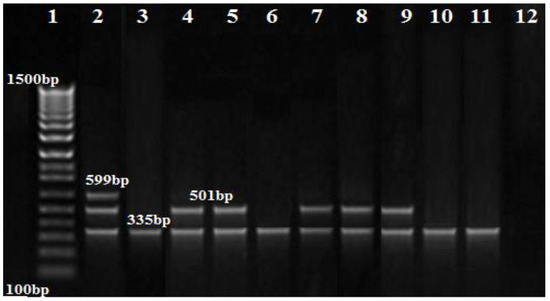
Figure 3.
Agarose gel image showing the separation of the OXA gene products amplified using multiplex PCR. Lane 1: DNA marker (100 bp ladder Biolabs Company, Cat.N3231S, London, England), lane 2: positive control, lane 3–11: positive for the blaOXA51 gene (335 bp), lane 4,5,7,8,9: positive for the blaOXA23 gene (501 bp); no band was seen for blaOXA58 (599 bp).
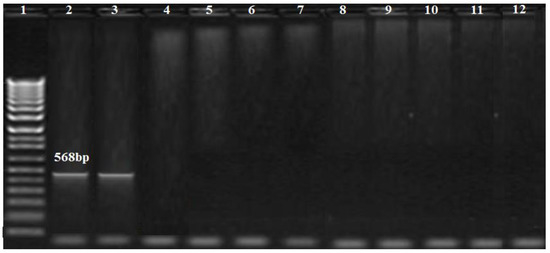
Figure 4.
Amplification profile of the blaIMP gene (568 bp). Lane 1: DNA marker (100 bp Biolabs Company, Cat.N3231S, London, England); lane 2: positive control; lane 3: positive for the blaIMP gene; lane 12: negative control.
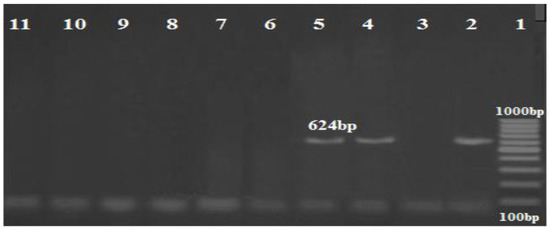
Figure 5.
Amplification profile of the blaNDM gene (624 bp). Lane 1: DNA marker (100 bp ladder GoldBio Company, Cat.D001, Olivette, Mo, USA); lane 2: positive control; lane (4,5): positive for the blaNDM gene; lane 11: negative control.
3.4. Biofilm Formation of A. baumannii Isolates
Furthermore, eight A. baumannii isolates (88.8%) produced black colonies on Congo red agar, demonstrating their biofilm-producing capacity, while just six isolates (66.6%) were able to form biofilm (one strong, three moderate and two weak biofilm formations) on the microtiter plate method (Figure 6 and Supplementary Table S3).
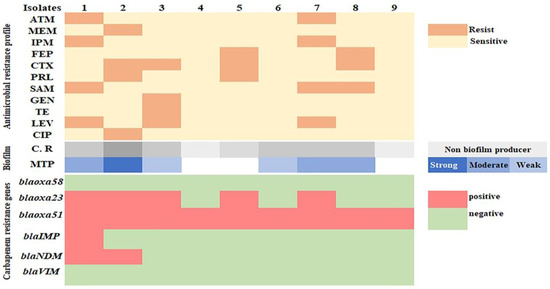
Figure 6.
Heat map showing the antimicrobial resistance and biofilm formation ability of A. baumannii isolates.
4. Discussion
Recently, A. baumannii has been significantly linked to several infections, including catheter-related infections, meningitis, bacteremia, soft-tissue infections, peritonitis and endocarditis, in intensive care units (ICU) due to its extraordinary capacity to obtain or enhance the antimicrobial resistance factors. Therefore, scientists are currently interested in discovering this novel, antibiotic-resistant strain [39].
We identified Acinetobacter spp. in 13 milk samples on CHROM agar media. Several authors have suggested using CHROM agar as a quick and easy medium for detecting Acinetobacter, as it contains chromogenic substrates cleaved by Acinetobacter spp. enzymes, resulting in unique, red-colored Acinetobacter colonies. This increases the efficiency of infection control procedures, decreases the time required to administer the right antibiotic therapy to the infected patients and, hence, lowers mortality [2,40].
However, further information about the interspecies relationships among the genus Acinetobacter is needed. It is challenging to distinguish between the Acinetobacter species, as they share several phonotypical traits. There are several methods for identifying the pathogenic Acinetobacter strains. Even though PCR is the preferred method for identifying Acinetobacter species, the sequencing of several genes is required for species-level identification [26]
In this study, due to the close relationship between Acinetobacter genomic species, especially those belonging to the A. calcoaceticus–baumannii complex, we used different primers to amplify and sequence target genes, such as rpoB, 16S-23S and gyrB, to identify Acinetobacter spp., especially A. bummanii. Several studies have found that the sequencing of the rpoB gene and the 16S-23S rRNA gene spacer region enables the identification of Acinetobacter isolates at the species level [2,26,41,42,43], A. bummanii and the 13TU genomic species showed interspecies variability, which could be discriminated by amplifying the gyrB gene [2,28,44].
We performed molecular identification to confirm the presence of Acinetobacter spp. DNA in 13 isolates. Among them, eight were identified as A. bummanii. A previous study [45] illustrated that 18 isolates of Acinetobacter species were isolated from 120 raw milk samples; among them, 12 were A. bummanii. Additionally, Gurung et al. [2] found that out of 2287 bulk milk samples, Acinetobacter spp. were isolated from 176 bulk samples. Among them, 57 were A. bummanii. Moreover, Jayarao et al. [46] identified Acinetobacter spp. in 28 out of 205 isolates from bulk milk samples. Additionally, Ndegwa et al. [47] found that 10 isolates of Acinetobacter species were identified from 21 goat milk samples in Kenya. Due to these varied results, we used various selective methods to isolate Acinetobacter spp. and to clarify the prevalence of Acinetobacter spp. as compared with these previous studies.
Infections by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, especially multi-resistant bacteria, are challenging to treat, resulting in serious health issues and even death due to extended hospital stays and unsuccessful treatment attempts [48].
In our study, some A. baumannii isolates showed resistance to different antibiotics. This is consistent with previous studies [49,50] which found that clinical A. bumannii isolates from humans were highly resistant to fluoroquinolone, amino-glycosides, cephalosporin and carbapenem. The resistance of some A. bumannii isolates is attributed to the AdeR–AdeS complex, encoded by the adeRS operon, which contributes to acquired antibiotic resistance against different antibiotics [51].
Another factor that might contribute to the resistance found in this study is the selection pressure exerted by using these antimicrobial drugs to treat sick cattle [49]. However, Gurung et al. [2] observed that most Acinetobacter isolates obtained from bulk milk tank samples were susceptible to several antibiotics. They hypothesized that this was because milk is generally extracted from healthy cattle, not those treated with antimicrobial agents.
Antibiotic resistance patterns varied among the nine A. bummannii isolates with an MAR index higher than 0.2. This is considered an indicator of serious contamination in milk, which is linked to the excessive use of antibiotics in animal treatments, which resulted in the creation of strains resistant to a number of antibiotics [52].
The carbapenem resistance observed in these isolates is a significant issue because carbapenem is generally used as an alternative for other β-lactam drugs, including penicillin and cephalosporins [53]. This resistance was mediated by several carbapenemase genes. OXA-type genes, which mainly cause carbapenem resistance in A. baumannii, are intrinsic and can be located on chromosomes and plasmids. The gene blaoxa encoded and expressed OXA-like enzymes and significantly increased carbapenem resistance [54,55].
The PCR results showed that blaOXA-51-like was amplified in all A. baumannii isolates, while blaOXA-23-like was amplified only in 55.5% of isolates. These findings were almost identical to previous studies [39,56], showing that 100% of A. baumannii had blaOXA-51-like genes, while 90% were positive for blaOXA-23-like genes. [57] The ubiquitous nature of OXA-51 in A. baumannii has made it a critical genetic marker for identifying Acinetobacter at the species level. Turton et al. [58] found that the blaOXA51-like genes played an important role in the identification and differentiation of A. bummannii from other Acinetobacter spp., and this explains the high incidence of the blaOXA-51-like genes compared to other genes in our study. Another study [59] discovered that the ability of OXA-51-like proteins to hydrolyze β-Lactam antibiotics, including penicillins (benzylpenicillin, ampicillin, ticarcillin and piperacillin) and carbapenems (imipenem and meropenem), was supported by the expression of other genes. However, blaOXA-23-like proteins were primarily responsible for imipenem resistance, and its plasmid location enhanced the possibility of the horizontal transfer of resistance.
Our findings also revealed that the blaIMP and blaNDM genes were amplified in one and two isolates, respectively, while the blaVIM gene was not amplified. However, previous studies reported that the blaIMP and blaVIM genes were not amplified in the isolates [34]. A study showed that the Verona integron-encoded MBL (VIM) genes were found to be extremely infrequent in Enterobacteriaceae [60], while another [61] discovered that MBL oxacillinases and blaNDM1 are the primary causes of carbapenem resistance.
Based on the MBL phenotypic screening results, 44.4% of A. baumannii isolates produced MBL. Despite phenotypic testing, only one amplicon for the blaimp gene was found among the studied MBL genes. This might be due to the presence of unidentified hereditary determinants, which PCR might not detect, as the PCR primers were only created for specific known genetic positions. Contrastingly, these results might be true-positive for other MBL genes [62].
A. baumannii can efficiently produce biofilms that enable it to tenaciously proliferate under challenging circumstances and habitats. A. baumannii can produce biofilms on biotic surfaces, including epithelial cells, and on abiotic surfaces, including glass and the medical equipment used in ICUs. Most of the A. baumannii isolates from our study were consistent with the findings Malta et al. [63], who found that 100% of A. baumannii isolated from goat milk formed biofilm. Several studies have also emphasized the severity of A. baumannii biofilm-associated infections, such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and catheter-related infections, both of which are resistant to antibiotic therapy and are most frequently caused by A. baumannii biofilms. [21,64,65].
The biofilm matrix around the bacterial cells enables them to withstand harsh conditions and promotes the propagation of antibiotic-resistance genes. Therefore, the current drugs that are available for treating infections caused by A. baumannii biofilms are ineffective [66]. Here, a microtiter plate test overcame the problem of false-positive results in two isolates on Congo red agar; these results are reinforced by Melo et al. [67], who recorded that that sensitivity of the Congo red agar test was 88.9%, while that of the microtiter plate test was 100%. Gaddy and Actis [68] found that A. baumannii can efficiently produce biofilms due to the presence of pili, outer membrane proteins and macromolecular secretions. When pili adhere to abiotic surfaces, they initiate the formation of microcolonies, followed by the formation of fully developed biofilms.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the detection of A. baumannii and its antimicrobial resistance is critical for controlling infections. Efficient molecular techniques, such as DNA sequencing, enable faster identification than other traditional techniques and can readily differentiate between closely related species, facilitating immediate prevention. Therefore, these techniques are necessary for the early detection of these microbes. A. baumannii isolates showed resistance to several antibiotics with MAR indices higher than 0.2, indicating that these are potentially hazardous to consumers. The antibiotic resistance in Acinetobacter spp. still needs further studies, especially the blaOXA51 gene, because the role of this gene in antibiotic resistance is linked to the mechanism of other genes. In addition to that, it has a major role in differentiating A. baumannii from other species.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology11121845/s1, Supplementary Tabel S1: Primers sequence, Supplementary Table S2: Biochemical profile of Acintobacter spp., Supplementary Table S3: Results of biofilm formation by microtiter plate (OD600)).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M.A.M. and M.A.E.-Z.; Formal analysis, H.M.A.M. and M.A.E.-Z.; Funding acquisition, H.M.A.M., M.A.E.-Z., H.H.A.-E. and O.A.A.-J.; Investigation, H.M.A.M., M.A.E.-Z. and H.H.A.-E.; Methodology, H.M.A.M., M.A.E.-Z.; project administration, H.M.A.M. and M.A.E.-Z.; Software, H.M.A.M., M.A.E.-Z., H.H.A.-E.; Validation, H.M.A.M. and M.A.E.-Z.; Visualization, H.M.A.M., M.A.E.-Z., H.H.A.-E.; writing–original draft, H.M.A.M. and M.A.E.-Z.; Writing-reviewer & editing, H.M.A.M., M.A.E.-Z., H.H.A.-E. and O.A.A.-J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was funded by the authors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The results and analyses presented in this paper are freely available upon request from Hams M.A. Mohamed and Mona A. El-Zamkan.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the personnel of the Microbiology Department and Food Control and Hygiene Department, South Valley University, Department of Cells and Tissues, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Assiut University, Department of Microbiology, Collage of Veterinary Medicine, King Faisal University for their support and technical assistance. We also thank the Egyptian Knowledge Bank for its review of linguistics and grammar in our paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Oliver, S.P.; Boor, K.J.; Murphy, S.C.; Murinda, S.E. Food Safety Hazards Associated with Consumption of Raw Milk. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, M.; Nam, H.M.; Tamang, M.D.; Chae, M.H.; Jang, G.C.; Jung, S.C.; Lim, S.K. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Acinetobacter from Raw Bulk Tank Milk in Korea. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1997–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucali, M.; Bava, L.; Tamburini, A.; Brasca, M.; Vanoni, L.; Sandrucci, A. Effects of Season, Milking Routine and Cow Cleanliness on Bacterial and Somatic Cell Counts of Bulk Tank Milk. J. Dairy Res. 2011, 78, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurcik-Trajkovska, B. Acinetobacter spp.—A Serious Enemy Threatening Hospitals Worldwide. Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 2, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergogne-Bérézin, E.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter spp. as Nosocomial Pathogens: Microbiological, Clinical, and Epidemiological Features. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doughari, H.J.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Human, I.S.; Benade, S. The Ecology, Biology and Pathogenesis of Acinetobacter spp.: An Overview. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Danziger, L.H. Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Infections: An Emerging Challenge to Clinicians. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.; Towner, K.J.; Humphreys, H. Survival of Acinetobacter on Three Clinically Related Inanimate Surfaces. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2000, 21, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, L.; Towner, K.J. Carriage of Class 1 Integrons and Antibiotic Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii from Northern Spain. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A. Raw Milk Consumption: Risks and Benefits. Nutr. Today 2015, 50, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Shinawy, S.A.; EL-Kholy, A.D.; Meshref, A.; Sharkawy, S. Mycological evaluation of milk and some milk products in Beni-suef city. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2018, 64, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, J.C.; Martinez, B.; Stratton, J.; Bianchini, A.; Krokstrom, R.; Hutkins, R. Survey of raw milk cheeses for microbiological quality and prevalence of foodborne pathogens. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.; Nielsen, T.B.; Bonomo, R.A.; Pantapalangkoor, P.; Luna, B.; Spellberg, B. Clinical and Pathophysiological Overview of Acinetobacter Infections: A Century of Challenges. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 409–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzer, H.J.F.; Rolling, T.; Schmiedel, S.; Klupp, E.M.; Lange, C.; Seifert, H. Severe Community-Acquired Bloodstream Infection with Acinetobacter ursingii in Person Who Injects Drugs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalheira, A.; Silva, J.; Teixeira, P. Acinetobacter spp. in Food and Drinking Water—A Review. Food Microbiol. 2021, 95, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiku, V. Acinetobacter baumannii: Virulence Strategies and Host Defense Mechanisms. DNA Cell Biol. 2022, 41, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, L.K.; Gandra, S.; Trett, A.; Weinstein, R.A.; Laxminarayan, R. Acinetobacter baumannii Resistance Trends in Children in the United States, 1999–2012. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2019, 8, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, I.; Cerqueira, G.M.; Bhuiyan, S.; Peleg, A.Y. Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Laboratory Challenges, Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Strategies. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawa, T.; Kooguchi, K.; Moriyama, K. Molecular Diversity of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases and Carbapenemases, and Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, R.A. β-Lactamases: A Focus on Current Challenges. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a025239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, E.C.; Chenia, H.Y.; El Zowalaty, M.E. Acinetobacter baumannii Biofilms: Effects of Physicochemical Factors, Virulence, Antibiotic Resistance Determinants, Gene Regulation, and Future Antimicrobial Treatments. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babapour, E.; Haddadi, A.; Mirnejad, R.; Angaji, S.-A.; Amirmozafari, N. Biofilm Formation in Clinical Isolates of Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii and Its Relationship with Multidrug Resistance. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardbari, A.M.; Arabestani, M.R.; Karami, M.; Keramat, F.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Bagheri, K.P. Correlation between Ability of Biofilm Formation with Their Responsible Genes and MDR Patterns in Clinical and Environmental Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 108, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, O.; Yu, C.-P.; Fernández, G.E.; Hu, Z. Interactions of Nanosilver with Escherichia Coli Cells in Planktonic and Biofilm Cultures. Water Res. 2010, 44, 6095–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantiniu, S.; Romaniuc, A.; Iancu, L.S.; Filimon, R.; Taraşi, I. Cultural and Biochemical Characteristics of Acinetobacter spp. Strains Isolated from Hospital Units. J. Prev. Med. 2004, 12, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- La Scola, B.; Gundi, V.A.K.B.; Khamis, A.; Raoult, D. Sequencing of the RpoB Gene and Flanking Spacers for Molecular Identification of Acinetobacter species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, T.; Colleran, G.; Glennon, M.; Dunican, L.K.; Gannon, F. The 16s/23s Ribosomal Spacer Region as a Target for DNA Probes to Identify Eubacteria. PCR Methods Appl. 1991, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.G.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Krut, O.; Seifert, H. A PCR-Based Method to Differentiate between Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter Genomic Species 13TU. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M100-S25; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Twenty-Fifth Informational Supplement; CLSI: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2015.
- EUCAST. Antimicrob. Susceptibility Testing. Break. Tables Interpret. MICs Zo. Diameters. Version 5.0. 2015. Available online: http//www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints (accessed on 31 August 2015).
- Ayandele, A.A.; Oladipo, E.K.; Oyebisi, O.; Kaka, M.O. Prevalence of Multi-antibiotic Resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species Obtained from a Tertiary Medical Institution in Oyo State, Nigeria. Qatar Med. J. 2020, 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwaluw, K.; de Haan, A.; Pluister, G.N.; Bootsma, H.J.; de Neeling, A.J.; Schouls, L.M. The carbapenem inactivation method (CIM), a simple and low-cost alternative for the Carba NP test to assess phenotypic carbapenemase activity in gram-negative rods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoja, S.; Moosavian, M.; Rostami, S.; Farahani, A.; Peymani, A.; Ahmadi, K.; Ebrahimifard, N. Dissemination of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Patients with Burn Injuries. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017, 80, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazi, M.; Khot, R.; Shetty, A.; Rodrigues, C. Rapid Detection of the Commonly Encountered Carbapenemases (New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase, OXA-48/181) Directly from Various Clinical Samples Using Multiplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 36, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.J.; Falkiner, F.R.; Keane, C.T. New Method for Detecting Slime Production by Coagulase Negative Staphylococci. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 42, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, S.; Eftekhar, F.; Hosseini, S.M. Biofilm Formation by Bacteria Isolated from Intravenous Catheters. J. Med Bacteriol. 2014, 3, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, D.H.; Souza, B.V.; Nascimento, J.S.; Amorim, A.M.B.; Medeiros, L.M.; Mattoso, J.M.V. A Reddish Problem: Antibiotic-Resistant Serratia marcescens in Dairy Food Commercialized in Rio de Janeiro. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 880–883. [Google Scholar]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Dakić, I.; Savić, B.; Švabić-Vlahović, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of Staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasaudi, S.B. Acinetobacter spp. as Nosocomial Pathogens: Epidemiology and Resistance Features. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajao, A.O.; Robinson, G.; Lee, M.S.; Ranke, T.D.; Venezia, R.A.; Furuno, J.P.; Harris, A.D.; Johnson, J.K. Comparison of Culture Media for Detection of Acinetobacter baumannii in Surveillance Cultures of Critically-ill Patients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 30, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Wei, Y.F.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Tang, C.T.; Chang, T.C. Species-Level Identification of Isolates of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-Acinetobacter baumannii Complex by Sequence Analysis of the 16S-23S RRNA Gene Spacer Region. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Nagao, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Hotta, G.; Matsushima, A.; Ito, Y.; Takakura, S.; Ichiyama, S. Regional Dissemination of Acinetobacter species Harbouring Metallo-β-Lactamase Genes in Japan. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslunka, C.; Gifford, B.; Tucci, J.; Gürtler, V.; Seviour, R.J. Insertions or Deletions (Indels) in the Rrn 16S-23S rRNA Gene Internal Transcribed Spacer Region (ITS) Compromise the Typing and Identification of Strains within the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii (Acb) Complex and Closely Related Members. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, P.G.; Lehmann, M.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Seifert, H. gyrB Multiplex PCR to Differentiate between Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Acinetobacter Genomic Species 3. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4592–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, N.M.; Amin, W.F.; Mostafa, S.M. Detection of Acinetobacter species in Milk and Some Dairy Products. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2018, 64, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jayarao, B.M.; Wang, L. A Study on the Prevalence of Gram-Negative Bacteria in Bulk Tank Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2620–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndegwa, E.N.; Munyua, S.J.M.; Mulei, C.M. Prevalence of Microorganisms Associated with Udder Infections in Dairy Goats on Small-Scale Farms in Kenya. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2001, 72, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, M.; Ehlers, M.M.; Ismail, F.; Peirano, G.; Becker, P.J.; Pitout, J.D.D.; Kock, M.M. Acinetobacter baumannii: Epidemiological and Beta-Lactamase Data from Two Tertiary Academic Hospitals in Tshwane, South Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.A.; Moon, H.W. In Vitro Activity of Antimicrobial Combination against Multidrug-Resistant Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2005, 25, 312–316. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Yong, D.; Jeong, S.H.; Chong, Y. Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter Spp.: Increasingly Problematic Nosocomial Pathogens. Yonsei Med. J. 2011, 52, 879–89148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damier-Piolle, L.; Magnet, S.; Brémont, S.; Lambert, T.; Courvalin, P. AdeIJK, a Resistance-Nodulation-Cell Division Pump Effluxing Multiple Antibiotics in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, R.; Dahiya, S.; Sayal, P. Evaluation of Multiple Antibiotic Resistance (MAR) Index and Doxycycline Susceptibility of Acinetobacter Species among Inpatients. Indian J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 3, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletis, G. Carbapenem resistance: Overview of the problem and future perspectives. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Figueiredo, S.; Cattoir, V.; Carattoli, A.; Nordmann, P. Acinetobacter Radioresistens as a Silent Source of Carbapenem Resistance for Acinetobacter Spp. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranathan, R.; Vasanth, V.; Vasanth, T.; Shabareesh, P.R.V.; Shashikala, P.; Devi, C.S.; Kalaivani, R.; Asir, J.; Sudhakar, P.; Prashanth, K. Emergence of Carbapenem Non-susceptible Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains of Clonal Complexes 103B and 92B Harboring OXA-type Carbapenemases and Metallo-β-lactamases in Southern India. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 59, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrice, N.; Poirel, L.; Carrër, A.; Toleman, M.A.; Walsh, T.R. How to Detect NDM-1 Producers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 718–721. [Google Scholar]
- Baquero, F.; Alvarez-Ortega, C.; Martinez, J.L. Ecology and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turton, J.F.; Woodford, N.; Glover, J.; Yarde, S.; Kaufmann, M.E.; Pitt, T.L. Identification of Acinetobacter baumannii by Detection of the blaOXA-51-like Carbapenemase Gene Intrinsic to This Species. JCM J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2974–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsik, F.J.; Nambiar, S. Review of Carbapenemases and AmpC-Beta Lactamases. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 1094–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Datta, S.; Roy, S.; Ramanan, L.; Saha, A.; Viswanathan, R.; Som, T.; Basu, S. Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii and Other Acinetobacter Spp. Causing Neonatal Sepsis: Focus on NDM-1 and Its Linkage to IS Aba125. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Agus, N.; Bozcal, E.; Uzel, A. Prevalence and Molecular Characterisation of Metallo-Beta-Lactamase Producing Strains of Imipenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Turkey. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 32, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajand, O.; Rezaee, M.A.; Nahaei, M.R.; Mahdian, R.; Aghazadeh, M.; Soroush, M.H.; Tabrizi, M.S.; Hojabri, Z. Study of the Carbapenem Resistance Mechanisms in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii: Comparison of Burn and Non-Burn Strains. Burns 2013, 39, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, R.C.R.; Ramos, G.L.d.P.A.; dos Santos Nascimento, J. From Food to Hospital: We Need to Talk about Acinetobacter Spp. Germs 2020, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, O.; Shahcheraghi, F.; Salimizand, H.; Modarresi, F.; Shakibaie, M.R.; Mansouri, S.; Ramazanzadeh, R.; Badmasti, F.; Nikbin, V. Molecular Analysis and Expression of Bap Gene in Biofilm-Forming Multi-Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for Combating Bacterial Biofilms: A Focus on Anti-Biofilm Agents and Their Mechanisms of Action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrilli, R.; Giannouli, M.; Tomasone, F.; Triassi, M.; Tsakris, A. Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: The Molecular Epidemic Features of an Emerging Problem in Health Care Facilities. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2009, 3, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, P.D.C.; Ferreira, L.M.; Nader Filho, A.; Zafalon, L.F.; Vicente, H.I.G.; Souza, V.D. Comparison of methods for the detection of biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine subclinical mastitis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddy, J.A.; Actis, L.A. Regulation of Acinetobacter baumannii biofilm formation. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).